⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-30 更新
HELIOS: Hierarchical Exploration for Language-grounded Interaction in Open Scenes
Authors:Katrina Ashton, Chahyon Ku, Shrey Shah, Wen Jiang, Kostas Daniilidis, Bernadette Bucher
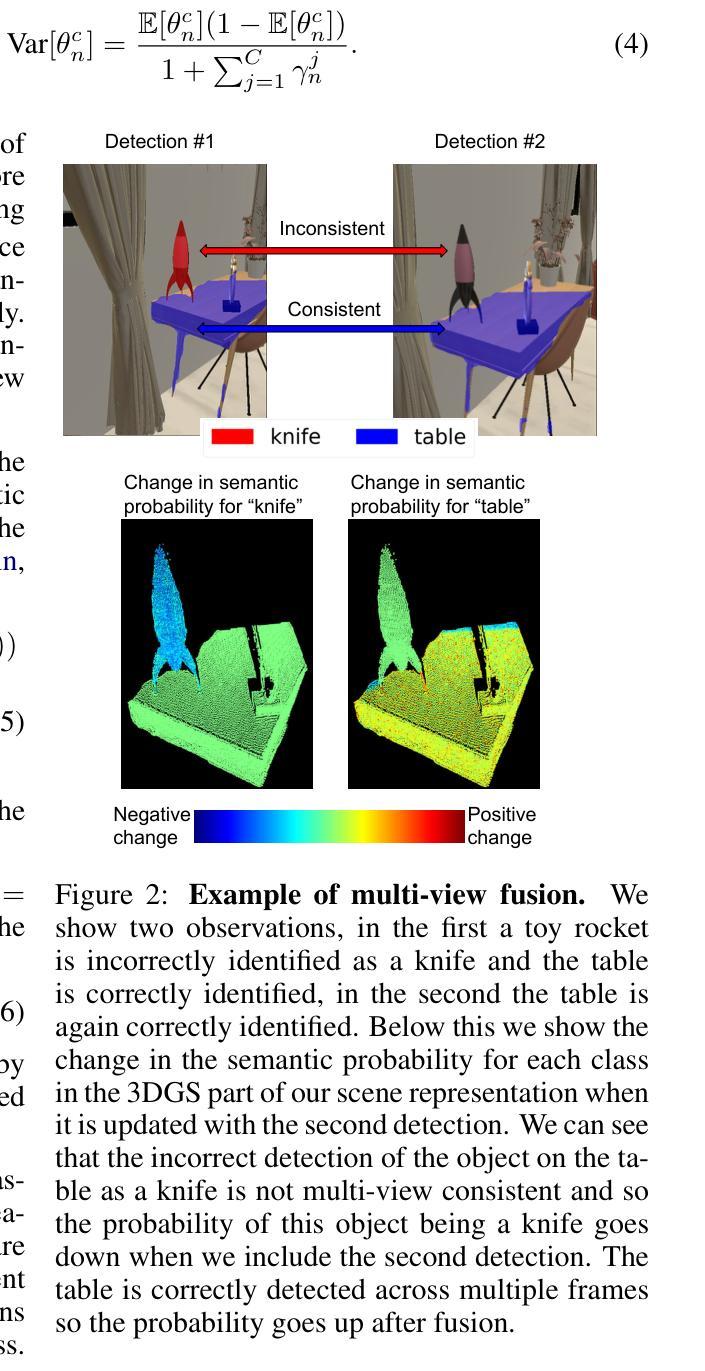
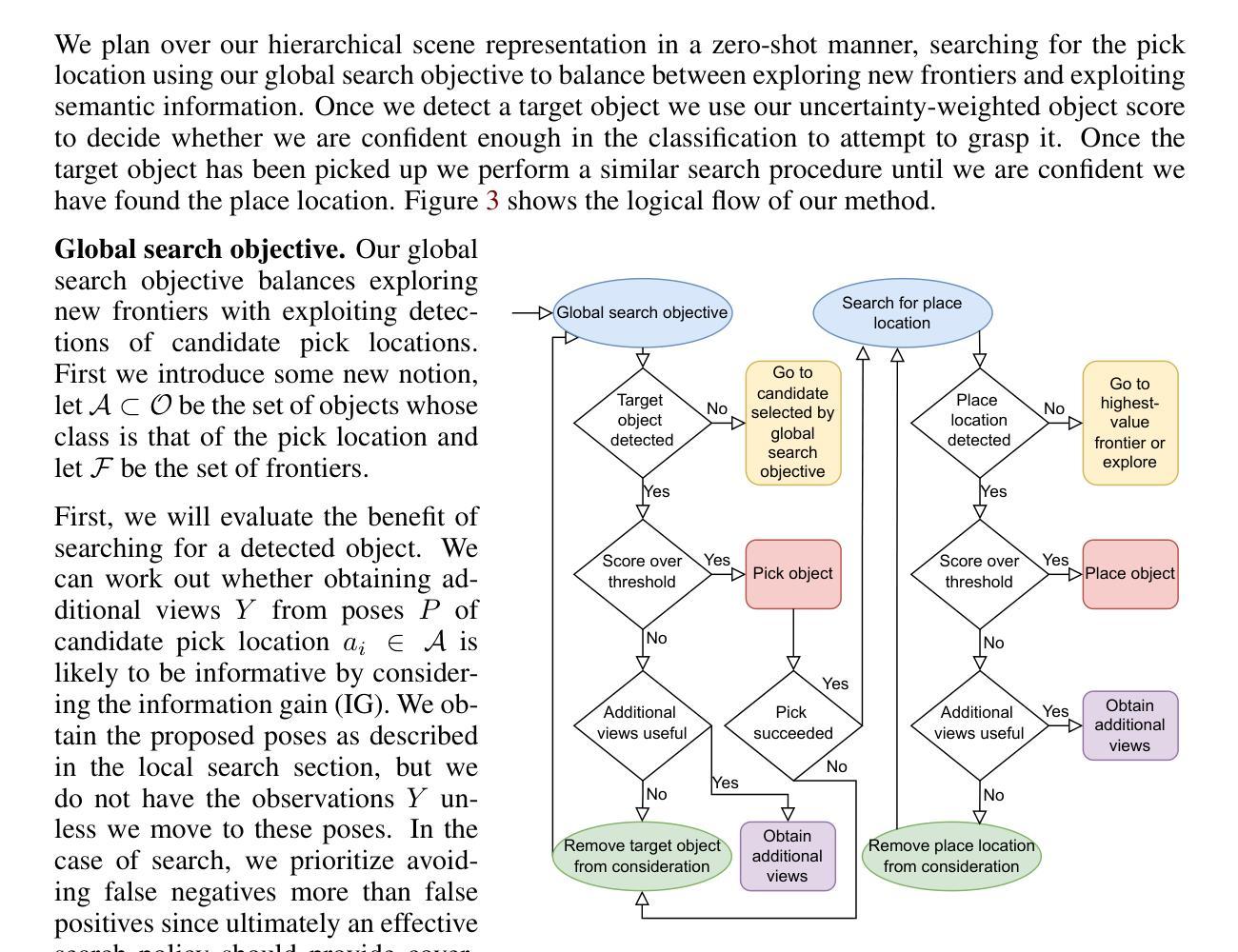
Language-specified mobile manipulation tasks in novel environments simultaneously face challenges interacting with a scene which is only partially observed, grounding semantic information from language instructions to the partially observed scene, and actively updating knowledge of the scene with new observations. To address these challenges, we propose HELIOS, a hierarchical scene representation and associated search objective to perform language specified pick and place mobile manipulation tasks. We construct 2D maps containing the relevant semantic and occupancy information for navigation while simultaneously actively constructing 3D Gaussian representations of task-relevant objects. We fuse observations across this multi-layered representation while explicitly modeling the multi-view consistency of the detections of each object. In order to efficiently search for the target object, we formulate an objective function balancing exploration of unobserved or uncertain regions with exploitation of scene semantic information. We evaluate HELIOS on the OVMM benchmark in the Habitat simulator, a pick and place benchmark in which perception is challenging due to large and complex scenes with comparatively small target objects. HELIOS achieves state-of-the-art results on OVMM. As our approach is zero-shot, HELIOS can also transfer to the real world without requiring additional data, as we illustrate by demonstrating it in a real world office environment on a Spot robot.
在新型环境中执行特定语言指导的移动操控任务时,同时面临着诸多挑战。这些挑战包括与仅部分观察到的场景进行交互、将语言指令中的语义信息关联到部分观察到的场景,以及通过新观察结果主动更新对场景的认识。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了HELIOS系统,这是一个层次化的场景表示和相关搜索目标,用于执行特定语言的拾取和放置移动操控任务。我们构建了包含相关语义和占用信息的二维地图,用于导航,同时主动构建任务相关对象的三维高斯表示。我们融合这种多层表示的观测结果,同时显式地建模每个对象检测的视图一致性。为了有效地搜索目标对象,我们制定了一个目标函数,平衡了未观测或不确定区域的探索与场景语义信息的利用。我们在 Habitat 模拟器的 OVMM 基准测试上评估了 HELIOS,这是一个拾取和放置的基准测试,由于场景大而复杂且目标对象相对较小,因此感知具有挑战性。HELIOS 在 OVMM 上达到了最先进的成果。由于我们的方法是零样本方法,HELIOS 还可以在没有额外数据的情况下转移到现实世界。我们通过演示它在真实世界办公室环境中的 Spot 机器人来证明这一点。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文探讨了在新型环境中执行特定语言指令的移动操纵任务所面临的挑战,包括场景部分观测、语义信息对接及场景知识的实时更新。为应对这些挑战,提出HELIOS系统,采用分层场景表征和搜索目标,执行特定语言的拾取和放置移动操纵任务。构建包含相关语义和占用信息的2D地图用于导航,同时积极构建任务相关对象的3D高斯表示。融合多层表示中的观察结果,显式地建模每个对象检测的多视角一致性。为了有效地搜索目标对象,制定目标函数,平衡未观测或不确定区域的探索与场景语义信息的利用。在 Habitat 模拟器的 OVMM 基准测试上评估 HELIOS,因场景大而复杂、目标对象相对较小,感知具有挑战性。HELIOS 在 OVMM 上取得最新成果。由于零射击方法,HELIOS 无需额外数据即可转移到现实世界,我们在真实的办公室环境中用 Spot 机器人进行演示。
Key Takeaways
- HELIOS系统应对移动操纵任务中的三大挑战:场景部分观测、语义信息对接及场景知识更新。
- HELIOS采用分层场景表征和搜索目标来执行任务。
- 2D地图包含相关语义和占用信息用于导航,同时构建任务相关对象的3D高斯表示。
- 融合多层表示中的观察结果,并显式建模对象检测的多视角一致性。
- 目标函数平衡探索与场景语义信息的利用,提高目标对象搜索效率。
- HELIOS在OVMM基准测试上取得最新成果,展示其性能优势。
点此查看论文截图

GS-2M: Gaussian Splatting for Joint Mesh Reconstruction and Material Decomposition
Authors:Dinh Minh Nguyen, Malte Avenhaus, Thomas Lindemeier
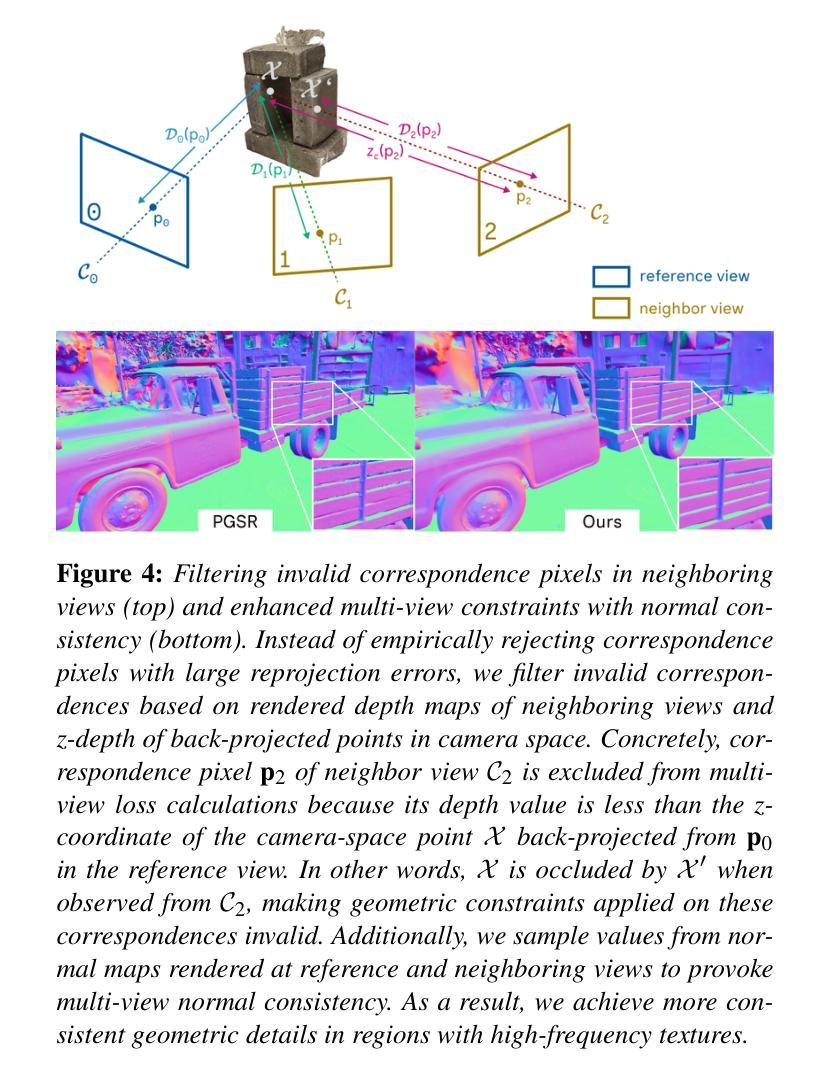
We propose a unified solution for mesh reconstruction and material decomposition from multi-view images based on 3D Gaussian Splatting, referred to as GS-2M. Previous works handle these tasks separately and struggle to reconstruct highly reflective surfaces, often relying on priors from external models to enhance the decomposition results. Conversely, our method addresses these two problems by jointly optimizing attributes relevant to the quality of rendered depth and normals, maintaining geometric details while being resilient to reflective surfaces. Although contemporary works effectively solve these tasks together, they often employ sophisticated neural components to learn scene properties, which hinders their performance at scale. To further eliminate these neural components, we propose a novel roughness supervision strategy based on multi-view photometric variation. When combined with a carefully designed loss and optimization process, our unified framework produces reconstruction results comparable to state-of-the-art methods, delivering triangle meshes and their associated material components for downstream tasks. We validate the effectiveness of our approach with widely used datasets from previous works and qualitative comparisons with state-of-the-art surface reconstruction methods.
我们提出了一种基于3D高斯拼贴的多视角图像网格重建和材料分解的统一解决方案,称为GS-2M。之前的工作是分别处理这两个任务,并且在重建高反射表面时面临困难,通常依赖外部模型的先验知识来增强分解结果。相反,我们的方法通过联合优化与渲染深度和法线质量相关的属性来解决这两个问题,在保持几何细节的同时,对反射表面具有弹性。虽然当代作品能有效地同时解决这两个任务,但它们通常使用复杂的神经网络组件来学习场景属性,这阻碍了它们在规模上的性能。为了进一步消除这些神经网络组件,我们提出了一种基于多视角光度变化的新型粗糙度监督策略。当与一个精心设计的损失和优化过程相结合时,我们的统一框架产生与最先进的方法相当的重建结果,为下游任务提供三角网格及其相关的材料组件。我们使用之前工作中广泛使用的数据集验证了我们的方法的有效性,并与最先进的表面重建方法进行定性比较。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文提出一种基于三维高斯延展技术的统一解决方案,简称GS-2M,用于从多视角图像进行网格重建和材料分解。该方法通过联合优化与渲染深度和法线质量相关的属性,解决了高度反射表面的重建问题,同时保持几何细节。与传统的独立处理这两个任务的方法相比,GS-2M无需依赖外部模型的先验知识即可提升分解结果。此外,通过采用基于多视角光度变化的新型粗糙度监督策略,该方法可进一步简化复杂的神经网络组件,从而提高性能。实验证明,该方法在广泛使用的数据集上与最先进的重建方法相比具有竞争力,可为下游任务提供三角网格及其相关材料组件。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种基于三维高斯延展技术的统一方法GS-2M,用于多视角图像下的网格重建和材料分解。
- 通过联合优化与渲染深度和法线质量相关的属性,解决了高度反射表面的重建问题。
- 不依赖外部模型的先验知识即可提升分解结果。
- 采用基于多视角光度变化的新型粗糙度监督策略,简化复杂的神经网络组件。
- 提出的框架在广泛使用的数据集上表现与最先进的重建方法相当。
- 为下游任务提供三角网格及其相关材料组件。
点此查看论文截图
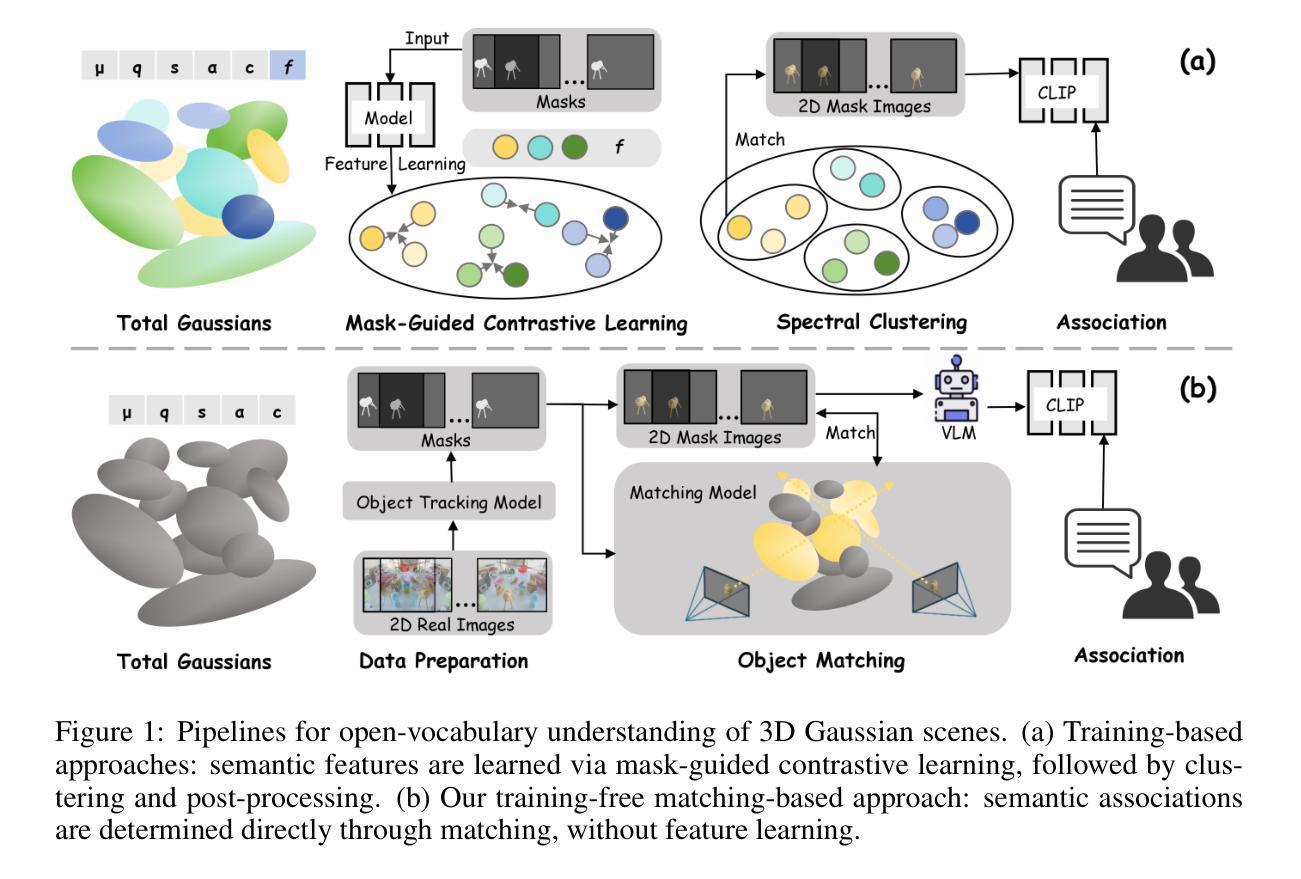
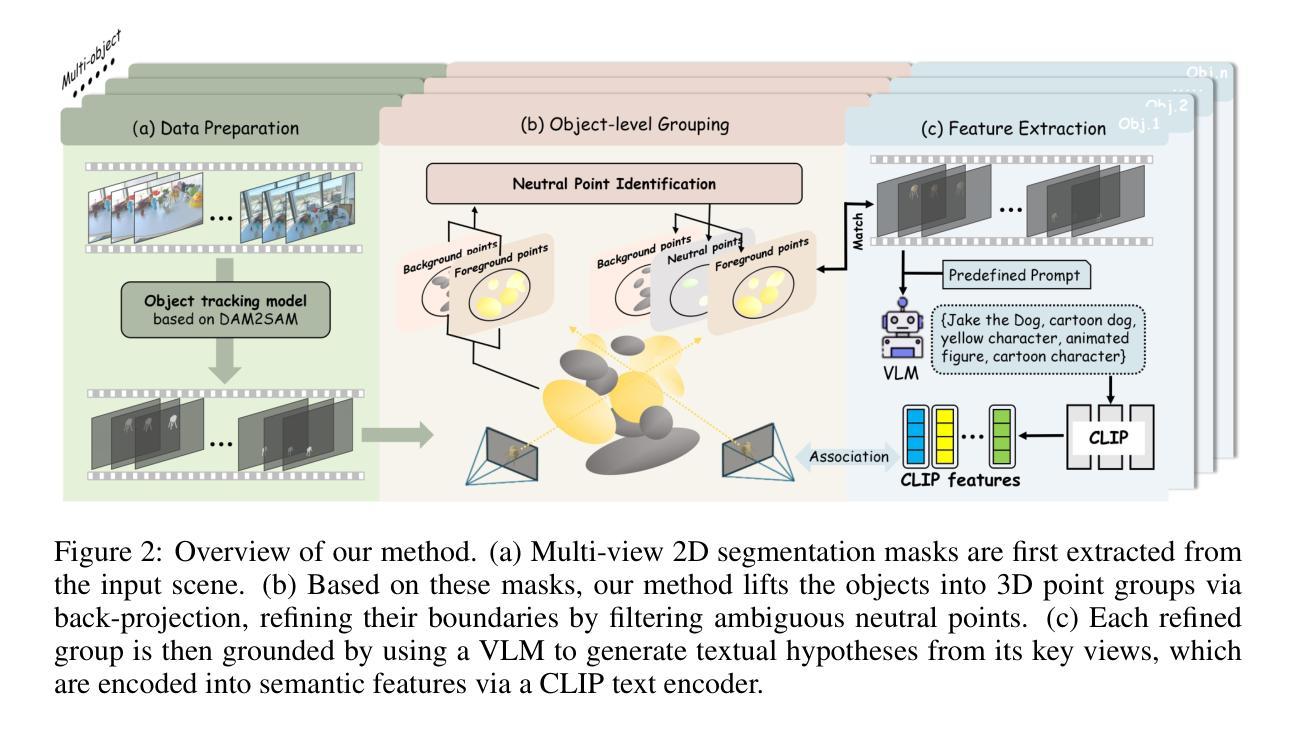
Polysemous Language Gaussian Splatting via Matching-based Mask Lifting
Authors:Jiayu Ding, Xinpeng Liu, Zhiyi Pan, Shiqiang Long, Ge Li
Lifting 2D open-vocabulary understanding into 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) scenes is a critical challenge. However, mainstream methods suffer from three key flaws: (i) their reliance on costly per-scene retraining prevents plug-and-play application; (ii) their restrictive monosemous design fails to represent complex, multi-concept semantics; and (iii) their vulnerability to cross-view semantic inconsistencies corrupts the final semantic representation. To overcome these limitations, we introduce MUSplat, a training-free framework that abandons feature optimization entirely. Leveraging a pre-trained 2D segmentation model, our pipeline generates and lifts multi-granularity 2D masks into 3D, where we estimate a foreground probability for each Gaussian point to form initial object groups. We then optimize the ambiguous boundaries of these initial groups using semantic entropy and geometric opacity. Subsequently, by interpreting the object’s appearance across its most representative viewpoints, a Vision-Language Model (VLM) distills robust textual features that reconciles visual inconsistencies, enabling open-vocabulary querying via semantic matching. By eliminating the costly per-scene training process, MUSplat reduces scene adaptation time from hours to mere minutes. On benchmark tasks for open-vocabulary 3D object selection and semantic segmentation, MUSplat outperforms established training-based frameworks while simultaneously addressing their monosemous limitations.
将二维开放词汇理解提升到三维高斯扩展(3DGS)场景是一个关键挑战。然而,主流方法存在三个主要缺陷:(i)它们依赖于昂贵的场景再训练,这阻碍了即插即用应用程序的使用;(ii)其限制性单语义设计无法表示复杂的多概念语义;(iii)它们对跨视图语义不一致的脆弱性会破坏最终语义表示。为了克服这些局限性,我们引入了MUSplat,这是一个无需训练的框架,完全放弃了特征优化。利用预训练的二维分割模型,我们的管道生成并提升多粒度二维蒙版到三维,我们为高斯点中的每个点估计前景概率以形成初始对象组。然后,我们使用语义熵和几何不透明度优化这些初始组的模糊边界。随后,通过解释对象在其最具代表性观点的外观,视觉语言模型(VLM)提炼出稳健的文本特征,解决视觉不一致问题,通过语义匹配实现开放词汇查询。通过消除昂贵的场景训练过程,MUSplat将场景适应时间从数小时缩短到几分钟。在开放词汇三维对象选择和语义分割的基准任务上,MUSplat的表现优于基于训练的框架,同时解决了它们的单语义限制问题。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
主流方法在处理将二维开放词汇理解提升到三维高斯分裂(3DGS)场景时面临三大挑战。为解决这些问题,我们推出MUSplat框架,无需训练,完全放弃特征优化。借助预训练的二维分割模型,生成并提升多粒度二维掩膜到三维,估计每个高斯点的前景概率形成初始对象组。优化这些初始组的模糊边界利用语义熵和几何透明度。然后,通过解读对象最具代表性的观点的外观,一个视觉语言模型(VLM)提取了稳健的文本特征,解决了视觉不一致问题,实现通过语义匹配进行开放词汇查询。通过消除昂贵的场景训练过程,MUSplat将场景适应时间从数小时缩短到几分钟。在开放词汇三维目标选择和语义分割的基准任务上,MUSplat表现出超越现有基于训练框架的性能,同时解决了它们单一语义的限制。
Key Takeaways
- Lifting 2D open-vocabulary understanding into 3DGS scenes poses significant challenges.
- Mainstream methods have limitations in per-scene retraining, monosemous design, and cross-view semantic inconsistencies.
- MUSplat framework is introduced as a training-free solution, eliminating feature optimization.
- Pre-trained 2D segmentation model is leveraged to generate and lift multi-granularity 2D masks into 3D.
- Initial object groups are formed by estimating foreground probabilities for each Gaussian point.
- The ambiguous boundaries of initial groups are optimized using semantic entropy and geometric opacity.
- A Vision-Language Model (VLM) resolves visual inconsistencies by interpreting object appearances across representative viewpoints.
- MUSplat achieves robust textual features for open-vocabulary querying via semantic matching.
点此查看论文截图

Rigidity-Aware 3D Gaussian Deformation from a Single Image
Authors:Jinhyeok Kim, Jaehun Bang, Seunghyun Seo, Kyungdon Joo
Reconstructing object deformation from a single image remains a significant challenge in computer vision and graphics. Existing methods typically rely on multi-view video to recover deformation, limiting their applicability under constrained scenarios. To address this, we propose DeformSplat, a novel framework that effectively guides 3D Gaussian deformation from only a single image. Our method introduces two main technical contributions. First, we present Gaussian-to-Pixel Matching which bridges the domain gap between 3D Gaussian representations and 2D pixel observations. This enables robust deformation guidance from sparse visual cues. Second, we propose Rigid Part Segmentation consisting of initialization and refinement. This segmentation explicitly identifies rigid regions, crucial for maintaining geometric coherence during deformation. By combining these two techniques, our approach can reconstruct consistent deformations from a single image. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing methods and naturally extends to various applications,such as frame interpolation and interactive object manipulation.
从单一图像重建物体变形在计算机视觉和图形学中仍然是一个巨大的挑战。现有方法通常依赖于多视角视频来恢复变形,这在受限场景下的应用受到局限。为解决此问题,我们提出了DeformSplat,这是一个从单一图像有效引导3D高斯变形的新框架。我们的方法引入了两个主要技术贡献。首先,我们提出了高斯到像素匹配,这缩小了3D高斯表示和2D像素观察之间的领域差距。这可以通过稀疏的视觉线索实现稳健的变形引导。其次,我们提出了刚性部分分割,包括初始化和优化。这种分割明确识别了刚性区域,对于在变形过程中保持几何连贯性至关重要。通过结合这两种技术,我们的方法可以从单一图像重建一致的变形。大量实验表明,我们的方法显著优于现有方法,并自然地扩展到各种应用,如帧内插和交互式对象操作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 11 figures, conference
Summary
本文提出了一种名为DeformSplat的新型框架,它能从单张图像有效地引导三维高斯变形。该框架包括两个主要技术贡献:一是高斯到像素匹配技术,缩小了三维高斯表示和二维像素观测之间的领域差距,从而实现了从稀疏视觉线索的稳健变形引导;二是刚性部分分割技术,包括初始化和细化,该技术能明确识别刚性区域,对于保持变形过程中的几何一致性至关重要。结合这两项技术,该方法能从单张图像重建出一致的变形。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新型框架DeformSplat,能从单张图像引导三维高斯变形。
- 高斯到像素匹配技术,实现了从稀疏视觉线索的稳健变形引导。
- 刚性部分分割技术,有助于明确识别刚性区域,维持变形时的几何一致性。
- 结合上述两项技术,实现了从单张图像重建出一致的变形。
- 该方法显著优于现有方法。
- 该方法可自然扩展到多种应用,如帧内插和交互式对象操作。
点此查看论文截图
Dynamic Novel View Synthesis in High Dynamic Range
Authors:Kaixuan Zhang, Zhipeng Xiong, Minxian Li, Mingwu Ren, Jiankang Deng, Xiatian Zhu
High Dynamic Range Novel View Synthesis (HDR NVS) seeks to learn an HDR 3D model from Low Dynamic Range (LDR) training images captured under conventional imaging conditions. Current methods primarily focus on static scenes, implicitly assuming all scene elements remain stationary and non-living. However, real-world scenarios frequently feature dynamic elements, such as moving objects, varying lighting conditions, and other temporal events, thereby presenting a significantly more challenging scenario. To address this gap, we propose a more realistic problem named HDR Dynamic Novel View Synthesis (HDR DNVS), where the additional dimension ``Dynamic’’ emphasizes the necessity of jointly modeling temporal radiance variations alongside sophisticated 3D translation between LDR and HDR. To tackle this complex, intertwined challenge, we introduce HDR-4DGS, a Gaussian Splatting-based architecture featured with an innovative dynamic tone-mapping module that explicitly connects HDR and LDR domains, maintaining temporal radiance coherence by dynamically adapting tone-mapping functions according to the evolving radiance distributions across the temporal dimension. As a result, HDR-4DGS achieves both temporal radiance consistency and spatially accurate color translation, enabling photorealistic HDR renderings from arbitrary viewpoints and time instances. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HDR-4DGS surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods in both quantitative performance and visual fidelity. Source code will be released.
高动态范围新型视图合成(HDR NVS)旨在从在常规成像条件下捕获的低动态范围(LDR)训练图像中学习HDR 3D模型。当前的方法主要侧重于静态场景,隐含地假设所有场景元素都是静止的且非活动的。然而,现实世界中的场景通常包含动态元素,例如移动物体、变化的照明条件和其他临时事件,因此呈现了一个更具挑战性的场景。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了一个更现实的问题,名为HDR动态新型视图合成(HDR DNVS),其中“动态”这一额外的维度强调了同时建模时间辐射变化以及LDR和HDR之间复杂3D转换的必要性。为了应对这一复杂且相互交织的挑战,我们引入了HDR-4DGS,这是一种基于高斯拼贴架构的算法,具有创新的动态色调映射模块,该模块显式连接HDR和LDR域,通过根据时间维度上不断变化的辐射分布动态地调整色调映射功能来保持时间辐射一致性。因此,HDR-4DGS实现了时间辐射一致性和空间精确的颜色转换,能够实现从任意观点和时间的真实感HDR渲染。大量实验表明,HDR-4DGS在定量性能和视觉保真度方面都超越了现有的最先进方法。源代码将被发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了HDR动态新型视图合成技术(HDR DNVS),旨在解决现实世界中动态元素对高动态范围图像生成带来的挑战。提出一种HDR-4DGS架构,基于高斯光斑映射技术,并配备动态色调映射模块,保持时间辐射一致性,实现了从任意视角和时间点的逼真HDR渲染。实验证明,HDR-4DGS在定量性能和视觉保真度方面均超越现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- HDR动态新型视图合成技术关注现实世界中存在的动态元素(如移动物体、变化的光线条件和时间事件)的挑战。
- HDR-4DGS架构是一种解决此挑战的创新方法,它结合了高斯光斑映射技术和动态色调映射模块。
- 动态色调映射模块可以根据时间维度上的辐射分布变化,动态地适应色调映射功能,保持时间辐射的一致性。
- HDR-4DGS实现了从任意视角和时间点的逼真HDR渲染,达到了时空准确色彩翻译的效果。
- 大量实验证明,HDR-4DGS在定量性能和视觉保真度方面超越了现有的先进技术。
- HDR-4DGS将发布源代码,便于其他研究者进行研究和进一步开发。
- 此技术对于扩展HDR技术在现实场景中的应用,特别是在处理包含动态元素的场景时具有重大意义。
点此查看论文截图

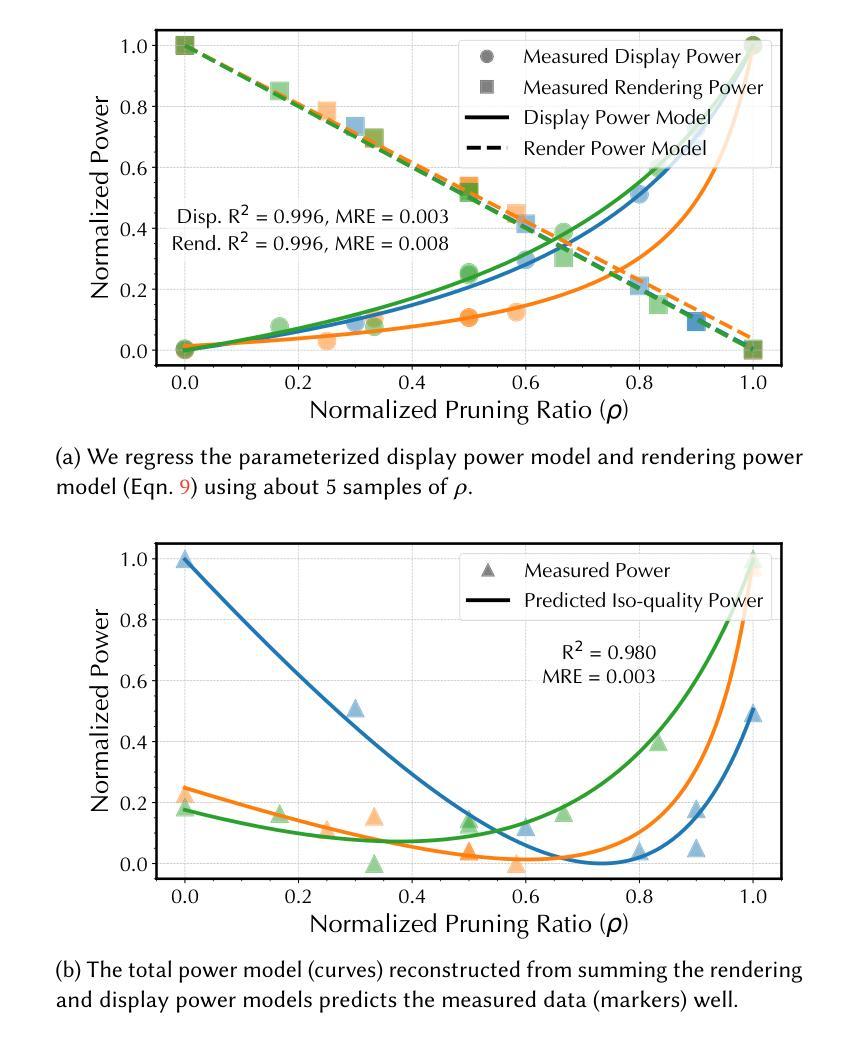
PowerGS: Display-Rendering Power Co-Optimization for Neural Rendering in Power-Constrained XR Systems
Authors:Weikai Lin, Sushant Kondguli, Carl Marshall, Yuhao Zhu
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) combines classic image-based rendering, pointbased graphics, and modern differentiable techniques, and offers an interesting alternative to traditional physically-based rendering. 3DGS-family models are far from efficient for power-constrained Extended Reality (XR) devices, which need to operate at a Watt-level. This paper introduces PowerGS, the first framework to jointly minimize the rendering and display power in 3DGS under a quality constraint. We present a general problem formulation and show that solving the problem amounts to 1) identifying the iso-quality curve(s) in the landscape subtended by the display and rendering power and 2) identifying the power-minimal point on a given curve, which has a closed-form solution given a proper parameterization of the curves. PowerGS also readily supports foveated rendering for further power savings. Extensive experiments and user studies show that PowerGS achieves up to 86% total power reduction compared to state-of-the-art 3DGS models, with minimal loss in both subjective and objective quality. Code is available at https://github.com/horizon-research/PowerGS.
3D高斯贴片(3DGS)结合了基于图像的经典渲染、点基图形和现代化可微技术,为传统基于物理的渲染提供了一种有趣的替代方案。然而,对于功率受限的扩展现实(XR)设备来说,3DGS系列模型效率远远不够,这些设备需要在瓦特级别运行。本文介绍了PowerGS,它是第一个在质量约束下联合最小化渲染和显示功率的框架。我们提出了一个普遍的问题公式,并证明解决问题相当于1)识别由显示和渲染功率所形成的地形中的等质量曲线;2)在给定的曲线上识别功率最小的点,这在曲线适当参数化的情况下具有闭式解。PowerGS也支持快速聚焦渲染以进一步节省功率。广泛的实验和用户研究表明,与最先进的3DGS模型相比,PowerGS在主观和客观质量方面几乎没有损失,总功率降低了高达86%。代码可在https://github.com/horizon-research/PowerGS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, Accepted to Siggraph Asia 2025
Summary
3DGS结合了基于图像的传统渲染技术、点基图形和现代化可微分技术,为传统基于物理的渲染提供了一种有趣的替代方案。然而,对于功率受限的扩展现实(XR)设备来说,3DGS系列模型效率较低。本文介绍了一种名为PowerGS的框架,它能够在保持质量的同时,联合优化渲染和显示功率。实验和用户研究证明,相较于其他先进的3DGS模型,PowerGS的总功率可降低高达86%,同时主观和客观质量损失极小。
Key Takeaways
- 3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)融合了多种技术,提供了一种传统物理渲染的替代方案。
- 对于功率有限的扩展现实(XR)设备,现有的3DGS模型效率不高。
- PowerGS框架旨在联合优化渲染和显示功率,同时保持图像质量。
- PowerGS通过识别显示和渲染功率下的等质量曲线以及每条曲线上的最小功率点来解决问题。
- PowerGS支持局部渲染技术,可进一步节省电力。
- 实验和用户研究显示,相比现有技术,PowerGS可大幅降低总功率消耗。
点此查看论文截图

MS-GS: Multi-Appearance Sparse-View 3D Gaussian Splatting in the Wild
Authors:Deming Li, Kaiwen Jiang, Yutao Tang, Ravi Ramamoorthi, Rama Chellappa, Cheng Peng
In-the-wild photo collections often contain limited volumes of imagery and exhibit multiple appearances, e.g., taken at different times of day or seasons, posing significant challenges to scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis. Although recent adaptations of Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have improved in these areas, they tend to oversmooth and are prone to overfitting. In this paper, we present MS-GS, a novel framework designed with Multi-appearance capabilities in Sparse-view scenarios using 3DGS. To address the lack of support due to sparse initializations, our approach is built on the geometric priors elicited from monocular depth estimations. The key lies in extracting and utilizing local semantic regions with a Structure-from-Motion (SfM) points anchored algorithm for reliable alignment and geometry cues. Then, to introduce multi-view constraints, we propose a series of geometry-guided supervision at virtual views in a fine-grained and coarse scheme to encourage 3D consistency and reduce overfitting. We also introduce a dataset and an in-the-wild experiment setting to set up more realistic benchmarks. We demonstrate that MS-GS achieves photorealistic renderings under various challenging sparse-view and multi-appearance conditions and outperforms existing approaches significantly across different datasets.
野外照片集通常包含有限数量的图像,并且展现出多种外观,如不同时间或季节拍摄的照片,给场景重建和新型视图合成带来重大挑战。尽管最近对神经辐射场(NeRF)和3D高斯喷射(3DGS)的改进已经在这一领域取得进展,但它们倾向于过度平滑并容易出现过度拟合。在本文中,我们提出了一种名为MS-GS的新型框架,它利用基于单眼深度估计引发的几何先验设计具有多重外观能力的稀疏视图场景使用3DGS。为了解决由于稀疏初始化而导致的支持不足问题,我们的方法建立在从单眼深度估计中提取的几何先验之上。关键在于使用结构从运动(SfM)点锚定算法提取和利用局部语义区域,以实现可靠的对齐和几何线索。然后,为了引入多视图约束,我们提出了一种在精细和粗略方案中在虚拟视图上进行几何指导监督的一系列方法,以鼓励三维一致性并减少过度拟合。我们还介绍了一个数据集和一个野外实验设置,以建立更现实的基准测试。我们证明,MS-GS在各种具有挑战性的稀疏视图和多重外观条件下实现了逼真的渲染,并在不同数据集上显著优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF fixed typos
Summary
本文提出了一种名为MS-GS的新框架,用于处理稀疏视图下的多外观场景。该框架基于单目深度估计的几何先验信息,利用结构从运动(SfM)点锚定算法提取和利用局部语义区域,实现可靠的对齐和几何线索。通过引入多视图约束和几何引导的精细和粗略监督方案,减少了过拟合现象并提高了3D一致性。实验证明,MS-GS在稀疏视图和多外观条件下实现了逼真的渲染效果,并在不同的数据集上显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- MS-GS是一个针对稀疏视图下多外观场景的全新框架。
- 利用单目深度估计的几何先验信息来处理稀疏初始化带来的问题。
- 使用结构从运动(SfM)点锚定算法提取局部语义区域,实现可靠对齐和几何线索。
- 通过引入多视图约束和几何引导的精细与粗略监督方案,提高3D一致性并减少过拟合。
- 引入新的数据集和实验设置,建立更现实的基准测试。
- MS-GS在各种具有挑战性的稀疏视图和多外观条件下实现了逼真的渲染效果。
点此查看论文截图

Mobi-$π$: Mobilizing Your Robot Learning Policy
Authors:Jingyun Yang, Isabella Huang, Brandon Vu, Max Bajracharya, Rika Antonova, Jeannette Bohg
Learned visuomotor policies are capable of performing increasingly complex manipulation tasks. However, most of these policies are trained on data collected from limited robot positions and camera viewpoints. This leads to poor generalization to novel robot positions, which limits the use of these policies on mobile platforms, especially for precise tasks like pressing buttons or turning faucets. In this work, we formulate the policy mobilization problem: find a mobile robot base pose in a novel environment that is in distribution with respect to a manipulation policy trained on a limited set of camera viewpoints. Compared to retraining the policy itself to be more robust to unseen robot base pose initializations, policy mobilization decouples navigation from manipulation and thus does not require additional demonstrations. Crucially, this problem formulation complements existing efforts to improve manipulation policy robustness to novel viewpoints and remains compatible with them. We propose a novel approach for policy mobilization that bridges navigation and manipulation by optimizing the robot’s base pose to align with an in-distribution base pose for a learned policy. Our approach utilizes 3D Gaussian Splatting for novel view synthesis, a score function to evaluate pose suitability, and sampling-based optimization to identify optimal robot poses. To understand policy mobilization in more depth, we also introduce the Mobi-$\pi$ framework, which includes: (1) metrics that quantify the difficulty of mobilizing a given policy, (2) a suite of simulated mobile manipulation tasks based on RoboCasa to evaluate policy mobilization, and (3) visualization tools for analysis. In both our developed simulation task suite and the real world, we show that our approach outperforms baselines, demonstrating its effectiveness for policy mobilization.
学习到的视觉运动策略能够执行越来越复杂的操作任务。然而,大多数这些策略都是在从有限的机器人位置和摄像头视角收集的数据上进行训练的。这导致了对新的机器人位置的泛化能力较差,从而限制了这些策略在移动平台上的使用,尤其是像按钮或水龙头这样的精确任务。在这项工作中,我们制定了策略动员问题:在一个新环境中找到一个移动机器人基座姿态,使其相对于在有限的摄像头视角集上训练的操纵策略处于分布状态。与重新训练策略本身以使其对看不见的机器人基座姿态初始化更具鲁棒性相比,策略动员将导航与操作解耦,因此不需要额外的演示。关键的是,该问题公式对现有努力形成补充,以提高操纵策略对新型视角的鲁棒性,并仍然与之兼容。我们提出了一种用于策略动员的新方法,它通过优化机器人的基座姿态来与学习的策略的分布基座姿态对齐,从而架起导航与操作之间的桥梁。我们的方法利用三维高斯拼贴进行新视角合成、评分函数来评估姿态的合适性,以及基于采样的优化来确定最佳的机器人姿态。为了更深入地了解策略动员,我们还引入了Mobi-$\pi$框架,其中包括:(1)量化给定策略动员难度的指标,(2)基于RoboCasa的一系列模拟移动操作任务来评估策略动员,(3)分析工具进行数据分析。在我们的开发仿真任务套件和真实世界中,我们的方法都优于基线方法,证明了其在策略动员方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CoRL 2025. Project website: https://mobipi.github.io/
摘要
针对移动机器人操作策略的问题,本文提出了一种新的解决方案。在有限的相机视角训练的操作策略无法很好地适应新的机器人位置,限制了策略在移动平台上的应用。本文旨在找到一种移动机器人底座姿态,使其在新的环境中与训练策略相适应。与重新训练策略以适应看不见的机器人底座姿态初始化相比,策略动员将导航和操作解耦,无需额外的演示。本文提出的方法结合了导航和操作,通过优化机器人底座姿态以符合训练策略的分布。利用三维高斯拼接实现新视角合成,评分函数评估姿态的合适性,并采用基于采样的优化确定最佳机器人姿态。此外,引入Mobi-$\pi$框架,包括量化政策动员难度的指标、基于RoboCasa的模拟移动操作任务套件以及分析工具等。在模拟任务和现实世界的实验中,该方法均表现出较好的效果。
关键见解
- 大多数操作策略是基于有限的机器人位置和相机视角进行训练的,导致在新的机器人位置上表现不佳。
- 策略动员问题旨在找到一种适应新环境的移动机器人底座姿态,使其与在有限的相机视角上训练的操作策略相适应。
- 与重新训练策略相比,策略动员方法将导航和操作解耦,不需要额外的演示。
- 提出了一种结合导航和操作的方法,通过优化机器人底座姿态来符合训练策略的分布。
- 利用三维高斯拼接实现新视角合成,采用评分函数和基于采样的优化技术来确定最佳机器人姿态。
- 引入了Mobi-$\pi$框架,包括用于评估策略动员难度的指标、模拟移动操作任务套件以及分析工具等。
点此查看论文截图
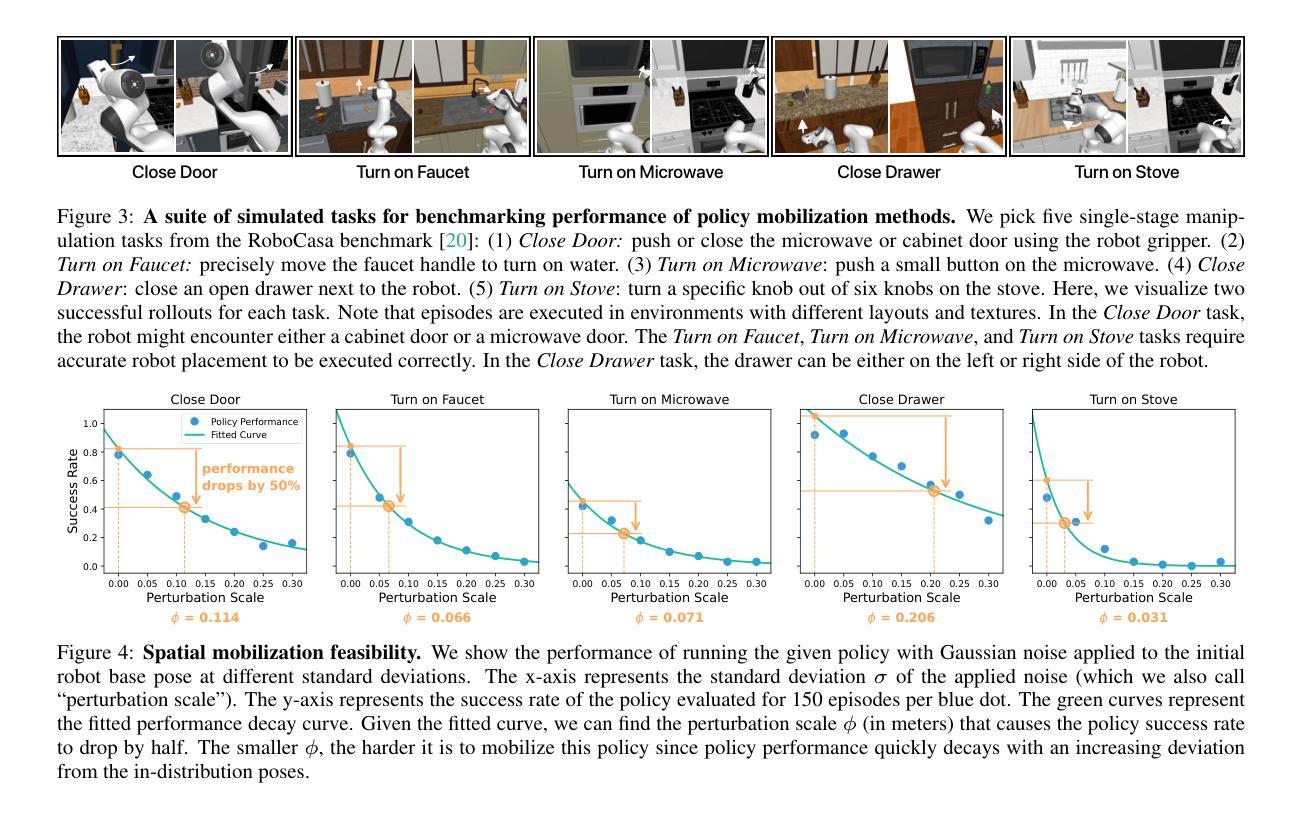
Pose-free 3D Gaussian splatting via shape-ray estimation
Authors:Youngju Na, Taeyeon Kim, Jumin Lee, Kyu Beom Han, Woo Jae Kim, Sung-eui Yoon
While generalizable 3D Gaussian splatting enables efficient, high-quality rendering of unseen scenes, it heavily depends on precise camera poses for accurate geometry. In real-world scenarios, obtaining accurate poses is challenging, leading to noisy pose estimates and geometric misalignments. To address this, we introduce SHARE, a pose-free, feed-forward Gaussian splatting framework that overcomes these ambiguities by joint shape and camera rays estimation. Instead of relying on explicit 3D transformations, SHARE builds a pose-aware canonical volume representation that seamlessly integrates multi-view information, reducing misalignment caused by inaccurate pose estimates. Additionally, anchor-aligned Gaussian prediction enhances scene reconstruction by refining local geometry around coarse anchors, allowing for more precise Gaussian placement. Extensive experiments on diverse real-world datasets show that our method achieves robust performance in pose-free generalizable Gaussian splatting.
虽然通用的三维高斯摊铺能够实现未见场景的高效高质量渲染,但它严重依赖于精确的相机姿态以获得准确的几何结构。在真实场景中,获得准确的姿态是一个挑战,导致姿态估计产生噪声和几何结构错位。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了SHARE,一个无需姿态的前馈高斯摊铺框架,通过联合形状和相机射线估计来克服这些不确定性。SHARE并没有依赖于明确的3D转换,而是构建了一个姿态感知的标准体积表示,无缝地集成了多视角信息,减少了因姿态估计不准确导致的错位。此外,锚点对齐的高斯预测通过改进粗糙锚点周围的局部几何结构,增强了场景重建,允许更精确的高斯放置。在多种真实数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在无需姿态的一般化高斯摊铺中实现了稳健的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICIP 2025 (Best Student Paper Award)
Summary
该文介绍了SHARE,一种无需姿态的前馈高斯展平框架。该框架解决了在现实世界场景中由于姿态估计不准确导致的几何错位问题。通过构建姿态感知的规范体积表示,该框架无缝集成多视图信息,减少了由于姿态估计不准确导致的不对齐现象。同时,锚点对齐的高斯预测提高了场景重建的质量,通过细化粗锚点周围的局部几何,实现更精确的高斯放置。实验证明,该方法在无需姿态的一般化高斯展平中实现了稳健的性能。
Key Takeaways
- SHARE是一种无需姿态的展平框架,解决了因姿态估计不准确导致的几何错位问题。
- 通过构建姿态感知的规范体积表示,SHARE能够无缝集成多视图信息。
- SHARE减少了由于不准确姿态估计导致的几何不对齐现象。
- 锚点对齐的高斯预测提高了场景重建质量。
- 通过细化粗锚点周围的局部几何,SHARE实现了更精确的高斯放置。
- 现实世界场景中的广泛实验证明了SHARE方法的稳健性能。
点此查看论文截图
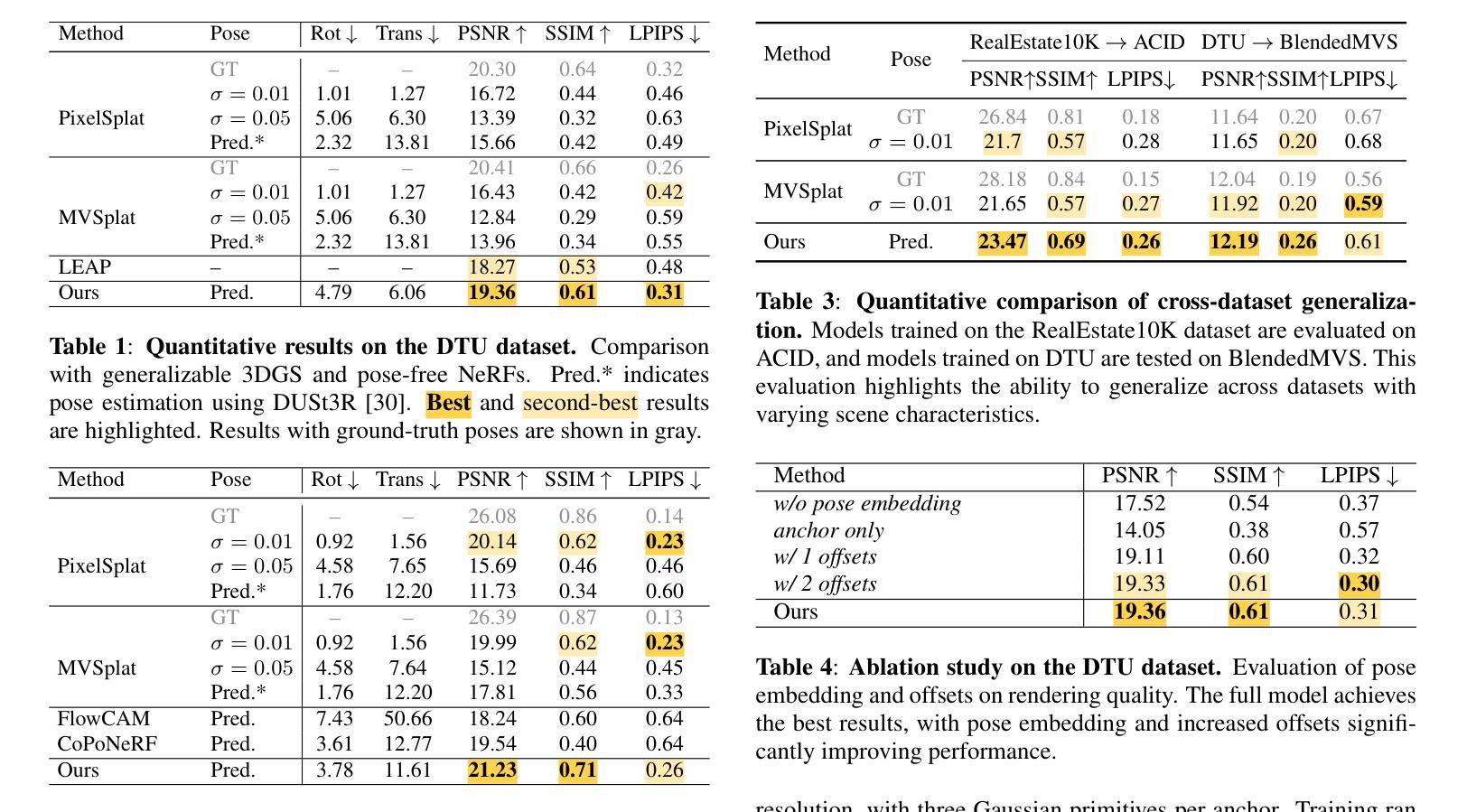

Semantic Consistent Language Gaussian Splatting for Point-Level Open-vocabulary Querying
Authors:Hairong Yin, Huangying Zhan, Yi Xu, Raymond A. Yeh
Open-vocabulary 3D scene understanding is crucial for robotics applications, such as natural language-driven manipulation, human-robot interaction, and autonomous navigation. Existing methods for querying 3D Gaussian Splatting often struggle with inconsistent 2D mask supervision and lack a robust 3D point-level retrieval mechanism. In this work, (i) we present a novel point-level querying framework that performs tracking on segmentation masks to establish a semantically consistent ground-truth for distilling the language Gaussians; (ii) we introduce a GT-anchored querying approach that first retrieves the distilled ground-truth and subsequently uses the ground-truth to query the individual Gaussians. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art performance. Our method achieves an mIoU improvement of +4.14, +20.42, and +1.7 on the LERF, 3D-OVS, and Replica datasets. These results validate our framework as a promising step toward open-vocabulary understanding in real-world robotic systems.
开放式词汇表的3D场景理解对于机器人应用至关重要,例如自然语言驱动的操控、人机互动和自主导航。现有的查询3D高斯拼接的方法往往面临2D掩膜监督不一致的问题,且缺乏稳健的3D点级检索机制。在这项工作中,(i)我们提出了一个新型的点级查询框架,通过对分割掩膜进行追踪来建立语义一致的真实地面来提炼语言高斯分布;(ii)我们引入了一种以GT为中心的查询方法,该方法首先检索提炼后的真实地面,然后利用真实地面来查询各个高斯分布。在三个基准数据集上的大量实验表明,所提出的方法优于最新技术。我们的方法在LERF、3D-OVS和Replica数据集上分别实现了+4.14、+20.42和+1.7的mIoU改进。这些结果验证了我们的框架在真实世界的机器人系统中进行开放式词汇表理解的可行性,是一项很有前景的尝试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种面向开放词汇场景理解的机器人应用新方法,解决了现有方法在查询三维高斯分裂时面临的二维掩膜监督不一致和缺乏稳健的三维点级检索机制的问题。通过引入点级查询框架和GT锚定查询方法,该方法在三个基准数据集上的表现优于现有技术,提高了mIoU指标。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇的3D场景理解对机器人应用至关重要,如自然语言驱动的操控、人机互动和自主导航。
- 现有方法在查询三维高斯分裂时面临二维掩膜监督不一致的问题。
- 引入了点级查询框架,通过跟踪分割掩膜建立语义一致的真实标签,用于提取语言高斯。
- 采用了GT锚定的查询方法,首先检索提取的真实标签,然后使用真实标签查询各个高斯。
- 在三个基准数据集上进行了广泛实验,提出的方法优于最新技术。
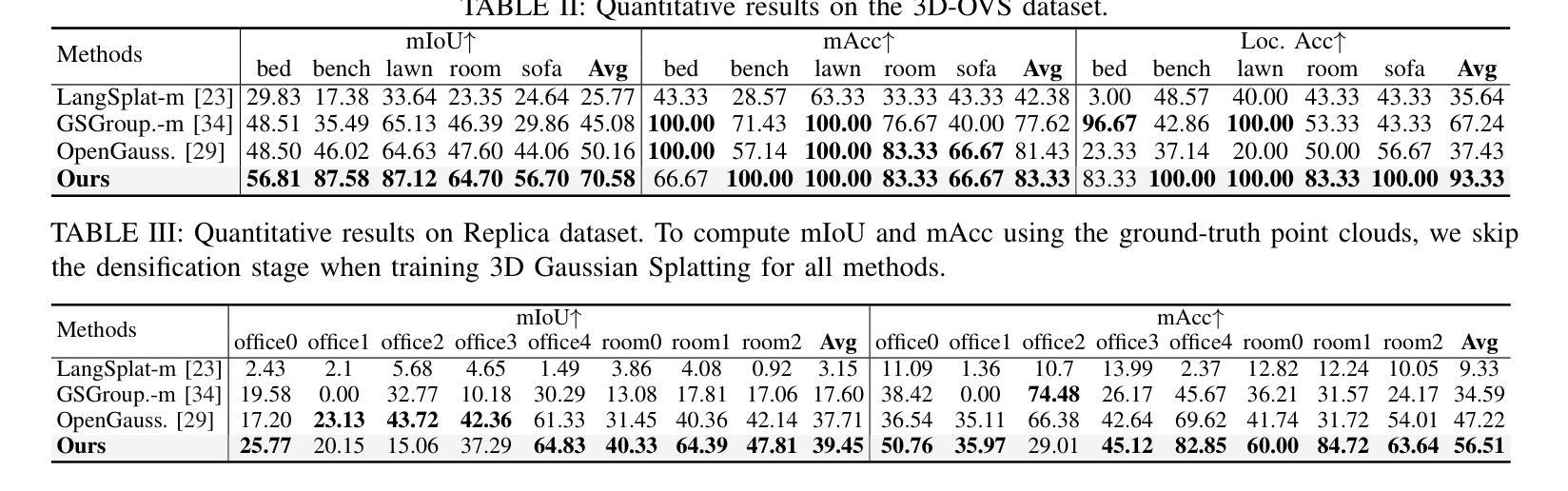
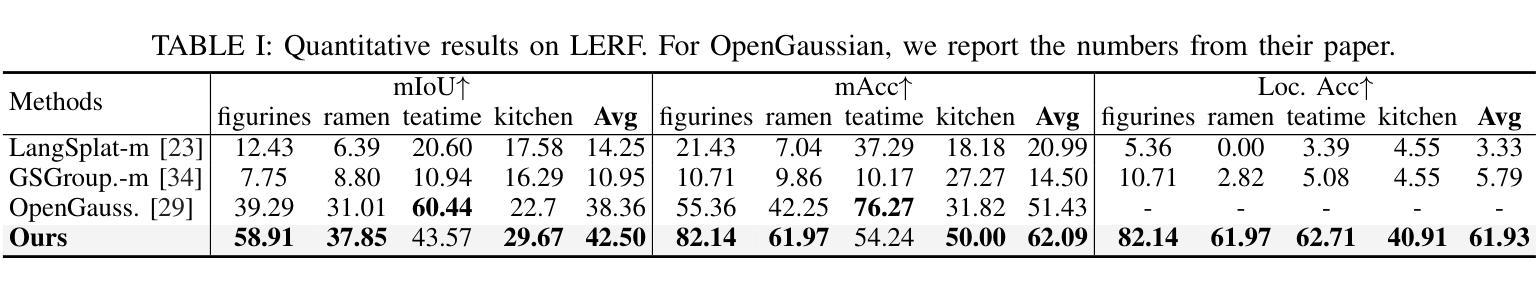
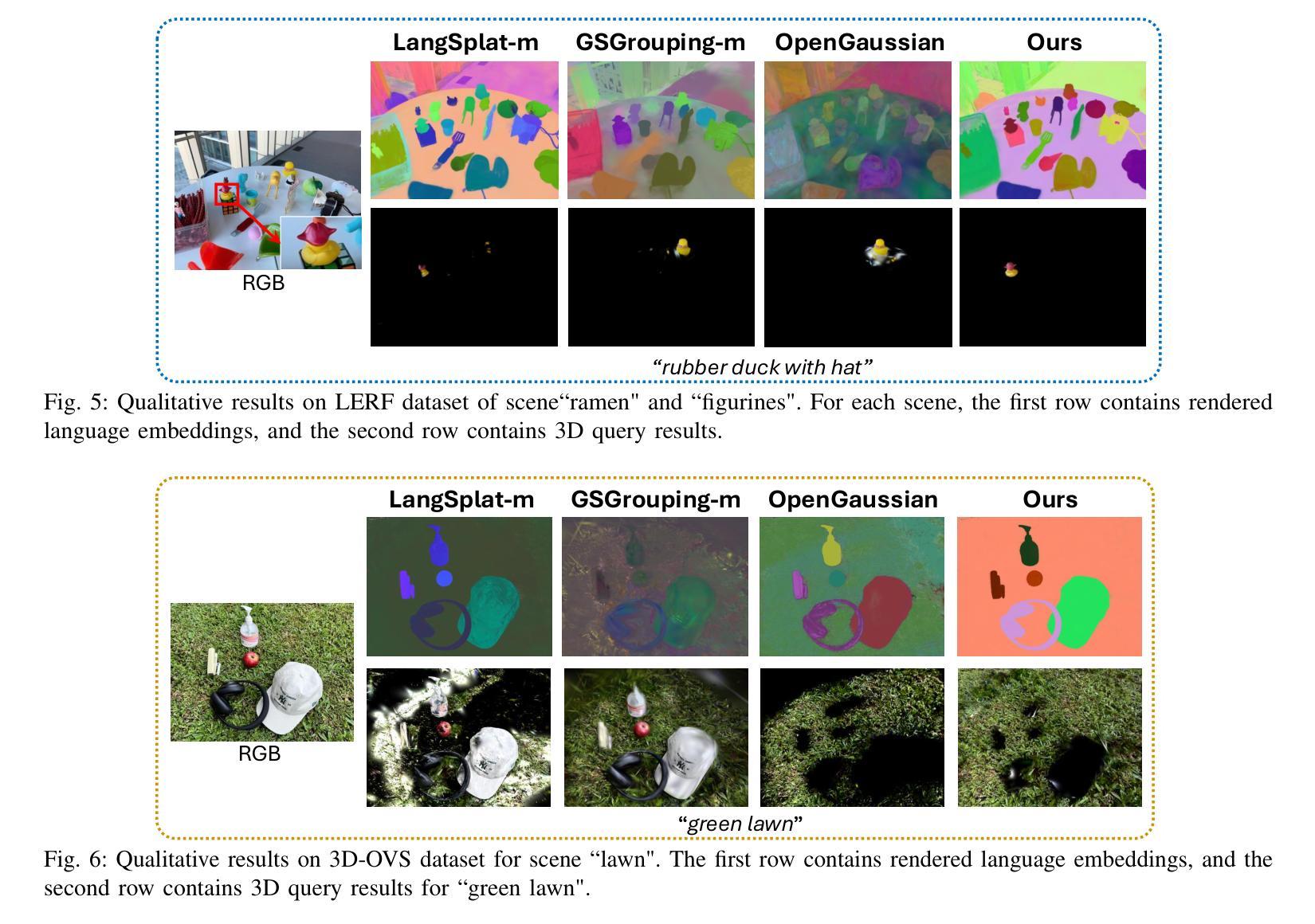
- 在LERF、3D-OVS和Replica数据集上,mIoU指标分别提高了+4.14、+20.42和+1.7。
点此查看论文截图

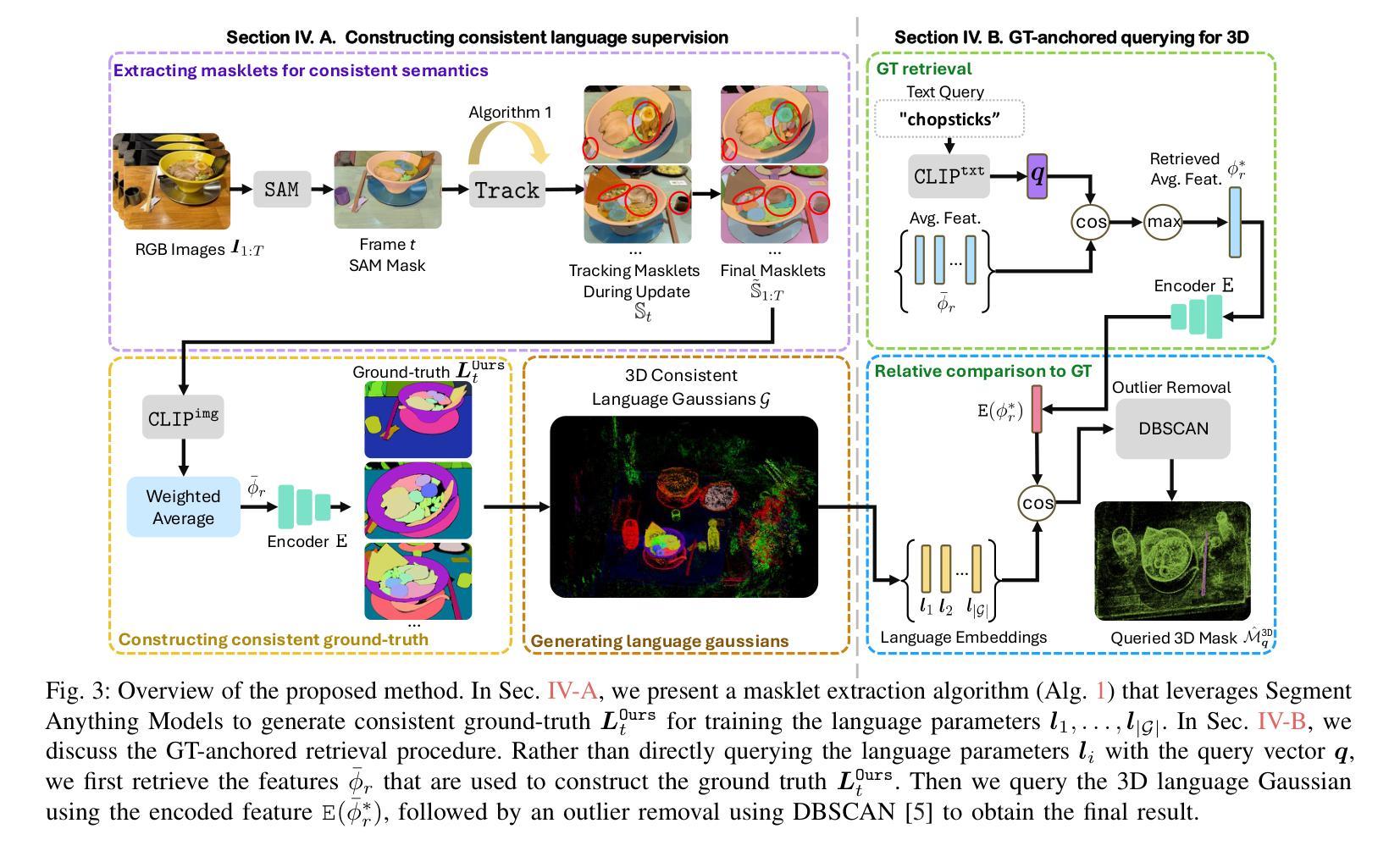
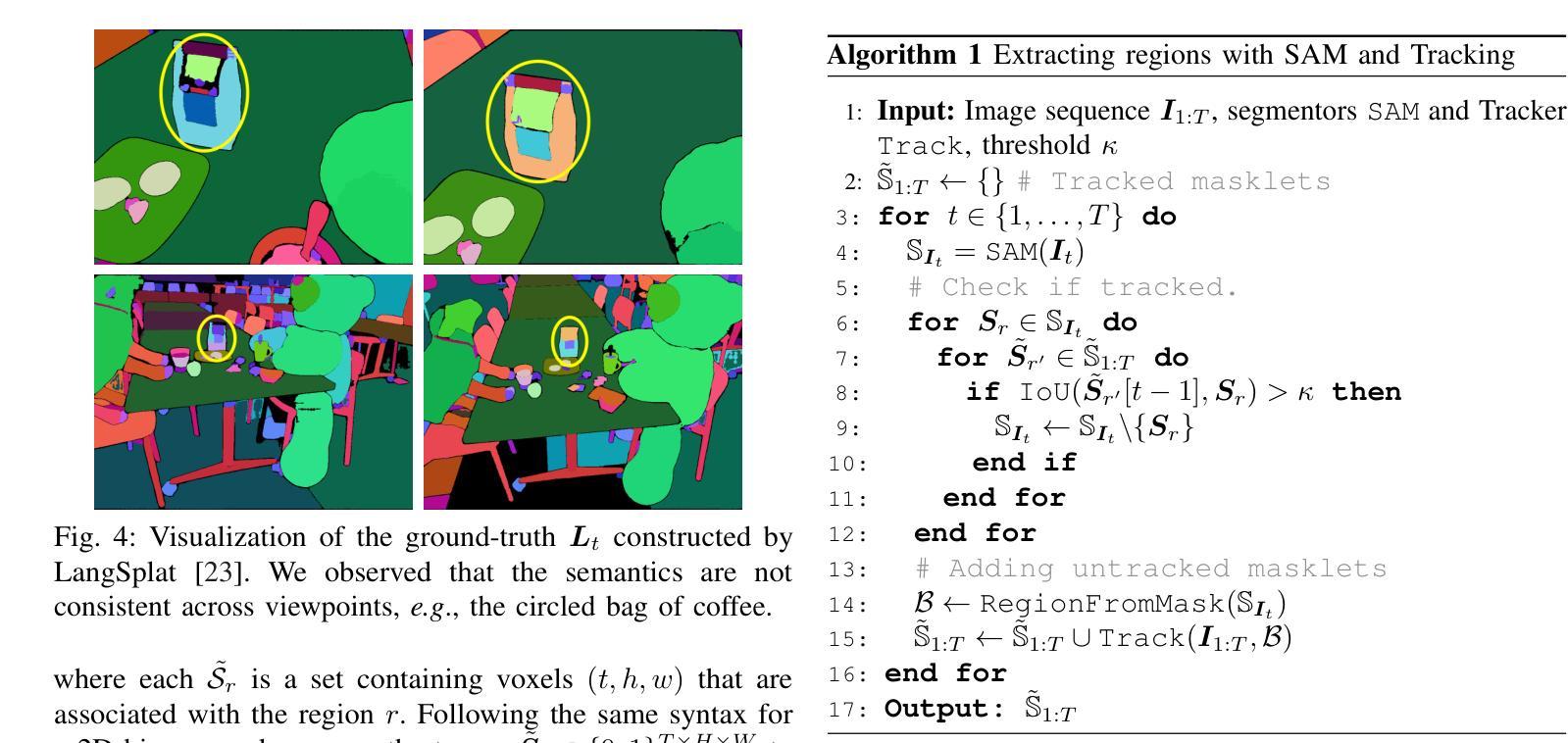
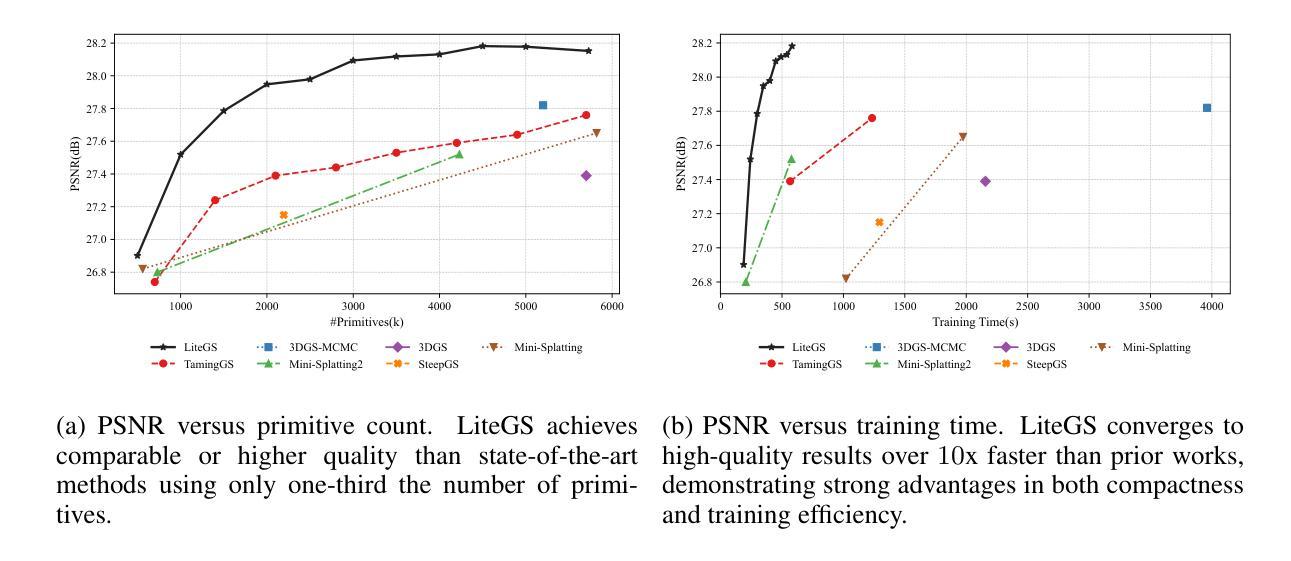
LiteGS: A High-performance Framework to Train 3DGS in Subminutes via System and Algorithm Codesign
Authors:Kaimin Liao, Hua Wang, Zhi Chen, Luchao Wang, Yaohua Tang
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as promising alternative in 3D representation. However, it still suffers from high training cost. This paper introduces LiteGS, a high performance framework that systematically optimizes the 3DGS training pipeline from multiple aspects. At the low-level computation layer, we design a warp-based raster'' associated with two hardware-aware optimizations to significantly reduce gradient reduction overhead. At the mid-level data management layer, we introduce dynamic spatial sorting based on Morton coding to enable a performant Cluster-Cull-Compact’’ pipeline and improve data locality, therefore reducing cache misses. At the top-level algorithm layer, we establish a new robust densification criterion based on the variance of the opacity gradient, paired with a more stable opacity control mechanism, to achieve more precise parameter growth. Experimental results demonstrate that LiteGS accelerates the original 3DGS training by up to 13.4x with comparable or superior quality and surpasses the current SOTA in lightweight models by up to 1.4x speedup. For high-quality reconstruction tasks, LiteGS sets a new accuracy record and decreases the training time by an order of magnitude.
3D高斯Splatting(3DGS)作为3D表示的一种有前途的替代方案已经出现。然而,它仍然存在着训练成本高的问题。本文介绍了LiteGS,一个高性能框架,从多个方面系统地优化了3DGS训练管道。在底层计算层,我们设计了一种基于warp的raster,并对其进行两项硬件感知优化,以显著降低梯度缩减的开销。在中层数据管理层,我们引入基于Morton编码的动态空间排序,以实现高效的“Cluster-Cull-Compact”管道,提高数据局部性,从而减少缓存未命中。在顶层算法层,我们建立了一个新的基于不透明度梯度方差稳健的致密化标准,配合更稳定的不透明度控制机制,实现更精确的参数增长。实验结果表明,LiteGS将原始3DGS训练速度提高了高达13.4倍,同时保持或提高了质量,并在轻量级模型上超越了当前最佳水平(SOTA),最高提速达1.4倍。对于高质量重建任务,LiteGS创造了新的精度记录,并将训练时间缩短了一个数量级。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了LiteGS框架,它是一个高性能的3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)训练管道优化方案。通过低层计算、中层数据管理和高层算法的优化,LiteGS显著减少了训练成本,提高了训练速度,同时保持了或提高了质量。
Key Takeaways
- LiteGS是首个对3DGS训练管道进行多方面优化的高性能框架。
- 在低层计算中,通过设计基于warp的raster和两个硬件优化,显著减少了梯度降低的开销。
- 在中层数据中,引入了基于Morton编码的动态空间排序,实现了高效的“Cluster-Cull-Compact”管道,提高了数据局部性,减少了缓存未命中。
- 在高层算法中,建立了基于不透明度梯度方差的新稳健致密化标准,配合更稳定的不透明度控制机制,实现了更精确的参数增长。
- 实验结果表明,LiteGS将原始3DGS训练速度提高了高达13.4倍,同时保持或提高了质量。
- LiteGS在轻量级模型中比当前最佳方案提速高达1.4倍。
点此查看论文截图