⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-30 更新
RefAM: Attention Magnets for Zero-Shot Referral Segmentation
Authors:Anna Kukleva, Enis Simsar, Alessio Tonioni, Muhammad Ferjad Naeem, Federico Tombari, Jan Eric Lenssen, Bernt Schiele
Most existing approaches to referring segmentation achieve strong performance only through fine-tuning or by composing multiple pre-trained models, often at the cost of additional training and architectural modifications. Meanwhile, large-scale generative diffusion models encode rich semantic information, making them attractive as general-purpose feature extractors. In this work, we introduce a new method that directly exploits features, attention scores, from diffusion transformers for downstream tasks, requiring neither architectural modifications nor additional training. To systematically evaluate these features, we extend benchmarks with vision-language grounding tasks spanning both images and videos. Our key insight is that stop words act as attention magnets: they accumulate surplus attention and can be filtered to reduce noise. Moreover, we identify global attention sinks (GAS) emerging in deeper layers and show that they can be safely suppressed or redirected onto auxiliary tokens, leading to sharper and more accurate grounding maps. We further propose an attention redistribution strategy, where appended stop words partition background activations into smaller clusters, yielding sharper and more localized heatmaps. Building on these findings, we develop RefAM, a simple training-free grounding framework that combines cross-attention maps, GAS handling, and redistribution. Across zero-shot referring image and video segmentation benchmarks, our approach consistently outperforms prior methods, establishing a new state of the art without fine-tuning or additional components.
目前大多数指代分割的方法只有通过对多个预训练模型进行微调或组合,才能取得良好的性能,这通常需要额外的训练和架构修改。与此同时,大规模的生成扩散模型编码了丰富的语义信息,使其成为通用的特征提取器的理想选择。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种新方法,它直接从扩散变压器中提取特征、注意力分数,用于下游任务,无需进行架构修改或额外的训练。为了系统地评估这些特性,我们扩展了涵盖图像和视频的视觉语言定位任务基准测试。我们的关键见解是,停用词充当注意力磁铁:它们积累了多余的注意力并且可以被过滤以减少噪音。此外,我们确定了在较深层次中出现的全局注意力汇点(GAS),并表明它们可以被安全地抑制或重定向到辅助标记,从而产生更清晰、更准确的定位图。我们进一步提出了注意力再分配策略,其中添加的停用词将背景激活划分为较小的集群,产生更清晰、更局部的热图。基于这些发现,我们开发了RefAM,这是一个简单的无需训练的定位框架,它结合了交叉注意力图、GAS处理和再分配。在无预设参照的图像和视频分割基准测试中,我们的方法始终优于以前的方法,建立了新的技术标杆,无需微调或额外的组件。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://refam-diffusion.github.io/
Summary:
本文介绍了一种新的方法,该方法直接利用扩散变压器的特征(注意力得分)进行下游任务,无需进行架构修改或额外的训练。研究的关键见解是停用词作为注意力磁铁积累过多的注意力并可以过滤以减少噪声。通过抑制或重定向全局注意力汇点(GAS),得到更清晰准确的定位图。基于这些发现,研究提出了一种未经训练的定位框架RefAM,结合交叉注意力图、GAS处理和重新分配,在零样本引用图像和视频分割基准测试中表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 现有引用分割方法大多需要通过微调或组合多个预训练模型来实现高性能,这通常需要额外的训练和架构修改。
- 大规模生成性扩散模型编码丰富的语义信息,可作为通用特征提取器。
- 停用词在模型中扮演注意力磁铁角色,积累过多注意力并可以过滤以减少噪声。
- 识别出全局注意力汇点(GAS),可以通过抑制或重定向来提升模型性能。
- 提出了一种注意力重新分配策略,通过附加停用词将背景激活分成较小的集群,产生更清晰、更局部化的热图。
- 基于上述发现,开发了一种无需训练的定位框架RefAM,该方法结合了交叉注意力图、GAS处理和重新分配策略。
点此查看论文截图
Training-Free Synthetic Data Generation with Dual IP-Adapter Guidance
Authors:Luc Boudier, Loris Manganelli, Eleftherios Tsonis, Nicolas Dufour, Vicky Kalogeiton
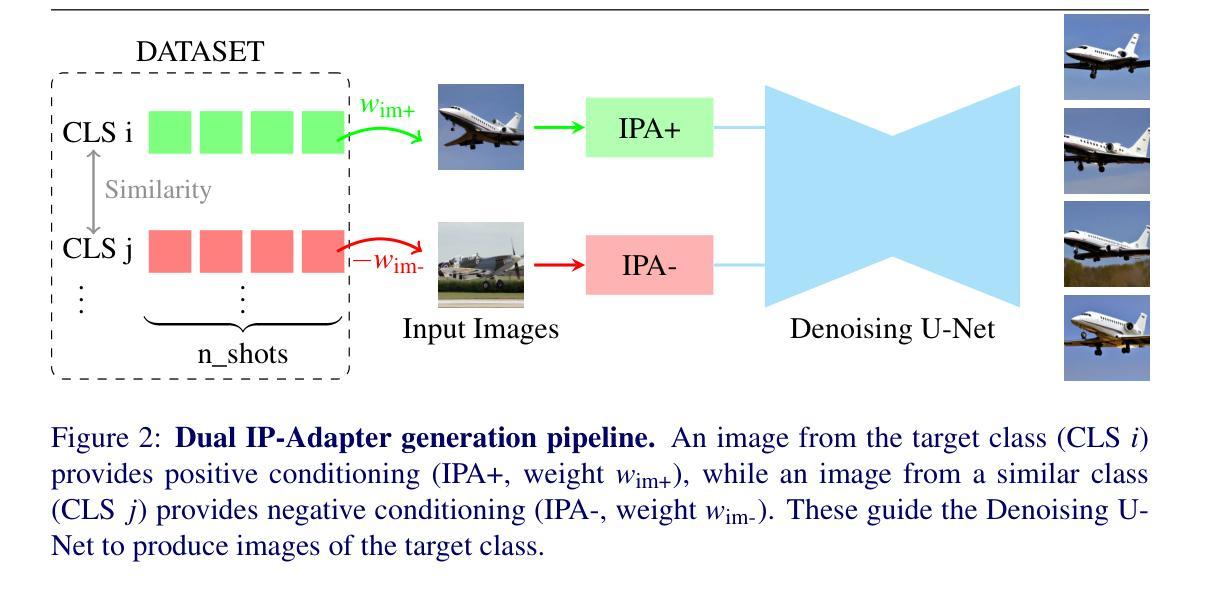
Few-shot image classification remains challenging due to the limited availability of labeled examples. Recent approaches have explored generating synthetic training data using text-to-image diffusion models, but often require extensive model fine-tuning or external information sources. We present a novel training-free approach, called DIPSY, that leverages IP-Adapter for image-to-image translation to generate highly discriminative synthetic images using only the available few-shot examples. DIPSY introduces three key innovations: (1) an extended classifier-free guidance scheme that enables independent control over positive and negative image conditioning; (2) a class similarity-based sampling strategy that identifies effective contrastive examples; and (3) a simple yet effective pipeline that requires no model fine-tuning or external captioning and filtering. Experiments across ten benchmark datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art or comparable performance, while eliminating the need for generative model adaptation or reliance on external tools for caption generation and image filtering. Our results highlight the effectiveness of leveraging dual image prompting with positive-negative guidance for generating class-discriminative features, particularly for fine-grained classification tasks.
图像分类的少量样本仍然是一个挑战,因为可用的标记样本有限。最近的方法已经尝试使用文本到图像的扩散模型生成合成训练数据,但这通常需要大量的模型微调或外部信息源。我们提出了一种新的无需训练的方法,称为DIPSY,它利用IP-Adapter进行图像到图像的翻译,仅使用可用的少量样本生成高度判别性的合成图像。DIPSY引入了三个关键创新点:(1)一种扩展的无分类器引导方案,实现对正负图像条件的独立控制;(2)一种基于类别相似性的采样策略,用于识别有效的对比示例;(3)一个简单有效的流程,无需模型微调或外部字幕标注和过滤。在十个基准数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的水平或相当的性能表现,同时消除了对生成模型适应性的需求或对生成字幕和图像过滤的外部工具的依赖。我们的结果强调了利用具有正负引导的双向图像提示生成类别判别特征的有效性,特别是对于精细分类任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF BMVC 2025. Project page: https://www.lix.polytechnique.fr/vista/projects/2025_bmvc_dipsy/
Summary
本文提出了一种基于图像到图像翻译的新方法DIPSY,利用IP-Adapter生成高度区分性的合成图像,仅使用有限的样本即可完成少样本图像分类任务。DIPSY引入三项关键技术:扩展的无分类器引导方案,基于类别相似度的采样策略,以及无需模型微调或外部描述的简单有效流程。实验证明,该方法在多个基准数据集上达到或优于现有技术水平,无需对生成模型进行适应或依赖外部工具进行描述生成和图像过滤。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的少样本图像分类方法DIPSY,基于图像到图像的翻译技术IP-Adapter。
- DIPSY利用有限的样本生成高度区分性的合成图像。
- 引入扩展的无分类器引导方案,实现对正负面图像条件的独立控制。
- 采用基于类别相似度的采样策略,有效选择对比样本。
- 流程简单有效,无需模型微调或外部描述、过滤工具。
- 在多个基准数据集上达到或超过现有技术水平。
点此查看论文截图

Overclocking Electrostatic Generative Models
Authors:Daniil Shlenskii, Alexander Korotin
Electrostatic generative models such as PFGM++ have recently emerged as a powerful framework, achieving state-of-the-art performance in image synthesis. PFGM++ operates in an extended data space with auxiliary dimensionality $D$, recovering the diffusion model framework as $D\to\infty$, while yielding superior empirical results for finite $D$. Like diffusion models, PFGM++ relies on expensive ODE simulations to generate samples, making it computationally costly. To address this, we propose Inverse Poisson Flow Matching (IPFM), a novel distillation framework that accelerates electrostatic generative models across all values of $D$. Our IPFM reformulates distillation as an inverse problem: learning a generator whose induced electrostatic field matches that of the teacher. We derive a tractable training objective for this problem and show that, as $D \to \infty$, our IPFM closely recovers Score Identity Distillation (SiD), a recent method for distilling diffusion models. Empirically, our IPFM produces distilled generators that achieve near-teacher or even superior sample quality using only a few function evaluations. Moreover, we observe that distillation converges faster for finite $D$ than in the $D \to \infty$ (diffusion) limit, which is consistent with prior findings that finite-$D$ PFGM++ models exhibit more favorable optimization and sampling properties.
静电生成模型如PFGM++最近作为一个强大的框架出现,在图像合成中达到了最先进的技术性能。PFGM++在一个扩展的数据空间中进行操作,具有辅助维度D,在D趋向无穷大时恢复扩散模型框架,而对于有限的D则产生优越的实证结果。与扩散模型一样,PFGM++依赖于昂贵的ODE模拟来生成样本,使其计算成本高昂。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了逆Poisson流匹配(IPFM),这是一种新的蒸馏框架,可以加速所有D值下的静电生成模型。我们的IPFM将蒸馏重新表述为一个反问题:学习一个生成器,其产生的静电场与教师的静电场相匹配。我们为这个问题推导了一个可行的训练目标,并表明当D趋向无穷大时,我们的IPFM几乎可以恢复分数身份蒸馏(SiD)——一种用于蒸馏扩散模型的最新方法。经验上,我们的IPFM产生的蒸馏生成器只使用少数几次函数评估就能达到接近教师甚至更好的样本质量。此外,我们观察到对于有限的D,蒸馏的收敛速度比D趋向无穷大(扩散)极限时更快,这与先前的发现一致,即有限D的PFGM++模型表现出更有利的优化和采样特性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
静电生成模型如PFGM++已成为图像合成领域的最前沿框架。为优化其计算成本,提出一种新的蒸馏框架——Inverse Poisson Flow Matching(IPFM),将蒸馏重构为逆问题:学习一个其感应静电场与教师相匹配的生成器。当$D$趋向无穷时,IPFM接近于Score Identity Distillation(SiD),一种用于蒸馏扩散模型的新方法。经验表明,IPFM生成的蒸馏器样本质量接近教师甚至更优,仅使用少量函数评估。此外,对于有限$D$的蒸馏收敛速度比$D$趋向无穷时更快。
Key Takeaways
- 静电生成模型如PFGM++在图像合成领域表现出卓越性能。
- PFGM++在扩展数据空间中使用辅助维度$D$,并在$D$趋向无穷时恢复扩散模型框架。
- 为优化计算成本,提出了Inverse Poisson Flow Matching(IPFM)蒸馏框架。
- IPFM将蒸馏重构为逆问题,学习感应静电场与教师相匹配的生成器。
- 当$D$趋向无穷时,IPFM接近Score Identity Distillation(SiD)。
- IPFM生成的蒸馏器样本质量接近甚至优于教师模型,且使用较少的函数评估。
点此查看论文截图
HiGS: History-Guided Sampling for Plug-and-Play Enhancement of Diffusion Models
Authors:Seyedmorteza Sadat, Farnood Salehi, Romann M. Weber
While diffusion models have made remarkable progress in image generation, their outputs can still appear unrealistic and lack fine details, especially when using fewer number of neural function evaluations (NFEs) or lower guidance scales. To address this issue, we propose a novel momentum-based sampling technique, termed history-guided sampling (HiGS), which enhances quality and efficiency of diffusion sampling by integrating recent model predictions into each inference step. Specifically, HiGS leverages the difference between the current prediction and a weighted average of past predictions to steer the sampling process toward more realistic outputs with better details and structure. Our approach introduces practically no additional computation and integrates seamlessly into existing diffusion frameworks, requiring neither extra training nor fine-tuning. Extensive experiments show that HiGS consistently improves image quality across diverse models and architectures and under varying sampling budgets and guidance scales. Moreover, using a pretrained SiT model, HiGS achieves a new state-of-the-art FID of 1.61 for unguided ImageNet generation at 256$\times$256 with only 30 sampling steps (instead of the standard 250). We thus present HiGS as a plug-and-play enhancement to standard diffusion sampling that enables faster generation with higher fidelity.
尽管扩散模型在图像生成方面取得了显著的进步,但其输出仍然可能出现不真实和缺乏细节的情况,特别是在使用较少的神经网络功能评估(NFEs)或较低的指导尺度时。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于动量采样技术的新型采样方法,称为历史引导采样(HiGS)。它通过集成最新的模型预测结果到每个推理步骤中,提高了扩散采样的质量和效率。具体来说,HiGS利用当前预测与过去预测加权平均值之间的差异来引导采样过程,使其产生更真实、细节和结构更好的输出。我们的方法几乎没有引入额外的计算量,并能无缝集成到现有的扩散框架中,无需额外的训练或微调。大量实验表明,HiGS在多种模型和架构下以及不同的采样预算和指导尺度下都能持续提高图像质量。此外,使用预训练的SiT模型,HiGS在不使用指导的情况下实现了ImageNet生成的新最佳FID分数为1.61,分辨率为256x256,仅使用30个采样步骤(而不是标准的250个)。因此,我们提出HiGS作为一种即插即用的增强版标准扩散采样方法,可实现更快、更高保真度的生成。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为历史引导采样(HiGS)的新型动量采样技术,旨在提高扩散采样的质量和效率。HiGS通过将当前预测与过去预测的加权平均之间的差异纳入考虑,引导采样过程生成更真实、细节和结构更好的图像。该方法无需额外的计算,可无缝集成到现有的扩散框架中,无需额外的训练或微调。实验表明,HiGS在不同模型和架构下,以及不同的采样预算和引导尺度下,都能提高图像质量。使用预训练的SiT模型时,HiGS在只有30个采样步骤的情况下实现了未引导ImageNet生成的最新技术指标的FID 1.61(而标准步骤为250)。因此,HiGS被提出作为一种标准的扩散采样的插件增强功能,能够实现更快、更高保真度的生成。
Key Takeaways
- HiGS是一种基于动量的采样技术,旨在提高扩散模型在图像生成中的质量和效率。
- HiGS通过将当前预测与过去预测的加权平均之间的差异纳入考虑,引导采样过程生成更真实的图像。
- HiGS方法无需额外的计算成本,并能无缝集成到现有的扩散框架中。
- HiGS在多种模型和架构下都能提高图像质量,适用于不同的采样预算和引导尺度。
- 使用预训练的SiT模型,HiGS在只有30个采样步骤的情况下实现了未引导ImageNet生成的FID 1.61。
- HiGS提高了扩散模型的生成速度并提升了生成图像的真实性。
点此查看论文截图

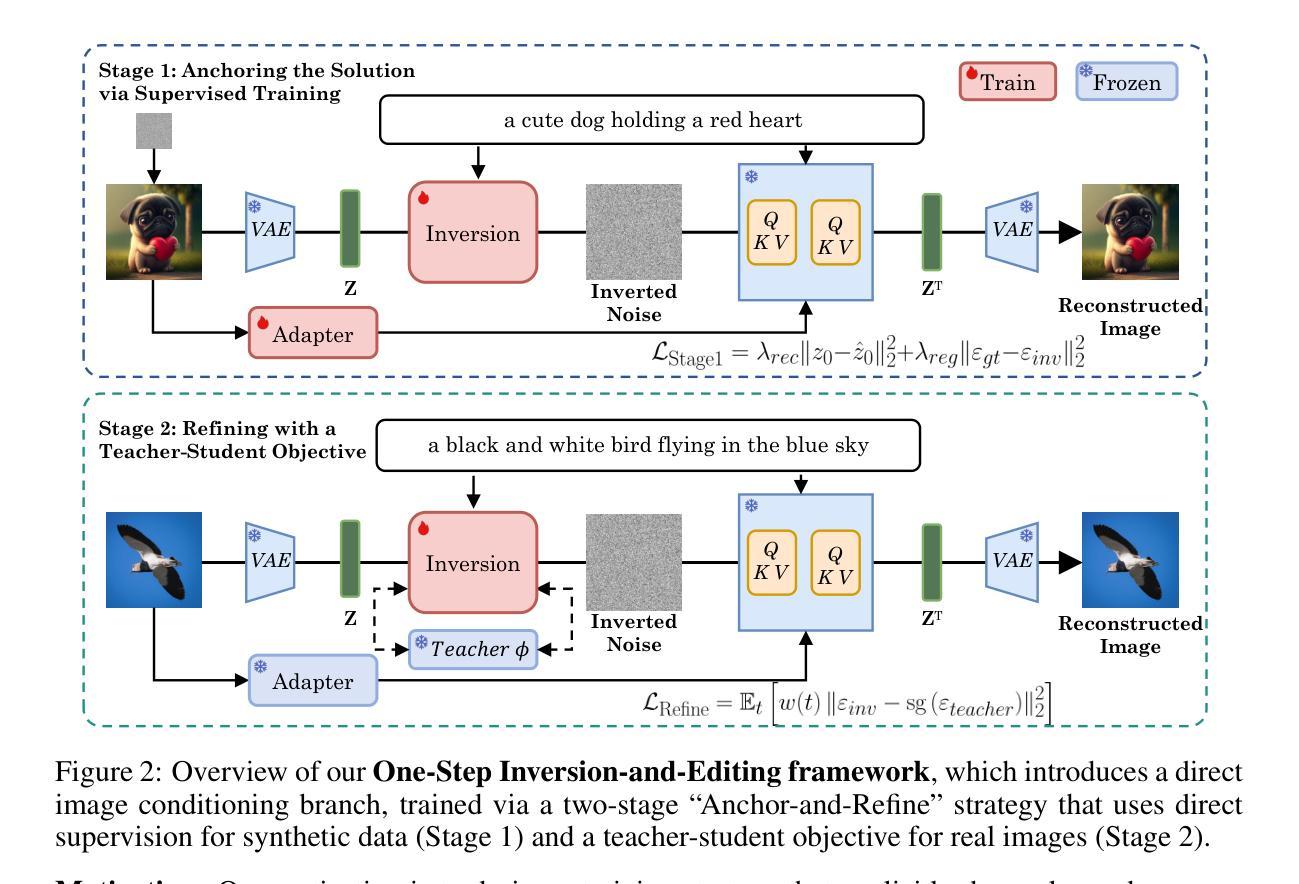
FlashEdit: Decoupling Speed, Structure, and Semantics for Precise Image Editing
Authors:Junyi Wu, Zhiteng Li, Haotong Qin, Xiaohong Liu, Linghe Kong, Yulun Zhang, Xiaokang Yang
Text-guided image editing with diffusion models has achieved remarkable quality but suffers from prohibitive latency, hindering real-world applications. We introduce FlashEdit, a novel framework designed to enable high-fidelity, real-time image editing. Its efficiency stems from three key innovations: (1) a One-Step Inversion-and-Editing (OSIE) pipeline that bypasses costly iterative processes; (2) a Background Shield (BG-Shield) technique that guarantees background preservation by selectively modifying features only within the edit region; and (3) a Sparsified Spatial Cross-Attention (SSCA) mechanism that ensures precise, localized edits by suppressing semantic leakage to the background. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FlashEdit maintains superior background consistency and structural integrity, while performing edits in under 0.2 seconds, which is an over 150$\times$ speedup compared to prior multi-step methods. Our code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/JunyiWuCode/FlashEdit.
基于扩散模型的文本引导图像编辑已经取得了显著的品质,但仍然存在延迟问题,阻碍了其在现实世界的运用。为了解决这一问题,我们推出了FlashEdit这一全新框架,旨在实现高保真实时图像编辑。其高效率来源于三个关键创新点:一是一步式反转和编辑(OSIE)管道,它绕过了昂贵的迭代过程;二是背景屏蔽(BG-Shield)技术,它通过选择性修改编辑区域内的特征来保证背景保留;三是稀疏空间交叉注意力(SSCA)机制,它通过抑制语义泄露到背景来确保精确、局部化的编辑。大量实验表明,FlashEdit在保持背景一致性和结构完整性的同时,能够在不到0.2秒内完成编辑,相较于之前的多步骤方法实现了超过150倍的速度提升。我们的代码将在https://github.com/JunyiWuCode/FlashEdit上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/JunyiWuCode/FlashEdit
Summary
本文介绍了针对扩散模型的新框架FlashEdit,旨在实现高保真实时图像编辑。其核心优势在于绕过昂贵的迭代过程,采用一步反转编辑管道、背景屏蔽技术和稀疏空间交叉注意力机制,确保精确局部编辑同时保持背景一致性。实验证明,FlashEdit在保持背景和结构完整性的同时,编辑速度达到每秒0.2帧以内,相比之前的多步骤方法实现了超过150倍的速度提升。
Key Takeaways
- FlashEdit框架实现了高保真实时图像编辑。
- 通过一步反转编辑管道(OSIE)提高了效率,绕过昂贵的迭代过程。
- 背景屏蔽技术(BG-Shield)保证了背景的一致性,只选择性地修改编辑区域内的特征。
- 稀疏空间交叉注意力机制(SSCA)确保了精确、局部的编辑,抑制了语义泄露到背景。
- 实验证明FlashEdit在保持背景和结构完整性的同时,实现了快速编辑。
- FlashEdit编辑速度达到每秒0.2帧以内,相比之前的方法有显著的速度提升。
点此查看论文截图
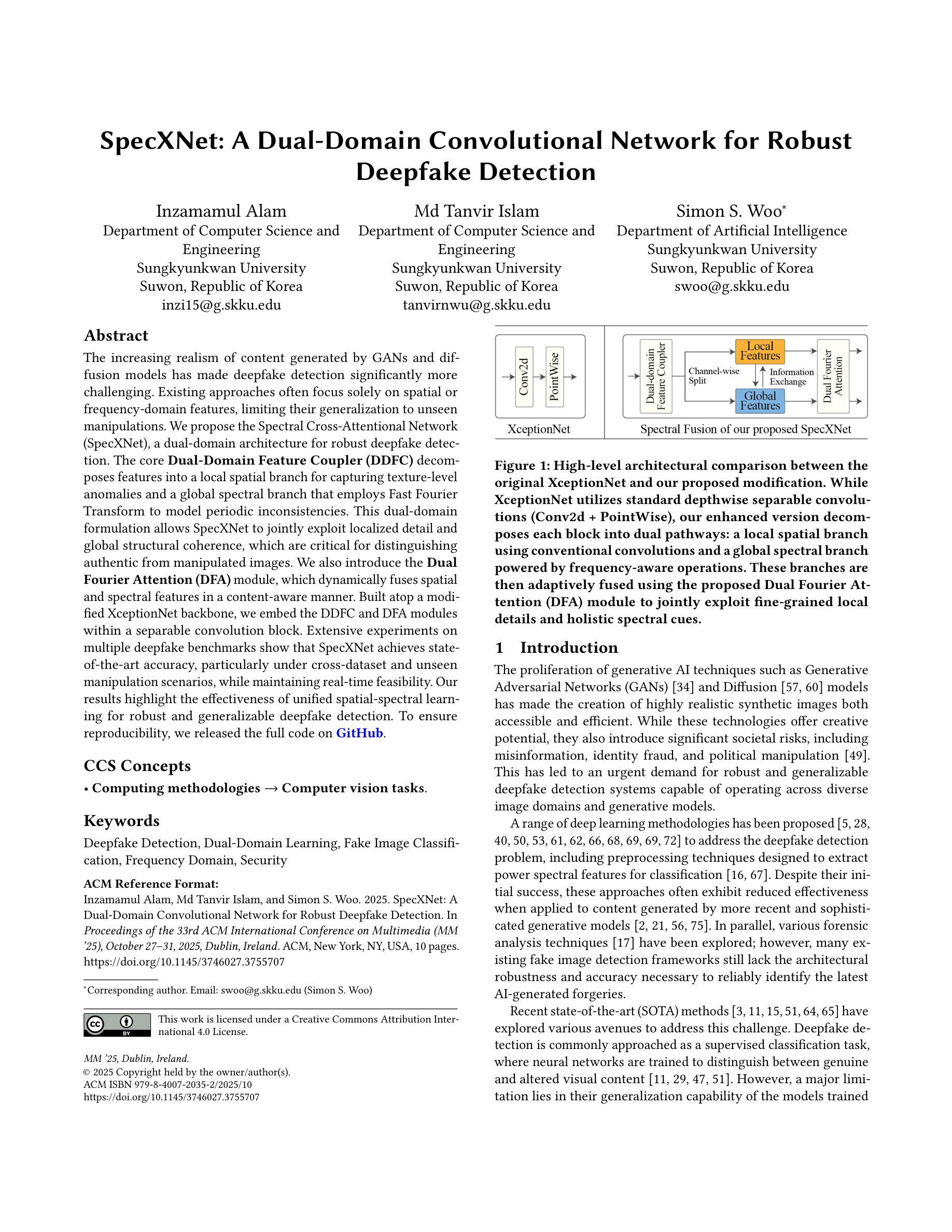
SpecXNet: A Dual-Domain Convolutional Network for Robust Deepfake Detection
Authors:Inzamamul Alam, Md Tanvir Islam, Simon S. Woo
The increasing realism of content generated by GANs and diffusion models has made deepfake detection significantly more challenging. Existing approaches often focus solely on spatial or frequency-domain features, limiting their generalization to unseen manipulations. We propose the Spectral Cross-Attentional Network (SpecXNet), a dual-domain architecture for robust deepfake detection. The core \textbf{Dual-Domain Feature Coupler (DDFC)} decomposes features into a local spatial branch for capturing texture-level anomalies and a global spectral branch that employs Fast Fourier Transform to model periodic inconsistencies. This dual-domain formulation allows SpecXNet to jointly exploit localized detail and global structural coherence, which are critical for distinguishing authentic from manipulated images. We also introduce the \textbf{Dual Fourier Attention (DFA)} module, which dynamically fuses spatial and spectral features in a content-aware manner. Built atop a modified XceptionNet backbone, we embed the DDFC and DFA modules within a separable convolution block. Extensive experiments on multiple deepfake benchmarks show that SpecXNet achieves state-of-the-art accuracy, particularly under cross-dataset and unseen manipulation scenarios, while maintaining real-time feasibility. Our results highlight the effectiveness of unified spatial-spectral learning for robust and generalizable deepfake detection. To ensure reproducibility, we released the full code on \href{https://github.com/inzamamulDU/SpecXNet}{\textcolor{blue}{\textbf{GitHub}}}.
由GAN和扩散模型生成的内容日益逼真的现实情况使得深度伪造检测面临更大的挑战。现有方法通常仅专注于空间或频域特征,这限制了它们对未见操作的泛化能力。我们提出了谱交叉注意力网络(SpecXNet),这是一种用于稳健深度伪造检测的双域架构。其核心双域特征耦合器(DDFC)将特征分解为局部空间分支,用于捕捉纹理级别的异常,和全局谱分支,该分支利用快速傅里叶变换来模拟周期性不一致。这种双域公式使SpecXNet能够共同利用局部细节和全局结构一致性,这对于区分真实图像和操纵过的图像至关重要。我们还引入了双傅里叶注意力(DFA)模块,它以内容感知的方式动态融合空间和谱特征。建立在修改后的XceptionNet主干之上,我们在可分离卷积块中嵌入了DDFC和DFA模块。在多个深度伪造基准测试上的广泛实验表明,SpecXNet达到了最先进的精度,特别是在跨数据集和未见操作场景中,同时保持了实时可行性。我们的结果突显了统一的空间-谱学习的有效性,可实现稳健且可泛化的深度伪造检测。为确保可重复性,我们已在GitHub上发布了完整的代码:[链接](具体链接需替换为实际的GitHub链接地址)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM MM Accepted
Summary
本文指出当前深度伪造检测面临的挑战,并介绍了提出的Spectral Cross-Attentional Network(SpecXNet)模型。该模型采用双域架构,通过Dual-Domain Feature Coupler(DDFC)分解特征,并结合Dual Fourier Attention(DFA)模块动态融合空间与光谱特征。实验证明,SpecXNet在多个深度伪造检测基准测试中实现了最先进的准确性,特别是在跨数据集和未见操作场景下,同时保持了实时可行性。
Key Takeaways
- GANs和扩散模型生成的内容越来越真实,使得深度伪造检测更具挑战性。
- 现有方法主要关注空间或频率域特征,但难以推广到未见操作。
- SpecXNet模型是一个双域架构,包括用于捕捉纹理异常的局部空间分支和利用快速傅里叶变换建模周期性不一致性的全局光谱分支。
- Dual-Domain Feature Coupler (DDFC) 是核心模块,允许模型同时利用局部细节和全局结构一致性。
- 引入的Dual Fourier Attention(DFA)模块以内容感知的方式动态融合空间和光谱特征。
- 实验证明,SpecXNet在多个深度伪造检测基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,尤其在跨数据集和未见操作场景下。
点此查看论文截图
FailureAtlas:Mapping the Failure Landscape of T2I Models via Active Exploration
Authors:Muxi Chen, Zhaohua Zhang, Chenchen Zhao, Mingyang Chen, Wenyu Jiang, Tianwen Jiang, Jianhuan Zhuo, Yu Tang, Qiuyong Xiao, Jihong Zhang, Qiang Xu
Static benchmarks have provided a valuable foundation for comparing Text-to-Image (T2I) models. However, their passive design offers limited diagnostic power, struggling to uncover the full landscape of systematic failures or isolate their root causes. We argue for a complementary paradigm: active exploration. We introduce FailureAtlas, the first framework designed to autonomously explore and map the vast failure landscape of T2I models at scale. FailureAtlas frames error discovery as a structured search for minimal, failure-inducing concepts. While it is a computationally explosive problem, we make it tractable with novel acceleration techniques. When applied to Stable Diffusion models, our method uncovers hundreds of thousands of previously unknown error slices (over 247,000 in SD1.5 alone) and provides the first large-scale evidence linking these failures to data scarcity in the training set. By providing a principled and scalable engine for deep model auditing, FailureAtlas establishes a new, diagnostic-first methodology to guide the development of more robust generative AI. The code is available at https://github.com/cure-lab/FailureAtlas
静态基准测试为文本到图像(T2I)模型的比较提供了宝贵的基石。然而,其被动设计提供了有限的诊断能力,难以揭示整个系统故障景观或隔离其根本原因。我们主张一种互补的方法:主动探索。我们引入了FailureAtlas,这是第一个旨在自主探索和大规模映射T2I模型庞大故障景观的框架。FailureAtlas将错误发现构建为针对最小失败诱导概念的结构化搜索。虽然这是一个计算爆炸性的问题,但我们使用新型加速技术使其易于处理。当应用于Stable Diffusion模型时,我们的方法揭示了数十万之前未知的误差切片(仅在SD1.5中就超过247,000个),并首次提供了大规模证据表明这些失败与训练集中的数据稀缺有关。通过提供一个有原则且可扩展的引擎来进行深度模型审计,FailureAtlas建立了一种以诊断为先的新方法来指导开发更稳健的生成式人工智能。代码可在https://github.com/cure-lab/FailureAtlas找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本指出静态基准测试为文本到图像模型比较提供了有价值的基础,但其被动设计导致诊断能力有限,难以揭示整体的系统故障或定位其根本原因。因此,作者提出了一种互补的方法:主动探索,并介绍了FailureAtlas框架,该框架旨在自主探索和大规模映射文本到图像模型的故障景观。FailureAtlas将错误发现定义为寻找最小的故障诱导概念的结构化搜索。作者采用新的加速技术使这一计算密集型问题变得可行。在应用于Stable Diffusion模型时,该方法发现了数十万个之前未知的错误切片,并为这些失败与训练集中的数据稀缺之间的联系提供了大规模证据。通过提供一个有原则的和可扩展的引擎进行深度模型审计,FailureAtlas建立了一种新的以诊断为主的方法,以指导开发更稳健的生成式人工智能。
Key Takeaways
- 静态基准测试对于评估文本到图像模型具有一定价值,但其被动设计限制了诊断能力。
- 主动探索方法作为静态基准测试的补充被提出,以更全面地揭示模型的失败点。
- FailureAtlas框架被介绍为第一个能够自主探索和大规模映射文本到图像模型的故障景观的框架。
- FailureAtlas将错误发现定义为寻找最小的故障诱导概念的结构化搜索问题。
- 作者使用新的加速技术使主动探索成为可能,该技术在计算上可能是密集型的。
- 在应用于Stable Diffusion模型时,FailureAtlas发现了大量的错误切片,并提供了与训练数据稀缺性相关的失败证据。
- FailureAtlas提供了一个有原则的和可扩展的引擎进行深度模型审计,推动发展更稳健的生成式人工智能的开发方法。
点此查看论文截图
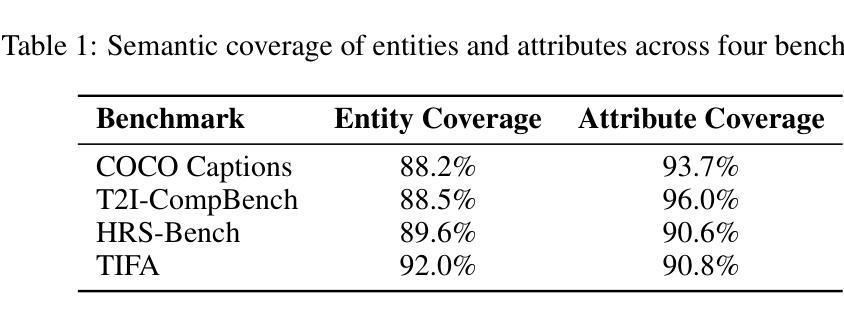
Mind-the-Glitch: Visual Correspondence for Detecting Inconsistencies in Subject-Driven Generation
Authors:Abdelrahman Eldesokey, Aleksandar Cvejic, Bernard Ghanem, Peter Wonka
We propose a novel approach for disentangling visual and semantic features from the backbones of pre-trained diffusion models, enabling visual correspondence in a manner analogous to the well-established semantic correspondence. While diffusion model backbones are known to encode semantically rich features, they must also contain visual features to support their image synthesis capabilities. However, isolating these visual features is challenging due to the absence of annotated datasets. To address this, we introduce an automated pipeline that constructs image pairs with annotated semantic and visual correspondences based on existing subject-driven image generation datasets, and design a contrastive architecture to separate the two feature types. Leveraging the disentangled representations, we propose a new metric, Visual Semantic Matching (VSM), that quantifies visual inconsistencies in subject-driven image generation. Empirical results show that our approach outperforms global feature-based metrics such as CLIP, DINO, and vision–language models in quantifying visual inconsistencies while also enabling spatial localization of inconsistent regions. To our knowledge, this is the first method that supports both quantification and localization of inconsistencies in subject-driven generation, offering a valuable tool for advancing this task. Project Page:https://abdo-eldesokey.github.io/mind-the-glitch/
我们提出了一种新型方法,用于从预训练的扩散模型的主干中分离视觉和语义特征,以类似于已建立的语义对应的方式实现视觉对应。虽然已知扩散模型的主干编码了丰富的语义特征,但它们也必然包含视觉特征以支持其图像合成能力。然而,由于缺乏标注数据集,隔离这些视觉特征是一项挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了一个自动化管道,该管道基于现有的主体驱动图像生成数据集构建具有标注语义和视觉对应的图像对,并设计了一种对比架构来分离这两种特征类型。利用解耦的表示形式,我们提出了一种新的度量标准——视觉语义匹配(VSM),用于量化主体驱动图像生成中的视觉不一致性。经验结果表明,我们的方法在量化视觉不一致性方面优于基于全局特征的度量标准,如CLIP、DINO和视觉语言模型,同时能够实现不一致区域的空间定位。据我们所知,这是第一种既支持不一致性的量化又支持定位的主体驱动生成方法,为推进这项任务提供了有价值的工具。项目页面:https://abdo-eldesokey.github.io/mind-the-glitch/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2025 (Spotlight). Project Page: https://abdo-eldesokey.github.io/mind-the-glitch/
Summary
本文提出了一种新的方法,通过利用预训练的扩散模型的主干来分离视觉和语义特征,实现视觉对应,类似于已经建立的语义对应。为解决没有标注数据集的问题,提出了一种自动化管道,根据现有的主题驱动图像生成数据集构建具有标注语义和视觉对应的图像对,并设计了一种对比架构来分离这两种特征类型。利用分离出的特征表示,提出了一种新的指标——视觉语义匹配(VSM),用于量化主题驱动图像生成中的视觉不一致性。实验结果表明,该方法在量化视觉不一致性方面优于CLIP、DINO和视觉语言模型等全局特征指标,并实现了不一致区域的空间定位。这是支持量化定位主题驱动生成中不一致性的首个方法,为推进此任务提供了有价值的工具。
Key Takeaways
- 利用预训练扩散模型的主干来分离视觉和语义特征,实现视觉对应。
- 提出一种自动化管道构建图像对,具有标注语义和视觉对应,基于现有主题驱动图像生成数据集。
- 设计对比架构以更有效地分离视觉和语义特征类型。
- 引入新的指标——视觉语义匹配(VSM),用于量化主题驱动图像生成中的视觉不一致性。
- 该方法在量化视觉不一致性方面优于全局特征指标,如CLIP、DINO等。
- 实现不一致区域的空间定位,这是其他方法尚未做到的。
点此查看论文截图
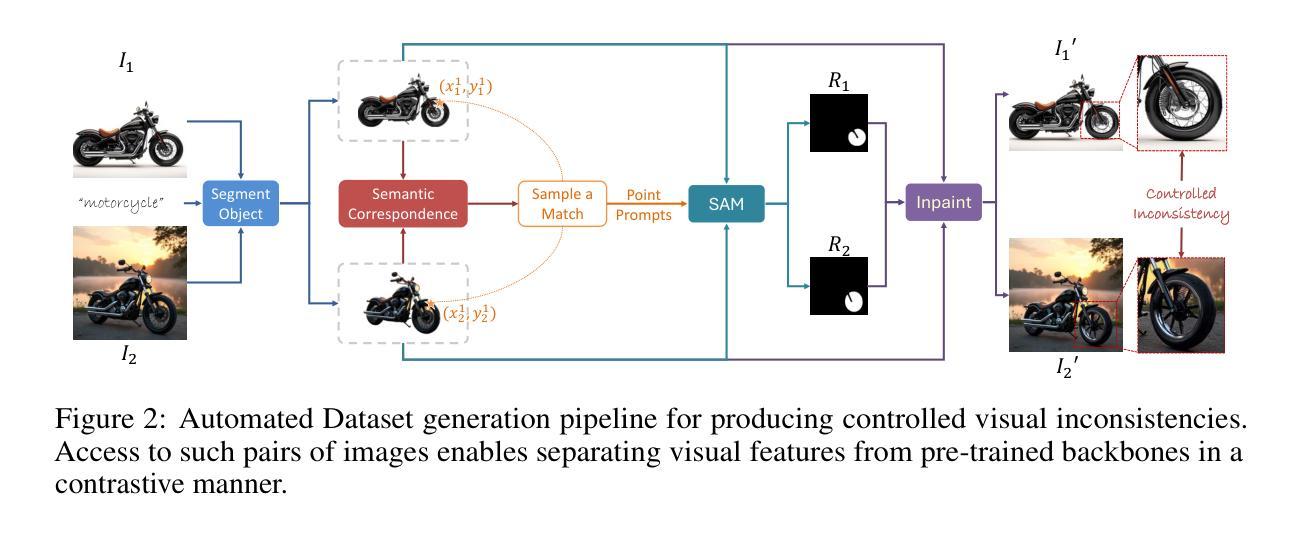
SemanticControl: A Training-Free Approach for Handling Loosely Aligned Visual Conditions in ControlNet
Authors:Woosung Joung, Daewon Chae, Jinkyu Kim
ControlNet has enabled detailed spatial control in text-to-image diffusion models by incorporating additional visual conditions such as depth or edge maps. However, its effectiveness heavily depends on the availability of visual conditions that are precisely aligned with the generation goal specified by text prompt-a requirement that often fails in practice, especially for uncommon or imaginative scenes. For example, generating an image of a cat cooking in a specific pose may be infeasible due to the lack of suitable visual conditions. In contrast, structurally similar cues can often be found in more common settings-for instance, poses of humans cooking are widely available and can serve as rough visual guides. Unfortunately, existing ControlNet models struggle to use such loosely aligned visual conditions, often resulting in low text fidelity or visual artifacts. To address this limitation, we propose SemanticControl, a training-free method for effectively leveraging misaligned but semantically relevant visual conditions. Our approach adaptively suppresses the influence of the visual condition where it conflicts with the prompt, while strengthening guidance from the text. The key idea is to first run an auxiliary denoising process using a surrogate prompt aligned with the visual condition (e.g., “a human playing guitar” for a human pose condition) to extract informative attention masks, and then utilize these masks during the denoising of the actual target prompt (e.g., cat playing guitar). Experimental results demonstrate that our method improves performance under loosely aligned conditions across various conditions, including depth maps, edge maps, and human skeletons, outperforming existing baselines. Our code is available at https://mung3477.github.io/semantic-control.
ControlNet通过引入深度或边缘映射等额外的视觉条件,实现了文本到图像扩散模型的详细空间控制。然而,其有效性严重依赖于与文本提示指定的生成目标精确对齐的视觉条件的存在,这一要求在实践中经常失败,特别是对于不常见或富有想象力的场景。例如,由于缺乏合适的视觉条件,生成一张特定姿势的猫做饭的图像可能是不可行的。相比之下,在更常见的设置中可以经常找到结构相似的线索——例如,人类的烹饪姿势是广泛可用的,可以作为粗略的视觉指南。遗憾的是,现有的ControlNet模型难以利用这种松散对齐的视觉条件,这往往导致文本保真度低或视觉失真。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了SemanticControl,这是一种无需训练即可有效利用错位但语义上相关的视觉条件的方法。我们的方法自适应地抑制了视觉条件的影响,当其与提示冲突时,同时加强文本的指导。关键的想法是首先使用一个与视觉条件对齐的替代提示运行一个辅助去噪过程(例如,“一个人弹吉他”对于人类姿势条件),以提取信息丰富的注意力掩码,然后在实际目标提示的去噪过程中利用这些掩码(例如,“猫弹吉他”)。实验结果表明,我们的方法在松散对齐的条件下,在各种条件下均提高了性能,包括深度图、边缘图和人类骨架,超越了现有基准。我们的代码可在https://mung3477.github.io/semantic-control上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF BMVC 2025
摘要
ControlNet通过引入深度或边缘映射等额外视觉条件,实现了文本到图像扩散模型的详细空间控制。但其有效性严重依赖于视觉条件与文本提示指定的生成目标之间的精确对齐,这在实践中尤其是对于不常见或想象场景常常难以实现。为解决现有ControlNet模型在处理错位但语义相关的视觉条件时的局限性,我们提出了SemanticControl,这是一种无需训练的方法,能够自适应地利用错位但语义相关的视觉条件。该方法在视觉条件与提示冲突时抑制其影响,同时强化文本指导。实验结果表明,该方法在多种条件下性能优异,包括深度图、边缘图和人类骨架,超越了现有基线。相关代码已公开。
关键见解
- ControlNet通过引入额外的视觉条件增强了文本到图像扩散模型的空间控制,但依赖于视觉条件与文本提示的精确对齐。
- 对于不常见或想象场景,获取适合的视觉条件可能困难,限制了ControlNet的有效性。
- SemanticControl是一种无需训练的方法,能有效利用错位但语义相关的视觉条件。
- SemanticControl通过自适应地抑制冲突的视觉条件并强化文本指导来改进性能。
- SemanticControl通过辅助去噪过程提取信息性注意力掩膜,然后利用这些掩膜进行实际目标提示的去噪。
- 实验结果表明,SemanticControl在多种条件下性能优越,包括深度图、边缘图和人类骨架等。
- 相关研究代码已公开,便于进一步研究和应用。
点此查看论文截图

Discrete Guidance Matching: Exact Guidance for Discrete Flow Matching
Authors:Zhengyan Wan, Yidong Ouyang, Liyan Xie, Fang Fang, Hongyuan Zha, Guang Cheng
Guidance provides a simple and effective framework for posterior sampling by steering the generation process towards the desired distribution. When modeling discrete data, existing approaches mostly focus on guidance with the first-order Taylor approximation to improve the sampling efficiency. However, such an approximation is inappropriate in discrete state spaces since the approximation error could be large. A novel guidance framework for discrete data is proposed to address this problem: We derive the exact transition rate for the desired distribution given a learned discrete flow matching model, leading to guidance that only requires a single forward pass in each sampling step, significantly improving efficiency. This unified novel framework is general enough, encompassing existing guidance methods as special cases, and it can also be seamlessly applied to the masked diffusion model. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed guidance on energy-guided simulations and preference alignment on text-to-image generation and multimodal understanding tasks. The code is available through https://github.com/WanZhengyan/Discrete-Guidance-Matching/tree/main.
指导(Guidance)通过引导生成过程朝向目标分布,为后采样提供了一个简单有效的框架。在离散数据建模中,现有的方法大多集中在用一阶泰勒近似进行引导以提高采样效率。然而,由于在离散状态空间中近似误差可能较大,这种近似是不恰当的。针对这一问题,我们提出了一种用于离散数据的新型指导框架:我们根据学习到的离散流匹配模型推导出目标分布的精确转移率,从而实现了一种指导方式,在每个采样步骤中只需进行一次前向传递,大大提高了效率。这种统一的全新框架足够通用,包含现有指导方法作为特例,并能无缝应用于带掩码的扩散模型。我们在能量引导的模拟和文本到图像生成和多模态理解任务中的偏好对齐方面验证了所提出指导的有效性。代码可通过https://github.com/WanZhengyan/Discrete-Guidance-Matching/tree/main获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本提出了一种新的离散数据引导框架,通过为期望分布推导精确转移率并使用学习到的离散流匹配模型,提高了采样效率。此框架统一并扩展了现有引导方法,可无缝应用于带掩码的扩散模型。在文本到图像生成和多模态理解任务中进行了有效的演示。代码可通过https://github.com/WanZhengyan/Discrete-Guidance-Matching/tree/main获取。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了针对离散数据的新型引导框架,解决了现有方法在处理离散数据时的问题。
- 通过推导精确转移率,实现了期望分布的引导,提高了采样效率。
- 框架具有通用性,涵盖现有引导方法作为特例,并能无缝应用于带掩码的扩散模型。
- 在能量引导模拟、文本到图像生成以及多模态理解任务中验证了框架的有效性。
- 框架的引入有助于提高模型的采样效率和性能。
- 代码已经公开,便于研究者和开发者进行进一步研究和应用。
点此查看论文截图

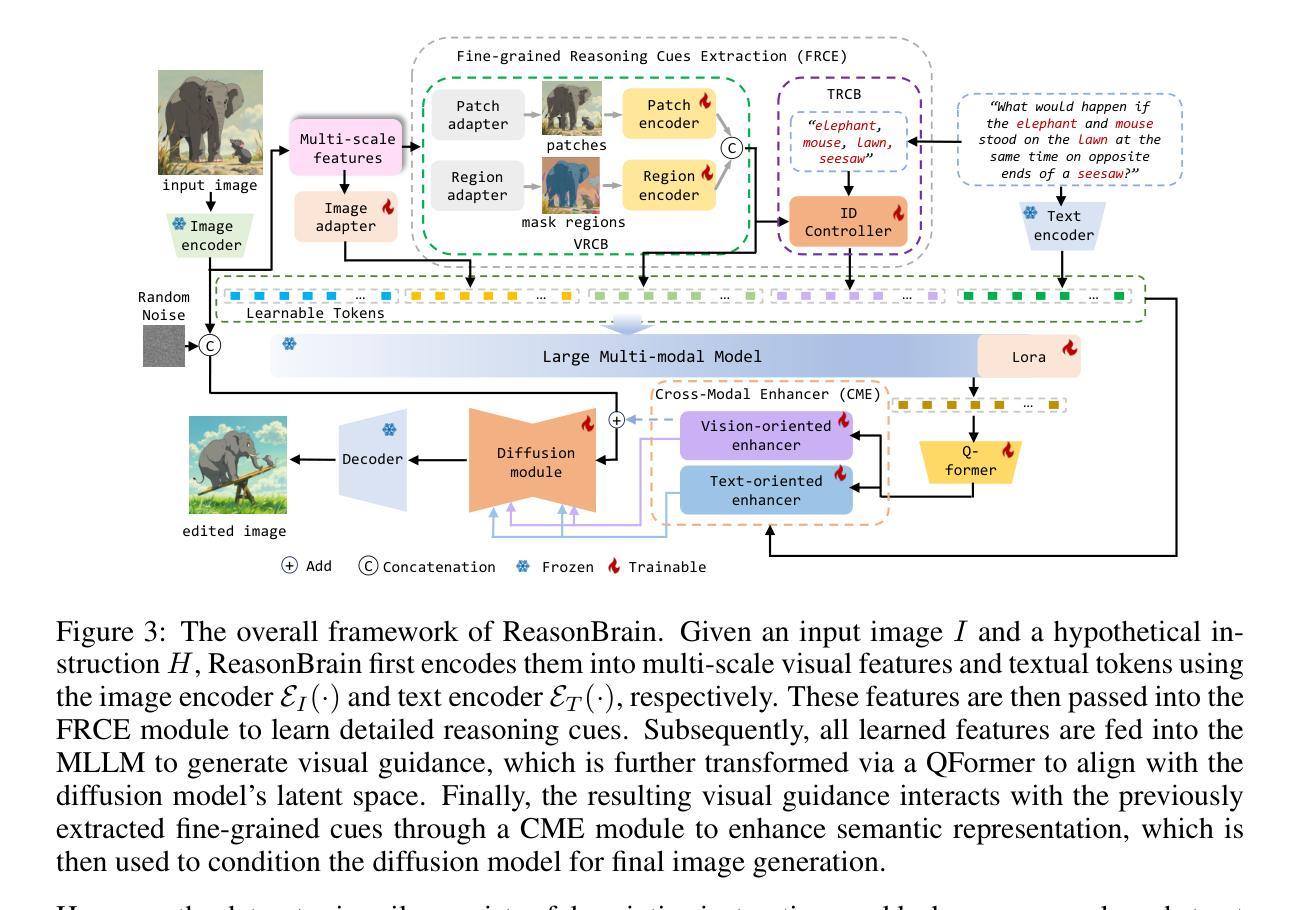
Reasoning to Edit: Hypothetical Instruction-Based Image Editing with Visual Reasoning
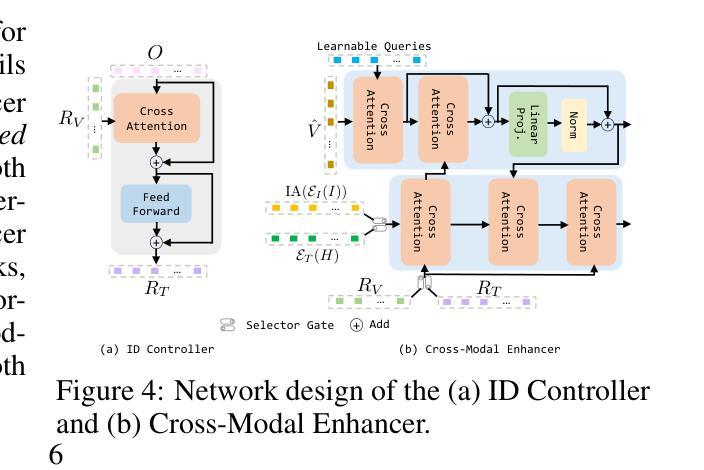
Authors:Qingdong He, Xueqin Chen, Chaoyi Wang, Yanjie Pan, Xiaobin Hu, Zhenye Gan, Yabiao Wang, Chengjie Wang, Xiangtai Li, Jiangning Zhang
Instruction-based image editing (IIE) has advanced rapidly with the success of diffusion models. However, existing efforts primarily focus on simple and explicit instructions to execute editing operations such as adding, deleting, moving, or swapping objects. They struggle to handle more complex implicit hypothetical instructions that require deeper reasoning to infer plausible visual changes and user intent. Additionally, current datasets provide limited support for training and evaluating reasoning-aware editing capabilities. Architecturally, these methods also lack mechanisms for fine-grained detail extraction that support such reasoning. To address these limitations, we propose Reason50K, a large-scale dataset specifically curated for training and evaluating hypothetical instruction reasoning image editing, along with ReasonBrain, a novel framework designed to reason over and execute implicit hypothetical instructions across diverse scenarios. Reason50K includes over 50K samples spanning four key reasoning scenarios: Physical, Temporal, Causal, and Story reasoning. ReasonBrain leverages Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) for editing guidance generation and a diffusion model for image synthesis, incorporating a Fine-grained Reasoning Cue Extraction (FRCE) module to capture detailed visual and textual semantics essential for supporting instruction reasoning. To mitigate the semantic loss, we further introduce a Cross-Modal Enhancer (CME) that enables rich interactions between the fine-grained cues and MLLM-derived features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ReasonBrain consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines on reasoning scenarios while exhibiting strong zero-shot generalization to conventional IIE tasks. Our dataset and code will be released publicly.
基于指令的图像编辑(IIE)随着扩散模型的成功而迅速发展。然而,现有的努力主要集中在执行编辑操作的简单明确指令上,例如添加、删除、移动或交换对象。他们很难处理更复杂的隐含假设指令,这些指令需要更深的推理来推断可能发生的视觉变化和用户意图。此外,当前的数据集在支持训练和评估推理感知编辑能力方面存在局限性。在结构上,这些方法也缺乏支持此类推理的精细细节提取机制。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了Reason50K,这是一个专门用于训练和评估假设指令推理图像编辑的大规模数据集,以及ReasonBrain,这是一个新型框架,旨在在多种场景中执行隐含假设指令的推理。Reason50K包含超过50K个样本,涵盖四种关键推理场景:物理推理、时间推理、因果推理和故事推理。ReasonBrain利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)进行编辑指导生成和扩散模型进行图像合成,并引入了一个精细的推理线索提取(FRCE)模块来捕捉支持指令推理的详细视觉和文本语义。为了减少语义损失,我们进一步引入了跨模态增强器(CME),它使精细线索与MLLM派生特征之间能够进行丰富的交互。大量实验表明,ReasonBrain在推理场景上持续超越最新基线,同时在传统的IIE任务上展现出强大的零样本泛化能力。我们的数据集和代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:基于指令的图像编辑(IIE)在扩散模型的推动下发展迅速。然而,现有努力主要集中在执行简单明确的编辑指令,如添加、删除、移动或交换对象。它们难以处理更复杂的隐含假设指令,需要更深的推理来推断可行的视觉变化和用户意图。此外,当前的数据集对训练评估推理感知编辑能力支持有限。针对这些局限性,我们提出了Reason50K,这是一个专门用于假设指令推理图像编辑的大型数据集,以及ReasonBrain,一个旨在在多种场景中执行隐含假设指令的新框架。Reason50K包括超过5万样本,涵盖四种关键推理场景:物理推理、时间推理、因果推理和故事推理。ReasonBrain利用多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)进行编辑指导生成和扩散模型进行图像合成,并引入精细推理线索提取(FRCE)模块来捕捉详细的视觉和文本语义,以支持指令推理。为了减轻语义损失,我们进一步引入了跨模态增强器(CME),使精细线索和MLLM衍生特征之间能够进行丰富的交互。实验表明,ReasonBrain在推理场景上持续优于最新技术基线,并在常规IIE任务上表现出强大的零样本泛化能力。我们的数据集和代码将公开发布。
Key Takeaways:
- 现有图像编辑主要处理简单明确的编辑指令,难以处理复杂的隐含假设指令。
- 当前数据集对训练评估推理感知编辑能力的支持有限。
- 提出了一种新的大型数据集Reason50K,包含多种关键推理场景的图像编辑样本。
- 引入了ReasonBrain框架,结合多模态大型语言模型和扩散模型,执行隐含假设指令的图像编辑。
- ReasonBrain包括精细推理线索提取模块(FRCE)和跨模态增强器(CME),以提高语义处理能力和交互性能。
- 实验表明,ReasonBrain在推理场景上的表现优于其他方法,并在常规图像编辑任务上具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

Forward-only Diffusion Probabilistic Models
Authors:Ziwei Luo, Fredrik K. Gustafsson, Jens Sjölund, Thomas B. Schön
This work presents a forward-only diffusion (FoD) approach for generative modelling. In contrast to traditional diffusion models that rely on a coupled forward-backward diffusion scheme, FoD directly learns data generation through a single forward diffusion process, yielding a simple yet efficient generative framework. The core of FoD is a state-dependent stochastic differential equation that involves a mean-reverting term in both the drift and diffusion functions. This mean-reversion property guarantees the convergence to clean data, naturally simulating a stochastic interpolation between source and target distributions. More importantly, FoD is analytically tractable and is trained using a simple stochastic flow matching objective, enabling a few-step non-Markov chain sampling during inference. The proposed FoD model, despite its simplicity, achieves state-of-the-art performance on various image restoration tasks. Its general applicability on image-conditioned generation is also demonstrated via qualitative results on image-to-image translation. Our code is available at https://github.com/Algolzw/FoD.
本文提出了一种只前向扩散(FoD)的生成建模方法。与传统的依赖于耦合的前向-后向扩散方案的扩散模型不同,FoD通过单一的前向扩散过程直接学习数据生成,从而构建了一个简单而高效的生成框架。FoD的核心是一个与状态相关的随机微分方程,该方程在漂移和扩散函数中均涉及均值回归项。这种均值回归属性保证了向清洁数据的收敛,自然地模拟了源和目标分布之间的随机插值。更重要的是,FoD分析起来易于处理,并且使用简单的随机流匹配目标进行训练,从而在推理过程中实现了几步非马尔可夫链采样。尽管FoD模型简单,但它在各种图像恢复任务上实现了最先进的性能。通过图像到图像翻译的定性结果,也证明了其在图像条件生成上的普遍适用性。我们的代码位于https://github.com/Algolzw/FoD。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://algolzw.github.io/fod
Summary
本文介绍了一种仅前向扩散(FoD)的生成建模方法。与传统依赖耦合前向-后向扩散方案的扩散模型不同,FoD通过单一的前向扩散过程直接学习数据生成,提供了一个简洁高效的生成框架。FoD的核心是一个涉及均值回归项的基于状态随机微分方程,在漂移和扩散函数中均有体现。这一均值回归属性保证了向清洁数据的收敛,自然模拟了源分布与目标分布之间的随机插值。此外,FoD具有分析可行性,使用简单的随机流匹配目标进行训练,在推理过程中实现了少数步骤的非马尔可夫链采样。尽管其简洁性,FoD在各项图像恢复任务上实现了卓越性能,且在图像条件生成上展现了广泛应用潜力。代码已发布于 https://github.com/Algolzw/FoD。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种名为FoD的仅前向扩散方法,用于生成建模。
- FoD通过单一的前向扩散过程学习数据生成,框架简洁高效。
- FoD的核心是基于状态的随机微分方程,包含均值回归项。
- 均值回归属性保证了向清洁数据的收敛,模拟了源分布与目标分布之间的随机插值。
- FoD具有分析可行性,使用简单的随机流匹配目标进行训练。
- 在推理过程中,FoD实现了少数步骤的非马尔可夫链采样。
点此查看论文截图

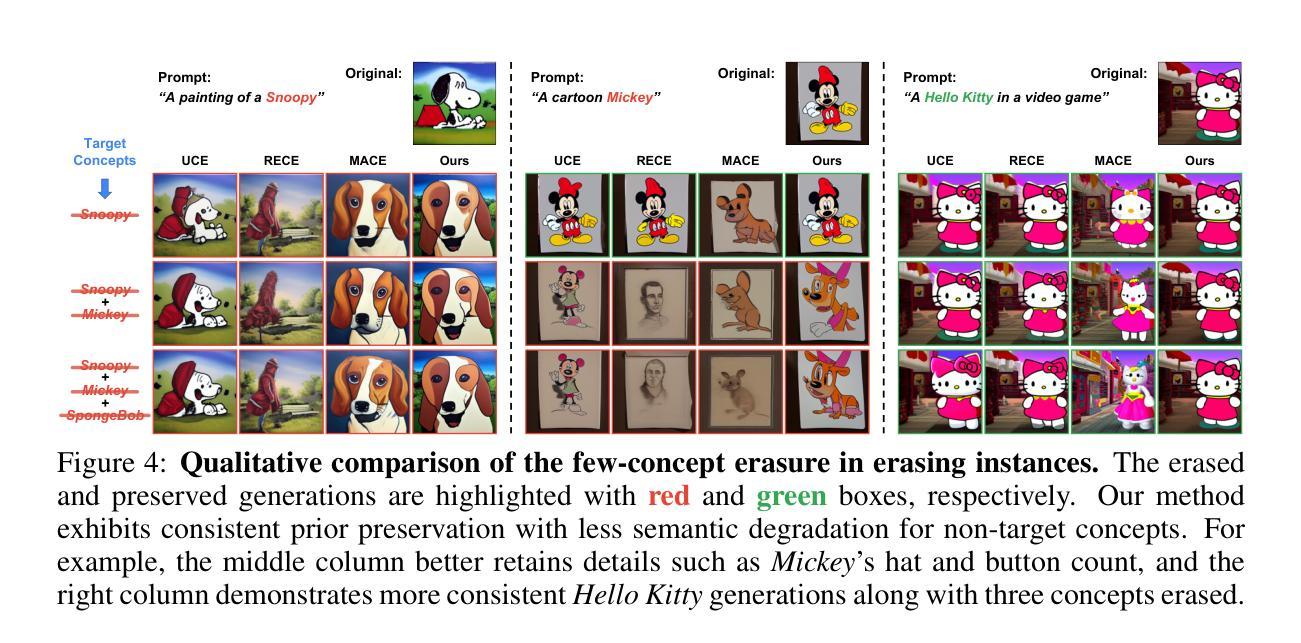
SPEED: Scalable, Precise, and Efficient Concept Erasure for Diffusion Models
Authors:Ouxiang Li, Yuan Wang, Xinting Hu, Houcheng Jiang, Tao Liang, Yanbin Hao, Guojun Ma, Fuli Feng
Erasing concepts from large-scale text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models has become increasingly crucial due to the growing concerns over copyright infringement, offensive content, and privacy violations. In scalable applications, fine-tuning-based methods are time-consuming to precisely erase multiple target concepts, while real-time editing-based methods often degrade the generation quality of non-target concepts due to conflicting optimization objectives. To address this dilemma, we introduce SPEED, an efficient concept erasure approach that directly edits model parameters. SPEED searches for a null space, a model editing space where parameter updates do not affect non-target concepts, to achieve scalable and precise erasure. To facilitate accurate null space optimization, we incorporate three complementary strategies: Influence-based Prior Filtering (IPF) to selectively retain the most affected non-target concepts, Directed Prior Augmentation (DPA) to enrich the filtered retain set with semantically consistent variations, and Invariant Equality Constraints (IEC) to preserve key invariants during the T2I generation process. Extensive evaluations across multiple concept erasure tasks demonstrate that SPEED consistently outperforms existing methods in non-target preservation while achieving efficient and high-fidelity concept erasure, successfully erasing 100 concepts within only 5 seconds. Our code and models are available at: https://github.com/Ouxiang-Li/SPEED.
在大规模文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型中消除概念变得越来越重要,因为人们对版权侵犯、冒犯性内容和隐私泄露的担忧日益加剧。在可扩展应用中,基于微调的方法在精确消除多个目标概念时非常耗时,而基于实时编辑的方法由于优化目标的冲突往往会降低非目标概念的生成质量。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了SPEED,这是一种高效的概念消除方法,它直接编辑模型参数。SPEED搜索一个零空间,即模型编辑空间,其中参数更新不会影响非目标概念,以实现可扩展和精确的消除。为了促进准确的零空间优化,我们结合了三种互补策略:基于影响的优先过滤(IPF)来选择保留受影响最严重的非目标概念,定向优先增强(DPA)以丰富过滤后的保留集语义上一致的变体,以及不变等式约束(IEC)以保持T2I生成过程中的关键不变性。在多个概念消除任务的广泛评估表明,SPEED在非目标保留方面始终优于现有方法,同时实现高效和高保真度的概念消除,在仅5秒内成功消除100个概念。我们的代码和模型可在:https://github.com/Ouxiang-Li/SPEED获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大規模文本轉圖像(T2I)擴散模型中的概念刪除日益重要,因為存在版權侵犯、冒犯性内容和違反隐私问题。面对精准删除多个目标概念时面临的挑战,一种高效的概念删除方法SPEED被提出,它直接編輯模型參數。SPEED在參數更新不會影響非目標概念的模型編輯空間中進行搜索,實現可擴展和精確的刪除。结合三种互補策略:基于影響的先擇濾除(IPF)來選擇性保留最受影響的非目標概念,有方向性的先擇增強(DPA)來豐富過濾後的保留集,以及保持T2I生成過程中的關鍵不變性(IEC)。在多重概念刪除任務上的廣泛評估顯示,SPEED在非目標保存方面表現優於現有方法,同時實現高效和高保真度的概念刪除,僅在5秒內成功刪除100個概念。相關代碼和模型可在https://github.com/Ouxiang-Li/SPEED查閱。
Key Takeaways
- 大規模文本轉圖像(T2I)擴散模型中的概念刪除現在非常重要,因為版權、冒犯性內容和隐私问题日益受到關注。
- 目前的方法如細調基礎方法和實時編輯基礎方法存在時間消耗和非目標概念質量下降問題。
- SPEED方法被提出以解決這個問題,它通过直接編輯模型參數,在不影响非目標概念的模型編輯空間中進行搜索。
- SPEED结合了三種策略:影響基礎先擇擇濾除、有方向性的先擇增強和保持不變性約束。
- SPEED在多个概念刪除任務上的表現優於現有方法,實現高效和高保真度的概念刪除。
- SPEED方法能夠在短短5秒內刪除100個概念。
点此查看论文截图
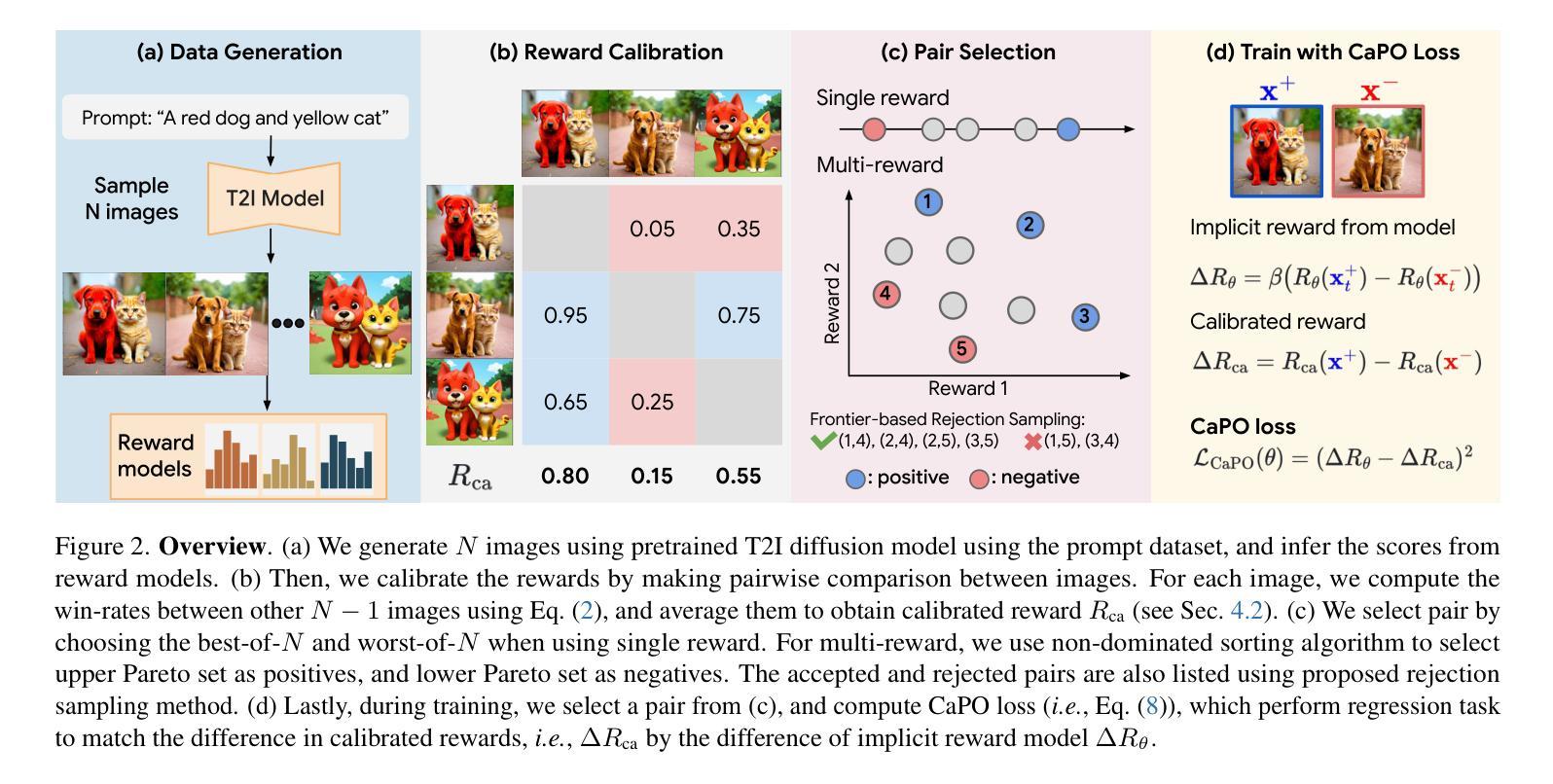
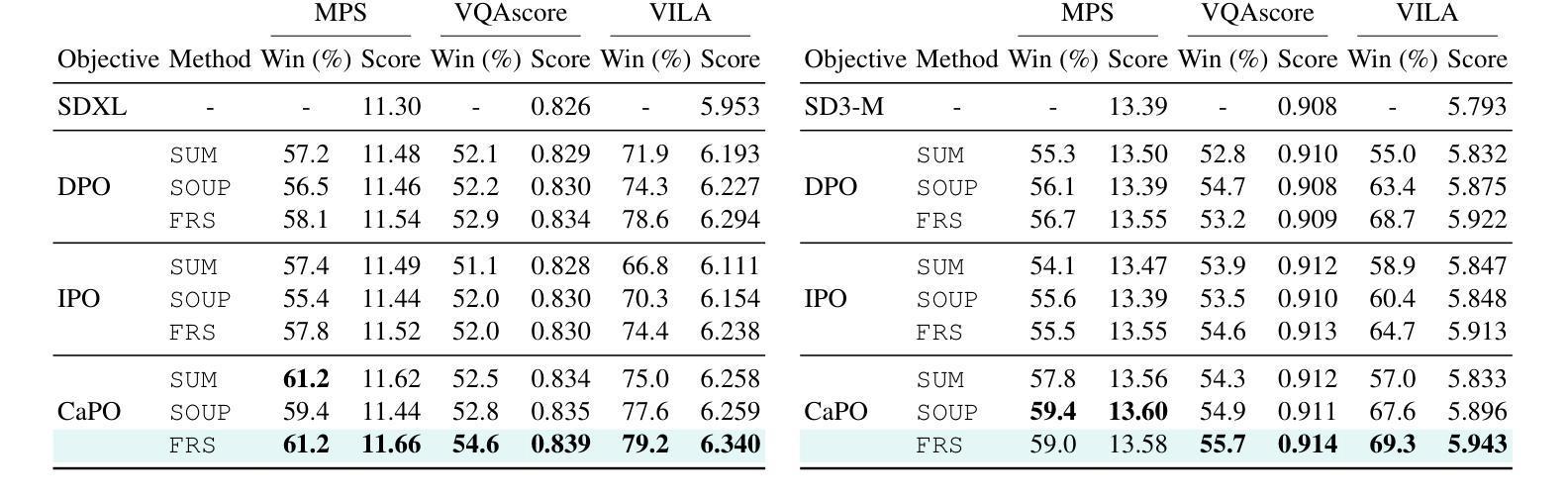
Calibrated Multi-Preference Optimization for Aligning Diffusion Models
Authors:Kyungmin Lee, Xiaohang Li, Qifei Wang, Junfeng He, Junjie Ke, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Irfan Essa, Jinwoo Shin, Feng Yang, Yinxiao Li
Aligning text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models with preference optimization is valuable for human-annotated datasets, but the heavy cost of manual data collection limits scalability. Using reward models offers an alternative, however, current preference optimization methods fall short in exploiting the rich information, as they only consider pairwise preference distribution. Furthermore, they lack generalization to multi-preference scenarios and struggle to handle inconsistencies between rewards. To address this, we present Calibrated Preference Optimization (CaPO), a novel method to align T2I diffusion models by incorporating the general preference from multiple reward models without human annotated data. The core of our approach involves a reward calibration method to approximate the general preference by computing the expected win-rate against the samples generated by the pretrained models. Additionally, we propose a frontier-based pair selection method that effectively manages the multi-preference distribution by selecting pairs from Pareto frontiers. Finally, we use regression loss to fine-tune diffusion models to match the difference between calibrated rewards of a selected pair. Experimental results show that CaPO consistently outperforms prior methods, such as Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), in both single and multi-reward settings validated by evaluation on T2I benchmarks, including GenEval and T2I-Compbench.
将文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型与偏好优化对齐对于人类注释数据集是有价值的,但手动数据收集的沉重成本限制了可扩展性。使用奖励模型提供了一种替代方案,然而,当前的偏好优化方法未能充分利用丰富信息,因为它们只考虑成对偏好分布。此外,它们缺乏在多种偏好场景下的泛化能力,并且难以处理奖励之间的一致性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了校准偏好优化(CaPO)这一新方法,通过结合多个奖励模型的通用偏好,无需人类注释数据即可对齐T2I扩散模型。我们的方法的核心在于奖励校准方法,通过计算预训练模型生成的样本的预期胜率来近似通用偏好。此外,我们提出了一种基于前沿的配对选择方法,通过从帕累托前沿选择配对,有效地管理多偏好分布。最后,我们使用回归损失对扩散模型进行微调,以匹配所选配对之间校准奖励的差异。实验结果表明,无论是在单一奖励还是多奖励设置下,经过GenEval和T2I-Compbench评估,CaPO始终优于先前的方法,如直接偏好优化(DPO)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CVPR 2025, Project page: https://kyungmnlee.github.io/capo.github.io/
Summary
本文提出一种无需人工标注数据的方法,即通过融合多个奖励模型的一般偏好,对文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型进行校准优化(CaPO)。该方法的核心包括奖励校准方法,用于计算预训练模型生成的样本的预期胜率,从而近似一般偏好;同时提出基于前沿的配对选择方法,有效管理多偏好分布;最后通过回归损失微调扩散模型,匹配选定配对的校准奖励差异。实验结果显示,CaPO在单奖励和多奖励设置下均优于先前的优化方法,如直接偏好优化(DPO),并在T2I基准测试中得到了验证。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型与偏好优化对于提高模型的性能至关重要。然而,人工数据收集的昂贵成本限制了其可扩展性。
- 使用奖励模型作为替代方案是一个可行的选择。然而,现有的偏好优化方法存在局限性,如未能充分利用丰富信息、仅考虑成对偏好分布等。
- 提出了校准偏好优化(CaPO)新方法,该方法能够融合多个奖励模型的一般偏好,无需人工标注数据。
- CaPO的核心包括奖励校准方法、基于前沿的配对选择方法以及通过回归损失微调扩散模型。
- 实验结果显示,CaPO在单奖励和多奖励设置下均表现出优异的性能。
- 与先前的优化方法相比,如直接偏好优化(DPO),CaPO具有更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图


Unforgettable Lessons from Forgettable Images: Intra-Class Memorability Matters in Computer Vision
Authors:Jie Jing, Yongjian Huang, Serena J. -W. Wang, Shuangpeng Han, Lucia Schiatti, Yen-Ling Kuo, Qing Lin, Mengmi Zhang
We introduce intra-class memorability, where certain images within the same class are more memorable than others despite shared category characteristics. To investigate what features make one object instance more memorable than others, we design and conduct human behavior experiments, where participants are shown a series of images, and they must identify when the current image matches the image presented a few steps back in the sequence. To quantify memorability, we propose the Intra-Class Memorability score (ICMscore), a novel metric that incorporates the temporal intervals between repeated image presentations into its calculation. Furthermore, we curate the Intra-Class Memorability Dataset (ICMD), comprising over 5,000 images across ten object classes with their ICMscores derived from 2,000 participants’ responses. Subsequently, we demonstrate the usefulness of ICMD by training AI models on this dataset for various downstream tasks: memorability prediction, image recognition, continual learning, and memorability-controlled image editing. Surprisingly, high-ICMscore images impair AI performance in image recognition and continual learning tasks, while low-ICMscore images improve outcomes in these tasks. Additionally, we fine-tune a state-of-the-art image diffusion model on ICMD image pairs with and without masked semantic objects. The diffusion model can successfully manipulate image elements to enhance or reduce memorability. Our contributions open new pathways in understanding intra-class memorability by scrutinizing fine-grained visual features behind the most and least memorable images and laying the groundwork for real-world applications in computer vision. We will release all code, data, and models publicly.
我们引入了类内记忆性的概念,即同一类别中的某些图像比其他图像更容易记住,尽管它们具有共享的分类特征。为了研究什么特征使得一个对象实例比其他实例更容易记住,我们设计并进行了人类行为实验,实验参与者会观看一系列图像,并必须判断当前图像是否与序列中几步之前的图像相匹配。为了量化记忆性,我们提出了类内记忆性得分(ICMscore)这一新指标,该指标将重复呈现图像之间的时间间隔纳入计算。此外,我们整理了类内记忆性数据集(ICMD),涵盖十大对象类别的超过5000张图像,其ICMscore来自2000名参与者的回答。接下来,我们通过在此数据集上训练AI模型来展示ICMD的实用性,用于各种下游任务:记忆性预测、图像识别、持续学习和记忆性控制图像处理。令人惊讶的是,高ICM得分的图像会在图像识别和持续学习任务中损害AI性能,而低ICM得分的图像则会改善这些任务的结果。此外,我们对最先进的图像扩散模型进行微调,处理带有和不带掩码语义对象的ICMD图像对。扩散模型能够成功操作图像元素以增强或减少记忆性。我们的研究通过仔细研究最难忘和最容易忘记的图像背后的精细视觉特征,为理解类内记忆性开辟了新途径,并为计算机视觉的实际应用奠定了基础。我们将公开发布所有代码、数据和模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究探讨了同一类别内不同图像的记忆性差异,并定义了“类内记忆性”的概念。为了确定使某一对象实例比其他对象更易于记忆的特征,进行了人类行为实验。为此提出量化记忆性的新指标——类内记忆性得分(ICMscore),并建立了包含超过五千张图片的类内记忆性数据集(ICMD)。研究表明,高ICMscore图像会降低AI在图像识别和持续学习任务中的性能,而低ICMscore图像则能提高结果。此外,微调图像扩散模型可用于提高或降低图像记忆性。该研究为理解最难忘和最易忘的图像背后的细微视觉特征以及计算机视觉的潜在应用开辟了新途径。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了“类内记忆性”概念,同一类别的图像之间也存在记忆性的差异。
- 通过人类行为实验探究了哪些特征使某一对象实例比其他对象更易于记忆。
- 提出了量化记忆性的新指标——类内记忆性得分(ICMscore),并结合时序间隔进行计算。
- 建立了类内记忆性数据集(ICMD),包含超过五千张图片和相应的ICMscore得分。
- 高ICMscore图像在AI的识别和持续学习任务上造成性能挑战,而低ICMscore图像有助于提高性能。
- 对图像扩散模型进行微调以提高或降低图像的类内记忆性效果。
点此查看论文截图


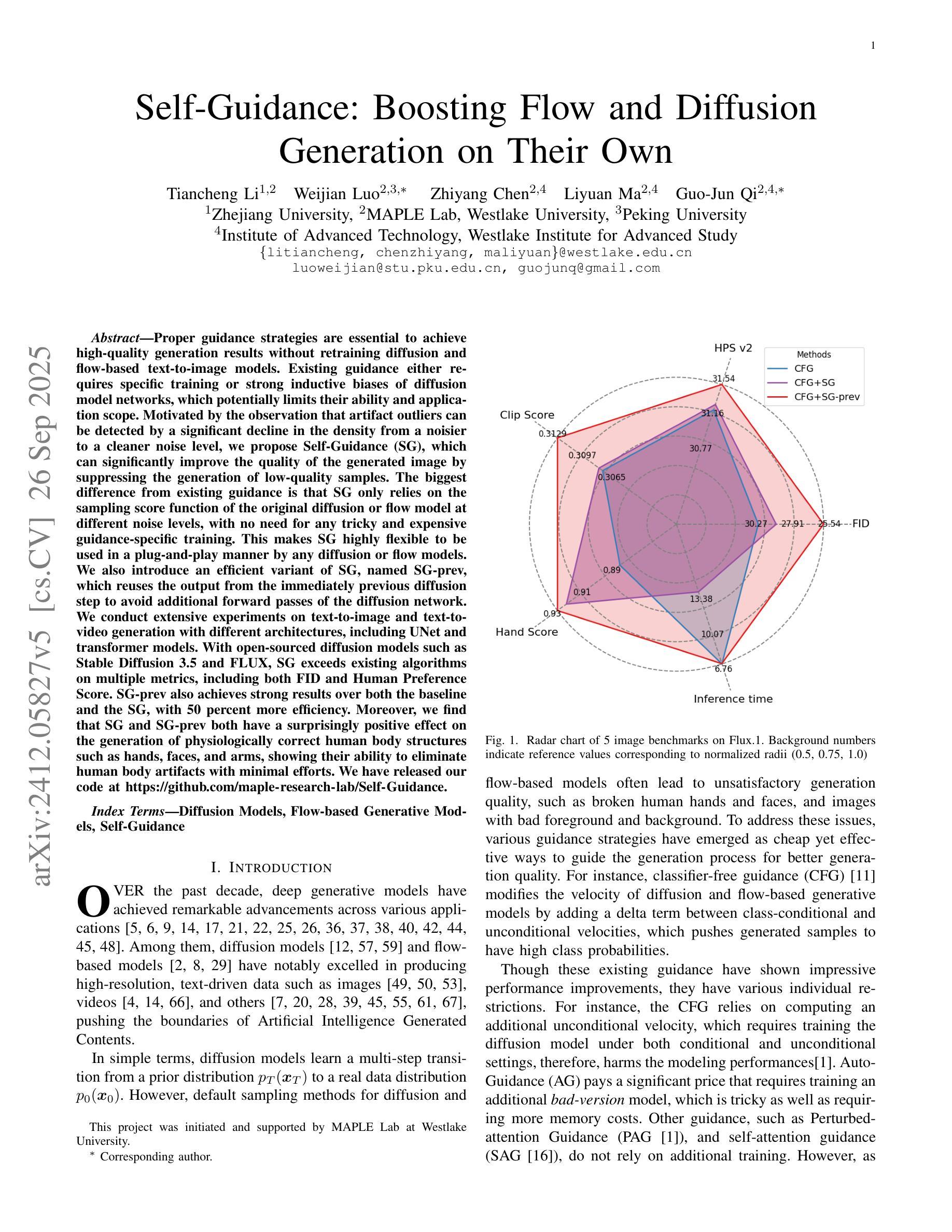
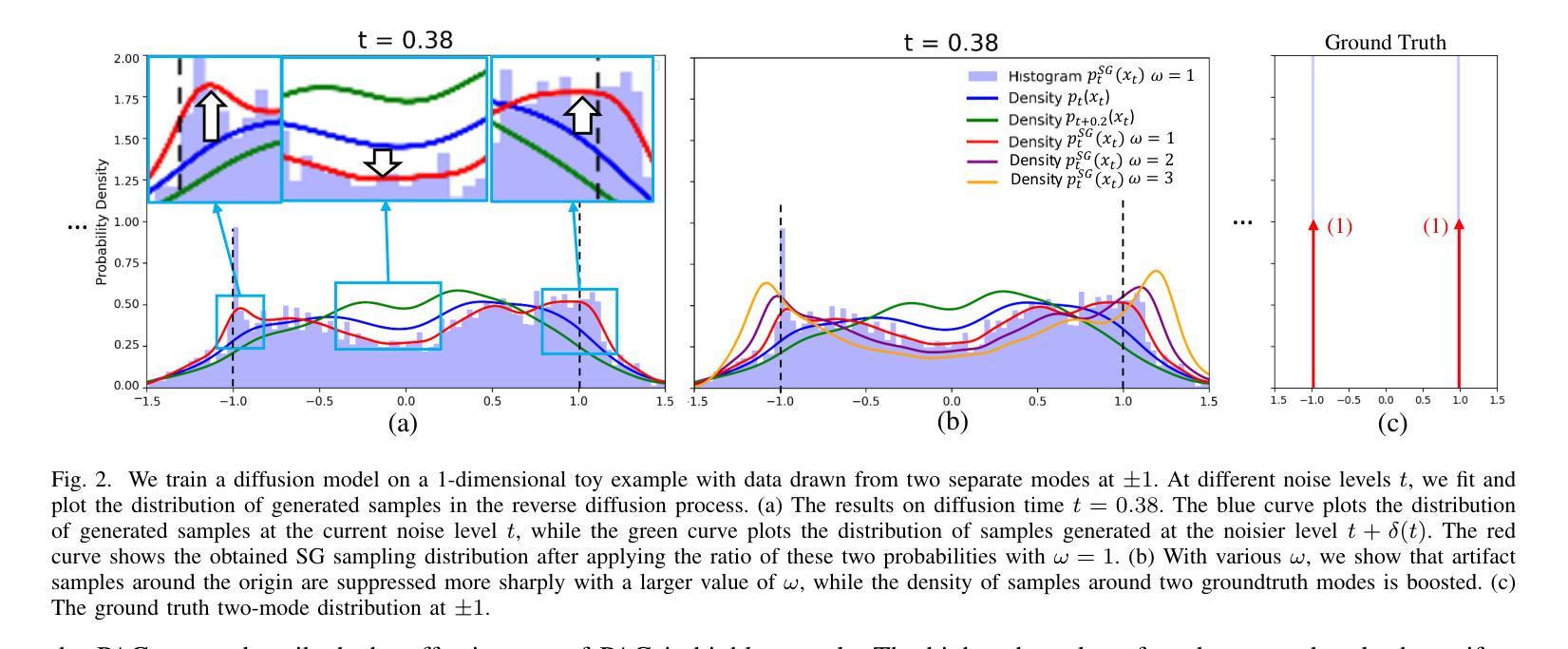
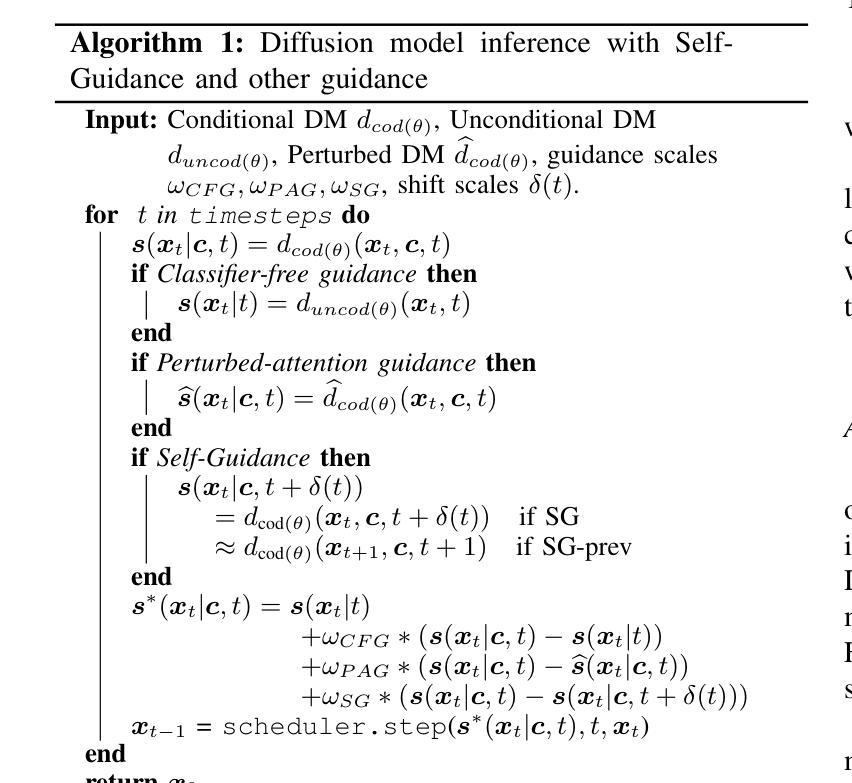
Self-Guidance: Boosting Flow and Diffusion Generation on Their Own
Authors:Tiancheng Li, Weijian Luo, Zhiyang Chen, Liyuan Ma, Guo-Jun Qi
Proper guidance strategies are essential to achieve high-quality generation results without retraining diffusion and flow-based text-to-image models. Existing guidance either requires specific training or strong inductive biases of diffusion model networks, which potentially limits their ability and application scope. Motivated by the observation that artifact outliers can be detected by a significant decline in the density from a noisier to a cleaner noise level, we propose Self-Guidance (SG), which can significantly improve the quality of the generated image by suppressing the generation of low-quality samples. The biggest difference from existing guidance is that SG only relies on the sampling score function of the original diffusion or flow model at different noise levels, with no need for any tricky and expensive guidance-specific training. This makes SG highly flexible to be used in a plug-and-play manner by any diffusion or flow models. We also introduce an efficient variant of SG, named SG-prev, which reuses the output from the immediately previous diffusion step to avoid additional forward passes of the diffusion network.We conduct extensive experiments on text-to-image and text-to-video generation with different architectures, including UNet and transformer models. With open-sourced diffusion models such as Stable Diffusion 3.5 and FLUX, SG exceeds existing algorithms on multiple metrics, including both FID and Human Preference Score. SG-prev also achieves strong results over both the baseline and the SG, with 50 percent more efficiency. Moreover, we find that SG and SG-prev both have a surprisingly positive effect on the generation of physiologically correct human body structures such as hands, faces, and arms, showing their ability to eliminate human body artifacts with minimal efforts. We have released our code at https://github.com/maple-research-lab/Self-Guidance.
适当的指导策略对于在不重新训练扩散和基于流的文本到图像模型的情况下实现高质量的生成结果至关重要。现有的指导方法要么需要特定的训练,要么需要扩散模型网络的强烈归纳偏见,这可能会限制其能力和应用范围。我们受到观察结果的启发,即可以通过从较嘈杂到较干净噪声水平的密度显着下降来检测异常值,因此提出了自引导(SG),可以通过抑制低质量样本的生成来显着提高生成图像的质量。与现有指导方法最大的不同是,SG仅依赖于不同噪声级别的原始扩散或流模型的采样分数函数,无需任何复杂且昂贵的特定指导训练。这使得SG高度灵活,可以以即插即用方式用于任何扩散或流模型。我们还介绍了SG的一个高效变体,名为SG-prev,它重用前一个扩散步骤的输出,以避免扩散网络的前向传递。我们在不同架构的文本到图像和文本到视频生成上进行了大量实验,包括UNet和transformer模型。使用开源扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion 3.5和FLUX),SG在多个指标(包括FID和人类偏好得分)上超过了现有算法。SG-prev在基准测试和SG方面都取得了强大结果,并且效率提高了50%。此外,我们发现SG和SG-prev在对生理上正确的人类身体结构(如手、脸和手臂)的生成方面产生了令人惊讶的积极影响,显示出它们以最小的努力消除人体伪影的能力。我们的代码已发布在https://github.com/maple-research-lab/Self-Guidance。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 13 figures
摘要
本文提出一种名为Self-Guidance(SG)的新策略,用于提高文本到图像扩散模型和流模型的生成图像质量。SG策略通过抑制低质量样本的生成,改进了图像生成质量。其最大特点是不需要复杂且昂贵的特定指导训练,仅依赖于不同噪声水平的扩散或流模型的采样分数函数,使其具有高度灵活性,可广泛应用于各种扩散和流模型。此外,本文还介绍了SG的变体SG-prev,它利用前一个扩散步骤的输出,避免额外的网络前向传递。实验证明,SG在多个指标上超越了现有算法,包括FID和人类偏好得分。SG-prev在基线测试和标准SG中都取得了强劲结果,效率提高了50%。SG和SG-prev在生成生理正确的人体结构(如手、脸、手臂等)方面表现出色,展示了其消除人体伪影的能力。
关键见解
- Self-Guidance策略通过抑制低质量样本生成,显著提高了扩散模型和流模型生成的图像质量。
- 该策略仅依赖于不同噪声水平的原始扩散或流模型的采样分数函数,无需特定的指导训练,具有高度灵活性。
- SG的变体SG-prev通过利用前一个扩散步骤的输出,提高了效率。
- 实验证明,SG在多个文本到图像和文本到视频生成实验中超越了现有算法。
- SG和SG-prev在生成生理正确的人体结构方面表现出色。
- 代码已公开,可供研究使用。
- Self-Guidance策略有望为扩散模型和流模型的应用开辟新的可能性,特别是在图像和视频生成领域。
点此查看论文截图
DynamicControl: Adaptive Condition Selection for Improved Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Qingdong He, Jinlong Peng, Pengcheng Xu, Boyuan Jiang, Xiaobin Hu, Donghao Luo, Yong Liu, Yabiao Wang, Chengjie Wang, Xiangtai Li, Jiangning Zhang
To enhance the controllability of text-to-image diffusion models, current ControlNet-like models have explored various control signals to dictate image attributes. However, existing methods either handle conditions inefficiently or use a fixed number of conditions, which does not fully address the complexity of multiple conditions and their potential conflicts. This underscores the need for innovative approaches to manage multiple conditions effectively for more reliable and detailed image synthesis. To address this issue, we propose a novel framework, DynamicControl, which supports dynamic combinations of diverse control signals, allowing adaptive selection of different numbers and types of conditions. Our approach begins with a double-cycle controller that generates an initial real score sorting for all input conditions by leveraging pre-trained conditional generation models and discriminative models. This controller evaluates the similarity between extracted conditions and input conditions, as well as the pixel-level similarity with the source image. Then, we integrate a Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) to build an efficient condition evaluator. This evaluator optimizes the ordering of conditions based on the double-cycle controller’s score ranking. Our method jointly optimizes MLLMs and diffusion models, utilizing MLLMs’ reasoning capabilities to facilitate multi-condition text-to-image (T2I) tasks. The final sorted conditions are fed into a parallel multi-control adapter, which learns feature maps from dynamic visual conditions and integrates them to modulate ControlNet, thereby enhancing control over generated images. Through both quantitative and qualitative comparisons, DynamicControl demonstrates its superiority over existing methods in terms of controllability, generation quality and composability under various conditional controls.
为了增强文本到图像扩散模型的可控性,当前的ControlNet类模型已经探索了各种控制信号来指示图像属性。然而,现有方法要么处理条件效率低下,要么使用固定数量的条件,这并没有完全解决多个条件的复杂性及其潜在冲突。这强调了对创新方法的需求,需要有效管理多个条件以进行更可靠和详细的图像合成。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新的框架DynamicControl,它支持各种控制信号的动态组合,允许灵活选择不同数量和类型的条件。我们的方法始于双重循环控制器,利用预训练的条件生成模型和判别模型,对所有输入条件生成初始真实分数排序。该控制器评估提取的条件与输入条件之间的相似性,以及与源图像的像素级相似性。然后,我们集成了多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),以构建有效的条件评估器。该评估器根据双重循环控制器的分数排名优化条件的顺序。我们的方法联合优化了MLLMs和扩散模型,利用MLLMs的推理能力促进多条件文本到图像(T2I)任务。最终的排序条件被输入到并行多控制适配器中,该适配器从动态视觉条件中学习特征映射并将其集成以调制ControlNet,从而增强对生成图像的控制。通过定量和定性比较,DynamicControl在可控性、生成质量和各种条件控制的组合能力方面均表现出其优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为DynamicControl的新型框架,用于改进文本到图像扩散模型的可控性。该框架支持多种控制信号动态组合,可适应性地选择不同数量和类型的条件。通过双重循环控制器、多模态大型语言模型和并行多控制适配器等技术,实现了对生成图像的更精细控制。相较于现有方法,DynamicControl在可控性、生成质量和组合性方面表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- DynamicControl框架旨在改进文本到图像扩散模型的可控性,通过动态组合多种控制信号实现更可靠和详细的图像合成。
- 该框架采用双重循环控制器生成初始真实分数排序,利用预训练的条件生成模型和判别模型对提取的条件和输入条件进行相似性评估。
- 集成多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)以构建高效的条件评估器,优化基于双重循环控制器得分排序的条件排序。
- DynamicControl联合优化MLLMs和扩散模型,利用MLLMs的推理能力促进多条件文本到图像(T2I)任务。
- 最后的排序条件被输入到并行多控制适配器中,该适配器从动态视觉条件学习特征映射并将其整合到ControlNet中,从而提高对生成图像的控制能力。
- DynamicControl在定量和定性比较中均表现出在可控性、生成质量和组合性方面的优越性。
- 该框架为解决现有扩散模型在处理复杂多条件时的局限性提供了一种新颖、有效的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图
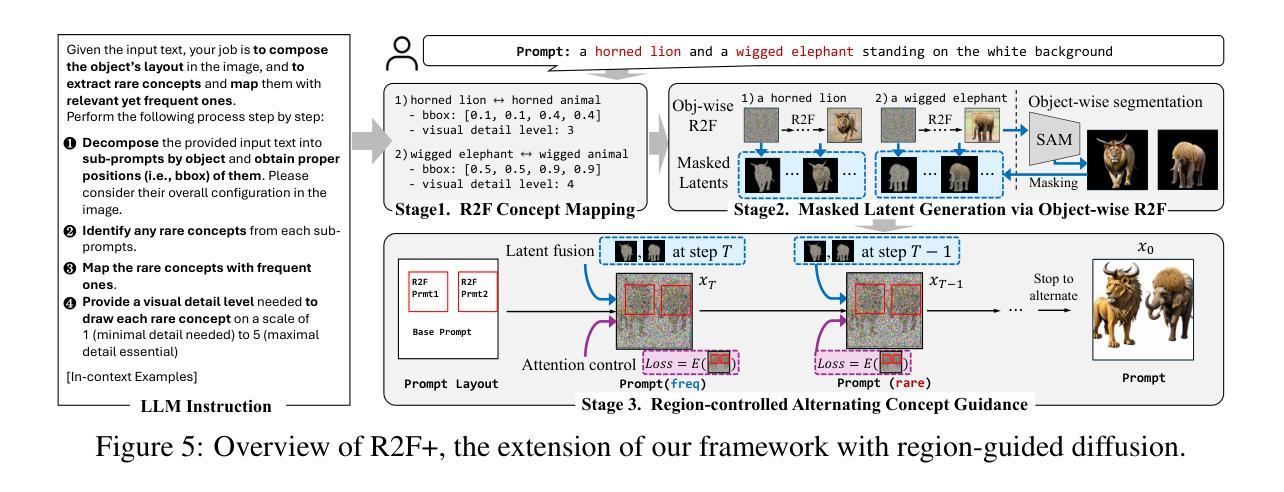
Rare-to-Frequent: Unlocking Compositional Generation Power of Diffusion Models on Rare Concepts with LLM Guidance
Authors:Dongmin Park, Sebin Kim, Taehong Moon, Minkyu Kim, Kangwook Lee, Jaewoong Cho
State-of-the-art text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models often struggle to generate rare compositions of concepts, e.g., objects with unusual attributes. In this paper, we show that the compositional generation power of diffusion models on such rare concepts can be significantly enhanced by the Large Language Model (LLM) guidance. We start with empirical and theoretical analysis, demonstrating that exposing frequent concepts relevant to the target rare concepts during the diffusion sampling process yields more accurate concept composition. Based on this, we propose a training-free approach, R2F, that plans and executes the overall rare-to-frequent concept guidance throughout the diffusion inference by leveraging the abundant semantic knowledge in LLMs. Our framework is flexible across any pre-trained diffusion models and LLMs, and can be seamlessly integrated with the region-guided diffusion approaches. Extensive experiments on three datasets, including our newly proposed benchmark, RareBench, containing various prompts with rare compositions of concepts, R2F significantly surpasses existing models including SD3.0 and FLUX by up to 28.1%p in T2I alignment. Code is available at https://github.com/krafton-ai/Rare-to-Frequent.
先进的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成罕见概念组合(例如具有不寻常属性的物体)时经常面临挑战。在本文中,我们展示了通过大型语言模型(LLM)的指导,可以显著增强扩散模型在这种罕见概念上的组合生成能力。我们从实证和理论分析开始,证明在扩散采样过程中暴露与目标罕见概念相关的频繁概念,可以产生更精确的概念组合。基于此,我们提出了一种无需训练的方法R2F,它利用LLM中丰富的语义知识,通过扩散推断,规划和执行从罕见到频繁的整体概念指导。我们的框架适用于任何预训练的扩散模型和LLM,并且可以与区域引导扩散方法无缝集成。在包括我们新提出的基准测试数据集RareBench在内的三个数据集上进行的大量实验表明,R2F在各种包含罕见概念组合的提示下,显著超越了SD3.0和FLUX模型,在T2I对齐方面的性能提高了高达28.1%。代码可在https://github.com/krafton-ai/Rare-to-Frequent找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 (spotlight)
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成罕见概念组合时面临挑战。本文展示通过大型语言模型(LLM)指导,可以显著提高扩散模型在罕见概念上的组合生成能力。通过实证和理论分析,表明在扩散采样过程中暴露与目标罕见概念相关的频繁概念,可以更准确地进行概念组合。基于此,我们提出了一种无需训练的方法R2F,利用LLM中的丰富语义知识,通过扩散推理,实现罕见到频繁的概念指导。该方法灵活适用于任何预训练的扩散模型和LLM,并可无缝集成到区域引导扩散方法中。在包括新提出的罕见概念基准测试集RareBench在内的三个数据集上进行的大量实验表明,R2F在T2I对齐方面显著超越了现有模型,包括SD3.0和FLUX,提高了高达28.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成罕见概念组合时具有挑战。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)指导有助于提高扩散模型在罕见概念上的组合生成能力。
- 在扩散采样过程中暴露与目标罕见概念相关的频繁概念,能更准确进行概念组合。
- 提出了一种无需训练的方法R2F,利用LLM的丰富语义知识,实现罕见到频繁的概念指导。
- R2F方法灵活适用于各种预训练扩散模型和LLM,并可集成到区域引导扩散方法中。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,R2F显著提高了T2I对齐性能,包括新提出的罕见概念基准测试集RareBench。
点此查看论文截图

Diffusion Curriculum: Synthetic-to-Real Data Curriculum via Image-Guided Diffusion
Authors:Yijun Liang, Shweta Bhardwaj, Tianyi Zhou
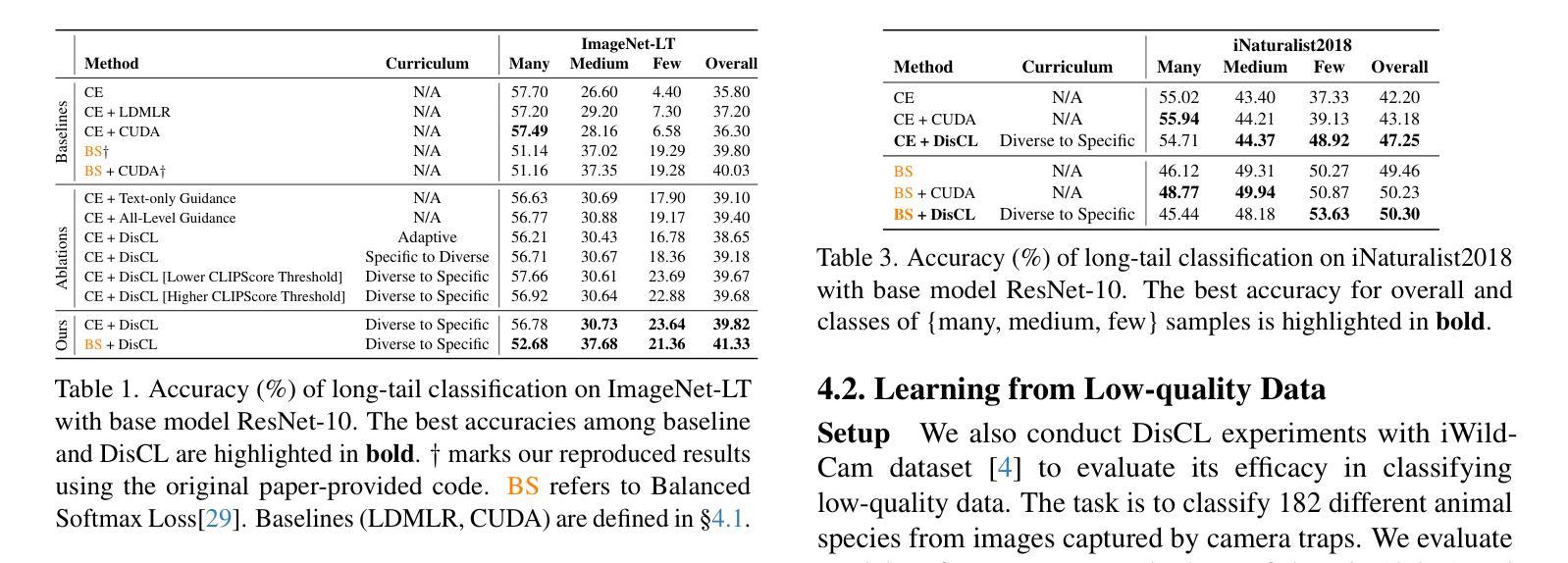
Low-quality or scarce data has posed significant challenges for training deep neural networks in practice. While classical data augmentation cannot contribute very different new data, diffusion models opens up a new door to build self-evolving AI by generating high-quality and diverse synthetic data through text-guided prompts. However, text-only guidance cannot control synthetic images’ proximity to the original images, resulting in out-of-distribution data detrimental to the model performance. To overcome the limitation, we study image guidance to achieve a spectrum of interpolations between synthetic and real images. With stronger image guidance, the generated images are similar to the training data but hard to learn. While with weaker image guidance, the synthetic images will be easier for model but contribute to a larger distribution gap with the original data. The generated full spectrum of data enables us to build a novel “Diffusion Curriculum (DisCL)”. DisCL adjusts the image guidance level of image synthesis for each training stage: It identifies and focuses on hard samples for the model and assesses the most effective guidance level of synthetic images to improve hard data learning. We apply DisCL to two challenging tasks: long-tail (LT) classification and learning from low-quality data. It focuses on lower-guidance images of high-quality to learn prototypical features as a warm-up of learning higher-guidance images that might be weak on diversity or quality. Extensive experiments showcase a gain of 2.7% and 2.1% in OOD and ID macro-accuracy when applying DisCL to iWildCam dataset. On ImageNet-LT, DisCL improves the base model’s tail-class accuracy from 4.4% to 23.64% and leads to a 4.02% improvement in all-class accuracy.
在实践中,低质量或稀缺数据为训练深度神经网络带来了重大挑战。虽然经典的数据增强无法提供非常不同的新数据,但扩散模型通过文本引导提示生成高质量和多样化的合成数据,为构建自我进化的AI打开了新门。然而,仅使用文本指导无法控制合成图像与原始图像的接近程度,从而导致对模型性能有害的分布外数据。为了克服这一局限性,我们研究了图像指导,以实现合成图像和真实图像之间的频谱插值。通过更强的图像指导,生成的图像与训练数据相似,但难以学习。而较弱的图像指导会使合成图像更容易被模型接受,但与原始数据的分布差距更大。生成的全数据频谱使我们能够建立一种新的“扩散课程(DisCL)”。DisCL针对每个训练阶段调整图像合成的图像指导级别:它识别并专注于模型的困难样本,并评估合成图像的最有效指导级别,以提高困难数据的学习效果。我们将DisCL应用于两个具有挑战性的任务:长尾(LT)分类和学习低质量数据。它专注于高质量但指导较少的图像,以学习典型特征,作为学习多样性或质量可能较弱的较高指导图像的预热。在iWildCam数据集上应用DisCL的实验显示,在OOD和ID宏准确率上分别提高了2.7%和2.1%。在ImageNet-LT上,DisCL将基础模型的尾类准确率从4.4%提高到23.64%,并导致所有类别准确率提高4.02%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in ICCV2025. 22 pages, including references and appendix. Code is available at http://github.com/tianyi-lab/DisCL
Summary
针对深度学习中的低质量或稀缺数据问题,本文研究了基于扩散模型的图像合成技术。为解决文本引导生成图像时产生的分布外数据问题,引入了图像指导策略。并提出了一种新的方法——扩散课程(DisCL),根据训练阶段调整图像合成中的图像指导水平,以提升模型的性能。通过长期分类和低质量数据学习任务验证其有效性。研究对于解决数据质量和多样性的挑战,特别是在大规模分类和低质量数据集方面具有重要指导意义。
Key Takeaways
- 低质量或稀缺数据对训练深度神经网络提出了挑战。
- 扩散模型通过文本指导生成高质量和多样化的合成数据。但纯文本指导存在生成图像与原图像距离不可控的问题,可能产生不利于模型性能的分外数据。
- 图像指导策略用于解决上述文本引导的问题,以实现合成与真实图像之间的不同插值水平。
- 强图像指导生成的图像相似于训练数据但难以学习;弱图像指导生成的图像学习较容易但与实际数据分布差距较大。
- 提出了一种名为“扩散课程(DisCL)”的新方法,根据训练阶段调整图像合成的图像指导水平,以提高模型对困难样本的学习效果。
- 在长期分类和低质量数据学习任务中,应用DisCL可有效提高模型性能。
点此查看论文截图
Leveraging Model Guidance to Extract Training Data from Personalized Diffusion Models
Authors:Xiaoyu Wu, Jiaru Zhang, Zhiwei Steven Wu
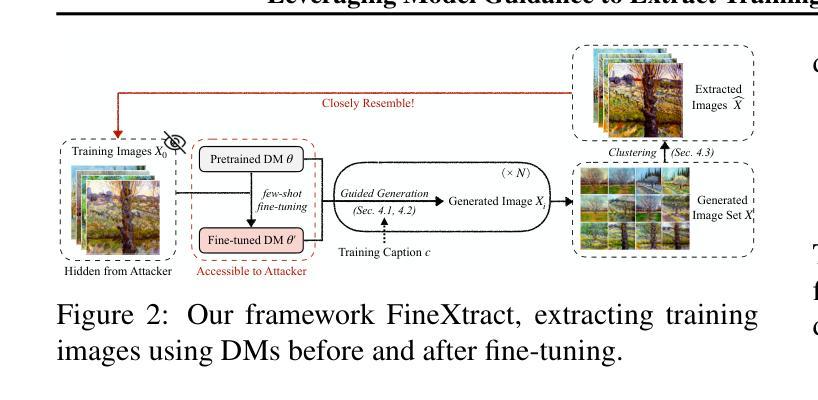
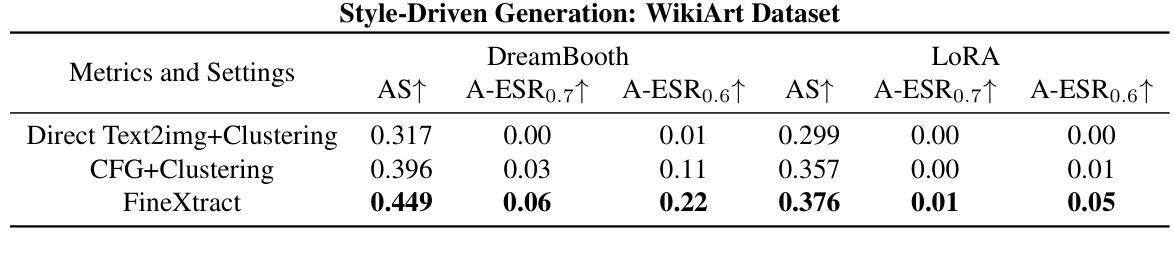
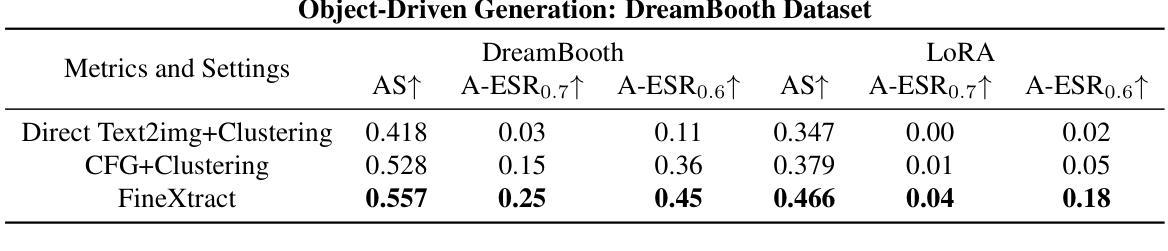
Diffusion Models (DMs) have become powerful image generation tools, especially for few-shot fine-tuning where a pretrained DM is fine-tuned on a small image set to capture specific styles or objects. Many people upload these personalized checkpoints online, fostering communities such as Civitai and HuggingFace. However, model owners may overlook the data leakage risks when releasing fine-tuned checkpoints. Moreover, concerns regarding copyright violations arise when unauthorized data is used during fine-tuning. In this paper, we ask: “Can training data be extracted from these fine-tuned DMs shared online?” A successful extraction would present not only data leakage threats but also offer tangible evidence of copyright infringement. To answer this, we propose FineXtract, a framework for extracting fine-tuning data. Our method approximates fine-tuning as a gradual shift in the model’s learned distribution – from the original pretrained DM toward the fine-tuning data. By extrapolating the models before and after fine-tuning, we guide the generation toward high-probability regions within the fine-tuned data distribution. We then apply a clustering algorithm to extract the most probable images from those generated using this extrapolated guidance. Experiments on DMs fine-tuned with datasets including WikiArt, DreamBooth, and real-world checkpoints posted online validate the effectiveness of our method, extracting about 20% of fine-tuning data in most cases. The code is available https://github.com/Nicholas0228/FineXtract.
扩散模型(DMs)已成为强大的图像生成工具,特别是在小样本微调中,预训练的DM被微调以捕捉特定的风格或对象。许多人在线上传这些个性化的检查点,促进了如Civitai和HuggingFace等社区的发展。然而,在发布微调检查点时,模型所有者可能会忽略数据泄露的风险。此外,当未经授权的数据用于微调时,就会出现版权违规的担忧。在本文中,我们提出的问题是:“可以从在线共享的这些微调过的扩散模型中提取训练数据吗?”成功的提取不仅会带来数据泄露的威胁,而且也会提供版权侵权的切实证据。为了回答这个问题,我们提出了FineXtract,一个用于提取微调数据的框架。我们的方法将微调近似为模型学习分布的一个逐渐变化——从原始的预训练DM向微调数据转变。通过对微调前后的模型进行外推,我们引导生成向微调数据分布中的高概率区域。然后,我们应用聚类算法从这些使用外推指导生成的图像中提取最可能的图像。在使用WikiArt、DreamBooth和在线发布的现实世界检查点等数据集进行微调的DM上的实验验证了我们方法的有效性,在大多数情况下,能够提取约20%的微调数据。代码可在链接中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML) 2025
Summary
扩散模型(DMs)在少量样本微调中展现出强大的图像生成能力,通过对预训练模型进行小样本图像集微调以捕捉特定风格或对象。但模型公开时可能存在数据泄露风险及版权侵犯问题。本文提出“FineXtract”框架,旨在从在线共享的微调后的DMs中提取微调数据。通过模拟微调过程,从预训练模型向微调数据集学习分布的逐渐转变,我们能够引导生成图像聚集于微调数据分布的高概率区域,并利用聚类算法提取最可能的图像。实验证明该方法在WikiArt、DreamBooth及在线真实数据集上有效,多数情况下可提取约20%的微调数据。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)在少量样本微调中展现出强大的图像生成能力。
- 模型公开时存在数据泄露风险及版权侵犯问题。
- FineXtract框架旨在从在线共享的微调后的DMs中提取微调数据。
- 通过模拟微调过程,FineXtract利用模型学习分布的逐渐转变来引导生成图像。
- 利用聚类算法提取最可能的图像。
- 实验证明该方法在多种数据集上有效,可提取约20%的微调数据。
点此查看论文截图