⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-09-30 更新
CCNeXt: An Effective Self-Supervised Stereo Depth Estimation Approach
Authors:Alexandre Lopes, Roberto Souza, Helio Pedrini
Depth Estimation plays a crucial role in recent applications in robotics, autonomous vehicles, and augmented reality. These scenarios commonly operate under constraints imposed by computational power. Stereo image pairs offer an effective solution for depth estimation since it only needs to estimate the disparity of pixels in image pairs to determine the depth in a known rectified system. Due to the difficulty in acquiring reliable ground-truth depth data across diverse scenarios, self-supervised techniques emerge as a solution, particularly when large unlabeled datasets are available. We propose a novel self-supervised convolutional approach that outperforms existing state-of-the-art Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformers (ViTs) while balancing computational cost. The proposed CCNeXt architecture employs a modern CNN feature extractor with a novel windowed epipolar cross-attention module in the encoder, complemented by a comprehensive redesign of the depth estimation decoder. Our experiments demonstrate that CCNeXt achieves competitive metrics on the KITTI Eigen Split test data while being 10.18$\times$ faster than the current best model and achieves state-of-the-art results in all metrics in the KITTI Eigen Split Improved Ground Truth and Driving Stereo datasets when compared to recently proposed techniques. To ensure complete reproducibility, our project is accessible at \href{https://github.com/alelopes/CCNext}{\texttt{https://github.com/alelopes/CCNext}}.
深度估计在机器人技术、自动驾驶汽车和增强现实等现代应用领域中扮演着至关重要的角色。这些场景通常在计算能力的限制下运行。立体图像对为深度估计提供了有效的解决方案,因为在已知的校正系统中,它只需要估计图像对中像素的视差来确定深度。由于在多种场景下获取可靠的地面真实深度数据具有挑战性,自监督技术应运而生,特别是在拥有大量无标签数据集的情况下。我们提出了一种新型自监督卷积方法,在平衡计算成本的同时,超越了现有的最先进的卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉变压器(ViT)。所提出的CCNeXt架构采用现代CNN特征提取器,在编码器中加入新型窗口化极线交叉注意模块,并对深度估计解码器进行了全面的重新设计。我们的实验表明,CCNeXt在KITTI Eigen Split测试数据上取得了具有竞争力的指标,并且比当前最佳模型快10.18倍。与最近提出的技术相比,在KITTIEigen Split改进地面真实和驾驶立体数据集中,其在所有指标上都达到了最新技术成果。为确保可重复性,我们的项目可通过https://github.com/alelopes/CCNext访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度估计在机器人技术、自动驾驶汽车和增强现实等现代应用中扮演重要角色,特别是在计算功率受限的场景中。我们提出了一种新型的自我监督卷积方法CCNeXt,它在深度估计方面超越了现有的最先进的卷积神经网络和视觉变压器,同时平衡了计算成本。CCNeXt在KITTI Eigen Split测试数据上表现良好,并且是现有最佳模型的10.18倍快,在KITTI Eigen Split改进地面真实和驾驶立体声数据集中与最近提出的技术相比在所有指标上都达到了最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- 深度估计在机器人技术、自动驾驶汽车和增强现实等领域具有关键作用。
- 在已知校正系统中,立体图像对为深度估计提供了有效解决方案,通过估计像素差异来确定深度。
- 由于在不同场景下获取可靠的地面真实深度数据具有挑战性,因此出现了自我监督技术,特别是在拥有大量无标签数据集的情况下。
- 提出的CCNeXt架构结合了现代CNN特征提取器和新颖的窗口化极线交叉注意力模块,重新设计了深度估计解码器。
- CCNeXt在KITTI Eigen Split测试数据上表现优秀,计算速度比现有最佳模型快10.18倍。
- 在KITTI Eigen Split改进地面真实和驾驶立体声数据集中,CCNeXt在所有指标上都达到了最新技术水平。
点此查看论文截图
LG-CD: Enhancing Language-Guided Change Detection through SAM2 Adaptation
Authors:Yixiao Liu, Yizhou Yang, Jinwen Li, Jun Tao, Ruoyu Li, Xiangkun Wang, Min Zhu, Junlong Cheng
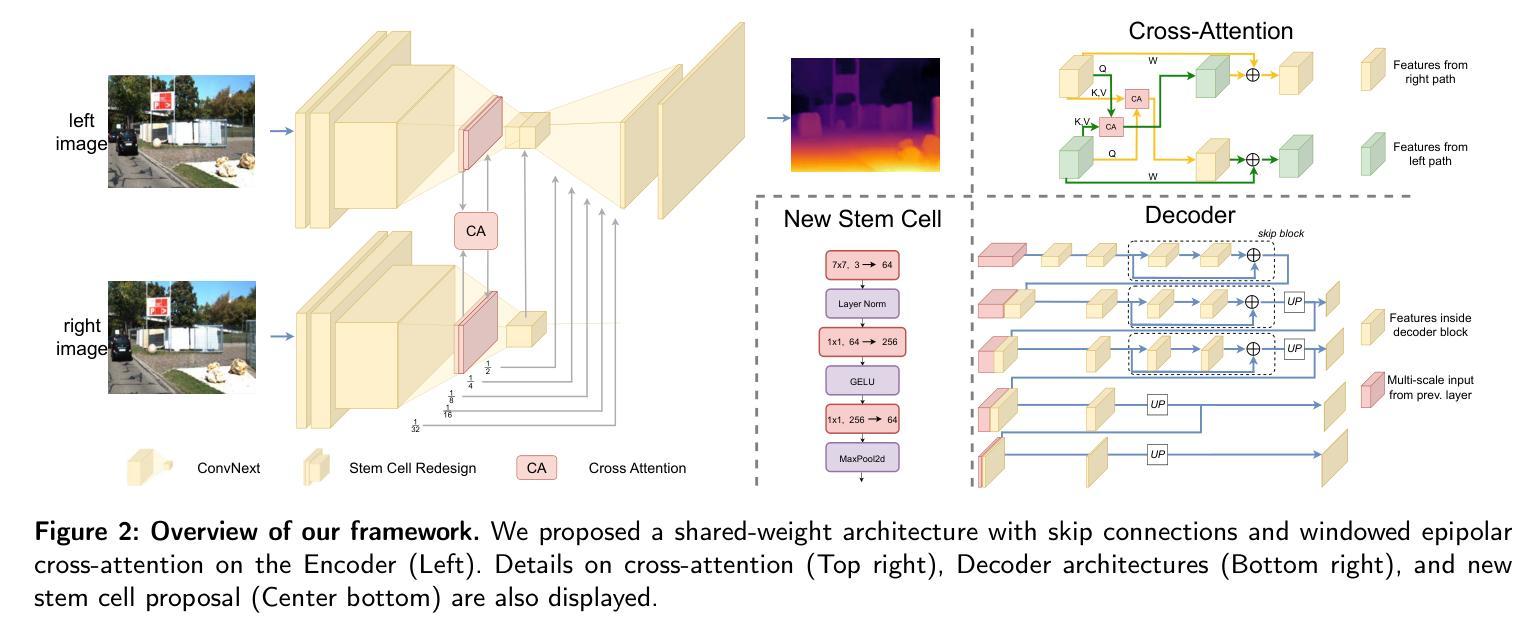
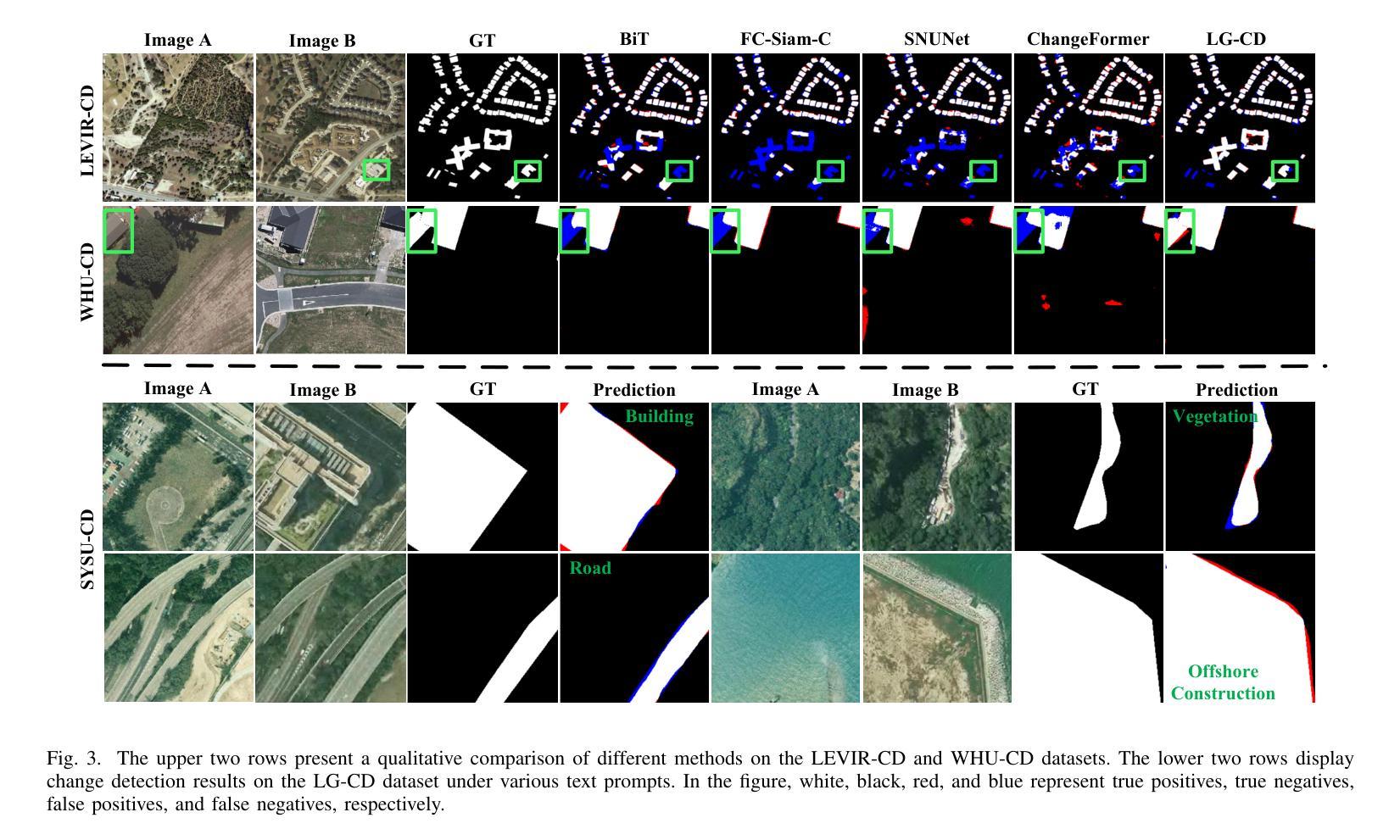
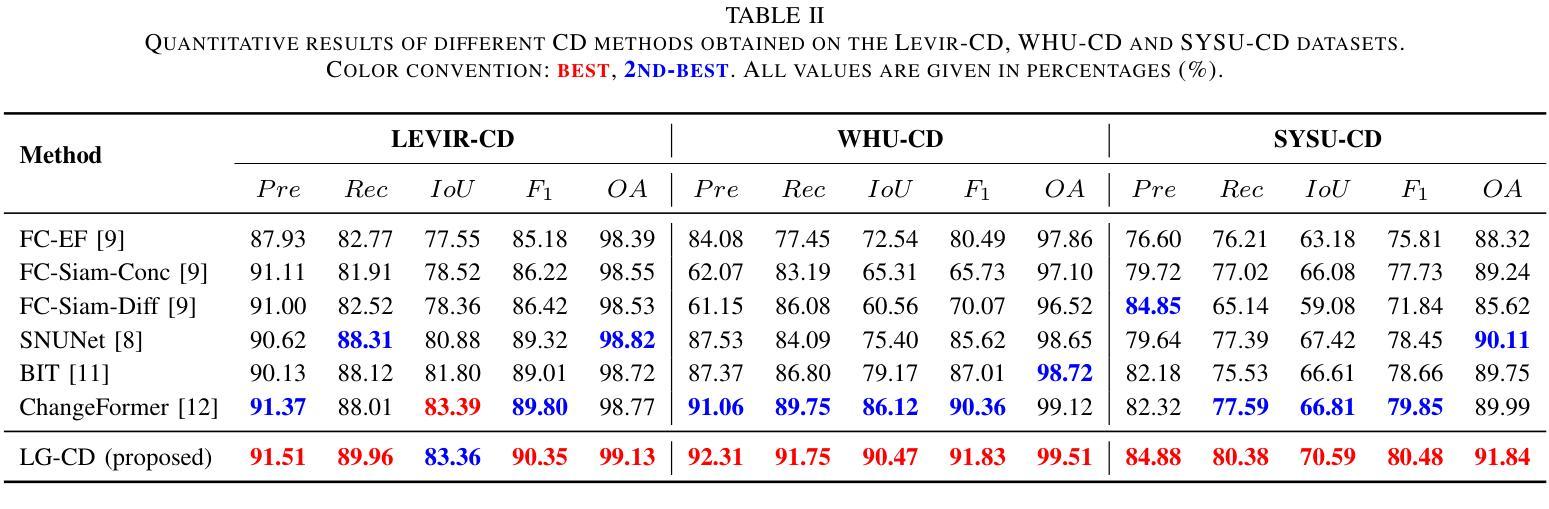
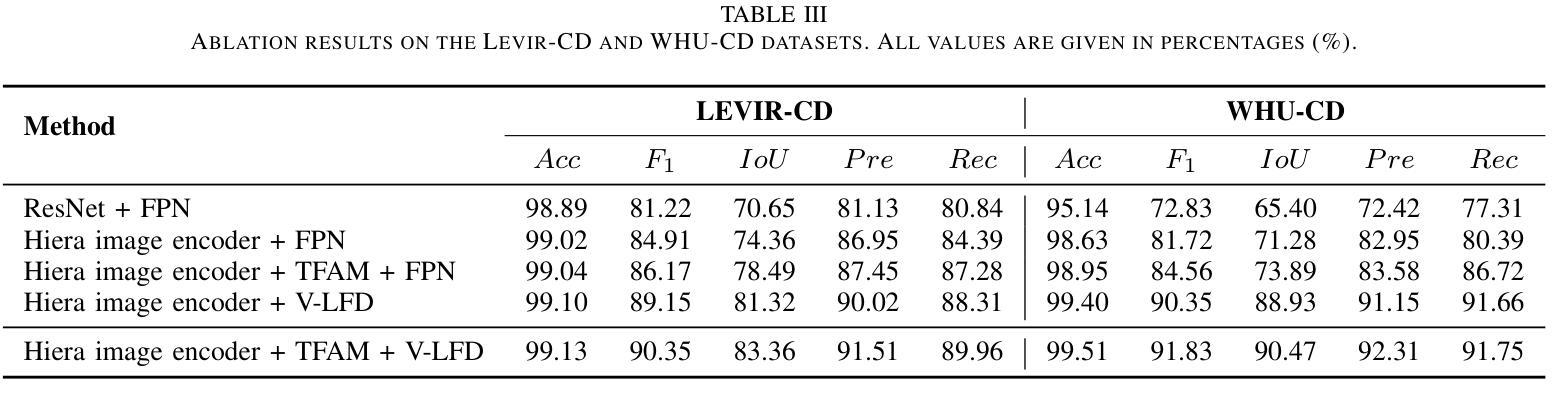
Remote Sensing Change Detection (RSCD) typically identifies changes in land cover or surface conditions by analyzing multi-temporal images. Currently, most deep learning-based methods primarily focus on learning unimodal visual information, while neglecting the rich semantic information provided by multimodal data such as text. To address this limitation, we propose a novel Language-Guided Change Detection model (LG-CD). This model leverages natural language prompts to direct the network’s attention to regions of interest, significantly improving the accuracy and robustness of change detection. Specifically, LG-CD utilizes a visual foundational model (SAM2) as a feature extractor to capture multi-scale pyramid features from high-resolution to low-resolution across bi-temporal remote sensing images. Subsequently, multi-layer adapters are employed to fine-tune the model for downstream tasks, ensuring its effectiveness in remote sensing change detection. Additionally, we design a Text Fusion Attention Module (TFAM) to align visual and textual information, enabling the model to focus on target change regions using text prompts. Finally, a Vision-Semantic Fusion Decoder (V-SFD) is implemented, which deeply integrates visual and semantic information through a cross-attention mechanism to produce highly accurate change detection masks. Our experiments on three datasets (LEVIR-CD, WHU-CD, and SYSU-CD) demonstrate that LG-CD consistently outperforms state-of-the-art change detection methods. Furthermore, our approach provides new insights into achieving generalized change detection by leveraging multimodal information.
遥感变化检测(RSCD)通常通过分析多时相图像来识别地表覆盖或地表条件的变化。目前,大多数基于深度学习的方法主要关注学习单模态视觉信息,而忽视由文本等多模态数据提供的丰富语义信息。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新颖的语言引导变化检测模型(LG-CD)。该模型利用自然语言提示来引导网络关注感兴趣区域,显著提高了变化检测的准确性和稳健性。具体来说,LG-CD利用视觉基础模型(SAM2)作为特征提取器,从高分辨率到低分辨率捕获双时态遥感图像的多尺度金字塔特征。随后,采用多层适配器对模型进行微调,以确保其在遥感变化检测中的有效性。此外,我们设计了一个文本融合注意力模块(TFAM),以对视觉和文本信息进行对齐,使模型能够使用文本提示关注目标变化区域。最后,实现了一个视觉语义融合解码器(V-SFD),它通过交叉注意力机制深入整合视觉和语义信息,生成高度准确的变化检测掩码。我们在LEVIR-CD、WHU-CD和SYSU-CD三个数据集上的实验表明,LG-CD始终优于最新的变化检测方法。此外,我们的方法通过利用多模态信息实现通用化变化检测,提供了新的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF *Corresponding authors: Min Zhu (min.zhu@scu.edu.cn) and Junlong Cheng (jlcheng@scu.edu.cn)
Summary
本文提出了一种新型的语言引导变化检测模型(LG-CD),该模型利用自然语言提示引导网络关注感兴趣区域,显著提高了变化检测的准确性和稳健性。LG-CD使用视觉基础模型(SAM2)提取多尺度金字塔特征,通过多层适配器进行微调,适用于遥感变化检测任务。设计文本融合注意力模块(TFAM)对齐视觉和文本信息,使模型能够利用文本提示关注目标变化区域。最后,实现了一个视觉语义融合解码器(V-SFD),通过跨注意力机制深度整合视觉和语义信息,生成高度准确的变化检测掩膜。在三个数据集上的实验表明,LG-CD始终优于最新的变化检测方法。
Key Takeaways
- LG-CD模型结合自然语言提示,提高遥感变化检测的准确性和稳健性。
- 使用视觉基础模型SAM2提取多尺度金字塔特征。
- 多层适配器用于微调模型,适应遥感变化检测任务。
- 文本融合注意力模块(TFAM)对齐视觉和文本信息。
- 视觉语义融合解码器(V-SFD)通过跨注意力机制整合信息。
- LG-CD在三个数据集上的实验表现优于现有变化检测方法。
点此查看论文截图

Degradation-Aware All-in-One Image Restoration via Latent Prior Encoding
Authors:S M A Sharif, Abdur Rehman, Fayaz Ali Dharejo, Radu Timofte, Rizwan Ali Naqvi
Real-world images often suffer from spatially diverse degradations such as haze, rain, snow, and low-light, significantly impacting visual quality and downstream vision tasks. Existing all-in-one restoration (AIR) approaches either depend on external text prompts or embed hand-crafted architectural priors (e.g., frequency heuristics); both impose discrete, brittle assumptions that weaken generalization to unseen or mixed degradations. To address this limitation, we propose to reframe AIR as learned latent prior inference, where degradation-aware representations are automatically inferred from the input without explicit task cues. Based on latent priors, we formulate AIR as a structured reasoning paradigm: (1) which features to route (adaptive feature selection), (2) where to restore (spatial localization), and (3) what to restore (degradation semantics). We design a lightweight decoding module that efficiently leverages these latent encoded cues for spatially-adaptive restoration. Extensive experiments across six common degradation tasks, five compound settings, and previously unseen degradations demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) approaches, achieving an average PSNR improvement of 1.68 dB while being three times more efficient.
现实世界中的图像经常受到空间多样的退化影响,如雾霾、雨水、雪和暗光,这些都会对图像质量和后续的视觉任务产生显著影响。现有的全能恢复(AIR)方法要么依赖于外部文本提示,要么嵌入手工设计的架构先验(如频率启发式);这两种方法都施加了离散、脆弱的假设,削弱了其对未见或混合退化的泛化能力。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出将AIR重新构建为学习潜在先验推断,其中退化感知表示自动从输入中推断出来,无需明确的任务提示。基于潜在先验,我们将AIR制定为结构化推理模式:(1)选择哪些特征进行路由(自适应特征选择)、(2)在哪里恢复(空间定位)和(3)恢复什么(退化语义)。我们设计了一个轻量级的解码模块,该模块能够高效利用这些潜在编码线索进行空间自适应恢复。在六个常见的退化任务、五个复合场景和之前未见的退化情况下进行的广泛实验表明,我们的方法优于当前最前沿的方法,平均峰值信噪比提高了1.68分贝,同时效率提高了三倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
空间多样退化如雾霾、雨水、雪和暗光等会对真实世界图像产生严重影响,现有的综合恢复方法存在缺陷。为此,我们提出一种基于潜在先验推断的方法,自动从输入中推断退化感知表示,并将其结构化为特征路由、恢复位置和退化语义三个方面的推理模式。设计了一种轻量级的解码模块,能高效利用这些潜在线索进行空间自适应恢复。实验表明,我们的方法在六个常见退化任务、五个复合设置和未知退化上均优于现有最佳方法,平均PSNR提高了1.68dB,且效率提高了三倍。
Key Takeaways
- 真实世界图像常常受到多种空间退化的影响,如雾霾、雨水、雪和暗光。
- 现有的综合恢复方法要么依赖外部文本提示,要么嵌入手工架构先验,这两种方法都存在局限性,难以推广到未见或混合退化。
- 我们提出一种基于潜在先验推断的方法,自动从输入中推断退化感知表示,无需明确的任务提示。
- 将恢复过程结构化为特征路由、恢复位置和退化语义三个方面的推理。
- 设计了一种轻量级的解码模块,利用潜在线索进行空间自适应恢复。
- 实验表明,我们的方法在多个退化任务、复合设置和未知退化上均优于现有最佳方法。
点此查看论文截图
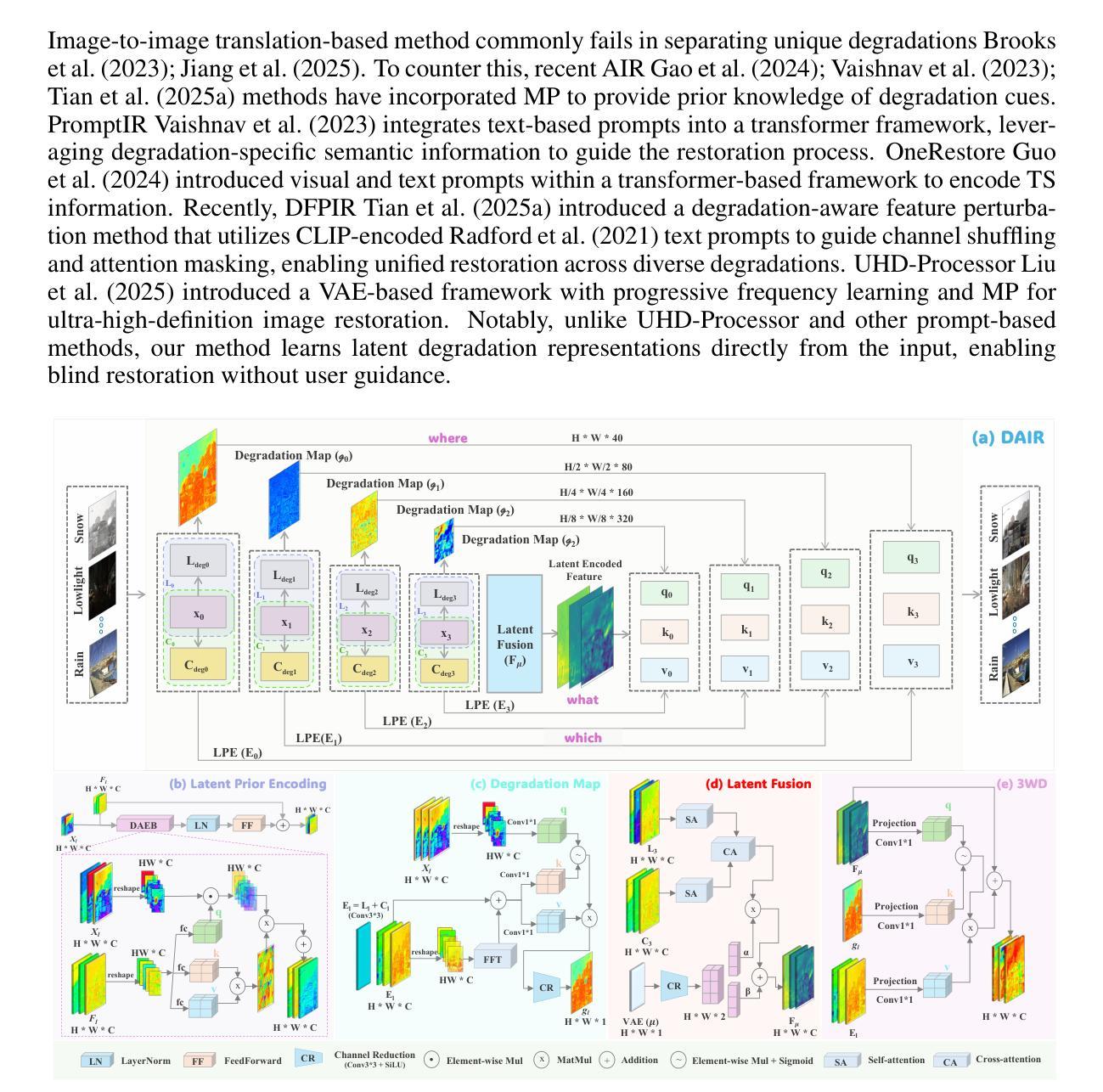
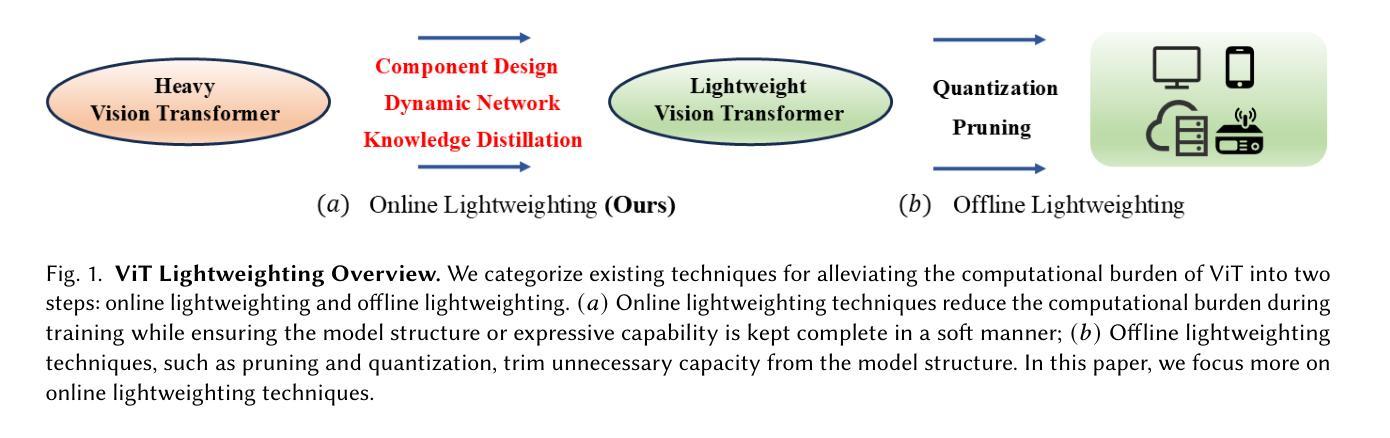
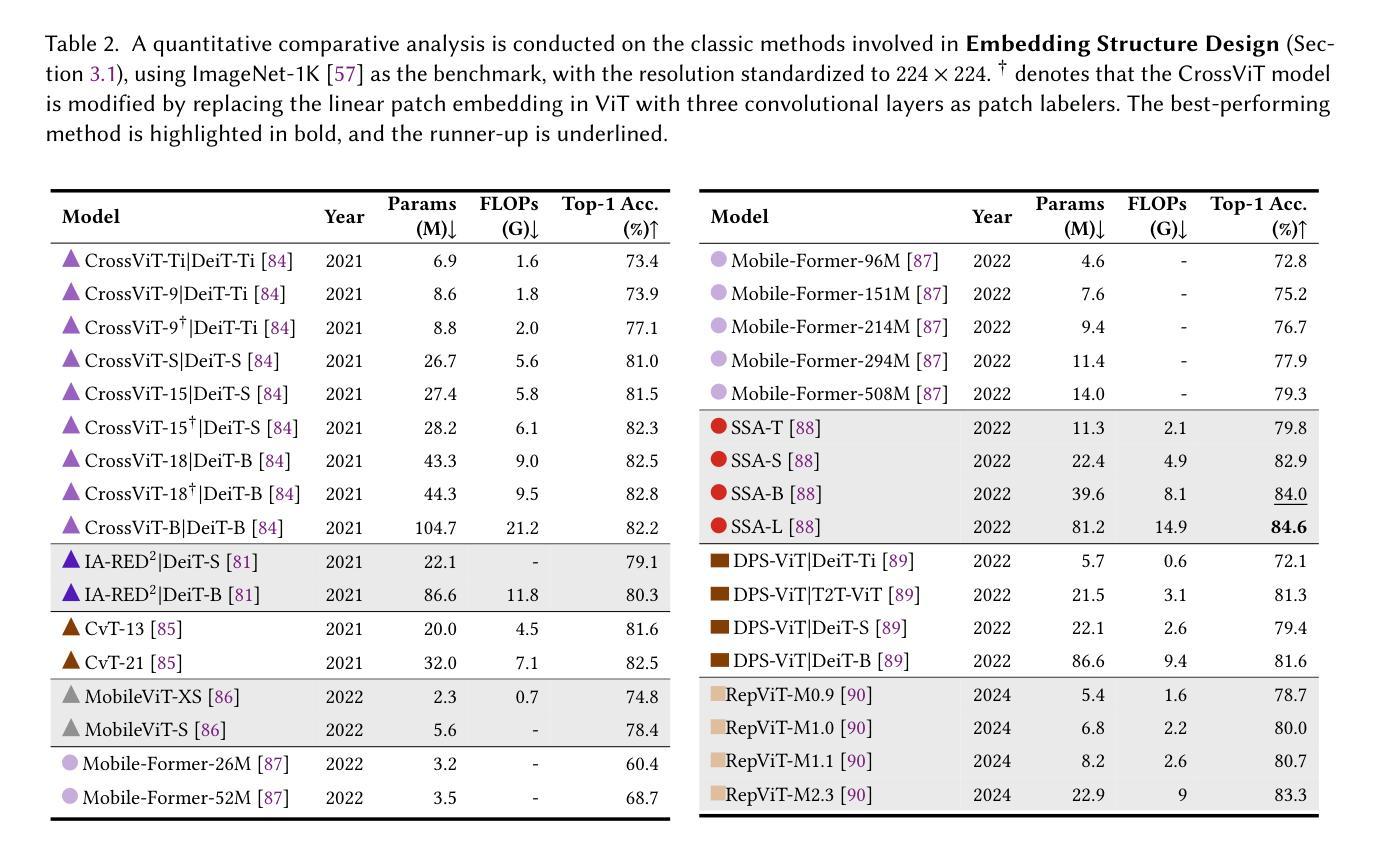
Image Recognition with Online Lightweight Vision Transformer: A Survey
Authors:Zherui Zhang, Rongtao Xu, Jie Zhou, Changwei Wang, Xingtian Pei, Wenhao Xu, Jiguang Zhang, Li Guo, Longxiang Gao, Wenbo Xu, Shibiao Xu
The Transformer architecture has achieved significant success in natural language processing, motivating its adaptation to computer vision tasks. Unlike convolutional neural networks, vision transformers inherently capture long-range dependencies and enable parallel processing, yet lack inductive biases and efficiency benefits, facing significant computational and memory challenges that limit its real-world applicability. This paper surveys various online strategies for generating lightweight vision transformers for image recognition, focusing on three key areas: Efficient Component Design, Dynamic Network, and Knowledge Distillation. We evaluate the relevant exploration for each topic on the ImageNet-1K benchmark, analyzing trade-offs among precision, parameters, throughput, and more to highlight their respective advantages, disadvantages, and flexibility. Finally, we propose future research directions and potential challenges in the lightweighting of vision transformers with the aim of inspiring further exploration and providing practical guidance for the community. Project Page: https://github.com/ajxklo/Lightweight-VIT
Transformer架构在自然语言处理领域取得了巨大成功,这促使其适应计算机视觉任务。与卷积神经网络不同,视觉Transformer天生就能捕捉长距离依赖关系并实现并行处理,然而由于缺乏归纳偏见和效率优势,它们面临着计算和内存方面的挑战,这些挑战限制了其在现实世界中的应用。本文调查了在线生成轻量级视觉Transformer进行图像识别的各种策略,重点关注三个关键领域:高效组件设计、动态网络和知识蒸馏。我们在ImageNet-1K基准测试上评估了每个主题的相关探索,分析了精度、参数、吞吐量等之间的权衡,以突出各自的优势、劣势和灵活性。最后,我们提出了轻量级视觉Transformer的未来研究方向和潜在挑战,旨在激发进一步的探索并为社区提供实践指导。项目页面:https://github.com/ajxklo/Lightweight-VIT
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了将Transformer架构应用于计算机视觉任务的策略,介绍了针对图像识别的轻量化视觉变压器的研究。文章重点介绍了三个关键领域:高效组件设计、动态网络和知识蒸馏。在ImageNet-1K基准测试上评估了相关探索,分析了精度、参数、吞吐量和灵活性之间的权衡,并指出了各自的优缺点。最后,本文提出了对轻量化视觉变压器的未来研究方向和潜在挑战,旨在为社区提供实际指导。
Key Takeaways
- Transformer架构在计算机视觉任务中的应用受到关注。
- 轻量化视觉变压器的研究涉及高效组件设计、动态网络和知识蒸馏等方面。
- ImageNet-1K基准测试被用于评估相关探索。
- 精确性、参数、吞吐量和灵活性之间的权衡是研究的重点。
- 现有的轻量化视觉变压器策略有其优点和局限性。
- 文中指出了未来研究方向和潜在挑战。
点此查看论文截图
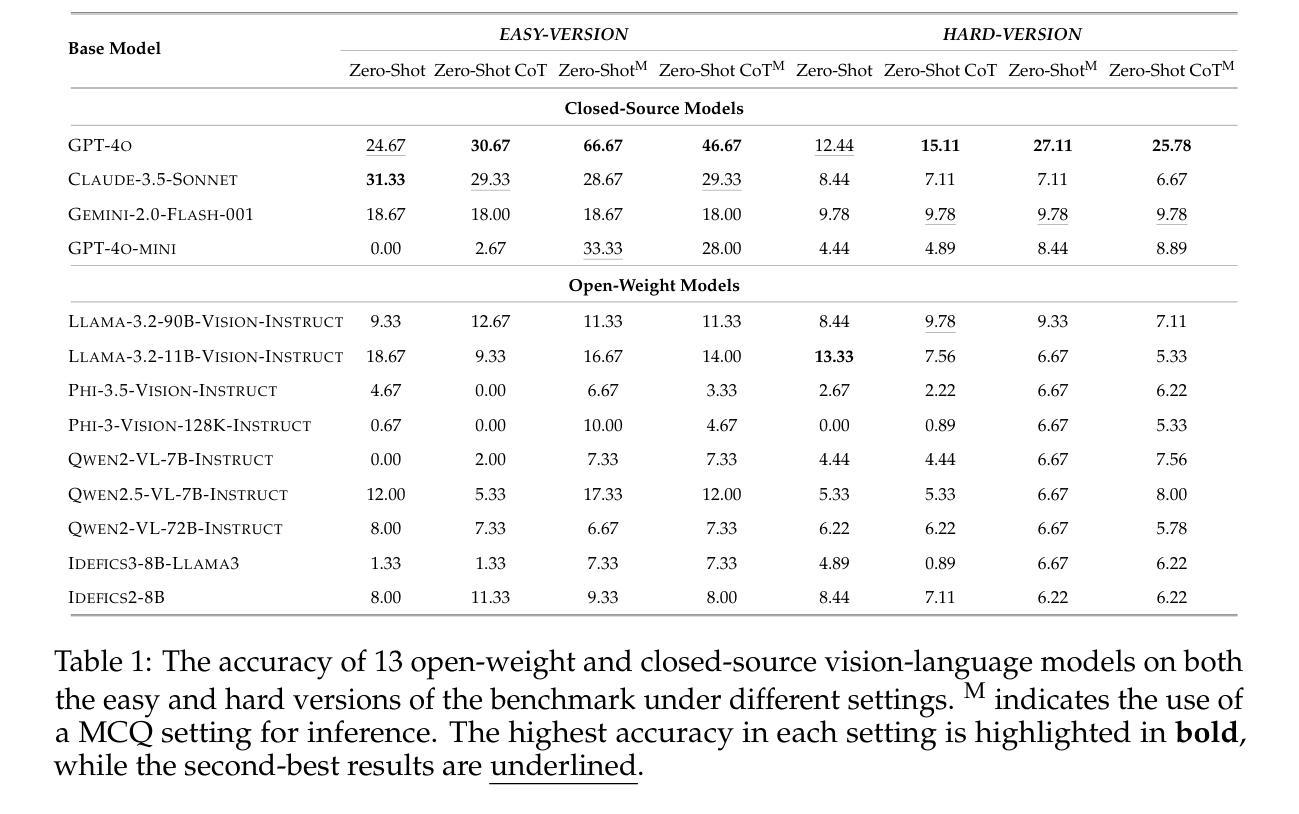
Texture or Semantics? Vision-Language Models Get Lost in Font Recognition
Authors:Zhecheng Li, Guoxian Song, Yujun Cai, Zhen Xiong, Junsong Yuan, Yiwei Wang
Modern Vision-Language Models (VLMs) exhibit remarkable visual and linguistic capabilities, achieving impressive performance in various tasks such as image recognition and object localization. However, their effectiveness in fine-grained tasks remains an open question. In everyday scenarios, individuals encountering design materials, such as magazines, typography tutorials, research papers, or branding content, may wish to identify aesthetically pleasing fonts used in the text. Given their multimodal capabilities and free accessibility, many VLMs are often considered potential tools for font recognition. This raises a fundamental question: Do VLMs truly possess the capability to recognize fonts? To investigate this, we introduce the Font Recognition Benchmark (FRB), a compact and well-structured dataset comprising 15 commonly used fonts. FRB includes two versions: (i) an easy version, where 10 sentences are rendered in different fonts, and (ii) a hard version, where each text sample consists of the names of the 15 fonts themselves, introducing a stroop effect that challenges model perception. Through extensive evaluation of various VLMs on font recognition tasks, we arrive at the following key findings: (i) Current VLMs exhibit limited font recognition capabilities, with many state-of-the-art models failing to achieve satisfactory performance and being easily affected by the stroop effect introduced by textual information. (ii) Few-shot learning and Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting provide minimal benefits in improving font recognition accuracy across different VLMs. (iii) Attention analysis sheds light on the inherent limitations of VLMs in capturing semantic features.
现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)展现出令人印象深刻的视觉和语言能力,在各种任务(如图像识别和对象定位)中取得了令人瞩目的性能。然而,它们在精细粒度任务中的有效性仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。在日常场景中,个人在遇到设计材料(如杂志、排版教程、研究论文或品牌内容)时,可能希望识别文本中视觉上令人愉悦的字体。考虑到它们的多模式能力和免费可访问性,许多VLMs通常被认为是字体识别的潜在工具。这引发了一个基本问题:VLMs真的具备识别字体的能力吗?为了调查这一点,我们引入了字体识别基准测试(FRB),这是一个包含15种常用字体的紧凑且结构良好的数据集。FRB包括两个版本:(i)简单版本,其中10句话呈现在不同的字体中,(ii)困难版本,其中每个文本样本由15种字体的名称本身组成,引入一种斯特鲁普效应,挑战模型的感知能力。通过对各种VLM在字体识别任务上的广泛评估,我们得出以下关键发现:(i)当前VLM在字体识别方面的能力有限,许多最先进的模型无法达到令人满意的性能,并且容易受到由文本信息引入的斯特鲁普效应的影响。(ii)在VLMs中,少样本学习和链式思维(CoT)提示在改进字体识别准确性方面提供的帮助微乎其微。(iii)注意力分析揭示了VLM在捕获语义特征方面的内在局限性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to COLM 2025
摘要
现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)在图像识别、物体定位等方面表现出强大的视觉和语言能力,但在精细任务上的效果仍有待探讨。针对设计材料中的字体识别问题,我们引入字体识别基准测试(FRB),包含两个版本:简单版与困难版。评估多个VLMs在字体识别任务上的表现,发现当前VLMs的字体识别能力有限,易受到文本信息的干扰;少样本学习与Chain-of-Thought(CoT)提示对提升字体识别准确率的帮助有限;注意力分析揭示了VLMs在捕捉语义特征上的内在局限。
关键见解
- 现代视觉语言模型(VLMs)在字体识别任务上的表现有限,难以满足高要求。
- 现有顶级VLMs容易受到文本信息的干扰,难以准确识别字体。
- 少样本学习与Chain-of-Thought(CoT)提示对改善VLMs在字体识别任务上的性能帮助不大。
- 注意力分析显示,VLMs在捕捉语义特征方面存在内在局限。
- 引入的字体识别基准测试(FRB)为评估VLMs在字体识别任务上的性能提供了有效工具。
- 简单版与困难版的FRB数据集设计巧妙,可有效测试模型在面临不同难度挑战时的表现。
点此查看论文截图