⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-01 更新
A Scalable Distributed Framework for Multimodal GigaVoxel Image Registration
Authors:Rohit Jena, Vedant Zope, Pratik Chaudhari, James C. Gee
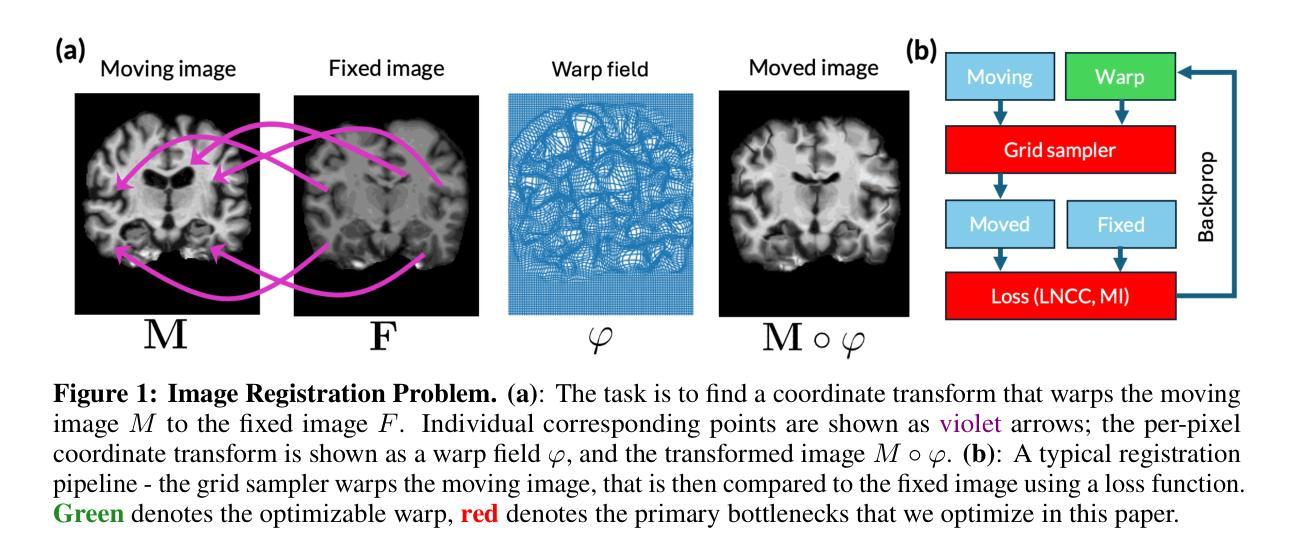
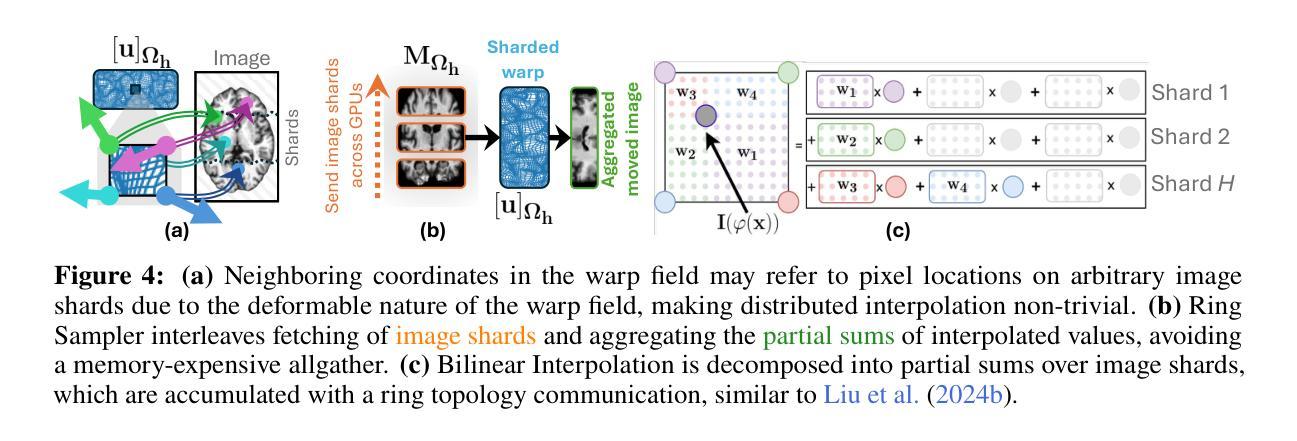
In this work, we propose FFDP, a set of IO-aware non-GEMM fused kernels supplemented with a distributed framework for image registration at unprecedented scales. Image registration is an inverse problem fundamental to biomedical and life sciences, but algorithms have not scaled in tandem with image acquisition capabilities. Our framework complements existing model parallelism techniques proposed for large-scale transformer training by optimizing non-GEMM bottlenecks and enabling convolution-aware tensor sharding. We demonstrate unprecedented capabilities by performing multimodal registration of a 100 micron ex-vivo human brain MRI volume at native resolution - an inverse problem more than 570x larger than a standard clinical datum in about a minute using only 8 A6000 GPUs. FFDP accelerates existing state-of-the-art optimization and deep learning registration pipelines by upto 6 - 7x while reducing peak memory consumption by 20 - 59%. Comparative analysis on a 250 micron dataset shows that FFDP can fit upto 64x larger problems than existing SOTA on a single GPU, and highlights both the performance and efficiency gains of FFDP compared to SOTA image registration methods.
在这项工作中,我们提出了FFDP,这是一组IO感知的非GEMM融合内核,辅以分布式框架,用于前所未有的大规模图像配准。图像配准是生物医学和生命科学中的基本逆向问题,但算法的扩展并没有与图像采集能力同步。我们的框架通过优化非GEMM瓶颈并启用卷积感知的张量分片,补充了针对大规模变换器训练提出的现有模型并行技术。我们通过以原生分辨率对离体人脑MRI体积进行100微米的多模态配准,展示了前所未有的能力——这是一个逆向问题,在大约一分钟内使用仅8个A6000 GPU解决了超过标准临床数据570倍的问题。FFDP通过高达6-7倍的速度,加速了现有的最先进的优化和深度学习配准管道,同时降低了峰值内存消耗20-59%。在250微米数据集上的对比分析显示,FFDP可以在单个GPU上适应比现有最先进技术高64倍的问题,并突出了FFDP相较于现有图像配准方法的性能和效率优势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出FFDP,一套面向IO的非GEMM融合内核,配合分布式框架,用于大规模图像注册。文章强调图像注册是生物医学和生命科学中的基本逆问题,但算法尚未与图像采集能力同步扩展。FFDP通过优化非GEMM瓶颈并实现卷积感知的张量分片,补充了现有针对大规模变换器训练提出的模型并行技术。在仅使用8个A6000 GPU的情况下,对分辨率为100微米的人体离体脑MRI体积进行多模式注册,不到一分钟就解决了比标准临床数据大570倍的逆问题。FFDP将现有最先进的优化和深度学习注册管道加速6-7倍,同时降低峰值内存消耗20-59%。对比分析显示,FFDP在单GPU上能解决的问题数量是现有最佳解决方案的64倍,并突出了FFDP相较于其他图像注册方法的性能和效率优势。
Key Takeaways
- FFDP是一套用于大规模图像注册的IO-aware非GEMM融合内核和分布式框架。
- 图像注册是生物医学和生命科学中的基本逆问题,但现有算法尚未与图像采集能力同步扩展。
- FFDP通过优化非GEMM瓶颈和卷积感知的张量分片技术,补充了模型并行技术。
- FFDP能在短时间内处理大规模图像注册问题,如处理分辨率为100微米的人体离体脑MRI体积。
- FFDP能显著提高现有注册方法的效率和性能,加速现有最先进的优化和深度学习注册管道6-7倍。
- FFDP降低了峰值内存消耗,减少了计算资源的需求。
点此查看论文截图
Stellar flare detection in XMM-Newton with gradient boosted trees
Authors:Mario Pasquato, Martino Marelli, Andrea De Luca, Ruben Salvaterra, Gaia Carenini, Andrea Belfiore, Andrea Tiengo, Paolo Esposito
The EXTraS project, based on data collected with the XMM-Newton observatory, provided us with a vast amount of light curves for X-ray sources. For each light curve, EXTraS also provided us with a set of features (https://extras.inaf.it). We extract from the EXTraS database a tabular dataset of 31,832 variable sources by 108 features. Of these, 13,851 sources were manually labeled as stellar flares or non-flares based on direct visual inspection. We employ a supervised learning approach to produce a catalog of stellar flares based on our dataset, releasing it to the community. We leverage explainable AI tools and interpretable features to better understand our classifier. We train a gradient boosting classifier on 80% of the data for which labels are available. We compute permutation feature importance scores, visualize feature space using UMAP, and analyze some false positive and false negative data points with the help of Shapley additive explanations – an AI explainability technique used to measure the importance of each feature in determining the classifier’s prediction for each instance. On the test set made up of the remainder 20% of our labeled data, we obtain an accuracy of 97.1%, with a precision of 82.4% and a recall of 73.3%. Our classifier outperforms a simple criterion based on fitting the light curve with a flare template and significantly surpasses a gradient-boosted classifier trained only on model-independent features. False positives appear related to flaring light curves that are not associated with a stellar counterpart, while false negatives often correspond to multiple flares or otherwise peculiar or noisy curves. We apply our trained classifier to currently unlabeled sources, releasing the largest catalog of X-ray stellar flares to date. [abridged]
基于XMM-牛顿天文台收集的数据,EXTraS项目为我们提供了大量的X射线光源光变曲线。对于每条光变曲线,EXTraS还为我们提供了一系列特征(https://extras.inaf.it)。我们从EXTraS数据库中提取了一个包含31,832个可变源和108个特征的表格数据集。其中,有13,851个源是根据直接视觉检测手动标记为恒星耀斑或非耀斑。我们采用监督学习方法,基于数据集生成恒星耀斑目录,并向社区发布。我们利用可解释的AI工具和可解释的特征来更好地理解我们的分类器。我们对可用标签数据的80%进行梯度提升分类器的训练。我们计算了特征置换重要性得分,使用UMAP可视化特征空间,并使用Shapley加法解释这一人工智能解释性技术分析了某些误报和漏报数据点,该技术用于衡量每个特征在确定分类器对每个实例的预测中的重要性。在由剩余20%标记数据组成的测试集上,我们获得了97.1%的准确率,精确度达到82.4%,召回率为73.3%。我们的分类器表现优于基于耀斑模板拟合光变曲线的简单标准,并且明显优于仅使用模型独立特征训练的梯度提升分类器。误报似乎与不与恒星对应的耀斑光变曲线有关,而漏报通常对应于多次耀斑发作或特殊或嘈杂的曲线。我们将训练好的分类器应用于当前未标记的源,发布了迄今为止最大的X射线恒星耀斑目录。[摘要]
【中文解释】(此处仅作参考,请酌情调整表达细节)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 14 figures, Accepted for publication by A&A
Summary
基于XMM-Newton天文台的数据,EXTraS项目为X射线源提供了大量的光变曲线。该项目提取了包含特征在内的数据表,包括标记为恒星耀斑或非耀斑的数据。通过监督学习方法生成恒星耀斑目录,并利用可解释的AI工具更好地理解分类器。训练梯度提升分类器后,其准确率达到了惊人的水平。该项目将已训练的分类器应用于当前未标记的源,发布了迄今为止最大的X射线恒星耀斑目录。简而言之,这是一个利用机器学习分类器基于X射线源光变曲线进行恒星耀斑识别和分类的项目。
Key Takeaways
- EXTraS项目基于XMM-Newton天文台数据提供了大量X射线源的光变曲线。
- 该项目通过特征集提取了数据表,包括手动标记为恒星耀斑或非耀斑的数据。
- 采用监督学习方法生成恒星耀斑目录,并利用可解释的AI工具进行特征分析以提高分类器性能。
- 通过训练梯度提升分类器并对其进行测试,实现了高达97.1%的准确率、82.4%的精度和73.3%的召回率。这一性能优于其他两种方法:单纯使用光变曲线匹配耀斑模板的简单准则和仅使用模型独立特征的梯度提升分类器。
- 分析了误报情况,发现假阳性通常与未与恒星对应的耀斑光变曲线有关,而假阴性则经常与多重耀斑或其他异常或噪声曲线有关。
点此查看论文截图

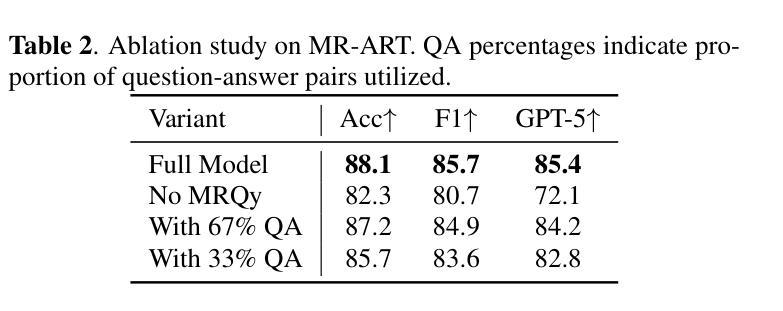
MMRQA: Signal-Enhanced Multimodal Large Language Models for MRI Quality Assessment
Authors:Fankai Jia, Daisong Gan, Zhe Zhang, Zhaochi Wen, Chenchen Dan, Dong Liang, Haifeng Wang
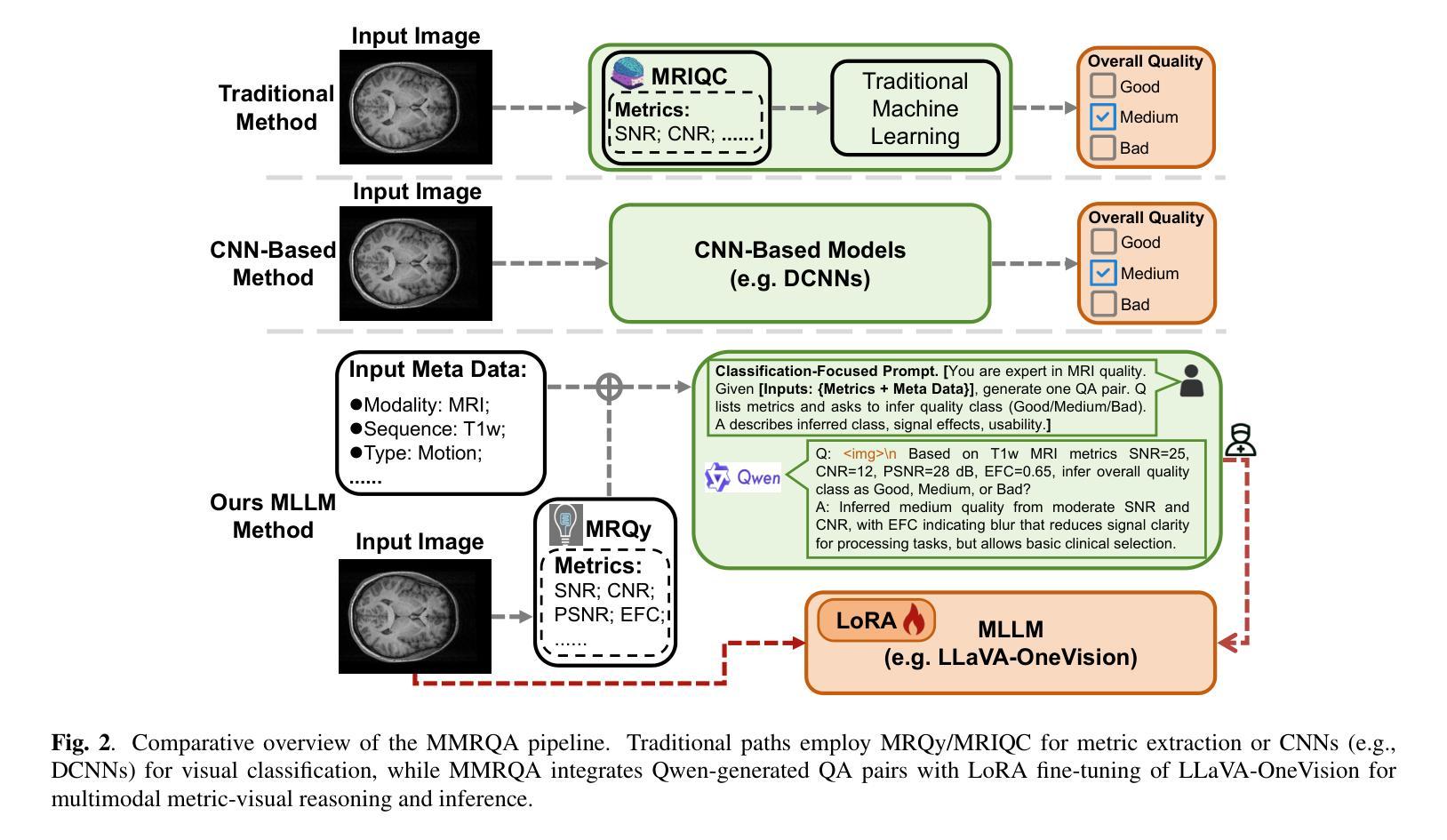
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) quality assessment is crucial for clinical decision-making, yet remains challenging due to data scarcity and protocol variability. Traditional approaches face fundamental trade-offs: signal-based methods like MRIQC provide quantitative metrics but lack semantic understanding, while deep learning approaches achieve high accuracy but sacrifice interpretability. To address these limitations, we introduce the Multimodal MRI Quality Assessment (MMRQA) framework, pioneering the integration of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) with acquisition-aware signal processing. MMRQA combines three key innovations: robust metric extraction via MRQy augmented with simulated artifacts, structured transformation of metrics into question-answer pairs using Qwen, and parameter-efficient fusion through Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) of LLaVA-OneVision. Evaluated on MR-ART, FastMRI, and MyConnectome benchmarks, MMRQA achieves state-of-the-art performance with strong zero-shot generalization, as validated by comprehensive ablation studies. By bridging quantitative analysis with semantic reasoning, our framework generates clinically interpretable outputs that enhance quality control in dynamic medical settings.
磁共振成像(MRI)质量评估对于临床决策至关重要,但由于数据稀缺和协议差异,仍面临挑战。传统方法面临基本权衡:MRIQC等基于信号的方法提供定量指标,但缺乏语义理解,而深度学习方法虽然准确度高,但牺牲了可解释性。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了多模式MRI质量评估(MMRQA)框架,率先将多模式大型语言模型(MLLMs)与采集感知信号处理相结合。MMRQA结合了三大关键创新:通过MRQy辅以模拟伪影进行稳健指标提取、使用Qwen将指标转换为问答对进行结构化转换,以及通过LoRA对LLaVA-OneVision进行参数有效融合。在MR-ART、FastMRI和MyConnectome基准测试上评估,MMRQA实现了最先进的性能,具有强大的零样本泛化能力,这已通过全面的消融研究得到验证。通过定量分析与语义推理之间的桥梁,我们的框架生成了可临床解释的输出结果,提高了动态医疗环境中的质量控制。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了磁共振成像(MRI)质量评估的重要性及其在临床决策中的挑战。针对传统方法的局限性,如缺乏语义理解和高准确性但牺牲了解释性,本文提出了多模态MRI质量评估(MMRQA)框架,率先将多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)与采集感知信号处理相结合。MMRQA结合了三项关键创新:通过MRQy增强模拟伪影进行稳健指标提取,使用Qwen将指标转换为问答对进行结构化转换,以及通过LoRA进行LLaVA-OneVision的参数高效融合。在MR-ART、FastMRI和MyConnectome基准测试上评估,MMRQA达到了最新技术水平,具有强大的零样本泛化能力,并通过综合消融研究得到验证。通过定量分析与语义推理的结合,该框架生成了临床可解释的输出,提高了动态医学环境中的质量控制。
Key Takeaways
- MRI质量评估在临床决策中至关重要,但面临数据稀缺和协议可变性的挑战。
- 传统方法存在局限性:基于信号的方法缺乏语义理解,而深度学习方法虽然准确但牺牲了解释性。
- 引入MMRQA框架,结合多模态大型语言模型与采集感知信号处理。
- MMRQA框架包括三项关键创新:MRQy模拟伪影的稳健指标提取、Qwen的结构化指标转换和LLaVA-OneVision的LoRA参数高效融合。
- 在多个基准测试上表现优异,具备强大的零样本泛化能力。
- MMRQA框架结合了定量分析与语义推理,生成临床可解释的输出。
点此查看论文截图
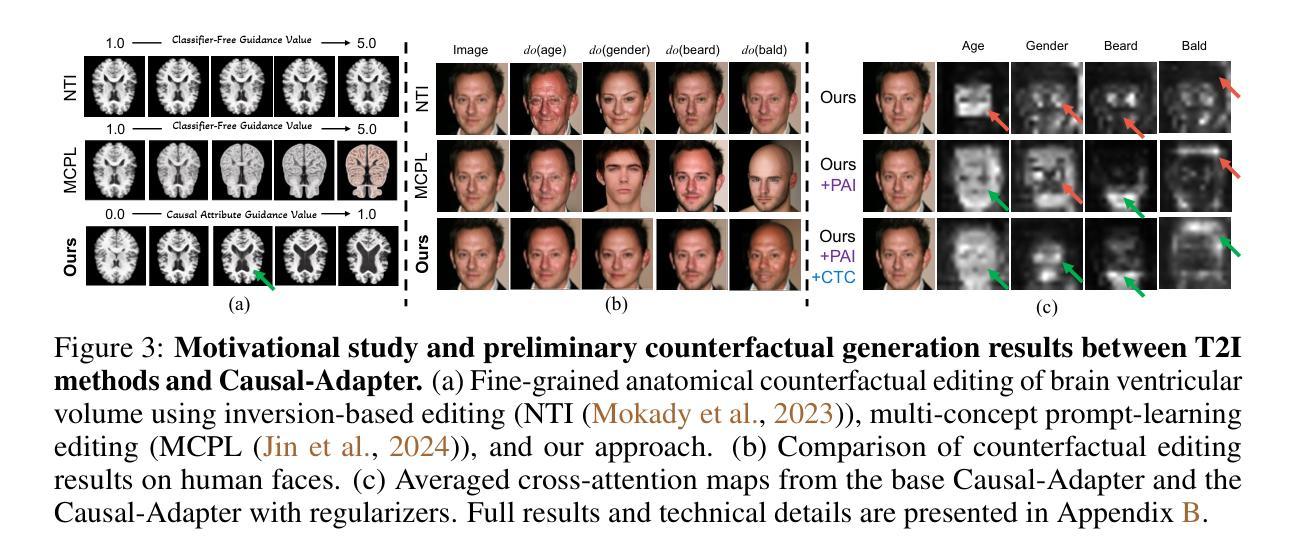
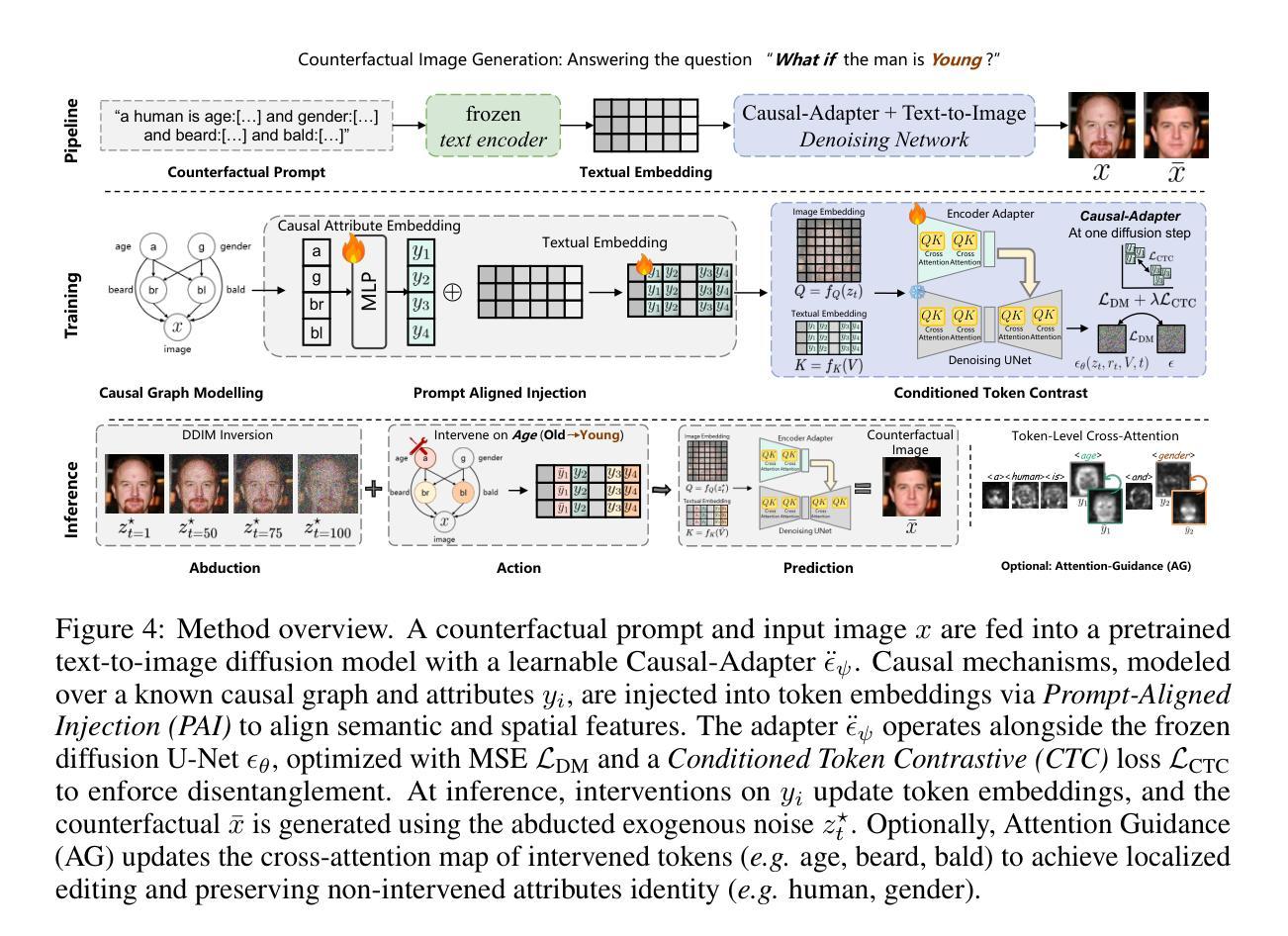
Causal-Adapter: Taming Text-to-Image Diffusion for Faithful Counterfactual Generation
Authors:Lei Tong, Zhihua Liu, Chaochao Lu, Dino Oglic, Tom Diethe, Philip Teare, Sotirios A. Tsaftaris, Chen Jin
We present Causal-Adapter, a modular framework that adapts frozen text-to-image diffusion backbones for counterfactual image generation. Our method enables causal interventions on target attributes, consistently propagating their effects to causal dependents without altering the core identity of the image. In contrast to prior approaches that rely on prompt engineering without explicit causal structure, Causal-Adapter leverages structural causal modeling augmented with two attribute regularization strategies: prompt-aligned injection, which aligns causal attributes with textual embeddings for precise semantic control, and a conditioned token contrastive loss to disentangle attribute factors and reduce spurious correlations. Causal-Adapter achieves state-of-the-art performance on both synthetic and real-world datasets, with up to 91% MAE reduction on Pendulum for accurate attribute control and 87% FID reduction on ADNI for high-fidelity MRI image generation. These results show that our approach enables robust, generalizable counterfactual editing with faithful attribute modification and strong identity preservation.
我们提出了因果适配器(Causal-Adapter)这一模块化框架,该框架能够针对文本到图像的扩散模型进行适配,用于生成反事实图像。我们的方法能够在目标属性上实施因果干预,并始终如一地将它们的效果传播到因果依赖关系上,同时不改变图像的核心身份。与之前依赖于提示工程但没有明确因果结构的方法不同,因果适配器利用结构因果模型并辅以两种属性正则化策略:提示对齐注入能够通过对齐因果属性与文本嵌入来进行精确语义控制,而条件标记对比损失有助于消除属性因素并减少误导关联。因果适配器在合成数据集和现实世界数据集上都实现了最先进的性能表现,在摆锤(Pendulum)上的平均绝对误差减少了高达91%,可实现准确的属性控制,而在ADNI上的弗雷歇特-贝雷蒂尼指数(FID)减少了高达87%,可实现高保真MRI图像生成。这些结果表明,我们的方法能够实现稳健、通用的反事实编辑,具有忠实的属性修改和强大的身份保留能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 26 figures
Summary
Causal-Adapter是一个模块化框架,用于适应冷冻文本到图像的扩散主干以进行反事实图像生成。此方法可实现目标属性的因果干预,并将这些效果一致地传播到因果依赖项中,而不改变图像的核心身份。通过利用结构因果建模并结合两种属性正则化策略,Causal-Adapter能够超越以往依赖提示工程而没有明确因果结构的方法。该方法通过对齐因果属性与文本嵌入来实现精确语义控制,并使用条件令牌对比损失来分离属性因素并减少偶然相关性。在合成和真实数据集上,Causal-Adapter均达到了卓越的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- Causal-Adapter是一个用于反事实图像生成的模块化框架,适应文本到图像的扩散模型。
- 它能够实现目标属性的因果干预,并传播这些效果而不改变图像的核心身份。
- 通过结构因果建模和两种属性正则化策略(提示对齐注入和条件令牌对比损失)提高性能。
- 提示对齐注入策略对齐因果属性与文本嵌入,实现精确语义控制。
- 条件令牌对比损失用于分离属性因素,减少偶然相关性。
- 在合成和真实数据集上,Causal-Adapter均取得了卓越的性能,包括在Pendulum上的MAE减少91%,在ADNI上的FID减少87%。
点此查看论文截图
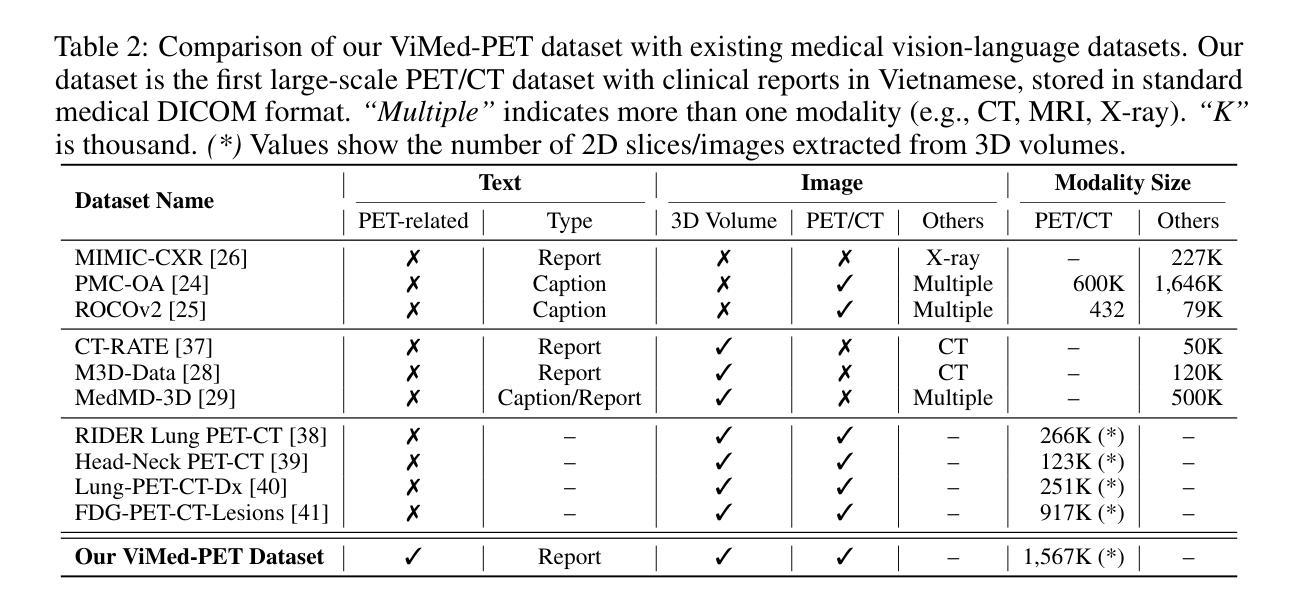
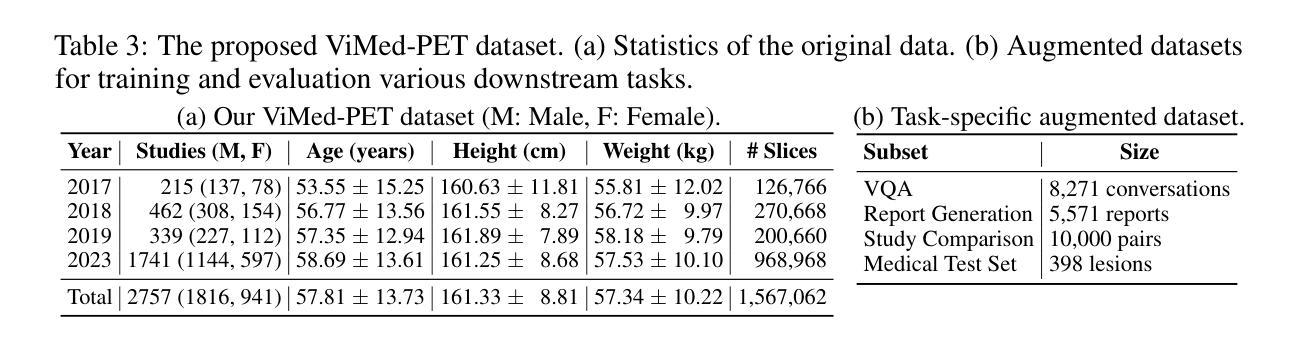
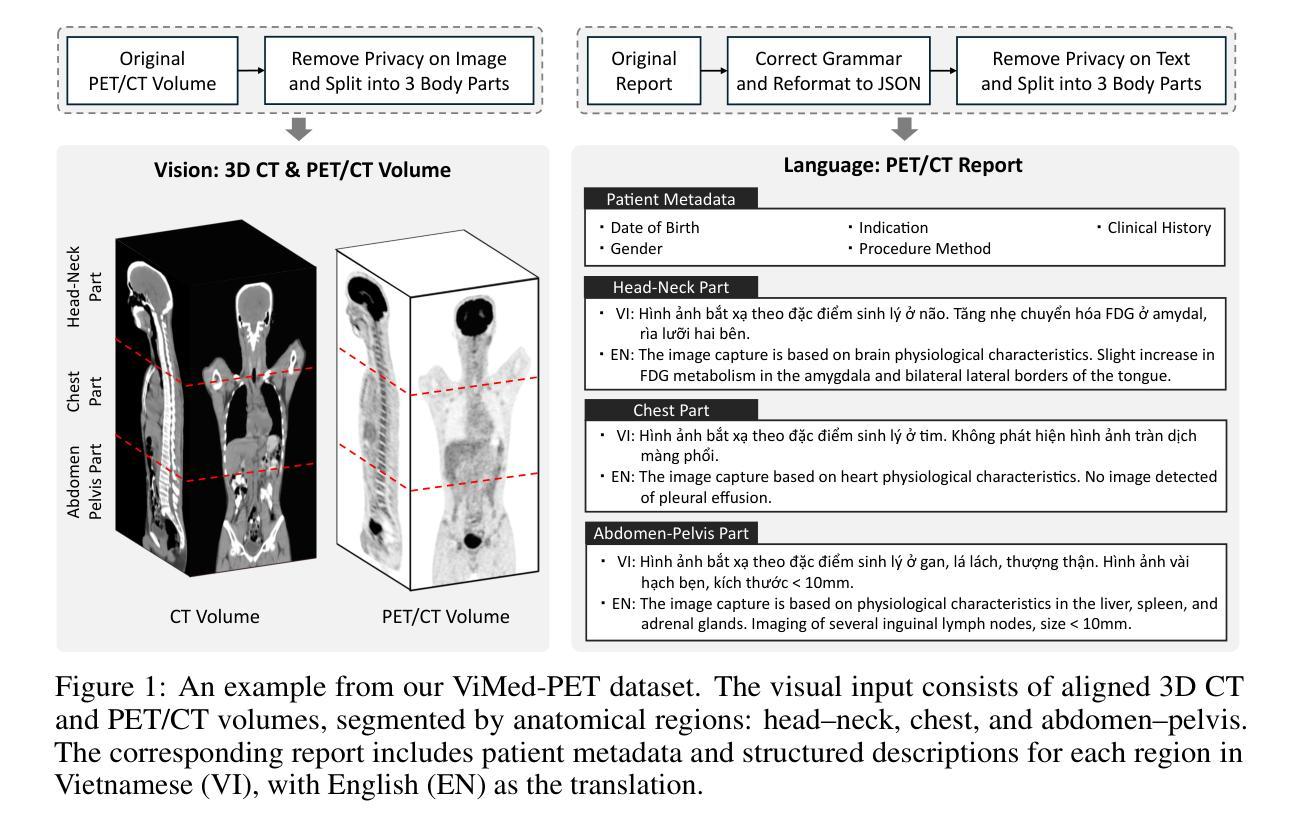
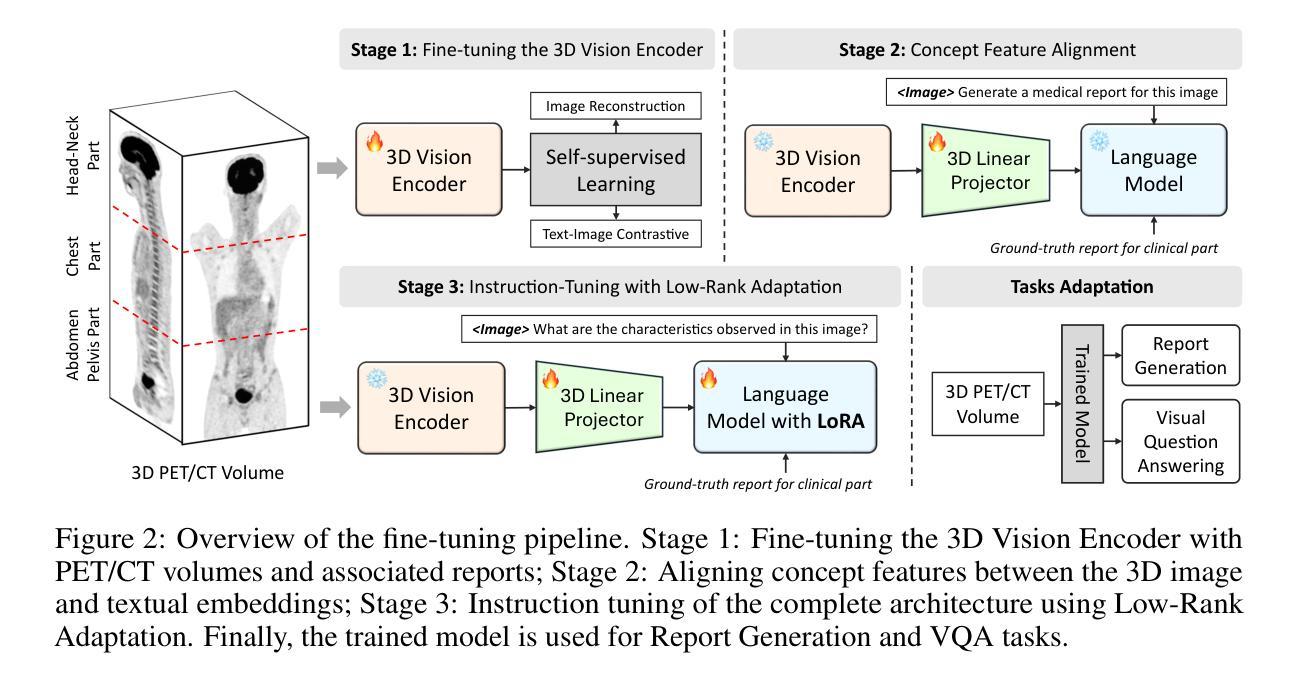
Toward a Vision-Language Foundation Model for Medical Data: Multimodal Dataset and Benchmarks for Vietnamese PET/CT Report Generation
Authors:Huu Tien Nguyen, Dac Thai Nguyen, The Minh Duc Nguyen, Trung Thanh Nguyen, Thao Nguyen Truong, Huy Hieu Pham, Johan Barthelemy, Minh Quan Tran, Thanh Tam Nguyen, Quoc Viet Hung Nguyen, Quynh Anh Chau, Hong Son Mai, Thanh Trung Nguyen, Phi Le Nguyen
Vision-Language Foundation Models (VLMs), trained on large-scale multimodal datasets, have driven significant advances in Artificial Intelligence by enabling rich cross-modal reasoning. Despite their success in general domains, applying these models to medical imaging remains challenging due to the limited availability of diverse imaging modalities and multilingual clinical data. Most existing medical VLMs are trained on a subset of imaging modalities and focus primarily on high-resource languages, thus limiting their generalizability and clinical utility. To address these limitations, we introduce a novel Vietnamese-language multimodal medical dataset comprising 1,567,062 paired CT-PET images and corresponding 2,757 full-length clinical reports. This dataset is designed to fill two pressing gaps in medical AI development: (1) the lack of PET/CT imaging data in existing VLMs training corpora, which hinders the development of models capable of handling functional imaging tasks; and (2) the underrepresentation of low-resource languages, particularly the Vietnamese language, in medical vision-language research. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first dataset to provide comprehensive PET/CT-report pairs in Vietnamese. We further introduce a training framework to enhance VLMs’ learning, including data augmentation and expert-validated test sets. We conduct comprehensive experiments benchmarking state-of-the-art VLMs on downstream tasks, including medical report generation and visual question answering. The experimental results show that incorporating our dataset significantly improves the performance of existing VLMs. We believe this dataset and benchmark will serve as a pivotal step in advancing the development of more robust VLMs for medical imaging, particularly in low-resource languages, and improving their clinical relevance in Vietnamese healthcare.
视觉语言基础模型(VLMs)通过大规模多模态数据集进行训练,实现了丰富的跨模态推理,为人工智能带来了重大进展。尽管它们在一般领域取得了成功,但将这些模型应用于医学影像仍存在挑战,这主要是由于缺乏多样化的成像模式和多种语言的临床数据。现有的大多数医学VLMs仅在一部分成像模式上进行训练,并主要关注资源丰富型语言,从而限制了其通用性和临床实用性。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了一个新的越南语多模态医学数据集,包含1,567,062对CT-PET图像和相应的2,757篇全文临床报告。该数据集旨在填补医学人工智能发展中的两个紧迫空白:(1)现有VLMs训练语料库中缺乏PET/CT成像数据,这阻碍了能够处理功能性成像任务的模型的发展;(2)低资源语言,特别是越南语,在医学视觉语言研究中的代表性不足。据我们所知,这是第一个提供越南语中全面的PET/CT报告对数据集。我们还介绍了一个增强VLMs学习的训练框架,包括数据增强和专家验证的测试集。我们进行了全面的实验,对最先进的VLMs进行下游任务评估,包括医学报告生成和视觉问答。实验结果表明,使用我们的数据集可以显着提高现有VLMs的性能。我们相信,该数据集和基准测试将在推动更稳健的VLMs用于医学影像的发展方面发挥关键作用,特别是在低资源语言领域,并提升越南语医疗保健中的临床相关性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 39th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2025)
Summary
本研究介绍了针对医学影像领域的越南语多模态医疗数据集,解决了现有VLM模型在功能成像任务和低资源语言方面的局限性。数据集包含1,567,062张配对的CT-PET图像和相应的2,757份完整临床报告,为越南语医疗视觉语言研究提供了重要资源。引入训练框架提升VLM模型学习,包括数据增强和专家验证测试集。实验表明,使用该数据集能显著提升现有VLM模型在医疗影像领域的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 引入越南语多模态医疗数据集,包含大量CT-PET图像和临床报告,解决医疗AI发展中的数据缺口问题。
- 数据集填补现有VLM模型中PET/CT成像数据的空白,提升模型处理功能成像任务的能力。
- 数据集关注低资源语言,特别是越南语的代表性不足问题,为医疗视觉语言研究提供重要资源。
- 引入训练框架,包括数据增强和专家验证测试集,以提升VLM模型的学习效果。
- 实验证明,使用此数据集能显著提高VLM模型在医疗报告生成和视觉问答等下游任务上的性能。
- 该数据集和基准测试对于推动更稳健的VLM模型在医学影像领域的发展至关重要,特别是在低资源语言环境中。
点此查看论文截图

Discrete Variational Autoencoding via Policy Search
Authors:Michael Drolet, Firas Al-Hafez, Aditya Bhatt, Jan Peters, Oleg Arenz
Discrete latent bottlenecks in variational autoencoders (VAEs) offer high bit efficiency and can be modeled with autoregressive discrete distributions, enabling parameter-efficient multimodal search with transformers. However, discrete random variables do not allow for exact differentiable parameterization; therefore, discrete VAEs typically rely on approximations, such as Gumbel-Softmax reparameterization or straight-through gradient estimates, or employ high-variance gradient-free methods such as REINFORCE that have had limited success on high-dimensional tasks such as image reconstruction. Inspired by popular techniques in policy search, we propose a training framework for discrete VAEs that leverages the natural gradient of a non-parametric encoder to update the parametric encoder without requiring reparameterization. Our method, combined with automatic step size adaptation and a transformer-based encoder, scales to challenging datasets such as ImageNet and outperforms both approximate reparameterization methods and quantization-based discrete autoencoders in reconstructing high-dimensional data from compact latent spaces, achieving a 20% improvement on FID Score for ImageNet 256.
在变分自编码器(VAEs)中的离散潜在瓶颈提供了高比特效率,并且可以使用自回归离散分布进行建模,从而实现了参数高效的多元搜索。然而,离散随机变量不允许精确的可微参数化;因此,离散VAE通常依赖于近似方法,如Gumbel-Softmax重参数化或直通梯度估计,或者采用无梯度的高方差方法,如REINFORCE等。在高维任务(如图像重建)中这些方法并不成功。受流行策略搜索技术的启发,我们为离散VAE提出了一个训练框架,该框架利用非参数编码器的自然梯度来更新参数编码器,无需重新参数化。我们的方法结合了自动步长调整和基于变压器的编码器,适用于大规模数据集(如ImageNet),并且在从紧凑潜在空间重建高维数据方面优于近似重参数化方法和基于量化的离散自编码器,实现了ImageNet 256的FID得分提高了20%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了离散隐变量瓶颈在变分自编码器(VAEs)中的应用,提出了一种基于非参数编码器自然梯度的训练框架,无需重新参数化即可更新参数编码器。该方法结合了自动步长调整和基于变压器的编码器,可扩展到高维数据集如ImageNet,并在重建高维数据方面优于近似重新参数化方法和基于量化的离散自编码器,提高了ImageNet 256的FID得分,达到20%的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 离散隐变量瓶颈在变分自编码器中具有高比特效率,并可通过自回归离散分布建模。
- 离散随机变量不允许精确的可微参数化,因此离散VAE通常依赖于近似方法,如Gumbel-Softmax重参数化或直通梯度估计。
- 提出了一种基于非参数编码器自然梯度的训练框架,用于更新参数编码器,无需重新参数化。
- 该方法与自动步长调整和基于变压器的编码器相结合,可扩展到高维数据集如ImageNet。
- 在重建高维数据方面,该方法优于近似重新参数化方法和基于量化的离散自编码器。
- 在ImageNet 256上实现了20%的FID得分改进。
点此查看论文截图

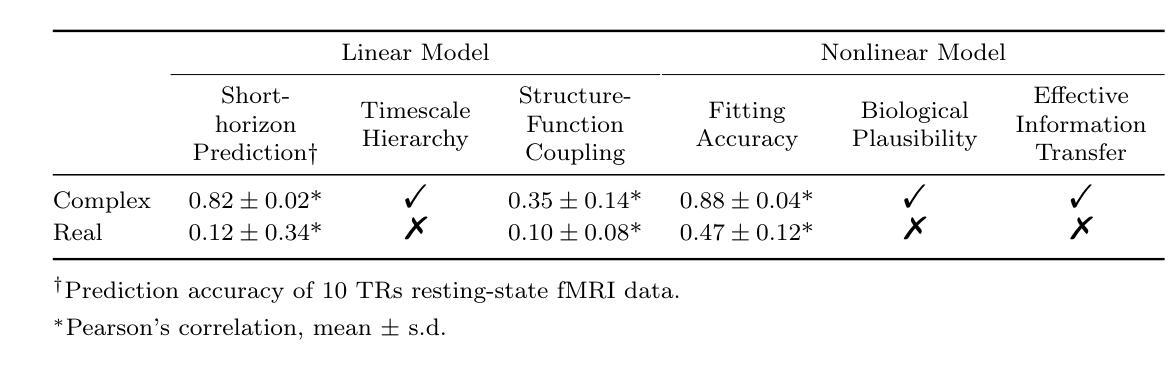
Dark Signals in the Brain: Augment Brain Network Dynamics to the Complex-valued Field
Authors:Jiangnan Zhang, Chengyuan Qian, Wenlian Lu, Gustavo Deco, Weiyang Ding, Jianfeng Feng
Recordings of brain activity, such as functional MRI (fMRI), provide low-dimensional, indirect observations of neural dynamics evolving in high-dimensional, unobservable spaces. Embedding observed brain dynamics into a higher-dimensional representation may help reveal functional organization, but precisely how remains unclear. Hamiltonian mechanics suggests that, by introducing an additional dimension of conjugate momenta, the dynamical behaviour of a conservative system can be formulated in a more compact and mathematically elegant manner. Here we develop a physics-informed, data-driven framework that lifts whole-brain activity to the complex-valued field. Specifically, we augment observed signals (generalized coordinates) with latent ``dark signals’’ that play the role of conjugate momenta in a whole-brain Hamiltonian system. We show that the Hilbert transform provides an augmentation approach with optimal fitting accuracy within this framework, yielding a Schr"odinger-like equation governing complex-valued, augmented brain dynamics. Empirically, this complex-valued model consistently outperforms its real-valued counterpart, improving short-horizon prediction in the linear regime (correlation 0.12$\to$0.82) and achieving superior fits under nonlinear, nonequilibrium dynamics (0.47$\to$0.88). The framework strengthens structure-function coupling, recovers hierarchical intrinsic timescales, and yields biologically plausible directed effective connectivity that varies systematically with age and reconfigures from rest to task via global rescaling plus targeted rewiring. Together, these results establish a principled, testable paradigm for network neuroscience and offer transformative insight into the spatiotemporal organization and functional roles of large-scale brain dynamics.
大脑活动记录,如功能磁共振成像(fMRI),提供了对高维不可观察空间中神经动力学的低维间接观察。将观察到的脑动力学嵌入到高维表示中可能有助于揭示功能组织,但其确切方式仍不清楚。哈密顿力学表明,通过引入共动量的附加维度,保守系统的动态行为可以以更紧凑和数学优雅的方式表述。在这里,我们开发了一个受物理学启发、数据驱动的分析框架,将全脑活动提升到复数场。具体来说,我们用潜在“暗信号”来增强观测信号(广义坐标),在全局哈密顿系统中扮演共动量的角色。我们展示了希尔伯特变换在此框架内提供了最佳的拟合精度增强方法,从而得出了控制复数增强脑动力学的薛定谔方程。从经验上看,这个复数模型始终优于其对应的实数模型,在线性范围内短期预测(相关性从0.12提升至0.82)改进明显,并在非线性非平衡动力学下获得更好的拟合效果(从0.47提升至0.88)。该框架加强了结构-功能耦合,恢复了分层内在时间尺度,并产生了符合生物学原理的有效连接性,这种连接性随着年龄的增长而系统地变化,并通过全局重新缩放和目标重新布线实现从静止到任务的转变。总的来说,这些结果建立了网络神经科学的测试原则,并为大规模脑动力学的时空组织和功能角色提供了变革性的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文利用物理学启发的方法,将全脑活动提升到复数场。通过引入潜在“暗信号”作为广义坐标的共轭动量,构建全脑哈密顿系统。采用Hilbert变换进行数据增强,建立描述复杂全脑动力学的薛定谔方程。该模型在预测短期线性动态和非线性非平衡动态方面均优于传统模型,并揭示了结构功能耦合、内在时间尺度层级以及任务诱导下的全球可重塑性与靶向重新连接的有效性。这标志着对网络神经科学的重要发展,并为我们提供大规模脑动力学的时间和空间组织和功能的洞察。
Key Takeaways
- 利用物理学启发的方法将全脑活动提升到复数场,以揭示其功能性组织。
- 通过引入广义坐标的共轭动量(即潜在“暗信号”)构建全脑哈密顿系统。
- 采用Hilbert变换进行数据增强,建立描述复杂全脑动力学的薛定谔方程。
- 模型的优化显著提升了短期预测的准确率。
- 模型揭示了结构功能耦合和内在时间尺度层级关系。
- 模型能够揭示大脑活动的全局可重塑性和靶向重新连接的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

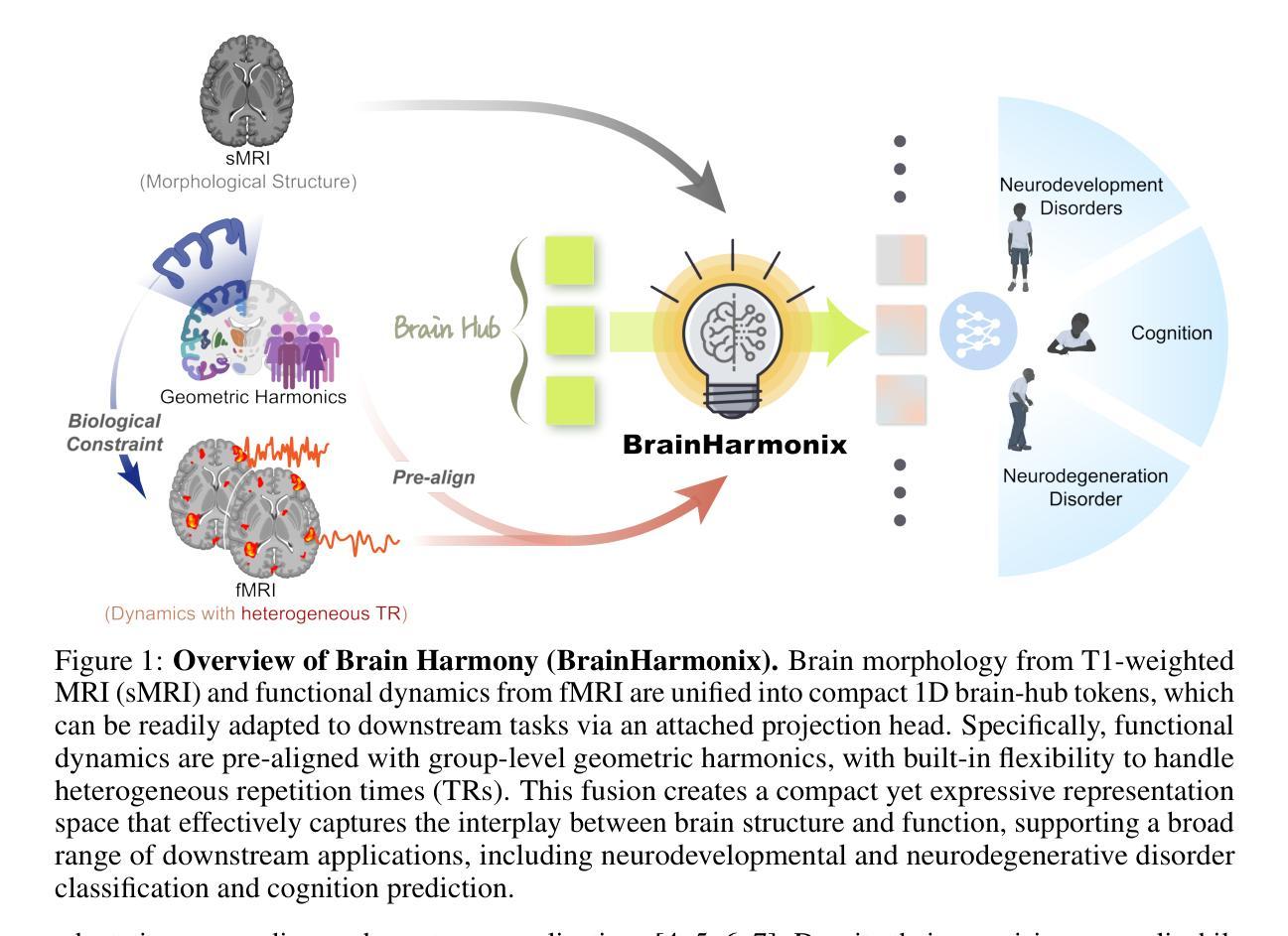
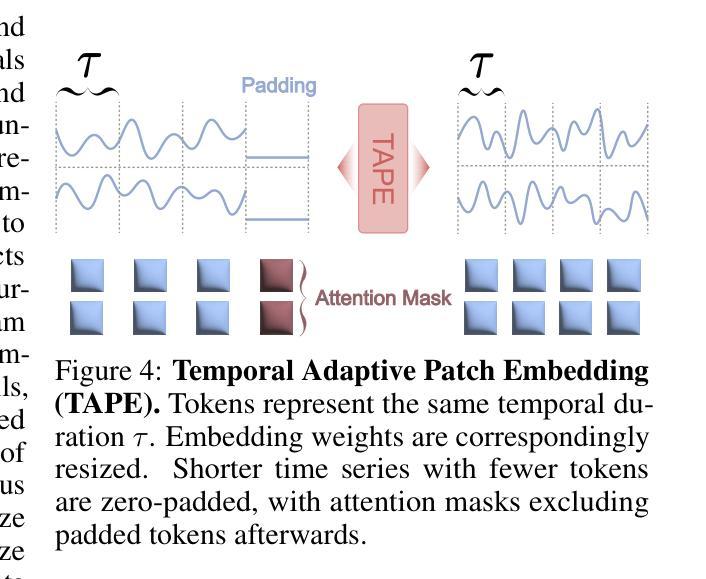
Brain Harmony: A Multimodal Foundation Model Unifying Morphology and Function into 1D Tokens
Authors:Zijian Dong, Ruilin Li, Joanna Su Xian Chong, Niousha Dehestani, Yinghui Teng, Yi Lin, Zhizhou Li, Yichi Zhang, Yapei Xie, Leon Qi Rong Ooi, B. T. Thomas Yeo, Juan Helen Zhou
We present Brain Harmony (BrainHarmonix), the first multimodal brain foundation model that unifies structural morphology and functional dynamics into compact 1D token representations. The model was pretrained on two of the largest neuroimaging datasets to date, encompassing 64,594 T1-weighted structural MRI 3D volumes (~ 14 million images) and 70,933 functional MRI (fMRI) time series. BrainHarmonix is grounded in two foundational neuroscience principles: structure complements function - structural and functional modalities offer distinct yet synergistic insights into brain organization; function follows structure - brain functional dynamics are shaped by cortical morphology. The modular pretraining process involves single-modality training with geometric pre-alignment followed by modality fusion through shared brain hub tokens. Notably, our dynamics encoder uniquely handles fMRI time series with heterogeneous repetition times (TRs), addressing a major limitation in existing models. BrainHarmonix is also the first to deeply compress high-dimensional neuroimaging signals into unified, continuous 1D tokens, forming a compact latent space of the human brain. BrainHarmonix achieves strong generalization across diverse downstream tasks, including neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorder classification and cognition prediction - consistently outperforming previous approaches. Our models - pretrained on 8 H100 GPUs - aim to catalyze a new era of AI-driven neuroscience powered by large-scale multimodal neuroimaging.
我们推出了Brain Harmony(BrainHarmonix),这是首个将结构形态和功能性动态统一到紧凑的1D令牌表示中的多模式脑基础模型。该模型在迄今为止最大的两个神经成像数据集上进行了预训练,涵盖了64594个T1加权结构MRI 3D体积(约1400万张图像)和70933个功能性磁共振成像(fMRI)时间序列。BrainHarmonix基于两项基础神经科学原则:结构补充功能——结构和功能模式为脑组织的组织提供了独特而协同的见解;功能是结构的延伸——大脑的功能动态是由皮层形态塑造的。模块化预训练过程涉及单模态训练与几何预对齐,然后通过共享的大脑中枢令牌进行模态融合。值得注意的是,我们的动态编码器能够独特地处理具有不同重复时间(TR)的fMRI时间序列,解决了现有模型的一个主要局限性。BrainHarmonix也是首个将高维神经成像信号深度压缩成统一、连续的1D令牌,形成一个紧凑的人类脑潜空间。BrainHarmonix在不同下游任务中实现了强大的泛化能力,包括神经发育和神经退行性疾病的分类以及认知预测——始终优于以前的方法。我们的模型在8个H100 GPU上进行预训练,旨在催化由大规模多模式神经成像驱动的新时代人工智能神经科学。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2025. The first two authors contributed equally
Summary
BrainHarmony(BrainHarmonix)是首个统一结构形态与功能动态的多模态脑基础模型,它将两者转化为紧凑的1D令牌表示。该模型在两大神经成像数据集上进行预训练,涵盖64,594个T1加权结构MRI 3D体积和70,933个功能MRI时间序列。它基于神经科学的两个基本原则:结构补充功能,功能和结构相互关联。BrainHarmonix通过模块化预训练过程,包括单模态训练与几何预对齐,以及通过共享脑中心令牌进行模态融合。它能独特地处理具有不同重复时间的fMRI时间序列,并将高维神经成像信号深深压缩成统一、连续的1D令牌,形成人类大脑紧凑的潜在空间。它在多种下游任务上实现了强大的泛化性能,包括神经发育和神经退行性疾病的分类以及认知预测。
Key Takeaways
- BrainHarmony(BrainHarmonix)是首个将结构形态与功能动态相结合的多模态脑基础模型。
- 该模型在两大神经成像数据集上进行预训练,涵盖大量MRI数据。
- BrainHarmonix基于神经科学的两个原则:结构与功能的互补性,以及功能由结构塑造的观点。
- BrainHarmonix采用模块化预训练过程,包括单模态训练、几何预对齐和模态融合。
- 动力学编码器能够处理具有不同重复时间的fMRI时间序列,这是一个现有模型的重大改进。
- BrainHarmonix能将高维神经成像信号压缩成紧凑的1D令牌表示。
点此查看论文截图

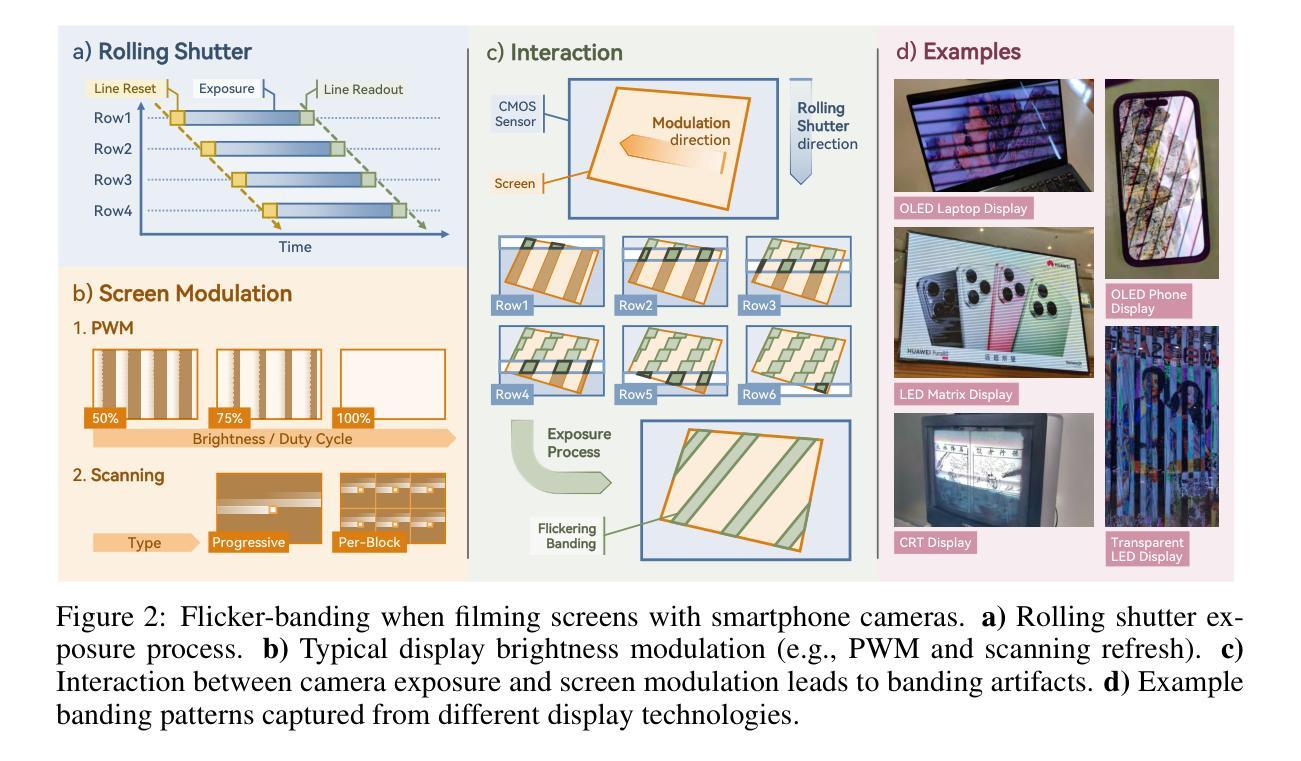
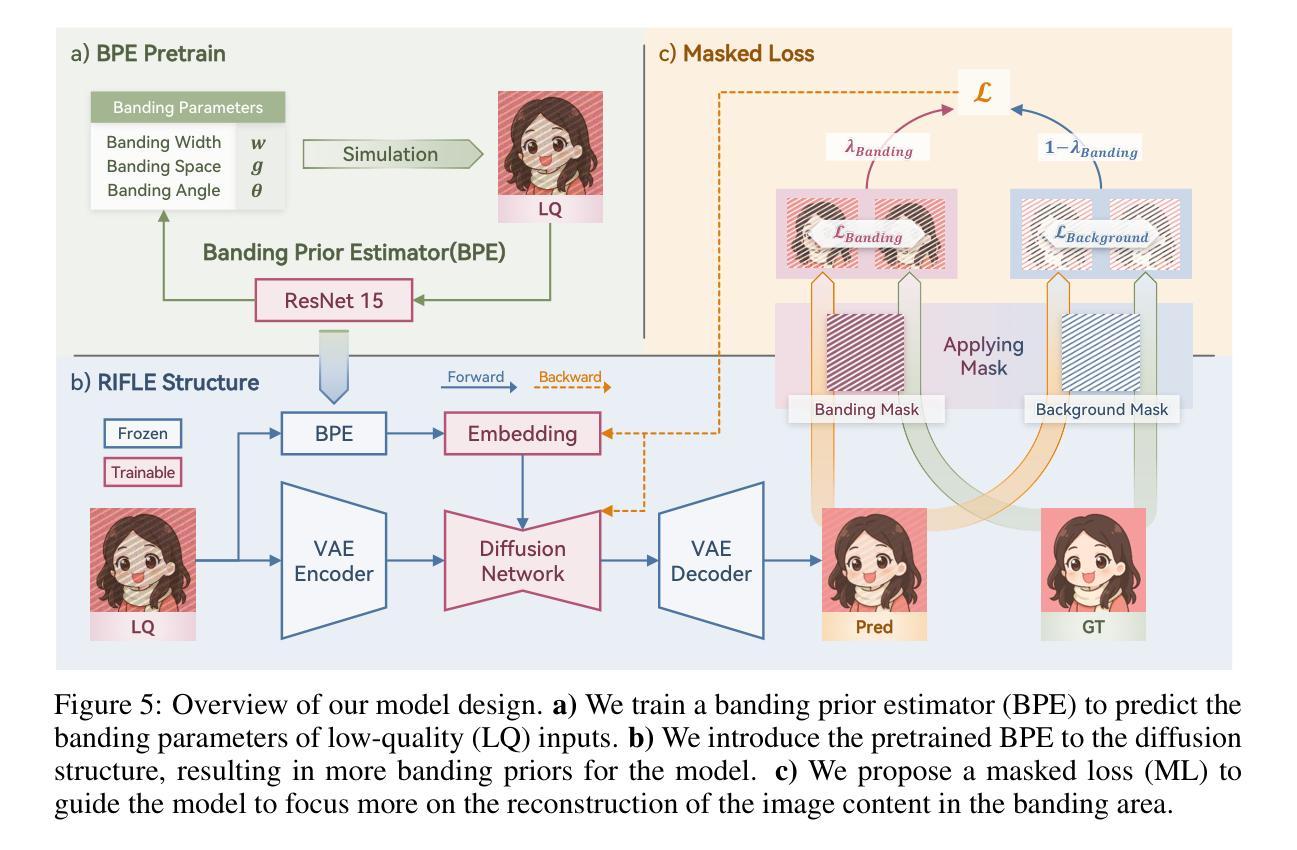
RIFLE: Removal of Image Flicker-Banding via Latent Diffusion Enhancement
Authors: Zhu, Libo, Zhou, Zihan, Liu, Xiaoyang, Zhang, Weihang, Shi, Keyu, Fu, Yifan, Zhang, Yulun
Capturing screens is now routine in our everyday lives. But the photographs of emissive displays are often influenced by the flicker-banding (FB), which is alternating bright%u2013dark stripes that arise from temporal aliasing between a camera’s rolling-shutter readout and the display’s brightness modulation. Unlike moire degradation, which has been extensively studied, the FB remains underexplored despite its frequent and severe impact on readability and perceived quality. We formulate FB removal as a dedicated restoration task and introduce Removal of Image Flicker-Banding via Latent Diffusion Enhancement, RIFLE, a diffusion-based framework designed to remove FB while preserving fine details. We propose the flicker-banding prior estimator (FPE) that predicts key banding attributes and injects it into the restoration network. Additionally, Masked Loss (ML) is proposed to concentrate supervision on banded regions without sacrificing global fidelity. To overcome data scarcity, we provide a simulation pipeline that synthesizes FB in the luminance domain with stochastic jitter in banding angle, banding spacing, and banding width. Feathered boundaries and sensor noise are also applied for a more realistic simulation. For evaluation, we collect a paired real-world FB dataset with pixel-aligned banding-free references captured via long exposure. Across quantitative metrics and visual comparisons on our real-world dataset, RIFLE consistently outperforms recent image reconstruction baselines from mild to severe flicker-banding. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first work to research the simulation and removal of FB. Our work establishes a great foundation for subsequent research in both the dataset construction and the removal model design. Our dataset and code will be released soon.
屏幕截图现在已经成为我们日常生活中的常规操作。然而,发光显示屏的照片往往会受到频闪条纹(FB)的影响,频闪条纹是由于相机滚动快门读出与显示屏亮度调制之间的时间混叠而产生的明暗交替条纹。与已被广泛研究的摩尔纹退化不同,尽管频闪条纹对可读性和感知质量造成频繁且严重的影响,但其仍然被较少探索。我们将频闪条纹的去除制定为一项专门的恢复任务,并引入了通过潜在扩散增强去除图像频闪条纹(RIFLE),这是一个基于扩散的框架,旨在去除频闪条纹同时保留细节。我们提出了频闪条纹先验估计器(FPE),用于预测关键条纹属性并将其注入恢复网络。此外,还提出了掩膜损失(ML),以将监督集中在带状区域上,而不牺牲全局保真度。为了克服数据稀缺的问题,我们提供了一个合成频闪条纹的模拟流程,该流程在亮度域中合成频闪条纹,并带有条纹角度、条纹间隔和条纹宽度的随机抖动。我们还应用了柔和的边界和传感器噪声,以进行更逼真的模拟。为了评估,我们收集了一对带有像素对齐的无频闪参考的真实世界频闪数据集,通过长时间曝光捕获。在我们真实世界的数据集上,根据定量指标和视觉比较,RIFLE在轻微到严重的频闪条纹情况下均表现优于最近的图像重建基线。据我们所知,它是第一项研究频闪条纹模拟和去除的工作。我们的工作为后续研究在数据集构建和去除模型设计方面奠定了坚实的基础。我们的数据集和代码将很快发布。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文研究了屏幕截图中的闪烁条纹(FB)问题,提出一种基于扩散的框架RIFLE,用于去除FB同时保留细节。文章介绍了闪烁条纹先验估计器(FPE)和遮罩损失(ML),并提出合成闪烁条纹数据集的方法。RIFLE在真实世界数据集上的表现优于其他图像重建方法。本文为FB的模拟和去除研究奠定了基础。
关键见解
- 闪烁条纹(FB)是屏幕截图常见的问题,影响可读性和感知质量。
- RIFLE框架旨在去除FB,同时保留细节。
- 引入闪烁条纹先验估计器(FPE)预测关键条纹属性并注入修复网络。
- 提出Masked Loss(ML)集中监督带状区域,同时保持全局保真度。
- 为克服数据稀缺问题,提出了一种合成FB的模拟管道,包括亮度域合成和随机抖动。
- 收集真实世界FB数据集,并进行定量评估和视觉对比。
点此查看论文截图


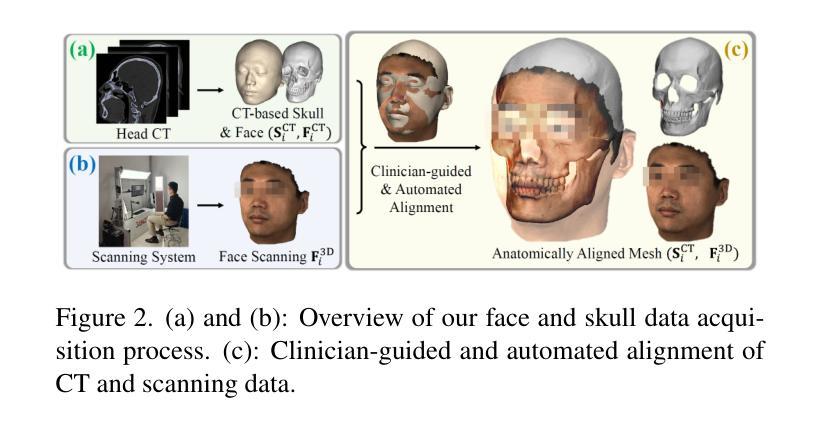
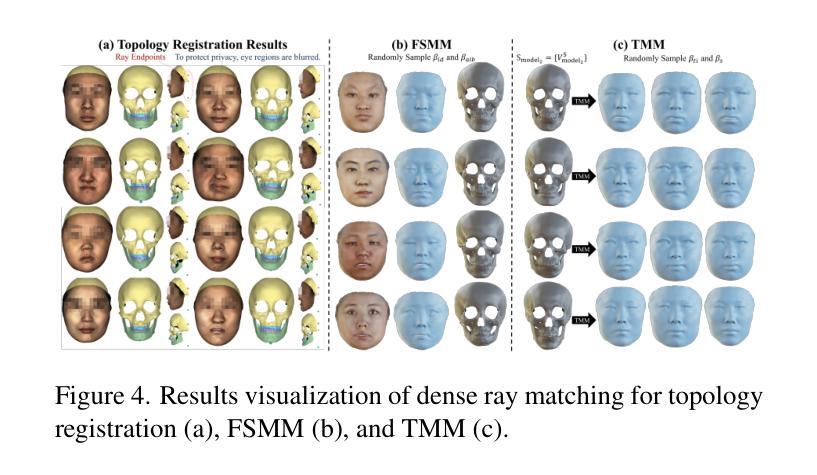
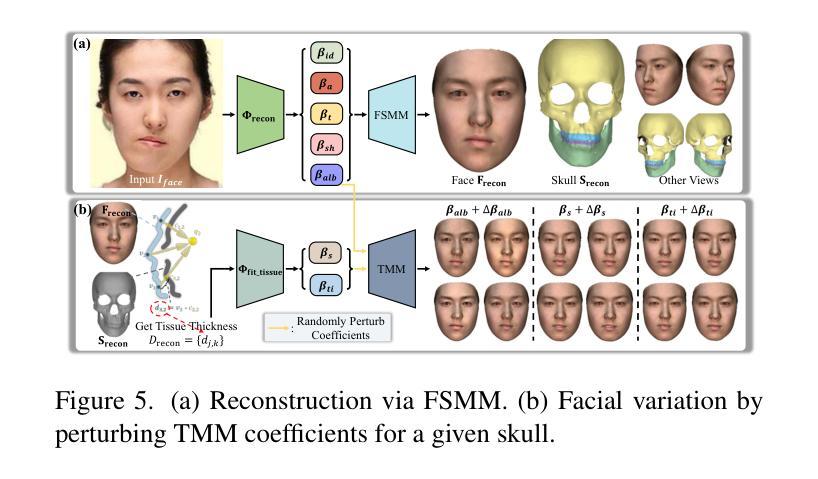
BFSM: 3D Bidirectional Face-Skull Morphable Model
Authors:Zidu Wang, Meng Xu, Miao Xu, Hengyuan Ma, Jiankuo Zhao, Xutao Li, Xiangyu Zhu, Zhen Lei
Building a joint face-skull morphable model holds great potential for applications such as remote diagnostics, surgical planning, medical education, and physically based facial simulation. However, realizing this vision is constrained by the scarcity of paired face-skull data, insufficient registration accuracy, and limited exploration of reconstruction and clinical applications. Moreover, individuals with craniofacial deformities are often overlooked, resulting in underrepresentation and limited inclusivity. To address these challenges, we first construct a dataset comprising over 200 samples, including both normal cases and rare craniofacial conditions. Each case contains a CT-based skull, a CT-based face, and a high-fidelity textured face scan. Secondly, we propose a novel dense ray matching registration method that ensures topological consistency across face, skull, and their tissue correspondences. Based on this, we introduce the 3D Bidirectional Face-Skull Morphable Model (BFSM), which enables shape inference between the face and skull through a shared coefficient space, while also modeling tissue thickness variation to support one-to-many facial reconstructions from the same skull, reflecting individual changes such as fat over time. Finally, we demonstrate the potential of BFSM in medical applications, including 3D face-skull reconstruction from a single image and surgical planning prediction. Extensive experiments confirm the robustness and accuracy of our method. BFSM is available at https://github.com/wang-zidu/BFSM
构建联合面部-颅骨可变形模型在远程诊断、手术规划、医学教育和基于物理的面部模拟等方面具有巨大潜力。然而,实现这一愿景受到配对面部-颅骨数据稀缺、注册精度不足以及重建和临床应用探索有限的制约。此外,颅面畸形患者往往被忽视,导致代表性不足和包容性有限。为了应对这些挑战,我们首先构建了一个包含200多个样本的数据集,其中包括正常病例和罕见的颅面异常病例。每个病例包含基于CT的颅骨、基于CT的面部图像和高清纹理面部扫描。其次,我们提出了一种新颖的密集射线匹配注册方法,确保面部、颅骨及其组织对应的拓扑一致性。基于此,我们推出了3D双向面部-颅骨可变形模型(BFSM),该模型通过共享系数空间实现面部和颅骨之间的形状推断,同时建模组织厚度变化,支持同一颅骨的一对多面部重建,反映个人随时间变化的特征,如脂肪变化。最后,我们通过3D面部-颅骨单图像重建和手术规划预测等医疗应用展示了BFSM的潜力。大量实验证实了我们方法的稳健性和准确性。BFSM可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/wang-zidu/BFSM 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
摘要
构建联合面部-颅骨可变形模型在远程诊断、手术规划、医学教育和物理面部模拟等方面具有巨大潜力。然而,实现这一愿景受到配对面部-颅骨数据缺乏、注册准确度不足和重建及临床应用探索有限的制约。此外,颅面畸形个体常被忽视,导致代表性不足和包容性有限。为应对这些挑战,我们构建了包含200多个样本的数据集,涵盖正常病例和罕见的颅面畸形。每个病例包括基于CT的颅骨和面部图像,以及高分辨率纹理面部扫描。其次,我们提出了一种新颖的密集射线匹配注册方法,确保面部、颅骨及其组织对应关系的拓扑一致性。基于此,我们引入了3D双向面部-颅骨可变形模型(BFSM),通过共享系数空间实现面部和颅骨之间的形状推断,同时建模组织厚度变化,支持从同一颅骨进行一对一和多面部重建,反映个人随时间变化。最后,我们通过医学应用展示了BFSM的潜力,包括从单一图像进行3D面部-颅骨重建和手术规划预测。广泛实验证实了我们方法的稳健性和准确性。BFSM可在https://github.com/wang-zidu/BFSM访问。
关键见解
- 构建面部-颅骨可变形模型具有广泛的应用前景,包括远程诊断、手术规划等。
- 当前面临的主要挑战是数据缺乏、注册准确度不足和临床应用探索有限。
- 引入了包含正常和颅面畸形病例的数据集。
- 提出了一种新的密集射线匹配注册方法,确保面部、颅骨和组织的拓扑一致性。
- 引入了3D双向面部-颅骨可变形模型(BFSM),实现面部和颅骨之间的形状推断,并考虑组织厚度变化。
- BFSM支持从同一颅骨进行一对一和多面部重建,反映个人随时间的变化。
点此查看论文截图
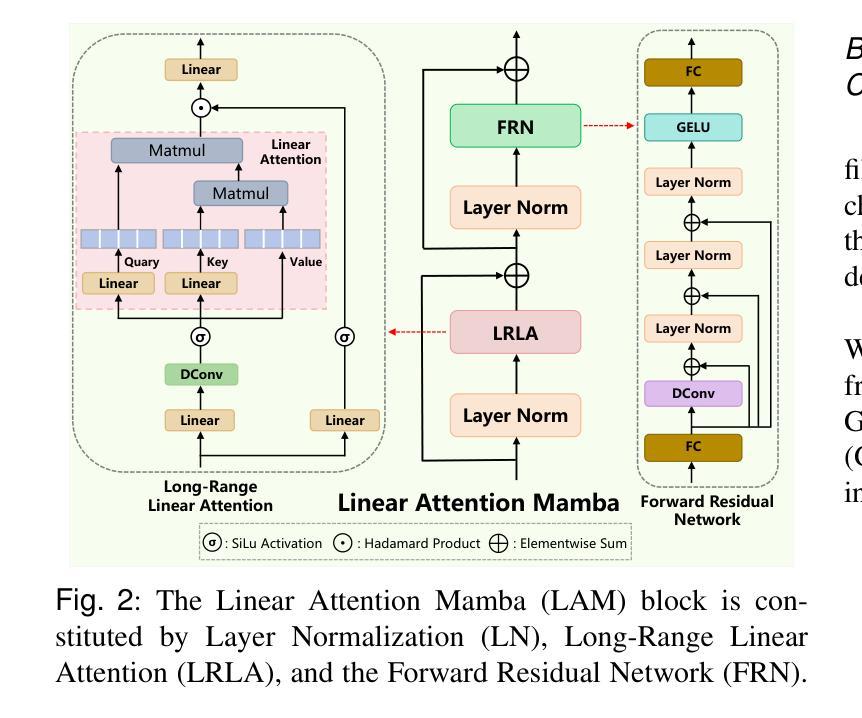
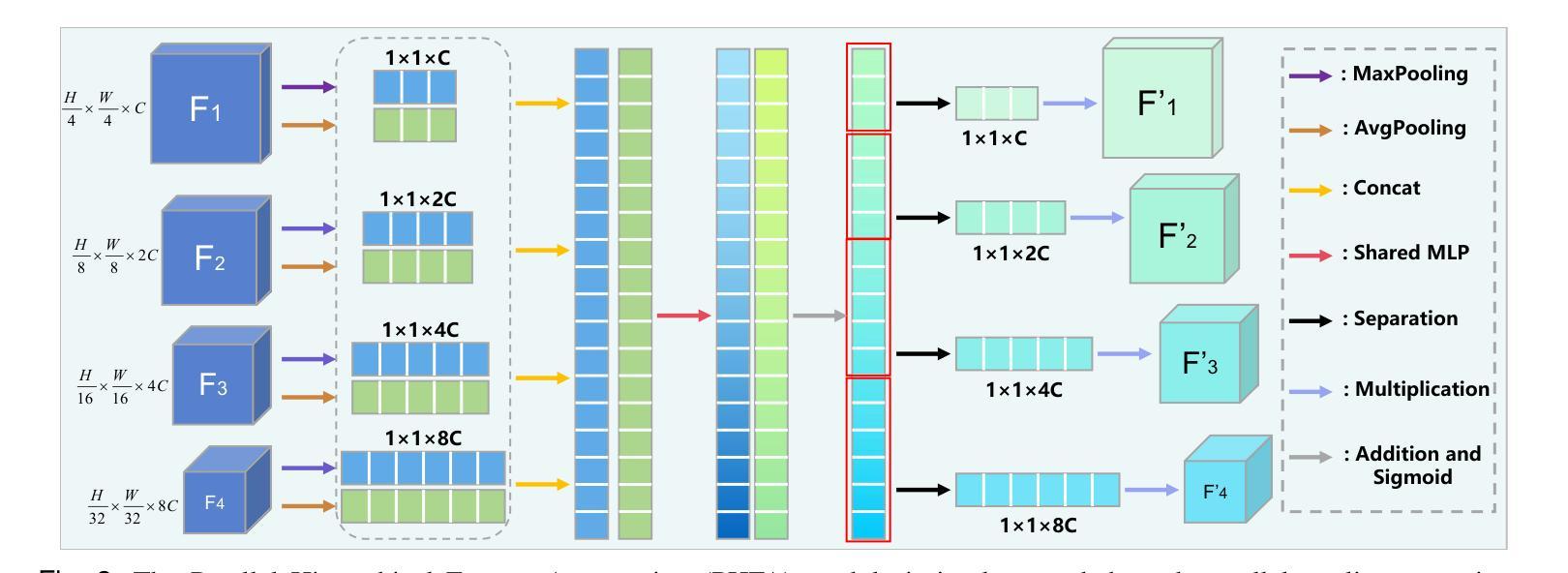
An Enhanced Pyramid Feature Network Based on Long-Range Dependencies for Multi-Organ Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Dayu Tan, Cheng Kong, Yansen Su, Hai Chen, Dongliang Yang, Junfeng Xia, Chunhou Zheng
In the field of multi-organ medical image segmentation, recent methods frequently employ Transformers to capture long-range dependencies from image features. However, these methods overlook the high computational cost of Transformers and their deficiencies in extracting local detailed information. To address high computational costs and inadequate local detail information, we reassess the design of feature extraction modules and propose a new deep-learning network called LamFormer for fine-grained segmentation tasks across multiple organs. LamFormer is a novel U-shaped network that employs Linear Attention Mamba (LAM) in an enhanced pyramid encoder to capture multi-scale long-range dependencies. We construct the Parallel Hierarchical Feature Aggregation (PHFA) module to aggregate features from different layers of the encoder, narrowing the semantic gap among features while filtering information. Finally, we design the Reduced Transformer (RT), which utilizes a distinct computational approach to globally model up-sampled features. RRT enhances the extraction of detailed local information and improves the network’s capability to capture long-range dependencies. LamFormer outperforms existing segmentation methods on seven complex and diverse datasets, demonstrating exceptional performance. Moreover, the proposed network achieves a balance between model performance and model complexity.
在医学图像多器官分割领域,近期的方法经常采用Transformer来捕捉图像特征的长程依赖关系。然而,这些方法忽略了Transformer的高计算成本和它们在提取局部详细信息方面的不足。为了解决高计算成本和局部细节信息不足的问题,我们重新评估特征提取模块的设计,并提出了一种新型的深度学习网络,称为LamFormer,用于多器官的精细分割任务。LamFormer是一个新型U型网络,在增强的金字塔编码器中使用线性注意力玛姆巴(LAM)来捕捉多尺度长程依赖关系。我们构建了并行层次特征聚合(PHFA)模块,以聚合编码器不同层级的特征,缩小特征之间的语义差距,同时过滤信息。最后,我们设计了精简Transformer(RT),它采用独特的计算方法对上采样特征进行全局建模。RRT增强了提取详细局部信息的能力,提高了网络捕捉长程依赖关系的能力。LamFormer在七个复杂且多样的数据集上的表现优于现有的分割方法,展现了卓越的性能。此外,所提出的网络在模型性能和模型复杂性之间达到了平衡。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对多器官医学图像分割领域的一种新型深度学习网络——LamFormer。为应对Transformer的高计算成本和局部细节信息提取不足的问题,LamFormer采用线性注意力机制Mamba增强金字塔编码器,捕捉多尺度长距离依赖关系,构建并行层次特征聚合模块以缩小特征间的语义差距并过滤信息。同时,通过采用独特的计算方法的简化版Transformer(RT),实现上采样特征的全局建模,提高了局部细节信息的提取能力。在七个复杂多样的数据集上,LamFormer表现出卓越的性能,并实现了模型性能和复杂性的平衡。
Key Takeaways
- LamFormer是一种用于多器官医学图像分割的深度学习网络。
- 该网络针对Transformer高计算成本和局部细节信息提取不足的问题进行了优化。
- LamFormer采用线性注意力机制Mamba增强金字塔编码器以捕捉多尺度长距离依赖关系。
- 构建了并行层次特征聚合模块以整合不同层次特征,缩小语义差距并过滤信息。
- 通过采用简化版Transformer(RT),实现了上采样特征的全局建模,提高了局部细节信息的提取能力。
- LamFormer在七个复杂数据集上的表现优于现有分割方法,具有卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图
In-situ X-ray imaging of reduction-nitridation in ferric oxide under high Pressure
Authors:Yu Tao, Depu Liu, Chunyin Zhou, Xv Jia, Jingyi Liu, Xue Chang, Yangbin Wang, Li Lei
The investigation of high-pressure chemical reaction dynamics has long been constrained by the absence of effective in-situ characterization methods. Here we performed the state-of-the-art synchrotron radiation in-situ X-ray imaging based on large-volume press (LVP) technology to uncover the crucial information on the dynamics of the underlying phenomena of the formation of iron-based spherical product in the high-pressure solid-state metathesis reaction (HSM). We successfully give access to the entire reduction-nitridation process of ferric oxide under the reaction conditions. By analyzing the variation of image intensity (Im) with temperature, two critical stages have been revealed, the formation of nitrogen-containing molten borate Fe[BO]+N[BO] melt and the phase separation of iron nitrides from molten borate. The experimental observation provides direct evidence for the existence of nitrogen-containing molten borate under high pressure, and the formation of molten borate plays a crucial role as a transport medium for nonmetallic ion exchange with metal elements. The M[BO]+N[BO] melt (M=other metals) represents a general pathway for the synthesis of metal nitrides under high pressure. The combination of LVP high-pressure experimental technology with X-ray radioscopy has resulted in a leap in the understanding of reaction dynamics and has opened new paths in the fields of high-pressure chemistry.
对于高压化学反应动力学的研究长期以来一直受限于缺乏有效的原位表征方法。在这里,我们采用了基于大体压(LVP)技术的最先进的同步辐射原位X射线成像,揭示了高压固态置换反应(HSM)中球形铁基产品形成过程中基本现象的动态过程中的关键信息。我们成功地获得了铁氧化物在整个还原氮化过程中的反应条件。通过分析图像强度(Im)随温度的变化,揭示了两个阶段的关键性转变:含氮熔硼酸盐Fe[BO]+N[BO]熔体的形成以及铁氮化物从熔硼酸盐中的相分离。实验观察为高压下含氮熔硼酸盐的存在提供了直接证据,熔硼酸盐的形成在高压下作为非金属离子交换与金属元素的传输介质起到了关键作用。M[BO]+N[BO](M为其他金属)熔体代表着高压合成金属氮化物的一般途径。将LVP高压实验技术与X射线放射照相术相结合,实现了对反应动力学的理解的飞跃,并为高压化学领域开辟了新的途径。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 4 figures
Summary
采用基于大体压技术的高压力同步辐射X射线成像,揭示铁基球形产物在高压力固态转换反应(HSM)中形成机理的重要信息。成功观察到氧化铁在反应条件下的整个还原氮化过程,发现氮化物熔体形成及铁氮化物从熔体中分离的关键阶段。实验观察为高压下含氮熔体的存在提供了直接证据,并证明了熔体形成作为非金属离子与金属元素交换的传输介质的重要作用。该研究对于高压下金属氮化物合成具有普遍意义,将高压实验技术与X射线放射照相术相结合,实现了反应动力学理解的飞跃,并为高压化学领域开辟了新途径。
Key Takeaways
- 利用先进的同步辐射X射线成像技术,实现了在高压力环境下的实时观察。
- 通过LVP技术揭示了铁基球形产物在高压固态转换反应(HSM)中的形成机理。
- 观察到了氧化铁在反应条件下的整个还原氮化过程。
- 发现了氮化物熔体的形成以及铁氮化物从熔体中的分离是两个关键阶段。
- 实验直接证据支持了高压下含氮熔体的存在。
- 熔体的形成对于非金属离子与金属元素的交换起到了关键的传输作用。
点此查看论文截图

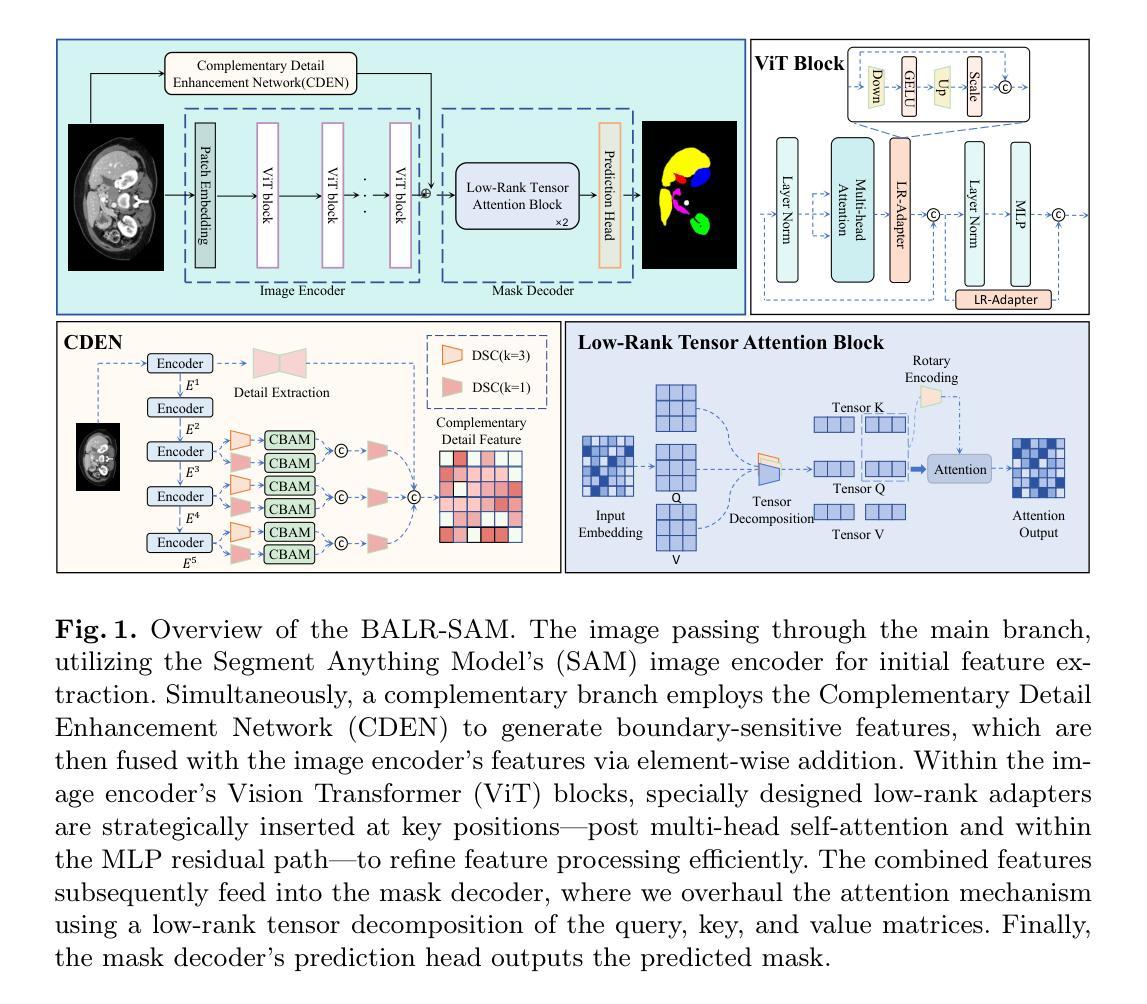
BALR-SAM: Boundary-Aware Low-Rank Adaptation of SAM for Resource-Efficient Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Zelin Liu, Sicheng Dong, Bocheng Li, Yixuan Yang, Jiacheng Ruan, Chenxu Zhou, Suncheng Xiang
Vision foundation models like the Segment Anything Model (SAM), pretrained on large-scale natural image datasets, often struggle in medical image segmentation due to a lack of domain-specific adaptation. In clinical practice, fine-tuning such models efficiently for medical downstream tasks with minimal resource demands, while maintaining strong performance, is challenging. To address these issues, we propose BALR-SAM, a boundary-aware low-rank adaptation framework that enhances SAM for medical imaging. It combines three tailored components: (1) a Complementary Detail Enhancement Network (CDEN) using depthwise separable convolutions and multi-scale fusion to capture boundary-sensitive features essential for accurate segmentation; (2) low-rank adapters integrated into SAM’s Vision Transformer blocks to optimize feature representation and attention for medical contexts, while simultaneously significantly reducing the parameter space; and (3) a low-rank tensor attention mechanism in the mask decoder, cutting memory usage by 75% and boosting inference speed. Experiments on standard medical segmentation datasets show that BALR-SAM, without requiring prompts, outperforms several state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods, including fully fine-tuned MedSAM, while updating just 1.8% (11.7M) of its parameters.
像Segment Anything Model(SAM)这样的视觉基础模型,在大规模自然图像数据集上进行预训练,往往由于缺少特定领域的适应性而在医学图像分割中表现挣扎。在临床实践中,以最小的资源需求高效地对这类模型进行医学下游任务的微调,同时保持强大的性能,是一项挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了BALR-SAM,这是一个边界感知的低秩适应框架,用于增强SAM在医学成像中的应用。它结合了三个定制组件:(1)使用深度可分离卷积和多尺度融合的互补细节增强网络(CDEN),以捕获对准确分割至关重要的边界敏感特征;(2)将低秩适配器集成到SAM的视觉转换器块中,以优化医疗环境下的特征表示和注意力,同时显著减少参数空间;(3)在掩膜解码器中使用低秩张量注意力机制,减少75%的内存使用,并提高推理速度。在标准医学分割数据集上的实验表明,BALR-SAM无需提示即可超越包括完全微调过的MedSAM在内的几种最新技术方法,同时仅更新其1.8%(11.7M)的参数。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Segment Anything Model(SAM)的预训练模型在大规模自然图像数据集上训练,但在医学图像分割方面存在领域特定适应不足的问题。为解决此问题,提出BALR-SAM模型,结合三种定制组件,包括细节增强网络、低秩适配器和低秩张量注意力机制。实验证明,BALR-SAM在不使用提示的情况下,仅更新少量参数即可超越多个先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练模型如SAM在医学图像分割上存在领域适应性挑战。
- BALR-SAM是一个边界感知的低秩适应框架,旨在解决此问题。
- BALR-SAM结合了三种定制组件:细节增强网络、低秩适配器和低秩张量注意力机制。
- 细节增强网络使用深度可分离卷积和多尺度融合来捕捉关键边界特征。
- 低秩适配器优化了特征表示和注意力,显著减少了参数空间。
- 低秩张量注意力机制减少了内存使用并提高了推理速度。
点此查看论文截图

An Efficient 3D Latent Diffusion Model for T1-contrast Enhanced MRI Generation
Authors:Zach Eidex, Mojtaba Safari, Jie Ding, Richard Qiu, Justin Roper, David Yu, Hui-Kuo Shu, Zhen Tian, Hui Mao, Xiaofeng Yang
Objective: Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) are commonly employed with T1w MRI to enhance lesion visualization but are restricted in patients at risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and variations in GBCA administration can introduce imaging inconsistencies. This study develops an efficient 3D deep-learning framework to generate T1-contrast enhanced images (T1C) from pre-contrast multiparametric MRI. Approach: We propose the 3D latent rectified flow (T1C-RFlow) model for generating high-quality T1C images. First, T1w and T2-FLAIR images are input into a pretrained autoencoder to acquire an efficient latent space representation. A rectified flow diffusion model is then trained in this latent space representation. The T1C-RFlow model was trained on a curated dataset comprised of the BraTS 2024 glioma (GLI; 1480 patients), meningioma (MEN; 1141 patients), and metastases (MET; 1475 patients) datasets. Selected patients were split into train (N=2860), validation (N=612), and test (N=614) sets. Results: Both qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate that the T1C-RFlow model outperforms benchmark 3D models (pix2pix, DDPM, Diffusion Transformers (DiT-3D)) trained in the same latent space. T1C-RFlow achieved the following metrics - GLI: NMSE 0.044 +/- 0.047, SSIM 0.935 +/- 0.025; MEN: NMSE 0.046 +/- 0.029, SSIM 0.937 +/- 0.021; MET: NMSE 0.098 +/- 0.088, SSIM 0.905 +/- 0.082. T1C-RFlow had the best tumor reconstruction performance and significantly faster denoising times (6.9 s/volume, 200 steps) than conventional DDPM models in both latent space (37.7s, 1000 steps) and patch-based in image space (4.3 hr/volume). Significance: Our proposed method generates synthetic T1C images that closely resemble ground truth T1C in much less time than previous diffusion models. Further development may permit a practical method for contrast-agent-free MRI for brain tumors.
目的:钆基造影剂(GBCAs)常与T1加权磁共振成像(MRI)一起使用,以提高病变的可视化程度,但对于有发生肾源性系统性纤维化风险的患者,其使用受到限制,且GBCA的给药变化可能会引入成像不一致性。本研究开发了一种高效的3D深度学习框架,用于从预造影的多参数MRI生成T1加权造影剂增强图像(T1C)。
方法:我们提出了用于生成高质量T1C图像的3D潜在校正流(T1C-RFlow)模型。首先,将T1加权和T2-FLAIR图像输入预训练的自编码器,以获得有效的潜在空间表示。然后,在此潜在空间表示中训练校正流扩散模型。T1C-RFlow模型是在精选数据集上进行训练的,该数据集由BraTS 2024胶质细胞瘤(GLI;1480名患者)、脑膜瘤(MEN;1141名患者)和转移瘤(MET;1475名患者)数据集组成。所选患者被分为训练集(N=2860)、验证集(N=612)和测试集(N=614)。
结果:定性和定量结果均表明,T1C-RFlow模型在相同的潜在空间内优于基准的3D模型(pix2pix、DDPM、Diffusion Transformers(DiT-3D))。T1C-RFlow的度量指标如下:GLI的NMSE为0.044±0.047,SSIM为0.935±0.025;MEN的NMSE为0.046±0.029,SSIM为0.937±0.021;MET的NMSE为0.098±0.088,SSIM为0.905±0.082。在肿瘤重建性能方面,T1C-RFlow表现最佳,并且其降噪时间(6.9秒/体积,200步)显著快于潜在空间的传统DDPM模型和基于图像的图像空间(4.3小时/体积)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究采用3D深度学习框架,基于T1加权磁共振成像(MRI)和非对比剂多参数MRI生成T1对比度增强图像(T1C)。提出的T1C-RFlow模型在生成高质量T1C图像方面表现出色,具有高效性和准确性,为对比剂相关的MRI提供了新的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 研究采用3D深度学习框架生成T1对比度增强图像(T1C)。
- T1C-RFlow模型用于生成高质量T1C图像。
- T1C-RFlow模型在多种疾病数据集上表现优异,包括胶质细胞瘤、脑膜瘤和转移瘤。
- T1C-RFlow模型在肿瘤重建方面表现出最佳性能,并且具有更快的去噪时间。
- 该方法生成的T1C图像与真实T1C图像高度相似。
- 与传统扩散模型相比,该方法的生成时间短。
- 研究为未来实现无对比剂的MRI提供了新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图

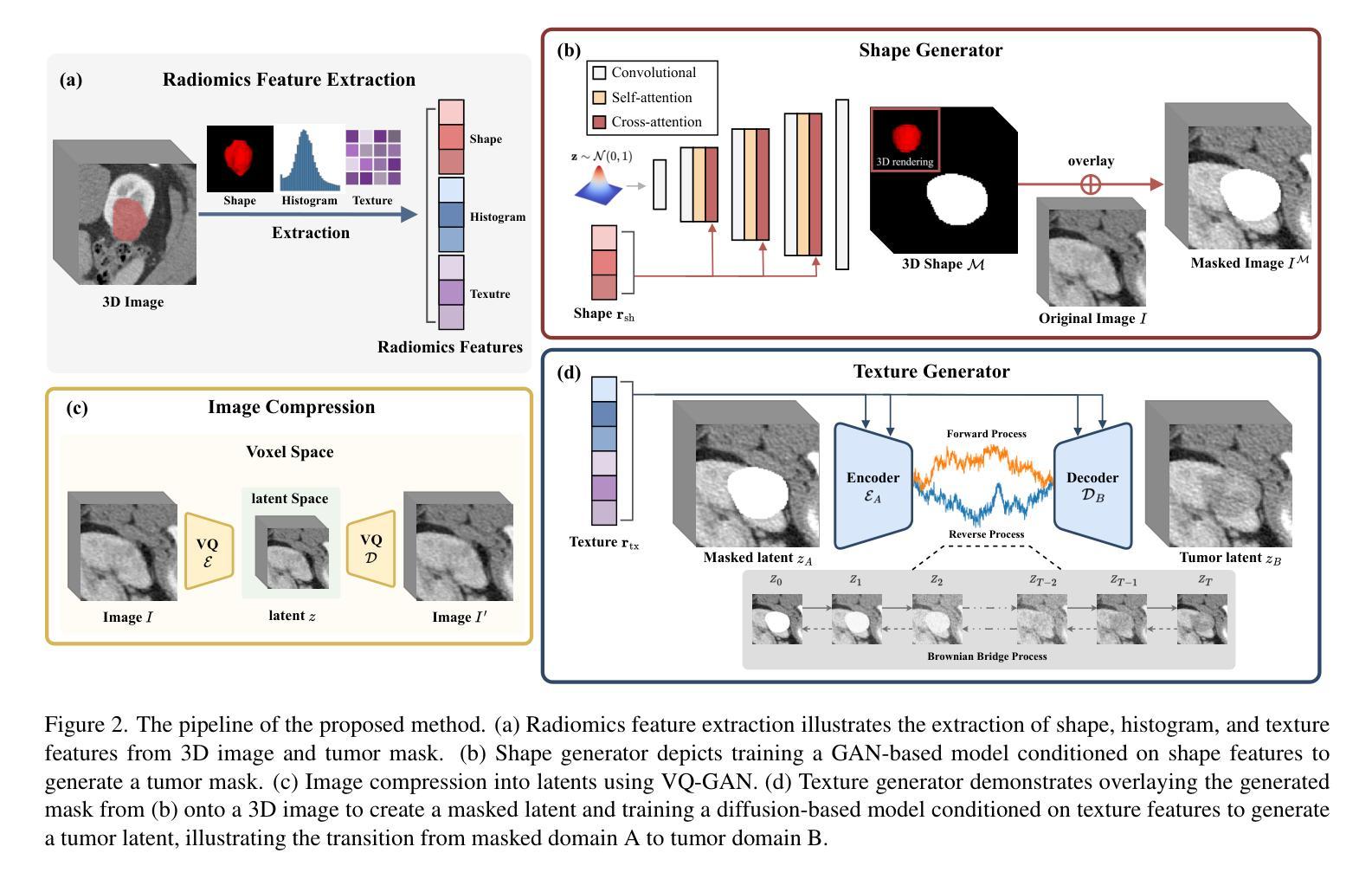
Tumor Synthesis conditioned on Radiomics
Authors:Jonghun Kim, Inye Na, Eun Sook Ko, Hyunjin Park
Due to privacy concerns, obtaining large datasets is challenging in medical image analysis, especially with 3D modalities like Computed Tomography (CT) and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Existing generative models, developed to address this issue, often face limitations in output diversity and thus cannot accurately represent 3D medical images. We propose a tumor-generation model that utilizes radiomics features as generative conditions. Radiomics features are high-dimensional handcrafted semantic features that are biologically well-grounded and thus are good candidates for conditioning. Our model employs a GAN-based model to generate tumor masks and a diffusion-based approach to generate tumor texture conditioned on radiomics features. Our method allows the user to generate tumor images according to user-specified radiomics features such as size, shape, and texture at an arbitrary location. This enables the physicians to easily visualize tumor images to better understand tumors according to changing radiomics features. Our approach allows for the removal, manipulation, and repositioning of tumors, generating various tumor types in different scenarios. The model has been tested on tumors in four different organs (kidney, lung, breast, and brain) across CT and MRI. The synthesized images are shown to effectively aid in training for downstream tasks and their authenticity was also evaluated through expert evaluations. Our method has potential usage in treatment planning with diverse synthesized tumors.
在医学图像分析中,由于隐私问题,获取大型数据集具有挑战性,特别是在使用如计算机断层扫描(CT)和磁共振成像(MRI)等3D模式的情况下。为解决此问题而开发的现有生成模型在输出多样性方面通常面临局限性,因此无法准确代表3D医学图像。我们提出了一种利用放射学特征进行肿瘤生成的模型。放射学特征是高维的手工语义特征,在生物学上有很好的依据,因此是条件设定的良好候选者。我们的模型采用基于GAN的模型来生成肿瘤掩膜,并采用基于扩散的方法,根据放射学特征生成肿瘤纹理。我们的方法允许用户根据用户指定的放射学特征(如大小、形状和纹理)在任意位置生成肿瘤图像。这使得医生能够轻松地根据变化的放射学特征可视化肿瘤图像,从而更好地理解肿瘤。我们的方法允许删除、操作和重新定位肿瘤,在不同场景下生成各种肿瘤类型。该模型已在CT和MRI中的四个不同器官(肾脏、肺部、乳房和大脑)的肿瘤上进行了测试。合成的图像已被证明可以有效地辅助下游任务训练,其真实性也通过专家评估得到了评估。我们的方法在具有多种合成肿瘤的治疗计划中具有潜在用途。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF WACV’25
Summary
该文本提出了一种基于放射学特征的肿瘤生成模型,利用GAN和扩散模型生成肿瘤掩膜和纹理,可以根据用户指定的放射学特征在任意位置生成肿瘤图像。此模型有助于提高医生对肿瘤变化的理解,辅助肿瘤治疗计划。该模型已经在四种不同器官(肾脏、肺部、乳房和大脑)的CT和MRI图像上进行了测试,并证实了其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分析中,获取大规模数据集面临隐私挑战,尤其是3D模态如CT和MRI。
- 现有生成模型在输出多样性方面存在局限,无法准确代表3D医学图像。
- 提出的肿瘤生成模型利用放射学特征作为生成条件,这些特征是生物上合理的高维手工语义特征。
- 模型采用GAN生成肿瘤掩膜,扩散方法生成条件化的肿瘤纹理。
- 用户可以根据指定的放射学特征(如大小、形状和纹理)在任意位置生成肿瘤图像。
- 该方法有助于医生更好地理解肿瘤变化,辅助肿瘤治疗计划。
点此查看论文截图
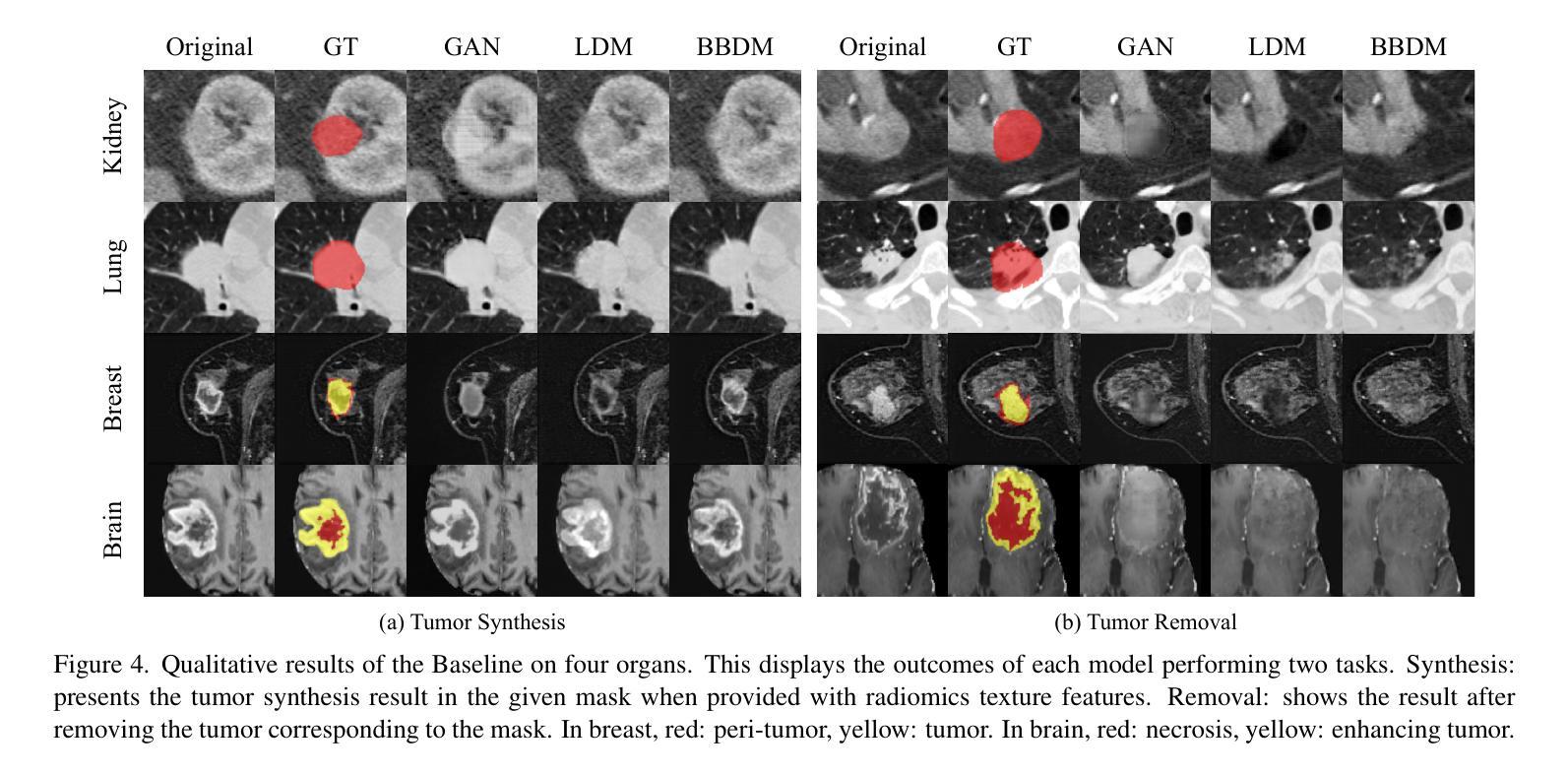
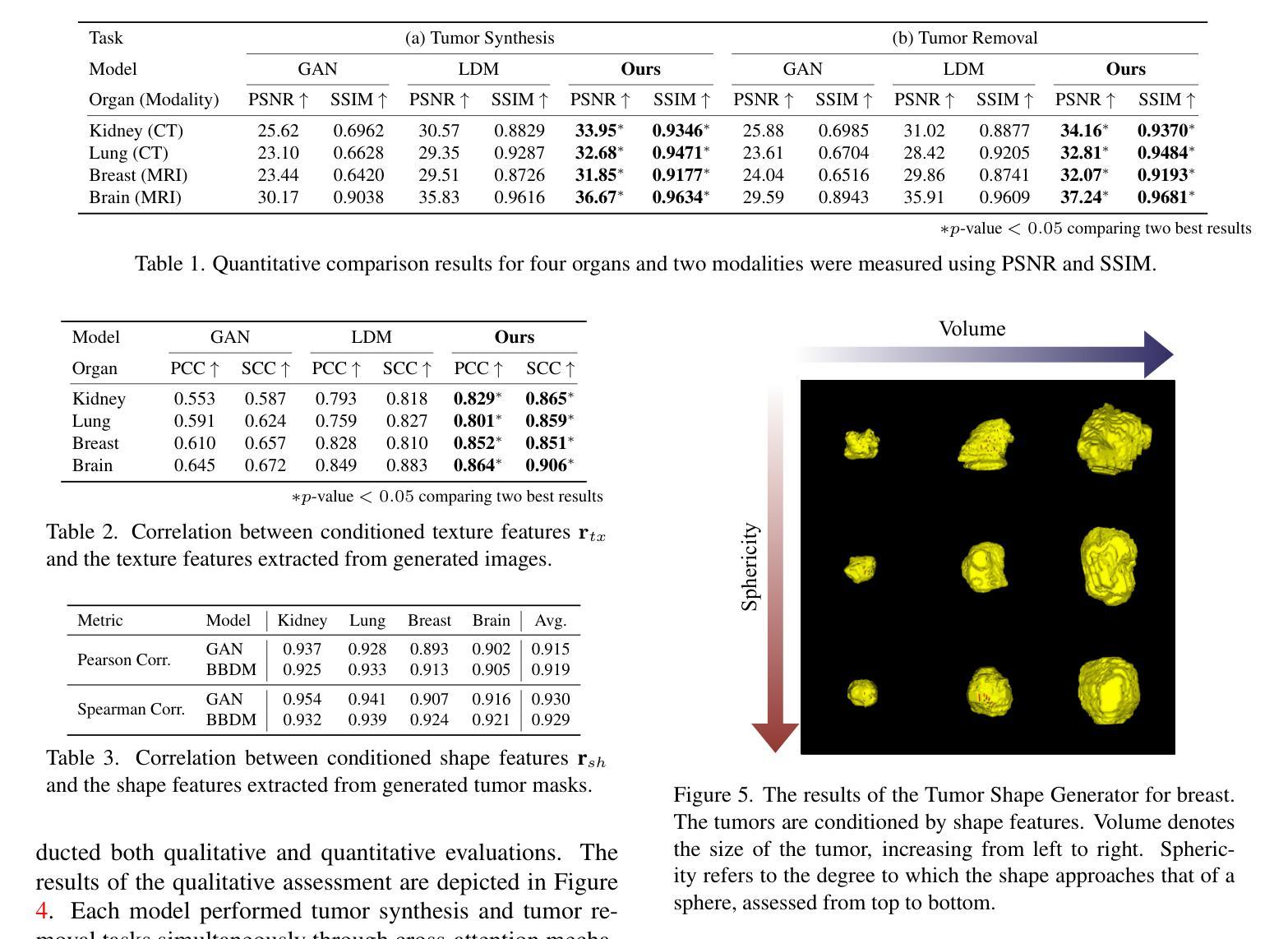
High-Order Progressive Trajectory Matching for Medical Image Dataset Distillation
Authors:Le Dong, Jinghao Bian, Jingyang Hou, Jingliang Hu, Yilei Shi, Weisheng Dong, Xiao Xiang Zhu, Lichao Mou
Medical image analysis faces significant challenges in data sharing due to privacy regulations and complex institutional protocols. Dataset distillation offers a solution to address these challenges by synthesizing compact datasets that capture essential information from real, large medical datasets. Trajectory matching has emerged as a promising methodology for dataset distillation; however, existing methods primarily focus on terminal states, overlooking crucial information in intermediate optimization states. We address this limitation by proposing a shape-wise potential that captures the geometric structure of parameter trajectories, and an easy-to-complex matching strategy that progressively addresses parameters based on their complexity. Experiments on medical image classification tasks demonstrate that our method improves distillation performance while preserving privacy and maintaining model accuracy comparable to training on the original datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/Bian-jh/HoP-TM.
医疗图像分析在数据共享方面面临着隐私法规和复杂机构协议的重大挑战。数据集蒸馏通过合成紧凑的数据集来解决这些挑战,这些合成数据集从真实的大型医疗数据集中提取了关键信息。轨迹匹配已成为数据集蒸馏的一种有前途的方法;然而,现有方法主要集中在终端状态,忽略了中间优化状态的关键信息。我们通过提出一种捕捉参数轨迹几何结构的形状势能,以及一种基于参数复杂性逐步解决的简单到复杂的匹配策略来解决这一局限性。在医疗图像分类任务上的实验表明,我们的方法在改善蒸馏性能的同时,也保留了隐私,并且模型精度与在原始数据集上进行训练相当。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Bian-jh/HoP-TM上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025 (early accept, top 9%)
Summary
医学图像分析在数据共享方面面临隐私法规和复杂机构协议的挑战。数据集蒸馏为解决这些挑战提供了一种解决方案,通过合成紧凑数据集来捕获来自真实大型医学数据集的本质信息。轨迹匹配已成为数据集蒸馏中一种有前途的方法,但现有方法主要关注终端状态,忽略了中间优化状态的关键信息。本研究通过提出一种捕捉参数轨迹几何结构的形状势能以及一种根据参数复杂性逐步解决的简单到复杂的匹配策略来解决这一局限性。在医学图像分类任务上的实验表明,该方法提高了蒸馏性能,同时保护了隐私,并保持模型准确率与在原始数据集上训练的准确率相当。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分析在数据共享方面存在挑战,主要由于隐私法规和复杂机构协议。
- 数据集蒸馏是解决这些挑战的一种解决方案,能够合成紧凑数据集,捕获真实大型医学数据集的本质信息。
- 轨迹匹配是数据集蒸馏的一种有前途的方法,但现有方法主要关注终端状态,忽略了中间优化状态。
- 本研究提出了一种形状势能,用于捕捉参数轨迹的几何结构。
- 研究还提出了一种简单到复杂的匹配策略,根据参数的复杂性逐步解决。
- 实验表明,该方法提高了蒸馏性能,同时保护了隐私。
点此查看论文截图
EYE-DEX: Eye Disease Detection and EXplanation System
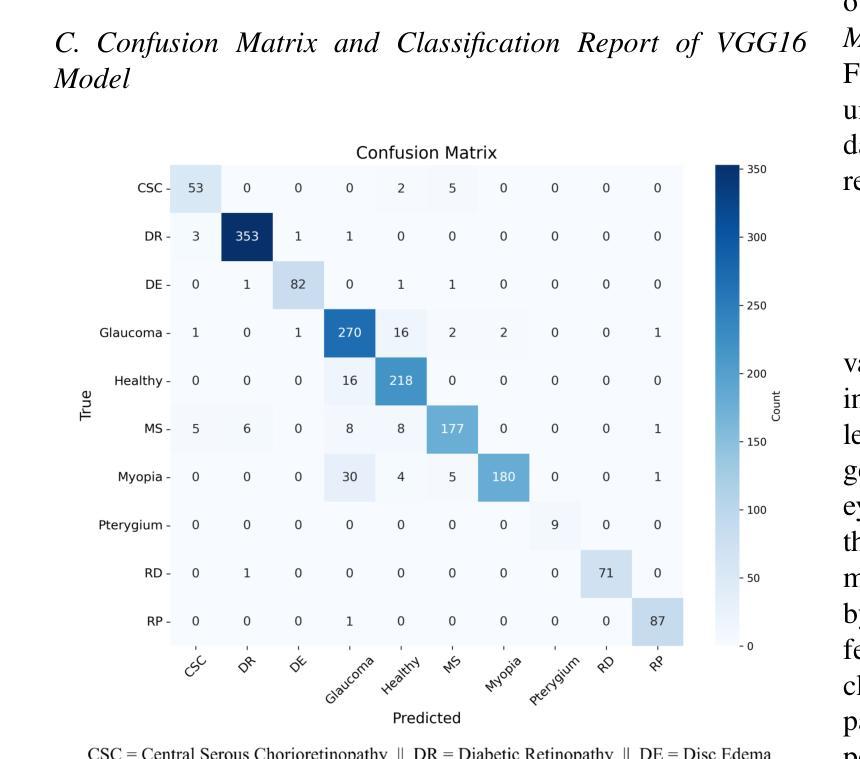
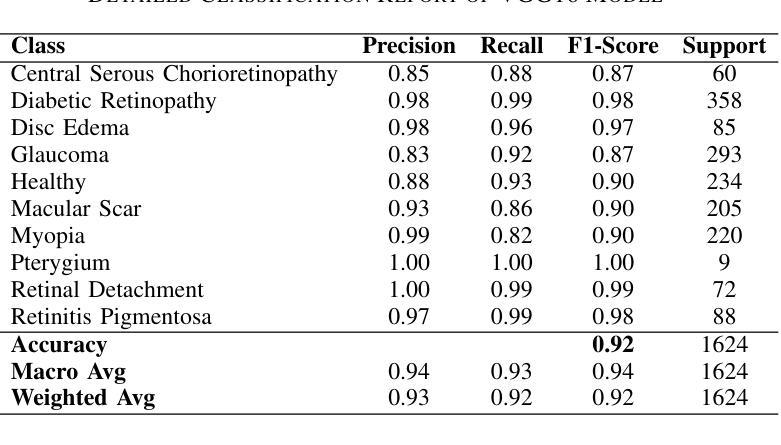
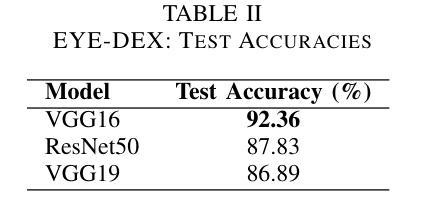
Authors:Youssef Sabiri, Walid Houmaidi, Amine Abouaomar
Retinal disease diagnosis is critical in preventing vision loss and reducing socioeconomic burdens. Globally, over 2.2 billion people are affected by some form of vision impairment, resulting in annual productivity losses estimated at $411 billion. Traditional manual grading of retinal fundus images by ophthalmologists is time-consuming and subjective. In contrast, deep learning has revolutionized medical diagnostics by automating retinal image analysis and achieving expert-level performance. In this study, we present EYE-DEX, an automated framework for classifying 10 retinal conditions using the large-scale Retinal Disease Dataset comprising 21,577 eye fundus images. We benchmark three pre-trained Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) models–VGG16, VGG19, and ResNet50–with our finetuned VGG16 achieving a state-of-the-art global benchmark test accuracy of 92.36%. To enhance transparency and explainability, we integrate the Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad-CAM) technique to generate visual explanations highlighting disease-specific regions, thereby fostering clinician trust and reliability in AI-assisted diagnostics.
视网膜疾病诊断对于预防视力丧失和减少社会经济负担至关重要。全球有超过2.2亿人受到某种形式的视力障碍影响,导致每年生产力损失估计为4.1万亿美元。眼科医生对视网膜眼底图像的传统手动分级耗时且主观。相比之下,深度学习通过自动化视网膜图像分析并达到专家级性能,从而彻底改变了医学诊断领域。在研究中,我们提出了EYE-DEX,这是一个使用大规模视网膜疾病数据集(包含21577张眼底图像)对10种视网膜状况进行分类的自动化框架。我们对三个预训练的卷积神经网络(CNN)模型——VGG16、VGG19和ResNet50进行了基准测试,我们微调后的VGG16在最新的全球基准测试中达到了92.36%的准确率。为了提高透明度和解释性,我们结合了梯度加权类激活映射(Grad-CAM)技术,生成视觉解释,突出显示特定于疾病的区域,从而促进临床医生对人工智能辅助诊断的信任和可靠性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 4 figures, 3 tables. Accepted at the 12th International Conference on Wireless Networks and Mobile Communications 2025 (WINCOM 2025)
Summary
本文介绍了使用深度学习技术对视网膜疾病进行自动诊断的重要性。全球有超过2.2亿人存在视力受损问题,导致每年生产力损失估计达411亿美元。本研究提出了一种名为EYE-DEX的自动化框架,用于对大型视网膜疾病数据集(包含21,577张眼底图像)中的10种视网膜病变进行分类。通过微调预训练的卷积神经网络(CNN)模型,如VGG16、VGG19和ResNet50,其中VGG16模型在基准测试中实现了最高的准确度为92.36%。为了提高透明度和解释性,集成了梯度加权类别激活映射(Grad-CAM)技术,生成突出显示病变特定区域的视觉解释,促进临床医生对AI辅助诊断的信任和可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- 视网膜疾病诊断对预防视力损失和减少社会经济负担至关重要。
- 全球有超过2.2亿人受到某种形式的视力障碍的影响。
- 传统的手动评估视网膜基金图像的方法既耗时又主观。
- 深度学习技术通过自动分析视网膜图像并实现专家级性能,已经彻底改变了医疗诊断。
- 在本研究中,提出了一个名为EYE-DEX的自动化框架,用于对视网膜疾病数据集进行分类,并使用大型数据集进行训练。
- 调优的VGG16模型在基准测试中实现了最高的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

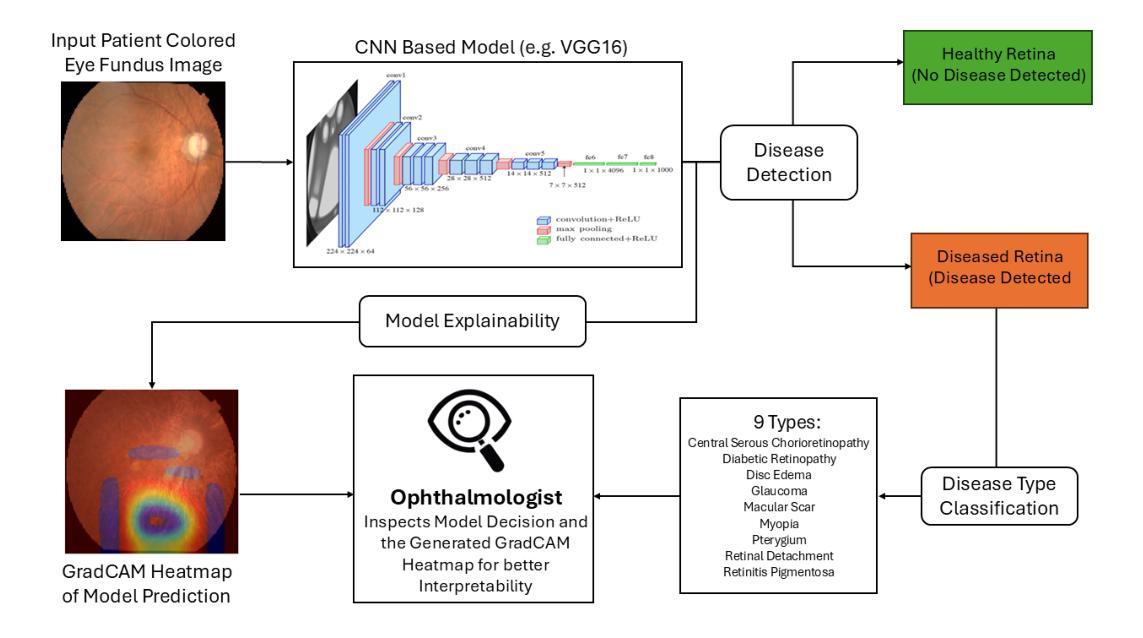
TREAT-Net: Tabular-Referenced Echocardiography Analysis for Acute Coronary Syndrome Treatment Prediction
Authors:Diane Kim, Minh Nguyen Nhat To, Sherif Abdalla, Teresa S. M. Tsang, Purang Abolmaesumi, and Christina Luong
Coronary angiography remains the gold standard for diagnosing Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS). However, its resource-intensive and invasive nature can expose patients to procedural risks and diagnostic delays, leading to postponed treatment initiation. In this work, we introduce TREAT-Net, a multimodal deep learning framework for ACS treatment prediction that leverages non-invasive modalities, including echocardiography videos and structured clinical records. TREAT-Net integrates tabular-guided cross-attention to enhance video interpretation, along with a late fusion mechanism to align predictions across modalities. Trained on a dataset of over 9000 ACS cases, the model outperforms unimodal and non-fused baselines, achieving a balanced accuracy of 67.6% and an AUROC of 71.1%. Cross-modality agreement analysis demonstrates 88.6% accuracy for intervention prediction. These findings highlight the potential of TREAT-Net as a non-invasive tool for timely and accurate patient triage, particularly in underserved populations with limited access to coronary angiography.
冠状动脉造影仍是急性冠状动脉综合征(ACS)诊断的金标准。然而,其资源密集型和侵入性的特性可能会使患者面临手术风险和诊断延误,导致治疗启动推迟。在这项工作中,我们介绍了TREAT-Net,这是一个用于ACS治疗预测的多模式深度学习框架,它利用非侵入性模式,包括超声心动图视频和结构化临床记录。TREAT-Net集成表格引导交叉注意以增强视频解释,以及后期融合机制以调整跨模式的预测。在超过9000例ACS病例数据集上训练的模型,其性能超过了单模态和非融合基线,实现了67.6%的平衡准确率和71.1%的AUROC。跨模式协议分析显示干预预测的准确率为88.6%。这些发现突显了TREAT-Net作为非侵入性工具在及时和准确的患者分流中的潜力,特别是在难以获得冠状动脉造影的人群中。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 2 figures, MICCAI ASMUS 2025 paper
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为TREAT-Net的多模态深度学习框架,用于急性冠脉综合征(ACS)治疗预测。该框架利用非侵入性方式,如超声心动图视频和结构化临床记录,进行预测。通过表格引导交叉注意力和晚期融合机制,模型在超过9000例ACS病例的数据集上表现出优越性能,平衡准确率达到了67.6%,AUROC为71.1%。此外,跨模态协议分析显示干预预测的准确率为88.6%。这些发现表明TREAT-Net作为非侵入性工具在及时和准确的患者分流方面具有潜力,特别是在难以获得冠状动脉造影的群体中有广阔应用前景。
Key Takeaways
- TREAT-Net是一个多模态深度学习框架,旨在预测急性冠脉综合征(ACS)的治疗。
- 该框架利用非侵入性方式(如超声心动图视频和结构化临床记录)进行预测,减少患者接受冠状动脉造影的程序风险和诊断延迟。
- TREAT-Net集成了表格引导交叉注意力来增强视频解读,并使用晚期融合机制来对齐不同模态的预测。
- 在超过9000例ACS病例的数据集上进行的训练表明,TREAT-Net的性能超越了单模态和非融合基线。
- TREAT-Net的平衡准确率为67.6%,AUROC为71.1%,显示出良好的预测性能。
- 跨模态协议分析显示,TREAT-Net在干预预测方面的准确率为88.6%。
点此查看论文截图
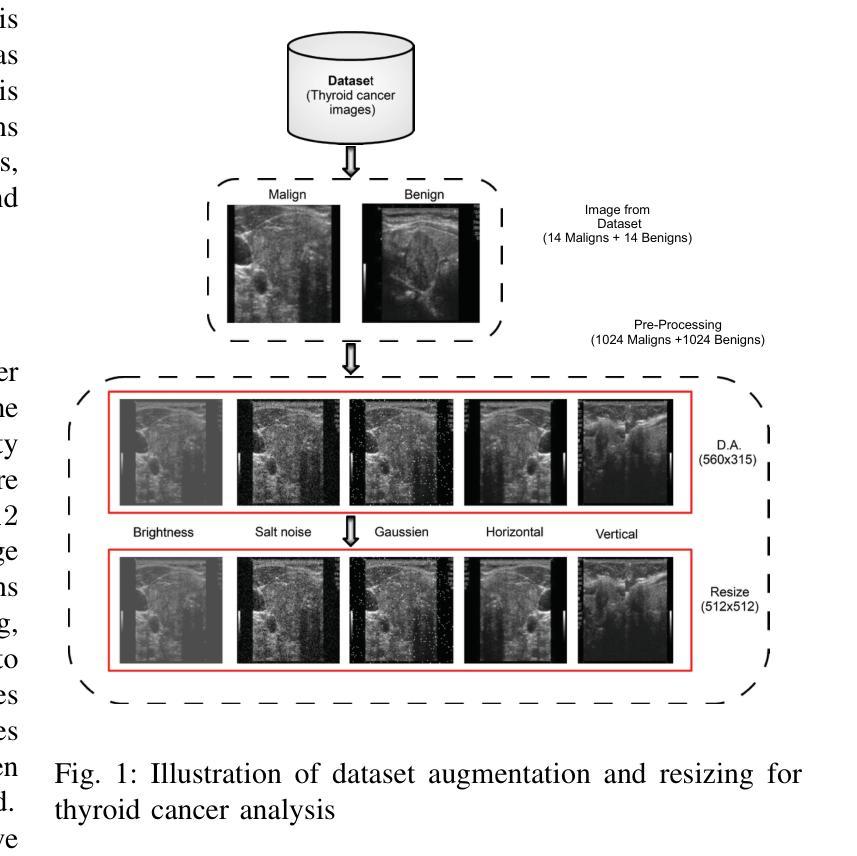
A Novel Hybrid Deep Learning and Chaotic Dynamics Approach for Thyroid Cancer Classification
Authors:Nada Bouchekout, Abdelkrim Boukabou, Morad Grimes, Yassine Habchi, Yassine Himeur, Hamzah Ali Alkhazaleh, Shadi Atalla, Wathiq Mansoor
Timely and accurate diagnosis is crucial in addressing the global rise in thyroid cancer, ensuring effective treatment strategies and improved patient outcomes. We present an intelligent classification method that couples an Adaptive Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) with Cohen-Daubechies-Feauveau (CDF9/7) wavelets whose detail coefficients are modulated by an n-scroll chaotic system to enrich discriminative features. We evaluate on the public DDTI thyroid ultrasound dataset (n = 1,638 images; 819 malignant / 819 benign) using 5-fold cross-validation, where the proposed method attains 98.17% accuracy, 98.76% sensitivity, 97.58% specificity, 97.55% F1-score, and an AUC of 0.9912. A controlled ablation shows that adding chaotic modulation to CDF9/7 improves accuracy by +8.79 percentage points over a CDF9/7-only CNN (from 89.38% to 98.17%). To objectively position our approach, we trained state-of-the-art backbones on the same data and splits: EfficientNetV2-S (96.58% accuracy; AUC 0.987), Swin-T (96.41%; 0.986), ViT-B/16 (95.72%; 0.983), and ConvNeXt-T (96.94%; 0.987). Our method outperforms the best of these by +1.23 points in accuracy and +0.0042 in AUC, while remaining computationally efficient (28.7 ms per image; 1,125 MB peak VRAM). Robustness is further supported by cross-dataset testing on TCIA (accuracy 95.82%) and transfer to an ISIC skin-lesion subset (n = 28 unique images, augmented to 2,048; accuracy 97.31%). Explainability analyses (Grad-CAM, SHAP, LIME) highlight clinically relevant regions. Altogether, the wavelet-chaos-CNN pipeline delivers state-of-the-art thyroid ultrasound classification with strong generalization and practical runtime characteristics suitable for clinical integration.
面对甲状腺癌全球发病率的上升,及时准确的诊断至关重要,它能确保有效的治疗策略和改善患者预后。我们提出了一种智能分类方法,它将自适应卷积神经网络(CNN)与Cohen-Daubechies-Feauveau(CDF9/7)小波相结合,其细节系数由n滚动混沌系统调制,以丰富判别特征。我们在公共DDTI甲状腺超声数据集(n=1638张图像;其中恶性819张,良性819张)上进行了五折交叉验证评估,该方法达到了98.17%的准确率、98.76%的灵敏度、97.58%的特异度、97.55%的F1得分和0.9912的AUC值。受控消融实验表明,在CDF9/7中加入混沌调制可提高准确率+提高了与只有CDF的CNN相比增加了百分之8.79个点(从百分之提高到百分之),我们比较了当前先进的骨干网络在同一数据集上的表现:EfficientNetV2-S(准确率百分之;AUC百分之),Swin-T(百分之;AUC百分之),ViT-B/16(准确率百分之;AUC百分之),以及ConvNeXt-T(准确率百分之;AUC百分之)。我们的方法在准确率和AUC方面分别优于最佳模型加上几点。我们的方法虽然运算效率极高,每张图片仅需约进行一步的计算并能在几秒钟内获得预测结果),但仍具有良好的计算性能峰值内存使用量为峰值),这为临床应用提供了良好的运行特性支持。在跨数据集测试上表现稳健,如在TCIA上的准确率达到了百分之在皮肤病变子集上的转移也取得了良好的表现(准确率为百分之,该子集由唯一的皮肤病变图像组成)。解释性分析(包括Grad-CAM、SHAP和LIME)突出了临床相关的区域。综上所述,小波混沌CNN管道提供了具有强大泛化能力的甲状腺超声分类,并具备适合临床整合的实际运行特性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Scientific Reports
Summary
本研究提出了一种智能分类方法,结合自适应卷积神经网络(CNN)与CDF9/7小波和混沌系统调制,以识别甲状腺癌图像特征。在公开DDTI甲状腺超声数据集上的评估表明,该方法准确性高,具有良好的敏感性和特异性,且具有良好的泛化能力。相较于其他先进模型,本研究方法在计算效率和准确性方面表现更佳。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了一种基于自适应卷积神经网络(CNN)与CDF9/7小波结合的方法,用于甲状腺癌图像分类。
- 通过引入混沌系统调制,增强了特征的判别能力。
- 在DDTI甲状腺超声数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法具有较高的准确性、敏感性和特异性。
- 与其他先进模型相比,本研究方法在准确性方面表现出优势。
- 该方法具有良好的泛化能力,能够在不同数据集上实现稳健的性能。
- 方法的计算效率高,适用于临床应用。
点此查看论文截图
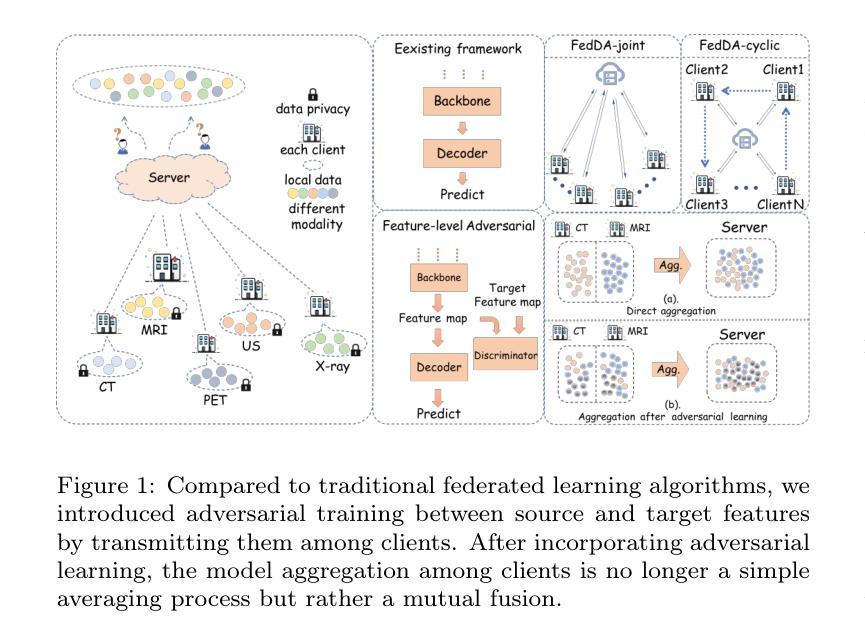
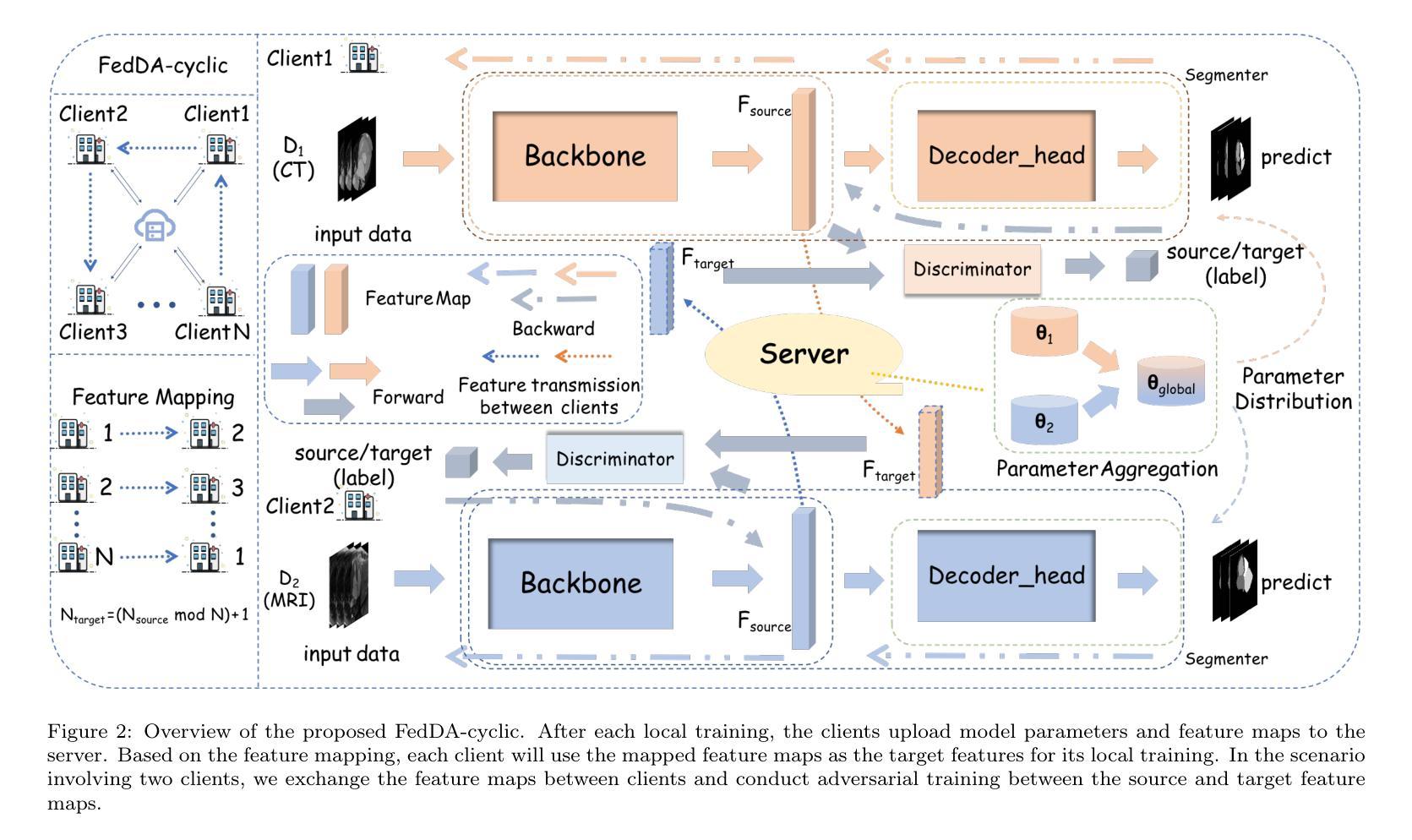
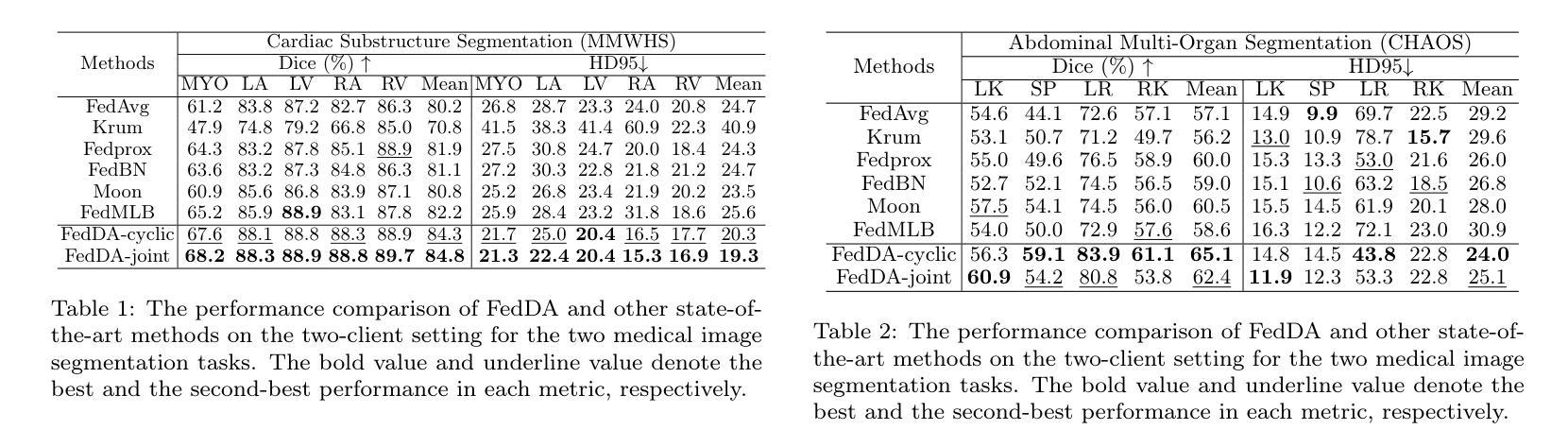
Adversarial Versus Federated: An Adversarial Learning based Multi-Modality Cross-Domain Federated Medical Segmentation
Authors:You Zhou, Lijiang Chen, Shuchang Lyu, Guangxia Cui, Wenpei Bai, Zheng Zhou, Meng Li, Guangliang Cheng, Huiyu Zhou, Qi Zhao
Federated learning enables collaborative training of machine learning models among different clients while ensuring data privacy, emerging as the mainstream for breaking data silos in the healthcare domain. However, the imbalance of medical resources, data corruption or improper data preservation may lead to a situation where different clients possess medical images of different modality. This heterogeneity poses a significant challenge for cross-domain medical image segmentation within the federated learning framework. To address this challenge, we propose a new Federated Domain Adaptation (FedDA) segmentation training framework. Specifically, we propose a feature-level adversarial learning among clients by aligning feature maps across clients through embedding an adversarial training mechanism. This design can enhance the model’s generalization on multiple domains and alleviate the negative impact from domain-shift. Comprehensive experiments on three medical image datasets demonstrate that our proposed FedDA substantially achieves cross-domain federated aggregation, endowing single modality client with cross-modality processing capabilities, and consistently delivers robust performance compared to state-of-the-art federated aggregation algorithms in objective and subjective assessment. Our code are available at https://github.com/GGbond-study/FedDA.
联邦学习能够在不同客户端之间进行机器学习模型的协同训练,同时确保数据隐私,成为医疗保健领域中打破数据孤岛的主流方法。然而,医疗资源的不平衡、数据损坏或不当的数据保存可能导致不同客户端拥有不同模态的医疗图像。这种异质性给联邦学习框架内的跨域医学图像分割带来了重大挑战。为解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种新的联邦域适应(FedDA)分割训练框架。具体来说,我们通过嵌入对抗训练机制,在客户端之间实现特征级别的对抗性学习,通过对齐客户端之间的特征图。这种设计可以增强模型在多域上的泛化能力,减轻域偏移的负面影响。在三个医学图像数据集上的综合实验表明,我们提出的FedDA实质地实现了跨域联邦聚合,赋予单模态客户端跨模态处理能力,与最新的联邦聚合算法相比,在客观和主观评估中均表现出稳健的性能。我们的代码可在https://github.com/GGbond-study/FedDA访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
联邦学习实现了不同客户端间的机器学习模型协同训练,同时保证了数据隐私,已成为打破医疗领域数据孤岛的主流方法。然而,医疗资源的不平衡、数据污染或数据保存不当可能导致不同客户端拥有不同模态的医疗图像,给联邦学习框架下的跨域医学图像分割带来重大挑战。为解决这一问题,我们提出了全新的联邦域适应(FedDA)分割训练框架,通过在客户端间进行特征级对抗性学习,通过对齐特征映射嵌入对抗训练机制,增强模型在多域上的泛化能力,减轻域偏移的负面影响。在三个医学图像数据集上的综合实验表明,我们提出的FedDA实现了跨域联邦聚合,赋予单模态客户端跨模态处理能力,与最先进的联邦聚合算法相比,在客观和主观评估中表现稳健。
Key Takeaways
- 联邦学习已成为医疗领域打破数据孤岛的主流方法,能够协同训练机器学习模型并保证数据隐私。
- 不同客户端医疗资源的差异可能导致拥有不同模态的医疗图像,给医学图像分割带来挑战。
- 提出的联邦域适应(FedDA)分割训练框架通过特征级对抗性学习增强模型在多域上的泛化能力。
- FedDA实现了跨域联邦聚合,单模态客户端具备跨模态处理能力。
- FedDA在客观和主观评估中表现稳健,相较于其他联邦聚合算法有优势。
- 联邦域适应方法的实现细节和效果通过三个医学图像数据集的综合实验得到验证。
点此查看论文截图