⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-01 更新
Perceive, Reflect and Understand Long Video: Progressive Multi-Granular Clue Exploration with Interactive Agents
Authors:Jiahua Li, Kun Wei, Zhe Xu, Zibo Su, Xu Yang, Cheng Deng
Long videos, characterized by temporal complexity and sparse task-relevant information, pose significant reasoning challenges for AI systems. Although various Large Language Model (LLM)-based approaches have advanced long video understanding, they still struggle to achieve both completeness and efficiency in capturing task-critical information. Inspired by human progressive visual cognition, we propose CogniGPT, a framework that leverages an interactive loop between Multi-Granular Perception Agent (MGPA) and Verification-Enhanced Reflection Agent (VERA) for efficient and reliable long video understanding. Specifically, MGPA mimics human visual divergent and focused attention to capture task-related information, while VERA verifies perceived key clues to mitigate hallucination and optimize subsequent perception strategies. Through this interactive process, CogniGPT explores a minimal set of informative and reliable task-related clues. Extensive experiments on EgoSchema, Video-MME, NExT-QA, and MovieChat datasets demonstrate CogniGPT’s superiority in both accuracy and efficiency. Notably, on EgoSchema, it surpasses existing training-free methods using only 11.2 frames and achieves performance comparable to Gemini 1.5-Pro.
长视频具有时间复杂性和稀疏的任务相关信息,为AI系统带来了重大的推理挑战。尽管基于大型语言模型(LLM)的各种方法已经推动了长视频理解的发展,但它们仍然难以在捕获任务关键信息时同时实现完整性和效率。受人类渐进式视觉认知的启发,我们提出了CogniGPT框架,它利用多粒度感知代理(MGPA)和增强验证反射代理(VERA)之间的交互循环,实现高效可靠的长视频理解。具体来说,MGPA模仿人类的视觉发散和集中注意力来捕获与任务相关的信息,而VERA验证感知到的关键线索,以减轻幻觉并优化随后的感知策略。通过这一交互过程,CogniGPT探索了一组信息丰富且可靠的任务相关线索。在EgoSchema、Video-MME、NExT-QA和MovieChat数据集上的大量实验表明,CogniGPT在准确性和效率方面都表现出卓越的性能。值得注意的是,在EgoSchema上,它仅使用11.2帧超越了现有的无训练方法,并实现了与Gemini 1.5-Pro相当的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
长视频由于时间复杂度高且任务相关信息稀疏,给AI系统带来推理挑战。尽管基于大型语言模型(LLM)的方法已经促进了长视频理解的发展,但它们仍难以在捕捉任务关键信息时同时实现完整性和效率。受人类渐进式视觉认知的启发,我们提出了CogniGPT框架,它通过多粒度感知代理(MGPA)和验证增强反射代理(VERA)之间的交互循环,实现高效可靠的长视频理解。具体来说,MGPA模仿人类的视觉发散和集中注意力来捕捉任务相关信息,而VERA验证感知到的关键线索,以减轻幻觉并优化后续的感知策略。通过这一交互过程,CogniGPT探索了少量信息丰富且可靠的与任务相关的线索。在EgoSchema、Video-MME、NExT-QA和MovieChat数据集上的大量实验表明,CogniGPT在准确性和效率上均表现出卓越的性能。特别是在EgoSchema数据集上,它仅使用11.2帧超越了现有的无训练方法,并实现了与Gemini 1.5-Pro相当的性能。
关键见解
- 长视频具有时间复杂度高和信息稀疏的特点,对AI系统的推理能力构成挑战。
- 当前基于大型语言模型(LLM)的方法在长视频理解上虽有所进展,但在捕捉任务关键信息的完整性和效率上仍有待提高。
- CogniGPT框架通过模拟人类渐进式视觉认知过程来提高长视频理解效率和可靠性。
- CogniGPT包含两个核心组件:多粒度感知代理(MGPA)和验证增强反射代理(VERA)。MGPA模仿人类视觉注意力机制捕捉任务相关信息,而VERA负责验证感知到的关键线索。
- 通过交互循环,CogniGPT能够探索信息丰富且可靠的与任务相关的线索。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,CogniGPT在视频理解任务的准确性和效率上表现优越。
点此查看论文截图
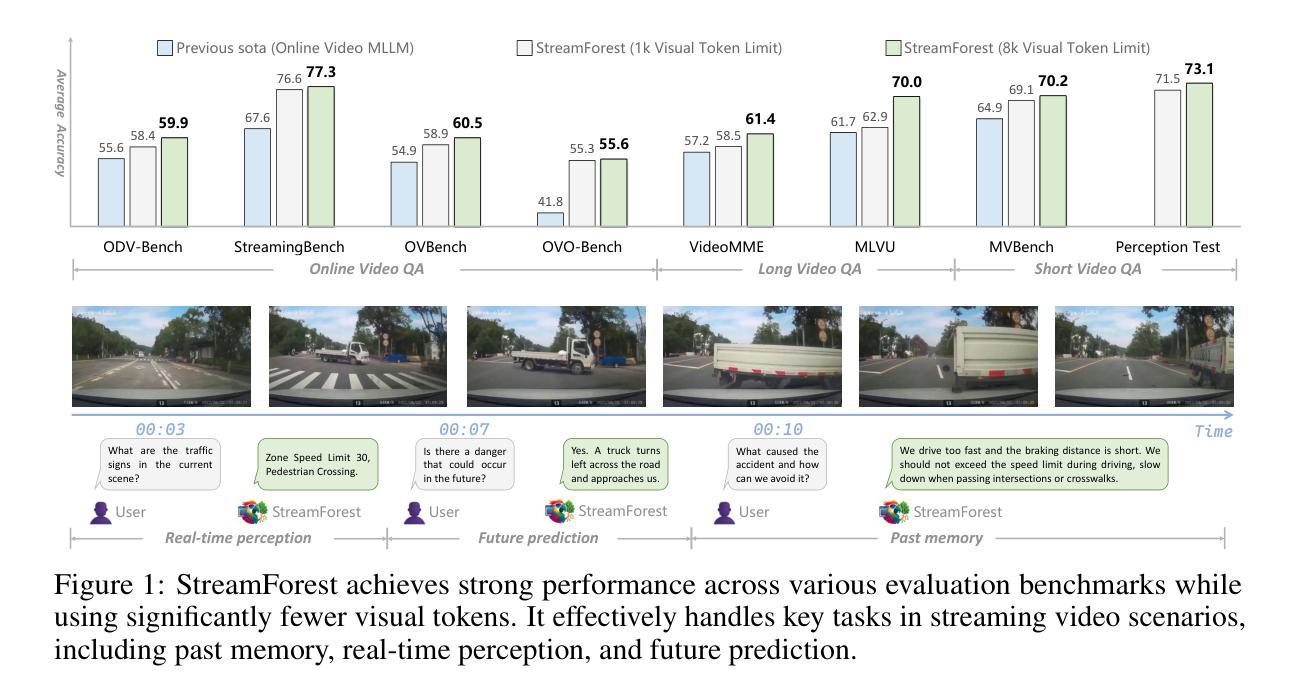
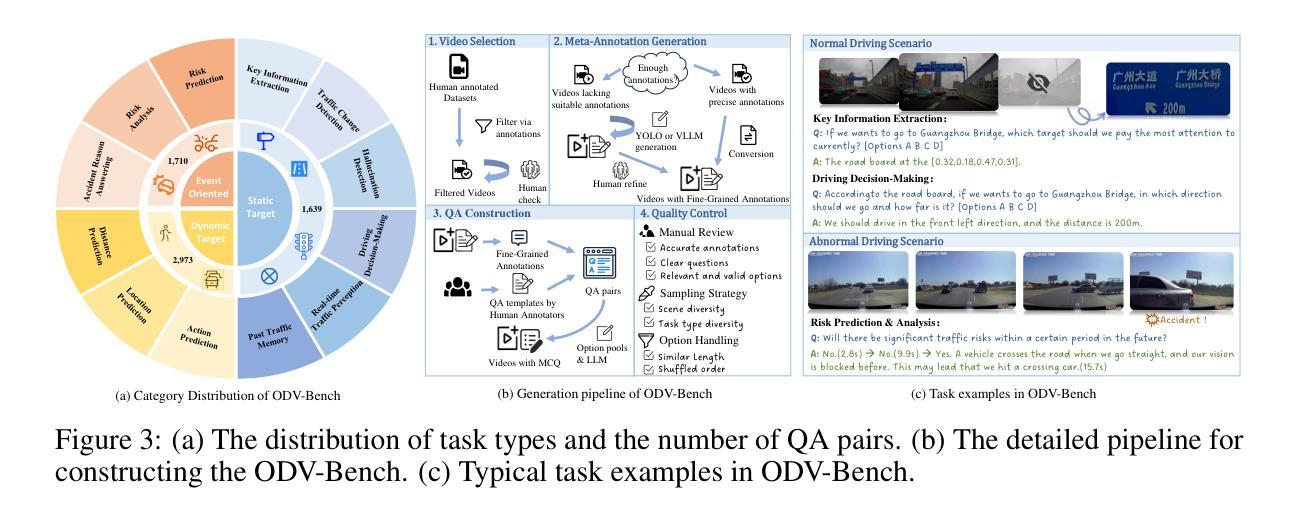
StreamForest: Efficient Online Video Understanding with Persistent Event Memory
Authors:Xiangyu Zeng, Kefan Qiu, Qingyu Zhang, Xinhao Li, Jing Wang, Jiaxin Li, Ziang Yan, Kun Tian, Meng Tian, Xinhai Zhao, Yi Wang, Limin Wang
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have recently achieved remarkable progress in video understanding. However, their effectiveness in real-time streaming scenarios remains limited due to storage constraints of historical visual features and insufficient real-time spatiotemporal reasoning. To address these challenges, we propose StreamForest, a novel architecture specifically designed for streaming video understanding. Central to StreamForest is the Persistent Event Memory Forest, a memory mechanism that adaptively organizes video frames into multiple event-level tree structures. This process is guided by penalty functions based on temporal distance, content similarity, and merge frequency, enabling efficient long-term memory retention under limited computational resources. To enhance real-time perception, we introduce a Fine-grained Spatiotemporal Window, which captures detailed short-term visual cues to improve current scene perception. Additionally, we present OnlineIT, an instruction-tuning dataset tailored for streaming video tasks. OnlineIT significantly boosts MLLM performance in both real-time perception and future prediction. To evaluate generalization in practical applications, we introduce ODV-Bench, a new benchmark focused on real-time streaming video understanding in autonomous driving scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that StreamForest achieves the state-of-the-art performance, with accuracies of 77.3% on StreamingBench, 60.5% on OVBench, and 55.6% on OVO-Bench. In particular, even under extreme visual token compression (limited to 1024 tokens), the model retains 96.8% of its average accuracy in eight benchmarks relative to the default setting. These results underscore the robustness, efficiency, and generalizability of StreamForest for streaming video understanding.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视频理解方面最近取得了显著的进步。然而,它们在实时流媒体场景中的有效性仍然有限,主要是由于历史视觉特征的存储约束和实时时空推理的不足。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了专门用于流媒体视频理解的全新架构StreamForest。StreamForest的核心是持久事件记忆森林(Persistent Event Memory Forest),这是一种记忆机制,能够自适应地将视频帧组织成多个事件级别的树结构。这一过程由基于时间距离、内容相似性和合并频率的惩罚函数引导,能够在有限的计算资源下实现高效的长效记忆保留。为了提高实时感知能力,我们引入了精细时空窗口(Fine-grained Spatiotemporal Window),它捕捉短期视觉线索,以提高对当前场景的感知。此外,我们还推出了OnlineIT,这是一个专为流媒体视频任务定制的指令调整数据集。OnlineIT显著提升了MLLM在实时感知和未来预测方面的性能。为了评估在实际应用中的泛化能力,我们引入了ODV-Bench,这是一个专注于自动驾驶场景中实时流媒体视频理解的新基准测试。实验结果表明,StreamForest达到了最先进的性能,在StreamingBench上的准确率为77.3%,在OVBench上为60.5%,在OVO-Bench上为55.6%。即使在极端视觉令牌压缩(限制为1024个令牌)下,该模型在八个基准测试中的平均准确率仍保持在默认设置的96.8%。这些结果证明了StreamForest在流媒体视频理解方面的稳健性、效率和泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as a Spotlight at NeurIPS 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对流媒体视频理解的最新研究成果。研究人员提出了StreamForest架构,包含Persistent Event Memory Forest和Fine-grained Spatiotemporal Window两大核心组件,并引入了OnlineIT数据集和ODV-Bench基准测试。实验结果显示,StreamForest在实时流媒体视频理解方面达到了领先水平,展现了其在处理压缩视觉令牌情况下的稳健性和效率。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视频理解方面取得了显著进展,但在实时流媒体场景中的有效性受限。
- StreamForest架构通过Persistent Event Memory Forest处理视频帧,形成事件级树结构,以优化长期内存保留并降低计算资源需求。
- Fine-grained Spatiotemporal Window能捕捉短期视觉线索,提高当前场景感知的实时性。
- OnlineIT数据集针对流媒体视频任务定制,显著提升了MLLM的性能。
- ODV-Bench基准测试专注于自动驾驶场景的实时流媒体视频理解评估。
- StreamForest在多个基准测试中实现了先进性能,并在极端视觉令牌压缩条件下仍能保持高准确率。
点此查看论文截图

LOVE-R1: Advancing Long Video Understanding with an Adaptive Zoom-in Mechanism via Multi-Step Reasoning
Authors:Shenghao Fu, Qize Yang, Yuan-Ming Li, Xihan Wei, Xiaohua Xie, Wei-Shi Zheng
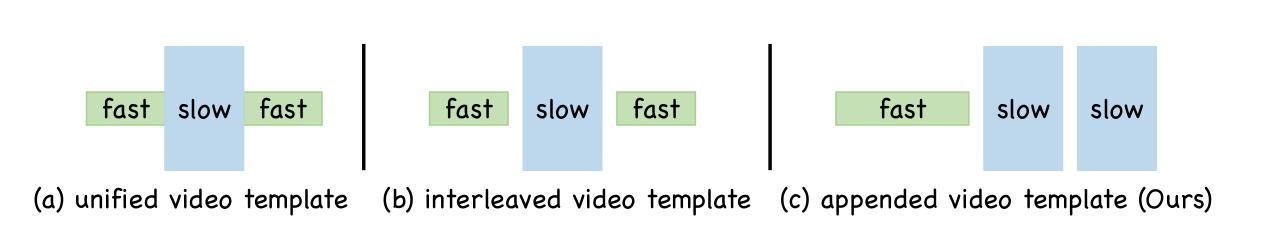
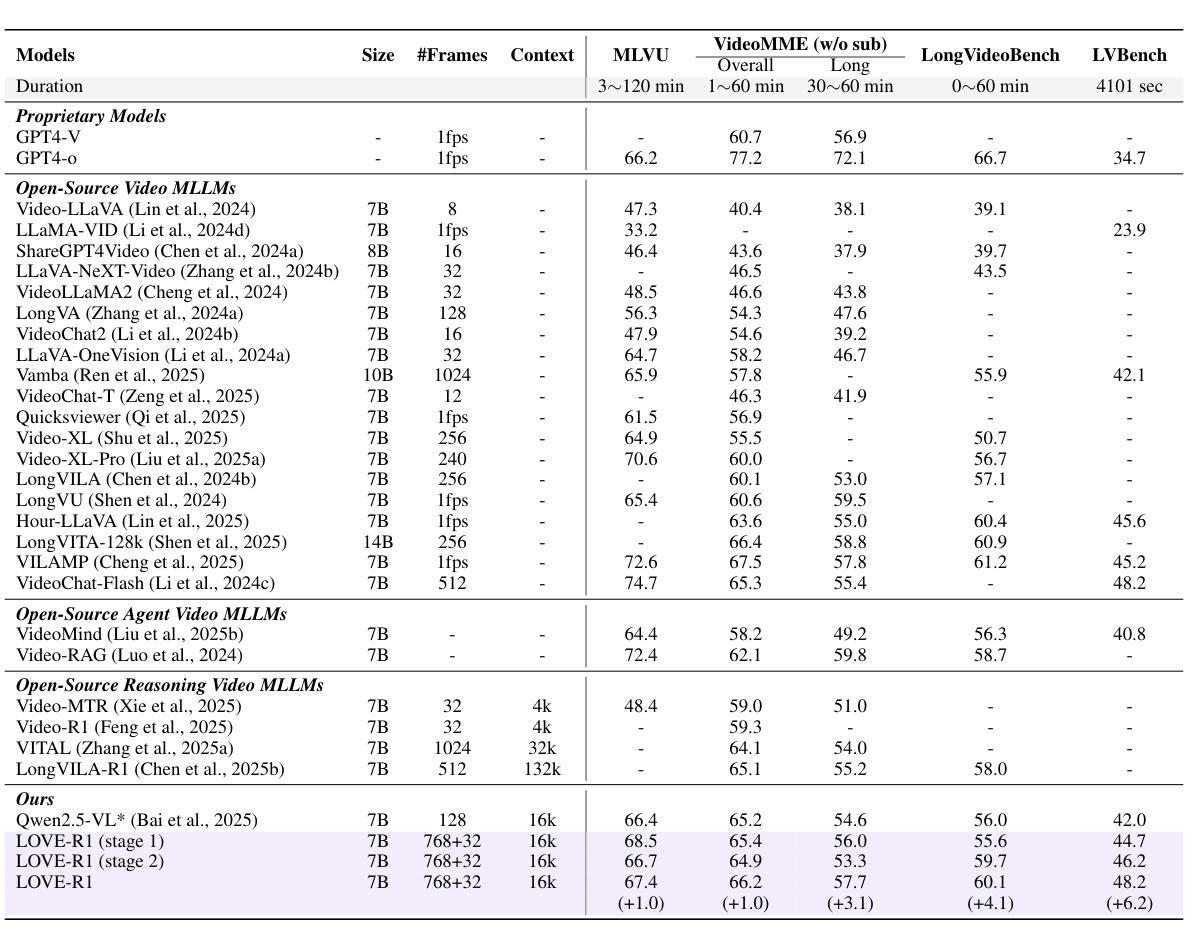
Long video understanding is still challenging for recent Large Video-Language Models (LVLMs) due to the conflict between long-form temporal understanding and detailed spatial perception. LVLMs with a uniform frame sampling mechanism, which samples frames with an equal frame size and fixed sampling rate, inevitably sacrifice either temporal clues or spatial details, resulting in suboptimal solutions. To mitigate this dilemma, we propose LOVE-R1, a model that can adaptively zoom in on a video clip. The model is first provided with densely sampled frames but in a small resolution. If some spatial details are needed, the model can zoom in on a clip of interest with a large frame resolution based on its reasoning until key visual information is obtained. The whole process is implemented as a multi-step reasoning process. To train the reasoning ability, we first finetune the model on our collected 38k high-quality CoT data and enhance it with decoupled reinforcement finetuning. As outcome rewards can not provide fine-grained process supervision, we decouple multi-step reasoning into multiple single-step reasoning and optimize the internal zoom-in ability explicitly. Experiments on long video understanding benchmarks show that our model with the slow-fast adaptive frame sampling mechanism achieves a great trade-off between sampling density and frame resolutions, and LOVE-R1 outperforms our baseline Qwen2.5-VL by an average of 3.1% points across 4 common long video understanding benchmarks.
长时间视频理解对于最近的大型视频语言模型(LVLMs)来说仍然是一个挑战,这是由于长时临时理解和详细空间感知之间的冲突导致的。具有统一框架采样机制的LVLMs以等大的框架尺寸和固定的采样率对框架进行采样,这不可避免地会牺牲时间线索或空间细节,导致次优解决方案。为了缓解这一困境,我们提出了LOVE-R1模型,该模型可以自适应地对视频片段进行放大。该模型首先以密集采样的方式获得小分辨率的框架。如果需要某些空间细节,模型可以根据推理放大感兴趣片段的视野,直到获得关键视觉信息。整个过程被实现为一个多步推理过程。为了训练模型的推理能力,我们首先使用收集的3.8万条高质量CoT数据进行微调,并使用解耦强化微调来增强模型的能力。由于结果奖励无法提供精细的过程监督,我们将多步推理解耦为多个单步推理,并显式优化内部放大能力。在长时间视频理解基准测试上的实验表明,我们的模型采用了快慢自适应框架采样机制,在采样密度和框架分辨率之间取得了很好的平衡,LOVE-R1在四个常见的长时间视频理解基准测试上的表现优于我们的基线Qwen2.5-VL,平均高出3.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了大型视频语言模型(LVLMs)在处理长视频理解时面临的挑战,包括长形式时间理解与详细空间感知之间的冲突。针对这一问题,提出了一种名为LOVE-R1的模型,该模型能够自适应地对视频片段进行缩放。该模型首先接受密集采样的低分辨率帧,根据需要空间细节,可以基于推理对感兴趣的片段进行高分辨率缩放,直至获取关键视觉信息。整个过程被实现为一个多步骤推理过程。通过收集的高质量的认知诊断数据(CoT)对模型进行微调,并通过解耦强化微调来提高其推理能力。在标准的长视频理解测试中,具有快慢自适应帧采样机制的LOVE-R1模型实现了采样密度与帧分辨率之间的良好平衡,并相较于基准模型Qwen2.5-VL有显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视频语言模型(LVLMs)在长视频理解上仍面临挑战,主要是长形式时间理解与详细空间感知之间的冲突。
- 当前采用均匀框架采样机制的LVLMs可能会在获取时间线索和空间细节上有所牺牲,导致结果不理想。
- LOVE-R1模型通过自适应缩放视频片段来解决这一问题,可以在获取关键视觉信息的同时保持对时间和空间的全面理解。
- 模型首先接受密集采样的低分辨率帧,根据需要逐步放大分辨率。
- 整个过程被构建为一个多步骤推理过程,增强了模型的推理能力。
- 使用收集的高质量认知诊断数据(CoT)进行微调,并通过解耦强化微调进一步提高性能。
点此查看论文截图

NeMo: Needle in a Montage for Video-Language Understanding
Authors:Zi-Yuan Hu, Shuo Liang, Duo Zheng, Yanyang Li, Yeyao Tao, Shijia Huang, Wei Feng, Jia Qin, Jianguang Yu, Jing Huang, Meng Fang, Yin Li, Liwei Wang
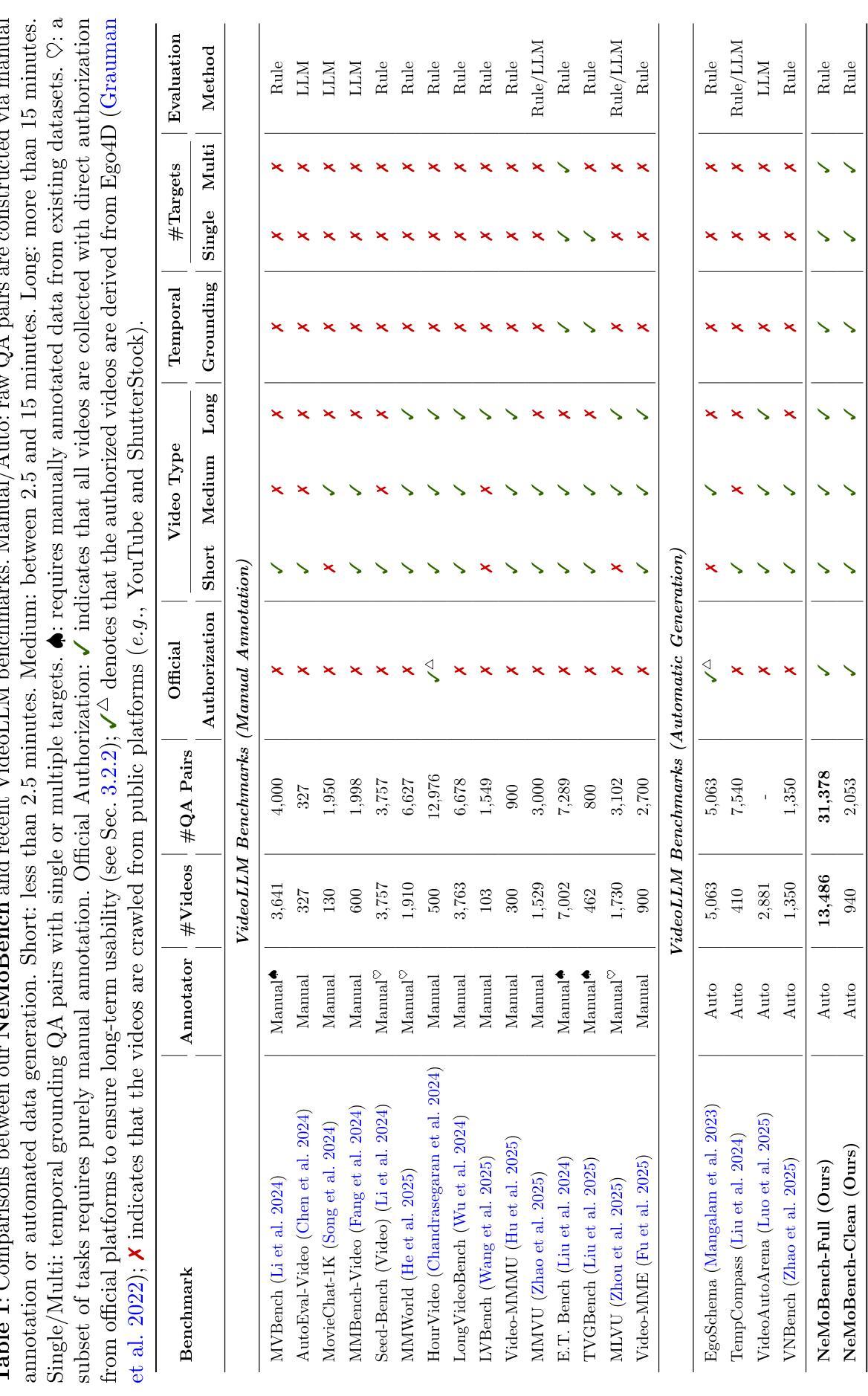
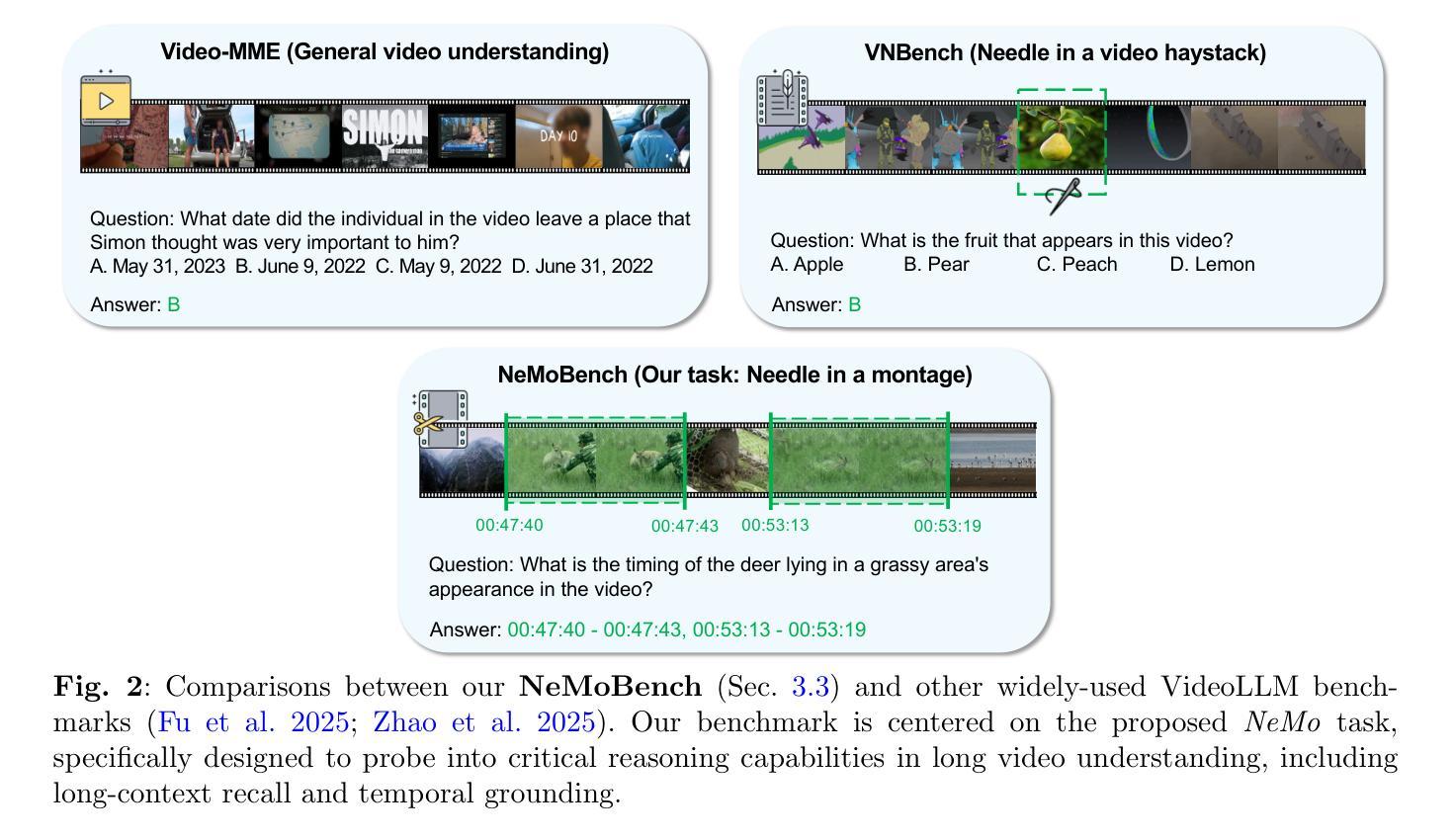
Recent advances in video large language models (VideoLLMs) call for new evaluation protocols and benchmarks for complex temporal reasoning in video-language understanding. Inspired by the needle in a haystack test widely used by LLMs, we introduce a novel task of Needle in a Montage (NeMo), designed to assess VideoLLMs’ critical reasoning capabilities, including long-context recall and temporal grounding. To generate video question answering data for our task, we develop a scalable automated data generation pipeline that facilitates high-quality data synthesis. Built upon the proposed pipeline, we present NeMoBench, a video-language benchmark centered on our task. Specifically, our full set of NeMoBench features 31,378 automatically generated question-answer (QA) pairs from 13,486 videos with various durations ranging from seconds to hours. Experiments demonstrate that our pipeline can reliably and automatically generate high-quality evaluation data, enabling NeMoBench to be continuously updated with the latest videos. We evaluate 20 state-of-the-art models on our benchmark, providing extensive results and key insights into their capabilities and limitations. Our project page is available at: https://lavi-lab.github.io/NeMoBench.
近年来,视频大型语言模型(VideoLLMs)的最新进展要求对视频语言理解中的复杂时间推理进行新的评估协议和基准测试。受广泛使用的“沙里淘金”测试的启发,我们介绍了一种名为“动态画面中找针(NeMo)”的新任务,旨在评估VideoLLMs的关键推理能力,包括长上下文回忆和时间定位。为了为我们的任务生成视频问答数据,我们开发了一个可扩展的自动化数据生成管道,便于高质量数据的合成。基于提出的管道,我们推出了以我们的任务为中心的NeMoBench视频语言基准测试。具体来说,我们的NeMoBench全套功能包含从13486个视频中自动生成的31378个问答对,这些视频时长各异,从几秒到几小时不等。实验表明,我们的管道能够可靠地自动生成高质量评估数据,使NeMoBench能够持续更新最新的视频。我们在基准测试上评估了20个最新模型,提供了关于它们能力和局限性的广泛结果和关键见解。我们的项目页面可访问于:https://lavi-lab.github.io/NeMoBench。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视频大语言模型(VideoLLM)的最新进展要求对视频语言理解的复杂时间推理有新的评估协议和基准测试。我们借鉴了LLM广泛使用的“大海捞针”测试,引入了一项名为“蒙太奇中的针”(NeMo)的新任务,旨在评估VideoLLM的关键推理能力,包括长语境回忆和时间定位。为了生成我们的任务所需的视频问答数据,我们开发了一个可扩展的自动化数据生成管道,以促进高质量数据的合成。基于该管道,我们推出了以NeMo任务为中心的NeMoBench视频语言基准测试。具体来说,NeMoBench全套功能包含来自13486个视频的自动生成的31378个问答对,视频时长从几秒到几小时不等。实验证明,我们的管道可以可靠地自动生成高质量的评价数据,使NeMoBench能够不断更新最新的视频。我们在该基准测试上评估了20个最先进模型,并对其性能和局限性提供了深入了解。项目页面位于:[链接](https://lavi-lab.github.io/NeMoBench)。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一项新的任务“蒙太奇中的针”(NeMo),旨在评估视频大语言模型(VideoLLM)的关键推理能力。
- 设计了自动化数据生成管道,用于生成高质量的视频问答数据。
- 推出了NeMoBench视频语言基准测试,以评估VideoLLM在复杂时间推理方面的性能。
- NeMoBench包含来自不同时长的视频的大量问答对数据。
- 自动化数据生成管道能够可靠地生成高质量的评价数据,并支持基准测试的持续更新。
- 在NeMoBench上评估了多个先进模型,并提供了性能洞察。
点此查看论文截图

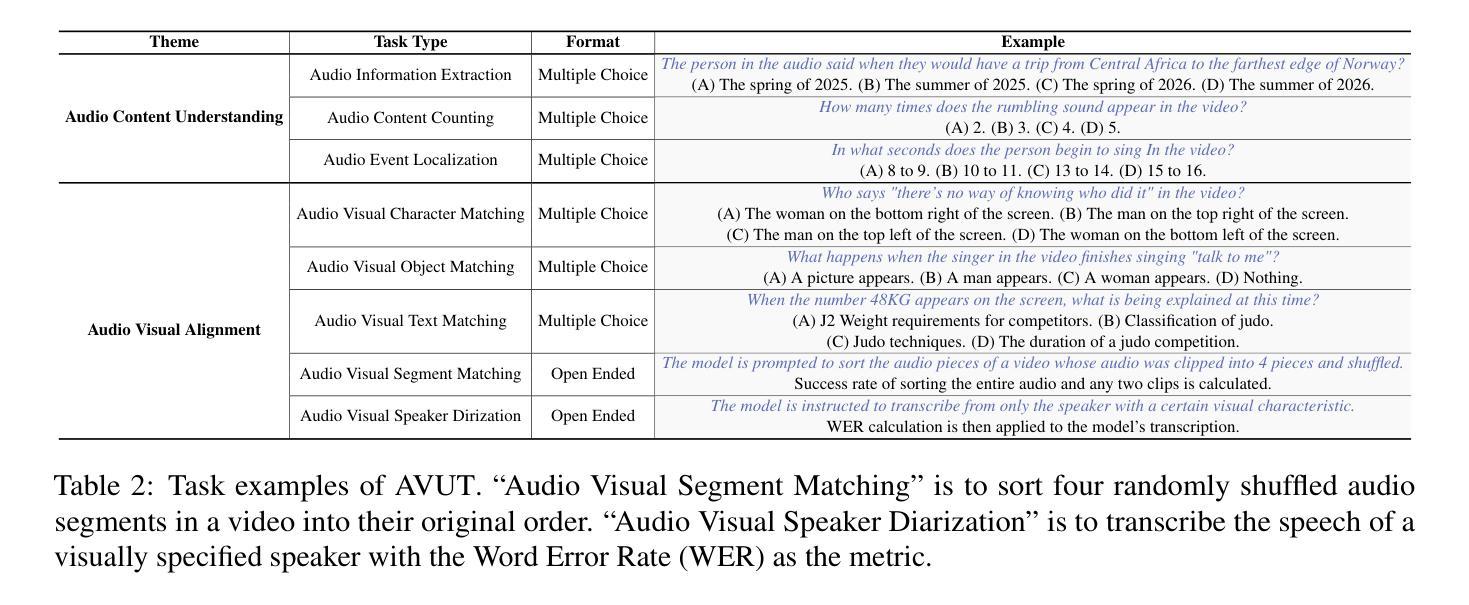
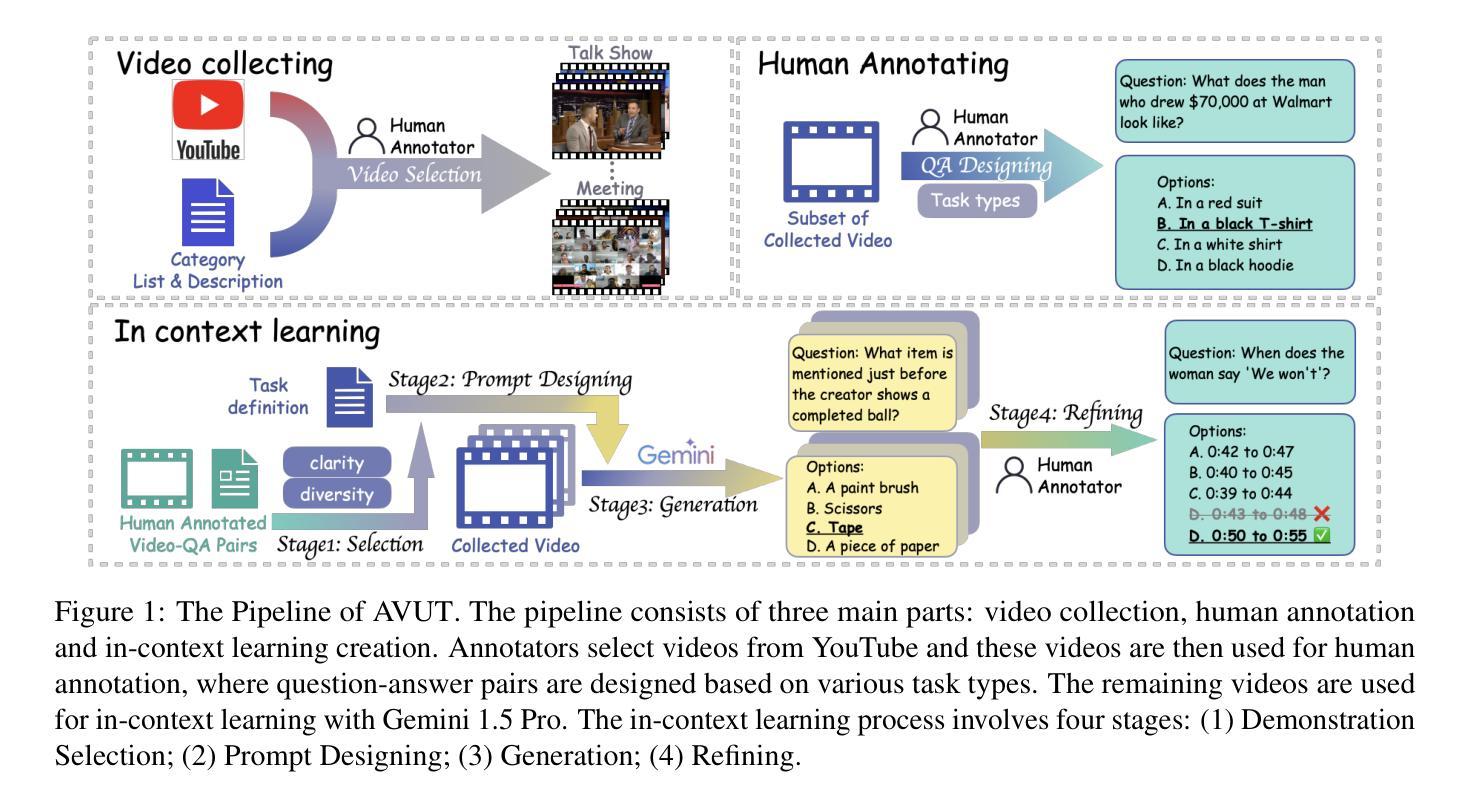
Audio-centric Video Understanding Benchmark without Text Shortcut
Authors:Yudong Yang, Jimin Zhuang, Guangzhi Sun, Changli Tang, Yixuan Li, Peihan Li, Yifan Jiang, Wei Li, Zejun Ma, Chao Zhang
Audio often serves as an auxiliary modality in video understanding tasks of audio-visual large language models (LLMs), merely assisting in the comprehension of visual information. However, a thorough understanding of videos significantly depends on auditory information, as audio offers critical context, emotional cues, and semantic meaning that visual data alone often lacks. This paper proposes an audio-centric video understanding benchmark (AVUT) to evaluate the video comprehension capabilities of multimodal LLMs with a particular focus on auditory information. AVUT introduces a suite of carefully designed audio-centric tasks, holistically testing the understanding of both audio content and audio-visual interactions in videos. Moreover, this work points out the text shortcut problem that largely exists in other benchmarks where the correct answer can be found from question text alone without needing videos. AVUT addresses this problem by proposing a answer permutation-based filtering mechanism. A thorough evaluation across a diverse range of open-source and proprietary multimodal LLMs is performed, followed by the analyses of deficiencies in audio-visual LLMs. Demos and data are available at https://github.com/lark-png/AVUT.
音频通常作为视听大型语言模型(LLM)的视频理解任务的辅助模态,仅帮助理解视觉信息。然而,对视频的深入理解在很大程度上依赖于音频信息,因为音频提供了关键上下文、情感线索和语义含义,而这些通常是视觉数据所缺乏的。本文提出了一个以音频为中心的视频理解基准测试(AVUT),旨在评估多模态LLM的视频理解能力,特别是其对音频信息的关注。AVUT引入了一系列精心设计的以音频为中心的任务,全面测试视频中的音频内容和视听交互的理解能力。此外,本文指出了在其他基准测试中大量存在的文本捷径问题,即正确答案仅存在于问题文本中,而无需观看视频。AVUT通过提出一种基于答案排列的过滤机制来解决这个问题。对一系列开源和专有的多模态LLM进行了全面评估,并对视听LLM的缺陷进行了分析。Demo和数据可在https://github.com/lark-png/AVUT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in the Proceedings of EMNLP 2025 (Main Conference)
Summary
这篇论文提出了一种以音频为中心的视频理解基准测试(AVUT),旨在评估多模态大型语言模型对视频的理解能力,特别关注音频信息。AVUT设计了一系列音频为中心的任务,全面测试模型对视频音频内容和视听交互的理解。同时,该论文也指出了现有基准测试中存在文本捷径问题,并提供了基于答案置换的过滤机制来解决这一问题。
Key Takeaways
- 音频在视频理解任务中扮演重要角色,提供关键上下文、情感线索和语义意义。
- 论文提出了一种新的视频理解基准测试(AVUT),专注于评估多模态大型语言模型对音频信息的理解能力。
- AVUT设计了一系列音频为中心的任务,测试模型对视频音频内容和视听交互的理解。
- 现有基准测试存在文本捷径问题,AVUT提出了基于答案置换的过滤机制来解决此问题。
- AVUT评估了多种开源和专有多模态大型语言模型的表现。
- 该论文分析了音频视觉大型语言模型的缺陷。
点此查看论文截图