⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-01 更新
Triangle Splatting+: Differentiable Rendering with Opaque Triangles
Authors:Jan Held, Renaud Vandeghen, Sanghyun Son, Daniel Rebain, Matheus Gadelha, Yi Zhou, Ming C. Lin, Marc Van Droogenbroeck, Andrea Tagliasacchi
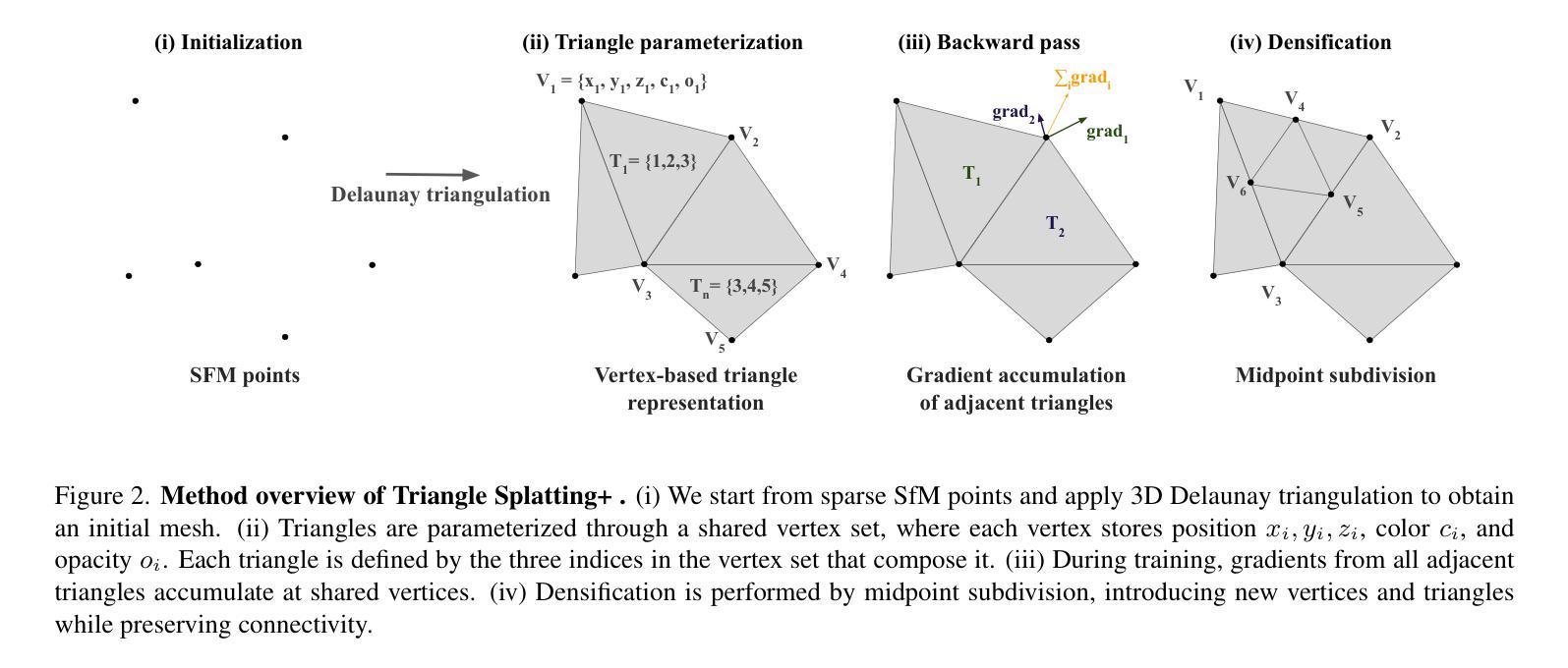
Reconstructing 3D scenes and synthesizing novel views has seen rapid progress in recent years. Neural Radiance Fields demonstrated that continuous volumetric radiance fields can achieve high-quality image synthesis, but their long training and rendering times limit practicality. 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) addressed these issues by representing scenes with millions of Gaussians, enabling real-time rendering and fast optimization. However, Gaussian primitives are not natively compatible with the mesh-based pipelines used in VR headsets, and real-time graphics applications. Existing solutions attempt to convert Gaussians into meshes through post-processing or two-stage pipelines, which increases complexity and degrades visual quality. In this work, we introduce Triangle Splatting+, which directly optimizes triangles, the fundamental primitive of computer graphics, within a differentiable splatting framework. We formulate triangle parametrization to enable connectivity through shared vertices, and we design a training strategy that enforces opaque triangles. The final output is immediately usable in standard graphics engines without post-processing. Experiments on the Mip-NeRF360 and Tanks & Temples datasets show that Triangle Splatting+achieves state-of-the-art performance in mesh-based novel view synthesis. Our method surpasses prior splatting approaches in visual fidelity while remaining efficient and fast to training. Moreover, the resulting semi-connected meshes support downstream applications such as physics-based simulation or interactive walkthroughs. The project page is https://trianglesplatting2.github.io/trianglesplatting2/.
重建三维场景和合成新颖视角的技术近年来取得了快速发展。神经辐射场(Neural Radiance Fields)证明了连续体积辐射场可以实现高质量图像合成,但其较长的训练和渲染时间限制了其实用性。三维高斯贴片(3DGS)通过用数百万个高斯函数表示场景解决了这些问题,实现了实时渲染和快速优化。然而,高斯基本实体与虚拟现实头盔和实时图形应用程序中使用的基于网格的管道原生不兼容。现有解决方案尝试通过后期处理或两阶段管道将高斯转换为网格,这增加了复杂性并降低了视觉质量。在这项工作中,我们引入了三角形贴片+(Triangle Splatting+),它直接在可微分的贴片框架内优化计算机图形的基本原始实体——三角形。我们制定三角形参数化,以通过共享顶点实现连接,并设计一种训练策略来强制执行不透明三角形。最终输出可立即在标准图形引擎中使用,无需后期处理。在Mip-NeRF360和Tanks & Temples数据集上的实验表明,三角形贴片+在基于网格的新颖视图合成中达到了最先进的性能。我们的方法在视觉保真度上超越了先前的贴片方法,同时保持了高效和快速的训练。此外,所得的半连接网格支持下游应用,如基于物理的模拟或交互式漫游。项目页面是https://trianglesplatting2.github.io/trianglesplatting2/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 6 figures, 2 tables
Summary
该文本介绍了三维场景重建和合成新视角的进展。Neural Radiance Fields虽然可以实现高质量图像合成,但其训练和渲染时间较长,限制了实际应用。为了解决这个问题,提出了三维高斯渲染(3DGS)技术,采用高斯基元来表示场景以实现实时渲染和快速优化。但高斯基元与VR头盔和实时图形应用程序中的网格基管道不兼容。本文提出了Triangle Splatting+技术,直接在可微分的渲染框架内优化计算机图形的基本基元三角形,并设计了一种训练策略来强制执行不透明的三角形。实验结果证明了该方法在基于网格的新视角合成中达到了最新水平的技术性能,提高了视觉保真度,同时保持了高效快速的训练过程。项目页面提供了更多信息。
Key Takeaways
- Neural Radiance Fields实现了高质量图像合成,但训练和渲染时间较长。
- 3DGS技术采用高斯基元表示场景以实现实时渲染和快速优化。
- 高斯基元与VR头盔和实时图形应用程序中的网格基管道不兼容。
- Triangle Splatting+直接在可微分的渲染框架内优化三角形基元。
- Triangle Splatting+实现了强制不透明的三角形训练策略。
- 该方法在基于网格的新视角合成中达到了最新技术性能。
- Triangle Splatting+技术提高了视觉保真度,同时保持高效快速的训练过程。
点此查看论文截图
UniLat3D: Geometry-Appearance Unified Latents for Single-Stage 3D Generation
Authors:Guanjun Wu, Jiemin Fang, Chen Yang, Sikuang Li, Taoran Yi, Jia Lu, Zanwei Zhou, Jiazhong Cen, Lingxi Xie, Xiaopeng Zhang, Wei Wei, Wenyu Liu, Xinggang Wang, Qi Tian
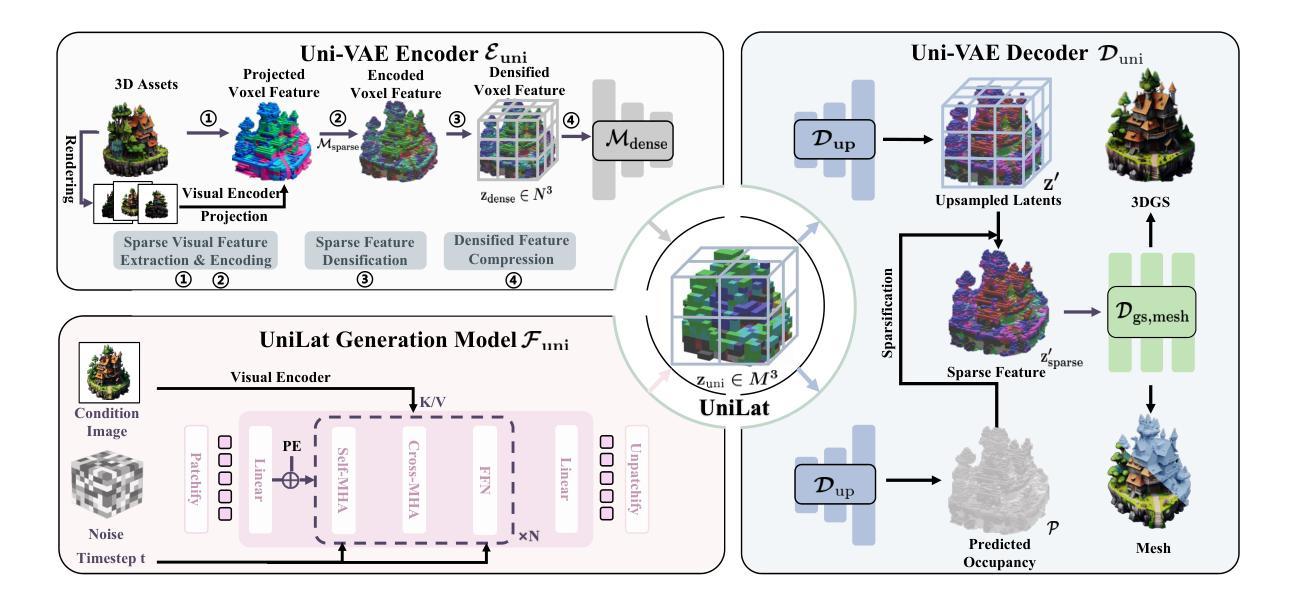
High-fidelity 3D asset generation is crucial for various industries. While recent 3D pretrained models show strong capability in producing realistic content, most are built upon diffusion models and follow a two-stage pipeline that first generates geometry and then synthesizes appearance. Such a decoupled design tends to produce geometry-texture misalignment and non-negligible cost. In this paper, we propose UniLat3D, a unified framework that encodes geometry and appearance in a single latent space, enabling direct single-stage generation. Our key contribution is a geometry-appearance Unified VAE, which compresses high-resolution sparse features into a compact latent representation – UniLat. UniLat integrates structural and visual information into a dense low-resolution latent, which can be efficiently decoded into diverse 3D formats, e.g., 3D Gaussians and meshes. Based on this unified representation, we train a single flow-matching model to map Gaussian noise directly into UniLat, eliminating redundant stages. Trained solely on public datasets, UniLat3D produces high-quality 3D assets in seconds from a single image, achieving superior appearance fidelity and geometric quality. More demos & code are available at https://unilat3d.github.io/
高保真三维资产生成对于各行各业来说至关重要。虽然最新的三维预训练模型在生成真实内容方面表现出强大的能力,但它们大多基于扩散模型,遵循一个两阶段流程,即首先生成几何结构,然后合成外观。这种分离设计往往导致几何纹理不匹配和成本高昂。在本文中,我们提出了UniLat3D,这是一个统一框架,在一个单一潜在空间中编码几何和外观信息,实现了直接的单阶段生成。我们的关键贡献是几何外观统一变分自编码器(VAE),它将高分辨率稀疏特征压缩成紧凑的潜在表示——UniLat。UniLat将结构和视觉信息集成到一个密集的低分辨率潜在空间中,可以高效地解码为多种三维格式,如三维高斯和网格。基于这种统一表示,我们训练了一个单一流匹配模型,直接将高斯噪声映射到UniLat,消除了冗余阶段。仅通过公共数据集进行训练,UniLat3D能够在几秒内生成高质量的三维资产,实现卓越的外观保真度和几何质量。更多演示和代码请访问:[https://unilat3d.github.io/]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://unilat3d.github.io/
Summary
本文提出一种名为UniLat3D的统一框架,用于高保真3D资产生成。该框架在单一潜在空间中编码几何和外观,实现直接的单阶段生成,解决了几何纹理不匹配和非微不足道的成本问题。其核心贡献是几何外观统一VAE,可将高分辨率稀疏特征压缩成紧凑的潜在表示——UniLat。这种统一表示可直接将高斯噪声映射到UniLat,消除冗余阶段,从而快速生成高质量3D资产。
Key Takeaways
- UniLat3D是一种统一框架,用于在单一潜在空间中编码几何和外观,实现直接的单阶段3D资产生成。
- 该框架解决了传统两阶段管道设计导致的几何纹理不匹配问题。
- UniLat是核心贡献,将高分辨率稀疏特征压缩成紧凑的潜在表示。
- UniLat能够整合结构和视觉信息,并可以高效地解码为多种3D格式。
- UniLat3D使用一个流匹配模型,直接将高斯噪声映射到UniLat潜在空间,消除了冗余阶段。
- 该框架可在公共数据集上训练,并能从单个图像在几秒内生成高质量3D资产。
点此查看论文截图
GEM: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Efficient and Accurate Cryo-EM Reconstruction
Authors:Huaizhi Qu, Xiao Wang, Gengwei Zhang, Jie Peng, Tianlong Chen
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has become a central tool for high-resolution structural biology, yet the massive scale of datasets (often exceeding 100k particle images) renders 3D reconstruction both computationally expensive and memory intensive. Traditional Fourier-space methods are efficient but lose fidelity due to repeated transforms, while recent real-space approaches based on neural radiance fields (NeRFs) improve accuracy but incur cubic memory and computation overhead. Therefore, we introduce GEM, a novel cryo-EM reconstruction framework built on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) that operates directly in real-space while maintaining high efficiency. Instead of modeling the entire density volume, GEM represents proteins with compact 3D Gaussians, each parameterized by only 11 values. To further improve the training efficiency, we designed a novel gradient computation to 3D Gaussians that contribute to each voxel. This design substantially reduced both memory footprint and training cost. On standard cryo-EM benchmarks, GEM achieves up to 48% faster training and 12% lower memory usage compared to state-of-the-art methods, while improving local resolution by as much as 38.8%. These results establish GEM as a practical and scalable paradigm for cryo-EM reconstruction, unifying speed, efficiency, and high-resolution accuracy. Our code is available at https://github.com/UNITES-Lab/GEM.
冷冻电子显微镜(cryo-EM)已成为高分辨率结构生物学的重要工具,但数据集规模庞大(通常超过10万张粒子图像),使得3D重建在计算上既昂贵又内存密集。传统的傅里叶空间方法虽然效率高,但由于重复变换而损失保真度,而最近基于神经辐射场(NeRFs)的实空间方法虽然提高了精度,但带来了立方级的内存和计算开销。因此,我们引入了GEM,这是一种新型的冷冻电镜重建框架,它基于三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)构建,直接在实空间操作,同时保持高效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)的新型冷冻电子显微镜(cryo-EM)重建框架——GEM。与传统的傅里叶空间方法相比,GEM直接在实空间操作,可高效表达蛋白质结构。通过采用紧凑的3D高斯表示法并设计新颖的梯度计算,GEM提高了训练效率和内存使用率。在标准cryo-EM基准测试中,GEM相较于其他先进方法实现了更快的训练和更低的内存占用,同时提高了局部分辨率。
Key Takeaways
- GEM是一种基于3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)的冷冻电子显微镜(cryo-EM)重建框架。
- GEM直接在实空间操作,改进了传统的傅里叶空间方法在某些情况下的保真度问题。
- GEM采用紧凑的3D高斯表示法表达蛋白质结构,通过参数优化提高计算效率。
- 设计了新颖的梯度计算,有助于提高训练效率和内存使用率。
- 与其他先进方法相比,GEM在cryo-EM基准测试中实现了更快的训练和更低的内存占用。
- GEM提高了局部分辨率,展现出其实用性和可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图
LVT: Large-Scale Scene Reconstruction via Local View Transformers
Authors:Tooba Imtiaz, Lucy Chai, Kathryn Heal, Xuan Luo, Jungyeon Park, Jennifer Dy, John Flynn
Large transformer models are proving to be a powerful tool for 3D vision and novel view synthesis. However, the standard Transformer’s well-known quadratic complexity makes it difficult to scale these methods to large scenes. To address this challenge, we propose the Local View Transformer (LVT), a large-scale scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis architecture that circumvents the need for the quadratic attention operation. Motivated by the insight that spatially nearby views provide more useful signal about the local scene composition than distant views, our model processes all information in a local neighborhood around each view. To attend to tokens in nearby views, we leverage a novel positional encoding that conditions on the relative geometric transformation between the query and nearby views. We decode the output of our model into a 3D Gaussian Splat scene representation that includes both color and opacity view-dependence. Taken together, the Local View Transformer enables reconstruction of arbitrarily large, high-resolution scenes in a single forward pass. See our project page for results and interactive demos https://toobaimt.github.io/lvt/.
大型Transformer模型被证明是3D视觉和新型视角合成的强大工具。然而,标准Transformer众所周知的二次复杂度使得将这些方法扩展到大型场景变得困难。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了局部视图Transformer(LVT),这是一种大规模场景重建和新型视角合成架构,它避免了二次注意力操作的需要。我们的见解是,空间上的邻近视图提供了关于局部场景组成的更有用的信号,而不是远处的视图。我们的模型处理每个视图周围局部区域的所有信息。为了关注邻近视图的标记,我们利用了一种新型的位置编码,该编码以查询和邻近视图之间的相对几何变换为条件。我们将模型的输出解码为3D高斯Splat场景表示,其中包括颜色和透明度视差依赖性。综上所述,局部视图Transformer能够在单次前向传递中进行任意大小、高分辨率场景的重建。有关结果和交互演示,请访问我们的项目页面:https://toobaimt.github.io/lvt/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH Asia 2025 camera-ready version; project page https://toobaimt.github.io/lvt/
摘要
大型Transformer模型在3D视觉和新颖视角合成方面展现出强大的能力。然而,其固有的二次复杂度使得难以将这些方法扩展到大型场景。为应对这一挑战,我们提出了局部视图Transformer(LVT),这是一种用于大规模场景重建和新颖视角合成的架构,它绕过了二次注意力操作的需求。我们的模型受到启发,即空间邻近的视图为局部场景组合提供了更有用的信号,而非远距离视图。该模型处理每个视图周围局部邻域的所有信息。为了关注邻近视图的标记,我们利用了一种新型的位置编码,该编码以查询和邻近视图之间的相对几何变换为条件。我们将模型的输出解码为包含颜色和透明度视差依赖性的3D高斯Splat场景表示。总的来说,Local View Transformer能够在单次前向传递中实现任意大规模高分辨率场景的重建。有关结果和交互式演示,请访问我们的项目页面 https://toobaimt.github.io/lvt/。
要点
- 大型Transformer模型在3D视觉和新颖视角合成中具有强大能力。
- 标准Transformer的二次复杂度限制了其在大型场景中的应用。
- 提出了局部视图Transformer(LVT)架构,以规避二次注意力操作。
- LVT利用空间邻近视图的信息,处理每个视图的局部邻域数据。
- 通过新型位置编码关注邻近视图的标记。
- 将模型输出解码为包含颜色和透明度视差依赖性的3D高斯Splat场景表示。
点此查看论文截图

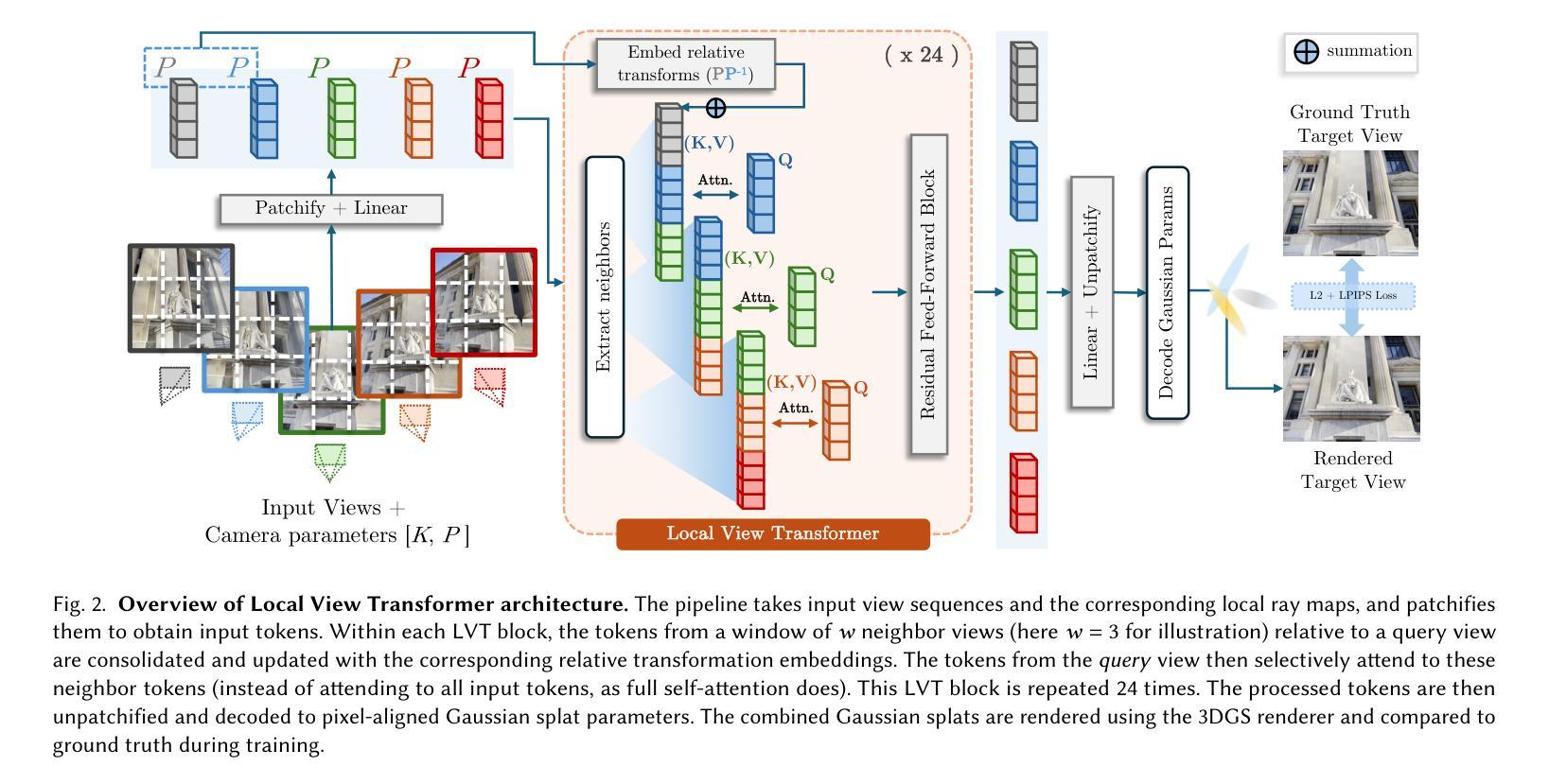
DWGS: Enhancing Sparse-View Gaussian Splatting with Hybrid-Loss Depth Estimation and Bidirectional Warping
Authors:Yu Ma, Guoliang Wei, Yue Cheng
Novel View Synthesis (NVS) from sparse views remains a core challenge in 3D reconstruction, typically suffering from overfitting, geometric distortion, and incomplete scene recovery due to limited multi-view constraints. Although 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) enables real-time, high-fidelity rendering, it suffers from floating artifacts and structural inconsistencies under sparse-input settings. To address these issues, we propose DWGS, a novel unified framework that enhances 3DGS for sparse-view synthesis by integrating robust structural cues, virtual view constraints, and occluded region completion. Our approach introduces three principal contributions: a Hybrid-Loss Depth Estimation module that leverages dense matching priors with reprojection, point propagation, and smoothness constraints to enforce multi-view consistency; a Bidirectional Warping Virtual View Synthesis method generates virtual training views to impose stronger geometric and photometric constraints; and an Occlusion-Aware Reconstruction component that utilizes depth-difference mask and a learning-based inpainting model to recover obscured regions. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks (LLFF, Blender, and DTU) show that DWGS achieves a new state-of-the-art, achieving up to 21.13 dB PSNR and 0.189 LPIPS, while retaining real-time inference capabilities.
针对稀疏视角进行的新视角合成(NVS)仍然是三维重建中的核心挑战。这通常由于有限的多角度约束而遭受过拟合、几何失真和场景恢复不完整等问题。虽然三维高斯延展(3DGS)能够实现实时高保真渲染,但在稀疏输入设置下会出现浮动伪影和结构不一致的问题。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了DWGS,这是一种新型统一框架,它通过集成稳健的结构线索、虚拟视图约束和遮挡区域完成来增强3DGS的稀疏视图合成功能。我们的方法引入了三个主要贡献:一个混合损失深度估计模块,它利用密集匹配先验与重投影、点传播和平滑约束来强制执行多视角一致性;一种双向扭曲虚拟视图合成方法,生成虚拟训练视图以施加更强的几何和光度约束;一个利用深度差异掩膜和学习型补全模型的遮挡感知重建组件,以恢复遮挡区域。在标准基准测试(LLFF、Blender和DTU)上的广泛实验表明,DWGS达到了最新水平的技术效果,PSNR达到了最高可达21.13分贝,LPIPS为0.189,同时保持了实时推理能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 21 figures
Summary
基于稀疏视角进行新型视图合成(NVS)是3D重建中的核心挑战之一,面临过拟合、几何失真和场景恢复不完全等问题。虽然3D高斯展布(3DGS)能够实现实时高保真渲染,但在稀疏输入设置下会出现浮动伪影和结构不一致等问题。为解决这些问题,本文提出了DWGS,一种增强3DGS用于稀疏视图合成的统一框架,通过集成稳健的结构线索、虚拟视图约束和遮挡区域完成等技术。
Key Takeaways
- NVS在3D重建中面临挑战,如过拟合、几何失真和场景恢复不完全。
- 3DGS能够实现实时高保真渲染,但在稀疏输入下存在浮动伪影和结构不一致问题。
- DWGS框架通过集成结构线索、虚拟视图约束和遮挡区域完成技术,增强了3DGS在稀疏视图合成中的性能。
- DWGS引入了Hybrid-Loss深度估计模块,利用密集匹配先验和重投影技术,实现多视角一致性。
- Bidirectional Warping Virtual View Synthesis方法生成虚拟训练视图,以加强几何和光度约束。
- DWGS具有遮挡感知重建组件,利用深度差异掩膜和学习型填充模型来恢复遮挡区域。
点此查看论文截图
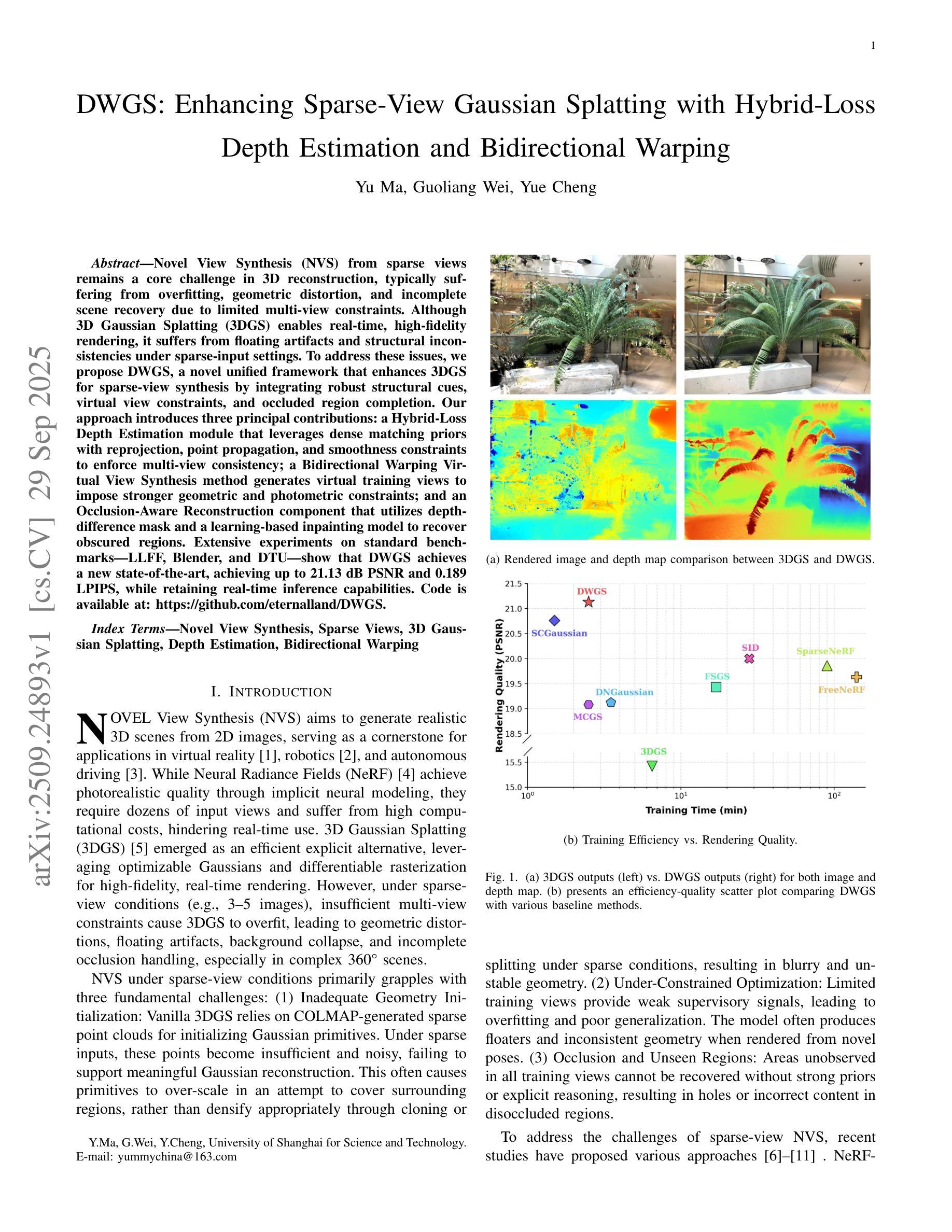
ExGS: Extreme 3D Gaussian Compression with Diffusion Priors
Authors:Jiaqi Chen, Xinhao Ji, Yuanyuan Gao, Hao Li, Yuning Gong, Yifei Liu, Dan Xu, Zhihang Zhong, Dingwen Zhang, Xiao Sun
Neural scene representations, such as 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), have enabled high-quality neural rendering; however, their large storage and transmission costs hinder deployment in resource-constrained environments. Existing compression methods either rely on costly optimization, which is slow and scene-specific, or adopt training-free pruning and quantization, which degrade rendering quality under high compression ratios. In contrast, recent data-driven approaches provide a promising direction to overcome this trade-off, enabling efficient compression while preserving high rendering quality. We introduce \textbf{ExGS}, a novel feed-forward framework that unifies \textbf{Universal Gaussian Compression} (UGC) with \textbf{GaussPainter} for \textbf{Ex}treme 3D\textbf{GS} compression. \textbf{UGC} performs re-optimization-free pruning to aggressively reduce Gaussian primitives while retaining only essential information, whereas \textbf{GaussPainter} leverages powerful diffusion priors with mask-guided refinement to restore high-quality renderings from heavily pruned Gaussian scenes. Unlike conventional inpainting, GaussPainter not only fills in missing regions but also enhances visible pixels, yielding substantial improvements in degraded renderings. To ensure practicality, it adopts a lightweight VAE and a one-step diffusion design, enabling real-time restoration. Our framework can even achieve over $100\times$ compression (reducing a typical 354.77 MB model to about 3.31 MB) while preserving fidelity and significantly improving image quality under challenging conditions. These results highlight the central role of diffusion priors in bridging the gap between extreme compression and high-quality neural rendering. Our code repository will be released at \href{https://github.com/chenttt2001/ExGS}{here}.
神经场景表示,如3D高斯拼贴(3DGS),已经实现了高质量的神级渲染;然而,其巨大的存储和传输成本阻碍了其在资源受限环境中的部署。现有的压缩方法要么依赖于昂贵的优化,这既缓慢又针对特定场景,要么采用无训练裁剪和量化,这在高压缩比的情况下会降低渲染质量。相比之下,最近的数据驱动方法提供了一个克服这种权衡的有前途的方向,能够在保持高渲染质量的同时实现高效压缩。我们介绍了ExGS,这是一种新颖的前馈框架,它将通用高斯压缩(UGC)与GaussPainter相结合,用于极端3DGS压缩。UGC通过无优化重新裁剪的方式,大幅减少高斯基本体,同时仅保留必要信息,而GaussPainter则利用强大的扩散先验和掩膜导向细化,从大量裁剪的高斯场景中恢复高质量渲染。与常规补全不同,GaussPainter不仅填充缺失区域,还增强可见像素,大大改善退化渲染的效果。为保证实用性,它采用轻量级VAE和一步扩散设计,实现实时恢复。我们的框架甚至可以实现超过100倍的压缩(将一个典型的354.77 MB模型压缩到约3.31 MB),同时保持保真度并在具有挑战性的条件下显著提高图像质量。这些结果凸显了扩散先验在弥合极端压缩与高质量神经渲染之间的差距中的核心作用。我们的代码仓库将发布在[https://github.com/chenttt2001/ExGS](点击此处)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于神经网络场景表示(如3DGS)的高质量神经渲染已经实现,但其存储和传输成本较高,不适用于资源受限的环境。现有压缩方法存在优化成本高或压缩质量下降的问题。本文提出一种新颖的前馈框架ExGS,结合通用高斯压缩(UGC)与GaussPainter技术实现极端3DGS压缩,可在保留重要信息的同时进行大幅度的高斯原始数据缩减,并利用扩散先验与掩膜导向的细化技术恢复高质量渲染。ExGS实现了超过$100\times$的压缩率,同时在具有挑战性的条件下保持了保真度和图像质量的显著提高。代码库已发布在https://github.com/chenttt2001/ExGS。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络场景表示(如3DGS)可实现高质量神经渲染,但存储和传输成本较高。
- 现有压缩方法存在优化成本高昂或压缩质量下降的问题。
- 本文提出的前馈框架ExGS结合了通用高斯压缩(UGC)与GaussPainter技术。
- UGC可进行无优化重构的修剪,大幅度减少高斯原始数据同时保留重要信息。
- GaussPainter利用扩散先验和掩膜导向细化技术恢复高质量渲染。
- ExGS实现了超过$100\times$的压缩率,显著降低存储和传输成本。
- ExGS在保持图像质量的同时,实现了高压缩率,代码库已公开发布。
点此查看论文截图
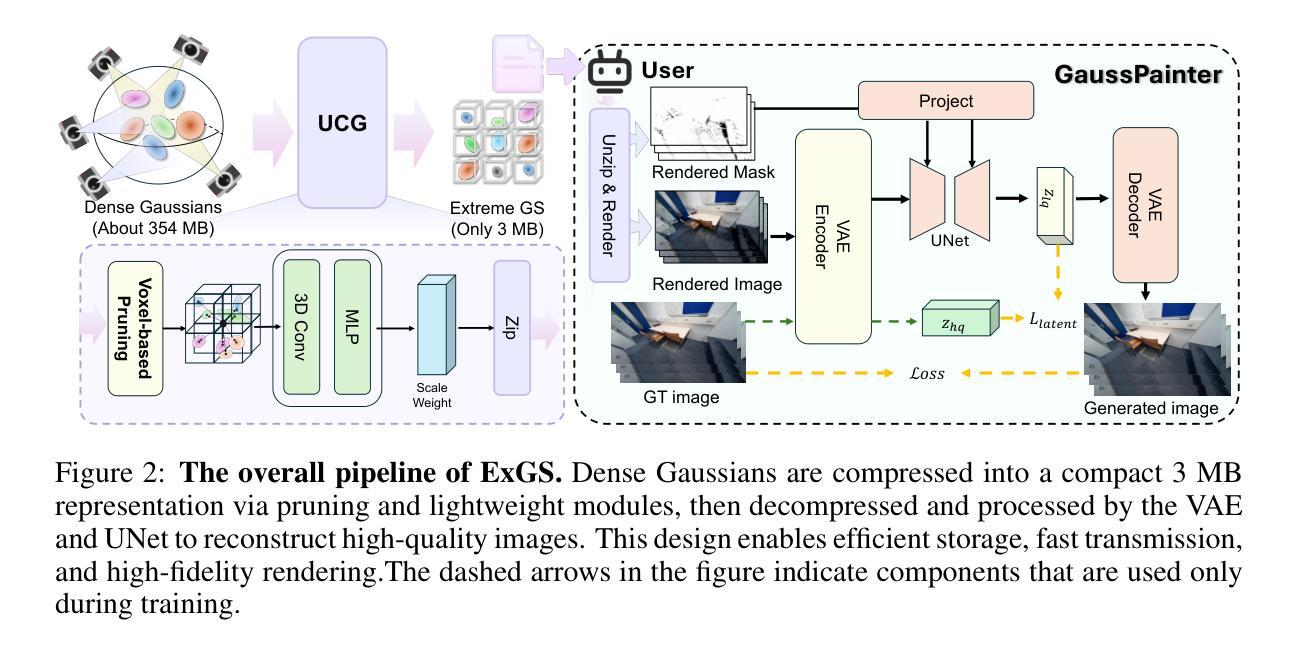
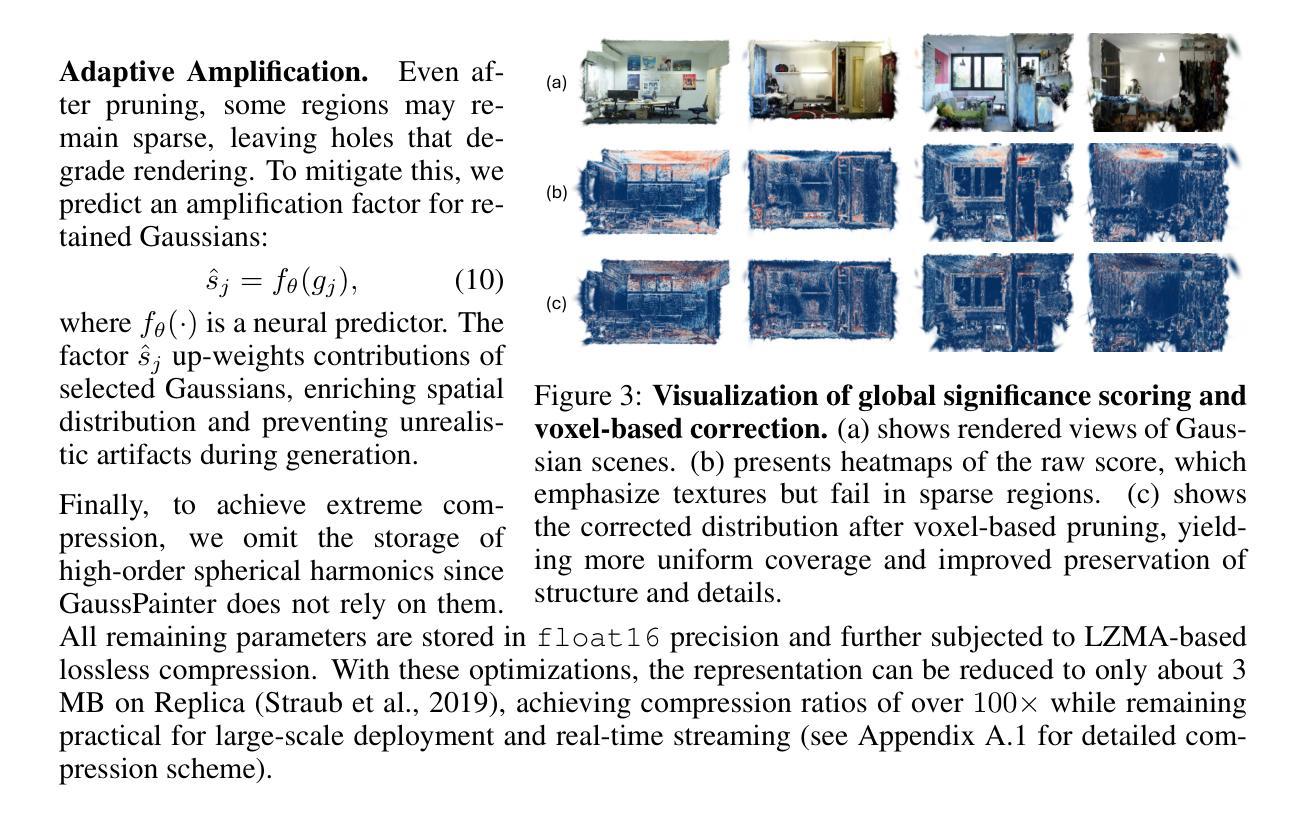

OMeGa: Joint Optimization of Explicit Meshes and Gaussian Splats for Robust Scene-Level Surface Reconstruction
Authors:Yuhang Cao, Haojun Yan, Danya Yao
Neural rendering with Gaussian splatting has advanced novel view synthesis, and most methods reconstruct surfaces via post-hoc mesh extraction. However, existing methods suffer from two limitations: (i) inaccurate geometry in texture-less indoor regions, and (ii) the decoupling of mesh extraction from optimization, thereby missing the opportunity to leverage mesh geometry to guide splat optimization. In this paper, we present OMeGa, an end-to-end framework that jointly optimizes an explicit triangle mesh and 2D Gaussian splats via a flexible binding strategy, where spatial attributes of Gaussian Splats are expressed in the mesh frame and texture attributes are retained on splats. To further improve reconstruction accuracy, we integrate mesh constraints and monocular normal supervision into the optimization, thereby regularizing geometry learning. In addition, we propose a heuristic, iterative mesh-refinement strategy that splits high-error faces and prunes unreliable ones to further improve the detail and accuracy of the reconstructed mesh. OMeGa achieves state-of-the-art performance on challenging indoor reconstruction benchmarks, reducing Chamfer-$L_1$ by 47.3% over the 2DGS baseline while maintaining competitive novel-view rendering quality. The experimental results demonstrate that OMeGa effectively addresses prior limitations in indoor texture-less reconstruction.
神经渲染与高斯平铺技术已经推动了新型视图合成的进步,大多数方法通过事后网格提取进行表面重建。然而,现有方法存在两个局限性:(i)在纹理较少的室内区域几何形状不准确;(ii)网格提取与优化之间的解耦,从而失去了利用网格几何来引导平铺优化的机会。在本文中,我们介绍了OMeGa,这是一个端到端的框架,它通过灵活的绑定策略联合优化明确的三角形网格和二维高斯平铺,其中高斯平铺的空间属性在网格框架中表示,纹理属性保留在平铺上。为了进一步提高重建精度,我们将网格约束和单目法线监督集成到优化中,从而规范几何学习。此外,我们提出了一种启发式迭代网格细化策略,分裂高误差面并删除不可靠的面,以进一步提高重建网格的细节和准确性。OMeGa在具有挑战性的室内重建基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,在保持竞争力新颖视图渲染质量的同时,相对于二维高斯平铺基线减少了Chamfer-$L_1$的误差百分比达47.3%。实验结果证明,OMeGa有效地解决了先前在室内无纹理重建中的局限性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 9 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种名为OMeGa的端到端框架,该框架通过灵活的绑定策略联合优化显式三角网格和2D高斯贴片。OMeGa在网格框架中表达高斯贴片的空间属性,同时保留贴图的纹理属性,以提高重建精度。通过整合网格约束和单眼正常监督到优化过程中,实现了几何学习的规范化。此外,OMeGa还提出了一种启发式迭代网格细化策略,通过分裂高误差面和剔除不可靠面,进一步提高重建网格的细节和精度。实验结果表明,OMeGa在具有挑战性的室内重建基准测试中取得了最先进的性能,相较于2DGS基线,Chamfer-L1降低了47.3%,同时保持了具有竞争力的新型视图渲染质量。
Key Takeaways
- OMeGa是一个端到端的框架,联合优化三角网格和2D高斯贴片,解决现有方法的两个限制。
- 通过灵活的绑定策略,OMeGa在网格框架中表达高斯贴片的空间属性,同时保留贴图的纹理属性。
- 整合网格约束和单眼正常监督到优化过程中,实现了几何学习的规范化,提高重建精度。
- OMeGa采用启发式迭代网格细化策略,通过分裂高误差面和剔除不可靠面,进一步提高重建网格的质量。
- OMeGa在具有挑战性的室内重建基准测试中取得了最先进的性能。
- 相较于2DGS基线,OMeGa的Chamfer-L1降低了47.3%,显示出其优秀的性能。
点此查看论文截图
Forge4D: Feed-Forward 4D Human Reconstruction and Interpolation from Uncalibrated Sparse-view Videos
Authors:Yingdong Hu, Yisheng He, Jinnan Chen, Weihao Yuan, Kejie Qiu, Zehong Lin, Siyu Zhu, Zilong Dong, Jun Zhang
Instant reconstruction of dynamic 3D humans from uncalibrated sparse-view videos is critical for numerous downstream applications. Existing methods, however, are either limited by the slow reconstruction speeds or incapable of generating novel-time representations. To address these challenges, we propose Forge4D, a feed-forward 4D human reconstruction and interpolation model that efficiently reconstructs temporally aligned representations from uncalibrated sparse-view videos, enabling both novel view and novel time synthesis. Our model simplifies the 4D reconstruction and interpolation problem as a joint task of streaming 3D Gaussian reconstruction and dense motion prediction. For the task of streaming 3D Gaussian reconstruction, we first reconstruct static 3D Gaussians from uncalibrated sparse-view images and then introduce learnable state tokens to enforce temporal consistency in a memory-friendly manner by interactively updating shared information across different timestamps. For novel time synthesis, we design a novel motion prediction module to predict dense motions for each 3D Gaussian between two adjacent frames, coupled with an occlusion-aware Gaussian fusion process to interpolate 3D Gaussians at arbitrary timestamps. To overcome the lack of the ground truth for dense motion supervision, we formulate dense motion prediction as a dense point matching task and introduce a self-supervised retargeting loss to optimize this module. An additional occlusion-aware optical flow loss is introduced to ensure motion consistency with plausible human movement, providing stronger regularization. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our model on both in-domain and out-of-domain datasets. Project page and code at: https://zhenliuzju.github.io/huyingdong/Forge4D.
从未校准的稀疏视角视频即时重建动态3D人体对于许多下游应用至关重要。然而,现有方法要么重建速度慢,要么无法生成新颖的时间表示。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了Forge4D,一个前馈的4D人体重建和插值模型,它可以从未校准的稀疏视角视频有效地重建时间对齐的表示,从而实现新颖视图和新颖时间的合成。我们的模型将4D重建和插值问题简化为流式3D高斯重建和密集运动预测的共同任务。对于流式3D高斯重建任务,我们首先从未校准的稀疏视角图像重建静态3D高斯,然后引入可学习的状态令牌,以交互方式更新不同时间戳之间的共享信息,以内存友好的方式强制执行时间一致性。对于新颖的时间合成,我们设计了一个新颖的运动预测模块,用于预测相邻两帧之间每个3D高斯密集运动,结合一个遮挡感知的高斯融合过程,以在任意时间戳插值3D高斯。为了克服缺乏密集运动监督的地面真实数据,我们将密集运动预测制定为密集点匹配任务,并引入自监督重定位损失来优化此模块。还引入了额外的遮挡感知光流损失,以确保与合理的人类运动一致的运动一致性,提供更强的正则化。大量实验表明,我们的模型在域内和域外数据集上均有效。项目页面和代码地址为:https://zhenliuzju.github.io/huyingdong/Forge4D。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Forge4D的前馈4D人体重建与插值模型,可从未校准的稀疏视角视频高效重建时间对齐的表示,实现新颖视角和时间合成。该模型简化了4D重建和插值问题,将其视为流式3D高斯重建和密集运动预测的共同任务。针对流式3D高斯重建任务,先从未校准的稀疏视角图像重建静态3D高斯,然后引入可学习状态令牌,以交互方式更新不同时间戳之间的共享信息,以内存友好的方式强制执行时间一致性。对于新颖时间合成,设计了一种新颖的运动预测模块,用于预测相邻两帧之间每个3D高斯密集运动,并结合遮挡感知高斯融合过程,对任意时间戳进行3D高斯插值。为了解决缺乏密集运动监督的地面真实问题,将密集运动预测公式化为密集点匹配任务,并引入自我监督的重新定位损失来优化此模块。另外,引入了遮挡感知的光流损失,以确保与合理的人类运动一致的运动一致性,提供更强大的正则化。
Key Takeaways
- Forge4D是一个前馈4D人体重建与插值模型,用于从稀疏视角视频重建动态3D人体。
- 模型能高效重建时间对齐的表示,实现新颖视角和时间合成。
- 模型简化4D重建和插值为流式3D高斯重建和密集运动预测任务。
- 引入可学习状态令牌以强制执行时间一致性。
- 设计新颖运动预测模块,预测每个3D高斯在相邻帧之间的密集运动。
- 密集运动预测被公式化为密集点匹配任务,通过自我监督的重新定位损失进行优化。
- 引入遮挡感知的光流损失以确保运动一致性,提供更强正则化。
点此查看论文截图
CrashSplat: 2D to 3D Vehicle Damage Segmentation in Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Dragoş-Andrei Chileban, Andrei-Ştefan Bulzan, Cosmin Cernǎzanu-Glǎvan
Automatic car damage detection has been a topic of significant interest for the auto insurance industry as it promises faster, accurate, and cost-effective damage assessments. However, few works have gone beyond 2D image analysis to leverage 3D reconstruction methods, which have the potential to provide a more comprehensive and geometrically accurate representation of the damage. Moreover, recent methods employing 3D representations for novel view synthesis, particularly 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS), have demonstrated the ability to generate accurate and coherent 3D reconstructions from a limited number of views. In this work we introduce an automatic car damage detection pipeline that performs 3D damage segmentation by up-lifting 2D masks. Additionally, we propose a simple yet effective learning-free approach for single-view 3D-GS segmentation. Specifically, Gaussians are projected onto the image plane using camera parameters obtained via Structure from Motion (SfM). They are then filtered through an algorithm that utilizes Z-buffering along with a normal distribution model of depth and opacities. Through experiments we found that this method is particularly effective for challenging scenarios like car damage detection, where target objects (e.g., scratches, small dents) may only be clearly visible in a single view, making multi-view consistency approaches impractical or impossible. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/DragosChileban/CrashSplat.
自动车辆损伤检测已成为车险行业关注的焦点话题,因为它能带来更快速、准确、且经济的损伤评估方法。然而,很少有研究超越二维图像分析,利用三维重建方法,这些方法具有提供更全面和几何上更准确的损伤表征的潜力。此外,最近采用三维表示进行新颖视图合成的方法,特别是三维高斯贴图(3D-GS),已经证明能够从有限的视角生成准确且连贯的三维重建。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个自动车辆损伤检测流程,通过提升二维蒙版来实现三维损伤分割。此外,我们提出了一种简单有效的无学习单视图3D-GS分割方法。具体来说,通过使用通过运动结构(SfM)获得的相机参数将高斯投影到图像平面上。然后,通过一个利用深度和不透明度正态分布模型的Z缓冲算法进行过滤。通过实验我们发现,该方法对于车辆损伤检测等具有挑战性的场景特别有效,在这些场景中,目标对象(例如划痕、小凹陷)可能仅在单个视图中清晰可见,使得多视图一致性方法不切实际或不可能。代码公开在:https://github.com/DragosChileban/CrashSplat。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于3D重建方法的自动汽车损伤检测管道,通过提升2D掩膜实现3D损伤分割,并提出了一种简单有效的学习无关的单视图3D-GS分割方法。该方法利用SfM获得的相机参数将高斯投影到图像平面上,并通过结合深度和不透明度的正态分布模型的Z缓冲算法进行过滤。此方法对于汽车损伤检测等挑战场景特别有效,目标物体可能仅在单一视图中可见。
Key Takeaways
- 自动汽车损伤检测已成为车险行业的关注焦点,追求更快、更准确、更经济的损伤评估。
- 现有工作多局限于2D图像分析,本文探索了3D重建方法在损伤检测中的应用潜力。
- 引入了一种基于3D重建的损伤检测管道,通过提升2D掩膜实现3D损伤分割。
- 提出了一种简单有效的学习无关的单视图3D-GS分割方法,利用SfM获得的相机参数进行高斯投影。
- 通过Z缓冲算法结合深度和不透明度的正态分布模型进行过滤,提升了检测方法的效果。
- 方法特别适用于汽车损伤检测等挑战场景,目标物体可能仅在单一视图中可见。
点此查看论文截图
Orientation-anchored Hyper-Gaussian for 4D Reconstruction from Casual Videos
Authors:Junyi Wu, Jiachen Tao, Haoxuan Wang, Gaowen Liu, Ramana Rao Kompella, Yan Yan
We present Orientation-anchored Gaussian Splatting (OriGS), a novel framework for high-quality 4D reconstruction from casually captured monocular videos. While recent advances extend 3D Gaussian Splatting to dynamic scenes via various motion anchors, such as graph nodes or spline control points, they often rely on low-rank assumptions and fall short in modeling complex, region-specific deformations inherent to unconstrained dynamics. OriGS addresses this by introducing a hyperdimensional representation grounded in scene orientation. We first estimate a Global Orientation Field that propagates principal forward directions across space and time, serving as stable structural guidance for dynamic modeling. Built upon this, we propose Orientation-aware Hyper-Gaussian, a unified formulation that embeds time, space, geometry, and orientation into a coherent probabilistic state. This enables inferring region-specific deformation through principled conditioned slicing, adaptively capturing diverse local dynamics in alignment with global motion intent. Experiments demonstrate the superior reconstruction fidelity of OriGS over mainstream methods in challenging real-world dynamic scenes.
我们提出了基于方向锚定的高斯延展(OriGS)方法,这是一种从随意捕捉的单目视频中实现高质量4D重建的新型框架。虽然最近的进展通过将3D高斯延展扩展到动态场景,利用各种运动锚点(如图节点或折线控制点)等方法,但它们经常依赖于低阶假设,并且在建模无约束动态所固有的复杂、区域特定变形方面表现不足。OriGS通过引入基于场景方向的高维表示来解决这一问题。我们首先估计全局方向场,该方向场在空间和时间上传播主要前向方向,为动态建模提供稳定的结构指导。在此基础上,我们提出了基于方向的超高斯公式,将时间、空间、几何和方向嵌入到一个连贯的概率状态中。这使得我们能够通过基于原理的条件切片推断区域特定的变形,自适应地捕捉与全局运动意图一致的多样局部动态。实验证明,在具有挑战性的真实世界动态场景中,OriGS的重建保真度优于主流方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2025. Code: \href{https://github.com/adreamwu/OriGS}{OriGS}
摘要
本文提出了基于方向锚定的高斯点云法(OriGS),这是一种从随意捕捉的单目视频中实现高质量4D重建的新型框架。虽然最近的进展通过将三维高斯点云法扩展到动态场景,利用各种运动锚(如图节点或样条控制点)取得了一定成果,但它们通常依赖于低秩假设,难以模拟无约束动态中固有的复杂区域特定变形。OriGS通过引入基于场景方向的高维表示来解决这一问题。首先估计全局方向场,该场在空间和时间上传播主要前进方向,为动态建模提供稳定的结构指导。在此基础上,我们提出了基于方向的超高斯公式,将时间、空间、几何和方向嵌入到一个连贯的概率状态中。这使得我们能够通过原则性条件切片推断区域特定变形,自适应地捕捉与全局运动意图相符的多样局部动态。实验证明,在具有挑战性的真实世界动态场景中,OriGS的重建保真度优于主流方法。
要点
- OriGS是一种新型框架,用于从单目视频中实现高质量4D重建。
- 引入基于场景方向的高维表示来解决复杂区域特定变形建模问题。
- 通过估计全局方向场传播主要前进方向,为动态建模提供稳定结构指导。
- 提出基于方向的超高斯公式,整合时间、空间、几何和方向于一个连贯的概率状态中。
- 通过原则性条件切片推断区域特定变形,自适应捕捉局部动态。
- 实验证明,OriGS在挑战性真实世界动态场景中具有优越重建性能。
点此查看论文截图

OracleGS: Grounding Generative Priors for Sparse-View Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Atakan Topaloglu, Kunyi Li, Michael Niemeyer, Nassir Navab, A. Murat Tekalp, Federico Tombari
Sparse-view novel view synthesis is fundamentally ill-posed due to severe geometric ambiguity. Current methods are caught in a trade-off: regressive models are geometrically faithful but incomplete, whereas generative models can complete scenes but often introduce structural inconsistencies. We propose OracleGS, a novel framework that reconciles generative completeness with regressive fidelity for sparse view Gaussian Splatting. Instead of using generative models to patch incomplete reconstructions, our “propose-and-validate” framework first leverages a pre-trained 3D-aware diffusion model to synthesize novel views to propose a complete scene. We then repurpose a multi-view stereo (MVS) model as a 3D-aware oracle to validate the 3D uncertainties of generated views, using its attention maps to reveal regions where the generated views are well-supported by multi-view evidence versus where they fall into regions of high uncertainty due to occlusion, lack of texture, or direct inconsistency. This uncertainty signal directly guides the optimization of a 3D Gaussian Splatting model via an uncertainty-weighted loss. Our approach conditions the powerful generative prior on multi-view geometric evidence, filtering hallucinatory artifacts while preserving plausible completions in under-constrained regions, outperforming state-of-the-art methods on datasets including Mip-NeRF 360 and NeRF Synthetic.
稀疏视角的新视角合成从根本上来说是不适定的,因为存在严重的几何歧义。当前的方法陷入了权衡之中:回归模型在几何上忠实但不够完整,而生成模型虽然能完成场景但往往引入结构不一致性。我们提出了OracleGS,这是一个新的框架,旨在调和生成模型的完整性与回归模型的忠实性,用于稀疏视角的高斯拼贴。我们并不使用生成模型来修补不完整的重建,而是采用“提出并验证”的框架。首先,我们利用预训练的3D感知扩散模型合成新视角,以提出一个完整的场景。然后,我们将多视图立体(MVS)模型重新用作3D感知的评判标准,以验证生成视角的3D不确定性。我们使用其注意力图来揭示哪些区域由多视角证据支持良好,哪些区域由于遮挡、缺少纹理或直接不一致而陷入高度不确定性的区域。这种不确定性信号直接指导了通过不确定性加权损失优化3D高斯拼贴模型。我们的方法在多视角几何证据的基础上,以强大的生成先验为条件,过滤了幻想产生的伪影,同时保留了缺乏约束区域的合理完成度,在Mip-NeRF 360和NeRF Synthetic等数据集上的表现优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为OracleGS的新型框架,用于稀疏视图下的高斯贴图技术。它结合了生成模型的完整性与回归模型的保真度。通过利用预训练的3D感知扩散模型合成新视图来提出完整场景,然后使用多视图立体(MVS)模型作为3D感知的Oracle来验证生成的视图的3D不确定性。该不确定性信号直接指导了通过不确定性加权损失优化的3D高斯贴图模型的优化。该方法在Mip-NeRF 360和NeRF合成等数据集上优于最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- 稀疏视图下的新颖视角合成具有严重的几何模糊性,因此是根本不适定的。
- 当前方法面临回归模型和生成模型的权衡:回归模型几何保真但不完全,而生成模型能完成场景但经常引入结构不一致性。
- OracleGS框架结合了生成模型的完整性与回归模型的保真度。
- 使用预训练的3D感知扩散模型合成新视图以提出完整场景。
- 利用多视图立体(MVS)模型验证生成的视图的3D不确定性,并通过其注意力图揭示哪些区域受多视图证据支持,哪些区域因遮挡、缺乏纹理或直接不一致而具有高不确定性。
- 不确定性信号直接指导了通过不确定性加权损失优化的3D高斯贴图模型的优化。
点此查看论文截图

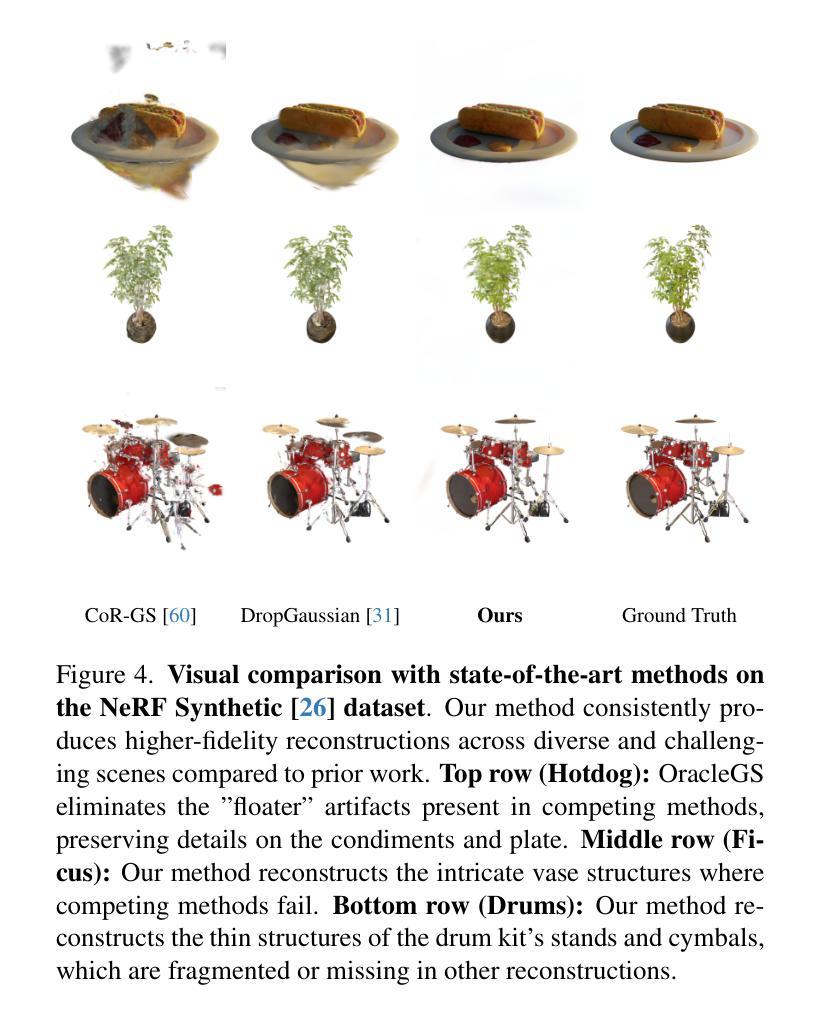
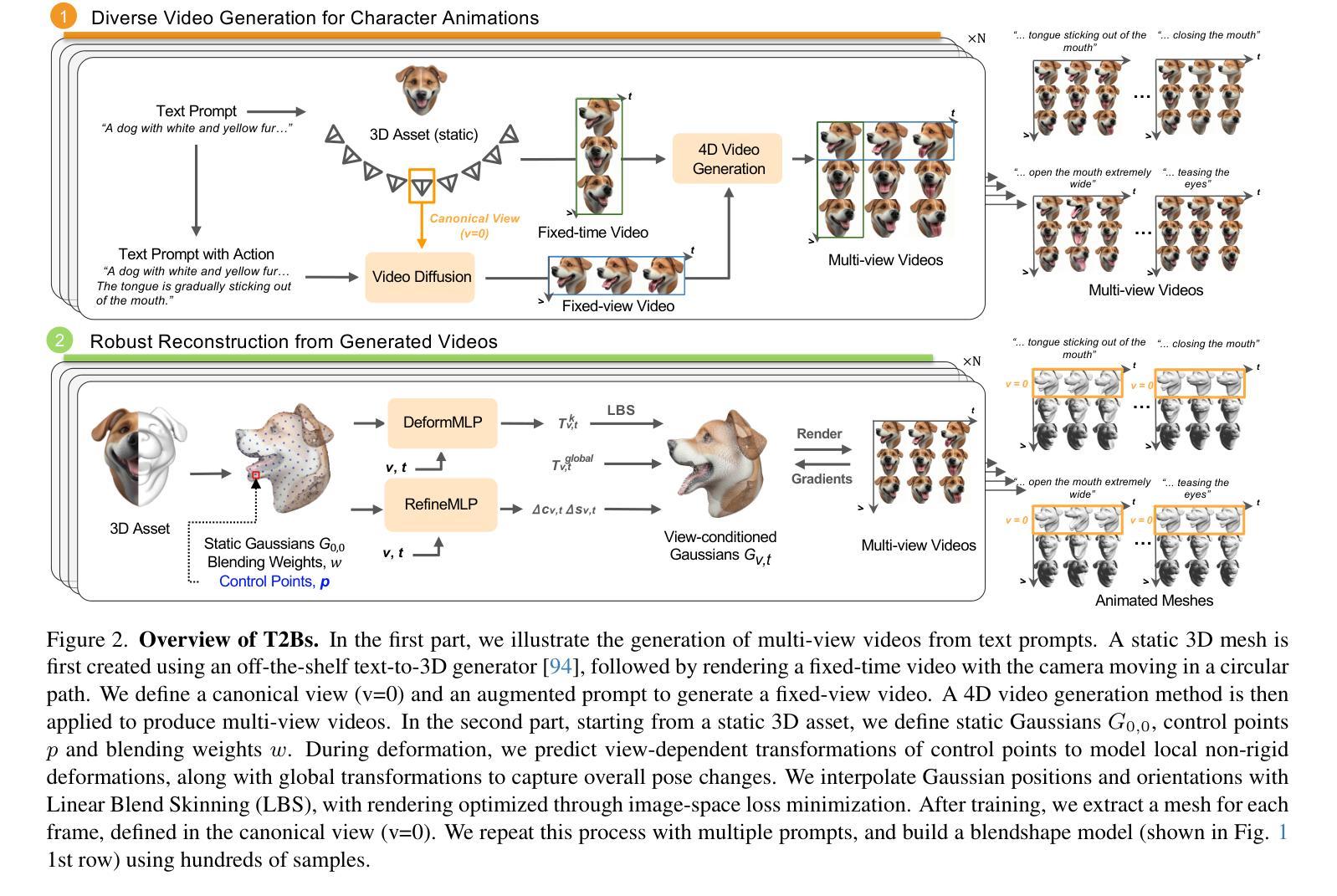
T2Bs: Text-to-Character Blendshapes via Video Generation
Authors:Jiahao Luo, Chaoyang Wang, Michael Vasilkovsky, Vladislav Shakhrai, Di Liu, Peiye Zhuang, Sergey Tulyakov, Peter Wonka, Hsin-Ying Lee, James Davis, Jian Wang
We present T2Bs, a framework for generating high-quality, animatable character head morphable models from text by combining static text-to-3D generation with video diffusion. Text-to-3D models produce detailed static geometry but lack motion synthesis, while video diffusion models generate motion with temporal and multi-view geometric inconsistencies. T2Bs bridges this gap by leveraging deformable 3D Gaussian splatting to align static 3D assets with video outputs. By constraining motion with static geometry and employing a view-dependent deformation MLP, T2Bs (i) outperforms existing 4D generation methods in accuracy and expressiveness while reducing video artifacts and view inconsistencies, and (ii) reconstructs smooth, coherent, fully registered 3D geometries designed to scale for building morphable models with diverse, realistic facial motions. This enables synthesizing expressive, animatable character heads that surpass current 4D generation techniques.
我们提出了T2Bs框架,它通过结合静态文本到3D生成和视频扩散技术,从文本生成高质量的可动画角色头部可变形模型。文本到3D模型可以生成详细的静态几何结构,但缺乏运动合成,而视频扩散模型虽然可以生成运动,但存在时间和多视角几何不一致的问题。T2Bs通过利用可变形3D高斯贴图技术,将静态3D资产与视频输出对齐,从而弥补了这一空白。通过用静态几何结构约束运动并采用视角相关变形多层感知器,T2Bs(i)在准确性和表现力方面优于现有的4D生成方法,同时减少了视频伪影和视角不一致问题;(ii)重建了平滑、连贯、完全配准的3D几何结构,旨在构建具有多样化和现实感的面部运动的可变形模型。这能够合成出超越当前4D生成技术的生动可动画角色头部。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了T2Bs框架,该框架结合了静态文本到3D生成和视频扩散技术,用于从文本生成高质量、可动画的角色头部可变形模型。T2Bs通过利用可变形的3D高斯喷绘技术,将静态3D资产与视频输出对齐,解决了文本到3D模型缺乏动作合成的问题以及视频扩散模型存在的时序和多视角几何不一致的问题。T2Bs提高了准确性和表现力,减少了视频伪影和视角不一致,重建了平滑、连贯、完全注册的3D几何,用于构建具有多样化和现实感的面部运动的可变形模型。
Key Takeaways
- T2Bs框架结合了静态文本到3D生成与视频扩散技术。
- 文本到3D模型产生静态几何,但缺乏动作合成。
- 视频扩散模型产生动作,但存在时序和多视角几何不一致的问题。
- T2Bs利用可变形3D高斯喷绘技术,将静态3D资产与视频输出对齐。
- T2Bs通过约束动作和静态几何,提高了准确性、表现力。
- T2Bs减少了视频伪影和视角不一致。
- T2Bs能够重建平滑、连贯、完全注册的3D几何,用于构建具有多样化和现实感的面部运动的可变形模型。
点此查看论文截图

GeoSplat: A Deep Dive into Geometry-Constrained Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yangming Li, Chaoyu Liu, Lihao Liu, Simon Masnou, Carola-Bibiane Schönlieb
A few recent works explored incorporating geometric priors to regularize the optimization of Gaussian splatting, further improving its performance. However, those early studies mainly focused on the use of low-order geometric priors (e.g., normal vector), and they might also be unreliably estimated by noise-sensitive methods, like local principal component analysis. To address their limitations, we first present GeoSplat, a general geometry-constrained optimization framework that exploits both first-order and second-order geometric quantities to improve the entire training pipeline of Gaussian splatting, including Gaussian initialization, gradient update, and densification. As an example, we initialize the scales of 3D Gaussian primitives in terms of principal curvatures, leading to a better coverage of the object surface than random initialization. Secondly, based on certain geometric structures (e.g., local manifold), we introduce efficient and noise-robust estimation methods that provide dynamic geometric priors for our framework. We conduct extensive experiments on multiple datasets for novel view synthesis, showing that our framework, GeoSplat, significantly improves the performance of Gaussian splatting and outperforms previous baselines.
近期有一些研究尝试将几何先验知识引入高斯摊铺的优化过程中,以进一步提高其性能。然而,早期的研究主要集中在低阶几何先验的使用上(如法向量),这些方法可能通过噪声敏感的方法(如局部主成分分析)进行估算,但估算结果可能不可靠。为了克服这些局限性,我们首先提出了GeoSplat,这是一个通用的几何约束优化框架,它利用一阶和二阶几何量来提高高斯摊铺的整个训练流程,包括高斯初始化、梯度更新和密集化。例如,我们根据主曲率初始化3D高斯原始数据的尺度,相对于随机初始化而言,这能更好地覆盖对象表面。其次,基于某些几何结构(如局部流形),我们引入了高效且噪声鲁棒的估计方法,为我们的框架提供动态几何先验。我们在多个数据集上进行了新颖视图合成的广泛实验,结果表明我们的框架GeoSplat显著提高了高斯摊铺的性能,并超过了以前的基线水平。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了GeoSplat,一个通用的几何约束优化框架,它利用一阶和二阶几何量改进了高斯贴图的整个训练流程,包括高斯初始化、梯度更新和稠密化。通过基于主曲率的初始化方法,实现了比随机初始化更好的对象表面覆盖。此外,基于某些几何结构(如局部流形),引入了高效且噪声鲁棒的估计方法,为我们的框架提供动态几何先验。在多个数据集上进行的新视角合成实验表明,GeoSplat显著提高了高斯贴图性能并超越了先前基线。
关键见解
- 引入了GeoSplat,一个结合几何先验的通用优化框架,用于改进高斯贴图的性能。
- 利用一阶和二阶几何量提升高斯贴图的整个训练流程。
- 通过基于主曲率的初始化方法,实现了对象表面覆盖的改进。
- 提出了基于某些几何结构的动态几何先验估计方法,提高了方法的效率和噪声鲁棒性。
- 方法在多个数据集上进行了新视角合成的实验验证。
- GeoSplat显著提高了高斯贴图性能并超越先前基线。
- 该框架为结合几何先验以改进优化提供了一种通用且高效的方法。
点此查看论文截图

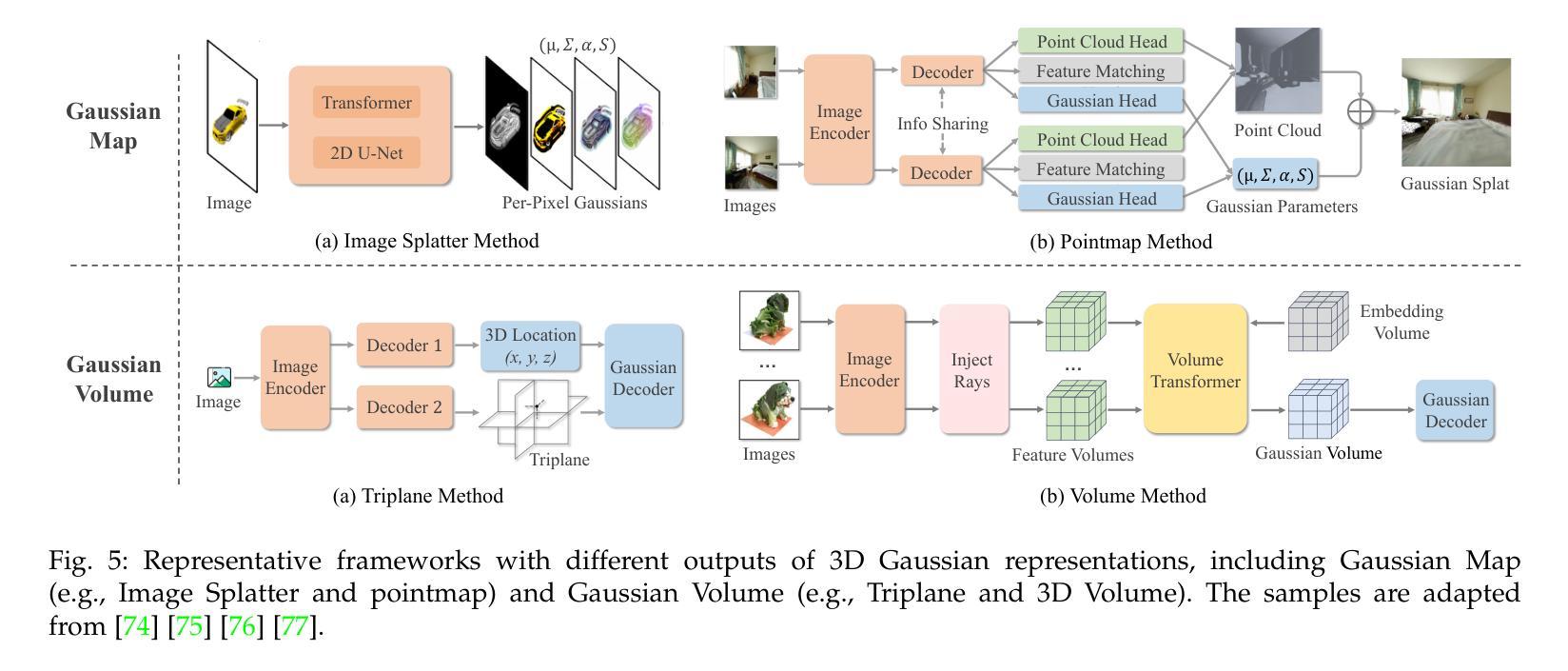
Advances in Feed-Forward 3D Reconstruction and View Synthesis: A Survey
Authors:Jiahui Zhang, Yuelei Li, Anpei Chen, Muyu Xu, Kunhao Liu, Jianyuan Wang, Xiao-Xiao Long, Hanxue Liang, Zexiang Xu, Hao Su, Christian Theobalt, Christian Rupprecht, Andrea Vedaldi, Kaichen Zhou, Paul Pu Liang, Shijian Lu, Fangneng Zhan
3D reconstruction and view synthesis are foundational problems in computer vision, graphics, and immersive technologies such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and digital twins. Traditional methods rely on computationally intensive iterative optimization in a complex chain, limiting their applicability in real-world scenarios. Recent advances in feed-forward approaches, driven by deep learning, have revolutionized this field by enabling fast and generalizable 3D reconstruction and view synthesis. This survey offers a comprehensive review of feed-forward techniques for 3D reconstruction and view synthesis, with a taxonomy according to the underlying representation architectures including point cloud, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), etc. We examine key tasks such as pose-free reconstruction, dynamic 3D reconstruction, and 3D-aware image and video synthesis, highlighting their applications in digital humans, SLAM, robotics, and beyond. In addition, we review commonly used datasets with detailed statistics, along with evaluation protocols for various downstream tasks. We conclude by discussing open research challenges and promising directions for future work, emphasizing the potential of feed-forward approaches to advance the state of the art in 3D vision.
3D重建和视图合成是计算机视觉、图形学以及增强现实(AR)、虚拟现实(VR)和数字孪生等沉浸式技术中的基础问题。传统方法依赖于复杂链中的计算密集型迭代优化,限制了它们在现实场景中的应用。最近,深度学习驱动的前馈方法的进步已经彻底改变了这一领域,实现了快速和通用的3D重建和视图合成。这篇综述对前馈技术在3D重建和视图合成方面的应用进行了全面回顾,并根据底层表示架构进行了分类,包括点云、3D高斯喷涂(3DGS)、神经辐射场(NeRF)等。我们研究了关键任务,如姿势无关重建、动态3D重建和3D感知图像和视频合成等,并强调了它们在数字人类、SLAM、机器人技术等领域的应用。此外,我们还回顾了常用数据集及其详细统计数据,以及各种下游任务的评估协议。最后,我们讨论了当前的研究挑战以及未来工作的有前途的方向,强调了前馈方法在推动3D视觉技术前沿的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF A project page associated with this survey is available at https://fnzhan.com/projects/Feed-Forward-3D
Summary
本文综述了基于深度学习的feed-forward技术在3D重建和视图合成方面的最新进展,介绍了其在计算机视觉、图形学和沉浸式技术等领域的应用。文章详细阐述了包括点云、3D高斯溅射(3DGS)、神经辐射场(NeRF)等在内的基础架构的税收分类,并强调了姿态自由重建、动态3D重建和3D感知图像和视频合成等关键任务在数字人类、SLAM、机器人等领域的应用。同时,本文还介绍了常用的数据集和评估协议,最后讨论了当前的研究挑战和未来有前景的研究方向,强调了feed-forward技术的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 3D重建和视图合成是计算机视觉、图形学和沉浸式技术的基础问题,涉及AR、VR和数字孪生等技术。
- 传统方法受限于计算密集型的迭代优化和复杂的链条,在真实场景中的应用有限。
- 基于深度学习的feed-forward方法已经革命化了3D重建和视图合成领域,实现了快速和通用的3D重建和视图合成。
- 文章介绍了包括点云、3DGS、NeRF等在内的基础架构的税收分类,并详细阐述了关键任务如姿态自由重建、动态3D重建和3D感知图像和视频合成等。
- 文章还讨论了数字人类、SLAM、机器人等领域的应用,并介绍了常用的数据集和评估协议。
- 当前的研究挑战和未来研究方向被强调,尤其是feed-forward技术的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

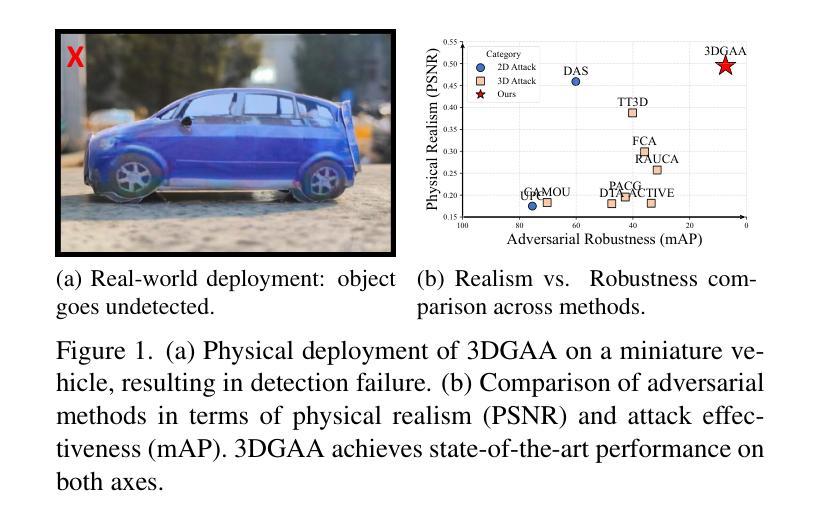
3DGAA: Realistic and Robust 3D Gaussian-based Adversarial Attack for Autonomous Driving
Authors:Yixun Zhang, Lizhi Wang, Junjun Zhao, Wending Zhao, Feng Zhou, Yonghao Dang, Jianqin Yin
Camera-based object detection systems play a vital role in autonomous driving, yet they remain vulnerable to adversarial threats in real-world environments. Existing 2D and 3D physical attacks, due to their focus on texture optimization, often struggle to balance physical realism and attack robustness. In this work, we propose 3D Gaussian-based Adversarial Attack (3DGAA), a novel adversarial object generation framework that leverages the full 14-dimensional parameterization of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) to jointly optimize geometry and appearance in physically realizable ways. Unlike prior works that rely on patches or texture optimization, 3DGAA jointly perturbs both geometric attributes (shape, scale, rotation) and appearance attributes (color, opacity) to produce physically realistic and transferable adversarial objects. We further introduce a physical filtering module that filters outliers to preserve geometric fidelity, and a physical augmentation module that simulates complex physical scenarios to enhance attack generalization under real-world conditions. We evaluate 3DGAA on both virtual benchmarks and physical-world setups using miniature vehicle models. Experimental results show that 3DGAA achieves to reduce the detection mAP from 87.21% to 7.38%, significantly outperforming existing 3D physical attacks. Moreover, our method maintains high transferability across different physical conditions, demonstrating a new state-of-the-art in physically realizable adversarial attacks.
基于摄像头的物体检测系统对于自动驾驶至关重要,但在真实世界环境中,它们仍然容易受到对抗性威胁的影响。现有的二维和三维物理攻击由于侧重于纹理优化,在平衡物理真实性和攻击稳健性方面往往面临挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了基于三维高斯的对抗攻击(3DGAA),这是一种新型的对抗性物体生成框架,它利用三维高斯模糊(3DGS)的完整的14维参数化,以物理可实现的方式联合优化几何和外观。与以往依赖补丁或纹理优化的工作不同,3DGAA联合扰动几何属性(形状、尺度、旋转)和外观属性(颜色、透明度),以产生物理真实性和可转移性的对抗性物体。我们还进一步引入了一个物理滤波模块,用于过滤异常值以保持几何保真度,以及一个物理增强模块,用于模拟复杂的物理场景,以增强在现实条件下的攻击通用性。我们在虚拟基准测试和物理环境设置中都使用了微型车辆模型来评估3DGAA。实验结果表明,3DGAA将检测mAP从87.21%降低到7.38%,显著优于现有的三维物理攻击。此外,我们的方法在不同的物理条件下保持了高可转移性,在物理可实现的对抗攻击中达到了最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to WACV 2026
摘要
相机基于物体检测系统在自动驾驶中起到重要作用,但在现实环境中易受对抗性威胁影响。现有的二维和三维物理攻击主要关注纹理优化,难以平衡物理真实性和攻击稳健性。本文提出基于三维高斯的新型对抗性物体生成框架——三维高斯对抗攻击(3DGAA)。该方法利用三维高斯插值(3DGS)的14维参数化进行几何和外观的联合优化,实现了物理可实现的优化方式。不同于依赖补丁或纹理优化的先前方法,3DGAA联合扰动几何属性(形状、尺度、旋转)和外观属性(颜色、透明度),生成具有物理真实性和可转移性的对抗性物体。此外,引入物理滤波模块过滤异常值以保持几何保真度,并引入物理增强模块模拟复杂物理场景以增强在现实条件下的攻击通用性。在虚拟基准测试和物理环境设置中,使用微型车辆模型对3DGAA进行评估。实验结果显示,3DGAA将检测mAP从87.21%降低到7.38%,显著优于现有三维物理攻击。此外,该方法在不同物理条件下保持高可转移性,成为物理可实现对抗攻击的最新顶尖技术。
关键要点
一、新型对抗性物体生成框架:提出了一种基于三维高斯的新型对抗攻击方法——三维高斯对抗攻击(3DGAA)。
二、优化方式:利用三维高斯插值(3DGS)的14维参数化进行几何和外观的联合优化,实现物理可实现的优化手段。
三、与传统方法的区别:与传统的依赖于补丁或纹理优化的方法不同,3DGAA同时扰动几何和外观属性。
四、物理滤波和增强模块:引入物理滤波模块保持几何真实性,引入物理增强模块以增强攻击在现实条件下的通用性。
五、实验验证:在虚拟基准和物理环境设置中的评估显示,3DGAA显著降低了物体检测精度,并表现出优秀的跨物理条件可转移性。
六、性能超越:相较于现有三维物理攻击,3DGAA取得了显著的优势。
点此查看论文截图

ODE-GS: Latent ODEs for Dynamic Scene Extrapolation with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Daniel Wang, Patrick Rim, Tian Tian, Alex Wong, Ganesh Sundaramoorthi
We introduce ODE-GS, a novel approach that integrates 3D Gaussian Splatting with latent neural ordinary differential equations (ODEs) to enable future extrapolation of dynamic 3D scenes. Unlike existing dynamic scene reconstruction methods, which rely on time-conditioned deformation networks and are limited to interpolation within a fixed time window, ODE-GS eliminates timestamp dependency by modeling Gaussian parameter trajectories as continuous-time latent dynamics. Our approach first learns an interpolation model to generate accurate Gaussian trajectories within the observed window, then trains a Transformer encoder to aggregate past trajectories into a latent state evolved via a neural ODE. Finally, numerical integration produces smooth, physically plausible future Gaussian trajectories, enabling rendering at arbitrary future timestamps. On the D-NeRF, NVFi, and HyperNeRF benchmarks, ODE-GS achieves state-of-the-art extrapolation performance, improving metrics by 19.8% compared to leading baselines, demonstrating its ability to accurately represent and predict 3D scene dynamics.
我们介绍了ODE-GS,这是一种将3D高斯Splatting与潜在神经常微分方程(ODEs)相结合的新型方法,能够对动态3D场景进行未来外推。与现有的依赖于时间条件变形网络且仅限于固定时间窗口内插值的动态场景重建方法不同,ODE-GS通过模拟高斯参数轨迹作为连续时间的潜在动态性,消除了时间戳依赖。我们的方法首先学习一个插值模型,在观察窗口内生成准确的高斯轨迹,然后训练一个Transformer编码器,将过去轨迹聚合成一个通过神经ODE演化的潜在状态。最后,数值积分生成平滑且物理上合理的未来高斯轨迹,能够在任意未来时间戳进行渲染。在D-NeRF、NVFi和HyperNeRF基准测试中,ODE-GS实现了最新的外推性能,与领先的基线相比,指标提高了19.8%,证明了其准确表示和预测3D场景动态的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
ODE-GS方法结合3D高斯融合与潜在神经常微分方程(ODEs),实现了动态3D场景的预测外推。不同于依赖时间条件变形网络的现有动态场景重建方法,ODE-GS通过模拟高斯参数轨迹的连续时间潜在动态,消除了时间戳的依赖,并能在观察到的窗口内生成准确的高斯轨迹。然后通过神经网络将过去的轨迹数据嵌入到一个潜在状态,最后通过数值积分生成平滑的未来高斯轨迹,可在任意未来时间戳进行渲染。在D-NeRF、NVFi和HyperNeRF基准测试中,ODE-GS实现了最先进的预测性能,与现有技术相比提高了19.8%,展现了其在预测复杂场景动态方面的强大能力。
Key Takeaways
- ODE-GS结合了3D高斯融合与潜在神经常微分方程(ODEs),实现了动态场景的外推预测。
- 该方法消除了时间戳依赖,通过模拟高斯参数轨迹的连续时间潜在动态来进行预测。
- ODE-GS能在观察窗口内生成准确的高斯轨迹。
- 该方法通过神经网络嵌入过去轨迹数据到一个潜在状态,并利用数值积分生成未来轨迹。
- ODE-GS在多个基准测试中实现了最先进的预测性能。
- 与现有技术相比,ODE-GS提高了预测性能,改进幅度达到19.8%。
点此查看论文截图

In-2-4D: Inbetweening from Two Single-View Images to 4D Generation
Authors:Sauradip Nag, Daniel Cohen-Or, Hao Zhang, Ali Mahdavi-Amiri
We pose a new problem, In-2-4D, for generative 4D (i.e., 3D + motion) inbetweening to interpolate two single-view images. In contrast to video/4D generation from only text or a single image, our interpolative task can leverage more precise motion control to better constrain the generation. Given two monocular RGB images representing the start and end states of an object in motion, our goal is to generate and reconstruct the motion in 4D, without making assumptions on the object category, motion type, length, or complexity. To handle such arbitrary and diverse motions, we utilize a foundational video interpolation model for motion prediction. However, large frame-to-frame motion gaps can lead to ambiguous interpretations. To this end, we employ a hierarchical approach to identify keyframes that are visually close to the input states while exhibiting significant motions, then generate smooth fragments between them. For each fragment, we construct a 3D representation of the keyframe using Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). The temporal frames within the fragment guide the motion, enabling their transformation into dynamic 3DGS through a deformation field. To improve temporal consistency and refine the 3D motion, we expand the self-attention of multi-view diffusion across timesteps and apply rigid transformation regularization. Finally, we merge the independently generated 3D motion segments by interpolating boundary deformation fields and optimizing them to align with the guiding video, ensuring smooth and flicker-free transitions. Through extensive qualitative and quantitive experiments as well as a user study, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our method and design choices.
我们针对生成式4D(即3D+运动)插值提出一个新问题,即In-2-4D,用以插值两个单视图图像。与仅从文本或单幅图像生成视频/4D内容不同,我们的插值任务可以利用更精确的运动控制来更好地约束生成。给定两个表示运动物体起始和结束状态的单目RGB图像,我们的目标是生成和重建4D中的运动,而不对物体类别、运动类型、长度或复杂性做出假设。为了处理这种任意和多样的运动,我们采用基础视频插值模型进行运动预测。然而,帧到帧的运动间隙过大可能会导致解释模糊。为此,我们采用分层方法识别视觉上接近输入状态且运动显著的关键帧,然后在它们之间生成平滑片段。对于每个片段,我们使用高斯拼贴(3DGS)构建关键帧的3D表示。片段内的临时帧指导运动,通过变形场将其转换为动态3DGS。为了提高时间一致性和优化3D运动,我们扩大了跨时间步的多视图扩散的自注意力,并应用了刚性变换正则化。最后,我们通过插值边界变形场并对其进行优化以与指导视频对齐,合并独立生成的3D运动片段,确保平滑无闪烁的过渡。通过广泛的定性和定量实验以及用户研究,我们验证了我们的方法和设计选择的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH ASIA 2025; Project page at https://in-2-4d.github.io/
Summary
本文提出一个新的生成问题,即In-2-4D问题,用于在二维图像之间进行四维(即三维加运动)插值。本文的目标是在给定的两个表示物体运动起始和结束状态的单视图图像之间生成和重建四维运动,无需假设物体类别、运动类型、长度或复杂性。通过采用分层方法识别视觉上接近输入状态且运动显著的关键帧,然后在它们之间生成平滑片段,并使用高斯拼贴技术(3DGS)构建每个片段的3D表示。时间帧指导运动,将其转化为动态3DGS。通过扩展跨时间步的多视图扩散的自注意力并应用刚性变换正则化,提高时间一致性和改进3D运动。最后,通过插值边界变形场并进行优化与指导视频对齐,确保平滑且无闪烁的过渡。通过定性和定量实验以及用户研究证明了方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出新的生成问题In-2-4D,用于在二维图像之间进行四维插值。
- 目标是从两个单视图图像生成和重建物体的四维运动,无需对物体类别、运动类型等做出假设。
- 采用分层方法识别关键帧,并使用高斯拼贴技术构建每个片段的3D表示。
- 时间帧指导运动,转化为动态3DGS。
- 通过扩展自注意力和应用刚性变换正则化,提高时间一致性和改进3D运动。
- 通过插值边界变形场并进行优化,确保平滑且无闪烁的过渡。
点此查看论文截图
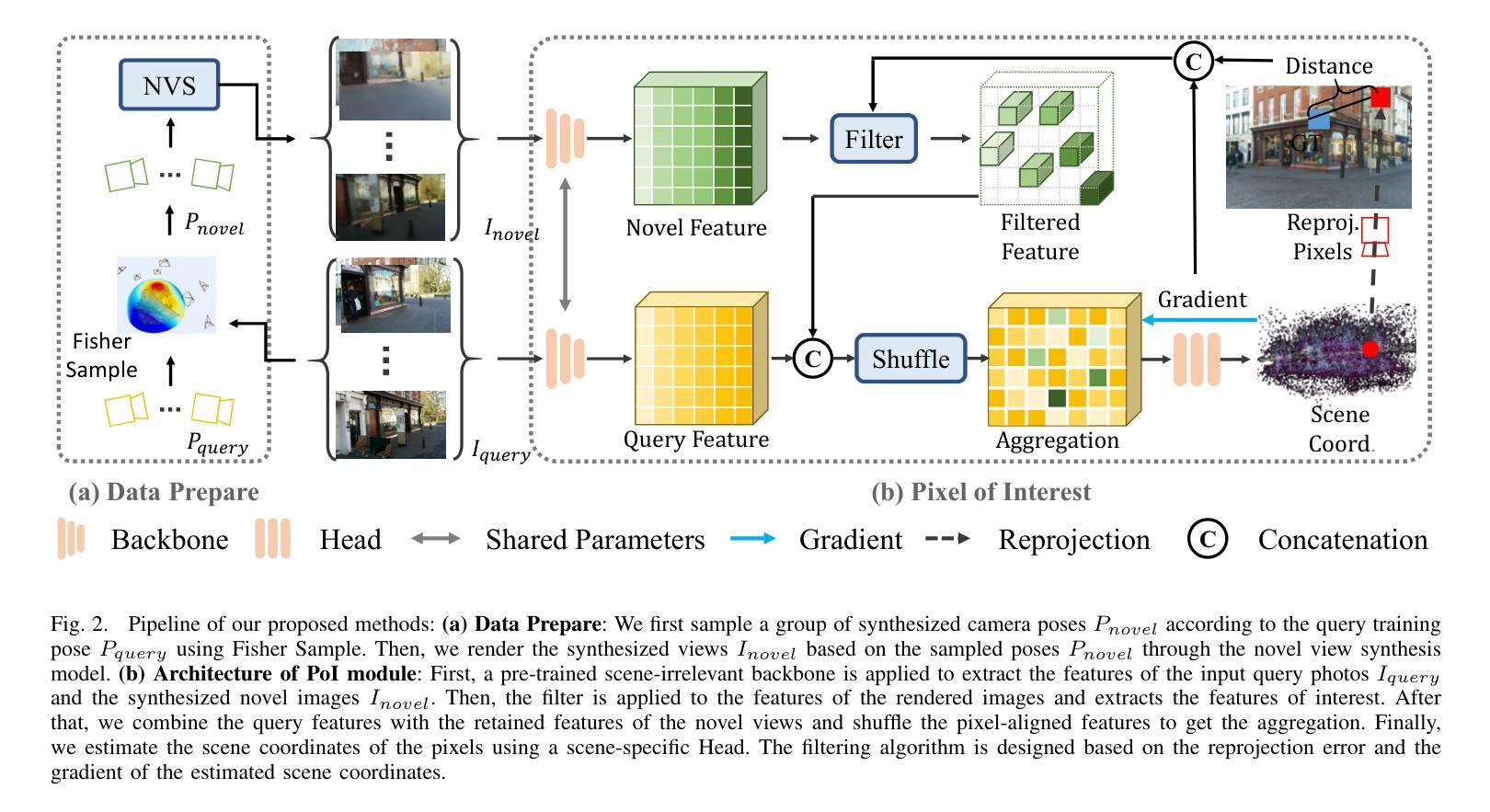
PoI: A Filter to Extract Pixel of Interest from Novel View Synthesis for Scene Coordinate Regression
Authors:Feifei Li, Qi Song, Chi Zhang, Hui Shuai, Rui Huang
Novel View synthesis (NVS) techniques, notably Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), can augment camera pose estimation by extending training data with rendered images. However, the images rendered by these methods are often plagued by blurring, undermining their reliability as training data for camera pose estimation. This limitation is particularly critical for Scene Coordinate Regression (SCR) methods, which aim at pixel-level 3D coordinate estimation, because rendering artifacts directly lead to estimation inaccuracies. To address this challenge, we propose a dual-criteria filtering mechanism that dynamically identifies and discards suboptimal pixels during training. The dual-criteria filter evaluates two concurrent metrics: (1) real-time SCR reprojection error, and (2) gradient threshold, across the coordinate regression domain. In addition, for visual localization problems in sparse input scenarios, it will be even more necessary to use data generated by NVS to assist the localization task. We design a coarse-to-fine PoI variant using sparse input NVS to solve this problem. Experiments across indoor and outdoor benchmarks confirm our method’s efficacy. It achieves state-of-the-art localization accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency.
新型视图合成(NVS)技术,特别是神经辐射场(NeRF)和3D高斯喷射(3DGS),可以通过使用渲染图像扩展训练数据来增强相机姿态估计。然而,这些方法呈现的渲染图像常常受到模糊的影响,这使得它们作为相机姿态估计的训练数据的可靠性降低。这一局限性对于场景坐标回归(SCR)方法尤为重要,因为SCR方法旨在进行像素级的3D坐标估计,渲染伪影直接导致估计不准确。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种双标准过滤机制,该机制在训练过程中动态识别并丢弃次优像素。双标准过滤器评估两个并行指标:(1)实时SCR重投影误差和(2)坐标回归域内的梯度阈值。此外,在稀疏输入的视觉定位问题中,使用NVS生成的数据辅助定位任务将变得更加必要。我们设计了一种使用稀疏输入NVS的由粗到细的PoI变体来解决这个问题。室内和室外基准测试的实验结果证实了我们的方法的有效性。它在保持计算效率的同时实现了最先进的定位精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
NeRF和3DGS等新型视图合成技术可以通过生成渲染图像来扩充训练数据,从而提升相机姿态估计的准确度。然而,这些技术生成的图像常常存在模糊问题,这会对作为相机姿态估计训练数据的可靠性造成影响。针对这一问题,文章提出了一种基于双重标准的过滤机制,该机制能在训练过程中动态识别并剔除表现不佳的像素点。双重标准过滤器同时评估实时场景坐标回归重投影误差和梯度阈值两个指标,以提高坐标回归领域的估计精度。此外,对于稀疏输入情况下的视觉定位问题,使用新型视图合成技术辅助定位任务尤为必要。设计了一种基于稀疏输入的粗到细的PoI变体方法来解决这一问题,并在室内和室外基准测试上进行了实验验证,该方法在计算效率的同时实现了最先进的定位精度。
Key Takeaways
- NVS技术如NeRF和3DGS能够生成渲染图像来丰富训练数据,进而改进相机姿态估计。
- 渲染图像中常见的模糊问题会影响训练数据作为相机姿态估计的可靠性。
- 双重标准的过滤机制能动态剔除表现不佳的像素点,同时考虑实时场景坐标回归重投影误差和梯度阈值两个指标。
- 提出的机制提高了坐标回归领域的估计精度。
- 在稀疏输入情况下,使用NVS技术辅助视觉定位任务十分重要。
- 设计的粗到细的PoI方法基于稀疏输入,旨在解决视觉定位问题。
点此查看论文截图
PERSE: Personalized 3D Generative Avatars from A Single Portrait
Authors:Hyunsoo Cha, Inhee Lee, Hanbyul Joo
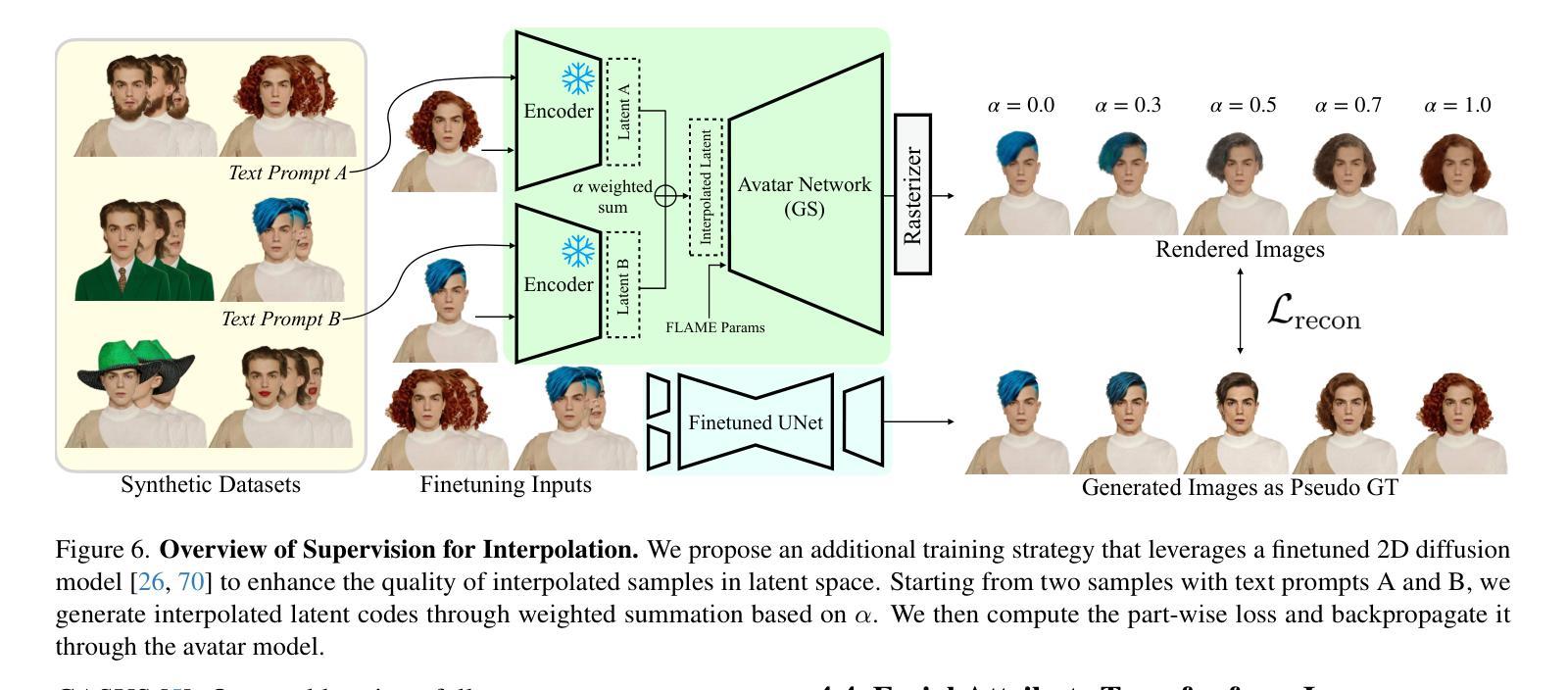
We present PERSE, a method for building a personalized 3D generative avatar from a reference portrait. Our avatar enables facial attribute editing in a continuous and disentangled latent space to control each facial attribute, while preserving the individual’s identity. To achieve this, our method begins by synthesizing large-scale synthetic 2D video datasets, where each video contains consistent changes in facial expression and viewpoint, along with variations in a specific facial attribute from the original input. We propose a novel pipeline to produce high-quality, photorealistic 2D videos with facial attribute editing. Leveraging this synthetic attribute dataset, we present a personalized avatar creation method based on 3D Gaussian Splatting, learning a continuous and disentangled latent space for intuitive facial attribute manipulation. To enforce smooth transitions in this latent space, we introduce a latent space regularization technique by using interpolated 2D faces as supervision. Compared to previous approaches, we demonstrate that PERSE generates high-quality avatars with interpolated attributes while preserving the identity of the reference individual.
我们提出了PERSE方法,该方法可以从参考肖像构建个性化的3D生成头像。我们的头像能够在连续且分离的特征空间中对面部特征进行编辑,以控制每个面部特征,同时保留个人的身份特征。为了实现这一点,我们的方法首先合成大规模合成二维视频数据集,每个视频都包含面部表情和视角的一致变化,以及原始输入中特定面部特征的变化。我们提出了一种新的流程来生成高质量、逼真的二维视频,并进行面部特征编辑。利用这个合成属性数据集,我们提出了一种基于个性化头像创建方法的三维高斯拼贴技术,学习一个连续且分离的特征空间,以便于直观地进行面部特征操作。为了在这个特征空间中实现平滑过渡,我们引入了一种特征空间正则化技术,使用插值二维面部作为监督。与以前的方法相比,我们证明PERSE可以生成高质量头像,具有插值属性,同时保留参考个体的身份特征。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2025, Project Page: https://hyunsoocha.github.io/perse/
Summary
该项目提出了一种基于参考肖像构建个性化3D生成头像的方法PERSE。该方法能够在连续的、分离的潜在空间中对头像的面部属性进行编辑,同时保持个体身份的识别。它通过合成大规模二维视频数据集开始,每个视频包含面部表情和视角的一致变化,以及来自原始输入的特定面部属性的变化。基于此合成属性数据集,研究提出了一种基于3D高斯拼贴的个人化头像创建方法,学习一个连续的、分离的潜在空间以进行直观的面部属性操作。通过插值二维面孔作为监督引入潜在空间的正则化技术,以确保在此潜在空间中实现平滑过渡。与以前的方法相比,PERSE生成的头像质量更高,属性插值自然,同时保持了参考个体的身份。
Key Takeaways
- PERSE方法能够基于参考肖像构建个性化3D生成头像。
- 它在连续的、分离的潜在空间中对头像的面部属性进行编辑。
- 该方法通过合成大规模二维视频数据集开始,包含面部表情、视角以及特定面部属性的变化。
- 利用合成属性数据集,采用基于3D高斯拼贴的方法创建个性化头像。
- 学习了一个连续的、分离的潜在空间以进行直观的面部属性操作。
- 通过插值二维面孔作为监督引入潜在空间的正则化技术。
点此查看论文截图