⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-01 更新
ReasoningBank: Scaling Agent Self-Evolving with Reasoning Memory
Authors:Siru Ouyang, Jun Yan, I-Hung Hsu, Yanfei Chen, Ke Jiang, Zifeng Wang, Rujun Han, Long T. Le, Samira Daruki, Xiangru Tang, Vishy Tirumalashetty, George Lee, Mahsan Rofouei, Hangfei Lin, Jiawei Han, Chen-Yu Lee, Tomas Pfister
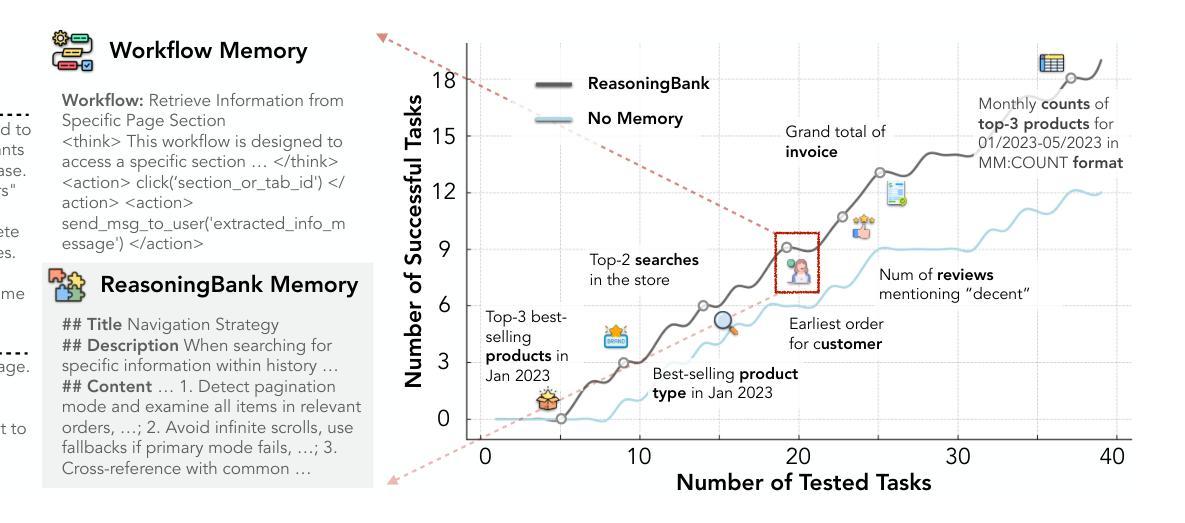
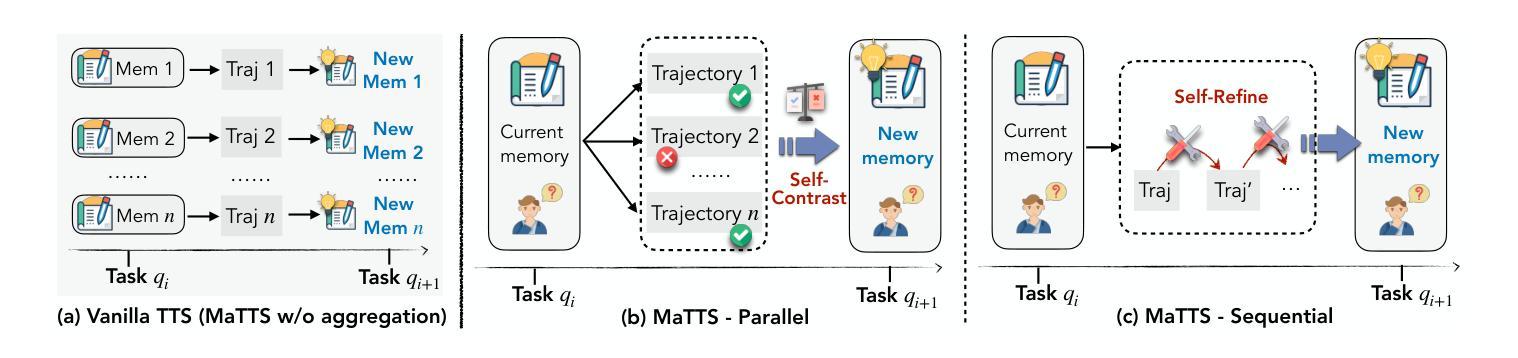
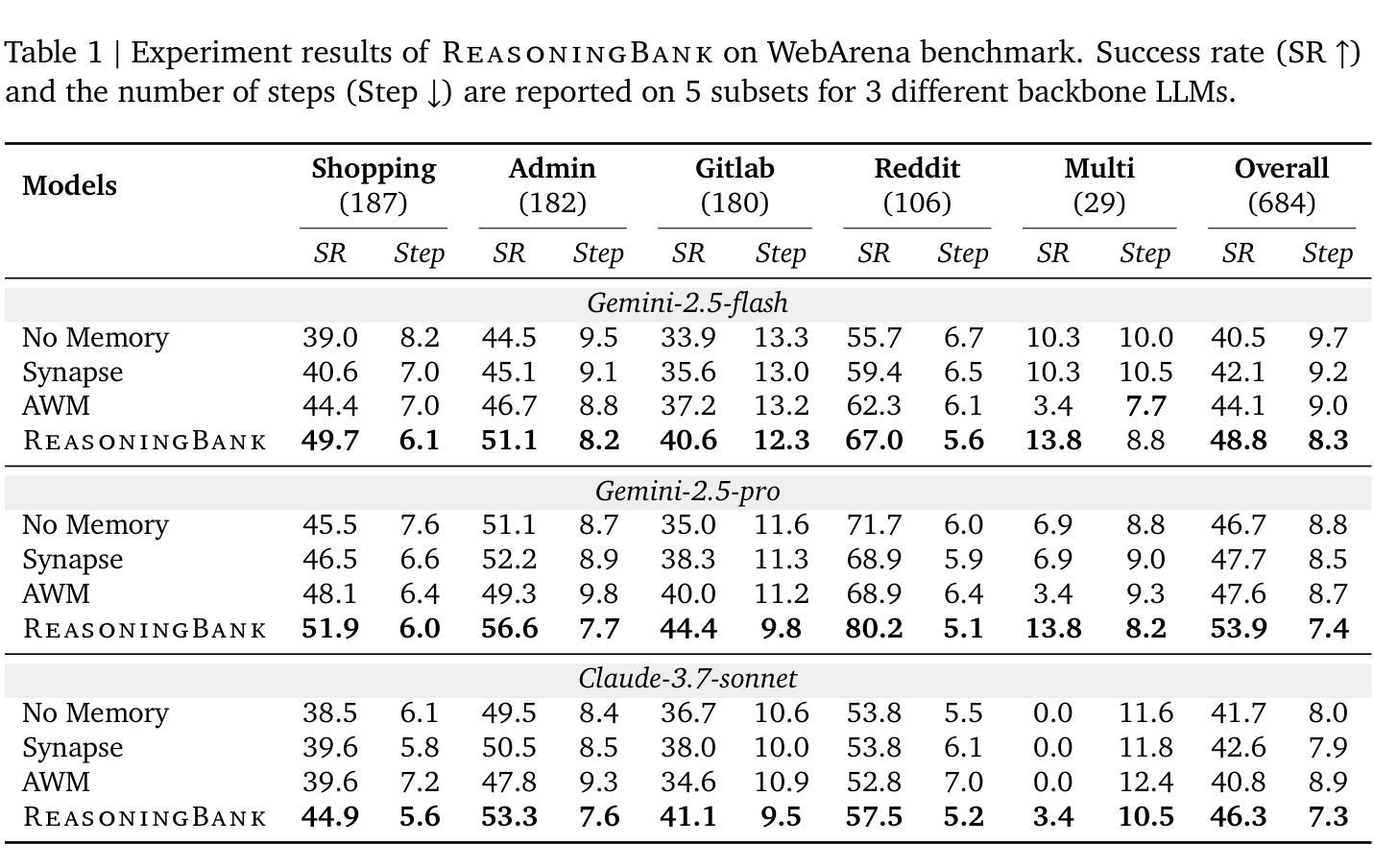
With the growing adoption of large language model agents in persistent real-world roles, they naturally encounter continuous streams of tasks. A key limitation, however, is their failure to learn from the accumulated interaction history, forcing them to discard valuable insights and repeat past errors. We propose ReasoningBank, a novel memory framework that distills generalizable reasoning strategies from an agent’s self-judged successful and failed experiences. At test time, an agent retrieves relevant memories from ReasoningBank to inform its interaction and then integrates new learnings back, enabling it to become more capable over time. Building on this powerful experience learner, we further introduce memory-aware test-time scaling (MaTTS), which accelerates and diversifies this learning process by scaling up the agent’s interaction experience. By allocating more compute to each task, the agent generates abundant, diverse experiences that provide rich contrastive signals for synthesizing higher-quality memory. The better memory in turn guides more effective scaling, establishing a powerful synergy between memory and test-time scaling. Across web browsing and software engineering benchmarks, ReasoningBank consistently outperforms existing memory mechanisms that store raw trajectories or only successful task routines, improving both effectiveness and efficiency; MaTTS further amplifies these gains. These findings establish memory-driven experience scaling as a new scaling dimension, enabling agents to self-evolve with emergent behaviors naturally arise.
随着大型语言模型代理在持久现实世界角色中的日益普及,它们自然会遇到连续的任务流。然而,它们的一个关键局限性在于无法从累积的交互历史中学习,迫使它们放弃有价值的见解并重复过去的错误。我们提出了ReasoningBank,这是一个新的记忆框架,它能从代理自我判断的成功和失败经验中提炼出可推广的推理策略。在测试时,代理从ReasoningBank中检索相关记忆以指导其交互,然后将新的学习成果整合回来,随着时间的推移,使其能力越来越强。在此基础上,我们进一步引入了记忆感知测试时缩放(MaTTS),它通过扩大代理的交互经验来加速和多样化学习过程。通过为每个任务分配更多的计算资源,代理生成了丰富、多样的经验,为合成高质量内存提供了丰富的对比信号。更好的内存反过来又指导更有效的缩放,在内存和测试时缩放之间建立了强大的协同作用。在网页浏览和软件工程基准测试中,ReasoningBank始终优于现有的存储原始轨迹或仅存储成功任务例程的记忆机制,提高了有效性和效率;MaTTS进一步放大了这些收益。这些发现确立了以记忆驱动的经验缩放作为新的缩放维度,使代理能够自然地出现自我进化行为和突发行为。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 7 figures, 4 tables
Summary
大型语言模型代理在实际持续场景中日益普及,但它们缺乏从累积的互动历史中学习,导致无法避免重复错误。为此,我们提出ReasoningBank,一种能够蒸馏代理成功与失败经验中的可推广策略的新型记忆框架。在测试时,代理能够从ReasoningBank中检索相关记忆以指导交互,并将新学习整合到记忆中,使其随时间变得更加有能力。在此基础上,我们进一步引入了记忆感知测试时缩放(MaTTS),通过扩大代理的交互经验来加速和多样化学习过程。ReasoningBank在网页浏览和软件工程基准测试中表现优异,优于现有仅存储原始轨迹或成功任务例程的记忆机制;MaTTS进一步扩大了这些优势。这些发现确立了以记忆驱动的经验缩放作为一种新型缩放维度,使代理能够自然地自我进化并出现新兴行为。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型代理在实际场景中遇到的主要挑战是无法从互动历史中学习。
- ReasoningBank是一种新型记忆框架,能够从代理的成功和失败经验中提炼出可推广的策略。
- 代理在测试时能够从ReasoningBank中检索相关记忆来指导交互,并整合新学习。
- Memory-aware test-time scaling(MaTTS)通过扩大代理的交互经验来加速学习过程并促进多样化。
- ReasoningBank在网页浏览和软件工程基准测试中表现优于现有记忆机制。
- MaTTS进一步增强了ReasoningBank的优势。
点此查看论文截图
HeDA: An Intelligent Agent System for Heatwave Risk Discovery through Automated Knowledge Graph Construction and Multi-layer Risk Propagation Analysis
Authors:Yiquan Wang, Tin-Yeh Huang, Qingyun Gao, Jialin Zhang
Heatwaves pose complex cascading risks across interconnected climate, social, and economic systems, but knowledge fragmentation in scientific literature hinders comprehensive understanding of these risk pathways. We introduce HeDA (Heatwave Discovery Agent), an intelligent multi-agent system designed for automated scientific discovery through knowledge graph construction and multi-layer risk propagation analysis. HeDA processes over 10,247 academic papers to construct a comprehensive knowledge graph with 23,156 nodes and 89,472 relationships, employing novel multi-layer risk propagation analysis to systematically identify overlooked risk transmission pathways. Our system achieves 78.9% accuracy on complex question-answering tasks, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines including GPT-4 by 13.7%. Critically, HeDA successfully discovered five previously unidentified high-impact risk chains, such as the pathway where a heatwave leads to a water demand surge, resulting in industrial water restrictions and ultimately causing small business disruption, which were validated through historical case studies and domain expert review. This work presents a new paradigm for AI-driven scientific discovery, providing actionable insights for developing more resilient climate adaptation strategies.
热浪在相互关联的气候、社会和经济系统中带来了复杂的连锁风险,但科学文献中的知识碎片化阻碍了对这些风险路径的全面理解。我们引入了HeDA(热浪发现代理),这是一个智能多代理系统,通过知识图谱构建和多层风险传播分析,实现自动化科学发现。HeDA处理了超过10,247篇学术论文,构建了一个包含23,156个节点和89,472个关系的知识图谱,采用新颖的多层风险传播分析,系统地识别被忽视的风险传播路径。我们的系统在复杂的问答任务上达到了78.9%的准确率,超过了包括GPT-4在内的最新基线13.7%。关键的是,HeDA成功发现了之前未被识别的五条高影响风险链,例如热浪导致用水需求激增,进而导致工业用水限制,最终造成小企业中断的路径,这些风险链已经通过历史案例研究和领域专家评审得到了验证。这项工作为AI驱动的科学发现提供了新的范式,为制定更具弹性的气候适应策略提供了可操作的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
热浪对气候、社会和经济的相互关联系统构成复杂的连锁风险,而科学文献的知识碎片化阻碍了对这些风险路径的全面理解。我们引入了HeatDA(热浪发现代理),这是一种智能多代理系统,通过知识图谱构建和多层风险传播分析,实现自动化科学发现。HeatDA处理了超过一万多篇学术论文,构建了包含两万多个节点和近十万条关系的知识图谱。该系统通过新颖的多层风险传播分析系统地识别出被忽视的风险传播路径,对复杂问答任务的准确率达到了百分之七十八点九,超越了包括GPT-4在内的最新技术水平标准百分之十三点七。此外,HeatDA成功发现了五条以前未被发现的高影响风险链,比如一条由热浪引发供水需求激增、进而采取工业用水限制措施并最终导致小企业受扰的路径等。这一发现得到了历史案例研究和领域专家的验证。本研究为人工智能驱动的科学发现提供了新范例,为制定更具适应性的气候适应策略提供了行动性见解。
Key Takeaways
- 热浪对气候、社会和经济的相互关联系统造成复杂连锁风险。
- 知识碎片化阻碍了科学文献中对这些风险路径的全面理解。
- HeatDA是一种智能多代理系统,旨在通过知识图谱构建和多层风险传播分析进行自动化科学发现。
- HeatDA处理了超过一万多篇学术论文以建立全面知识图谱,包含了广泛的数据关系和节点信息。
- 系统展现出较高的性能准确性(准确率达到了百分之七十八点九),超越了现有的技术水平标准。
点此查看论文截图
Scaling Generalist Data-Analytic Agents
Authors:Shuofei Qiao, Yanqiu Zhao, Zhisong Qiu, Xiaobin Wang, Jintian Zhang, Zhao Bin, Ningyu Zhang, Yong Jiang, Pengjun Xie, Fei Huang, Huajun Chen
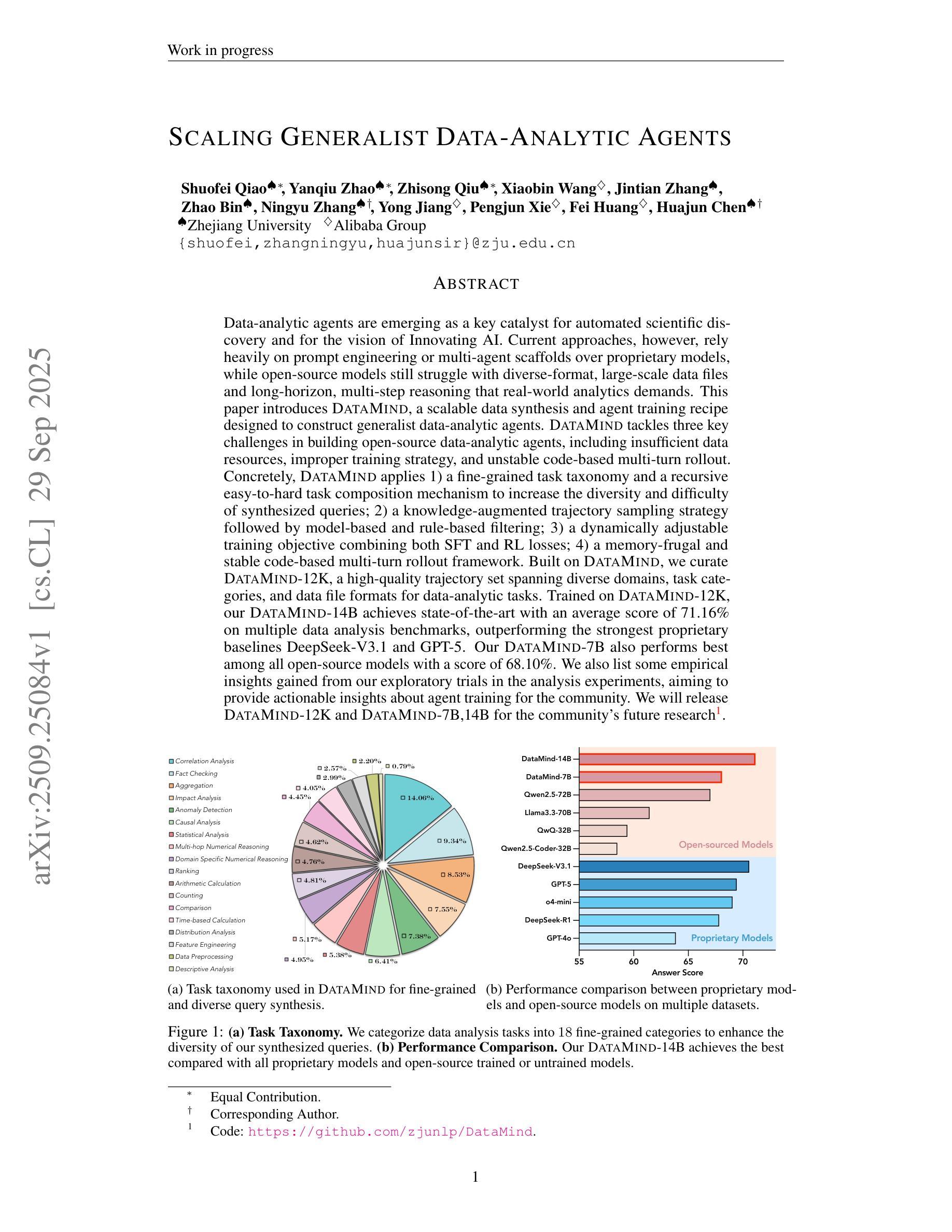
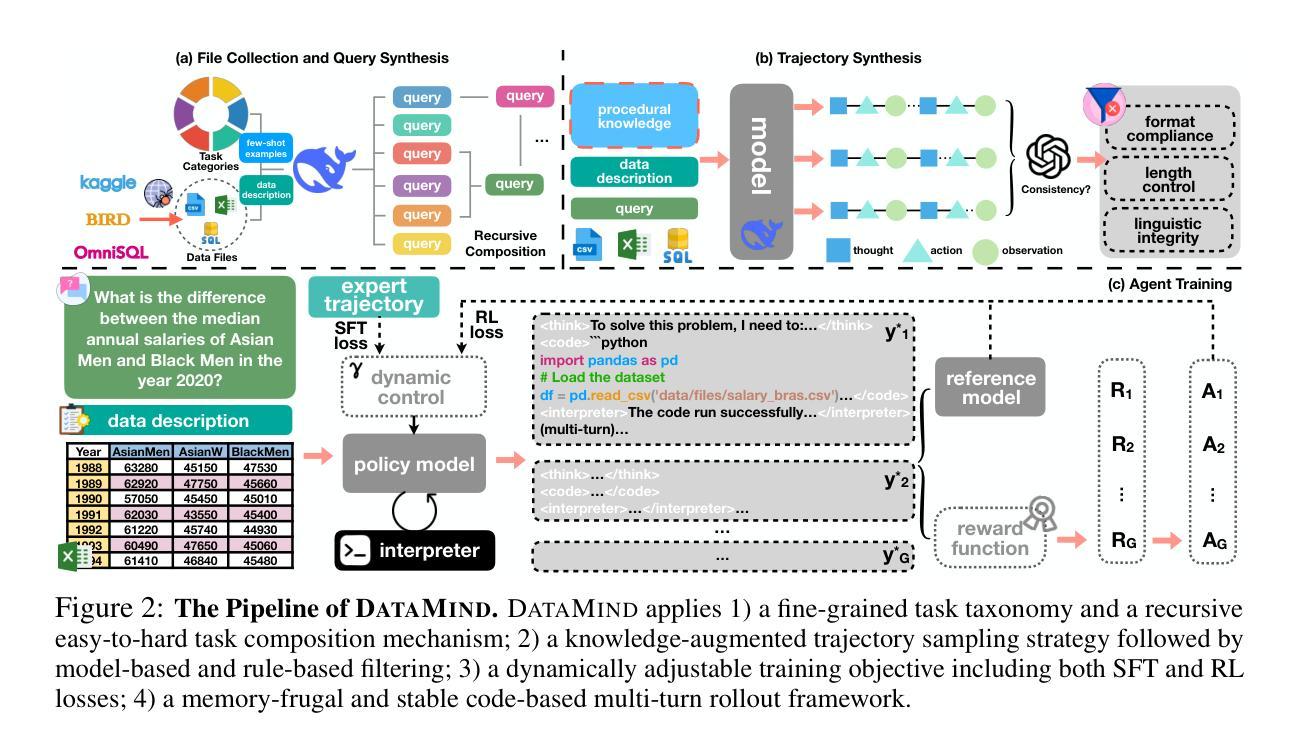
Data-analytic agents are emerging as a key catalyst for automated scientific discovery and for the vision of Innovating AI. Current approaches, however, rely heavily on prompt engineering over proprietary models, while open-source models struggle to face diverse-format, large-scale data files and long-horizon, multi-step reasoning that real-world analytics demands. This paper introduces DataMind, a scalable data synthesis and agent training recipe designed to build generalist data-analytic agents. DataMind tackles three key challenges in building open-source data-analytic agents, including insufficient data resources, improper training strategy, and unstable code-based multi-turn rollout. Concretely, DataMind applies 1) a fine-grained task taxonomy and a recursive easy-to-hard task composition mechanism to increase the diversity and difficulty of synthesized queries; 2) a knowledge-augmented trajectory sampling strategy followed by model-based and rule-based filtering; 3) a dynamically adjustable training objective combining both SFT and RL losses; 4) a memory-frugal and stable code-based multi-turn rollout framework. Built on DataMind, we curate DataMind-12K, a high-quality trajectory set spanning diverse domains, task categories, and data file formats for data-analytic tasks. Trained on DataMind-12K, our DataMind-14B achieves state-of-the-art with an average score of 71.16% on multiple data analysis benchmarks, outperforming the strongest proprietary baselines DeepSeek-V3.1 and GPT-5. Our DataMind-7B also performs best among all open-source models with a score of 68.10%. We also incorporate some empirical insights gained from our exploratory trials into the analysis experiments, aiming to provide actionable insights about agentic training for the community. We will release DataMind-12K and DataMind-7B,14B for the community’s future research.
数据解析代理正成为推动自动化科学发现和人工智能创新愿景的关键催化剂。然而,当前的方法严重依赖于专有模型的即时工程,而开源模型则面临现实世界分析所要求的多样格式的大规模数据文件以及长期、多步骤推理的挑战。本文介绍了DataMind,这是一种可扩展的数据合成和代理训练配方,旨在构建通用数据解析代理。DataMind解决了构建开源数据解析代理的三个关键挑战,包括数据资源不足、不当的训练策略以及基于代码的多轮不稳定滚动。具体来说,DataMind采用了1)精细的任务分类和递归的易至难任务组合机制,以增加合成查询的多样性和难度;2)知识增强轨迹采样策略,随后是模型驱动的过滤规则和基于模型的过滤;3)动态可调整的训练目标,结合SFT和RL损失;4)内存紧凑且稳定基于代码的多轮滚动框架。基于DataMind,我们创建了DataMind-12K,这是一组高质量轨迹集,涵盖多个领域、任务类别和数据文件格式的数据分析任务。在DataMind-12K上训练的DataMind-14B在多数据分析基准测试中达到了平均得分71.16%,超过了最强的专有基线DeepSeek-V3.1和GPT-5。我们的DataMind-7B在所有开源模型中也表现最佳,得分为68.10%。我们还从探索性试验中获得了一些经验见解,并将其纳入分析实验,旨在为社区提供有关代理训练的可行见解。我们将为社区未来的研究发布DataMind-12K和DataMind-7B、14B。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
数据解析代理正成为自动化科学发现和人工智能创新的关键催化剂。当前方法过于依赖专有模型的提示工程,而开源模型难以应对多样格式、大规模数据文件以及真实世界分析所需的长周期、多步骤推理。本文介绍DataMind,一种用于构建通用数据解析代理的可扩展数据合成和代理训练配方。DataMind解决了构建开源数据解析代理的三个关键挑战,包括数据资源不足、不当的训练策略以及基于代码的滚动不稳定问题。其应用包括精细化任务分类和递归易至难的任务组合机制,增加合成查询的多样性和难度;知识增强轨迹采样策略,辅以模型与规则过滤;动态可调的训练目标结合SFT和RL损失;以及内存紧凑且稳定的基于代码的多轮滚动框架。基于DataMind构建的数据集DataMind-12K包含跨越不同领域、任务类别和数据文件格式的数据分析任务高质量轨迹集。在多个数据分析基准测试中,经过DataMind-12K训练的DataMind-14B以平均得分71.16%达到最新水平,超越了最先进的专有基线DeepSeek-V3.1和GPT-5。开源模型DataMind-7B也以得分68.10%表现最佳。本文还结合分析实验中的经验见解,旨在为社区提供关于代理训练的实际见解。我们将为社区的未来研究发布DataMind-12K和DataMind-7B、DataMind-14B。
Key Takeaways
- 数据解析代理在自动化科学发现和人工智能创新中起关键作用。
- 当前方法依赖专有模型的提示工程,而开源模型面临多样格式数据、长周期多步骤推理等挑战。
- DataMind提出一种构建通用数据解析代理的方法,解决数据资源、训练策略和代码滚动不稳定等问题。
- DataMind包括精细化任务分类、知识增强轨迹采样、动态可调训练目标和基于代码的多轮滚动框架等关键应用。
- 基于DataMind构建的数据集DataMind-12K适用于多种数据分析任务。
- DataMind训练的模型在多个数据分析基准测试中表现最佳,超过现有先进模型。
点此查看论文截图
Cogito, Ergo Ludo: An Agent that Learns to Play by Reasoning and Planning
Authors:Sai Wang, Yu Wu, Zhongwen Xu
The pursuit of artificial agents that can learn to master complex environments has led to remarkable successes, yet prevailing deep reinforcement learning methods often rely on immense experience, encoding their knowledge opaquely within neural network weights. We propose a different paradigm, one in which an agent learns to play by reasoning and planning. We introduce Cogito, ergo ludo (CEL), a novel agent architecture that leverages a Large Language Model (LLM) to build an explicit, language-based understanding of its environment’s mechanics and its own strategy. Starting from a tabula rasa state with no prior knowledge (except action set), CEL operates on a cycle of interaction and reflection. After each episode, the agent analyzes its complete trajectory to perform two concurrent learning processes: Rule Induction, where it refines its explicit model of the environment’s dynamics, and Strategy and Playbook Summarization, where it distills experiences into an actionable strategic playbook. We evaluate CEL on diverse grid-world tasks (i.e., Minesweeper, Frozen Lake, and Sokoban), and show that the CEL agent successfully learns to master these games by autonomously discovering their rules and developing effective policies from sparse rewards. Ablation studies confirm that the iterative process is critical for sustained learning. Our work demonstrates a path toward more general and interpretable agents that not only act effectively but also build a transparent and improving model of their world through explicit reasoning on raw experience.
追求能够学习掌握复杂环境的智能体已经取得了显著的成果。然而,当前流行的深度强化学习方法往往依赖于大量的经验,将知识以不透明的方式编码在神经网络权重中。我们提出了一种不同的范式,即一个通过推理和规划来学习的智能体。我们引入了Cogito,ergo ludo(CEL),这是一种新型智能体架构,它利用大型语言模型(LLM)来建立基于语言的对环境机制和自身策略的明确理解。从无知的状态开始(除了动作集之外没有任何先验知识),CEL通过互动和反思进行循环操作。在每一集之后,智能体会对其完整轨迹进行分析,同时进行两个并行学习过程:规则归纳,它精炼了对环境动力学的明确模型;策略和剧本摘要,它将经验提炼成可操作的战略剧本。我们在多种网格世界任务(如扫雷、冰冻湖和搬运工)中评估了CEL,结果显示CEL智能体通过自主发现规则并从稀疏奖励中制定有效策略,成功掌握了这些游戏。消融研究证实,迭代过程对于持续学习至关重要。我们的工作展示了一条通往更通用和可解释的智能体的道路,这些智能体不仅有效地行动,而且通过明确推理原始经验来建立透明且不断改善的世界模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
提出一种新型智能体架构Cogito,ergo ludo(CEL),利用大型语言模型(LLM)构建基于语言的环境机制及自身策略明确理解。CEL通过交互与反思循环工作,在经历每一回合后,进行规则归纳与策略及手册摘要学习。在网格世界任务中评估,CEL智能体可自主发现规则并发展有效策略,从稀疏奖励中学习掌握游戏。
Key Takeaways
- 新型智能体架构Cogito,ergo ludo(CEL)被提出,结合大型语言模型(LLM)技术。
- CEL智能体通过交互与反思循环工作,实现规则归纳和策略及手册摘要学习。
- CEL智能体能够从稀疏奖励中学习掌握游戏,展现出强大的学习能力。
- 在多种网格世界任务中评估,包括Minesweeper、Frozen Lake和Sokoban等游戏,CEL智能体成功掌握游戏规则并发展有效策略。
- 迭代过程对于持续学习至关重要,这是CEL智能体成功学习的重要机制。
- CEL智能体的架构走向更加通用和可解释性,不仅能有效行动,还能通过理性分析建立对世界的透明改善模型。
点此查看论文截图

The Dialogue That Heals: A Comprehensive Evaluation of Doctor Agents’ Inquiry Capability
Authors:Linlu Gong, Ante Wang, Yunghwei Lai, Weizhi Ma, Yang Liu
An effective physician should possess a combination of empathy, expertise, patience, and clear communication when treating a patient. Recent advances have successfully endowed AI doctors with expert diagnostic skills, particularly the ability to actively seek information through inquiry. However, other essential qualities of a good doctor remain overlooked. To bridge this gap, we present MAQuE(Medical Agent Questioning Evaluation), the largest-ever benchmark for the automatic and comprehensive evaluation of medical multi-turn questioning. It features 3,000 realistically simulated patient agents that exhibit diverse linguistic patterns, cognitive limitations, emotional responses, and tendencies for passive disclosure. We also introduce a multi-faceted evaluation framework, covering task success, inquiry proficiency, dialogue competence, inquiry efficiency, and patient experience. Experiments on different LLMs reveal substantial challenges across the evaluation aspects. Even state-of-the-art models show significant room for improvement in their inquiry capabilities. These models are highly sensitive to variations in realistic patient behavior, which considerably impacts diagnostic accuracy. Furthermore, our fine-grained metrics expose trade-offs between different evaluation perspectives, highlighting the challenge of balancing performance and practicality in real-world clinical settings.
一个出色的医生在医治病人时,应具备同情心、专业知识、耐心和清晰的沟通能力。最近的技术进步已经成功赋予AI医生专业的诊断技能,尤其是通过询问主动获取信息的能力。然而,其他作为好医生的重要品质仍然被忽视。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了MAQuE(医疗代理询问评估),这是迄今为止最大的医疗多轮询问自动综合评估基准。它拥有3000个模拟的真实患者代理,展现了多样化的语言模式、认知局限、情绪反应和被动披露的倾向。我们还引入了一个多方面的评估框架,涵盖任务成功、询问能力、对话能力、询问效率和患者体验。在不同的大型语言模型上的实验表明,在评估方面存在很大的挑战。即使是最新技术水平的模型也显示出其在询问能力方面仍有很大的提升空间。这些模型对现实患者行为的敏感性很高,这会对诊断的准确性产生重大影响。此外,我们的精细指标暴露了不同评估角度之间的权衡,突出了在真实世界临床环境中平衡性能和实用性的挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
AI医生在诊断技能上已具备专家级水平,尤其在通过询问主动获取信息方面。但MAQuE(医疗代理问答评估)提出,优秀医生的其他重要品质仍被忽视。该评估系统模拟真实患者,推出医疗多轮问答的自动综合评估。评估框架涵盖任务成功、询问能力、对话能力、询问效率及患者体验。不同大型语言模型的实验表明,存在多方面的挑战。即使是顶尖模型,在询问能力上也有待提高,尤其是在面对真实患者行为的变化时,诊断准确性受影响较大。此外,精细的评估指标揭示了不同评估角度之间的权衡问题,凸显了在现实临床环境中平衡性能和实用性的挑战。
Key Takeaways
- AI医生已具备专家级诊断技能,尤其在主动获取信息方面。
- MAQuE系统强调优秀医生的其他品质,如共情、耐心和清晰沟通的重要性。
- MAQuE系统模拟真实患者,提供医疗多轮问答的自动综合评估。
- 评估框架涵盖任务成功、询问能力、对话能力等多个方面。
- 实验显示,不同大型语言模型在医疗问答方面面临多方面的挑战。
- 顶尖模型在询问能力上仍有待提高,面对真实患者行为变化时诊断准确性受影响。
点此查看论文截图
Perceive, Reflect and Understand Long Video: Progressive Multi-Granular Clue Exploration with Interactive Agents
Authors:Jiahua Li, Kun Wei, Zhe Xu, Zibo Su, Xu Yang, Cheng Deng
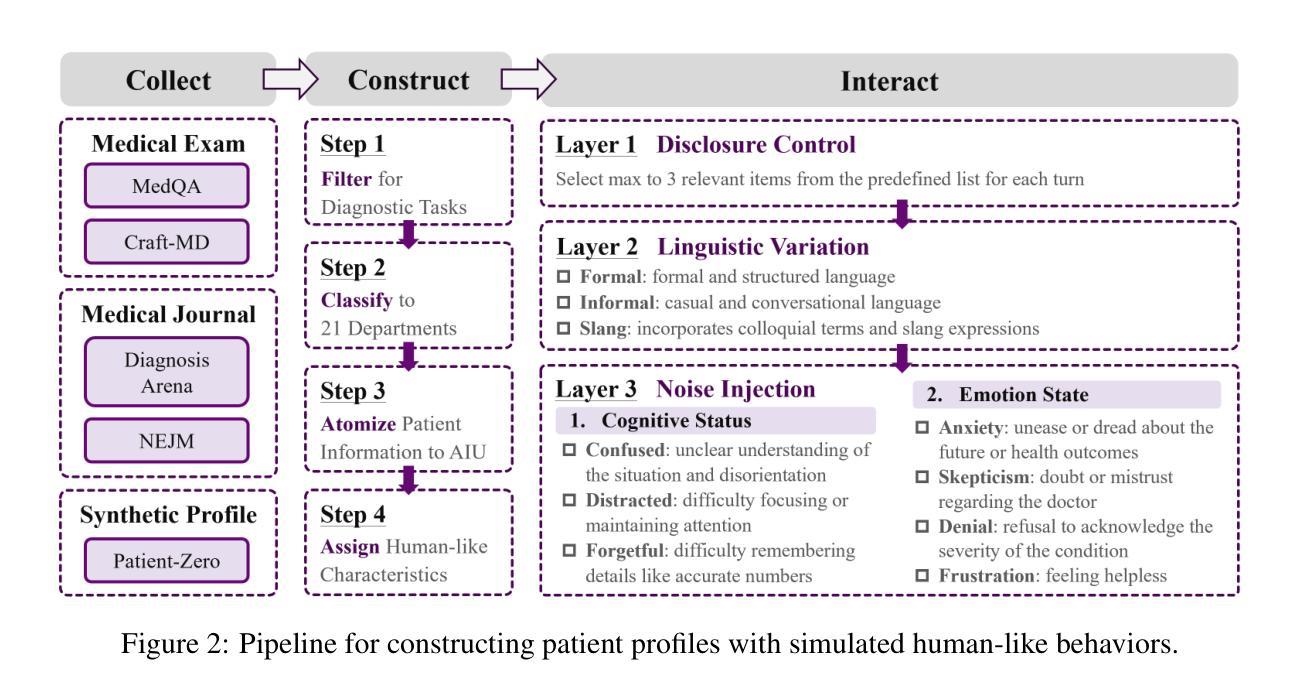
Long videos, characterized by temporal complexity and sparse task-relevant information, pose significant reasoning challenges for AI systems. Although various Large Language Model (LLM)-based approaches have advanced long video understanding, they still struggle to achieve both completeness and efficiency in capturing task-critical information. Inspired by human progressive visual cognition, we propose CogniGPT, a framework that leverages an interactive loop between Multi-Granular Perception Agent (MGPA) and Verification-Enhanced Reflection Agent (VERA) for efficient and reliable long video understanding. Specifically, MGPA mimics human visual divergent and focused attention to capture task-related information, while VERA verifies perceived key clues to mitigate hallucination and optimize subsequent perception strategies. Through this interactive process, CogniGPT explores a minimal set of informative and reliable task-related clues. Extensive experiments on EgoSchema, Video-MME, NExT-QA, and MovieChat datasets demonstrate CogniGPT’s superiority in both accuracy and efficiency. Notably, on EgoSchema, it surpasses existing training-free methods using only 11.2 frames and achieves performance comparable to Gemini 1.5-Pro.
长视频具有时间复杂性和稀疏的任务相关信息,为AI系统带来了重大的推理挑战。尽管基于大型语言模型(LLM)的各种方法已经推动了长视频理解的发展,但它们仍然难以在捕捉任务关键信息时同时实现完整性和效率。受到人类渐进式视觉认知的启发,我们提出了CogniGPT框架,它利用多粒度感知代理(MGPA)和增强验证反射代理(VERA)之间的交互循环,实现高效可靠的长视频理解。具体来说,MGPA模仿人类的视觉发散和集中注意力来捕捉与任务相关的信息,而VERA验证感知到的关键线索,以减轻幻觉并优化随后的感知策略。通过这一交互过程,CogniGPT探索了一组信息丰富且可靠的任务相关线索。在EgoSchema、Video-MME、NExT-QA和MovieChat数据集上的大量实验表明,CogniGPT在准确性和效率方面都表现出卓越的性能。值得注意的是,在EgoSchema上,它仅使用11.2帧超越了现有的无训练方法,并实现了与Gemini 1.5-Pro相当的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于人类渐进式视觉认知的启发,提出了一种名为CogniGPT的框架,用于高效可靠地理解长视频内容。该框架通过多粒度感知代理(MGPA)与验证增强反射代理(VERA)之间的交互循环实现这一目标。CogniGPT在多个数据集上的表现证明了其在准确性和效率方面的优势。通过模仿人类视觉注意力机制以及采用验证过程来修正错误和提高感知策略,实现更为可靠的视频理解。此外,通过选择最少但可靠的任务相关线索来降低推理复杂度,从而进一步提高效率。实验证明,相较于现有方法,该框架性能优异。总体来说,它解决了AI系统对长视频理解的推理挑战,特别是在内容复杂度较高、任务相关信息稀疏的情况下展现出明显优势。具体实现方法是通过模仿人类视觉认知机制以及结合验证过程实现高效准确的长视频理解。对于内容较长的视频信息理解和推理而言具有重要的实用价值和应用前景。通过有效的数据处理方式显著提高了处理效率和准确性。这一框架有望推动AI系统在长视频内容理解方面的进一步发展。认知图谱技术在实际应用中表现出良好的性能和潜力。
Key Takeaways
点此查看论文截图

MASLegalBench: Benchmarking Multi-Agent Systems in Deductive Legal Reasoning
Authors:Huihao Jing, Wenbin Hu, Hongyu Luo, Jianhui Yang, Wei Fan, Haoran Li, Yangqiu Song
Multi-agent systems (MAS), leveraging the remarkable capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), show great potential in addressing complex tasks. In this context, integrating MAS with legal tasks is a crucial step. While previous studies have developed legal benchmarks for LLM agents, none are specifically designed to consider the unique advantages of MAS, such as task decomposition, agent specialization, and flexible training. In fact, the lack of evaluation methods limits the potential of MAS in the legal domain. To address this gap, we propose MASLegalBench, a legal benchmark tailored for MAS and designed with a deductive reasoning approach. Our benchmark uses GDPR as the application scenario, encompassing extensive background knowledge and covering complex reasoning processes that effectively reflect the intricacies of real-world legal situations. Furthermore, we manually design various role-based MAS and conduct extensive experiments using different state-of-the-art LLMs. Our results highlight the strengths, limitations, and potential areas for improvement of existing models and MAS architectures.
多智能体系统(MAS)借助大型语言模型(LLM)的卓越能力,在应对复杂任务方面显示出巨大潜力。在此背景之下,将MAS与法律任务相结合是至关重要的一步。尽管已有研究为LLM智能体开发了法律基准测试,但尚无专门针对MAS的独特优势设计的基准测试,如任务分解、智能体专业化和灵活训练等。事实上,缺乏评估方法限制了MAS在法律领域的潜力。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了MASLegalBench,这是一个专为MAS定制的法律基准测试,采用演绎推理方法设计。我们的基准测试以GDPR为应用场景,包含丰富的背景知识,涵盖有效的推理过程,充分反映了现实法律情境的复杂性。此外,我们还手动设计了各种基于角色的MAS,并使用不同的先进LLM进行了广泛的实验。我们的结果突显了现有模型和MAS架构的优势、局限性和潜在的改进方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于多代理系统(MAS)利用大型语言模型(LLM)的突出功能,展现出解决复杂任务的巨大潜力。在整合法律任务方面,MAS尤为重要。虽然已有法律基准针对LLM代理开发,但没有专门考虑MAS的独特优势,如任务分解、代理专业化以及灵活的训练等。为解决这一空白,我们提出MASLegalBench,一个专为MAS设计的法律基准,采用演绎推理方法。此基准以GDPR为应用场景,包含丰富的背景知识,涵盖有效反映现实法律情境的复杂推理过程。此外,我们手动设计了各种基于角色的MAS,并使用不同的先进LLM进行广泛实验。结果突显了现有模型和MAS架构的优势、局限性和改进潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 多代理系统(MAS)借助大型语言模型(LLM)在处理复杂任务时具有巨大潜力。
- 在法律任务方面,MAS具有独特优势,如任务分解和灵活训练等。
- 目前缺乏专为MAS设计的法律基准,限制了其在法律领域的应用潜力。
- MASLegalBench是一个专为MAS设计的法律基准,采用演绎推理方法,以GDPR为应用场景。
- MASLegalBench包含丰富的背景知识,能有效反映现实法律情境的复杂推理过程。
- 实验结果表明,现有模型和MAS架构存在优势、局限性和改进空间。
点此查看论文截图
AIPOM: Agent-aware Interactive Planning for Multi-Agent Systems
Authors:Hannah Kim, Kushan Mitra, Chen Shen, Dan Zhang, Estevam Hruschka
Large language models (LLMs) are being increasingly used for planning in orchestrated multi-agent systems. However, existing LLM-based approaches often fall short of human expectations and, critically, lack effective mechanisms for users to inspect, understand, and control their behaviors. These limitations call for enhanced transparency, controllability, and human oversight. To address this, we introduce AIPOM, a system supporting human-in-the-loop planning through conversational and graph-based interfaces. AIPOM enables users to transparently inspect, refine, and collaboratively guide LLM-generated plans, significantly enhancing user control and trust in multi-agent workflows. Our code and demo video are available at https://github.com/megagonlabs/aipom.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)在多智能体系统协同规划中的应用越来越广泛,但基于LLM的方法往往不能满足人类期望,并且缺乏有效的机制让用户检查、理解和控制其行为。这些局限性要求对透明度、可控性和人类监督进行改进。为解决这一问题,我们引入了AIPOM系统,该系统通过基于对话和图的用户界面支持人类循环规划。AIPOM使用户能够透明地检查、优化和协同指导LLM生成的计划,从而显著提高了用户对多智能体工作流程的控制力和信任度。我们的代码和演示视频可在https://github.com/megagonlabs/aipom获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF EMNLP 2025 Demo
Summary:
大型语言模型(LLM)在多智能体系统的协同规划中被广泛应用,但现有方法往往未能达到人类期望,缺乏有效机制让用户检查、理解并控制其行为。为解决这一问题,我们提出了AIPOM系统,它通过对话和图形界面支持人类参与规划。AIPOM使用户能够透明地检查、优化并协作指导LLM生成的计划,从而显著提高用户对多智能体工作流程的控制和信任度。详情访问我们的GitHub仓库:https://github.com/megagonlabs/aipom。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在多智能体系统的协同规划中得到广泛应用。
- 现有LLM方法存在未能满足人类期望的问题。
- LLM缺乏有效机制让用户检查、理解并控制其行为。
- 为解决这些问题,提出了AIPOM系统。
- AIPOM系统通过对话和图形界面支持人类参与规划。
- AIPOM提高了用户对多智能体工作流程的控制和信任度。
点此查看论文截图

From Ambiguity to Verdict: A Semiotic-Grounded Multi-Perspective Agent for LLM Logical Reasoning
Authors:Yunyao Zhang, Xinglang Zhang, Junxi Sheng, Wenbing Li, Junqing Yu, Wei Yang, Zikai Song
Logical reasoning is a fundamental capability of large language models (LLMs). However, existing studies largely overlook the interplay between logical complexity and semantic complexity, resulting in methods that struggle to address challenging scenarios involving abstract propositions, ambiguous contexts, and conflicting stances, which are central to human reasoning. For this gap, we propose LogicAgent, a semiotic-square-guided framework designed to jointly address logical complexity and semantic complexity. LogicAgent explicitly performs multi-perspective deduction in first-order logic (FOL), while mitigating vacuous reasoning through existential import checks that incorporate a three-valued decision scheme (True, False, Uncertain) to handle boundary cases more faithfully. Furthermore, to overcome the semantic simplicity and low logical complexity of existing datasets, we introduce RepublicQA, a benchmark that reaches college-level difficulty (FKGL = 11.94) and exhibits substantially greater lexical and structural diversity than prior benchmarks. RepublicQA is grounded in philosophical concepts, featuring abstract propositions and systematically organized contrary and contradictory relations, making it the most semantically rich resource for evaluating logical reasoning. Experiments demonstrate that LogicAgent achieves state-of-the-art performance on RepublicQA, with a 6.25% average gain over strong baselines, and generalizes effectively to mainstream logical reasoning benchmarks including ProntoQA, ProofWriter, FOLIO, and ProverQA, achieving an additional 7.05% average gain. These results highlight the strong effectiveness of our semiotic-grounded multi-perspective reasoning in boosting LLMs’ logical performance.
逻辑推理是大型语言模型(LLM)的基本能力。然而,现有研究大多忽视了逻辑复杂性与语义复杂性之间的相互作用,导致现有方法难以应对涉及抽象命题、模糊上下文和冲突立场的挑战场景,而这些是人类推理的核心。针对这一差距,我们提出了LogicAgent,这是一个以符号平方为指导的框架,旨在共同解决逻辑复杂性和语义复杂性。LogicAgent明确地在第一范式逻辑(FOL)中进行多角度推理,同时通过存在性导入检查来缓解空洞推理,该检查结合了三种值决策方案(真、假、不确定)以更真实地处理边界情况。此外,为了克服现有数据集语义简单、逻辑复杂度低的问题,我们推出了RepublicQA,这是一个难度达到大学水平(FKGL=11.94)的基准测试,其词汇和结构多样性明显高于以前的基准测试。RepublicQA以哲学概念为基础,具有抽象命题和系统组织的相反和矛盾关系,成为评估逻辑推理方面最语义丰富的资源。实验表明,LogicAgent在RepublicQA上达到了最新技术水平,平均优于强基线6.25%,并能有效地推广到主流逻辑推理基准测试,包括ProntoQA、ProofWriter、FOLIO和ProverQA,平均增益额外达到7.05%。这些结果凸显了我们基于符号的多角度推理的强大有效性,提升了LLM的逻辑性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了大型语言模型在逻辑与语义双重复杂性场景下的推理能力问题。为此,提出LogicAgent框架,结合数理逻辑的第一视角推理和多视角分析来解决这一问题。此外,还推出了全新的数据集RepublicQA来强化评估模型的逻辑水平,以应对现有的评估标准的不足。实验表明,LogicAgent框架能有效提升模型性能,并且在主流逻辑推理测试集上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在应对逻辑与语义双重复杂性场景下的推理存在挑战。
- 现有研究忽略了逻辑复杂性和语义复杂性之间的交互影响。
- LogicAgent框架结合数理逻辑的第一视角推理和多视角分析来解决这一问题。
- LogicAgent通过存在性检查来避免空洞推理,并采用三值决策方案处理边界情况。
- RepublicQA数据集用以强化评估模型的逻辑水平,具有更高的难度和丰富的词汇和结构多样性。
- LogicAgent在RepublicQA上的表现优于其他基线模型,平均提升了6.25%。
点此查看论文截图
Socratic-Zero : Bootstrapping Reasoning via Data-Free Agent Co-evolution
Authors:Shaobo Wang, Zhengbo Jiao, Zifan Zhang, Yilang Peng, Xu Ze, Boyu Yang, Wei Wang, Hu Wei, Linfeng Zhang
Recent breakthroughs in large language models (LLMs) on reasoning tasks rely heavily on massive, high-quality datasets-typically human-annotated and thus difficult to scale. While data synthesis or distillation offers a promising alternative, existing methods struggle with inconsistent data quality and an inability to dynamically adapt to the evolving capabilities of the model, leading to suboptimal training signals. To address these limitations, we introduce Socratic-Zero, a fully autonomous framework that generates high-quality training data from minimal seed examples through the co-evolution of three agents: the Teacher, the Solver, and the Generator. The Solver continuously refines its reasoning by learning from preference feedback on both successful and failed trajectories; the Teacher adaptively crafts increasingly challenging questions based on the Solver’s weaknesses; and the Generator distills the Teacher’s question-design strategy to enable scalable, high-fidelity curriculum generation. This closed-loop system produces a self-improving curriculum-requiring no pre-existing tasks or labels. Remarkably, starting from only 100 seed questions, our Socratic-Solver-8B achieves an average gain of +20.2 percentage points over prior data synthesis methods across seven mathematical reasoning benchmarks (AMC23, AIME24-25, Olympiad, MATH-500, Minerva, and GSM8K), with consistent gains on both Qwen3 and GLM4 series models. Even more surprisingly, synthetic data from Socratic-Generator-32B enables student LLMs to achieve superior performance compared to other state-of-the-art (SOTA) commercial LLMs on these benchmarks, including Qwen3-235B-A22B, DeepSeek-V3.1-671B, GPT-5, Gemini-2.5-Pro, Grok-4, and Claude-4.1-Opus.
最近,大型语言模型(LLM)在推理任务方面的突破严重依赖于大规模的高质量数据集,这些数据集通常是人工标注的,因此难以扩展。虽然数据合成或蒸馏提供了一种有前途的替代方案,但现有方法在数据质量不一致和无法动态适应模型不断发展的能力方面存在困难,导致训练信号不佳。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了Socratic-Zero,这是一个完全自主的框架,它可以从少量种子示例生成高质量的训练数据,通过三个代理的协同进化:教师、求解器和生成器。求解器通过成功和失败轨迹的偏好反馈不断磨练其推理能力;教师根据求解器的弱点自适应地制定越来越具有挑战性的问题;生成器提炼教师的提问设计策略,以实现可扩展的高保真课程生成。这个闭环系统产生了一种自我改进的课程,无需预先存在的任务或标签。值得注意的是,仅从100个种子问题开始,我们的Socratic-Solver-8B在七个数学推理基准测试(AMC23、AIME24-25、Olympiad、MATH-500、Minerva和GSM8K)上相较于先前的数据合成方法平均提高了20.2个百分点,在Qwen3和GLM4系列模型上均实现了持续的收益。更令人惊讶的是,来自Socratic-Generator-32B的合成数据使学生LLM在这些基准测试上的表现优于其他先进(SOTA)的商业LLM,包括Qwen3-235B-A22B、DeepSeek-V3.1-671B、GPT-5、Gemini-2.5-Pro、Grok-4和Claude-4.1-Opus。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文介绍了Socratic-Zero框架,一个可以自主生成高质量训练数据的方法,仅需少量种子示例即可。该框架通过教师、求解器和生成器三个代理的协同进化,在无需预先存在的任务或标签的情况下,产生自我改进的课程。Socratic-Solver能在数学推理基准测试中取得平均+20.2%的增益,而Socratic-Generator产生的合成数据还能让学生LLM在基准测试中表现超过其他顶尖商业LLM。
Key Takeaways
- Socratic-Zero框架是一种用于生成高质量训练数据的方法,尤其适用于大规模语言模型(LLM)。
- 它使用教师、求解器和生成器三个代理的协同进化,以生成自我改进的课程。
- 该方法从少量种子示例开始,无需预先存在的任务或标签。
- Socratic-Solver在数学推理基准测试中取得了显著的平均增益。
- Socratic-Generator产生的合成数据使得学生LLM的表现在基准测试中超过了其他顶尖的商业LLM。
- 这个框架能够适应不断演变的模型能力,通过持续反馈来优化数据质量。
点此查看论文截图

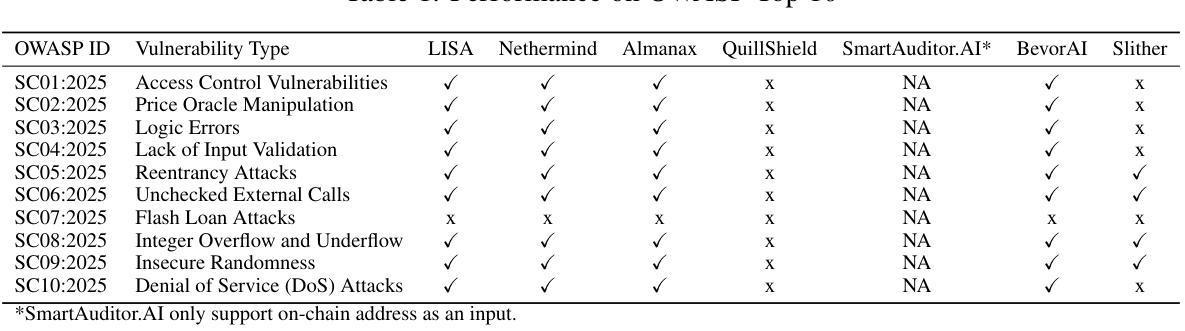
LISA Technical Report: An Agentic Framework for Smart Contract Auditing
Authors:Izaiah Sun, Daniel Tan, Andy Deng
We present LISA, an agentic smart contract vulnerability detection framework that combines rule-based and logic-based methods to address a broad spectrum of vulnerabilities in smart contracts. LISA leverages data from historical audit reports to learn the detection experience (without model fine-tuning), enabling it to generalize learned patterns to unseen projects and evolving threat profiles. In our evaluation, LISA significantly outperforms both LLM-based approaches and traditional static analysis tools, achieving superior coverage of vulnerability types and higher detection accuracy. Our results suggest that LISA offers a compelling solution for industry: delivering more reliable and comprehensive vulnerability detection while reducing the dependence on manual effort.
我们推出了LISA,这是一个智能合约漏洞检测框架,它结合了基于规则和基于逻辑的方法,以解决智能合约中的广泛漏洞问题。LISA利用历史审计报告的数据来学习检测经验(无需对模型进行微调),使其能够将学习到的模式推广到未见过的项目和不断变化的威胁配置文件。在我们的评估中,LISA显著优于基于LLM的方法和传统的静态分析工具,实现了对漏洞类型的卓越覆盖和更高的检测精度。我们的结果表明,LISA为行业提供了一个吸引人的解决方案:提供更可靠和全面的漏洞检测,同时减少对人工的依赖。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF A technical report with 10 pages
Summary
LISA是一个智能合约漏洞检测框架,结合规则基础和逻辑基础方法,针对智能合约的广泛漏洞进行解决。LISA利用历史审计报告的数据来学习检测经验,无需模型微调,并能够推广学到的模式到未见过的项目和不断变化的威胁配置文件。在评估中,LISA显著优于基于LLM的方法和传统的静态分析工具,实现了对漏洞类型的优越覆盖和更高的检测准确性,为行业提供了可靠且全面的漏洞检测解决方案,同时减少了人工干预的依赖。
Key Takeaways
- LISA是一个智能合约漏洞检测框架,融合了规则基础和逻辑基础方法。
- LISA能够从历史审计报告中学习检测经验,无需模型微调。
- LISA能够推广学到的模式到未见过的项目和适应不断变化的威胁配置文件。
- LISA在评估中表现出色,优于传统的静态分析工具和基于LLM的方法。
- LISA实现了对漏洞类型的优越覆盖和更高的检测准确性。
- LISA为行业提供了全面的解决方案,实现了可靠的漏洞检测。
点此查看论文截图
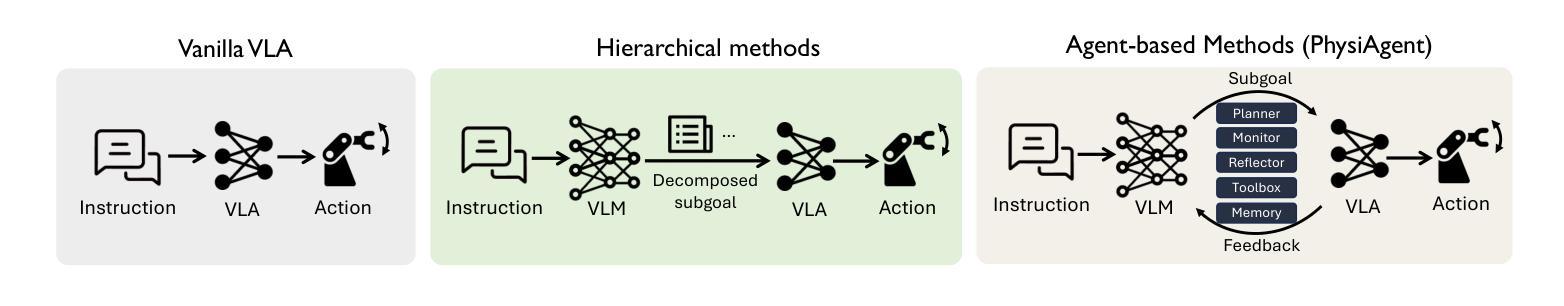
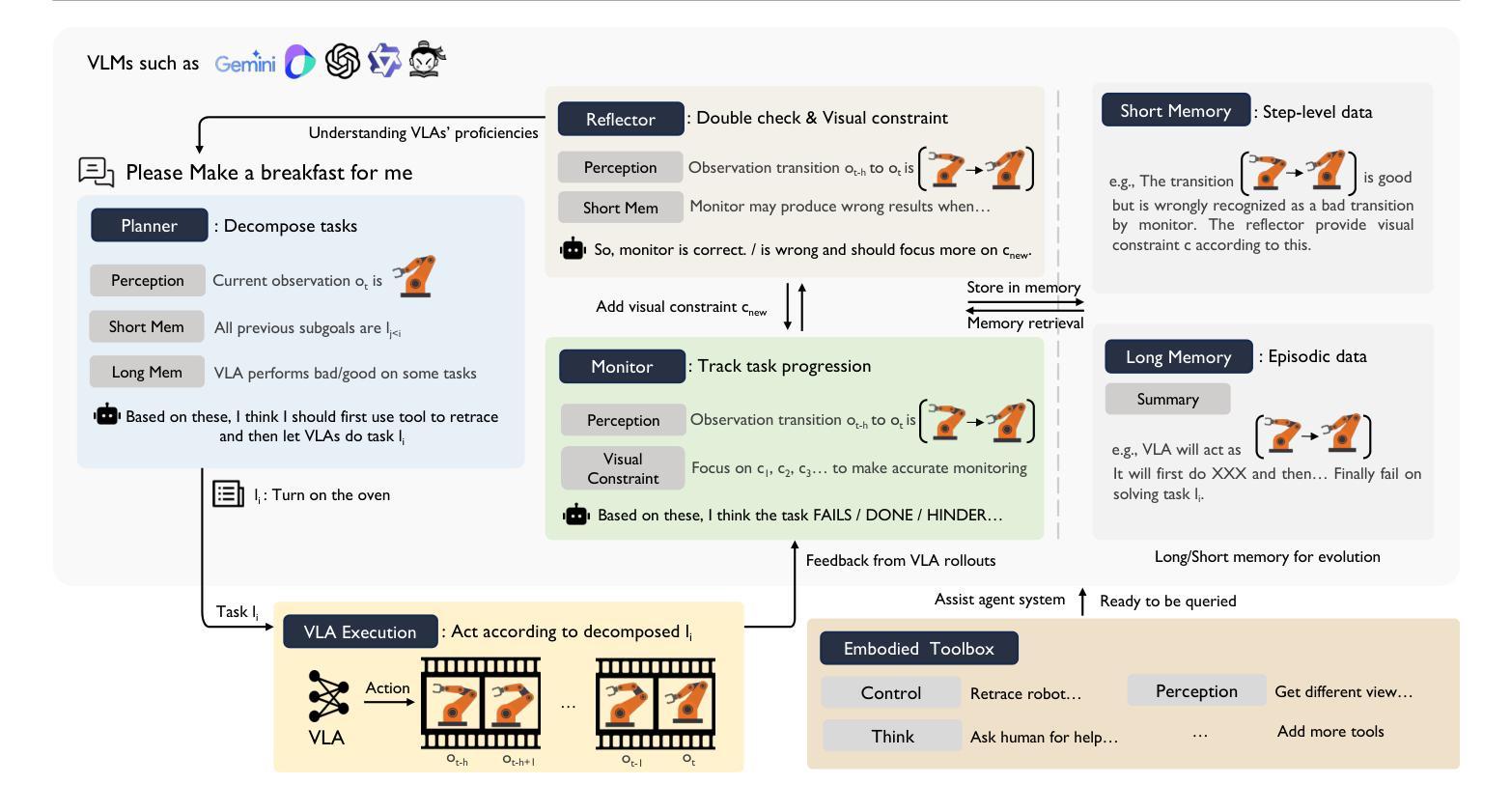
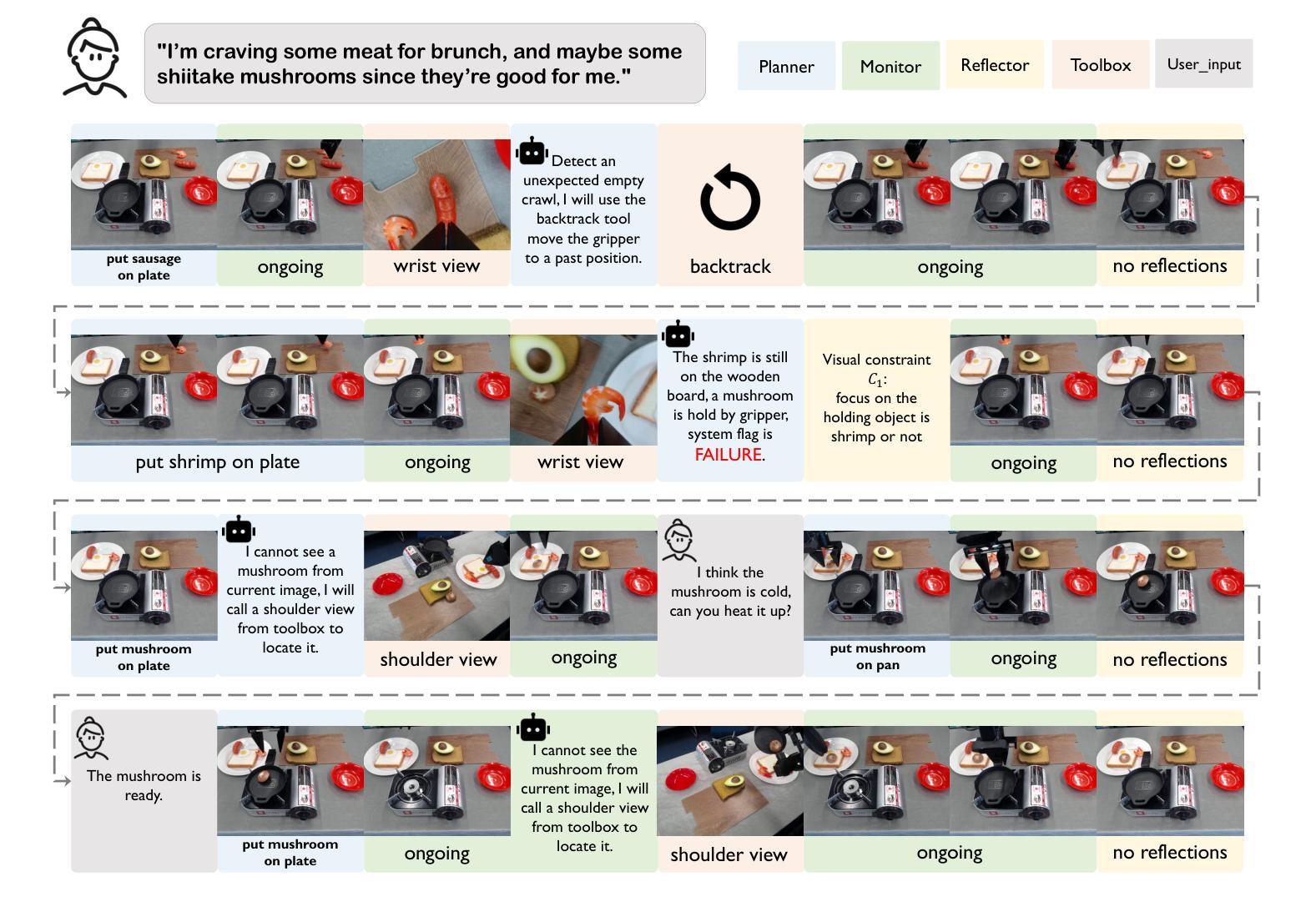
PhysiAgent: An Embodied Agent Framework in Physical World
Authors:Zhihao Wang, Jianxiong Li, Jinliang Zheng, Wencong Zhang, Dongxiu Liu, Yinan Zheng, Haoyi Niu, Junzhi Yu, Xianyuan Zhan
Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have achieved notable success but often struggle with limited generalizations. To address this, integrating generalized Vision-Language Models (VLMs) as assistants to VLAs has emerged as a popular solution. However, current approaches often combine these models in rigid, sequential structures: using VLMs primarily for high-level scene understanding and task planning, and VLAs merely as executors of lower-level actions, leading to ineffective collaboration and poor grounding challenges. In this paper, we propose an embodied agent framework, PhysiAgent, tailored to operate effectively in physical environments. By incorporating monitor, memory, self-reflection mechanisms, and lightweight off-the-shelf toolboxes, PhysiAgent offers an autonomous scaffolding framework to prompt VLMs to organize different components based on real-time proficiency feedback from VLAs to maximally exploit VLAs’ capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate significant improvements in task-solving performance on complex real-world robotic tasks, showcasing effective self-regulation of VLMs, coherent tool collaboration, and adaptive evolution of the framework during execution. PhysiAgent makes practical and pioneering efforts to integrate VLMs and VLAs, effectively grounding embodied agent frameworks in real-world settings.
视觉-语言-行动(VLA)模型已经取得了显著的成果,但在有限泛化方面常常遇到困难。为了解决这一问题,将泛化的视觉-语言模型(VLMs)作为VLA的辅助工具开始成为一种流行的解决方案。然而,当前的方法往往将这些模型以僵化的、顺序的结构进行组合:使用VLMs主要用于高级场景理解和任务规划,而VLAs仅作为执行低级动作的机构,导致合作无效和地面定位挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一个适应在物理环境中有效操作的实体代理框架PhysiAgent。通过融入监控、记忆、自我反思机制和轻量现成的工具箱,PhysiAgent提供了一个自主架构框架,可促使VLMs根据VLAs的实时熟练度反馈来组织不同的组件,以最大程度地利用VLAs的能力。实验结果表明,在复杂的真实世界机器人任务上,该框架在任务解决性能上实现了显著的提升,展示了VLMs的有效自我调节、工具之间的连贯协作以及框架在执行过程中的自适应进化。PhysiAgent在整合VLMs和VLAs方面进行了实用和开创性的努力,有效地将实体代理框架根植于真实世界环境中。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种针对物理环境的自主式代理框架PhysiAgent,通过引入监视器、内存、自我反思机制和轻量级现成的工具箱来整合通用的视觉语言模型(VLMs)与行动辅助视觉语言动作(VLA)模型。PhysiAgent框架能够根据实时反馈自主组织不同组件,最大化利用VLA的能力,从而提高解决复杂现实机器人任务的效果。实验结果表明,该框架能有效实现VLMs的自我调节、工具协同和自适应进化。
Key Takeaways
- VLA模型虽然取得显著成功,但在泛化能力上有所局限,需要整合更广义的VLM模型以增强其能力。
- 当前结合VLM和VLA的方法往往是僵化的、顺序性的,导致协作不够有效和接地挑战。
- PhysiAgent框架通过引入监视器、内存和自我反思机制来优化VLM和VLA的协作。
- PhysiAgent提供了一个自主式脚手架框架,可以根据实时反馈调整和优化组件,最大化利用VLA的能力。
- 实验结果显示,PhysiAgent在解决复杂的现实机器人任务上取得了显著的性能提升。
- PhysiAgent框架能够实现VLMs的自我调节、工具协同和自适应进化。
点此查看论文截图

Agentic Specification Generator for Move Programs
Authors:Yu-Fu Fu, Meng Xu, Taesoo Kim
While LLM-based specification generation is gaining traction, existing tools primarily focus on mainstream programming languages like C, Java, and even Solidity, leaving emerging and yet verification-oriented languages like Move underexplored. In this paper, we introduce MSG, an automated specification generation tool designed for Move smart contracts. MSG aims to highlight key insights that uniquely present when applying LLM-based specification generation to a new ecosystem. Specifically, MSG demonstrates that LLMs exhibit robust code comprehension and generation capabilities even for non-mainstream languages. MSG successfully generates verifiable specifications for 84% of tested Move functions and even identifies clauses previously overlooked by experts. Additionally, MSG shows that explicitly leveraging specification language features through an agentic, modular design improves specification quality substantially (generating 57% more verifiable clauses than conventional designs). Incorporating feedback from the verification toolchain further enhances the effectiveness of MSG, leading to a 30% increase in generated verifiable specifications.
虽然基于LLM(大型预训练模型)的规格生成正在受到关注,但现有的工具主要集中在主流的编程语言上,如C、Java和Solidity等,而新兴且以验证为导向的语言如Move却被忽略。在本文中,我们介绍了MSG,这是一个专为Move智能合约设计的自动化规格生成工具。MSG旨在强调当将基于LLM的规格生成应用于新生态系统时出现的独特见解。具体来说,MSG证明了即使在非主流语言方面,LLM也展现出强大的代码理解和生成能力。MSG成功为测试的Move函数中84%生成了可验证的规格,并发现专家之前忽略的条款。此外,MSG显示通过代理模块化设计明确利用规格语言特征可以大大提高规格质量(比传统设计生成更多可验证条款的57%)。结合验证工具链的反馈进一步提高了MSG的有效性,导致其生成的验证规格增加了30%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages; Extended version of ASE’25 paper with extra appendices
Summary
自动生成合约规格工具MSG,专注于为Move智能合约生成规格。该工具展示了大模型在非主流语言上的代码理解和生成能力,可生成可验证的规格并提高规格质量。
Key Takeaways
- LLM可用于为新兴且注重验证的语言如Move生成智能合约规格。
- MSG工具成功为84%的测试Move函数生成可验证的规格。
- MSG能识别出专家之前忽略的条款。
- 通过代理、模块化的设计,MSG能显著提高规格质量,生成的可验证条款比传统设计多57%。
- 验证工具链的反馈能进一步提升MSG的有效性,增加生成的可验证规格达30%。
- MSG证明了大模型在代码理解和生成方面的强大能力,即使是非主流语言也能有效应用。
点此查看论文截图



Communicating Plans, Not Percepts: Scalable Multi-Agent Coordination with Embodied World Models
Authors:Brennen A. Hill, Mant Koh En Wei, Thangavel Jishnuanandh
Robust coordination is critical for effective decision-making in multi-agent systems, especially under partial observability. A central question in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) is whether to engineer communication protocols or learn them end-to-end. We investigate this dichotomy using embodied world models. We propose and compare two communication strategies for a cooperative task-allocation problem. The first, Learned Direct Communication (LDC), learns a protocol end-to-end, with agents generating messages and actions concurrently. The second, Intention Communication, uses an engineered inductive bias: a compact, learned world model, the Imagined Trajectory Generation Module (ITGM), to simulate future states. Agents then communicate a summary of this plan. We evaluate these approaches on goal-directed interaction in a grid world, a canonical abstraction for embodied AI problems. Our experiments reveal that while emergent communication is viable in simple settings, the engineered, world model-based approach shows superior performance, sample efficiency, and scalability as complexity increases. These findings advocate for integrating structured, predictive models into MARL agents to enable active, goal-driven coordination.
在多智能体系统中进行有效的决策制定,特别是在部分可观察的情况下,稳健的协调至关重要。多智能体强化学习(MARL)中的一个核心问题是应该设计通信协议还是进行端到端的自主学习。我们通过模拟实体世界模型来探讨这一区别。我们针对合作任务分配问题提出了两种通信策略并进行比较。第一种是“学习直接通信”(LDC),这是一种端到端的协议学习,智能体同时生成消息和动作。第二种是“意图通信”,它使用设计好的归纳偏见:一个紧凑的、通过学习得到的世界模型——即想象中的轨迹生成模块(ITGM),来模拟未来的状态。然后智能体传达此计划的摘要。我们在网格世界中的目标导向交互任务上评估了这些方法,这是实体人工智能问题的一个典型抽象。我们的实验表明,虽然新兴通信在简单环境中是可行的,但随着复杂性的增加,基于世界模型的工程设计方法表现出更好的性能、样本效率和可扩展性。这些发现主张将结构化、预测模型集成到MARL智能体中,以实现主动、目标驱动协调。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in the Proceedings of the 39th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2025) Workshop: Scaling Environments for Agents (SEA). Additionally accepted for presentation in the NeurIPS 2025 Workshop: Embodied World Models for Decision Making (EWM) and the NeurIPS 2025 Workshop: Optimization for Machine Learning (OPT)
Summary
在多智能体系统中,强大的协调是进行有效决策的关键,特别是在部分可观察的情况下。本研究探讨了多智能体强化学习(MARL)中的通信协议是自主构建还是端到端学习的问题。本研究提出了两种通信策略,一种是端到端学习的直接通信策略,另一种是意图通信策略,该策略采用工程诱导偏差和基于学习的世界模型模拟未来状态。在网格世界中的目标导向交互评估显示,随着复杂度的增加,基于世界模型的工程化方法表现出更高的性能、样本效率和可扩展性。这表明在MARL中集成结构化预测模型有助于实现主动的目标驱动协调。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体系统决策中,协调的重要性及其在面对部分可观察环境时的挑战。
- 研究探讨了多智能体强化学习(MARL)中通信协议的选择问题,涉及自主构建和端到端学习两种方式。
- 提出两种通信策略:一种是端到端学习的直接通信策略(LDC),另一种是采用工程诱导偏差的意图通信策略,包括基于学习的世界模型模拟未来状态。
- 在网格世界中的目标导向交互评估显示,随着任务复杂度的增加,基于世界模型的工程化方法表现出更高的性能。
- 相比简单环境,复杂环境中采用端到端产生的通信方式具有一定可行性,但表现不如工程化方法。
- 融合结构化预测模型的MARL展现出更高的样本效率和可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图

Prover Agent: An Agent-Based Framework for Formal Mathematical Proofs
Authors:Kaito Baba, Chaoran Liu, Shuhei Kurita, Akiyoshi Sannai
We present Prover Agent, a novel AI agent for automated theorem proving that integrates large language models (LLMs) with a formal proof assistant, Lean. Prover Agent coordinates an informal reasoning LLM, a formal prover model, and feedback from Lean while also generating auxiliary lemmas. These auxiliary lemmas are not limited to subgoals in the formal proof but can also include special cases or potentially useful facts derived from the assumptions, which help in discovering a viable proof strategy. It achieves an 88.1% success rate on the MiniF2F benchmark, establishing a new state-of-the-art among methods using small language models (SLMs) with a much lower sample budget than previous approaches. We also present theoretical analyses and case studies that illustrate how these generated lemmas contribute to solving challenging problems.
我们推出了Prover Agent,这是一个用于自动定理证明的新型AI代理,它将大型语言模型(LLM)与形式化证明助手Lean集成在一起。Prover Agent协调非正式推理LLM、形式化证明模型以及来自Lean的反馈,同时生成辅助引理。这些辅助引理不限于形式证明中的子目标,还可以包括从假设中得出的特殊情况或可能有用的事实,这有助于发现可行的证明策略。它在MiniF2F基准测试上达到了88.1%的成功率,在采用小型语言模型(SLM)的方法中建立了最新 state-of-the-art 的技术,并且样本预算远低于之前的方法。我们还提供了理论分析和案例研究,说明了这些生成的引理如何解决具有挑战性的问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 36 pages, 3 figures
Summary
Prover Agent是一个新型AI定理证明代理,集成了大型语言模型(LLM)和形式化证明助手Lean。它能协调非正式推理的LLM、形式化证明模型以及与Lean的反馈,同时生成辅助引理。这些辅助引理不仅限于形式证明中的子目标,还包括基于假设的特殊情况或可能有用的事实,有助于发现可行的证明策略。在MiniF2F基准测试中,其成功率达到了88.1%,在小型语言模型(SLM)方法中创造了新的最佳水平,并且样本预算远低于以前的方法。我们还提供了理论分析和案例研究,说明了这些生成的引理如何解决具有挑战性的问题。
Key Takeaways
- Prover Agent是一个集成了大型语言模型(LLM)和形式化证明助手Lean的新型AI定理证明代理。
- Prover Agent能协调非正式推理的LLM、形式化证明模型以及与Lean的反馈。
- Prover Agent生成辅助引理,这些引理有助于发现可行的证明策略。
- 辅助引理不仅限于形式证明中的子目标,还包括基于假设的特殊情况或可能有用的信息。
- Prover Agent在MiniF2F基准测试中的成功率达到了88.1%,创造了新的最佳水平。
- Prover Agent的样本预算远低于之前的方法。
点此查看论文截图
