⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-01 更新
UniLat3D: Geometry-Appearance Unified Latents for Single-Stage 3D Generation
Authors:Guanjun Wu, Jiemin Fang, Chen Yang, Sikuang Li, Taoran Yi, Jia Lu, Zanwei Zhou, Jiazhong Cen, Lingxi Xie, Xiaopeng Zhang, Wei Wei, Wenyu Liu, Xinggang Wang, Qi Tian
High-fidelity 3D asset generation is crucial for various industries. While recent 3D pretrained models show strong capability in producing realistic content, most are built upon diffusion models and follow a two-stage pipeline that first generates geometry and then synthesizes appearance. Such a decoupled design tends to produce geometry-texture misalignment and non-negligible cost. In this paper, we propose UniLat3D, a unified framework that encodes geometry and appearance in a single latent space, enabling direct single-stage generation. Our key contribution is a geometry-appearance Unified VAE, which compresses high-resolution sparse features into a compact latent representation – UniLat. UniLat integrates structural and visual information into a dense low-resolution latent, which can be efficiently decoded into diverse 3D formats, e.g., 3D Gaussians and meshes. Based on this unified representation, we train a single flow-matching model to map Gaussian noise directly into UniLat, eliminating redundant stages. Trained solely on public datasets, UniLat3D produces high-quality 3D assets in seconds from a single image, achieving superior appearance fidelity and geometric quality. More demos & code are available at https://unilat3d.github.io/
高保真3D资产生成对于各行各业来说至关重要。虽然最近的3D预训练模型在生成真实内容方面表现出强大的能力,但大多数基于扩散模型,并遵循一个两阶段的管道,首先生成几何结构,然后合成外观。这种解耦的设计往往会导致几何纹理不对齐和不可忽视的成本。在本文中,我们提出了UniLat3D,这是一个统一框架,将几何和外观编码到单个潜在空间中,实现直接的单阶段生成。我们的关键贡献是几何外观统一变分自编码器(Unified VAE),它将高分辨率稀疏特征压缩成紧凑的潜在表示——UniLat。UniLat将结构和视觉信息集成到密集的低分辨率潜在空间中,可以高效地解码为多种3D格式,例如3D高斯和网格。基于这种统一表示,我们训练了一个单一流量匹配模型,直接将高斯噪声映射到UniLat,消除了冗余阶段。仅通过公共数据集进行训练,UniLat3D可在几秒钟内生成高质量3D资产,从单张图像开始,实现卓越的外观保真度和几何质量。更多演示和代码可见于https://unilat3d.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://unilat3d.github.io/
Summary
本文提出了一种名为UniLat3D的统一框架,用于高保真3D资产生成。该框架将几何和外观信息编码在单个潜在空间中,实现直接单阶段生成。其核心贡献是几何外观统一VAE,可将高分辨率稀疏特征压缩成紧凑的潜在表示形式——UniLat。基于这种统一表示,训练了一个单一流程匹配模型,直接将高斯噪声映射到UniLat,消除了冗余阶段。该框架在公开数据集上训练,能在几秒内生成高质量3D资产,实现出色的外观保真度和几何质量。
Key Takeaways
- UniLat3D是一个统一框架,用于高保真3D资产生成,可将几何和外观信息整合在单个潜在空间中。
- UniLat是核心组件,将高分辨率稀疏特征压缩成紧凑的潜在表示形式。
- UniLat将结构和视觉信息集成到密集的低分辨率潜在空间中。
- 该框架实现了直接单阶段生成,避免了传统两阶段管道设计的缺点。
- 通过训练单一流程匹配模型,直接将高斯噪声映射到UniLat表示中。
- UniLat3D在公开数据集上训练,生成高质量3D资产的速度快,仅需几秒钟。
点此查看论文截图
CharGen: Fast and Fluent Portrait Modification
Authors:Jan-Niklas Dihlmann, Arnela Killguss, Hendrik P. A. Lensch
Interactive editing of character images with diffusion models remains challenging due to the inherent trade-off between fine-grained control, generation speed, and visual fidelity. We introduce CharGen, a character-focused editor that combines attribute-specific Concept Sliders, trained to isolate and manipulate attributes such as facial feature size, expression, and decoration with the StreamDiffusion sampling pipeline for more interactive performance. To counteract the loss of detail that often accompanies accelerated sampling, we propose a lightweight Repair Step that reinstates fine textures without compromising structural consistency. Throughout extensive ablation studies and in comparison to open-source InstructPix2Pix and closed-source Google Gemini, and a comprehensive user study, CharGen achieves two-to-four-fold faster edit turnaround with precise editing control and identity-consistent results. Project page: https://chargen.jdihlmann.com/
基于扩散模型对字符图像进行交互编辑仍然具有挑战性,因为精细控制、生成速度和视觉保真度之间存在着固有的权衡。我们引入了CharGen,这是一款面向字符的编辑器,它结合了属性特定的概念滑块(Concept Sliders),通过训练来隔离和操作诸如面部特征大小、表情和装饰等属性,并使用StreamDiffusion采样管道来提高交互性能。为了抵消加速采样通常伴随的细节损失,我们提出了一种轻量级的修复步骤(Repair Step),可以在不损害结构一致性的情况下重新建立细腻纹理。通过广泛的消融研究、与开源的InstructPix2Pix和闭源的Google Gemini的对比,以及全面的用户研究,CharGen实现了两到四倍的快速编辑周转时间,具有精确的编辑控制和身份一致性结果。项目页面:https://chargen.jdihlmann.com/(https://chargen.jdihlmann.com/)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://chargen.jdihlmann.com/
Summary
基于扩散模型的字符图像交互编辑仍面临精细控制、生成速度和视觉保真度之间的固有权衡挑战。我们推出CharGen这一面向字符的编辑器,它结合了属性特定的概念滑块,通过训练来隔离和操作如面部特征大小、表情和装饰等属性,并采用StreamDiffusion采样管道以提高交互性能。为了抵消加速采样带来的细节损失,我们提出了轻量级的修复步骤,以恢复精细纹理而不损害结构一致性。通过广泛消融研究以及与开源InstructPix2Pix和闭源Google Gemini的对比以及全面的用户研究,CharGen实现了两到四倍的快速编辑周转,具有精确的编辑控制和身份一致性结果。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在字符图像交互编辑中面临精细控制、生成速度和视觉保真度的挑战。
- CharGen是一个面向字符的编辑器,通过结合属性特定的概念滑块来解决这些挑战。
- 概念滑块经过训练,可以隔离和操纵如面部特征大小、表情和装饰等属性。
- CharGen采用StreamDiffusion采样管道,提高交互性能。
- 为了弥补加速采样可能导致的细节损失,CharGen提出了轻量级的修复步骤。
- CharGen实现了快速编辑周转,与现有方法相比,具有精确的编辑控制和身份一致性结果。
点此查看论文截图

SDPose: Exploiting Diffusion Priors for Out-of-Domain and Robust Pose Estimation
Authors:Shuang Liang, Jing He, Chuanmeizhi Wang, Lejun Liao, Guo Zhang, Yingcong Chen, Yuan Yuan
Pre-trained diffusion models provide rich multi-scale latent features and are emerging as powerful vision backbones. While recent works such as Marigold\citep{ke2024repurposing} and Lotus\citep{he2024lotus} adapt diffusion priors for dense prediction with strong cross-domain generalization, their potential for structured outputs (e.g., human pose estimation) remains underexplored. In this paper, we propose \textbf{SDPose}, a fine-tuning framework built upon Stable Diffusion to fully exploit pre-trained diffusion priors for human pose estimation. First, rather than modifying cross-attention modules or introducing learnable embeddings, we directly predict keypoint heatmaps in the SD U-Net’s image latent space to preserve the original generative priors. Second, we map these latent features into keypoint heatmaps through a lightweight convolutional pose head, which avoids disrupting the pre-trained backbone. Finally, to prevent overfitting and enhance out-of-distribution robustness, we incorporate an auxiliary RGB reconstruction branch that preserves domain-transferable generative semantics. To evaluate robustness under domain shift, we further construct \textbf{COCO-OOD}, a style-transferred variant of COCO with preserved annotations. With just one-fifth of the training schedule used by Sapiens on COCO, SDPose attains parity with Sapiens-1B/2B on the COCO validation set and establishes a new state of the art on the cross-domain benchmarks HumanArt and COCO-OOD. Furthermore, we showcase SDPose as a zero-shot pose annotator for downstream controllable generation tasks, including ControlNet-based image synthesis and video generation, where it delivers qualitatively superior pose guidance.
预训练扩散模型提供了丰富的多尺度潜在特征,并作为强大的视觉主干正逐渐崭露头角。虽然最近的Marigold(Ke等,2024年)和Lotus(He等,2024年)等作品适应了扩散先验进行密集预测,并具备强大的跨域泛化能力,但它们对于结构化输出(例如人体姿态估计)的潜力尚未得到充分探索。在本文中,我们提出了基于Stable Diffusion构建的微调框架SDPose,以充分利用预训练的扩散先验进行人体姿态估计。首先,我们不是在交叉注意力模块中进行修改或引入可学习嵌入,而是在SD U-Net的图像潜在空间中直接预测关键点热图,以保留原始的生成先验。其次,我们通过轻量级的卷积姿态头将这些潜在特征映射到关键点热图,这避免了破坏预训练的主干网络。最后,为了防止过拟合并增强分布外的稳健性,我们引入了辅助RGB重建分支,该分支能够保留域可迁移的生成语义。为了评估在域偏移下的稳健性,我们进一步构建了COCO-OOD数据集,这是具有保留注释的风格转移COCO数据集。仅使用Sapiens在COCO上训练时间的五分之一时间表和超参设置的前提下,SDPose实现了与Sapiens-1B/2B相当的COCO验证集性能并达到了人体姿态估计跨域基准测试的前沿水平,包括HumanArt和COCO-OOD等基准测试均创下了最新世界纪录。此外,我们展示了SDPose可作为针对下游可控生成任务的零样本姿态标注器,包括基于ControlNet的图像合成和视频生成等任务场景下的实际应用示例证明了其在姿势指导方面具有良好的性能优势。在这一应用场景下凸显其姿态引导的出色性能和可靠性,不仅在仿真模拟中有实用价值且在面向复杂现实世界环境的可应用范围内体现明显优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 9 figures, 9 tables
Summary
预训练扩散模型具备多尺度潜在特征,正成为强大的视觉主干。本研究提出SDPose框架,基于Stable Diffusion进行微调,充分利用预训练扩散先验进行人体姿态估计。通过直接在SD U-Net的图像潜在空间中预测关键点热图,并映射这些潜在特征到关键点热图,实现姿态估计。为提高鲁棒性和跨域性能,引入辅助RGB重建分支。实验显示SDPose在COCO验证集上达到最新水平,并在跨域基准测试上表现优异。此外,SDPose还可作为下游可控生成任务的零样本姿态标注器。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练扩散模型具备多尺度潜在特征,是强大的视觉主干。
- SDPose框架基于Stable Diffusion微调,利用预训练扩散先验进行人体姿态估计。
- 直接预测关键点热图在SD U-Net的图像潜在空间中,保留原始生成先验。
- 通过映射潜在特征到关键点热图,实现姿态估计,避免干扰预训练主干。
- 引入辅助RGB重建分支,防止过拟合,增强跨域稳健性。
- SDPose在COCO验证集上表现优异,达到最新水平。
点此查看论文截图

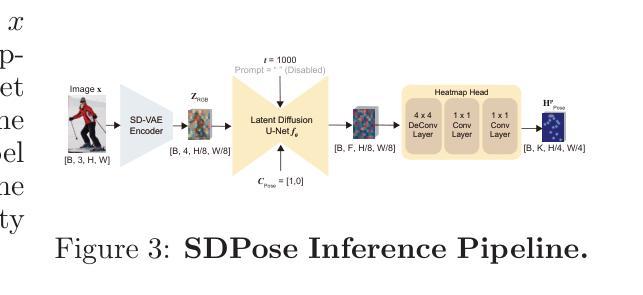
Environment-Aware Satellite Image Generation with Diffusion Models
Authors:Nikos Kostagiolas, Pantelis Georgiades, Yannis Panagakis, Mihalis A. Nicolaou
Diffusion-based foundation models have recently garnered much attention in the field of generative modeling due to their ability to generate images of high quality and fidelity. Although not straightforward, their recent application to the field of remote sensing signaled the first successful trials towards harnessing the large volume of publicly available datasets containing multimodal information. Despite their success, existing methods face considerable limitations: they rely on limited environmental context, struggle with missing or corrupted data, and often fail to reliably reflect user intentions in generated outputs. In this work, we propose a novel diffusion model conditioned on environmental context, that is able to generate satellite images by conditioning from any combination of three different control signals: a) text, b) metadata, and c) visual data. In contrast to previous works, the proposed method is i) to our knowledge, the first of its kind to condition satellite image generation on dynamic environmental conditions as part of its control signals, and ii) incorporating a metadata fusion strategy that models attribute embedding interactions to account for partially corrupt and/or missing observations. Our method outperforms previous methods both qualitatively (robustness to missing metadata, higher responsiveness to control inputs) and quantitatively (higher fidelity, accuracy, and quality of generations measured using 6 different metrics) in the trials of single-image and temporal generation. The reported results support our hypothesis that conditioning on environmental context can improve the performance of foundation models for satellite imagery, and render our model a promising candidate for usage in downstream tasks. The collected 3-modal dataset is to our knowledge, the first publicly-available dataset to combine data from these three different mediums.
基于扩散的基础模型因其生成高质量和高保真度图像的能力而在生成建模领域引起了广泛关注。虽然应用起来并不简单,但它们最近在遥感领域的应用标志着利用包含多模式信息的公开数据集的大体积数据的首次成功尝试。尽管它们取得了成功,但现有方法面临相当大的局限性:它们依赖于有限的环境上下文,在处理缺失或损坏的数据时表现挣扎,并且往往不能在生成的输出中可靠地反映用户意图。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的基于环境上下文的扩散模型,它能够通过三种不同控制信号的任何组合来生成卫星图像:a)文本,b)元数据,c)视觉数据。与之前的工作相比,所提出的方法i)据我们所知,是首个在动态环境条件下对卫星图像生成进行控制的此类方法,并且其二)采用了一种元数据融合策略,对属性嵌入交互进行建模以解释部分损坏和/或缺失的观察结果。我们的方法在单图像和临时生成测试中,在定性(对缺失元数据的稳健性,对控制输入的更高响应能力)和定量(更高的保真度、准确性和生成的测量使用6个不同的指标的质量)方面均优于以前的方法。报告的结果支持我们的假设,即基于环境上下文的条件可以改善卫星图像基础模型的性能,并使我们的模型成为下游任务中颇有前景的候选模型。所收集的3模态数据集是据我们所知,第一个公开可用的数据集,结合了这三种不同媒体的数据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于扩散模型的环境上下文条件生成卫星图像的方法。该方法结合了文本、元数据和视觉数据三种控制信号,能在动态环境条件下生成卫星图像。相较于现有方法,该方法在单图像和时序生成测试中表现出更高的性能,为卫星图像的基础模型提供了新的改进方向。同时,本文首次公开了一个三模态数据集,为下游任务提供了有力的数据支持。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成建模领域受到广泛关注,特别是在遥感领域的应用。
- 现有扩散模型面临环境上下文有限、数据缺失或损坏以及无法反映用户意图的局限性。
- 本文提出了一种基于环境上下文的扩散模型,结合了文本、元数据和视觉数据三种控制信号来生成卫星图像。
- 该方法首次在动态环境条件下进行卫星图像生成,并采用属性嵌入交互模型来处理部分损坏或缺失的观察数据。
- 方法在单图像和时序生成测试中表现出优异性能,定量和定性评估均优于以前的方法。
- 收集的三模态数据集是首个公开的三模态数据集,为下游任务提供了有力的数据支持。
点此查看论文截图
Learning Object-Centric Representations Based on Slots in Real World Scenarios
Authors:Adil Kaan Akan
A central goal in AI is to represent scenes as compositions of discrete objects, enabling fine-grained, controllable image and video generation. Yet leading diffusion models treat images holistically and rely on text conditioning, creating a mismatch for object-level editing. This thesis introduces a framework that adapts powerful pretrained diffusion models for object-centric synthesis while retaining their generative capacity. We identify a core challenge: balancing global scene coherence with disentangled object control. Our method integrates lightweight, slot-based conditioning into pretrained models, preserving their visual priors while providing object-specific manipulation. For images, SlotAdapt augments diffusion models with a register token for background/style and slot-conditioned modules for objects, reducing text-conditioning bias and achieving state-of-the-art results in object discovery, segmentation, compositional editing, and controllable image generation. We further extend the framework to video. Using Invariant Slot Attention (ISA) to separate object identity from pose and a Transformer-based temporal aggregator, our approach maintains consistent object representations and dynamics across frames. This yields new benchmarks in unsupervised video object segmentation and reconstruction, and supports advanced editing tasks such as object removal, replacement, and insertion without explicit supervision. Overall, this work establishes a general and scalable approach to object-centric generative modeling for images and videos. By bridging human object-based perception and machine learning, it expands the design space for interactive, structured, and user-driven generative tools in creative, scientific, and practical domains.
人工智能的核心目标是将场景表示为离散对象的组合,从而实现精细可控的图像和视频生成。然而,领先的扩散模型以整体方式处理图像,并依赖于文本条件,这对对象级别的编辑造成了不匹配。本论文介绍了一个框架,该框架适应强大的预训练扩散模型进行以对象为中心的合成,同时保留其生成能力。我们确定了一个核心挑战:平衡全局场景连贯性与解耦的对象控制。我们的方法将轻量级的基于插槽的条件集成到预训练模型中,保留其视觉先验知识,同时为特定对象提供操作。对于图像,SlotAdapt通过为背景和风格增加一个注册令牌以及为对象提供插槽条件模块来增强扩散模型,从而减少文本条件的偏见,并在对象发现、分割、组合编辑和可控图像生成方面达到最新水平的结果。我们将框架进一步扩展到视频。通过使用不变插槽注意力(ISA)来分离对象身份和姿势以及基于Transformer的临时聚合器,我们的方法在帧之间保持一致的对象表示和动态。这为实现无监督视频对象分割和重建的新基准铺平了道路,并支持高级编辑任务,如对象移除、替换和插入,无需明确的监督。总体而言,这项工作为图像和视频建立了一种通用且可扩展的对象中心生成模型的方法。它通过弥合基于人类对象的感知和机器学习之间的鸿沟,扩展了交互式、结构化、用户驱动的生成工具在创意、科学和实际领域的设计空间。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF PhD Thesis, overlap with arXiv:2507.20855 and arXiv:2501.15878
Summary
本文介绍了一种适应于对象中心合成的框架,该框架旨在解决人工智能中场景表示为离散对象组合的中心问题。它通过对预训练的扩散模型进行改进,使其能在保持生成能力的同时,实现对象级别的编辑。方法包括在预训练模型中加入基于插槽的调节机制,以减少文本调节的偏见,并在图像和视频中实现对象发现、分割、组合编辑和控制生成等任务。这项工作建立了一种通用且可扩展的对象中心生成模型,为图像和视频设计提供了更多的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型现在能够更有效地表示场景作为离散对象的组合,支持精细粒度的图像和视频生成。
- 本文提出了一种新的框架,使预训练的扩散模型能够适应对象中心的合成,同时保持其生成能力。
- 核心挑战在于平衡全局场景连贯性和解耦的对象控制。
- 通过对预训练模型进行基于插槽的调节,可以在保留视觉先验的同时,实现对特定对象的操作。
- SlotAdapt方法通过在扩散模型中增加注册令牌和插槽条件模块,减少了文本调节的偏见,并在对象发现、分割、组合编辑和控制生成等方面达到了最先进的成果。
- 该框架已成功扩展到视频领域,通过使用不变插槽注意力和基于Transformer的临时聚合器,可以在各帧之间保持一致的对象表示和动态。
点此查看论文截图
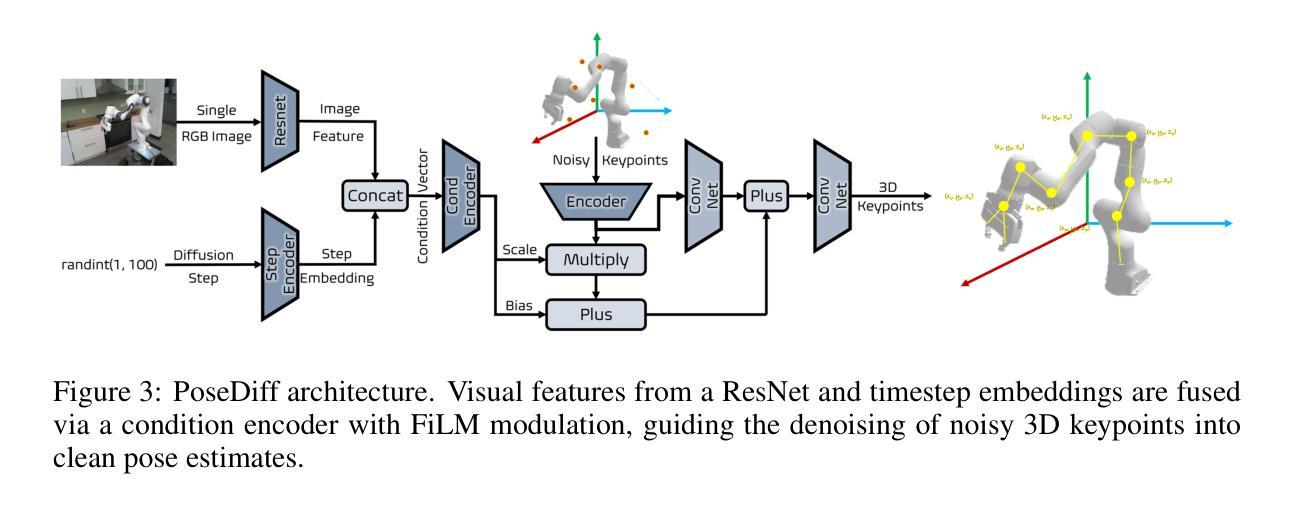
PoseDiff: A Unified Diffusion Model Bridging Robot Pose Estimation and Video-to-Action Control
Authors:Haozhuo Zhang, Michele Caprio, Jing Shao, Qiang Zhang, Jian Tang, Shanghang Zhang, Wei Pan
We present PoseDiff, a conditional diffusion model that unifies robot state estimation and control within a single framework. At its core, PoseDiff maps raw visual observations into structured robot states-such as 3D keypoints or joint angles-from a single RGB image, eliminating the need for multi-stage pipelines or auxiliary modalities. Building upon this foundation, PoseDiff extends naturally to video-to-action inverse dynamics: by conditioning on sparse video keyframes generated by world models, it produces smooth and continuous long-horizon action sequences through an overlap-averaging strategy. This unified design enables scalable and efficient integration of perception and control. On the DREAM dataset, PoseDiff achieves state-of-the-art accuracy and real-time performance for pose estimation. On Libero-Object manipulation tasks, it substantially improves success rates over existing inverse dynamics modules, even under strict offline settings. Together, these results show that PoseDiff provides a scalable, accurate, and efficient bridge between perception, planning, and control in embodied AI. The video visualization results can be found on the project page: https://haozhuo-zhang.github.io/PoseDiff-project-page/.
我们提出了PoseDiff,这是一种条件扩散模型,在一个统一的框架内融合了机器人的状态估计和控制。PoseDiff的核心功能是将原始视觉观察映射到结构化机器人状态(例如从单个RGB图像中的3D关键点或关节角度),从而无需多阶段管道或辅助模式。在此基础上,PoseDiff自然地扩展到了视频到动作的逆向动力学:通过以世界模型生成稀疏视频关键帧为条件,它采用重叠平均策略生成平滑且连续的长周期动作序列。这种统一的设计实现了感知和控制的可扩展和有效集成。在DREAM数据集上,PoseDiff实现了姿态估计的先进准确性和实时性能。在Libero-Object操作任务上,即使在严格的离线设置下,它也大大提高了现有逆向动力学模块的成功率。总的来说,这些结果表明PoseDiff在嵌入式人工智能的感知、规划和控制之间提供了可扩展、准确和有效的桥梁。视频可视化结果可在项目页面找到:https://haozhuo-zhang.github.io/PoseDiff-project-page/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
PoseDiff是一个条件扩散模型,它将机器人状态估计和控制整合到一个单一的框架中。PoseDiff能够将原始视觉观察映射到结构化机器人状态(如从单个RGB图像的3D关键点或关节角),从而不需要多阶段管道或辅助模式。此外,PoseDiff自然地扩展到视频到动作逆向动力学:通过以世界模型生成的稀疏视频关键帧为条件,它采用重叠平均策略产生平滑和连续的长周期动作序列。这一统一的设计实现了感知和控制的可伸缩和高效集成。PoseDiff在DREAM数据集上实现了姿态估计的先进准确性和实时性能,并在Libero对象操作任务上大幅度提高了现有逆向动力学模块的成功率,即使在严格的离线设置下也是如此。总的来说,PoseDiff为感知、规划和控制在嵌入式人工智能之间提供了可伸缩、准确和高效的桥梁。
Key Takeaways
- PoseDiff是一个条件扩散模型,统一了机器人状态估计和控制。
- PoseDiff能够将原始视觉观察映射到结构化机器人状态。
- PoseDiff扩展了视频到动作逆向动力学,生成平滑和连续的动作序列。
- PoseDiff实现了感知和控制的可伸缩和高效集成。
- PoseDiff在DREAM数据集上实现了先进的姿态估计性能。
- 在Libero对象操作任务上,PoseDiff提高了逆向动力学模块的成功率。
点此查看论文截图

ASIA: Adaptive 3D Segmentation using Few Image Annotations
Authors:Sai Raj Kishore Perla, Aditya Vora, Sauradip Nag, Ali Mahdavi-Amiri, Hao Zhang
We introduce ASIA (Adaptive 3D Segmentation using few Image Annotations), a novel framework that enables segmentation of possibly non-semantic and non-text-describable “parts” in 3D. Our segmentation is controllable through a few user-annotated in-the-wild images, which are easier to collect than multi-view images, less demanding to annotate than 3D models, and more precise than potentially ambiguous text descriptions. Our method leverages the rich priors of text-to-image diffusion models, such as Stable Diffusion (SD), to transfer segmentations from image space to 3D, even when the annotated and target objects differ significantly in geometry or structure. During training, we optimize a text token for each segment and fine-tune our model with a novel cross-view part correspondence loss. At inference, we segment multi-view renderings of the 3D mesh, fuse the labels in UV-space via voting, refine them with our novel Noise Optimization technique, and finally map the UV-labels back onto the mesh. ASIA provides a practical and generalizable solution for both semantic and non-semantic 3D segmentation tasks, outperforming existing methods by a noticeable margin in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations.
我们介绍了ASIA(使用少量图像标注进行自适应3D分割),这是一种新的框架,能够对可能是非语义和非文本描述的3D“部分”进行分割。我们的分割可以通过少数用户标注的野外图像进行控制,这些图像比多角度图像更容易收集,比3D模型更易于标注,并且比潜在模糊文本描述更准确。我们的方法利用文本到图像扩散模型的丰富先验知识,如Stable Diffusion(SD),将图像空间的分割转移到3D,即使标注和目标对象在几何或结构上存在显著差异。在训练过程中,我们对每个分段进行优化文本标记,并通过新的跨视图部分对应损失微调我们的模型。在推理过程中,我们对3D网格的多视角渲染进行分割,通过投票在UV空间融合标签,使用我们新的噪声优化技术进行细化处理,最后将UV标签映射回网格。ASIA为语义和非语义的3D分割任务提供了实用且通用的解决方案,在定量和定性评估中都以明显的优势超越了现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH Asia, 2025. Project Page: https://sairajk.github.io/asia/
Summary
ASIA(基于少量图像标注的自适应3D分割)是一种新框架,可通过少数用户标注的野外图像控制3D中可能非语义和非文本描述的“部分”分割。该方法利用文本到图像扩散模型的丰富先验知识(如Stable Diffusion),将分割从图像空间转移到3D,即使标注和目标对象在几何或结构上存在显著差异。通过优化文本标记和新型跨视图部分对应关系损失进行训练,并在推断时进行多视图渲染、UV空间标签融合、噪声优化技术,最终将UV标签映射回网格。ASIA为语义和非语义3D分割任务提供了实用且通用的解决方案,在定量和定性评估上都优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- ASIA是一种新的3D分割框架,能够通过少量用户标注的野外图像进行控制。
- 它利用文本到图像扩散模型的丰富先验知识。
- ASIA可以处理非语义和非文本描述的“部分”分割。
- 该方法通过优化文本标记和新型跨视图部分对应关系损失进行训练。
- 在推断过程中,ASIA进行多视图渲染、UV空间标签融合和噪声优化。
- ASIA为语义和非语义3D分割任务提供了实用且通用的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图


An Efficient 3D Latent Diffusion Model for T1-contrast Enhanced MRI Generation
Authors:Zach Eidex, Mojtaba Safari, Jie Ding, Richard Qiu, Justin Roper, David Yu, Hui-Kuo Shu, Zhen Tian, Hui Mao, Xiaofeng Yang
Objective: Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) are commonly employed with T1w MRI to enhance lesion visualization but are restricted in patients at risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and variations in GBCA administration can introduce imaging inconsistencies. This study develops an efficient 3D deep-learning framework to generate T1-contrast enhanced images (T1C) from pre-contrast multiparametric MRI. Approach: We propose the 3D latent rectified flow (T1C-RFlow) model for generating high-quality T1C images. First, T1w and T2-FLAIR images are input into a pretrained autoencoder to acquire an efficient latent space representation. A rectified flow diffusion model is then trained in this latent space representation. The T1C-RFlow model was trained on a curated dataset comprised of the BraTS 2024 glioma (GLI; 1480 patients), meningioma (MEN; 1141 patients), and metastases (MET; 1475 patients) datasets. Selected patients were split into train (N=2860), validation (N=612), and test (N=614) sets. Results: Both qualitative and quantitative results demonstrate that the T1C-RFlow model outperforms benchmark 3D models (pix2pix, DDPM, Diffusion Transformers (DiT-3D)) trained in the same latent space. T1C-RFlow achieved the following metrics - GLI: NMSE 0.044 +/- 0.047, SSIM 0.935 +/- 0.025; MEN: NMSE 0.046 +/- 0.029, SSIM 0.937 +/- 0.021; MET: NMSE 0.098 +/- 0.088, SSIM 0.905 +/- 0.082. T1C-RFlow had the best tumor reconstruction performance and significantly faster denoising times (6.9 s/volume, 200 steps) than conventional DDPM models in both latent space (37.7s, 1000 steps) and patch-based in image space (4.3 hr/volume). Significance: Our proposed method generates synthetic T1C images that closely resemble ground truth T1C in much less time than previous diffusion models. Further development may permit a practical method for contrast-agent-free MRI for brain tumors.
目标:钆类造影剂(GBCAs)通常与T1加权磁共振成像(MRI)一起使用,以提高病变的可视化效果,但是对于患有肾源性系统性纤维化风险的患者有所限制,GBCA管理的变化可能会引入成像的不一致性。本研究开发了一个高效的3D深度学习框架,用于从预造影多参数MRI生成T1加权增强图像(T1C)。方法:我们提出了用于生成高质量T1C图像的3D潜在校正流(T1C-RFlow)模型。首先,将T1w和T2-FLAIR图像输入预训练的自动编码器,以获得有效的潜在空间表示。然后在此潜在空间表示中训练校正流扩散模型。T1C-RFlow模型是在精选数据集上进行训练的,该数据集由BraTS 2024胶质细胞瘤(GLI;1480名患者)、脑膜瘤(MEN;1141名患者)和转移瘤(MET;1475名患者)数据集组成。所选患者被分为训练集(N=2860)、验证集(N=612)和测试集(N=614)。结果:定性和定量结果均表明,T1C-RFlow模型在相同的潜在空间中超越了基准的3D模型(pix2pix、DDPM、Diffusion Transformers(DiT-3D))。在GLI中,T1C-RFlow达到了NMSE 0.044 +/- 0.047,SSIM 0.935 +/- 0.025;在MEN中,NMSE 0.046 +/- 0.029,SSIM 0.937 +/- 0.021;在MET中,NMSE 0.098 +/- 0.088,SSIM 0.905 +/- 0.082。T1C-RFlow具有最佳的肿瘤重建性能,并且去噪时间显著快于传统DDPM模型,无论是潜在空间还是去图像空间的补丁基础。意义:我们提出的方法能够在比以前的扩散模型更短的时间内生成模拟T1C图像。进一步的开发可能会提供一种无需造影剂的MRI检测脑部肿瘤的实际方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究开发了一种高效的3D深度学习框架,可从预对比的多参数MRI生成T1对比增强图像(T1C)。该研究使用3D潜在整流流(T1C-RFlow)模型生成高质量T1C图像,该模型在包含胶质肿瘤的数据库上进行训练并实现了优异的性能。此模型比其它基准3D模型更快,对肿瘤重建具有最佳性能。此研究为实现无造影剂MRI的实用方法提供了潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 研究使用3D深度学习框架生成T1对比增强图像(T1C)。
- T1C-RFlow模型使用预对比的T1w和T2-FLAIR图像进行训练,生成高质量T1C图像。
- T1C-RFlow模型在多种疾病数据集(包括胶质肿瘤、脑膜瘤和转移瘤)上进行了训练和验证。
- T1C-RFlow模型的性能优于其他基准3D模型,具有更好的肿瘤重建能力和更快的去噪时间。
- 该模型能够实现对比剂MRI的快速成像,具有无造影剂MRI的潜力。
- 此研究为解决钆类造影剂使用受限问题提供了新的解决方案,如肾源性系统性纤维化和成像不一致等问题。
点此查看论文截图

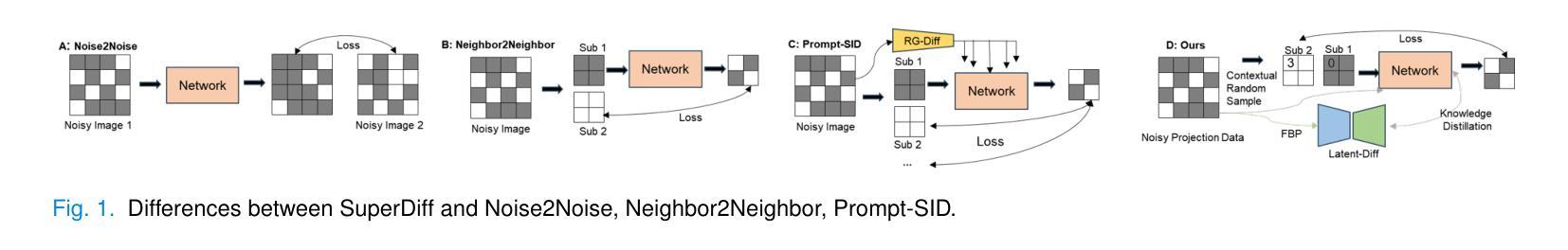
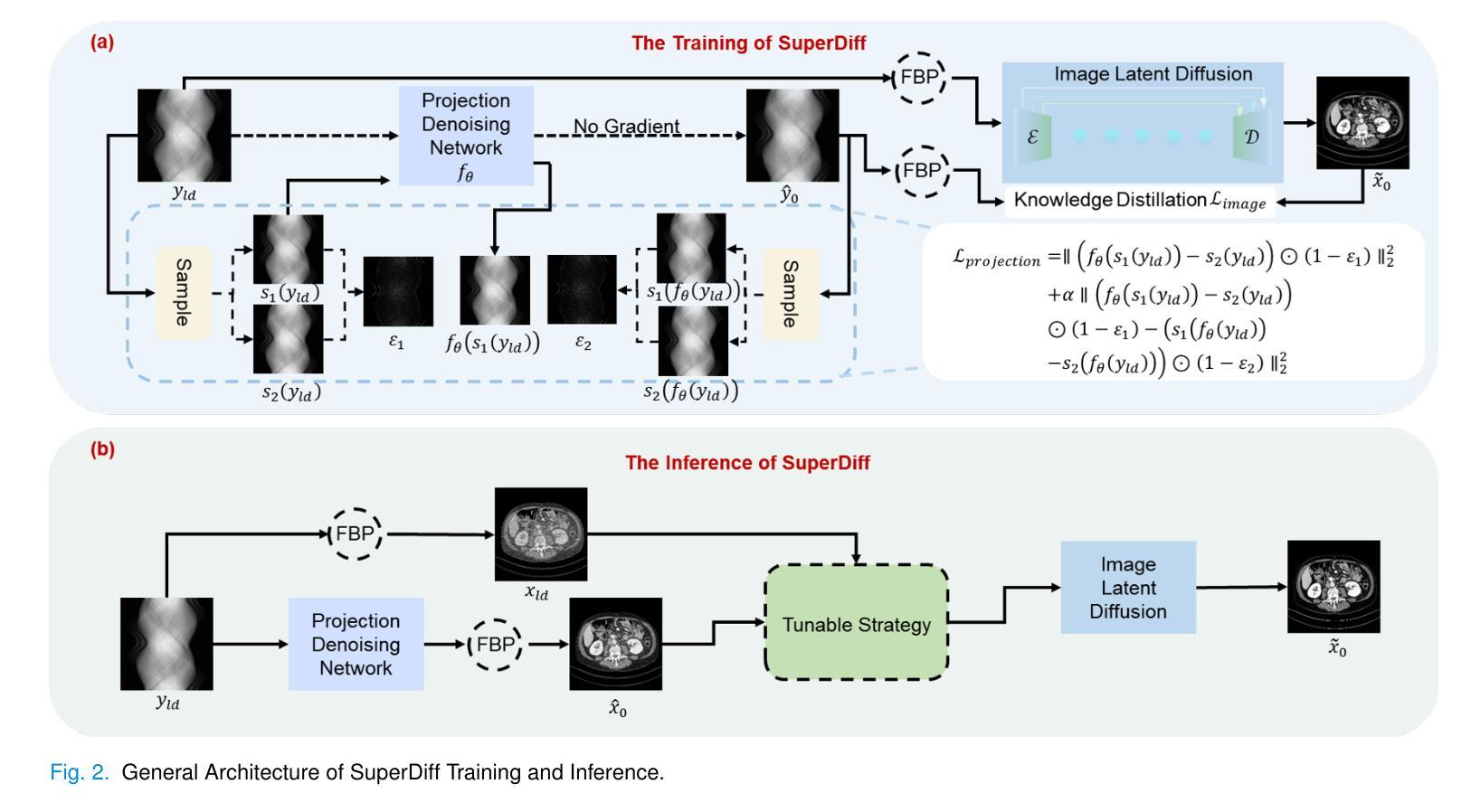
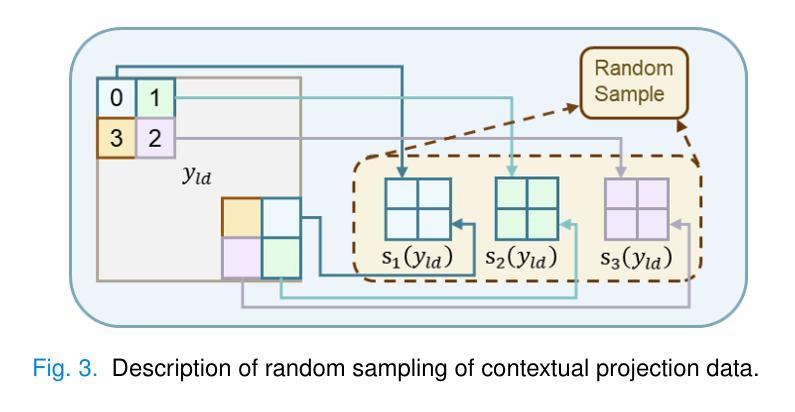
Tunable-Generalization Diffusion Powered by Self-Supervised Contextual Sub-Data for Low-Dose CT Reconstruction
Authors:Guoquan Wei, Zekun Zhou, Liu Shi, Wenzhe Shan, Qiegen Liu
Current models based on deep learning for low-dose CT denoising rely heavily on paired data and generalize poorly. Even the more concerned diffusion models need to learn the distribution of clean data for reconstruction, which is difficult to satisfy in medical clinical applications. At the same time, self-supervised-based methods face the challenge of significant degradation of generalizability of models pre-trained for the current dose to expand to other doses. To address these issues, this paper proposes a novel method of tunable-generalization diffusion powered by self-supervised contextual sub-data for low-dose CT reconstruction, named SuperDiff. Firstly, a contextual subdata similarity adaptive sensing strategy is designed for denoising centered on the LDCT projection domain, which provides an initial prior for the subsequent progress. Subsequently, the initial prior is used to combine knowledge distillation with a deep combination of latent diffusion models for optimizing image details. The pre-trained model is used for inference reconstruction, and the pixel-level self-correcting fusion technique is proposed for fine-grained reconstruction of the image domain to enhance the image fidelity, using the initial prior and the LDCT image as a guide. In addition, the technique is flexibly applied to the generalization of upper and lower doses or even unseen doses. Dual-domain strategy cascade for self-supervised LDCT denoising, SuperDiff requires only LDCT projection domain data for training and testing. Full qualitative and quantitative evaluations on both datasets and real data show that SuperDiff consistently outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of reconstruction and generalization performance.
当前基于深度学习的低剂量CT去噪模型很大程度上依赖于配对数据,其泛化能力较差。即使更受关注的扩散模型也需要学习清洁数据的分布来进行重建,这在医学临床应用中是难以满足的。同时,基于自监督的方法还面临着挑战,即当前剂量预训练模型的泛化能力在扩展到其他剂量时显著下降。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了一种新型的可调节通用扩散模型,该模型通过自监督上下文子数据进行低剂量CT重建,名为SuperDiff。首先,设计了一种基于LDCT投影域的上下文子数据相似性自适应感知策略,为去噪提供初始先验,为后续进展打下基础。随后,利用初始先验结合知识蒸馏和深度潜扩散模型优化图像细节。使用预训练模型进行推理重建,并提出像素级自校正融合技术,以初始先验和LDCT图像为指导,对图像域进行精细重建,提高图像保真度。此外,该技术可灵活应用于高低剂量甚至未见剂量的泛化。SuperDiff采用双域策略级联自监督LDCT去噪,仅需要LDCT投影域数据进行训练和测试。在数据集和真实数据上的全面定性和定量评估表明,SuperDiff在重建和泛化性能上均优于现有最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了一种基于自监督上下文子数据的可调通用扩散模型(SuperDiff),用于低剂量CT重建,以解决当前深度学习模型在低剂量CT去噪中过度依赖配对数据、通用性较差的问题。SuperDiff首先设计了一种基于LDCT投影域的上下文子数据相似性自适应感知策略,为后续进程提供初始先验。然后结合知识蒸馏和深度潜扩散模型优化图像细节。使用预训练模型进行推断重建,并提出像素级自我校正融合技术,以初始先验和LDCT图像为指导,对图像域进行精细重建,提高图像保真度。此外,该技术可灵活应用于上下剂量甚至未见剂量的推广。SuperDiff只需LDCT投影域数据进行训练和测试,采用双域策略级联进行自监督LDCT去噪。在数据集和真实数据上的全面定性和定量评估表明,SuperDiff在重建和泛化性能上均优于现有最先进的方法。
关键见解
- 当前深度学习模型在低剂量CT去噪中过于依赖配对数据,通用性较差。
- SuperDiff通过结合自监督学习和扩散模型解决这一问题。
- SuperDiff采用基于LDCT投影域的上下文子数据相似性自适应感知策略,为后续进程提供初始先验。
- 结合知识蒸馏和深度潜扩散模型优化图像细节。
- 像素级自我校正融合技术用于提高图像保真度的精细重建。
- SuperDiff技术可灵活应用于不同剂量的泛化。
- 仅需LDCT投影域数据进行训练和测试的SuperDiff,在重建和泛化性能上表现出卓越的效果。
点此查看论文截图

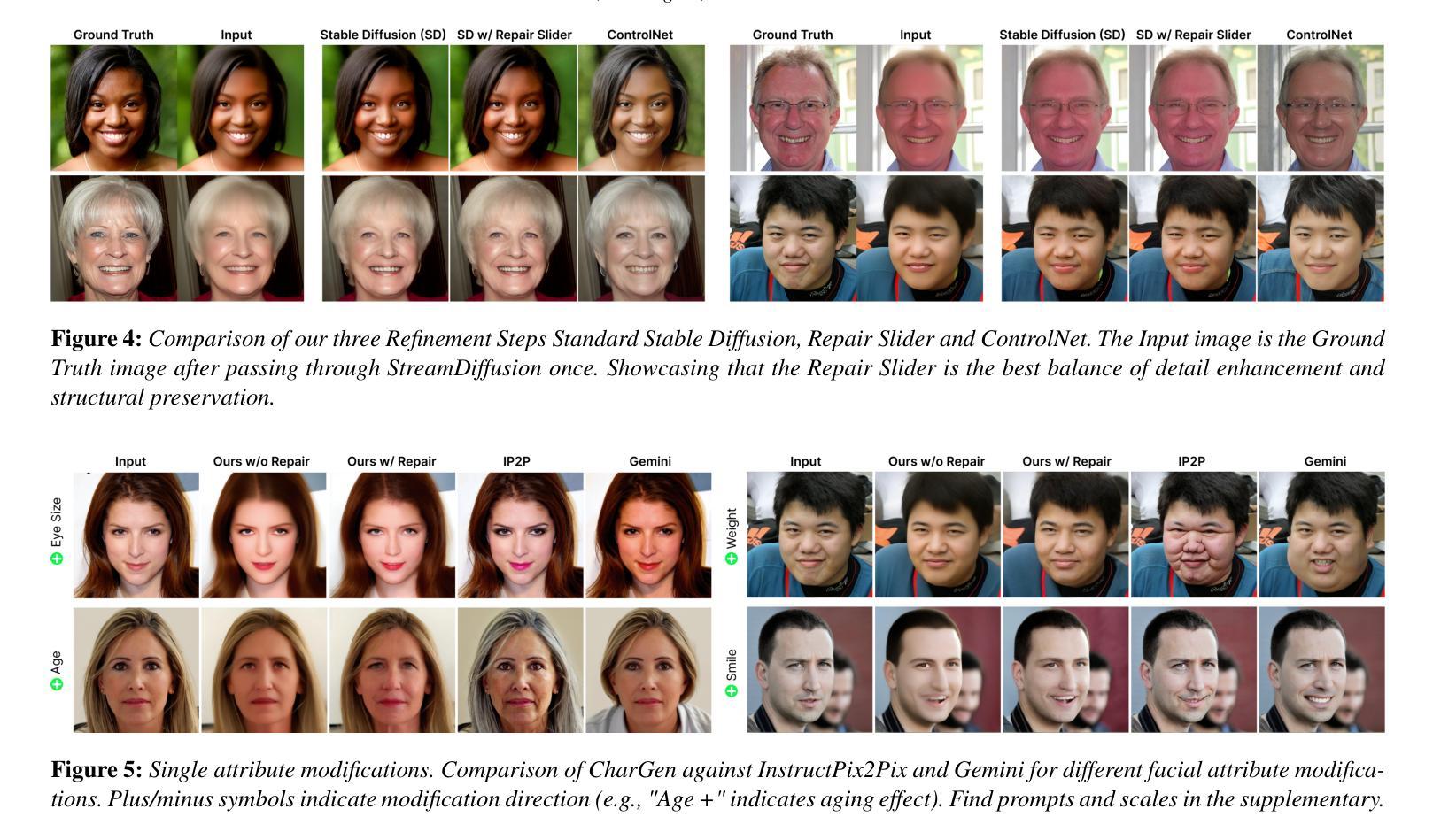
FlashEdit: Decoupling Speed, Structure, and Semantics for Precise Image Editing
Authors:Junyi Wu, Zhiteng Li, Haotong Qin, Xiaohong Liu, Linghe Kong, Yulun Zhang, Xiaokang Yang
Text-guided image editing with diffusion models has achieved remarkable quality but suffers from prohibitive latency, hindering real-world applications. We introduce FlashEdit, a novel framework designed to enable high-fidelity, real-time image editing. Its efficiency stems from three key innovations: (1) a One-Step Inversion-and-Editing (OSIE) pipeline that bypasses costly iterative processes; (2) a Background Shield (BG-Shield) technique that guarantees background preservation by selectively modifying features only within the edit region; and (3) a Sparsified Spatial Cross-Attention (SSCA) mechanism that ensures precise, localized edits by suppressing semantic leakage to the background. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FlashEdit maintains superior background consistency and structural integrity, while performing edits in under 0.2 seconds, which is an over 150$\times$ speedup compared to prior multi-step methods. Our code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/JunyiWuCode/FlashEdit.
基于扩散模型的文本引导图像编辑已经取得了显著的品质,但仍然存在延迟问题,阻碍了其在现实世界中的应用。我们引入了FlashEdit,这是一种新型框架,旨在实现高保真、实时的图像编辑。其效率源于三个关键创新点:(1)一步反演编辑(OSIE)管道,绕过昂贵的迭代过程;(2)背景屏蔽(BG-Shield)技术,通过选择性修改编辑区域内的特征来保证背景保留;(3)稀疏空间交叉注意力(SSCA)机制,通过抑制语义泄露到背景来确保精确、局部化的编辑。大量实验表明,FlashEdit在保持背景一致性和结构完整性的同时,编辑时间缩短至0.2秒以内,相较于先前的多步骤方法实现了超过150倍的速度提升。我们的代码将在https://github.com/JunyiWuCode/FlashEdit上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF We need to further improve our research
Summary
本文介绍了针对扩散模型的新框架FlashEdit,实现了高保真实时图像编辑。其通过三项创新技术提高编辑效率:一步反转编辑流程(OSIE)、背景屏蔽技术保证背景一致性和精确定位编辑。实验证明,FlashEdit在保证背景和结构一致性的同时,编辑速度在0.2秒内,较传统多步骤方法提高了超过150倍。代码将在https://github.com/JunyiWuCode/FlashEdit公开。
Key Takeaways
- FlashEdit实现了基于扩散模型的高保真实时图像编辑。
- 通过一步反转编辑流程(OSIE)提高了图像编辑效率。
- 背景屏蔽技术(BG-Shield)保证了图像背景的一致性。
- Sparsified Spatial Cross-Attention(SSCA)机制确保精准、局部化的编辑。
- FlashEdit通过抑制语义泄漏至背景实现精确编辑。
- 实验表明,FlashEdit的编辑速度达到了惊人的速度提升,仅需不到0.2秒完成。与之前的多步方法相比,提升了超过150倍。
点此查看论文截图
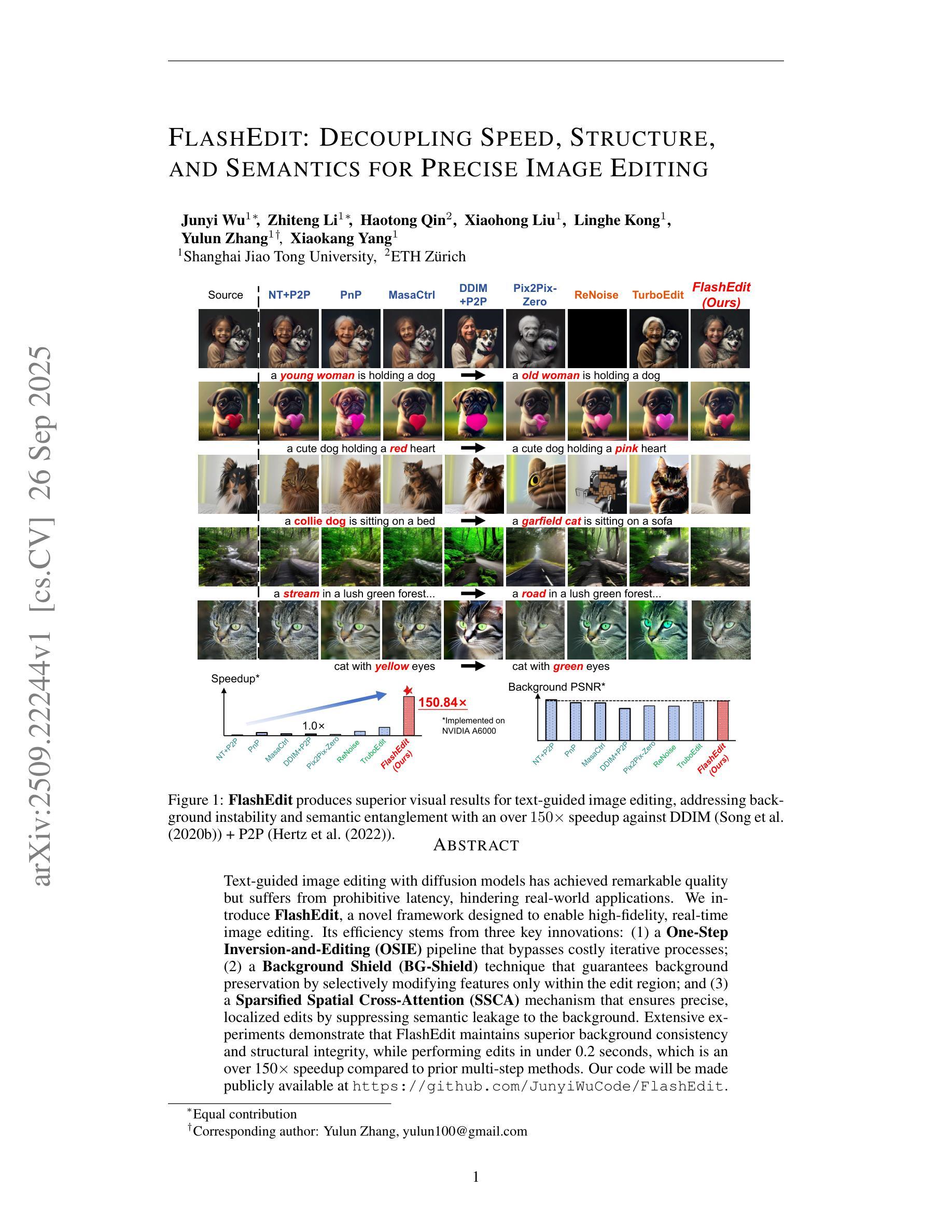
Physics-Guided Null-Space Diffusion with Sparse Masking for Corrective Sparse-View CT Reconstruction
Authors:Zekun Zhou, Yanru Gong, Liu Shi, Qiegen Liu
Diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable generative capabilities in image processing tasks. We propose a Sparse condition Temporal Rewighted Integrated Distribution Estimation guided diffusion model (STRIDE) for sparse-view CT reconstruction. Specifically, we design a joint training mechanism guided by sparse conditional probabilities to facilitate the model effective learning of missing projection view completion and global information modeling. Based on systematic theoretical analysis, we propose a temporally varying sparse condition reweighting guidance strategy to dynamically adjusts weights during the progressive denoising process from pure noise to the real image, enabling the model to progressively perceive sparse-view information. The linear regression is employed to correct distributional shifts between known and generated data, mitigating inconsistencies arising during the guidance process. Furthermore, we construct a dual-network parallel architecture to perform global correction and optimization across multiple sub-frequency components, thereby effectively improving the model capability in both detail restoration and structural preservation, ultimately achieving high-quality image reconstruction. Experimental results on both public and real datasets demonstrate that the proposed method achieves the best improvement of 2.58 dB in PSNR, increase of 2.37% in SSIM, and reduction of 0.236 in MSE compared to the best-performing baseline methods. The reconstructed images exhibit excellent generalization and robustness in terms of structural consistency, detail restoration, and artifact suppression.
扩散模型在图像处理任务中表现出了显著的生成能力。我们提出了一种用于稀疏视图CT重建的稀疏条件时间加权综合分布估计导向扩散模型(STRIDE)。具体来说,我们设计了一种由稀疏条件概率引导的联合训练机制,以促进模型有效地学习缺失投影视图补全和全局信息建模。基于系统的理论分析,我们提出了一种时间变化的稀疏条件重加权指导策略,在从纯噪声到真实图像的渐进去噪过程中动态调整权重,使模型能够逐步感知稀疏视图信息。采用线性回归来校正已知数据和生成数据之间的分布偏移,减轻指导过程中产生的不一致性。此外,我们构建了一个双网络并行架构,以在多个子频率分量上执行全局校正和优化,从而有效地提高了模型在细节恢复和结构保持方面的能力,最终实现了高质量图像重建。在公共和真实数据集上的实验结果表扩散模型展示出了出色的生成能力。我们提出了一种用于稀疏视图CT重建的稀疏条件临时加权集成分布估计导向扩散模型(STRIDE)。具体而言,我们设计了一种由稀疏条件概率引导的联合训练机制,帮助模型有效学习缺失投影视图的补全和全局信息的建模。通过系统的理论分析,我们提出了一种随时间变化的稀疏条件重加权指导策略,在由纯噪声至清晰图像的渐进去噪过程中动态调整权重分配。这样能使模型逐步感知稀疏视图的信息。此外还采用了线性回归的方法,用以校正已知和生成数据之间的分布偏移情况,以此减少指导过程中可能出现的不一致问题。更进一步的是,我们设计了一个双网络并行架构,用以在不同子频率分量上进行全局的校正与优化,进而有效提高模型在细节复原和结构保持方面的性能,并最终实现高质量的图像重建。在公共和真实数据集上的实验结果表明,相较于表现最佳的基准方法,所提方法在提高峰值信噪比(PSNR)方面取得了2.58分贝的最佳改进,在提高结构相似性度量(SSIM)方面增加了2.37%,在均方误差(MSE)方面减少了0.236。重建的图像在结构一致性、细节恢复和伪影抑制等方面表现出优异泛化和稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
提出的Sparse condition Temporal Rewighted Integrated Distribution Estimation扩散模型(STRIDE)用于稀疏视图CT重建。通过联合训练机制和稀疏条件概率指导,模型能更有效地学习缺失投影视图补全和全局信息建模。该模型在渐进去噪过程中动态调整权重,实现稀疏视图信息的逐步感知。通过线性回归校正已知和生成数据之间的分布偏移,减少指导过程中的不一致性。此外,构建双网络并行架构,进行多子频率组件的全局校正和优化,提高模型在细节恢复和结构保持方面的能力,实现高质量图像重建。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像处理任务中表现出强大的生成能力。
- 提出的Sparse condition Temporal Rewighted Integrated Distribution Estimation扩散模型(STRIDE)用于稀疏视图CT重建。
- 通过联合训练机制和稀疏条件概率指导,模型能学习缺失投影视图补全和全局信息建模。
- 模型在渐进去噪过程中动态调整权重,实现稀疏视图信息的逐步感知。
- 线性回归用于校正已知和生成数据之间的分布偏移。
- 构建双网络并行架构,以提高模型在细节恢复和结构保持方面的能力。
点此查看论文截图
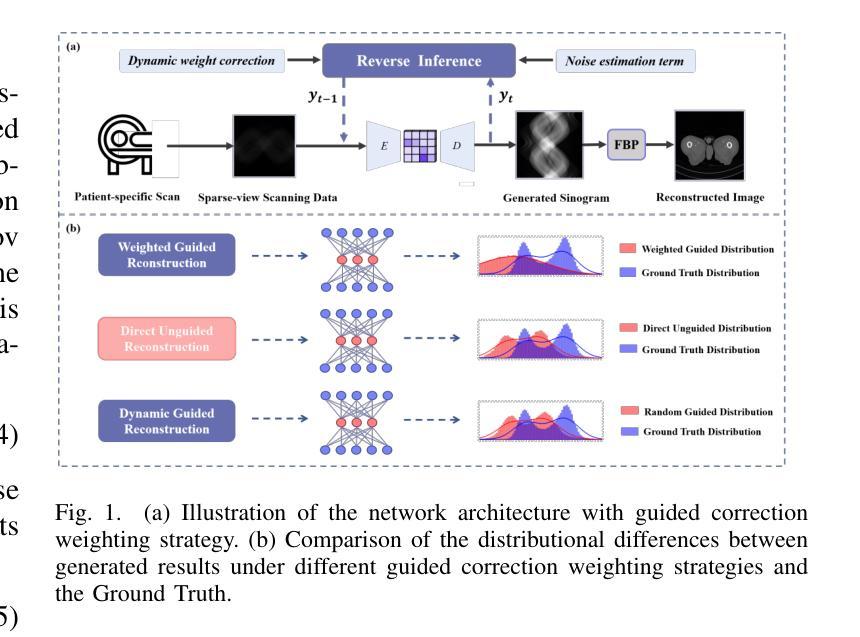
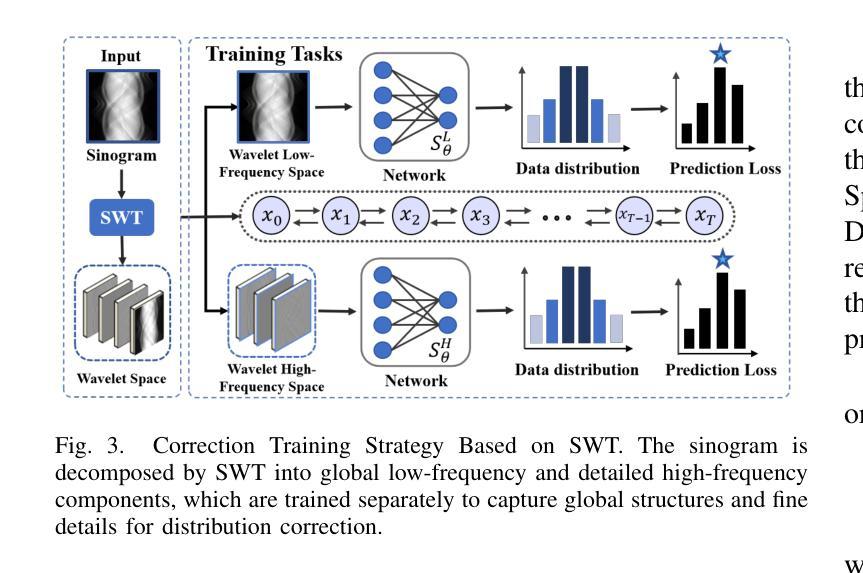
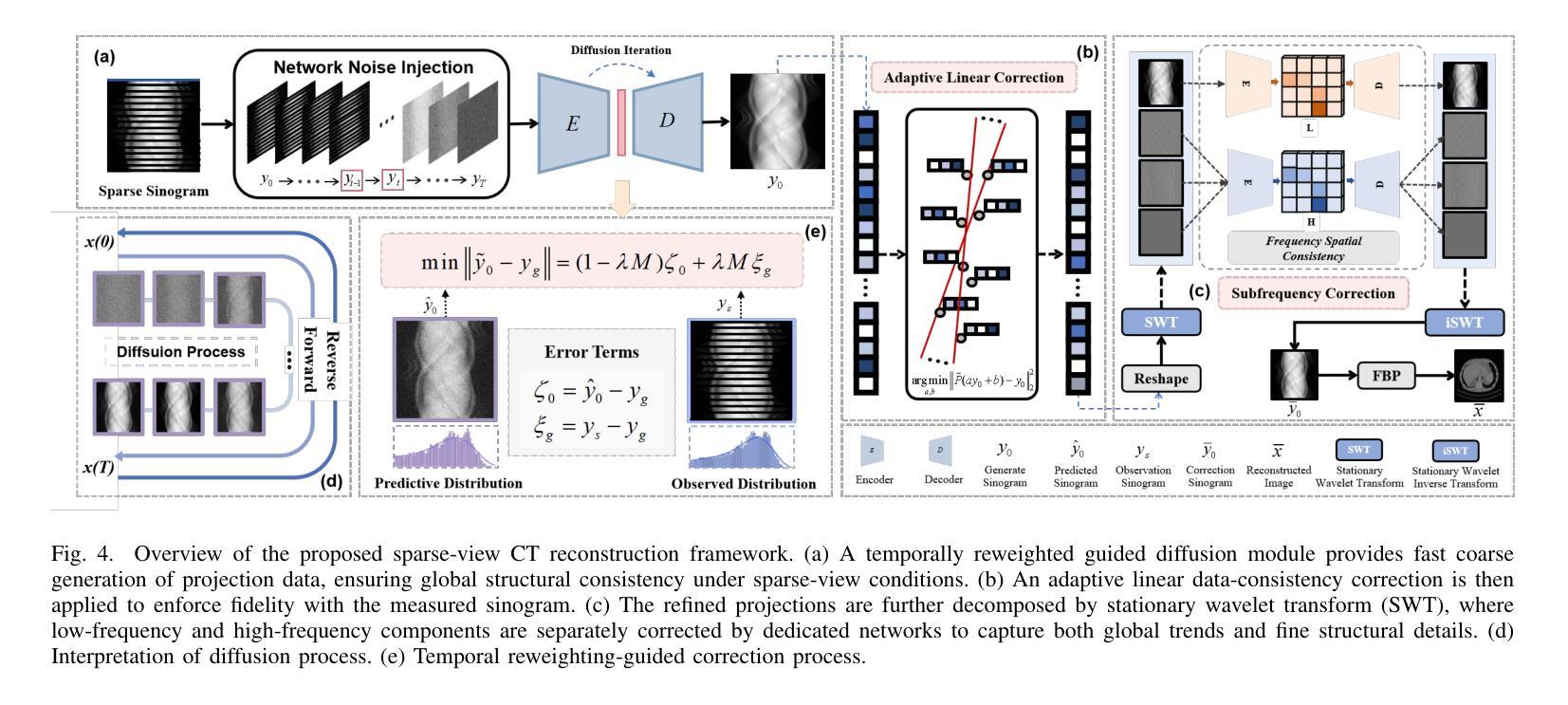
Diffusion Generative Models Meet Compressed Sensing, with Applications to Imaging and Finance
Authors:Zhengyi Guo, Jiatu Li, Wenpin Tang, David D. Yao
In this study we develop dimension-reduction techniques to accelerate diffusion model inference in the context of synthetic data generation. The idea is to integrate compressed sensing into diffusion models (hence, CSDM): First, compress the dataset into a latent space (from an ambient space), and train a diffusion model in the latent space; next, apply a compressed sensing algorithm to the samples generated in the latent space for decoding back to the original space; and the goal is to facilitate the efficiency of both model training and inference. Under certain sparsity assumptions on data, our proposed approach achieves provably faster convergence, via combining diffusion model inference with sparse recovery. It also sheds light on the best choice of the latent space dimension. To illustrate the effectiveness of this approach, we run numerical experiments on a range of datasets, including handwritten digits, medical and climate images, and financial time series for stress testing.
本研究中,我们开发降维技术来加速合成数据生成背景下的扩散模型推理。我们的想法是将压缩感知技术集成到扩散模型中(因此称为CSDM):首先,将数据集压缩到潜在空间(从环境空间中);在潜在空间中训练扩散模型;然后,对潜在空间中生成的样本应用压缩感知算法以解码回原始空间;我们的目标是提高模型训练和推理的效率。在数据的某些稀疏性假设下,我们提出的方法通过结合扩散模型推理和稀疏恢复,能够实现更快的收敛速度。它还指出了选择潜在空间维度的最佳方法。为了说明该方法的有效性,我们在一系列数据集上进行了数值实验,包括手写数字、医疗和气候图像以及金融时间序列的压力测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究开发降维技术以加速合成数据生成中的扩散模型推理。研究将压缩感知集成到扩散模型中(即CSDM):首先,将数据压缩到潜在空间(从环境空间),在潜在空间训练扩散模型;然后,对潜在空间生成的样本应用压缩感知算法以解码回原始空间;目标是促进模型训练和推理的效率。在数据的某些稀疏性假设下,所提出的方法通过结合扩散模型推理与稀疏恢复,可实现更快的收敛速度。此外,该研究还阐释了选择潜在空间维度的最佳做法。通过在手写数字、医疗和气候图像以及金融时间序列等数据集上进行的数值实验,验证了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出将压缩感知集成到扩散模型中,形成CSDM方法,旨在加速扩散模型推理并促进模型训练效率。
- CSDM方法通过在潜在空间进行数据和模型操作,有效降低数据复杂性。
- 该方法利用压缩感知算法将潜在空间中的样本解码回原始空间。
- 在数据的某些稀疏性假设下,CSDM方法通过结合扩散模型推理与稀疏恢复实现更快收敛。
- 研究阐释了如何选择潜在空间的最佳维度。
- 通过多种数据集上的数值实验,验证了CSDM方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图
3D-LATTE: Latent Space 3D Editing from Textual Instructions
Authors:Maria Parelli, Michael Oechsle, Michael Niemeyer, Federico Tombari, Andreas Geiger
Despite the recent success of multi-view diffusion models for text/image-based 3D asset generation, instruction-based editing of 3D assets lacks surprisingly far behind the quality of generation models. The main reason is that recent approaches using 2D priors suffer from view-inconsistent editing signals. Going beyond 2D prior distillation methods and multi-view editing strategies, we propose a training-free editing method that operates within the latent space of a native 3D diffusion model, allowing us to directly manipulate 3D geometry. We guide the edit synthesis by blending 3D attention maps from the generation with the source object. Coupled with geometry-aware regularization guidance, a spectral modulation strategy in the Fourier domain and a refinement step for 3D enhancement, our method outperforms previous 3D editing methods enabling high-fidelity, precise, and robust edits across a wide range of shapes and semantic manipulations.
尽管基于多视角的扩散模型在文本/图像驱动的3D资产生成方面取得了最新成功,但基于指令的3D资产编辑却出人意料地远远落后于生成模型的质量。主要原因是近期使用二维先验的方法受到了视角不一致编辑信号的影响。超越二维先验蒸馏方法和多视角编辑策略,我们提出了一种无需训练的编辑方法,该方法在原生三维扩散模型的潜在空间内进行操作,允许我们直接操作三维几何。我们通过混合生成中的三维注意力图与源对象来指导编辑合成。结合几何感知正则化指导、傅里叶域的频谱调制策略以及用于三维增强的细化步骤,我们的方法在广泛的形状和语义操作方面超越了之前的3D编辑方法,实现了高保真、精确和稳健的编辑。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要讨论了多视图扩散模型在文本和图像驱动的3D资产生成中的成功应用,但令人惊讶的是,关于基于指令的编辑技术相对滞后的问题。原因在于采用二维先验的方法会出现视图不一致的编辑信号。为此,我们提出了一种基于原生三维扩散模型的训练式外编辑方法,可以在其潜在空间内操作而不进行任何训练,从而实现直接的几何图形操作。通过将生成的三维注意力地图与原始对象相结合进行合成编辑指导,辅以几何感知正则化指导、频域光谱调制策略和用于三维增强的精炼步骤,该方法超越了先前的三维编辑技术,能够实现高质量、精确且稳健的跨各种形状和语义操纵编辑。
Key Takeaways
- 多视图扩散模型在文本和图像驱动的3D资产生成中取得了成功。
- 基于指令的编辑技术在质量和表现方面仍存在挑战。其主要问题在于采用二维先验方法产生的视图不一致编辑信号。
- 研究人员提出了一种新型的无训练编辑方法,直接在原生三维扩散模型的潜在空间内操作,以实现精确的几何图形操作。
- 该方法结合了生成的三维注意力地图与原始对象进行合成编辑指导。
- 通过几何感知正则化指导、频域光谱调制策略和用于三维增强的精炼步骤,该方法实现了高质量、精确且稳健的跨各种形状和语义操纵编辑。
- 该方法超越了先前的三维编辑技术,展现出在多种形状和语义操纵方面的优势。
点此查看论文截图
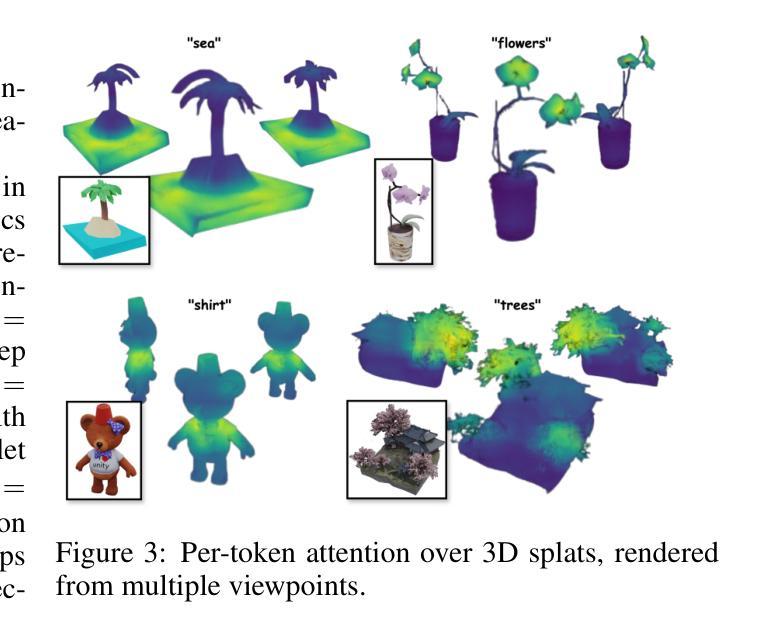
Representation Entanglement for Generation: Training Diffusion Transformers Is Much Easier Than You Think
Authors:Ge Wu, Shen Zhang, Ruijing Shi, Shanghua Gao, Zhenyuan Chen, Lei Wang, Zhaowei Chen, Hongcheng Gao, Yao Tang, Jian Yang, Ming-Ming Cheng, Xiang Li
REPA and its variants effectively mitigate training challenges in diffusion models by incorporating external visual representations from pretrained models, through alignment between the noisy hidden projections of denoising networks and foundational clean image representations. We argue that the external alignment, which is absent during the entire denoising inference process, falls short of fully harnessing the potential of discriminative representations. In this work, we propose a straightforward method called Representation Entanglement for Generation (REG), which entangles low-level image latents with a single high-level class token from pretrained foundation models for denoising. REG acquires the capability to produce coherent image-class pairs directly from pure noise, substantially improving both generation quality and training efficiency. This is accomplished with negligible additional inference overhead, requiring only one single additional token for denoising (<0.5% increase in FLOPs and latency). The inference process concurrently reconstructs both image latents and their corresponding global semantics, where the acquired semantic knowledge actively guides and enhances the image generation process. On ImageNet 256$\times$256, SiT-XL/2 + REG demonstrates remarkable convergence acceleration, achieving $\textbf{63}\times$ and $\textbf{23}\times$ faster training than SiT-XL/2 and SiT-XL/2 + REPA, respectively. More impressively, SiT-L/2 + REG trained for merely 400K iterations outperforms SiT-XL/2 + REPA trained for 4M iterations ($\textbf{10}\times$ longer). Code is available at: https://github.com/Martinser/REG.
REPA及其变体通过融入预训练模型的外部视觉表征,以及通过对去噪网络的噪声隐藏投影和基础性干净图像表征之间的对齐,有效缓解了扩散模型中的训练挑战。我们认为,在整个去噪推理过程中缺失的外部对齐,未能充分利用判别性表征的潜力。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种名为生成表示纠缠(REG)的直观方法,它将图像的低级潜在特征与预训练基础模型的单个高级类别令牌纠缠在一起,用于去噪。REG具备直接从纯噪声中产生连贯的图像类别对的能力,可大幅提高生成质量和训练效率。这只需增加极少量的推理开销,仅需要一个额外的令牌用于去噪(增加FLOPs和延迟的时间不到0.5%)。推理过程同时重建图像潜在特征及其对应的全局语义,所获取的语义知识积极指导并增强图像生成过程。在ImageNet 256×256上,SiT-XL/2 + REG显示出令人瞩目的收敛加速效果,相对于SiT-XL/2和SiT-XL/2 + REPA分别达到了63倍和23倍的更快训练速度。更令人印象深刻的是,仅经过40万次迭代的SiT-L/2 + REG的性能超越了经过4百万次迭代(长达10倍)的SiT-XL/2 + REPA。相关代码可在以下链接中找到:https://github.com/Martinser/REG。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
REPA及其变体通过融入预训练模型的外部视觉表征,有效缓解了扩散模型在训练方面的挑战。本文通过对齐去噪网络的噪声隐藏投影和清洁图像的基础表征,实现了这一点。然而,本文认为,在去噪推断过程中完全缺失的外部对齐,未能充分利用判别式表征的潜力。因此,本文提出了一种名为REG(用于生成的表示纠缠)的直观方法,该方法将低级别图像潜能与预训练基础模型中的单个高级类别令牌纠缠在一起,用于去噪。REG能够从纯噪声中直接生成连贯的图像类别对,从而大大提高了生成质量和训练效率。这一切的实现只需增加一个额外的令牌用于去噪(增加的计算量和延迟均不到0.5%),几乎无需增加任何推理开销。在ImageNet 256×256上,SiT-XL/2 + REG显示出令人瞩目的收敛加速能力,相对于SiT-XL/2和SiT-XL/2 + REPA分别达到了63倍和23倍的训练加速。更令人印象深刻的是,仅训练了40万次的SiT-L/2 + REG超过了训练了4百万次的SiT-XL/2 + REPA(时间长达十倍)。相关代码可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/Martinser/REG。
关键见解
- REPA及其变体通过融入外部视觉表征缓解了扩散模型的训练挑战。
- 提出的REG方法结合了低级别图像潜能和预训练基础模型中的高级类别令牌,用于去噪。
- REG能直接从噪声生成连贯的图像类别对,提高了生成质量和训练效率。
- REG增加的计算量和延迟微乎其微(不到0.5%)。
- SiT-XL/2 + REG在ImageNet 256×256上实现了快速收敛,相较于其他模型有显著加速。
- SiT-L/2 + REG在较短的训练时间内(仅40万次迭代)表现出优异的性能,超越了长时间训练的SiT-XL/2 + REPA。
点此查看论文截图
Reward-Agnostic Prompt Optimization for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Semin Kim, Yeonwoo Cha, Jaehoon Yoo, Seunghoon Hong
We investigate a general approach for improving user prompts in text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models by finding prompts that maximize a reward function specified at test-time. Although diverse reward models are used for evaluating image generation, existing automated prompt engineering methods typically target specific reward configurations. Consequently, these specialized designs exhibit suboptimal performance when applied to new prompt engineering scenarios involving different reward models. To address this limitation, we introduce RATTPO (Reward-Agnostic Test-Time Prompt Optimization), a flexible test-time optimization method applicable across various reward scenarios without modification. RATTPO iteratively searches for optimized prompts by querying large language models (LLMs) \textit{without} requiring reward-specific task descriptions. Instead, it uses the optimization trajectory and a novel reward-aware feedback signal (termed a “hint”) as context. Empirical results demonstrate the versatility of RATTPO, effectively enhancing user prompts across diverse reward setups that assess various generation aspects, such as aesthetics, general human preference, or spatial relationships between objects. RATTPO surpasses other test-time search baselines in search efficiency, running 4.8 times faster than naive reward-agnostic test-time search baseline on average. Furthermore, with sufficient inference budget, it can achieve comparable performance to learning-based baselines that require reward-specific fine-tuning. The code is available at https://github.com/seminkim/RATTPO.
我们研究了一种通过寻找最大化测试时指定奖励函数的提示来改善文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型中的用户提示的通用方法。尽管用于评估图像生成的不同奖励模型已经被使用,但现有的自动化提示工程方法通常针对特定的奖励配置。因此,当将这些特殊设计应用于涉及不同奖励模型的新提示工程场景时,其性能表现并不理想。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了奖励无关测试时间提示优化(RATTPO),这是一种灵活的测试时间优化方法,可跨各种奖励场景进行应用,无需进行修改。RATTPO通过查询大型语言模型(LLM)来迭代搜索优化的提示,而无需特定的奖励任务描述。相反,它使用优化轨迹和一种新颖的奖励感知反馈信号(称为“线索”)作为上下文。经验结果表明RATTPO的通用性,可以有效地增强用户在不同奖励设置下的提示,这些奖励设置评估了诸如美学、一般人类偏好或对象之间的空间关系等各种生成方面。RATTPO在搜索效率上超越了其他测试时间搜索基线,平均速度比简单的奖励无关测试时间搜索基线快4.8倍。此外,在足够的推理预算下,它可以实现与学习型基线的相当性能,而学习型基线需要针对奖励进行特定微调。代码可在https://github.com/seminkim/RATTPO上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 29 pages, Under review
Summary
本文研究了通过找到最大化测试时指定的奖励函数的用户提示来改进文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型中的用户提示的通用方法。针对图像生成评估中使用的不同奖励模型,本文提出了一种灵活的在测试时进行优化方法——RATTPO(奖励无关测试时间提示优化)。RATTPO通过查询大型语言模型(LLM)而无需特定奖励任务的描述,利用优化轨迹和一种新颖的奖励感知反馈信号(称为“线索”)作为上下文来迭代搜索优化的提示。实验结果表明,RATTPO在各种奖励设置下都能有效地增强用户提示,并在搜索效率上超越了其他测试时间搜索基线,在平均情况下运行速度是朴素奖励无关测试时间搜索基线的4.8倍。在充足推理预算下,其性能可与需要奖励特定微调的学习基线相媲美。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种通用的方法,通过找到最大化测试时奖励函数的提示来改善文本到图像扩散模型中的用户提示。
- 介绍了RATTPO(奖励无关测试时间提示优化),这是一种灵活的方法,可应用于各种奖励场景,而无需进行修改。
- RATTPO通过查询大型语言模型(LLM)来迭代搜索优化的提示,不需要特定奖励任务的描述。
- RATTPO利用优化轨迹和一种新颖的奖励感知反馈信号(称为“线索”)作为上下文。
- RATTPO在各种奖励设置下都能有效地增强用户提示,实验结果表明其搜索效率超越了其他测试时间搜索基线。
- RATTPO运行速度快,在平均情况下是朴素搜索基线的4.8倍。
- 在充足推理预算下,RATTPO的性能可与需要奖励特定微调的学习基线相媲美。
点此查看论文截图
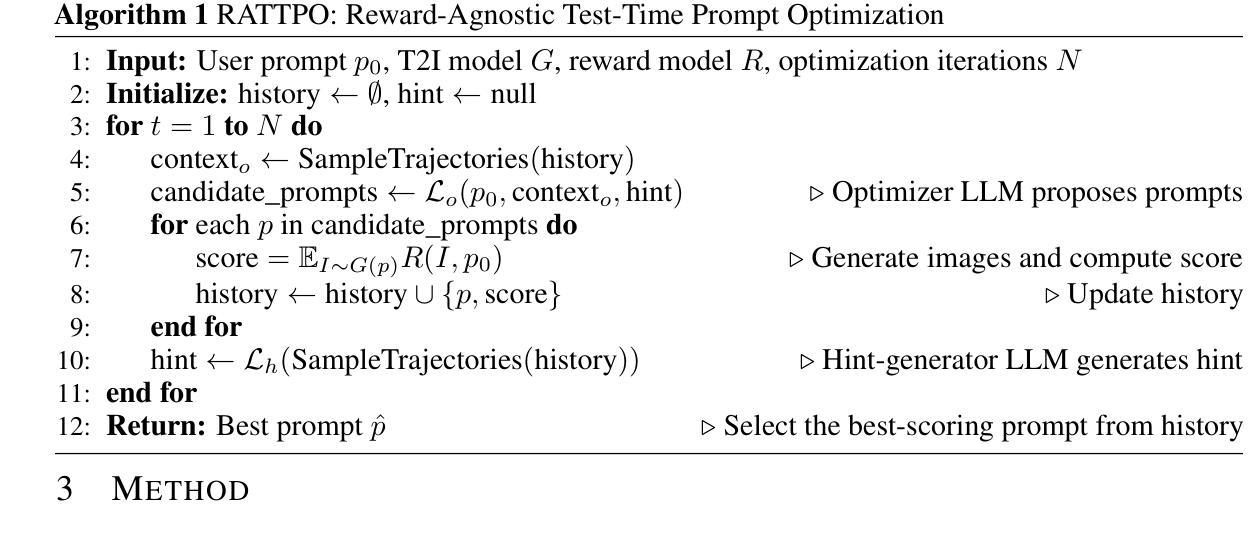
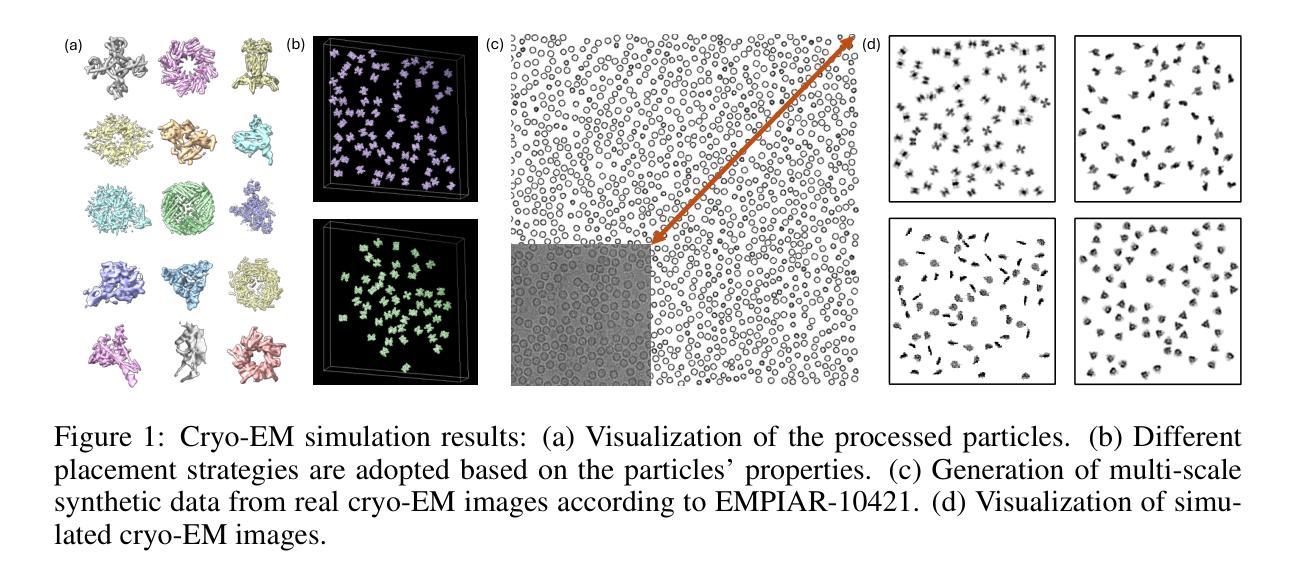
CryoCCD: Conditional Cycle-consistent Diffusion with Biophysical Modeling for Cryo-EM Synthesis
Authors:Runmin Jiang, Genpei Zhang, Yuntian Yang, Siqi Wu, Minhao Wu, Wanyue Feng, Yizhou Zhao, Xi Xiao, Xiao Wang, Tianyang Wang, Xingjian Li, Muyuan Chen, Min Xu
Single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has become a cornerstone of structural biology, enabling near-atomic resolution analysis of macromolecules through advanced computational methods. However, the development of cryo-EM processing tools is constrained by the scarcity of high-quality annotated datasets. Synthetic data generation offers a promising alternative, but existing approaches lack thorough biophysical modeling of heterogeneity and fail to reproduce the complex noise observed in real imaging. To address these limitations, we present CryoCCD, a synthesis framework that unifies versatile biophysical modeling with the first conditional cycle-consistent diffusion model tailored for cryo-EM. The biophysical engine provides multi-functional generation capabilities to capture authentic biological organization, and the diffusion model is enhanced with cycle consistency and mask-guided contrastive learning to ensure realistic noise while preserving structural fidelity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CryoCCD generates structurally faithful micrographs, enhances particle picking and pose estimation, as well as achieves superior performance over state-of-the-art baselines, while also generalizing effectively to held-out protein families.
单颗粒冷冻电子显微镜(cryo-EM)已成为结构生物学的核心,能够通过先进的计算方法实现对大分子的接近原子分辨率分析。然而,由于高质量注释数据集的稀缺,冷冻电镜处理工具的发展受到限制。合成数据生成提供了一个有前途的替代方案,但现有方法缺乏异质性的彻底生物物理建模,且无法复制真实成像中观察到的复杂噪声。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了CryoCCD,这是一个合成框架,它将通用的生物物理建模与首个针对冷冻电镜设计的条件循环一致扩散模型相结合。生物物理引擎提供多功能生成能力,以捕捉真实的生物组织,扩散模型通过循环一致性和掩膜引导对比学习进行增强,以确保产生逼真的噪声同时保持结构保真度。大量实验表明,CryoCCD生成的结构忠实显微图,提高了粒子挑选和姿态估计,并且相较于最先进的基础线模型实现了卓越性能,同时有效地推广到未参与训练的蛋白质家族。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
单颗粒冷冻电子显微镜(cryo-EM)是结构生物学领域的核心,可通过先进的计算方法实现近原子分辨率的分子分析。然而,由于高质量标注数据集的稀缺,cryo-EM处理工具的发展受到限制。本文提出了CryoCCD合成框架,结合了多功能生物物理建模与针对cryo-EM的首个条件循环一致性扩散模型。实验表明,CryoCCD生成的结构忠实于微图,提高了粒子选取和姿态估计的精确度,且在对比前沿基线时表现出卓越性能,同时可有效推广到未知蛋白质家族。
Key Takeaways
- 单颗粒冷冻电子显微镜(cryo-EM)已成为结构生物学中的核心技术,具有近原子分辨率分析功能。
- 现有的合成数据生成方法缺乏生物物理异质性的建模,未能完全复制真实成像中的复杂噪声。
- 针对这一局限性,本文提出了CryoCCD合成框架,融合了多功能生物物理建模和专为cryo-EM设计的首个条件循环一致性扩散模型。
- 生物物理引擎可模拟真实的生物组织结构。扩散模型则通过循环一致性和掩膜引导对比学习确保生成的噪声具有真实性并维持结构忠实度。
- 实验证明CryoCCD生成的微图结构真实可靠,改进了粒子选取和姿态估计的准确度。
- 与当前最前沿的方法相比,CryoCCD展现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

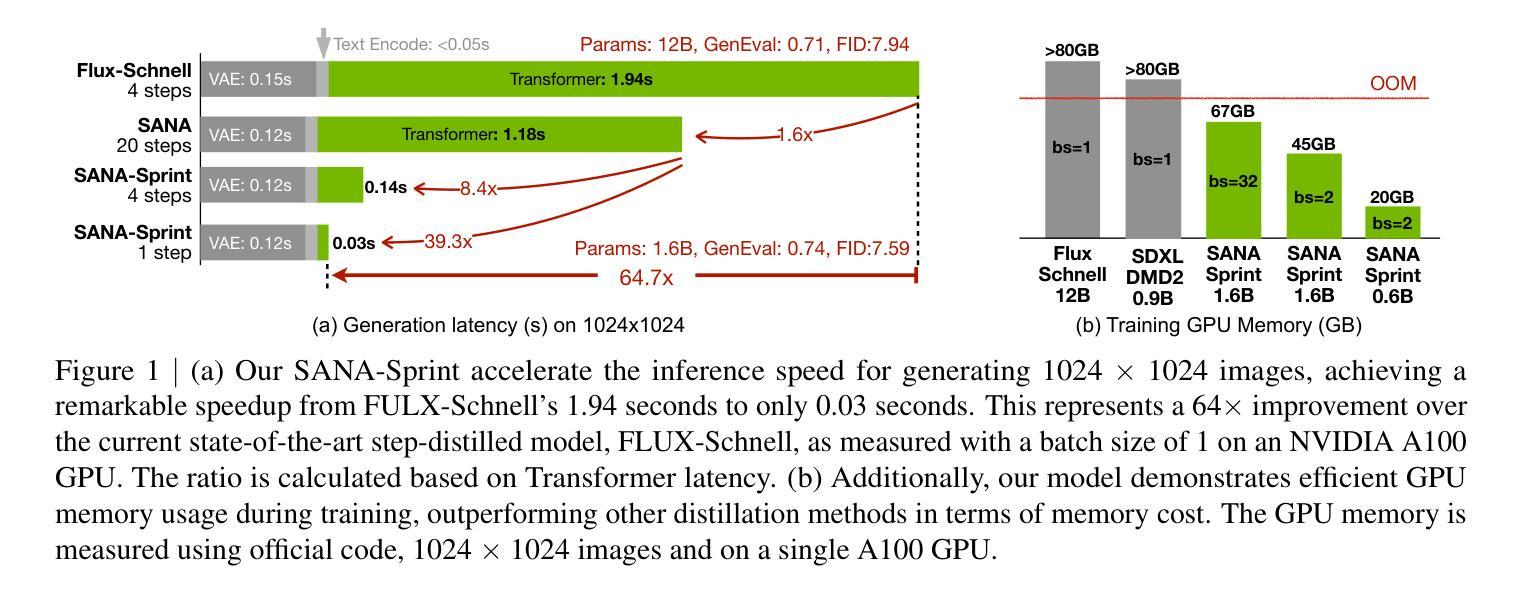
SANA-Sprint: One-Step Diffusion with Continuous-Time Consistency Distillation
Authors:Junsong Chen, Shuchen Xue, Yuyang Zhao, Jincheng Yu, Sayak Paul, Junyu Chen, Han Cai, Song Han, Enze Xie
This paper presents SANA-Sprint, an efficient diffusion model for ultra-fast text-to-image (T2I) generation. SANA-Sprint is built on a pre-trained foundation model and augmented with hybrid distillation, dramatically reducing inference steps from 20 to 1-4. We introduce three key innovations: (1) We propose a training-free approach that transforms a pre-trained flow-matching model for continuous-time consistency distillation (sCM), eliminating costly training from scratch and achieving high training efficiency. Our hybrid distillation strategy combines sCM with latent adversarial distillation (LADD): sCM ensures alignment with the teacher model, while LADD enhances single-step generation fidelity. (2) SANA-Sprint is a unified step-adaptive model that achieves high-quality generation in 1-4 steps, eliminating step-specific training and improving efficiency. (3) We integrate ControlNet with SANA-Sprint for real-time interactive image generation, enabling instant visual feedback for user interaction. SANA-Sprint establishes a new Pareto frontier in speed-quality tradeoffs, achieving state-of-the-art performance with 7.59 FID and 0.74 GenEval in only 1 step - outperforming FLUX-schnell (7.94 FID / 0.71 GenEval) while being 10x faster (0.1s vs 1.1s on H100). It also achieves 0.1s (T2I) and 0.25s (ControlNet) latency for 1024 x 1024 images on H100, and 0.31s (T2I) on an RTX 4090, showcasing its exceptional efficiency and potential for AI-powered consumer applications (AIPC). Code and pre-trained models will be open-sourced.
本文介绍了SANA-Sprint,这是一种高效的扩散模型,用于超快速文本到图像(T2I)生成。SANA-Sprint建立在预训练基础模型上,并辅以混合蒸馏技术,将推理步骤从20步大幅减少到1-4步。我们引入了三项关键创新:(1)我们提出了一种无需训练的方法,将预训练的流匹配模型转换为连续时间一致性蒸馏(sCM),消除了从头开始的高成本训练,实现了高训练效率。我们的混合蒸馏策略结合了sCM和潜在对抗性蒸馏(LADD):sCM确保与教师模型的对齐,而LADD增强单步生成保真度。(2)SANA-Sprint是一种统一的步长自适应模型,在1-4步内实现高质量生成,消除了针对特定步骤的训练,提高了效率。(3)我们将ControlNet与SANA-Sprint集成,用于实时交互式图像生成,实现即时视觉反馈以供用户交互。SANA-Sprint在速度与质量权衡方面建立了新的帕累托前沿,以7.59的FID和0.74的GenEval在仅1步内实现了最新性能——优于FLUX-schnell(7.94 FID / 0.71 GenEval),同时速度提高了10倍(H100上为0.1秒对1.1秒)。在H100上,对于1024 x 1024图像,它的T2I和ControlNet延迟分别达到了0.1秒和0.25秒;在RTX 4090上,T2I延迟为0.31秒,展示了其卓越的效率和在AI驱动的消费级应用中的潜力。代码和预训练模型将开源。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 11 figures, 8 tables, In submission
Summary
本文介绍了SANA-Sprint,这是一种高效的扩散模型,用于超快速文本到图像(T2I)生成。它通过预训练基础模型构建,并采用混合蒸馏技术,显著将推理步骤从20减少到1-4步。引入三种关键技术:训练自由方法、统一步长自适应模型和与控制网的集成。SANA-Sprint在速度和质量的权衡方面建立了新的帕累托前沿,实现了卓越的性能和效率。
Key Takeaways
- SANA-Sprint是基于预训练基础模型的扩散模型,用于超快速文本到图像生成。
- 通过混合蒸馏技术,显著减少推理步骤,从20步降至1-4步。
- 引入训练自由方法,实现与预训练流匹配模型的转换,提高训练效率。
- 混合蒸馏策略结合sCM和LADD,提高生成质量和效率。
- SANA-Sprint是统一步长自适应模型,实现高质量生成在1-4步内。
- 与ControlNet集成,实现实时交互式图像生成,提供用户即时视觉反馈。
- SANA-Sprint在速度和质量的权衡方面表现出卓越性能,达到业界领先水平。
点此查看论文截图


Diffusion-Based mmWave Radar Point Cloud Enhancement Driven by Range Images
Authors:Ruixin Wu, Zihan Li, Jin Wang, Xiangyu Xu, Zhi Zheng, Kaixiang Huang, Guodong Lu
Millimeter-wave (mmWave) radar has attracted significant attention in robotics and autonomous driving. However, despite the perception stability in harsh environments, the point cloud generated by mmWave radar is relatively sparse while containing significant noise, which limits its further development. Traditional mmWave radar enhancement approaches often struggle to leverage the effectiveness of diffusion models in super-resolution, largely due to the unnatural range-azimuth heatmap (RAH) or bird’s eye view (BEV) representation. To overcome this limitation, we propose a novel method that pioneers the application of fusing range images with image diffusion models, achieving accurate and dense mmWave radar point clouds that are similar to LiDAR. Benefitting from the projection that aligns with human observation, the range image representation of mmWave radar is close to natural images, allowing the knowledge from pre-trained image diffusion models to be effectively transferred, significantly improving the overall performance. Extensive evaluations on both public datasets and self-constructed datasets demonstrate that our approach provides substantial improvements, establishing a new state-of-the-art performance in generating truly three-dimensional LiDAR-like point clouds via mmWave radar. Code will be released after publication.
毫米波雷达(mmWave radar)在机器人技术和自动驾驶领域引起了广泛关注。然而,尽管毫米波雷达在恶劣环境下的感知稳定性良好,但其生成的点云相对稀疏且含有大量噪声,限制了其进一步发展。传统的毫米波雷达增强方法往往难以利用扩散模型在超分辨率方面的优势,这主要是因为范围-方位热图(RAH)或鸟瞰图(BEV)表示不自然。为了克服这一局限性,我们提出了一种新方法,率先将范围图像与图像扩散模型融合应用。该方法可实现准确且密集的毫米波雷达点云,类似于激光雷达点云。得益于与人类观察相匹配的投影,毫米波雷达的范围图像表示接近自然图像,这使得预训练的图像扩散模型的知识可以高效迁移,从而显著提高整体性能。在公共数据集和自我构建的数据集上的广泛评估表明,我们的方法在生成真正三维激光雷达类点云方面提供了重大改进,确立了利用毫米波雷达生成点云的新先进性能标准。代码将在发表后发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 7 figures. This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
摘要
毫米波雷达在机器人和自动驾驶领域受到广泛关注,但其生成的点云相对稀疏且含噪,限制了其进一步发展。传统方法难以利用扩散模型实现超分辨率增强。本研究提出了一种融合范围图像与图像扩散模型的新方法,可生成准确、密集的毫米波雷达点云,类似于激光雷达点云。范围图像表示法与人类观察相符,接近自然图像,可有效地迁移预训练的图像扩散模型的知识,显著提高整体性能。在公共和自制数据集上的评估显示,该方法在生成真正的三维激光雷达点云方面达到了最新水平。
要点
- 毫米波雷达在恶劣环境下具有稳定的感知能力,但其生成的点云稀疏且含噪。
- 传统方法难以利用扩散模型进行有效增强。
- 提出了一种融合范围图像与图像扩散模型的新方法,用于增强毫米波雷达点云。
- 范围图像表示法与人类观察相符,允许迁移预训练的图像扩散模型知识。
- 该方法生成的点云性能接近激光雷达点云。
- 在公共和自制数据集上的评估显示,该方法在生成三维激光雷达点云方面达到了最新水平。
- 代码将在发表后公开。
点此查看论文截图
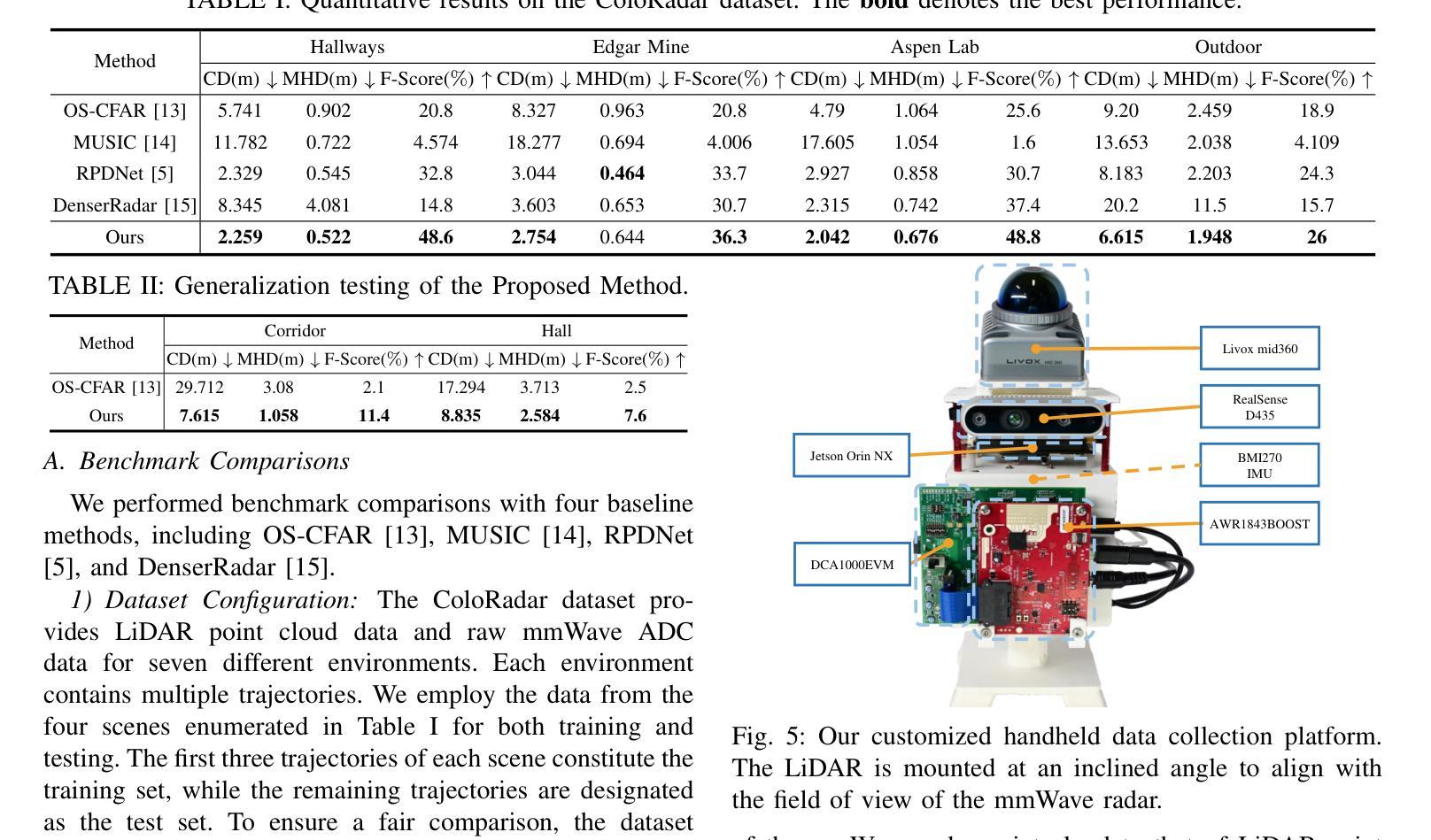
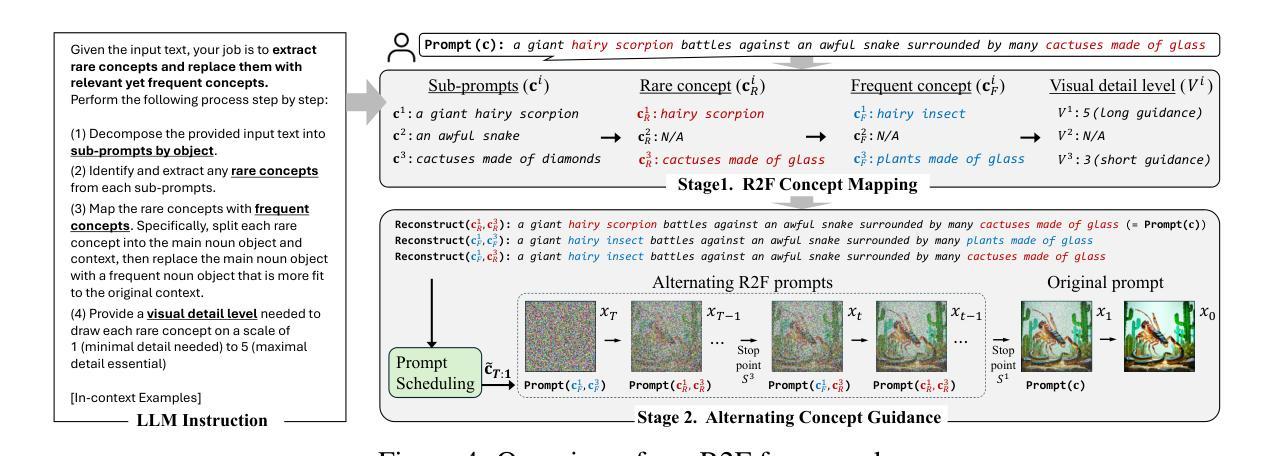
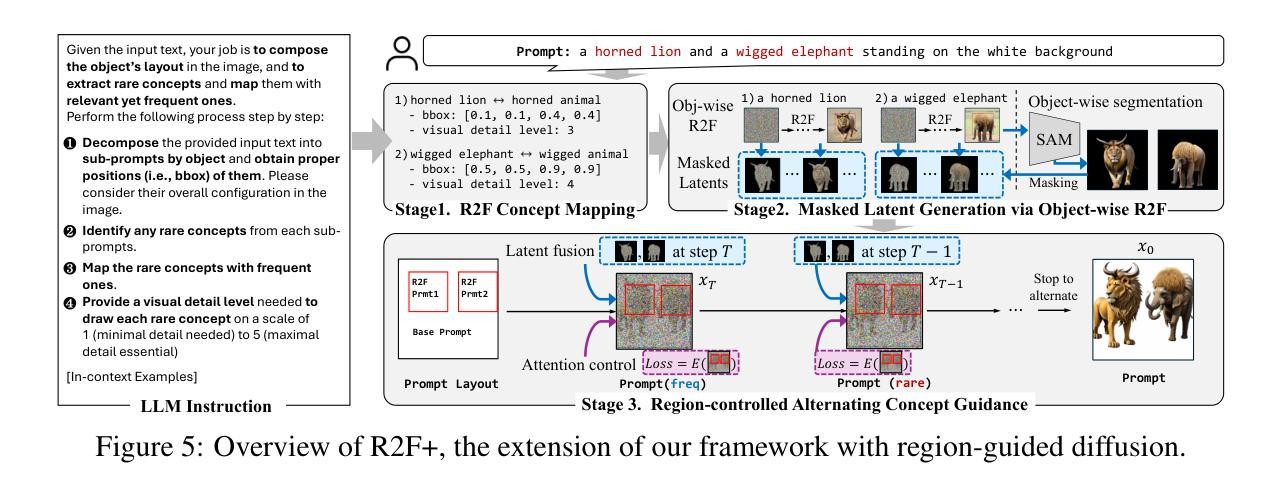
Rare-to-Frequent: Unlocking Compositional Generation Power of Diffusion Models on Rare Concepts with LLM Guidance
Authors:Dongmin Park, Sebin Kim, Taehong Moon, Minkyu Kim, Kangwook Lee, Jaewoong Cho
State-of-the-art text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models often struggle to generate rare compositions of concepts, e.g., objects with unusual attributes. In this paper, we show that the compositional generation power of diffusion models on such rare concepts can be significantly enhanced by the Large Language Model (LLM) guidance. We start with empirical and theoretical analysis, demonstrating that exposing frequent concepts relevant to the target rare concepts during the diffusion sampling process yields more accurate concept composition. Based on this, we propose a training-free approach, R2F, that plans and executes the overall rare-to-frequent concept guidance throughout the diffusion inference by leveraging the abundant semantic knowledge in LLMs. Our framework is flexible across any pre-trained diffusion models and LLMs, and can be seamlessly integrated with the region-guided diffusion approaches. Extensive experiments on three datasets, including our newly proposed benchmark, RareBench, containing various prompts with rare compositions of concepts, R2F significantly surpasses existing models including SD3.0 and FLUX by up to 28.1%p in T2I alignment. Code is available at https://github.com/krafton-ai/Rare-to-Frequent.
先进的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成罕见概念组合(例如具有不寻常属性的物体)时经常面临挑战。在本文中,我们展示了通过大型语言模型(LLM)的指导,可以显著增强扩散模型在这种罕见概念上的组合生成能力。我们从实证和理论分析开始,证明在扩散采样过程中暴露与目标罕见概念相关的频繁概念,可以产生更精确的概念组合。基于此,我们提出了一种无需训练的R2F方法,它利用LLM中的丰富语义知识,通过扩散推断,规划和执行从罕见到频繁概念的总体指导。我们的框架适用于任何预训练的扩散模型和LLM,并能无缝地与区域引导扩散方法相结合。在包括我们新提出的基准测试集RareBench在内的三个数据集上进行的大量实验表明,R2F在各种包含罕见概念组合的提示下,显著超越了SD3.0和FLUX模型,在T2I对齐方面的性能提高了高达28.1%。代码可在https://github.com/krafton-ai/Rare-to-Frequent找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR 2025 (spotlight)
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成罕见概念组合时面临挑战。本文展示通过大型语言模型(LLM)指导,可以显著提高扩散模型在罕见概念上的组合生成能力。通过实证和理论分析,表明在扩散采样过程中暴露与目标罕见概念相关的频繁概念,可以更准确地进行概念组合。基于此,我们提出了一种无需训练的方法R2F,利用LLM中的丰富语义知识,通过扩散推理,实现罕见到频繁的概念指导。该方法灵活适用于任何预训练的扩散模型和LLM,并可无缝集成到区域引导扩散方法中。在包括新提出的基准测试数据集RareBench上的广泛实验表明,R2F在T2I对齐方面显著超越了SD3.0和FLUX模型,提高了高达28.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成罕见概念组合时存在挑战。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)指导能提高扩散模型在罕见概念上的组合生成能力。
- 在扩散采样过程中暴露与目标罕见概念相关的频繁概念,能更准确进行概念组合。
- 提出了一种无需训练的R2F方法,利用LLM的丰富语义知识,实现罕见到频繁的概念指导。
- R2F方法灵活适用于各种预训练的扩散模型和LLM,并可集成到区域引导扩散方法中。
- 在新的基准测试数据集RareBench上的实验表明,R2F显著提高了T2I对齐性能。
点此查看论文截图
DiffusionGuard: A Robust Defense Against Malicious Diffusion-based Image Editing
Authors:June Suk Choi, Kyungmin Lee, Jongheon Jeong, Saining Xie, Jinwoo Shin, Kimin Lee
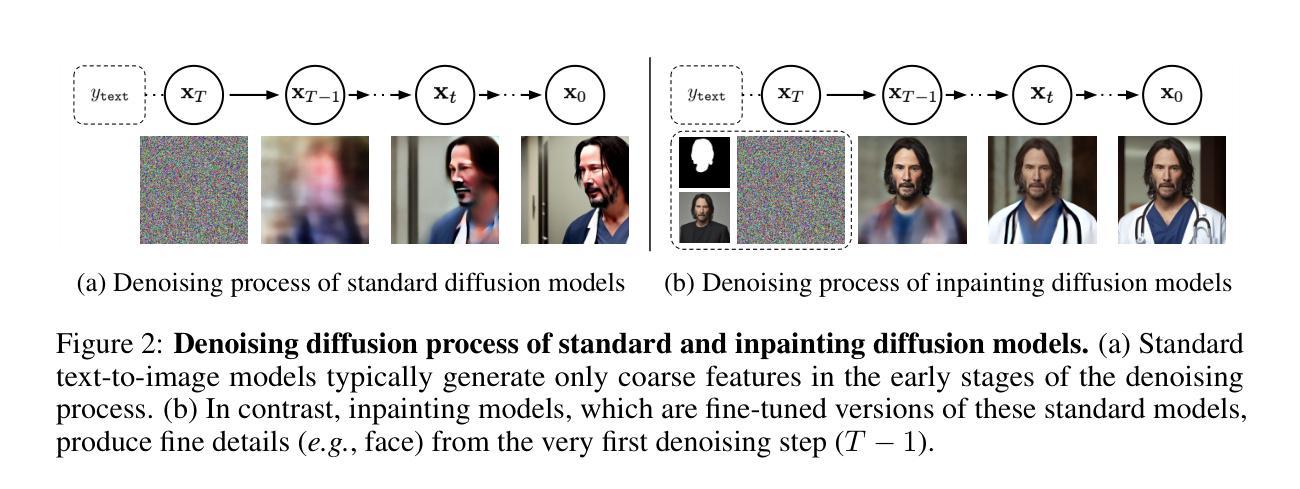
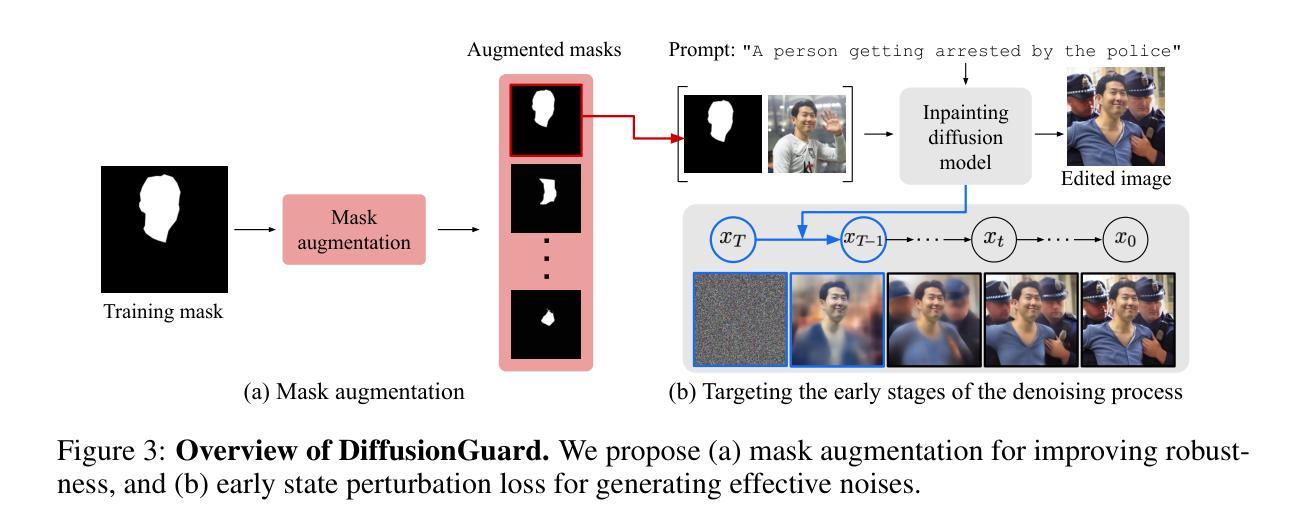
Recent advances in diffusion models have introduced a new era of text-guided image manipulation, enabling users to create realistic edited images with simple textual prompts. However, there is significant concern about the potential misuse of these methods, especially in creating misleading or harmful content. Although recent defense strategies, which introduce imperceptible adversarial noise to induce model failure, have shown promise, they remain ineffective against more sophisticated manipulations, such as editing with a mask. In this work, we propose DiffusionGuard, a robust and effective defense method against unauthorized edits by diffusion-based image editing models, even in challenging setups. Through a detailed analysis of these models, we introduce a novel objective that generates adversarial noise targeting the early stage of the diffusion process. This approach significantly improves the efficiency and effectiveness of adversarial noises. We also introduce a mask-augmentation technique to enhance robustness against various masks during test time. Finally, we introduce a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate the effectiveness and robustness of methods in protecting against privacy threats in realistic scenarios. Through extensive experiments, we show that our method achieves stronger protection and improved mask robustness with lower computational costs compared to the strongest baseline. Additionally, our method exhibits superior transferability and better resilience to noise removal techniques compared to all baseline methods. Our source code is publicly available at https://github.com/choi403/DiffusionGuard.
近期扩散模型(Diffusion Models)的进展引领了文本引导的图像操作新纪元,使用户能够通过简单的文本提示创建逼真的编辑图像。然而,关于这些方法可能被误用的担忧也日益显著,特别是在创建误导性或有害内容上。尽管最近的防御策略通过在模型中引入几乎无法察觉的对抗噪声来引发模型失效,但它们对于更复杂的操作(如使用遮罩进行编辑)仍然无效。在此工作中,我们提出了DiffusionGuard,这是一种针对基于扩散的图像编辑模型的未经授权编辑的稳健且有效的防御方法,即使在具有挑战性的设置中也是如此。通过对这些模型的深入分析,我们引入了一种新的目标,该目标生成针对扩散过程早期的对抗性噪声。这种方法大大提高了对抗性噪声的效率和有效性。我们还引入了一种掩膜增强技术,以提高在测试期间对各种掩膜的稳健性。最后,我们引入了一个综合基准测试,旨在评估方法在真实场景中抵御隐私威胁的有效性和稳健性。通过大量实验,我们证明我们的方法在保护强度、掩膜稳健性和计算成本方面优于最强基线。此外,我们的方法还表现出卓越的迁移性和对去噪技术的更好适应性,优于所有基线方法。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/choi403/DiffusionGuard上公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint. Under review
Summary
近期扩散模型的新进展开启了文本引导的图像操作新时代,使用户能够通过简单的文本提示创建逼真的编辑图像。然而,人们担心这些方法可能被滥用,用于制造误导性或有害内容。尽管最近的防御策略通过在模型中引入几乎无法察觉的对抗噪声来使其失效,但在面对更复杂的操作(如使用遮罩进行编辑)时,这些策略仍显得不够有效。本研究提出了DiffusionGuard,这是一种针对基于扩散的图像编辑模型的未经授权编辑的稳健有效防御方法,即使在具有挑战性的环境中也是如此。通过深入分析这些模型,我们引入了一种新的目标,该目标生成针对扩散过程早期的对抗性噪声。我们还引入了一种掩膜增强技术,以提高对各种掩膜在测试时的鲁棒性。最后,我们建立了一个全面的基准测试,旨在评估保护方法抵御现实场景中的隐私威胁的有效性和稳健性。实验表明,我们的方法在计算成本较低的情况下实现了更强的保护和更好的遮罩稳健性。相较于所有基线方法,我们的方法展现出更高的可迁移性和对去噪技术的更好韧性。代码公开在 https://github.com/choi403/DiffusionGuard。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型的新进展让文本引导的图像操作更加便捷和逼真。
- 滥用扩散模型可能导致误导性或有害内容的产生,引发关注。
- 当前防御策略在面对复杂图像编辑(如使用遮罩)时存在局限性。
- DiffusionGuard方法被提出,旨在有效防御未经授权的基于扩散模型的图像编辑。
- DiffusionGuard通过针对扩散过程早期生成对抗性噪声来提高效率和效果。
- 引入掩膜增强技术,增强对测试时不同掩膜的鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图