⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-01 更新
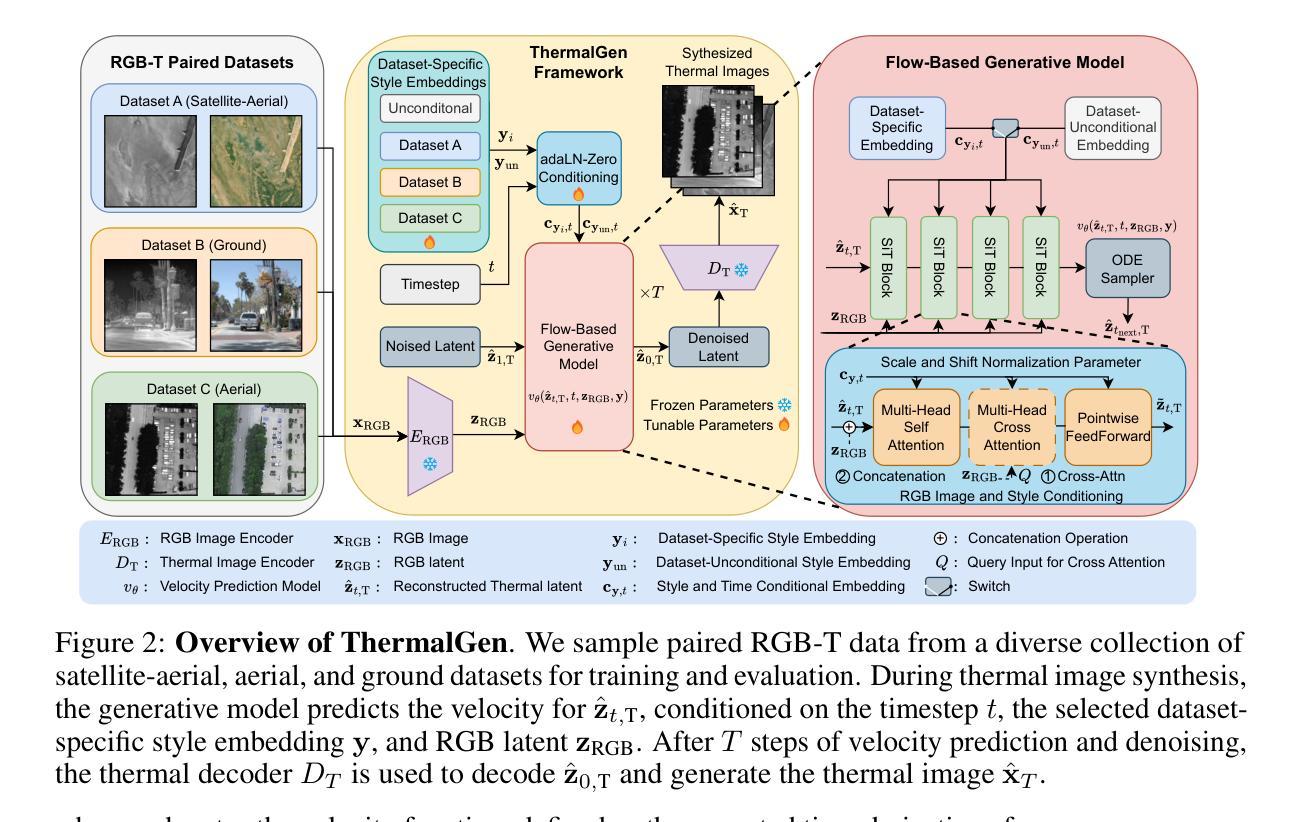
ThermalGen: Style-Disentangled Flow-Based Generative Models for RGB-to-Thermal Image Translation
Authors:Jiuhong Xiao, Roshan Nayak, Ning Zhang, Daniel Tortei, Giuseppe Loianno
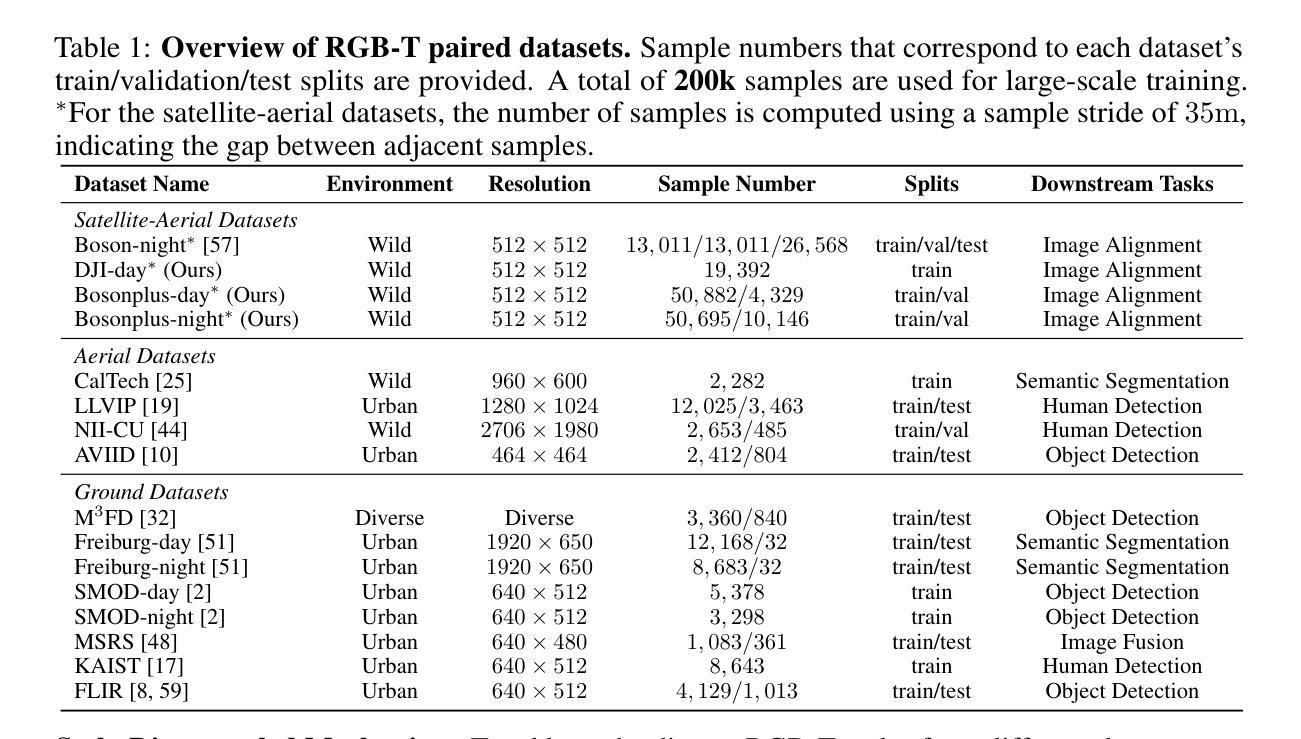
Paired RGB-thermal data is crucial for visual-thermal sensor fusion and cross-modality tasks, including important applications such as multi-modal image alignment and retrieval. However, the scarcity of synchronized and calibrated RGB-thermal image pairs presents a major obstacle to progress in these areas. To overcome this challenge, RGB-to-Thermal (RGB-T) image translation has emerged as a promising solution, enabling the synthesis of thermal images from abundant RGB datasets for training purposes. In this study, we propose ThermalGen, an adaptive flow-based generative model for RGB-T image translation, incorporating an RGB image conditioning architecture and a style-disentangled mechanism. To support large-scale training, we curated eight public satellite-aerial, aerial, and ground RGB-T paired datasets, and introduced three new large-scale satellite-aerial RGB-T datasets–DJI-day, Bosonplus-day, and Bosonplus-night–captured across diverse times, sensor types, and geographic regions. Extensive evaluations across multiple RGB-T benchmarks demonstrate that ThermalGen achieves comparable or superior translation performance compared to existing GAN-based and diffusion-based methods. To our knowledge, ThermalGen is the first RGB-T image translation model capable of synthesizing thermal images that reflect significant variations in viewpoints, sensor characteristics, and environmental conditions. Project page: http://xjh19971.github.io/ThermalGen
配对RGB-热数据对于视觉-热传感器融合和跨模态任务至关重要,包括多模态图像对齐和检索等重要应用。然而,同步且校准的RGB-热图像对稀缺,成为这些领域进步的主要障碍。为了克服这一挑战,RGB到热(RGB-T)图像翻译作为一种有前景的解决方案应运而生,它能够从丰富的RGB数据集中合成热图像,用于训练目的。在这项研究中,我们提出了ThermalGen,这是一种基于自适应流的RGB-T图像翻译生成模型,它结合了RGB图像条件结构和风格分离机制。为了支持大规模训练,我们精选了八个公共卫星航空、航空和地面RGB-T配对数据集,并引入了三个新的大规模卫星航空RGB-T数据集——DJI日间、博森加日间和博森加夜间,这些数据集在多种时间、传感器类型和地理区域下捕获。在多个RGB-T基准测试上的广泛评估表明,ThermalGen与现有的基于GAN和扩散的方法相比,实现了相当的或更优的翻译性能。据我们所知,ThermalGen是首个能够合成反映视点、传感器特性和环境条件的热图像的RGB-T图像翻译模型。项目页面:http://xjh19971.github.io/ThermalGen
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages including the checklist and appendix. Accepted at NeurIPS 2025
Summary:
本文介绍了RGB-T图像翻译技术的重要性及其在研究中的应用。为克服同步校准RGB-热图像对缺乏的难题,研究团队提出一种基于流的自适应生成模型ThermalGen。它采用RGB图像调节架构和风格分离机制,能够合成反映视点、传感器特性、环境条件等多种变化的热图像。同时,研究还引入了三个新的大规模卫星RGB-T数据集,并在多个RGB-T基准测试中证明了ThermalGen的优异性能。
Key Takeaways:
- RGB-热数据对在视觉热传感器融合和跨模态任务中至关重要,如多模态图像对齐和检索。
- 缺乏同步和校准的RGB-热图像对是这些领域的主要挑战之一。
- RGB-T图像翻译技术作为解决方案出现,能从丰富的RGB数据集中合成热图像以供训练用途。
- ThermalGen是一个基于流的自适应生成模型,用于RGB-T图像翻译,包含RGB图像调节架构和风格分离机制。
- ThermalGen能够合成反映视点、传感器特性和环境条件的热图像。
- 研究引入了三个新的大规模卫星RGB-T数据集:DJI-day、Bosonplus-day和Bosonplus-night。
点此查看论文截图

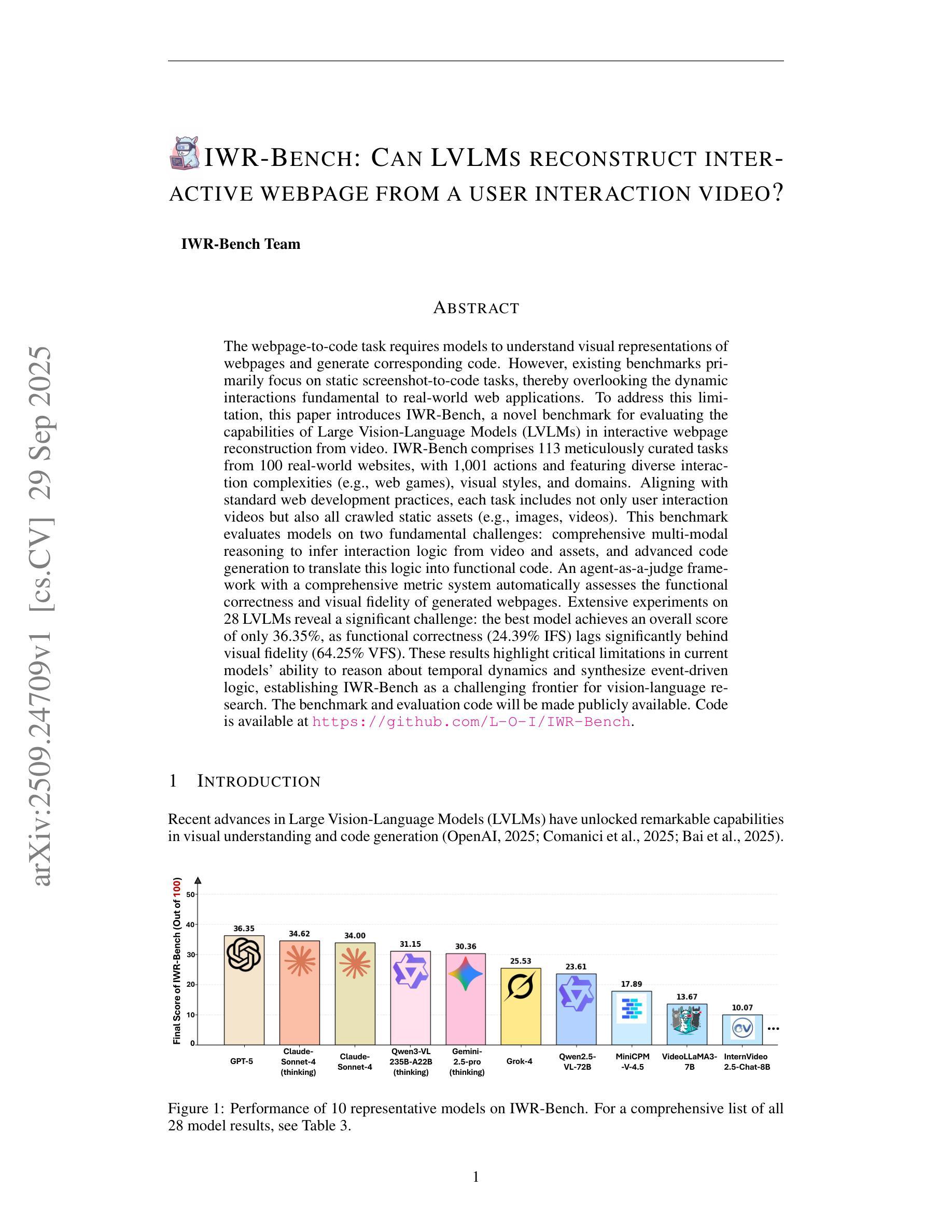
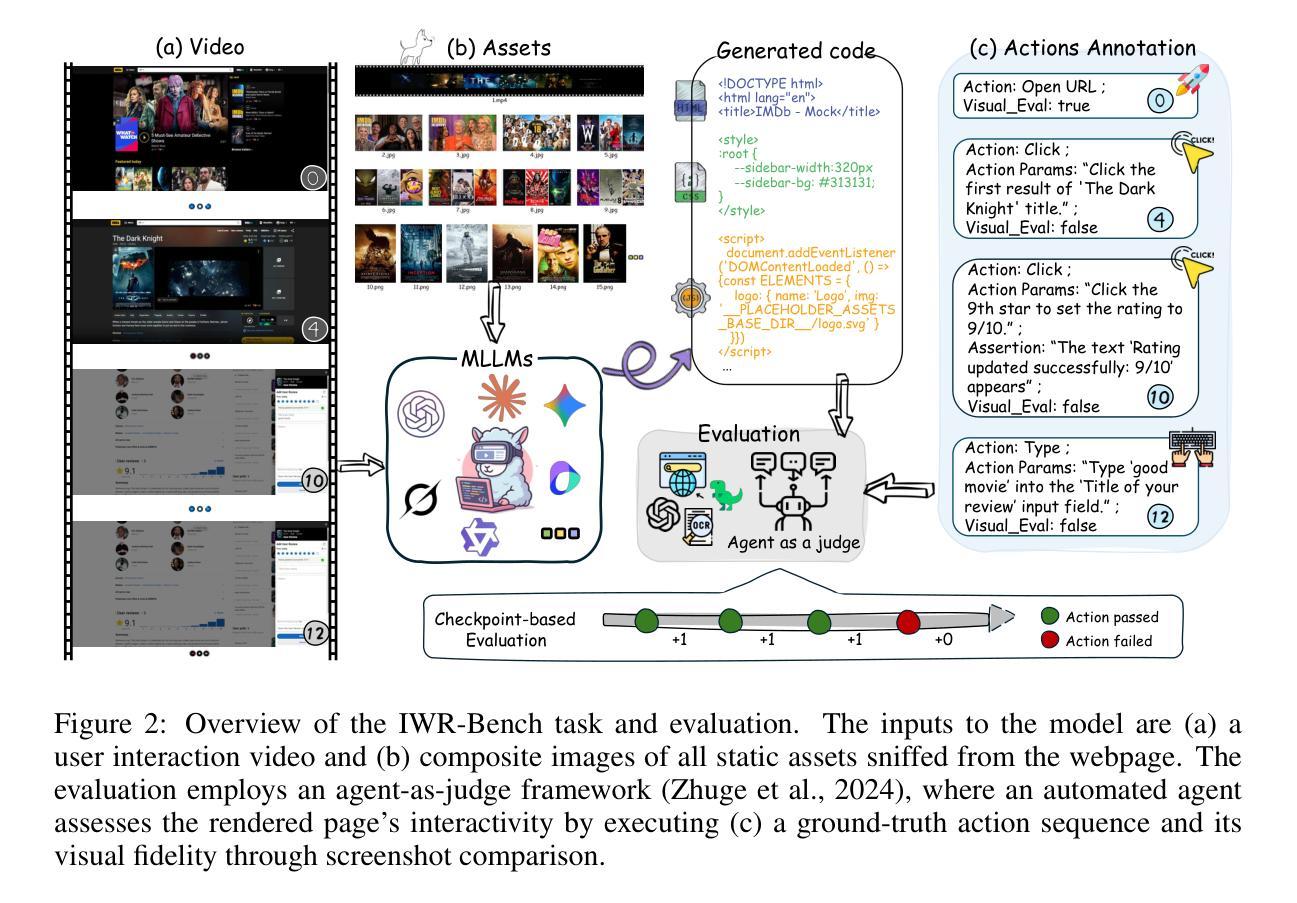
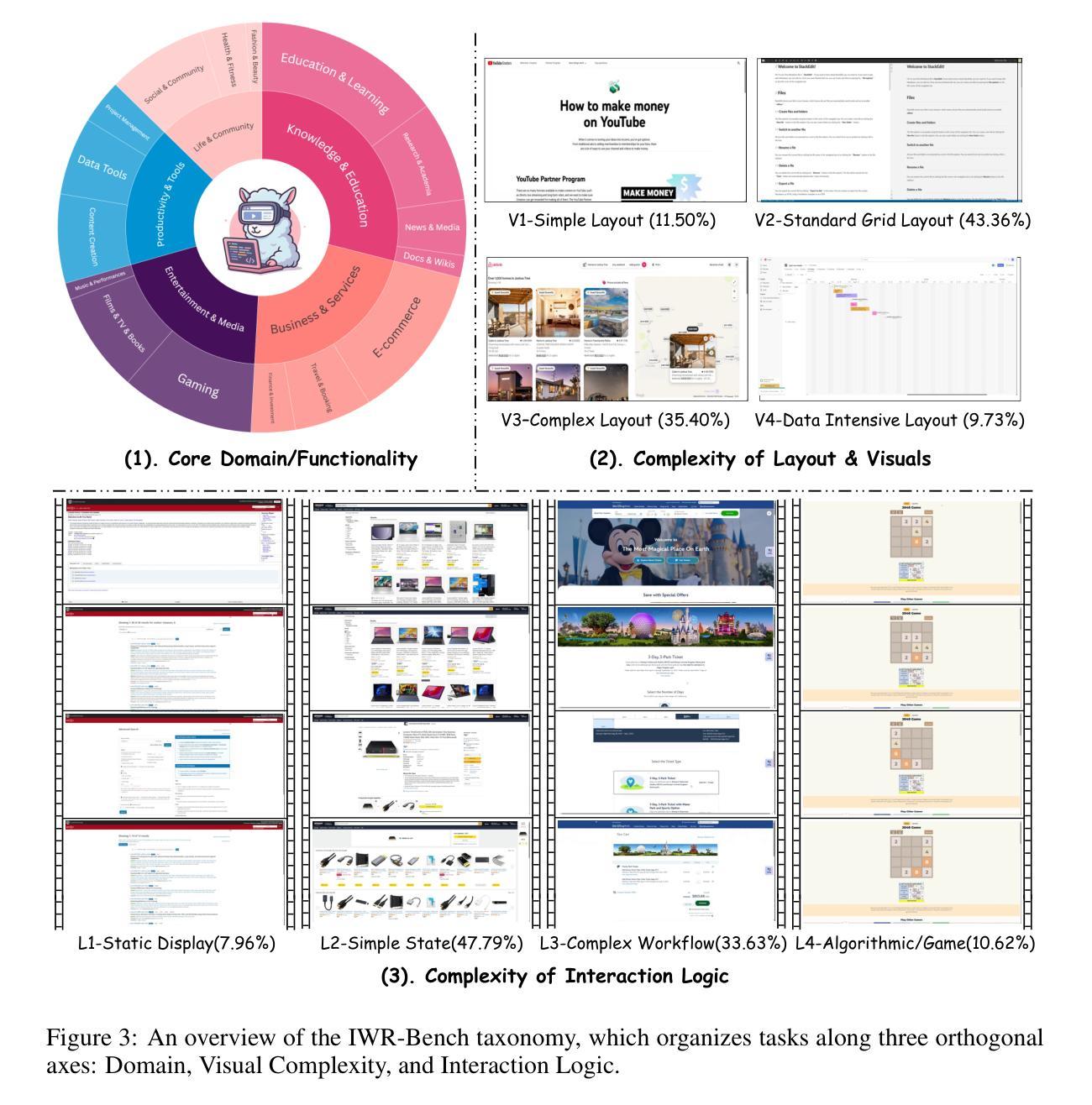
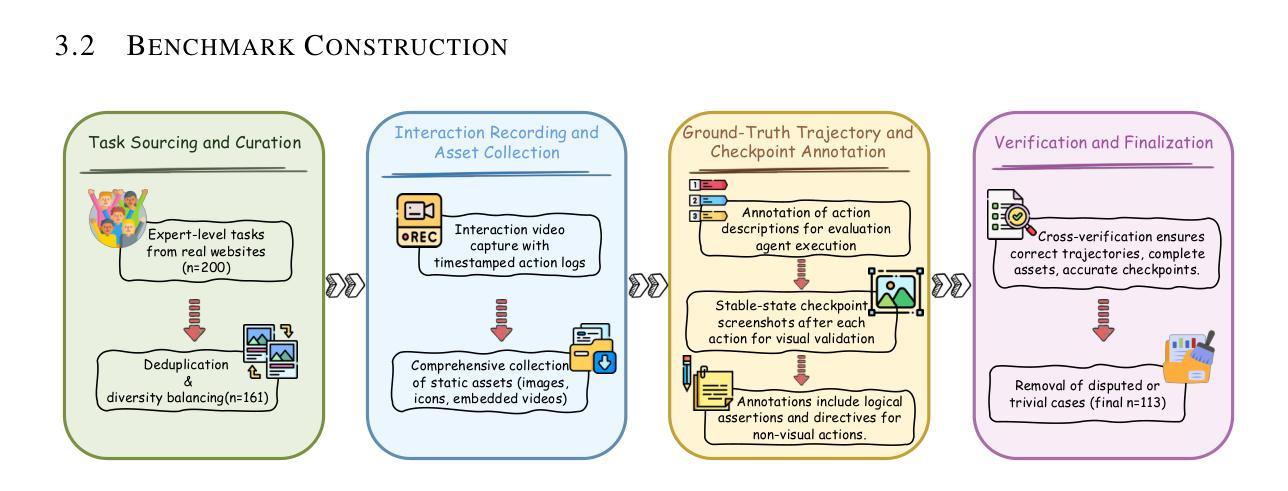
IWR-Bench: Can LVLMs reconstruct interactive webpage from a user interaction video?
Authors:Yang Chen, Minghao Liu, Yufan Shen, Yunwen Li, Tianyuan Huang, Xinyu Fang, Tianyu Zheng, Wenxuan Huang, Cheng Yang, Daocheng Fu, Jianbiao Mei, Rong Wu, Licheng Wen, Xuemeng Yang, Song Mao, Qunshu Lin, Zhi Yu, Yongliang Shen, Yu Qiao, Botian Shi
The webpage-to-code task requires models to understand visual representations of webpages and generate corresponding code. However, existing benchmarks primarily focus on static screenshot-to-code tasks, thereby overlooking the dynamic interactions fundamental to real-world web applications. To address this limitation, this paper introduces IWR-Bench, a novel benchmark for evaluating the capabilities of Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) in interactive webpage reconstruction from video. IWR-Bench comprises 113 meticulously curated tasks from 100 real-world websites, with 1,001 actions and featuring diverse interaction complexities (e.g., web games), visual styles, and domains. Aligning with standard web development practices, each task includes not only user interaction videos but also all crawled static assets (e.g., images, videos). This benchmark evaluates models on two fundamental challenges: comprehensive multi-modal reasoning to infer interaction logic from video and assets, and advanced code generation to translate this logic into functional code. An agent-as-a-judge framework with a comprehensive metric system automatically assesses the functional correctness and visual fidelity of generated webpages. Extensive experiments on 28 LVLMs reveal a significant challenge: the best model achieves an overall score of only 36.35%, as functional correctness (24.39% IFS) lags significantly behind visual fidelity (64.25% VFS). These results highlight critical limitations in current models’ ability to reason about temporal dynamics and synthesize event-driven logic, establishing IWR-Bench as a challenging frontier for vision-language research. The benchmark and evaluation code will be made publicly available. Code is available at https://github.com/L-O-I/IWR-Bench.
网页到代码的任务要求模型理解网页的视觉表示并生成相应的代码。然而,现有的基准测试主要关注静态截图到代码的任务,从而忽略了现实世界网页应用中的基本动态交互。为了解决这一局限性,本文介绍了IWR-Bench,这是一个新的基准测试,用于评估大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)从视频中进行交互式网页重建的能力。IWR-Bench包含113个精心策划的任务,来自100个真实网站,包含1001个动作,并展示多样的交互复杂性(如网页游戏)、视觉风格和领域。与标准的网页开发实践相一致,每个任务不仅包括用户交互视频,还包括所有爬取的静态资产(如图像、视频)。此基准测试评估了模型两个基本挑战:通过视频和资产进行全面的多模式推理以推断交互逻辑,以及将这一逻辑转化为功能代码的先进代码生成。一个以代理作为法官的框架,配合一个综合的度量系统,可以自动评估生成网页的功能正确性和视觉保真度。在28个LVLMs上的大量实验显示了一个重大挑战:最好的模型总体得分只有36.35%,因为功能正确性(24.39% IFS)远远落后于视觉保真度(64.25% VFS)。这些结果突显了当前模型在推理时间动态和合成事件驱动逻辑方面的关键局限性,使IWR-Bench成为视觉语言研究的前沿挑战。基准测试和评估代码将公开提供。代码可在链接中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
网页到代码的转换任务需要模型理解网页的视觉表示并生成相应的代码。然而,现有的基准测试主要关注静态截图到代码的转换,忽略了网页实际交互的重要性。为解决这一问题,本文引入了IWR-Bench,这是一个新的基准测试,旨在评估大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)从视频重建交互式网页的能力。IWR-Bench包含来自真实网站的113个精心策划的任务,涵盖丰富的交互复杂性(如网页游戏)、视觉风格和领域。该基准测试评估模型两个基本挑战的能力:从视频和资产中推断交互逻辑的综合多模态推理,以及将这一逻辑转化为功能代码的先进代码生成能力。通过大量实验发现,现有模型面临巨大挑战,最佳模型总体得分仅为36.35%,功能正确性远远落后于视觉保真度。这表明当前模型在理解时间动态和合成事件驱动逻辑方面存在关键局限。
Key Takeaways
- 现有网页到代码的基准测试主要关注静态截图,忽略了真实网页的交互性。
- IWR-Bench是一个新的基准测试,旨在评估模型从视频重建交互式网页的能力。
- IWR-Bench包含来自真实网站的多样化任务,涵盖复杂的交互、视觉风格和领域。
- 模型需要综合多模态推理来推断交互逻辑,并将逻辑转化为功能代码。
- 当前模型在理解和生成交互式网页方面面临挑战,功能正确性远低于视觉保真度。
- 最佳模型的总体得分仅为36.35%,表明在理解时间动态和合成事件驱动逻辑方面存在局限。
点此查看论文截图
Diffusion Bridge or Flow Matching? A Unifying Framework and Comparative Analysis
Authors:Kaizhen Zhu, Mokai Pan, Zhechuan Yu, Jingya Wang, Jingyi Yu, Ye Shi
Diffusion Bridge and Flow Matching have both demonstrated compelling empirical performance in transformation between arbitrary distributions. However, there remains confusion about which approach is generally preferable, and the substantial discrepancies in their modeling assumptions and practical implementations have hindered a unified theoretical account of their relative merits. We have, for the first time, provided a unified theoretical and experimental validation of these two models. We recast their frameworks through the lens of Stochastic Optimal Control and prove that the cost function of the Diffusion Bridge is lower, guiding the system toward more stable and natural trajectories. Simultaneously, from the perspective of Optimal Transport, interpolation coefficients $t$ and $1-t$ of Flow Matching become increasingly ineffective when the training data size is reduced. To corroborate these theoretical claims, we propose a novel, powerful architecture for Diffusion Bridge built on a latent Transformer, and implement a Flow Matching model with the same structure to enable a fair performance comparison in various experiments. Comprehensive experiments are conducted across Image Inpainting, Super-Resolution, Deblurring, Denoising, Translation, and Style Transfer tasks, systematically varying both the distributional discrepancy (different difficulty) and the training data size. Extensive empirical results align perfectly with our theoretical predictions and allow us to delineate the respective advantages and disadvantages of these two models. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DBFM-3E8E/.
扩散桥和流匹配在任意分布转换中都表现出令人信服的实证性能。然而,关于哪种方法通常更可取仍存在困惑,它们建模假设和实践实施中的巨大差异阻碍了对它们相对优势进行统一的理论解释。我们首次为这两种模型提供了统一的理论和实验验证。我们通过随机最优控制的视角重塑了它们的框架,并证明扩散桥的成本函数较低,引导系统走向更稳定、更自然的轨迹。同时,从最优传输的角度来看,当训练数据规模减少时,流匹配的插值系数t和1-t变得越来越无效。为了证实这些理论主张,我们提出了一种基于潜在变压器的扩散桥新型强大架构,并使用相同结构实现了流匹配模型,以便在各种实验中公平比较性能。在图像修复、超分辨率、去模糊、去噪、翻译和风格转换等任务上进行了全面的实验,系统地改变了分布差异(不同难度)和训练数据规模。广泛的实证结果与我们的理论预测完美吻合,使我们能够详细阐述这两种模型的各自优缺点。我们的代码可在https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DBFM-3E8E/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文对Diffusion Bridge和Flow Matching两种模型进行了统一的理论和实验验证。通过引入随机最优控制,证明了Diffusion Bridge的成本函数较低,使系统轨迹更稳定自然。从最优传输角度看,Flow Matching的插值系数$t$和$1-t$在训练数据量减少时效果减弱。新型Diffusion Bridge架构在图像修复、超分辨率、去模糊、去噪、翻译和风格转换等任务上的实验结果与理论预测一致,凸显了各自的优势和不足。
Key Takeaways
- Diffusion Bridge和Flow Matching在任意分布转换上表现出强大的性能,但两者的建模假设和实际实施存在显著差异。
- 通过引入随机最优控制,证明了Diffusion Bridge的成本函数较低,使系统轨迹更稳定自然。
- 从最优传输角度看,Flow Matching的插值系数在训练数据量减少时效果减弱。
- 新型Diffusion Bridge架构基于潜在Transformer,与Flow Matching模型在同一结构中进行公平的性能比较。
- 全面的实验在多种任务上进行,包括图像修复、超分辨率、去模糊、去噪、翻译和风格转换等。
- 实验结果与理论预测一致,凸显了Diffusion Bridge和Flow Matching各自的优势和不足。
点此查看论文截图

LatXGen: Towards Radiation-Free and Accurate Quantitative Analysis of Sagittal Spinal Alignment Via Cross-Modal Radiographic View Synthesis
Authors:Moxin Zhao, Nan Meng, Jason Pui Yin Cheung, Chris Yuk Kwan Tang, Chenxi Yu, Wenting Zhong, Pengyu Lu, Chang Shi, Yipeng Zhuang, Teng Zhang
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis (AIS) is a complex three-dimensional spinal deformity, and accurate morphological assessment requires evaluating both coronal and sagittal alignment. While previous research has made significant progress in developing radiation-free methods for coronal plane assessment, reliable and accurate evaluation of sagittal alignment without ionizing radiation remains largely underexplored. To address this gap, we propose LatXGen, a novel generative framework that synthesizes realistic lateral spinal radiographs from posterior Red-Green-Blue and Depth (RGBD) images of unclothed backs. This enables accurate, radiation-free estimation of sagittal spinal alignment. LatXGen tackles two core challenges: (1) inferring sagittal spinal morphology changes from a lateral perspective based on posteroanterior surface geometry, and (2) performing cross-modality translation from RGBD input to the radiographic domain. The framework adopts a dual-stage architecture that progressively estimates lateral spinal structure and synthesizes corresponding radiographs. To enhance anatomical consistency, we introduce an attention-based Fast Fourier Convolution (FFC) module for integrating anatomical features from RGBD images and 3D landmarks, and a Spatial Deformation Network (SDN) to model morphological variations in the lateral view. Additionally, we construct the first large-scale paired dataset for this task, comprising 3,264 RGBD and lateral radiograph pairs. Experimental results demonstrate that LatXGen produces anatomically accurate radiographs and outperforms existing GAN-based methods in both visual fidelity and quantitative metrics. This study offers a promising, radiation-free solution for sagittal spine assessment and advances comprehensive AIS evaluation.
青少年特发性脊柱侧弯(AIS)是一种复杂的三维脊柱畸形,准确的形态学评估需要评估冠状面和矢状面的排列。虽然之前的研究在开发无辐射的冠状面评估方法方面取得了重大进展,但无电离辐射的矢状面排列的可靠和准确评估仍然在很大程度上被忽视。为了解决这一空白,我们提出了LatXGen,这是一种新的生成框架,它可以从裸露背部后方的红绿蓝深度(RGBD)图像合成逼真的侧位脊柱X光片,从而实现准确的无辐射矢状面脊柱排列估计。LatXGen解决了两个核心挑战:(1)基于前后表面几何的侧位矢状面形态变化推断;(2)实现从RGBD输入到放射学领域的跨模态转换。该框架采用两阶段架构,逐步估计侧位脊柱结构并合成相应的X光片。为了提高解剖一致性,我们引入了一个基于注意力的快速傅立叶卷积(FFC)模块,用于整合RGBD图像和3D地标的解剖特征,以及一个空间变形网络(SDN)来模拟侧视图中的形态变化。此外,我们为此任务构建了第一个大规模配对数据集,包含3264个RGBD和侧位X光片对。实验结果表明,LatXGen产生的X光图像解剖准确,且在视觉保真度和定量指标上均优于现有的基于GAN的方法。这项研究为矢状面评估提供了有前景的无辐射解决方案,并推动了全面的AIS评估的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures
Summary
青少年特发性脊柱侧弯(AIS)是一种复杂的三维脊柱畸形,准确的形态学评估需要评估冠状面和矢状面的对齐情况。针对矢状面对齐的无辐射评估方法尚待探索,本研究提出LatXGen,一种能从后部红绿蓝深度(RGBD)图像合成逼真的侧位脊柱放射图像的新颖生成框架,从而实现准确、无辐射的矢状位脊柱对齐评估。LatXGen解决了两个核心挑战:一是基于前后表面几何的侧位脊柱形态变化的推断,二是从RGBD输入到放射领域的跨模态转换。该框架采用分阶段架构,逐步估计侧位脊柱结构并合成相应的放射图像。通过引入基于注意力的快速傅立叶卷积(FFC)模块和空间变形网络(SDN),提高了解剖一致性和形态变化的建模能力。此外,本研究构建了首个大规模配对数据集,包含3264个RGBD和侧位放射图像对。实验结果表明,LatXGen生成的解剖图像准确度高,在视觉保真度和定量指标上均优于现有的基于GAN的方法。本研究为矢状面脊柱评估和全面的AIS评估提供了有前景的无辐射解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 青少年特发性脊柱侧弯(AIS)需要同时评估冠状面和矢状面的对齐情况。
- 矢状面对齐的无辐射评估方法尚待探索。
- LatXGen是一种生成框架,能从RGBD图像合成侧位脊柱放射图像。
- LatXGen解决了侧位脊柱形态变化的推断和跨模态转换两个核心挑战。
- 该框架采用分阶段架构,并引入FFC模块和SDN提高解剖一致性和形态变化建模。
- 构建了首个大规模配对数据集用于此任务。
点此查看论文截图

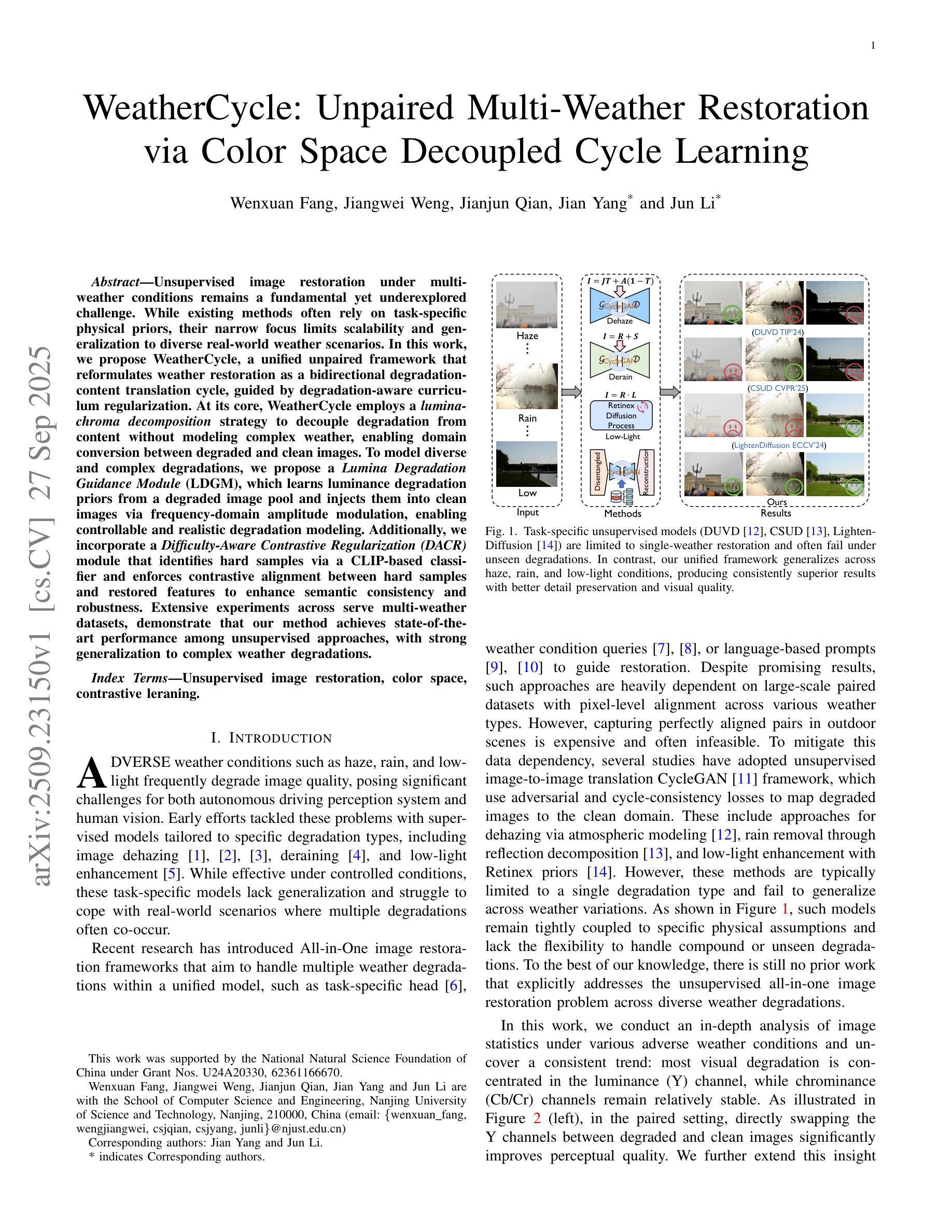
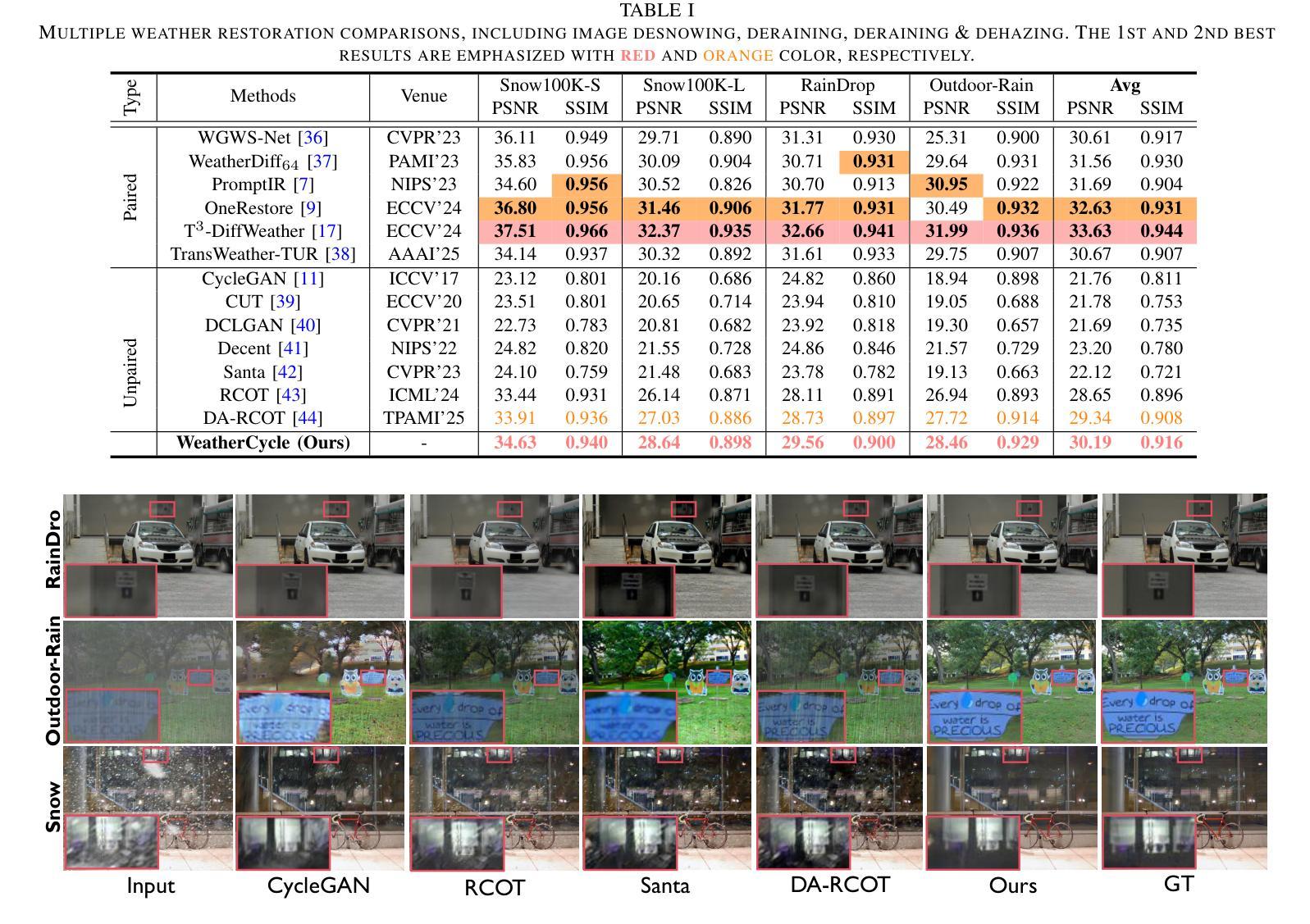
WeatherCycle: Unpaired Multi-Weather Restoration via Color Space Decoupled Cycle Learning
Authors:Wenxuan Fang, Jiangwei Weng, Jianjun Qian, Jian Yang, Jun Li
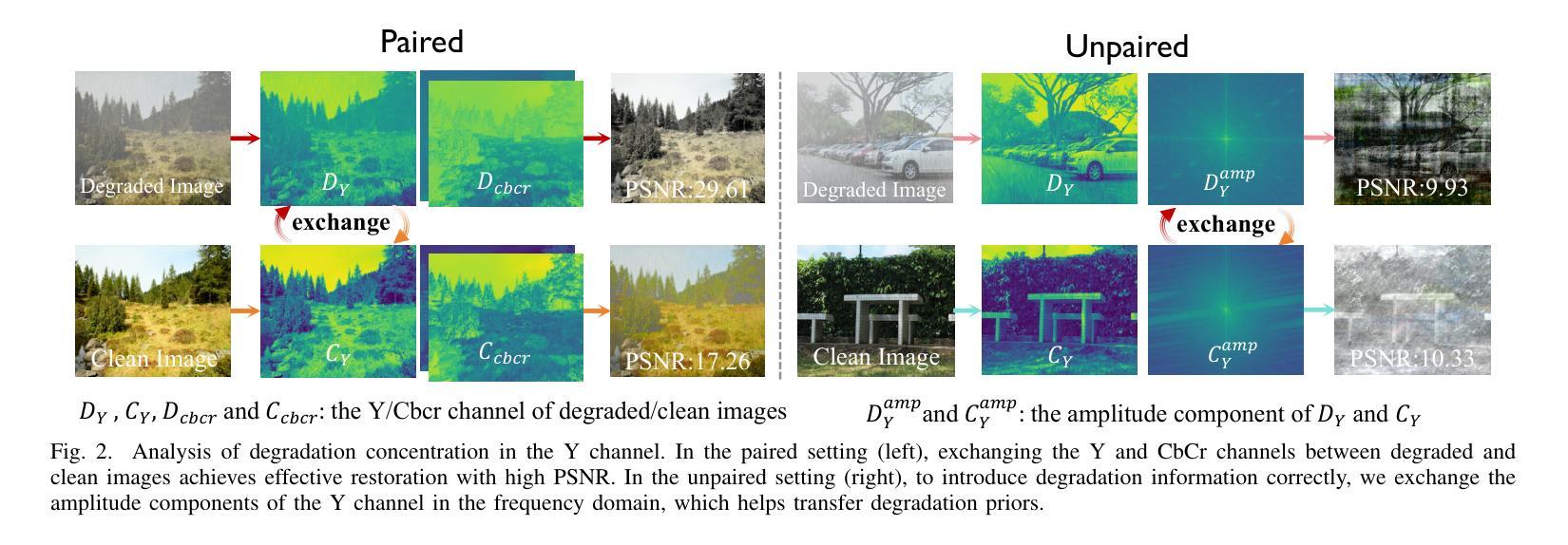
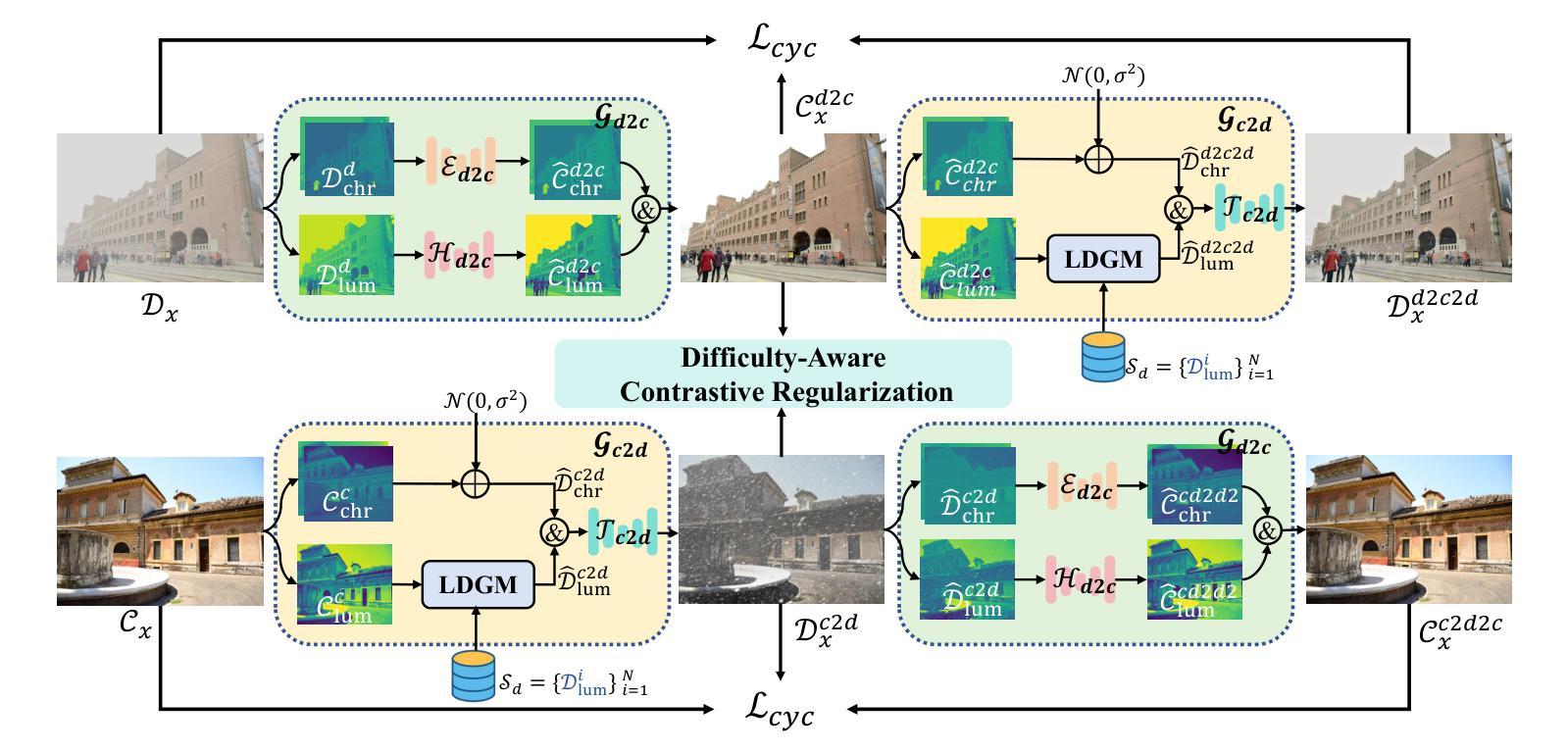
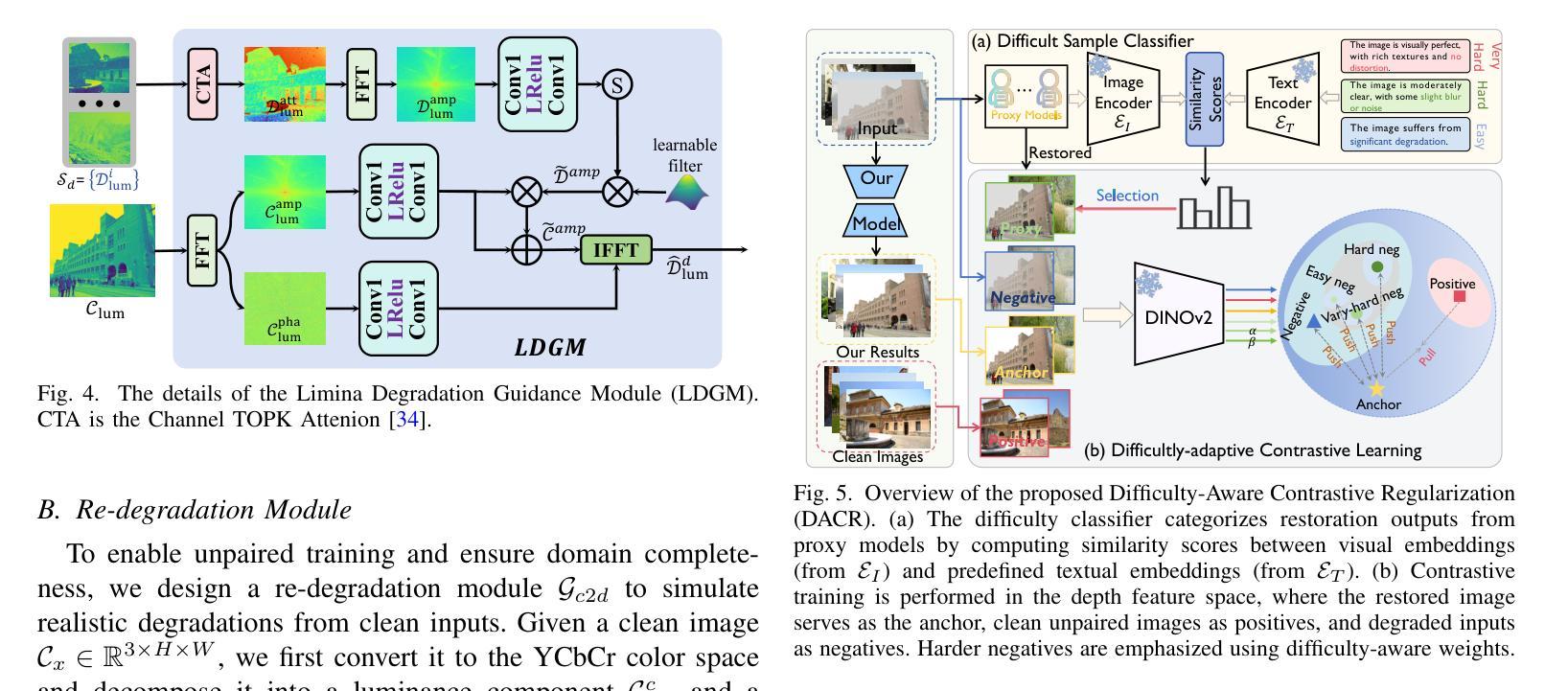
Unsupervised image restoration under multi-weather conditions remains a fundamental yet underexplored challenge. While existing methods often rely on task-specific physical priors, their narrow focus limits scalability and generalization to diverse real-world weather scenarios. In this work, we propose \textbf{WeatherCycle}, a unified unpaired framework that reformulates weather restoration as a bidirectional degradation-content translation cycle, guided by degradation-aware curriculum regularization. At its core, WeatherCycle employs a \textit{lumina-chroma decomposition} strategy to decouple degradation from content without modeling complex weather, enabling domain conversion between degraded and clean images. To model diverse and complex degradations, we propose a \textit{Lumina Degradation Guidance Module} (LDGM), which learns luminance degradation priors from a degraded image pool and injects them into clean images via frequency-domain amplitude modulation, enabling controllable and realistic degradation modeling. Additionally, we incorporate a \textit{Difficulty-Aware Contrastive Regularization (DACR)} module that identifies hard samples via a CLIP-based classifier and enforces contrastive alignment between hard samples and restored features to enhance semantic consistency and robustness. Extensive experiments across serve multi-weather datasets, demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance among unsupervised approaches, with strong generalization to complex weather degradations.
在多天气条件下的无监督图像修复仍然是一个基础但尚未被充分探索的挑战。尽管现有方法经常依赖于特定任务的物理先验知识,但它们狭窄的焦点限制了其在多种现实世界天气场景中的可扩展性和泛化能力。在这项工作中,我们提出了WeatherCycle,这是一个统一的非配对框架,它将天气修复重新制定为一个双向的退化内容翻译周期,由退化感知课程正则化指导。WeatherCycle的核心采用了一种亮度-色度分解策略,能够在不建立复杂天气模型的情况下将退化与内容进行分离,从而实现退化图像和干净图像之间的域转换。为了模拟多样化和复杂的退化,我们提出了一个亮度退化指导模块(LDGM),该模块从退化图像池中学习亮度退化先验知识,并通过频率域振幅调制将其注入干净图像,从而实现可控且逼真的退化建模。此外,我们融入了一个难度感知对比正则化(DACR)模块,该模块通过基于CLIP的分类器识别硬样本,并在硬样本和恢复的特征之间强制执行对比对齐,以增强语义一致性和稳健性。在多天气数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在无监督方法中达到了最新性能,对复杂天气退化具有很强的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
天气多变条件下的无监督图像修复是一个基础但尚未被充分研究的问题。现有方法通常依赖于特定任务的物理先验,但其局限性在于难以扩展到多种真实世界天气场景。本研究提出一种统一的非配对框架——WeatherCycle,它将天气修复重新定义为双向的退化-内容翻译循环,受退化感知课程正则化的引导。WeatherCycle采用亮度-色度分解策略,无需建模复杂天气即可实现退化与内容的解耦,实现退化图像与干净图像之间的域转换。为模拟多样化和复杂的退化,我们提出了亮度退化引导模块(LDGM),从退化图像池中学习亮度退化先验,并通过频率域振幅调制将其注入干净图像,从而实现可控且真实的退化建模。此外,还引入了难度感知对比正则化(DACR)模块,通过CLIP分类器识别困难样本,并在困难样本与恢复特征之间执行对比对齐,以增强语义一致性和稳健性。跨多天气数据集的广泛实验表明,该方法在无监督方法中达到最佳性能,对复杂天气退化具有较强的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究解决了多天气条件下的无监督图像修复问题,这是一个尚未被充分探索的基础挑战。
- 提出了统一的非配对框架——WeatherCycle,将天气修复重新定义为双向的退化-内容翻译循环。
- 采用亮度-色度分解策略,实现退化与内容的解耦,使得在不需要建模复杂天气的情况下进行域转换。
- 提出亮度退化引导模块(LDGM),能够从退化图像池中学习亮度退化先验,实现可控且真实的退化建模。
- 引入难度感知对比正则化(DACR)模块,增强语义一致性和模型稳健性。
- 跨多天气数据集的实验表明,该方法在无监督方法中表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图
ML2B: Multi-Lingual ML Benchmark For AutoML
Authors:Ekaterina Trofimova, Zosia Shamina, Maria Selifanova, Artem Zaitsev, Remi Savchuk, Maxim Minets, Daria Ozerova, Emil Sataev, Denis Zuenko, Andrey E. Ustyuzhanin
Large language models (LLMs) have recently demonstrated strong capabilities in generating machine learning (ML) code, enabling end-to-end pipeline construction from natural language instructions. However, existing benchmarks for ML code generation are mainly restricted to English, overlooking the global and multilingual nature of ML research and practice. To address this gap, we present ML2B, the first benchmark for evaluating multilingual ML code generation. ML2B consists of 30 Kaggle competitions translated into 13 natural languages, covering tabular, text, and image data types, with structured metadata and validated human-reviewed translations. For evaluation, we employ AIDE, an automated framework for end-to-end assessment of data science pipelines, and provide insights into cross-lingual model performance. Our results reveal substantial 15-45% performance degradation on non-English tasks, highlighting critical challenges in multilingual representation learning for code generation. The benchmark, evaluation framework, and comprehensive results are made available through our GitHub repository to facilitate future research in multilingual ML code generation: https://github.com/enaix/ml2b.
大型语言模型(LLM)最近展现出强大的生成机器学习(ML)代码的能力,能够通过自然语言指令实现端到端的管道构建。然而,现有的ML代码生成基准测试主要局限于英语,忽略了ML研究和实践的全球和多语言性质。为了弥补这一空白,我们推出了ML2B,这是首个用于评估多语言ML代码生成的基准测试。ML2B由30个Kaggle竞赛的题目组成,这些题目被翻译为13种自然语言,涵盖了表格、文本和图像数据类型,具备结构化元数据和经过验证的人工审查翻译。为了进行评估,我们采用了AIDE,这是一个用于数据科学管道端到端评估的自动化框架,并提供了关于跨语言模型性能的见解。我们的结果表明,在非英语任务上的性能降低了15-45%,这突显了代码生成中多语言表示学习的关键挑战。基准测试、评估框架和全面结果已通过我们的GitHub仓库公开,以促进未来在多语言ML代码生成方面的研究:https://github.com/enaix/ml2b。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在生成机器学习代码方面展现出强大能力,能够实现从自然语言指令到端到端管道构建的全程自动化。然而,现有机器学习代码生成基准测试主要局限于英语,忽略了机器学习研究和实践的全球和多语言特性。为解决这一差距,我们推出了ML2B,首个多语言机器学习代码生成评估基准。ML2B包含翻译为13种自然语言的30个Kaggle竞赛,涵盖表格、文本和图像数据类型,具备结构化元数据和经过验证的人工审查翻译。我们使用AIDE对数据安全管道进行端到端评估的自动化框架进行评估,并深入洞察跨语言模型性能。结果显示,在非英语任务上性能下降15-45%,突显出代码生成中多语言表示学习的关键挑战。基准测试、评估框架和全面结果已发布至GitHub仓库,以便未来研究多语言机器学习代码生成。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型具备强大的机器学习代码生成能力,实现从自然语言指令到端到端管道构建的自动化。
- 现有机器学习代码生成基准测试主要局限于英语,忽略了多语言特性。
- ML2B是首个多语言机器学习代码生成评估基准,包含30个Kaggle竞赛,翻译为13种自然语言。
- ML2B涵盖表格、文本和图像数据类型,具备结构化元数据和经过验证的人工审查翻译。
- 采用AIDE进行数据安全管道的端到端评估,深入了解跨语言模型性能。
- 在非英语任务上,模型性能下降15-45%,突显出多语言表示学习的关键挑战。
- 基准测试、评估框架和结果已发布至GitHub仓库,以促进多语言机器学习代码生成的研究。
点此查看论文截图

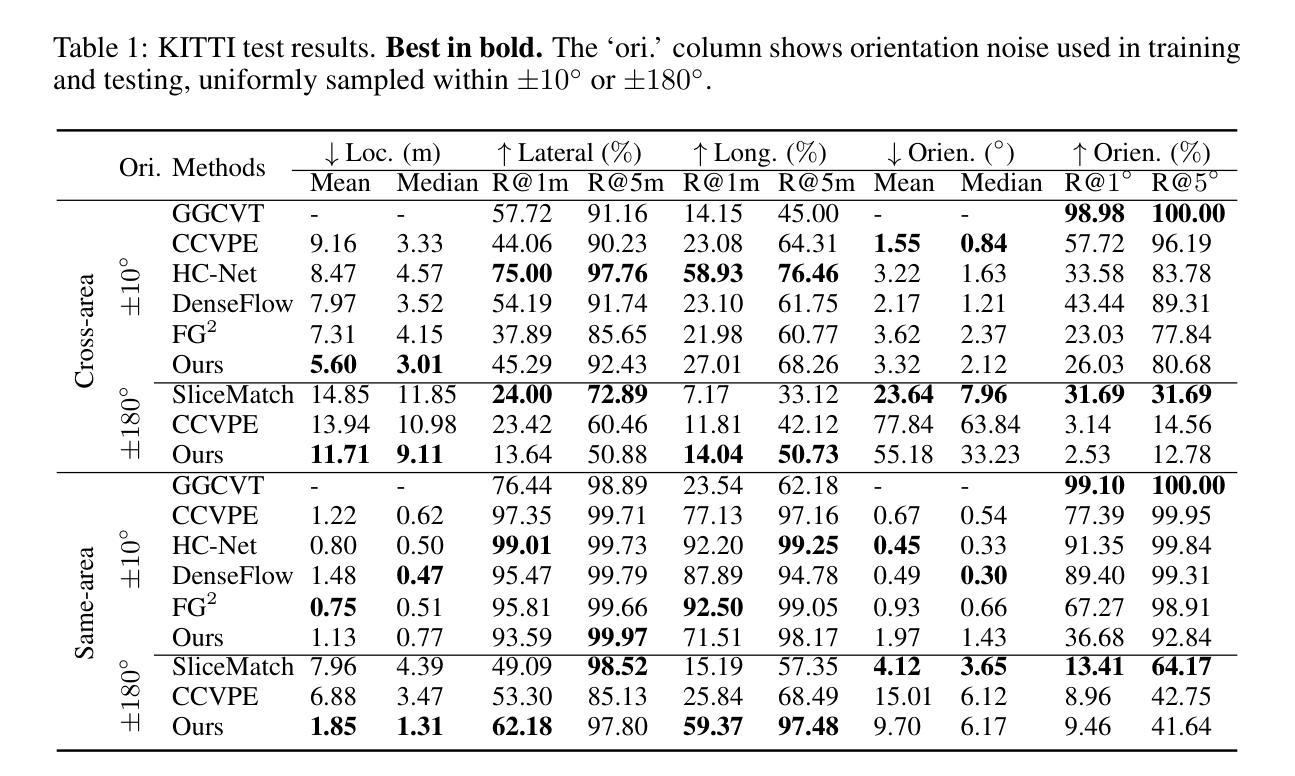
Loc$^2$: Interpretable Cross-View Localization via Depth-Lifted Local Feature Matching
Authors:Zimin Xia, Chenghao Xu, Alexandre Alahi
We propose an accurate and interpretable fine-grained cross-view localization method that estimates the 3 Degrees of Freedom (DoF) pose of a ground-level image by matching its local features with a reference aerial image. Unlike prior approaches that rely on global descriptors or bird’s-eye-view (BEV) transformations, our method directly learns ground-aerial image-plane correspondences using weak supervision from camera poses. The matched ground points are lifted into BEV space with monocular depth predictions, and scale-aware Procrustes alignment is then applied to estimate camera rotation, translation, and optionally the scale between relative depth and the aerial metric space. This formulation is lightweight, end-to-end trainable, and requires no pixel-level annotations. Experiments show state-of-the-art accuracy in challenging scenarios such as cross-area testing and unknown orientation. Furthermore, our method offers strong interpretability: correspondence quality directly reflects localization accuracy and enables outlier rejection via RANSAC, while overlaying the re-scaled ground layout on the aerial image provides an intuitive visual cue of localization accuracy.
我们提出了一种准确且可解释性的细粒度跨视图定位方法。该方法通过匹配地面图像的局部特征与参考的航空图像,来估计地面图像的3自由度(DoF)姿态。不同于依赖全局描述符或鸟瞰图转换的先前方法,我们的方法直接使用来自相机姿态的弱监督来学习地面-航空图像平面的对应关系。匹配的地面点通过单目深度预测提升到鸟瞰图空间,然后应用规模感知Procrustes对齐来估计相机旋转、平移以及可选的相对深度与航空度量空间之间的比例。这种公式轻巧、端对端可训练,并且无需像素级的注释。实验表明,在跨区域测试和未知方向等具有挑战性的场景中,其准确性处于最新技术的前沿。此外,我们的方法具有很强的可解释性:对应质量直接反映定位精度,并通过RANSAC实现了异常值剔除,同时把重新调整比例的地面布局覆盖在航空图像上提供了直观的定位精度视觉提示。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种准确且可解释的细粒度跨视图定位方法,通过匹配地面图像与参考航拍图像的局部特征来估计地面图像的3自由度姿态。该方法通过弱监督学习直接学习地面与航拍图像平面之间的对应关系,无需全局描述符或鸟瞰变换。通过单目测距预测将匹配的地面点提升到鸟瞰空间,并应用规模感知的Procrustes对齐来估计相机旋转、平移以及可选的相对深度与航拍度量空间之间的比例。该方法具有轻量级、端到端可训练的特点,无需像素级注释。实验表明,在跨区域测试和未知方向等挑战场景下具有最先进的准确性。此外,该方法具有很强的可解释性,对应质量直接反映定位精度,可通过RANSAC拒绝异常值,通过在航拍图像上叠加重新缩放的地面布局提供直观的定位精度视觉线索。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新颖的跨视图定位方法,通过匹配地面与航拍图像的局部特征进行姿态估计。
- 采用弱监督学习直接学习图像平面间的对应关系。
- 通过单目测距预测将地面点提升到鸟瞰空间,应用Procrustes对齐进行相机姿态估计。
- 方法具有轻量级、端到端可训练的特点,无需像素级注释。
- 在挑战场景下具有最先进的准确性,如跨区域测试和未知方向。
- 对应质量直接反映定位精度,可通过RANSAC拒绝异常值。
点此查看论文截图