⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-01 更新
The Dialogue That Heals: A Comprehensive Evaluation of Doctor Agents’ Inquiry Capability
Authors:Linlu Gong, Ante Wang, Yunghwei Lai, Weizhi Ma, Yang Liu
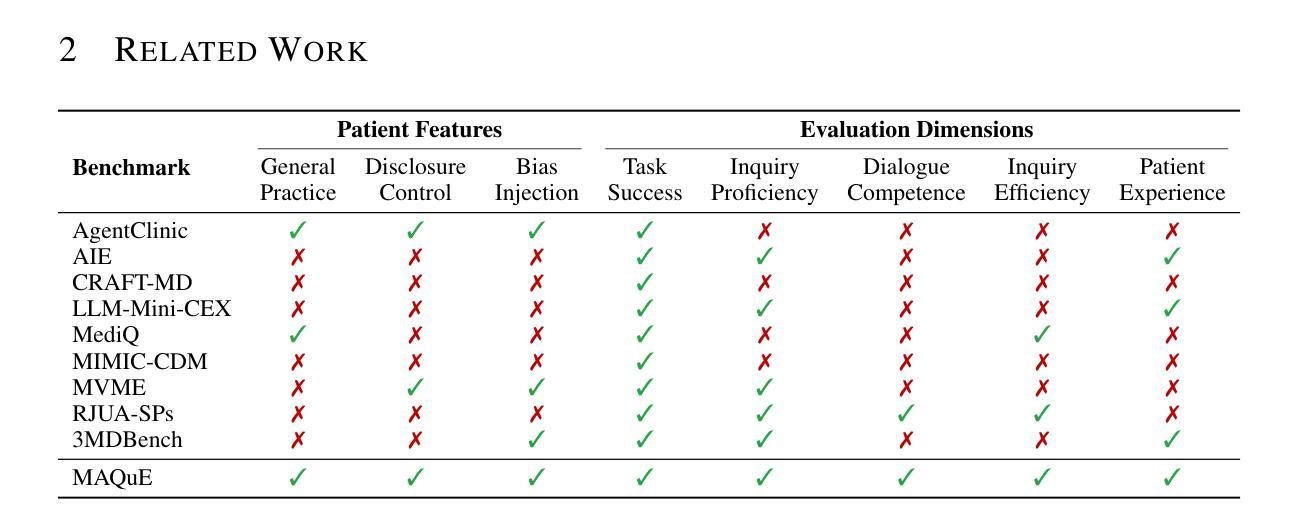
An effective physician should possess a combination of empathy, expertise, patience, and clear communication when treating a patient. Recent advances have successfully endowed AI doctors with expert diagnostic skills, particularly the ability to actively seek information through inquiry. However, other essential qualities of a good doctor remain overlooked. To bridge this gap, we present MAQuE(Medical Agent Questioning Evaluation), the largest-ever benchmark for the automatic and comprehensive evaluation of medical multi-turn questioning. It features 3,000 realistically simulated patient agents that exhibit diverse linguistic patterns, cognitive limitations, emotional responses, and tendencies for passive disclosure. We also introduce a multi-faceted evaluation framework, covering task success, inquiry proficiency, dialogue competence, inquiry efficiency, and patient experience. Experiments on different LLMs reveal substantial challenges across the evaluation aspects. Even state-of-the-art models show significant room for improvement in their inquiry capabilities. These models are highly sensitive to variations in realistic patient behavior, which considerably impacts diagnostic accuracy. Furthermore, our fine-grained metrics expose trade-offs between different evaluation perspectives, highlighting the challenge of balancing performance and practicality in real-world clinical settings.
一个优秀的医生在治疗病人时,应具备同情心、专业知识、耐心和清晰的沟通能力。最近的进步已经成功赋予AI医生专业的诊断技能,尤其是通过询问主动获取信息的能力。然而,其他作为好医生的基本素质仍然被忽视。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了MAQuE(医疗代理问答评估),这是迄今为止最大的医疗多轮问答自动综合评估基准。它拥有3000个模拟的真实患者代理,展现了多样化的语言模式、认知局限、情绪反应和被动披露的倾向。我们还引入了一个多方面的评估框架,涵盖任务成功、询问能力、对话能力、询问效率和患者体验。在不同的大型语言模型上的实验揭示了评估方面的巨大挑战。即使是最先进的模型也显示出其在查询能力方面还有很大的提升空间。这些模型对现实患者行为的变化高度敏感,这会显著影响诊断的准确性。此外,我们的精细指标暴露了不同评估角度之间的权衡,强调了在实际临床环境中平衡性能和实用性的挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
AI医生虽具备专家诊断技能,但仍需具备同情心、专业知识、耐心和清晰沟通等品质。为评估医生的多轮询问能力,提出MAQuE基准测试,模拟真实患者代理,并引入多方面评估框架。实验显示大型语言模型面临挑战,在真实患者行为面前存在显著不足。
Key Takeaways
- AI医生需要更多关注除诊断技能外的医生品质,如同情心、专业知识和沟通。
- MAQuE是首个用于评估医生多轮询问能力的基准测试。
- MAQuE模拟真实患者代理,展示多样的语言模式、认知限制和情感反应。
- 评估框架涵盖任务成功、询问能力、对话能力、询问效率和患者体验。
- 实验显示大型语言模型面临挑战,在真实情境下存在显著不足。
- 最先进的模型在询问能力方面仍有很大提升空间。
点此查看论文截图

DiaCDM: Cognitive Diagnosis in Teacher-Student Dialogues using the Initiation-Response-Evaluation Framework
Authors:Rui Jia, Yuang Wei, Ruijia Li, Yuang-Hao Jiang, Xinyu Xie, Yaomin Shen, Min Zhang, Bo Jiang
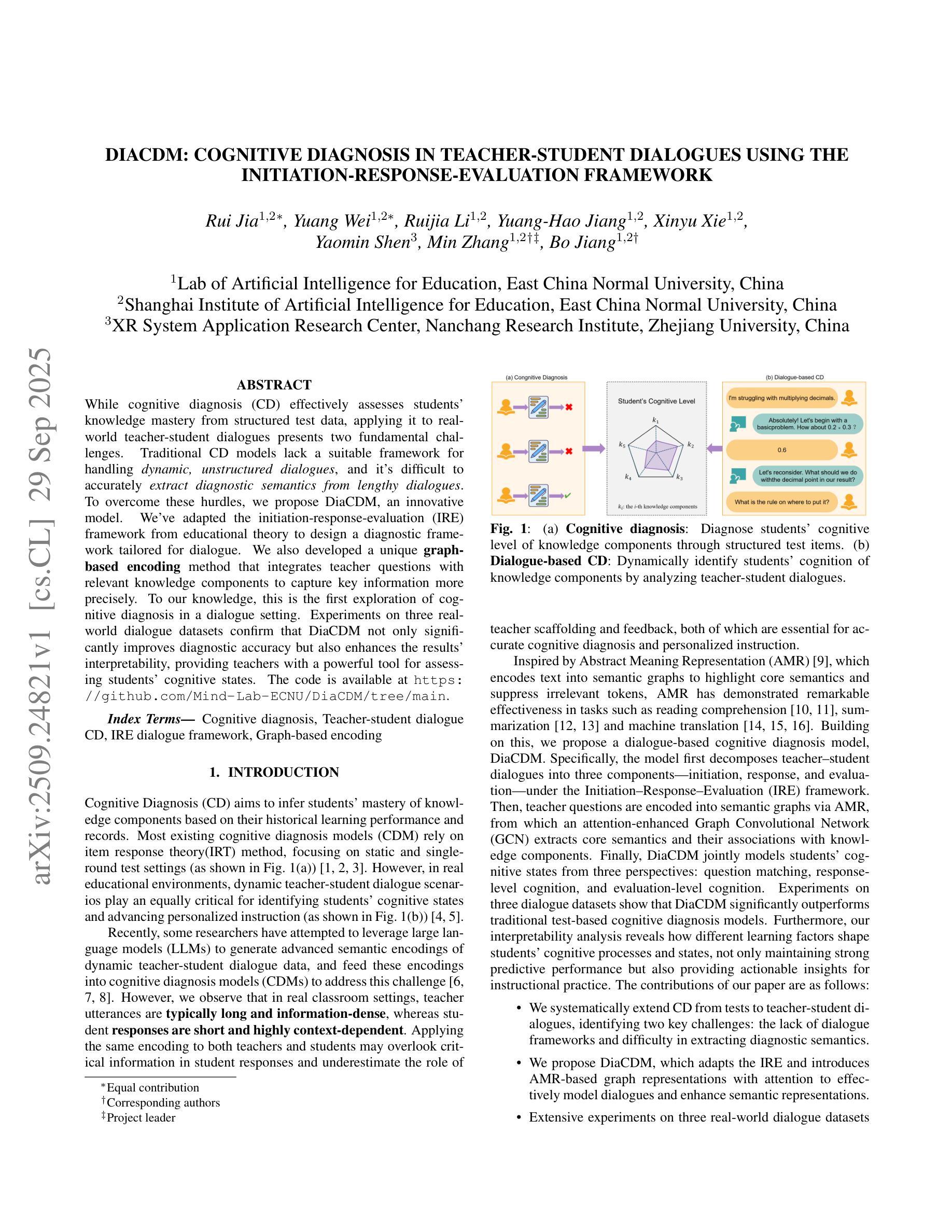
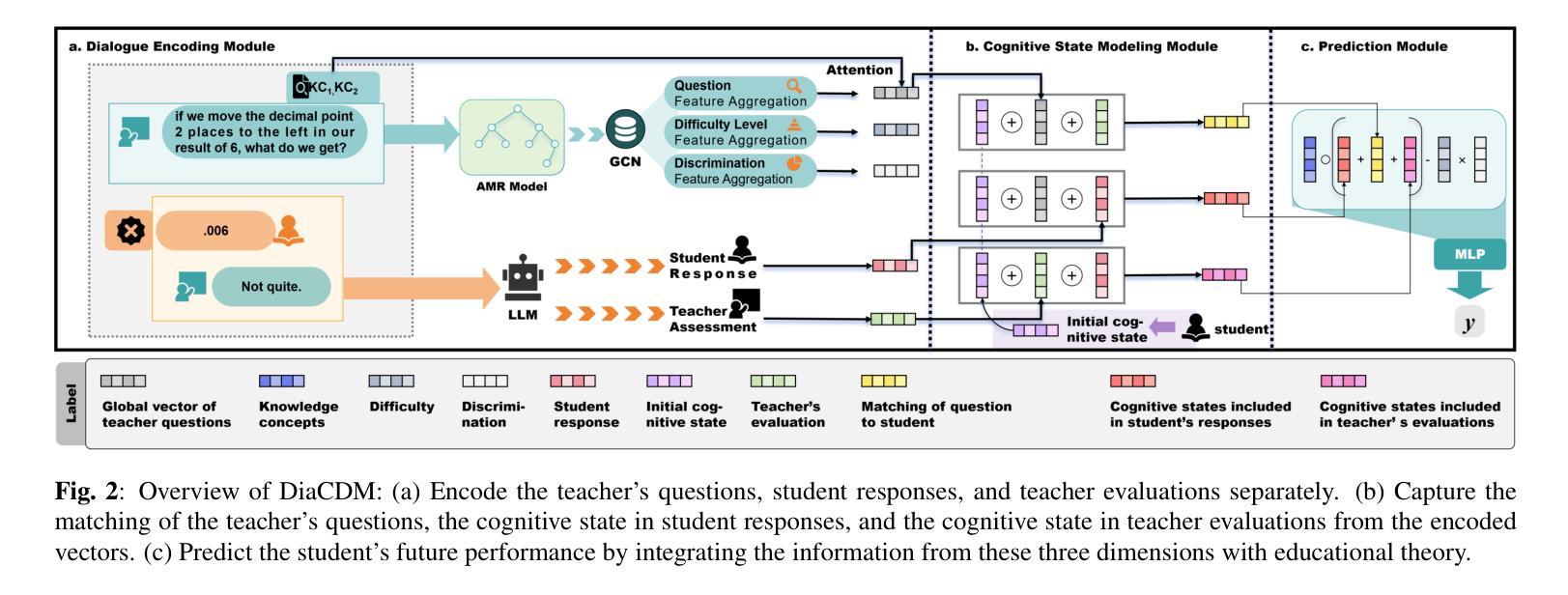
While cognitive diagnosis (CD) effectively assesses students’ knowledge mastery from structured test data, applying it to real-world teacher-student dialogues presents two fundamental challenges. Traditional CD models lack a suitable framework for handling dynamic, unstructured dialogues, and it’s difficult to accurately extract diagnostic semantics from lengthy dialogues. To overcome these hurdles, we propose DiaCDM, an innovative model. We’ve adapted the initiation-response-evaluation (IRE) framework from educational theory to design a diagnostic framework tailored for dialogue. We also developed a unique graph-based encoding method that integrates teacher questions with relevant knowledge components to capture key information more precisely. To our knowledge, this is the first exploration of cognitive diagnosis in a dialogue setting. Experiments on three real-world dialogue datasets confirm that DiaCDM not only significantly improves diagnostic accuracy but also enhances the results’ interpretability, providing teachers with a powerful tool for assessing students’ cognitive states. The code is available at https://github.com/Mind-Lab-ECNU/DiaCDM/tree/main.
认知诊断(CD)在评估结构化测试数据中的学生知识掌握方面非常有效,但将其应用于现实世界的师生互动对话中却存在两个基本挑战。传统的CD模型缺乏处理动态、非结构化对话的适当框架,而且很难从冗长的对话中准确提取诊断语义。为了克服这些障碍,我们提出了一种创新的模型DiaCDM。我们对教育理论中启动-响应-评估(IRE)框架进行了改编,设计了一个适合对话的认知诊断框架。我们还开发了一种独特的基于图的编码方法,将教师的问题与相关的知识成分结合起来,以更精确地捕获关键信息。据我们所知,这是对话环境中认知诊断的首次探索。在三个真实对话数据集上的实验证实,DiaCDM不仅显著提高了诊断的准确性,还提高了结果的解释性,为教师评估学生的认知状态提供了有力的工具。代码可在https://github.com/Mind-Lab-ECNU/DiaCDM/tree/main找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了认知诊断(CD)在真实世界中的教师学生对话中的挑战及解决方案。传统CD模型难以处理动态、非结构化的对话,难以从冗长的对话中提取诊断语义。为此,提出了DiaCDM模型,采用教育理论的IRE框架设计对话诊断框架,并开发了基于图的编码方法,整合教师问题与相关知识组件,提高诊断准确性和结果解释性。
Key Takeaways
- 认知诊断(CD)在真实世界教师学生对话中的应用面临两大挑战:处理动态、非结构化对话和从冗长对话中提取诊断语义。
- DiaCDM模型解决了这些问题,它结合了教育理论的IRE框架来设计针对对话的诊断框架。
- DiaCDM采用独特的基于图的编码方法,整合教师问题与相关知识组件。
- 该方法不仅提高了诊断的准确性,还增强了结果的可解释性。
- 这是首个探索认知诊断在对话环境下的研究。
- 通过在三个真实世界对话数据集上的实验,证明了DiaCDM模型的有效性。
点此查看论文截图
Model Fusion with Multi-LoRA Inference for Tool-Enhanced Game Dialogue Agents
Authors:Kangxu Wang, Ze Chen, Chengcheng Wei, Jiewen Zheng, Jiarong He, Max Gao
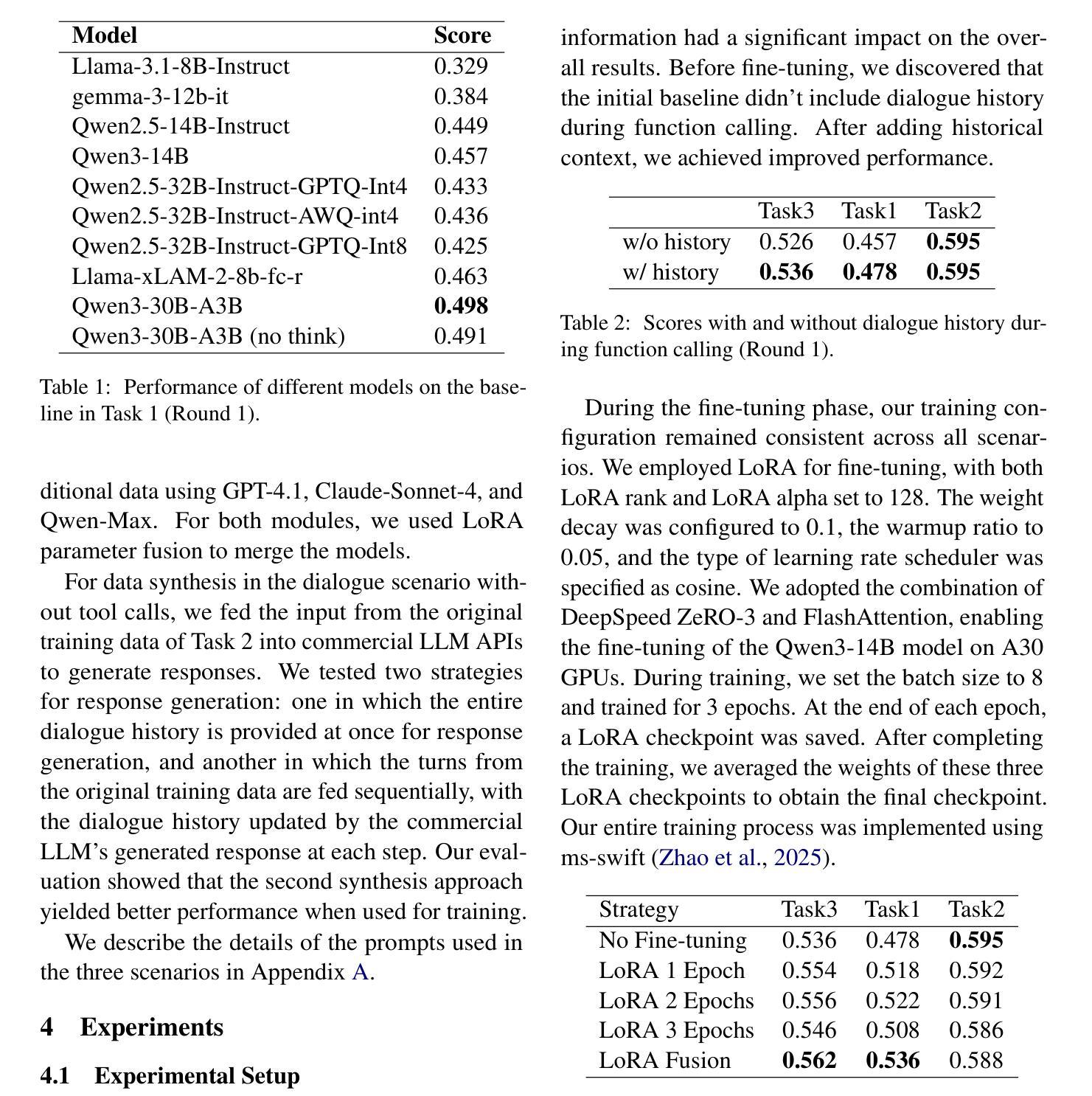
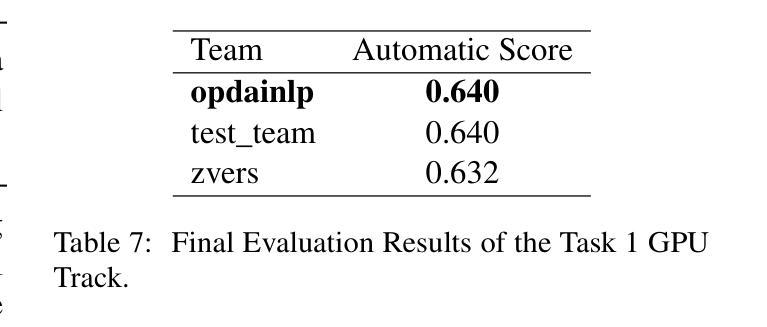
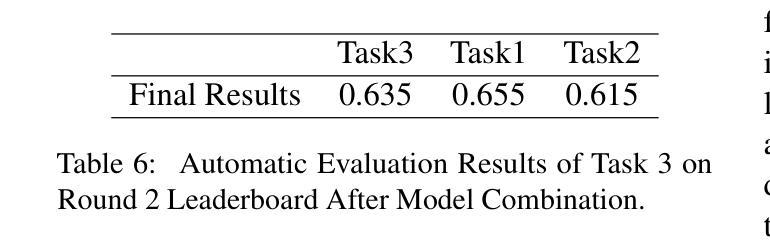
This paper presents the opdainlp team’s solution for the GPU track of the CPDC 2025 challenge. The challenge consists of three tasks, aiming to build an in-game conversational AI that adheres to character personas, aligns with the game’s worldview, and supports function calling. Considering both effectiveness and resource/time constraints during inference, we synthesized data for some of the tasks based on the datasets provided by the competition organizers. We employed Qwen3-14B with LoRA fine-tuning and model fusion, and utilized a base model integrated with multiple LoRA adapters during inference. Specifically, in the competition, we used three distinct LoRA adapters to handle tool calling, response generation with tool call results, and response generation without tool call results, respectively. MultiLoRA inference was implemented using vLLM. Our solution achieved the first place in Task 1 and Task 3, and the second place in Task 2 of the GPU track.
本文介绍了opdainlp团队在CPDC 2025挑战赛GPU赛道上的解决方案。该挑战包含三个任务,旨在构建一款符合角色个性的游戏内对话AI,与游戏世界观保持一致,并支持函数调用。考虑到推理过程中的有效性和资源/时间限制,我们根据竞赛组织者提供的数据集对一些任务进行了数据合成。我们采用了带有LoRA微调技术和模型融合的Qwen3-14B模型,并在推理过程中使用一个集成了多个LoRA适配器的基础模型。具体来说,在比赛中,我们使用了三个不同的LoRA适配器来处理工具调用、带有工具调用结果的响应生成以及没有工具调用结果的响应生成。MultiLoRA推理使用vLLM实现。我们的解决方案在GPU赛道的第一项和第三项任务中获得了第一名,第二项任务获得了第二名。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages
Summary
本文介绍了opdainlp团队在CPDC 2025挑战中的GPU轨道解决方案。挑战包含三个任务,旨在构建符合角色性格、与游戏世界观相符并支持函数调用功能的游戏内对话AI。团队结合了比赛组织者提供的数据集进行部分任务的数据合成,采用Qwen3-14B模型进行LoRA微调与模型融合,并在推理过程中使用集成基础模型与多个LoRA适配器的方案。具体在比赛中,我们使用了三个不同的LoRA适配器来处理工具调用、带有工具调用结果的响应生成以及没有工具调用结果的响应生成。最终,我们的解决方案在Task 1和Task 3中获得第一名,在Task 2中获得第二名。
Key Takeaways
- opdainlp团队参与了CPDC 2025挑战中的GPU轨道解决方案。
- 挑战包含构建符合角色性格和游戏世界观的游戏内对话AI的任务,并需要支持函数调用功能。
- 团队采用了数据合成方法,结合比赛组织者提供的数据集进行部分任务处理。
- 使用Qwen3-14B模型进行LoRA微调与模型融合。
- 在推理过程中,团队使用集成基础模型与多个LoRA适配器的方案。
- 三个不同的LoRA适配器分别处理工具调用、带有工具调用结果的响应生成以及没有工具调用结果的响应生成。
点此查看论文截图
Easy Turn: Integrating Acoustic and Linguistic Modalities for Robust Turn-Taking in Full-Duplex Spoken Dialogue Systems
Authors:Guojian Li, Chengyou Wang, Hongfei Xue, Shuiyuan Wang, Dehui Gao, Zihan Zhang, Yuke Lin, Wenjie Li, Longshuai Xiao, Zhonghua Fu, Lei Xie
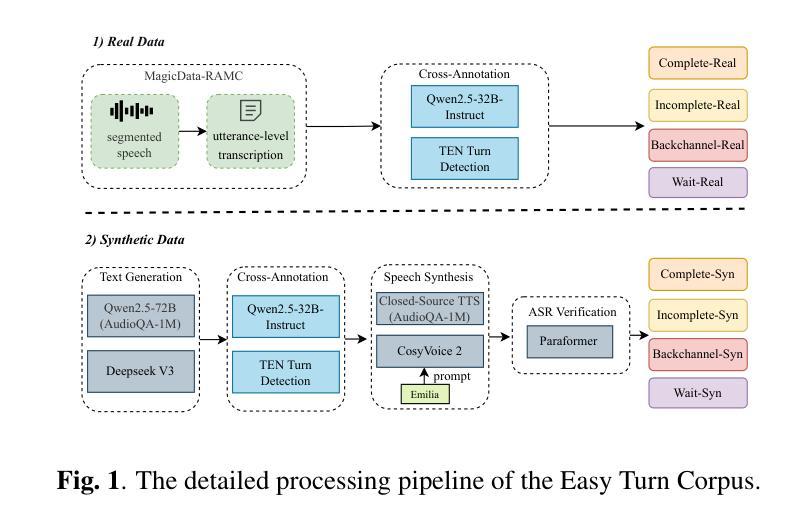
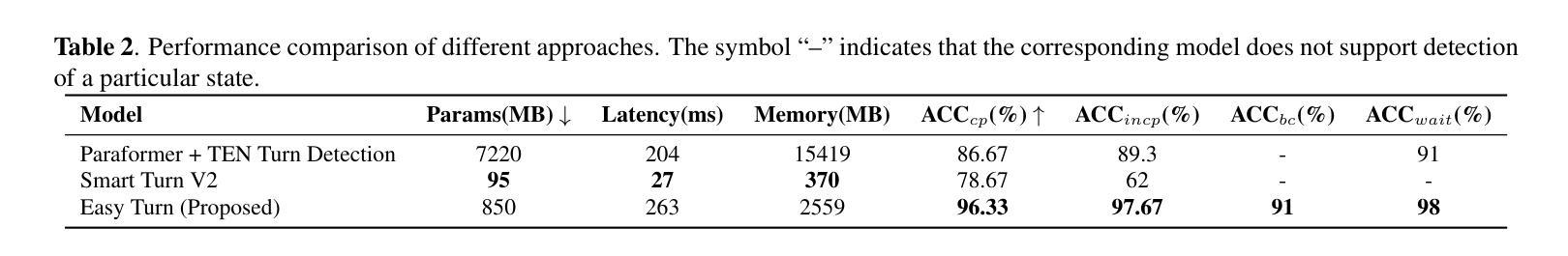
Full-duplex interaction is crucial for natural human-machine communication, yet remains challenging as it requires robust turn-taking detection to decide when the system should speak, listen, or remain silent. Existing solutions either rely on dedicated turn-taking models, most of which are not open-sourced. The few available ones are limited by their large parameter size or by supporting only a single modality, such as acoustic or linguistic. Alternatively, some approaches finetune LLM backbones to enable full-duplex capability, but this requires large amounts of full-duplex data, which remain scarce in open-source form. To address these issues, we propose Easy Turn, an open-source, modular turn-taking detection model that integrates acoustic and linguistic bimodal information to predict four dialogue turn states: complete, incomplete, backchannel, and wait, accompanied by the release of Easy Turn trainset, a 1,145-hour speech dataset designed for training turn-taking detection models. Compared to existing open-source models like TEN Turn Detection and Smart Turn V2, our model achieves state-of-the-art turn-taking detection accuracy on our open-source Easy Turn testset. The data and model will be made publicly available on GitHub.
全双工交互对于自然的人机通信至关重要,但它仍然是一个挑战,因为它需要鲁棒的轮替检测来决定系统何时应该说话、倾听或保持沉默。现有解决方案要么依赖于专门的轮替模型,其中大多数都不是开源的。现有的少数几个受到其庞大参数大小的限制,或者仅支持单一模态,如声音或语言。另外,一些方法通过对大型语言模型(LLM)进行微调以启用全双工功能,但这需要大量的全双工数据,而在开源形式中这些数据仍然很稀缺。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Easy Turn,这是一个开源的模块化轮替检测模型,它结合了声音和语言双模态信息来预测四种对话轮替状态:完成、未完成、后台通道和等待,并伴随着Easy Turn训练集的发布,这是一个专为训练轮替检测模型而设计的1145小时语音数据集。与现有的开源模型如TEN Turn Detection和Smart Turn V2相比,我们的模型在开源Easy Turn测试集上实现了最先进的轮替检测精度。数据和模型将在GitHub上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了全双工交互在人机自然通信中的重要性及其所面临的挑战,特别是需要鲁棒的转话检测以决定系统何时应该说话、倾听或保持沉默。现有解决方案要么依赖于专门的转话模型(大多数未开源),要么通过微调大型语言模型(LLM)来实现全双工功能,但需要大量的全双工数据,这在开源形式中仍然很稀缺。为了解决这些问题,本文提出了一种开源的模块化转话检测模型Easy Turn,它结合了声音和语言双模态信息来预测四个对话状态,并伴随着Easy Turn训练集的发布,这是一个专门用于训练转话检测模型的1,145小时语音数据集。与现有的开源模型相比,如TEN Turn Detection和Smart Turn V2,Easy Turn模型在开源测试集上实现了最先进的转话检测精度。数据和模型将在GitHub上公开可用。
Key Takeaways
- 全双工交互对于自然人机通信至关重要,需要鲁棒的转话检测。
- 当前解决方案存在依赖未开源的转话模型或需要大量全双工数据的问题。
- Easy Turn是一种开源的模块化转话检测模型,结合了声音和语言双模态信息。
- Easy Turn模型可以预测四个对话状态:完成、未完成、后台通道和等待。
- Easy Turn训练集是一个专门用于训练转话检测模型的1,145小时语音数据集。
- Easy Turn模型在开源测试集上实现了最先进的转话检测精度。
点此查看论文截图


From What to Why: A Multi-Agent System for Evidence-based Chemical Reaction Condition Reasoning
Authors:Cheng Yang, Jiaxuan Lu, Haiyuan Wan, Junchi Yu, Feiwei Qin
The chemical reaction recommendation is to select proper reaction condition parameters for chemical reactions, which is pivotal to accelerating chemical science. With the rapid development of large language models (LLMs), there is growing interest in leveraging their reasoning and planning capabilities for reaction condition recommendation. Despite their success, existing methods rarely explain the rationale behind the recommended reaction conditions, limiting their utility in high-stakes scientific workflows. In this work, we propose ChemMAS, a multi-agent system that reframes condition prediction as an evidence-based reasoning task. ChemMAS decomposes the task into mechanistic grounding, multi-channel recall, constraint-aware agentic debate, and rationale aggregation. Each decision is backed by interpretable justifications grounded in chemical knowledge and retrieved precedents. Experiments show that ChemMAS achieves 20-35% gains over domain-specific baselines and outperforms general-purpose LLMs by 10-15% in Top-1 accuracy, while offering falsifiable, human-trustable rationales, which establishes a new paradigm for explainable AI in scientific discovery.
化学反应建议的关键在于为化学反应选择合适的反应条件参数,这对于加速化学科学至关重要。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,人们越来越有兴趣利用它们的推理和规划能力来进行反应条件推荐。尽管取得了一定的成功,但现有方法很少解释推荐反应条件的依据,限制了它们在高风险科学工作流程中的实用性。在这项工作中,我们提出了ChemMAS,这是一个多代理系统,它将条件预测重新构建为基于证据推理的任务。ChemMAS将任务分解为机制基础、多渠道回忆、约束感知代理辩论和理由聚合。每个决策都有可解释的依据,依据的是化学知识和检索到的先例。实验表明,ChemMAS相较于特定领域的基线实现了20-35%的增益,在Top-1准确率方面比通用LLM高出10-15%,同时提供可验证的、值得信赖的理由,这为科学发现中的可解释人工智能建立了新的范式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
借助多智能体系统ChemMAS,通过证据推理任务的方式重构反应条件预测,为化学反应选择合适的反应条件参数,加速化学科学的发展。该系统将任务分解为机械基础、多渠道回忆、约束感知的智能体辩论和理由聚合,每个决策都由基于化学知识和检索先例的可解释理由支持。实验表明,ChemMAS在特定领域基准测试上取得了20-35%的增益,在Top-1准确率上比通用LLM高出10-15%,同时提供可验证、可信赖的人类理由,为科学发现中的可解释人工智能建立了新范式。
Key Takeaways
- ChemMAS利用多智能体系统,以证据推理的方式预测反应条件,促进化学反应研究。
- 系统通过分解任务,包括机械基础、多渠道回忆、约束感知的智能体辩论和理由聚合,提高决策的可解释性。
- ChemMAS结合化学知识和检索先例,为每个决策提供理由支持。
- 实验显示,ChemMAS在特定领域相比基线方法有显著提高,同时在Top-1准确率上优于通用LLM。
- 系统提供了可验证、可信赖的人类理由,增强了决策的透明度和可信度。
- ChemMAS的建立为科学发现中的可解释人工智能树立了新典范。
点此查看论文截图

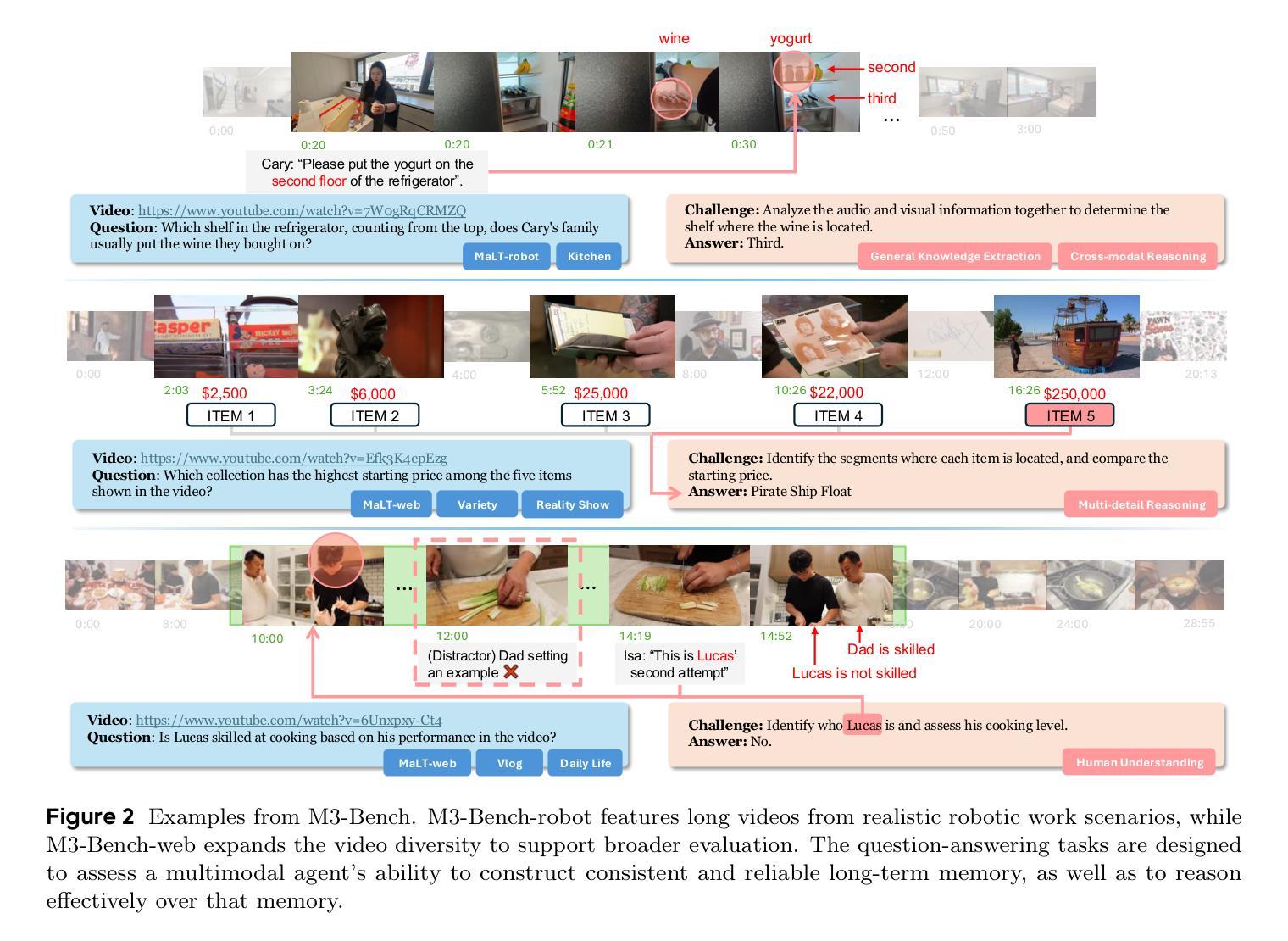
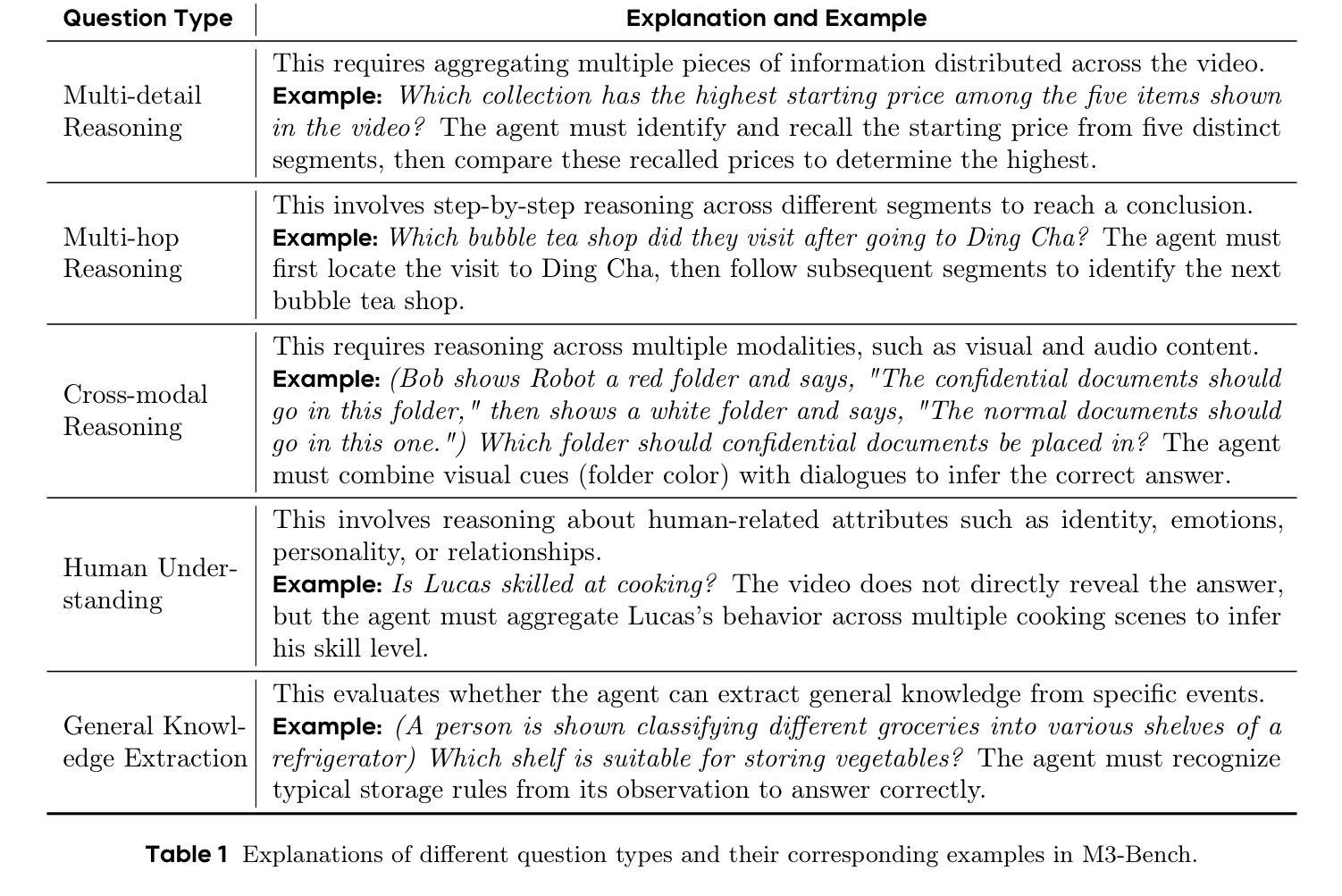
Seeing, Listening, Remembering, and Reasoning: A Multimodal Agent with Long-Term Memory
Authors:Lin Long, Yichen He, Wentao Ye, Yiyuan Pan, Yuan Lin, Hang Li, Junbo Zhao, Wei Li
We introduce M3-Agent, a novel multimodal agent framework equipped with long-term memory. Like humans, M3-Agent can process real-time visual and auditory inputs to build and update episodic and semantic memories, gradually accumulating world knowledge. Its memory is organized in an entity-centric, multimodal manner, enabling deeper and more consistent understanding of the environment. Given an instruction, M3-Agent autonomously performs multi-turn reasoning and retrieves relevant memories to complete tasks. To evaluate memory effectiveness and memory-based reasoning in multimodal agents, we develop M3-Bench, a long-video question answering benchmark comprising 100 newly recorded robot-perspective videos (M3-Bench-robot) and 920 diverse web-sourced videos (M3-Bench-web). We annotate QA pairs designed to test capabilities essential for agent applications, such as person understanding, general knowledge extraction, and cross-modal reasoning. Experimental results show that M3-Agent, trained via reinforcement learning, outperforms the strongest baseline, a prompting agent using Gemini-1.5-pro and GPT-4o, achieving 6.7%, 7.7%, and 5.3% higher accuracy on M3-Bench-robot, M3-Bench-web and VideoMME-long, respectively. Our work advances multimodal agents toward more human-like long-term memory and provides insights for their practical design. Model, code and data are available at https://github.com/bytedance-seed/m3-agent.
我们介绍了M3-Agent,这是一个配备长期记忆的新型多模态代理框架。与人类类似,M3-Agent可以处理实时视觉和听觉输入,以构建和更新事件和语义记忆,逐渐积累世界知识。它的记忆以实体为中心,多模态的方式组织,使对环境有更深更一致的理解。给定指令后,M3-Agent可自主进行多轮推理并检索相关记忆以完成任务。为了评估多模态代理中的记忆效果和基于记忆推理的能力,我们开发了M3-Bench,这是一个长视频问答基准测试,包括由新录制的从机器人视角出发的100个视频(M3-Bench机器人)和从网上获取的920个多样化视频(M3-Bench网络)。我们标注了问答对,旨在测试代理应用程序所需的能力,如人物理解、通用知识提取和跨模态推理。实验结果表明,通过强化学习训练的M3-Agent超越了最强的基线——使用Gemini-1.5-pro和GPT-4o的提示代理,在M3-Bench机器人、M3-Bench网络和VideoMME长视频上的准确率分别提高了6.7%、7.7%和5.3%。我们的工作推动了多模态代理向更具人类特色的长期记忆发展,并为其实用设计提供了见解。模型、代码和数据可在https://github.com/bytedance-seed/m3-agent获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
M3-Agent是一款配备长期记忆的多模态代理框架,能处理实时视觉和听觉输入,构建和更新情境和语义记忆,逐步积累世界知识。其记忆以实体为中心、多模态的方式组织,使对环境的理解更为深入和一致。接受指令后,M3-Agent可自主进行多轮推理并检索相关记忆以完成任务。为评估多模态代理的记忆效果和基于记忆推理能力,研究团队开发了M3-Bench基准测试,包含机器人视角的视频和网页来源的视频。实验结果显示,通过强化学习训练的M3-Agent表现优于基线模型,在M3-Bench测试中取得更高准确率。
Key Takeaways
- M3-Agent是一款配备长期记忆的多模态代理框架,能处理视觉和听觉输入并积累世界知识。
- M3-Agent的记忆以实体为中心、多模态方式组织,提升对环境的深入理解。
- M3-Agent可自主进行多轮推理并检索相关记忆以完成任务。
- 为评估多模态代理的记忆和推理能力,研发了M3-Bench基准测试。
- M3-Bench包含机器人视角和网页来源的视频,测试关键能力如人物理解、一般知识提取和跨模态推理。
- M3-Agent在M3-Bench测试中表现优于基线模型,具有更高的准确率。
- M3-Agent的研究为推进多模态代理向更人性化长期记忆发展提供了见解。
点此查看论文截图