⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-01 更新
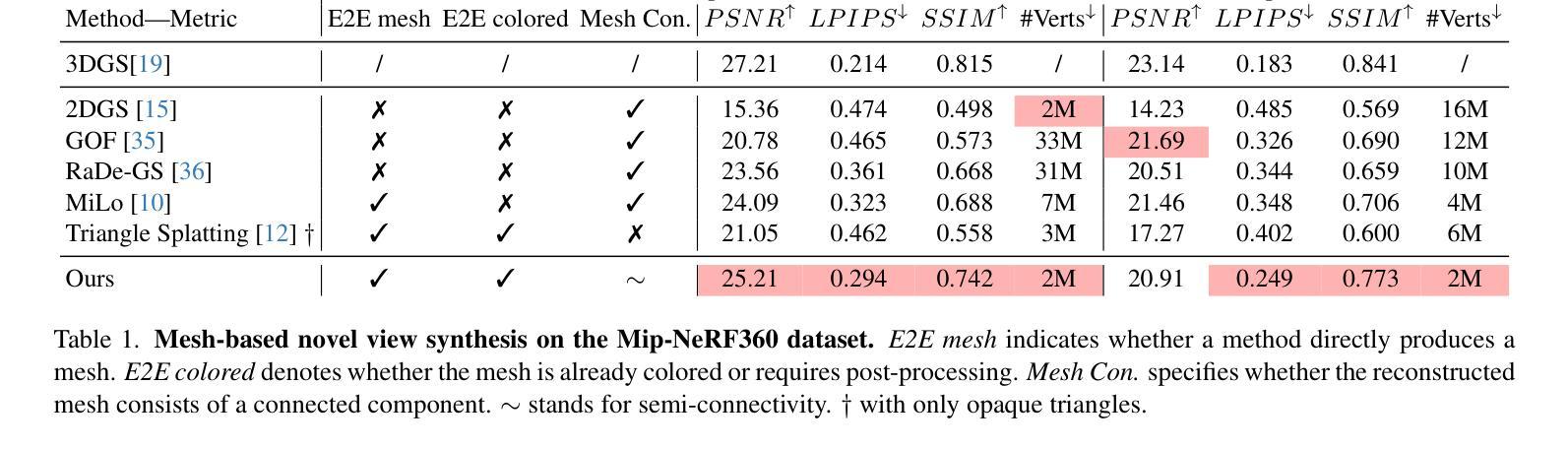
Triangle Splatting+: Differentiable Rendering with Opaque Triangles
Authors:Jan Held, Renaud Vandeghen, Sanghyun Son, Daniel Rebain, Matheus Gadelha, Yi Zhou, Ming C. Lin, Marc Van Droogenbroeck, Andrea Tagliasacchi
Reconstructing 3D scenes and synthesizing novel views has seen rapid progress in recent years. Neural Radiance Fields demonstrated that continuous volumetric radiance fields can achieve high-quality image synthesis, but their long training and rendering times limit practicality. 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) addressed these issues by representing scenes with millions of Gaussians, enabling real-time rendering and fast optimization. However, Gaussian primitives are not natively compatible with the mesh-based pipelines used in VR headsets, and real-time graphics applications. Existing solutions attempt to convert Gaussians into meshes through post-processing or two-stage pipelines, which increases complexity and degrades visual quality. In this work, we introduce Triangle Splatting+, which directly optimizes triangles, the fundamental primitive of computer graphics, within a differentiable splatting framework. We formulate triangle parametrization to enable connectivity through shared vertices, and we design a training strategy that enforces opaque triangles. The final output is immediately usable in standard graphics engines without post-processing. Experiments on the Mip-NeRF360 and Tanks & Temples datasets show that Triangle Splatting+achieves state-of-the-art performance in mesh-based novel view synthesis. Our method surpasses prior splatting approaches in visual fidelity while remaining efficient and fast to training. Moreover, the resulting semi-connected meshes support downstream applications such as physics-based simulation or interactive walkthroughs. The project page is https://trianglesplatting2.github.io/trianglesplatting2/.
近年来,重建三维场景和合成新视角的技术取得了快速发展。神经辐射场证明连续体积辐射场可以实现高质量图像合成,但其漫长的训练和渲染时间限制了实用性。3D高斯贴合(3DGS)通过用数百万个高斯表示场景解决了这些问题,实现了实时渲染和快速优化。然而,高斯原始数据并不兼容VR头盔和实时图形应用程序所使用的基于网格的管道。现有解决方案尝试通过后期处理或两阶段管道将高斯转换为网格,这增加了复杂性并降低了视觉质量。在这项工作中,我们引入了Triangle Splatting+,它在可微分的贴合框架内直接优化计算机图形的基本原始元素——三角形。我们制定三角形参数化,通过共享顶点实现连接,并设计了一种训练策略,强制实施不透明三角形。最终输出物可立即在标准图形引擎中使用,无需后期处理。在Mip-NeRF360和Tanks & Temples数据集上的实验表明,Triangle Splatting+在基于网格的新视角合成中达到了最新技术水平。我们的方法在视觉保真度上超越了先前的贴合方法,同时保持了高效和快速的训练。此外,所得的半连接网格支持下游应用,如基于物理的模拟或交互式浏览。项目页面为https://trianglesplatting2.github.io/trianglesplatting2/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 6 figures, 2 tables
Summary
神经网络辐射场在三维场景重建和合成新视角方面取得了进展,但其训练与渲染时间较长限制了实际应用。为解决这个问题,研究者提出使用三维高斯贴图技术表示场景,实现实时渲染和快速优化。然而,高斯原始数据并不兼容VR头盔和实时图形应用中的网格基础管道。现有解决方案尝试将高斯转换为网格,但增加了复杂性和降低了视觉质量。本研究引入Triangle Splatting+,直接在可微分的贴图框架内优化计算机图形的基本原始元素——三角形。我们制定了三角形参数化公式以实现通过共享顶点进行连接,并设计了一种训练策略以强制执行不透明的三角形。最终输出可以直接在标准图形引擎中使用,无需后处理。实验结果展示了该方法在基于网格的新型视图合成中的卓越性能,超越先前的贴图方法,同时保持高效和快速的训练过程。此外,所得半连接网格支持下游应用如物理模拟或交互式漫游等。项目页面为:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络辐射场在三维场景重建和图像合成方面取得了重要进展,但存在训练和渲染时间较长的问题。
- 三维高斯贴图技术为解决这一问题提供了新的思路,实现了实时渲染和快速优化。
- 当前方法面临高斯原始数据与VR头盔和实时图形应用中网格基础管道的不兼容问题。
- Triangle Splatting+方法直接优化计算机图形的基本元素——三角形,实现了高效且高质量的渲染结果。
- Triangle Splatting+通过共享顶点实现三角形连接,同时设计训练策略以生成不透明三角形,增强了视觉质量。
- 最终输出可以直接在标准图形引擎中使用,无需后处理步骤。
点此查看论文截图

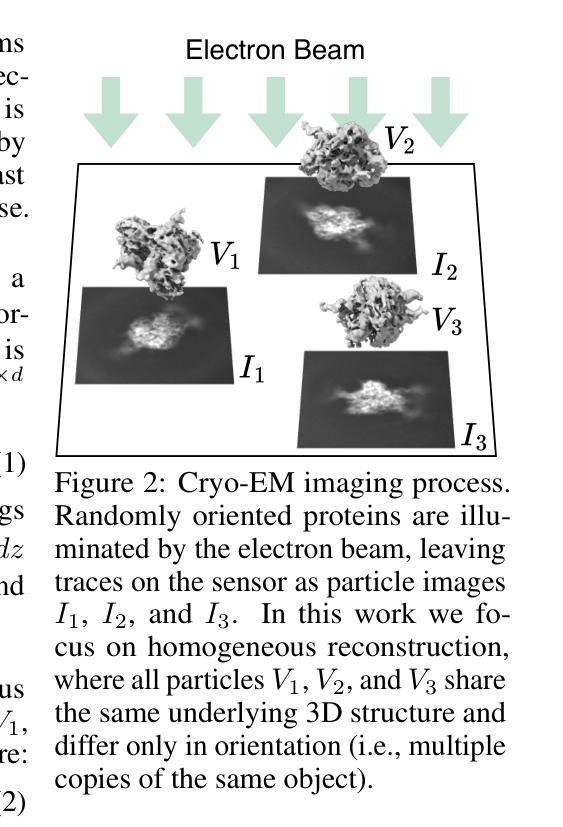
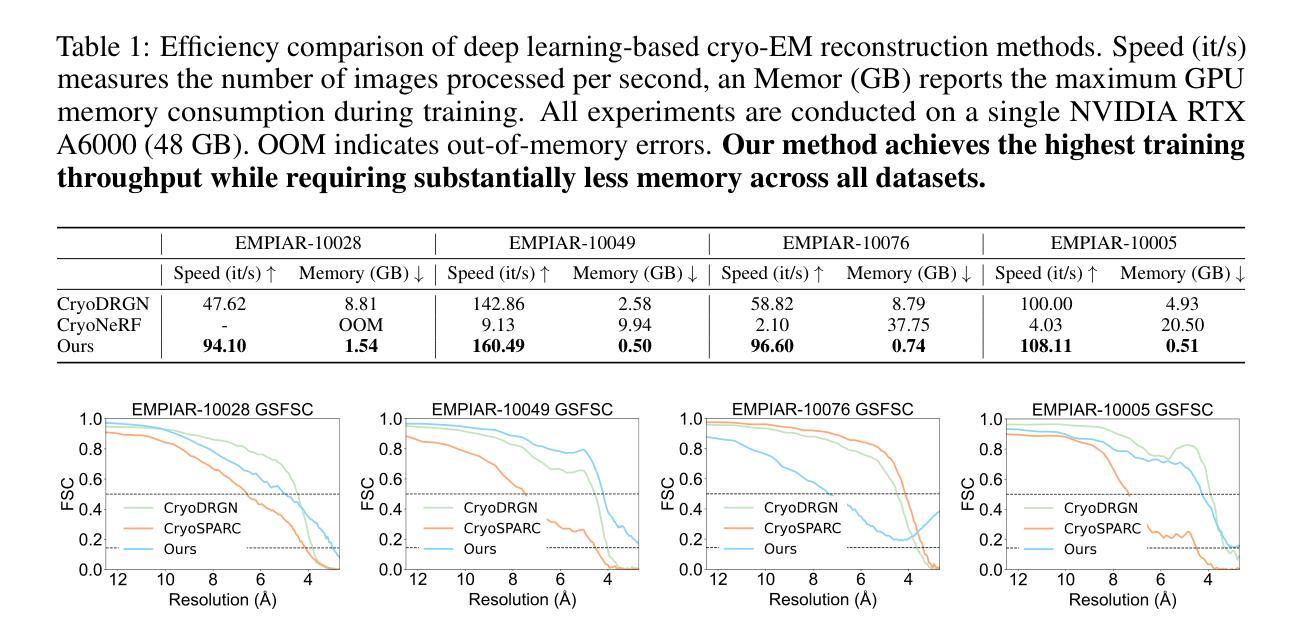
GEM: 3D Gaussian Splatting for Efficient and Accurate Cryo-EM Reconstruction
Authors:Huaizhi Qu, Xiao Wang, Gengwei Zhang, Jie Peng, Tianlong Chen
Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) has become a central tool for high-resolution structural biology, yet the massive scale of datasets (often exceeding 100k particle images) renders 3D reconstruction both computationally expensive and memory intensive. Traditional Fourier-space methods are efficient but lose fidelity due to repeated transforms, while recent real-space approaches based on neural radiance fields (NeRFs) improve accuracy but incur cubic memory and computation overhead. Therefore, we introduce GEM, a novel cryo-EM reconstruction framework built on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) that operates directly in real-space while maintaining high efficiency. Instead of modeling the entire density volume, GEM represents proteins with compact 3D Gaussians, each parameterized by only 11 values. To further improve the training efficiency, we designed a novel gradient computation to 3D Gaussians that contribute to each voxel. This design substantially reduced both memory footprint and training cost. On standard cryo-EM benchmarks, GEM achieves up to 48% faster training and 12% lower memory usage compared to state-of-the-art methods, while improving local resolution by as much as 38.8%. These results establish GEM as a practical and scalable paradigm for cryo-EM reconstruction, unifying speed, efficiency, and high-resolution accuracy. Our code is available at https://github.com/UNITES-Lab/GEM.
冷冻电子显微镜(cryo-EM)已成为高分辨率结构生物学的重要工具,但数据集的大规模(通常超过10万张粒子图像)使得3D重建在计算和内存方面都很昂贵。传统的傅里叶空间方法虽然效率高,但由于重复变换而失去精度,而最近基于神经辐射场(NeRFs)的实空间方法提高了准确性,但产生了立方级的内存和计算开销。因此,我们引入了GEM,这是一个新的冷冻电镜重建框架,它基于三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)技术,直接在实空间中运行,同时保持高效率。GEM不是对整个密度体积进行建模,而是用紧凑的三维高斯来表示蛋白质,每个高斯仅由11个值参数化。为了进一步改进训练效率,我们设计了一种新型的三维高斯梯度计算,为每个体素做出贡献。这一设计大大减少了内存占用和训练成本。在标准的冷冻电镜基准测试中,与最新方法相比,GEM实现了最多达48%更快的训练和12%更低的内存使用率,同时局部分辨率提高了高达38.8%。这些结果证明了GEM作为冷冻电镜重建实用且可扩展的范式,统一了速度、效率和高分辨率的准确性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/UNITES-Lab/GEM获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经辐射场(NeRF)在冷冻电子显微镜(cryo-EM)重建中展现出高精度,但计算量大且内存密集。本研究提出一种新型框架GEM,采用三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)直接在实空间操作并保持高效率。通过用紧凑的三维高斯代表蛋白质而非模拟整个密度体积,并利用一种新型的梯度计算方法提高训练效率,达到提升训练速度和内存使用效率的目的。在标准冷冻电镜基准测试中,与现有顶尖方法相比,GEM训练速度提升48%,内存使用率降低12%,同时局部分辨率提高高达38.8%。本研究表明GEM是一个实用、可伸缩的冷冻电镜重建范式。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出一种新的冷冻电子显微镜(cryo-EM)重建框架GEM,结合了实空间方法和神经辐射场(NeRF)的优势。
- GEM采用三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)技术,通过紧凑的三维高斯代表蛋白质,减少计算量和内存需求。
- GEM设计了一种新颖的梯度计算方法,提高了训练效率。
- 与现有顶尖方法相比,GEM在标准冷冻电镜基准测试中表现出更高的效率和更高的局部分辨率。
- GEM训练速度提升显著,达到最快48%,内存使用效率也得到提升。
点此查看论文截图
Scalable GANs with Transformers
Authors:Sangeek Hyun, MinKyu Lee, Jae-Pil Heo
Scalability has driven recent advances in generative modeling, yet its principles remain underexplored for adversarial learning. We investigate the scalability of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) through two design choices that have proven to be effective in other types of generative models: training in a compact Variational Autoencoder latent space and adopting purely transformer-based generators and discriminators. Training in latent space enables efficient computation while preserving perceptual fidelity, and this efficiency pairs naturally with plain transformers, whose performance scales with computational budget. Building on these choices, we analyze failure modes that emerge when naively scaling GANs. Specifically, we find issues as underutilization of early layers in the generator and optimization instability as the network scales. Accordingly, we provide simple and scale-friendly solutions as lightweight intermediate supervision and width-aware learning-rate adjustment. Our experiments show that GAT, a purely transformer-based and latent-space GANs, can be easily trained reliably across a wide range of capacities (S through XL). Moreover, GAT-XL/2 achieves state-of-the-art single-step, class-conditional generation performance (FID of 2.96) on ImageNet-256 in just 40 epochs, 6x fewer epochs than strong baselines.
可扩展性推动了生成模型的最新发展,但对于对抗性学习,其原理仍未得到充分探索。我们通过两项在其他类型的生成模型中证明有效的设计选择来研究生成对抗网络(GANs)的可扩展性:在紧凑的变分自动编码器潜在空间中进行训练,并采用纯基于变压器的生成器和鉴别器。在潜在空间中进行训练既提高了计算效率又保持了感知保真度,这种效率与普通的变压器自然地结合在一起,其性能随计算预算而扩展。基于这些选择,我们分析了在简单扩展GAN时出现的失败模式。具体来说,我们发现生成器前几层利用不足以及网络扩展时的优化不稳定等问题。因此,我们提供了简单且适合规模的解决方案,如轻量级中间监督和宽度感知学习率调整。我们的实验表明,GAT是一种纯基于变压器和潜在空间的GANs,可以轻松地跨广泛的能力范围(S到XL)进行可靠训练。此外,GAT-XL/2在仅40个周期内就在ImageNet-256上实现了最先进的单步、有条件生成性能(FID为2.96),这是基线模型的六分之一周期。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇论文研究了生成对抗网络(GANs)的可扩展性,通过采用其他生成模型证明有效的两种设计选择:在紧凑的变分自动编码器潜在空间中进行训练以及采用纯基于变换器的生成器和鉴别器。论文分析了在扩大GAN规模时出现的失败模式,并提供了简单的可扩展解决方案。实验表明,GAT能够在广泛的容量范围内可靠地进行训练,并在ImageNet-256上实现了最先进的单步类条件生成性能。
Key Takeaways
- 论文探讨了生成对抗网络(GANs)的可扩展性,并分析了其面临的挑战。
- 通过在变分自动编码器的潜在空间中进行训练,提高了GANs的计算效率和感知保真度。
- 采用纯基于变换器的生成器和鉴别器,与潜在空间训练相结合,增强了GANs的性能。
- 在扩大GAN规模时,出现了如生成器早期层利用不足和优化不稳定等问题。
- 论文提供了针对这些问题的简单且可扩展的解决方案,如轻量级中间监督和宽度感知的学习率调整。
- 实验表明,GAT在广泛的容量范围内能够可靠地进行训练,并在ImageNet-256上实现了卓越的单步类条件生成性能。
点此查看论文截图

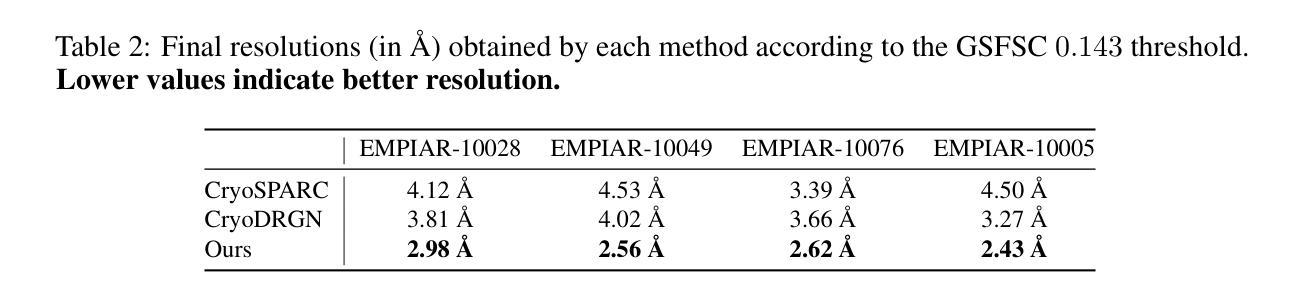
OracleGS: Grounding Generative Priors for Sparse-View Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Atakan Topaloglu, Kunyi Li, Michael Niemeyer, Nassir Navab, A. Murat Tekalp, Federico Tombari
Sparse-view novel view synthesis is fundamentally ill-posed due to severe geometric ambiguity. Current methods are caught in a trade-off: regressive models are geometrically faithful but incomplete, whereas generative models can complete scenes but often introduce structural inconsistencies. We propose OracleGS, a novel framework that reconciles generative completeness with regressive fidelity for sparse view Gaussian Splatting. Instead of using generative models to patch incomplete reconstructions, our “propose-and-validate” framework first leverages a pre-trained 3D-aware diffusion model to synthesize novel views to propose a complete scene. We then repurpose a multi-view stereo (MVS) model as a 3D-aware oracle to validate the 3D uncertainties of generated views, using its attention maps to reveal regions where the generated views are well-supported by multi-view evidence versus where they fall into regions of high uncertainty due to occlusion, lack of texture, or direct inconsistency. This uncertainty signal directly guides the optimization of a 3D Gaussian Splatting model via an uncertainty-weighted loss. Our approach conditions the powerful generative prior on multi-view geometric evidence, filtering hallucinatory artifacts while preserving plausible completions in under-constrained regions, outperforming state-of-the-art methods on datasets including Mip-NeRF 360 and NeRF Synthetic.
稀疏视角的新视角合成(Novel View Synthesis)因严重的几何模糊性而根本不适定。当前的方法陷入了权衡困境:回归模型在几何上忠实但不完整,而生成模型虽然能完成场景但经常引入结构不一致性。我们提出了OracleGS这一新型框架,旨在调和生成模型的完整性与回归模型的忠实性,用于稀疏视角的高斯拼贴(Gaussian Splatting)。与其他方法不同,我们并不使用生成模型来修复不完整的重建结果,而是采用“提出并验证”的框架。首先,我们利用预训练的3D感知扩散模型(diffusion model)来合成新视角以提出一个完整的场景。然后,我们将多视角立体(MVS)模型重新定位为一个3D感知的验证器,以验证生成视角的3D不确定性,利用其注意力图来揭示哪些区域受到多视角证据的有力支持,以及哪些区域因遮挡、缺乏纹理或直接不一致而陷入高度不确定性的区域。这种不确定性信号直接指导了通过不确定性加权损失优化的3D高斯拼贴模型。我们的方法将强大的生成先验条件与多视角几何证据相结合,在过滤幻觉伪影的同时保留可能完成的无约束区域,在Mip-NeRF 360和NeRF Synthetic等数据集上的表现优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为OracleGS的新框架,旨在解决稀疏视图下的新颖视角合成问题。该方法结合了生成模型的完整性与回归模型的忠实性,采用“提出并验证”的方式,利用预训练的3D感知扩散模型合成新颖视图以提出完整场景,再使用多视角立体(MVS)模型作为3D感知的顾问,验证生成视图的3D不确定性。这种方法利用注意力地图揭示哪些区域的多视角证据支持生成视图,哪些区域因遮挡、缺乏纹理或直接不一致而具有不确定性。这种不确定性信号直接指导了基于3D高斯拼贴模型的不确定性加权损失优化。此方法在包括Mip-NeRF 360和NeRF Synthetic在内的数据集上表现优于其他先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- OracleGS框架结合了生成模型的完整性与回归模型的忠实性,解决了稀疏视图下的新颖视角合成问题的根本难题。
- 提出并验证的方法首先利用预训练的3D感知扩散模型合成完整场景的新颖视图。
- 多视角立体(MVS)模型作为3D感知的顾问,用于验证生成视图的3D不确定性。
- 注意力地图用于揭示哪些区域的多视角证据支持生成视图,哪些区域存在不确定性。
- 不确定性信号直接指导了基于3D高斯拼贴模型的不确定性加权损失优化。
- 该方法利用生成模型的强大先验知识,结合多视角几何证据,能够在过滤掉幻觉伪影的同时,保留在约束不足区域的合理完成。
点此查看论文截图
Seeing Isn’t Believing: Context-Aware Adversarial Patch Synthesis via Conditional GAN
Authors:Roie Kazoom, Alon Goldberg, Hodaya Cohen, Ofer Hadar
Adversarial patch attacks pose a severe threat to deep neural networks, yet most existing approaches rely on unrealistic white-box assumptions, untargeted objectives, or produce visually conspicuous patches that limit real-world applicability. In this work, we introduce a novel framework for fully controllable adversarial patch generation, where the attacker can freely choose both the input image x and the target class y target, thereby dictating the exact misclassification outcome. Our method combines a generative U-Net design with Grad-CAM-guided patch placement, enabling semantic-aware localization that maximizes attack effectiveness while preserving visual realism. Extensive experiments across convolutional networks (DenseNet-121, ResNet-50) and vision transformers (ViT-B/16, Swin-B/16, among others) demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across all settings, with attack success rates (ASR) and target-class success (TCS) consistently exceeding 99%. Importantly, we show that our method not only outperforms prior white-box attacks and untargeted baselines, but also surpasses existing non-realistic approaches that produce detectable artifacts. By simultaneously ensuring realism, targeted control, and black-box applicability-the three most challenging dimensions of patch-based attacks-our framework establishes a new benchmark for adversarial robustness research, bridging the gap between theoretical attack strength and practical stealthiness.
对抗性补丁攻击对深度神经网络构成了严重威胁,但大多数现有方法依赖于不切实际的白色盒子假设、非目标性目标,或产生视觉显著的补丁,限制了其在现实世界中的应用性。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个全新的可控对抗性补丁生成框架,攻击者可以自由选择输入图像x和目标类别y target,从而决定确切的误分类结果。我们的方法结合了生成式U-Net设计和由Grad-CAM引导的补丁放置,实现了语义感知的定位,最大化攻击效果的同时保持视觉真实性。在卷积网络(DenseNet-121、ResNet-50)和视觉转换器(ViT-B/16、Swin-B/16等)上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在所有设置中都实现了最先进的性能,攻击成功率(ASR)和目标类别成功率(TCS)均超过99%。重要的是,我们证明我们的方法不仅优于先前的白色盒子攻击和非目标基线,而且超越了现有产生可检测伪影的非现实方法。通过同时确保真实性、目标控制和黑色盒子适用性——补丁攻击的三大最具挑战性的维度,我们的框架为对抗性稳健性研究建立了新的基准,缩小了理论攻击强度与实际隐蔽性之间的差距。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
深度神经网络面临着对抗性补丁攻击的巨大威胁。但现有方法依赖不合理的假设或未涵盖现实攻击场景中特定的目标类别选择。本研究引入了一种全新的可控对抗性补丁生成框架,攻击者可以自由选择输入图像和目标类别,从而精确控制误分类结果。结合生成式U-Net设计和基于Grad-CAM的补丁放置策略,实现了语义感知的定位,在保持视觉真实性的同时最大化攻击效果。实验证明,该方法在所有场景下均表现优异,攻击成功率和目标类别成功率均超过99%。该方法不仅优于先前的白盒攻击和非目标基线,还超越了产生可检测伪影的非现实攻击方法。同时确保现实性、目标控制及黑盒应用的三重挑战为基于补丁的攻击开辟了新方向,为我们的框架建立了新的基准点,弥合了理论攻击强度和实际应用隐秘性之间的差距。
关键见解
- 介绍了对抗性补丁攻击对深度神经网络构成严重威胁的现状。
- 当前多数方法存在局限性,依赖于白盒假设或缺乏实际应用的现实攻击场景目标类别选择能力。
- 提出了一种全新的可控对抗性补丁生成框架,能够自由选择输入图像和目标类别,精确控制误分类结果。
- 结合生成式U-Net设计和Grad-CAM指导的补丁放置策略,实现了攻击效果最大化并保持视觉真实性的能力。
- 实验证明该方法在所有场景下均表现优异,攻击成功率和目标类别成功率超过99%。
- 方法优于先前的白盒和非目标基线攻击,并能超越现有产生可检测伪影的非现实攻击方法。
点此查看论文截图

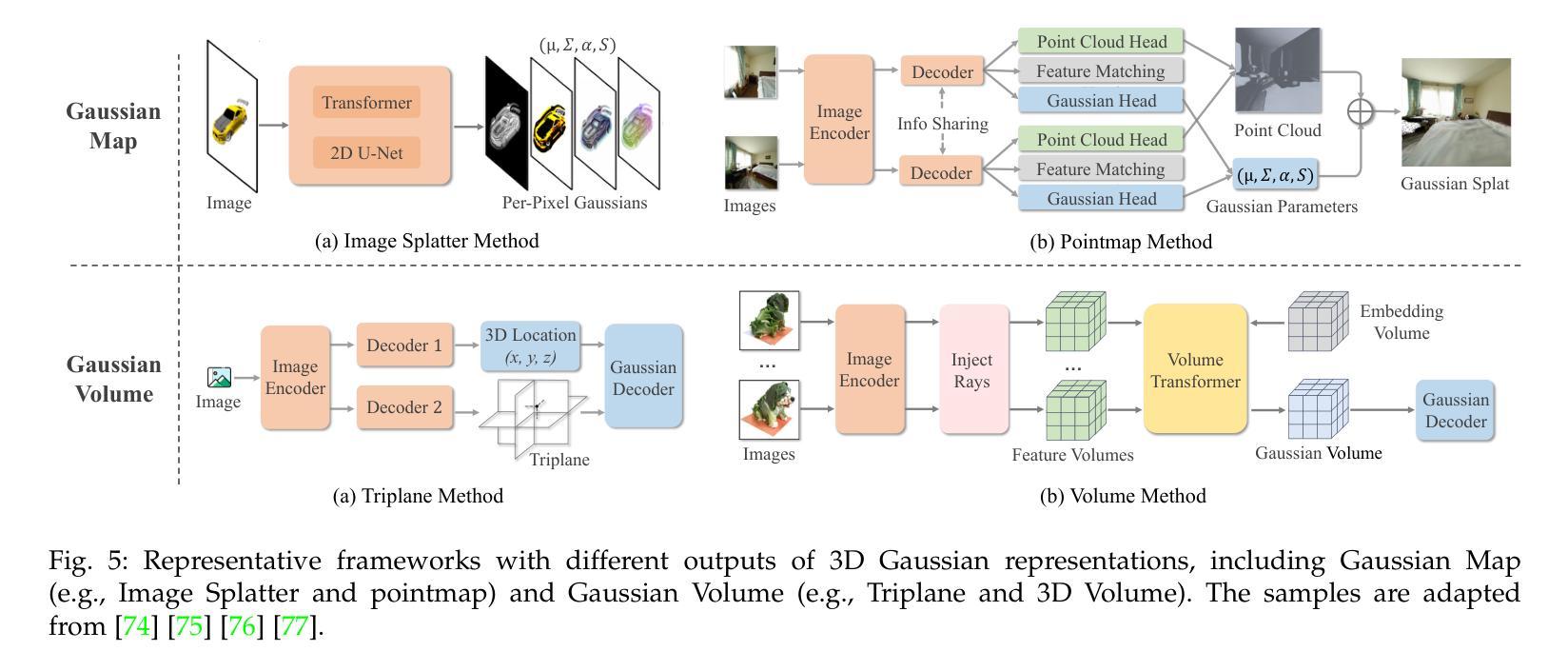
Advances in Feed-Forward 3D Reconstruction and View Synthesis: A Survey
Authors:Jiahui Zhang, Yuelei Li, Anpei Chen, Muyu Xu, Kunhao Liu, Jianyuan Wang, Xiao-Xiao Long, Hanxue Liang, Zexiang Xu, Hao Su, Christian Theobalt, Christian Rupprecht, Andrea Vedaldi, Kaichen Zhou, Paul Pu Liang, Shijian Lu, Fangneng Zhan
3D reconstruction and view synthesis are foundational problems in computer vision, graphics, and immersive technologies such as augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and digital twins. Traditional methods rely on computationally intensive iterative optimization in a complex chain, limiting their applicability in real-world scenarios. Recent advances in feed-forward approaches, driven by deep learning, have revolutionized this field by enabling fast and generalizable 3D reconstruction and view synthesis. This survey offers a comprehensive review of feed-forward techniques for 3D reconstruction and view synthesis, with a taxonomy according to the underlying representation architectures including point cloud, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), etc. We examine key tasks such as pose-free reconstruction, dynamic 3D reconstruction, and 3D-aware image and video synthesis, highlighting their applications in digital humans, SLAM, robotics, and beyond. In addition, we review commonly used datasets with detailed statistics, along with evaluation protocols for various downstream tasks. We conclude by discussing open research challenges and promising directions for future work, emphasizing the potential of feed-forward approaches to advance the state of the art in 3D vision.
3D重建和视图合成是计算机视觉、图形学和沉浸式技术(如增强现实AR、虚拟现实VR和数字孪生)中的基础问题。传统方法依赖于复杂链中的计算密集型迭代优化,这在现实场景的应用中存在一定的局限性。最近,以深度学习为驱动的前馈方法的进步,已经彻底改变了这一领域,实现了快速和通用的3D重建和视图合成。这篇综述对前馈技术在3D重建和视图合成方面的应用进行了全面的回顾,并根据基础表示架构进行了分类,包括点云、3D高斯贴片(3DGS)、神经辐射场(NeRF)等。我们研究了姿势无关重建、动态3D重建和3D感知图像和视频合成等关键任务,并强调了它们在数字人类、SLAM、机器人技术等领域的应用。此外,我们还回顾了常用数据集及其详细统计数据,以及用于各种下游任务的评估协议。最后,我们讨论了当前研究的开放挑战和未来工作的有前途的方向,并强调了前馈方法在推动计算机视觉前沿方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF A project page associated with this survey is available at https://fnzhan.com/projects/Feed-Forward-3D
Summary
神经网络辐射场(NeRF)等前沿技术为三维重建和视图合成领域带来了革命性的变革。这篇综述全面回顾了基于前馈技术的三维重建和视图合成的研究,从底层结构角度介绍了点云、三维高斯展开等。重点讨论了姿势自由重建、动态三维重建以及用于数字人、SLAM等场景的三维感知图像和视频合成等关键任务。此外,还介绍了常用的数据集和评估协议,并探讨了开放的研究挑战和未来研究方向的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 前馈技术已改变三维重建和视图合成领域,实现快速通用化。
- 神经网络辐射场(NeRF)等新技术在此领域有广泛应用。
- 综述涵盖了包括点云、三维高斯展开在内的多种底层结构。
- 关键任务包括姿势自由重建、动态三维重建以及三维感知图像和视频合成等。
- 这些技术在数字人、SLAM、机器人等领域有实际应用。
- 文章提供了详细的常用数据集和评估协议介绍。
点此查看论文截图

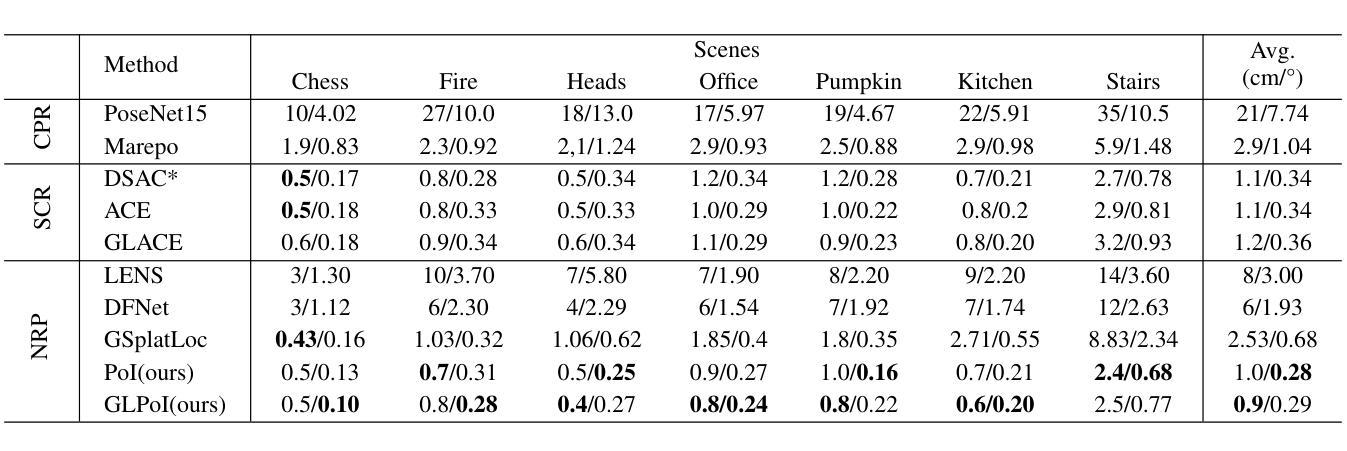
PoI: A Filter to Extract Pixel of Interest from Novel View Synthesis for Scene Coordinate Regression
Authors:Feifei Li, Qi Song, Chi Zhang, Hui Shuai, Rui Huang
Novel View synthesis (NVS) techniques, notably Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), can augment camera pose estimation by extending training data with rendered images. However, the images rendered by these methods are often plagued by blurring, undermining their reliability as training data for camera pose estimation. This limitation is particularly critical for Scene Coordinate Regression (SCR) methods, which aim at pixel-level 3D coordinate estimation, because rendering artifacts directly lead to estimation inaccuracies. To address this challenge, we propose a dual-criteria filtering mechanism that dynamically identifies and discards suboptimal pixels during training. The dual-criteria filter evaluates two concurrent metrics: (1) real-time SCR reprojection error, and (2) gradient threshold, across the coordinate regression domain. In addition, for visual localization problems in sparse input scenarios, it will be even more necessary to use data generated by NVS to assist the localization task. We design a coarse-to-fine PoI variant using sparse input NVS to solve this problem. Experiments across indoor and outdoor benchmarks confirm our method’s efficacy. It achieves state-of-the-art localization accuracy while maintaining computational efficiency.
新型视图合成(NVS)技术,特别是神经辐射场(NeRF)和3D高斯喷涂(3DGS)技术,可以通过使用渲染图像扩展训练数据来增强相机姿态估计。然而,这些方法渲染的图像往往受到模糊的影响,降低了它们作为相机姿态估计训练数据的可靠性。这一局限性对于场景坐标回归(SCR)方法尤为关键,因为SCR方法旨在进行像素级3D坐标估计,而渲染伪影直接导致估计不准确。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种基于双标准的过滤机制,该机制能够在训练过程中动态识别并丢弃次优像素。双标准过滤器评估两个并行指标:(1)实时SCR重投影误差和(2)坐标回归域中的梯度阈值。此外,在稀疏输入的视觉定位问题中,使用NVS生成的数据辅助定位任务将更为必要。我们设计了一种使用稀疏输入NVS的由粗到细的PoI变体来解决这个问题。室内和室外基准测试的实验结果证实了我们的方法的有效性。它在保持计算效率的同时实现了最先进的定位精度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了如何利用神经辐射场(NeRF)和三维高斯描影(3DGS)等新型视图合成(NVS)技术增强相机姿态估计。然而,NVS渲染的图像常存在模糊问题,影响了其作为相机姿态估计训练数据的可靠性。针对场景坐标回归(SCR)方法中的这一问题,本文提出了一种基于双重标准的过滤机制,该机制能在训练过程中动态识别并丢弃不符合要求的像素。同时,针对稀疏输入场景下的视觉定位问题,本文设计了一种由粗到细的感兴趣点变体,利用稀疏输入的NVS数据辅助定位任务。实验证明,该方法在室内外基准测试中都取得了卓越的效果,实现了高定位精度与计算效率。
Key Takeaways
- NVS技术如NeRF和3DGS能增强相机姿态估计,通过扩展训练数据使用渲染图像。
- NVS渲染的图像常存在模糊问题,影响作为相机姿态估计训练数据的可靠性。
- 针对SCR方法,提出了一种基于双重标准的过滤机制,能动态识别并丢弃训练中的不符合要求的像素。
- 该双重标准包括实时SCR重投影误差和坐标回归域内的梯度阈值。
- 对于稀疏输入场景下的视觉定位问题,设计了一种利用稀疏输入NVS数据的粗到细PoI变体解决方案。
- 实验证明该方法在室内外基准测试中实现高定位精度与计算效率。
点此查看论文截图