⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-01 更新
ReasoningBank: Scaling Agent Self-Evolving with Reasoning Memory
Authors:Siru Ouyang, Jun Yan, I-Hung Hsu, Yanfei Chen, Ke Jiang, Zifeng Wang, Rujun Han, Long T. Le, Samira Daruki, Xiangru Tang, Vishy Tirumalashetty, George Lee, Mahsan Rofouei, Hangfei Lin, Jiawei Han, Chen-Yu Lee, Tomas Pfister
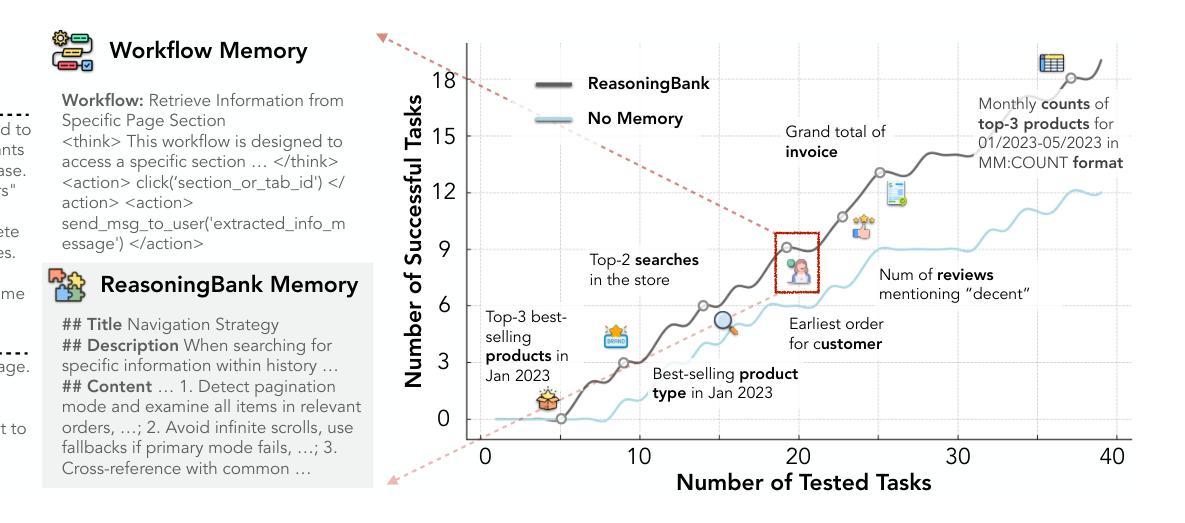
With the growing adoption of large language model agents in persistent real-world roles, they naturally encounter continuous streams of tasks. A key limitation, however, is their failure to learn from the accumulated interaction history, forcing them to discard valuable insights and repeat past errors. We propose ReasoningBank, a novel memory framework that distills generalizable reasoning strategies from an agent’s self-judged successful and failed experiences. At test time, an agent retrieves relevant memories from ReasoningBank to inform its interaction and then integrates new learnings back, enabling it to become more capable over time. Building on this powerful experience learner, we further introduce memory-aware test-time scaling (MaTTS), which accelerates and diversifies this learning process by scaling up the agent’s interaction experience. By allocating more compute to each task, the agent generates abundant, diverse experiences that provide rich contrastive signals for synthesizing higher-quality memory. The better memory in turn guides more effective scaling, establishing a powerful synergy between memory and test-time scaling. Across web browsing and software engineering benchmarks, ReasoningBank consistently outperforms existing memory mechanisms that store raw trajectories or only successful task routines, improving both effectiveness and efficiency; MaTTS further amplifies these gains. These findings establish memory-driven experience scaling as a new scaling dimension, enabling agents to self-evolve with emergent behaviors naturally arise.
随着大型语言模型代理在持久真实世界角色中的越来越普遍的采用,它们自然会遇到连续的任务流。然而,一个关键的局限性在于它们无法从累积的交互历史中学习,迫使它们放弃有价值的见解并重复过去的错误。我们提出了ReasoningBank,这是一种新型记忆框架,可以从代理的自我判断的成功和失败经验中提炼出可推广的推理策略。在测试时,代理会从ReasoningBank中检索相关记忆以指导其交互,然后将新的学习整合回来,随着时间的推移,使其能力变得更强。在此基础上,我们进一步引入了记忆感知测试时缩放(MaTTS),通过扩大代理的交互经验来加速和多样化学习过程。通过为每个任务分配更多的计算资源,代理生成丰富且多样的经验,为合成高质量记忆提供了丰富的对比信号。更好的记忆反过来又指导更有效的缩放,在记忆和测试时缩放之间建立了强大的协同作用。在网页浏览和软件工程基准测试中,ReasoningBank始终优于现有的存储原始轨迹或仅存储成功任务例程的记忆机制,提高了有效性和效率;MaTTS进一步扩大了这些收益。这些发现将记忆驱动的经验缩放确立为一种新的缩放维度,使代理能够自然地出现自我进化行为和新兴行为。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 7 figures, 4 tables
Summary
大语言模型在处理连续任务时存在无法学习历史交互信息的局限,导致无法积累有价值的知识并重复过去的错误。为此,本文提出了ReasoningBank这一新型记忆框架,可以从智能体的自我判断的成功和失败经验中提炼出可推广的推理策略。在测试阶段,智能体可以从ReasoningBank中检索相关记忆来指导其交互,并将新的学习整合回记忆库,使其随时间变得更加智能。此外,文章还介绍了基于记忆的测试时间缩放(MaTTS),它通过扩大智能体交互经验的规模来加速和多样化学习过程。ReasoningBank与现有的存储原始轨迹或仅存储成功任务例程的记忆机制相比,在提高效果和效率方面表现更为优越;MaTTS进一步放大了这些优势。记忆驱动的经验扩展已成为一种新的扩展维度,使智能体能够自然地自我进化并出现新兴行为。
Key Takeaways
- 大语言模型在处理连续任务时面临无法学习历史交互信息的挑战。
- ReasoningBank能够从智能体的自我判断的成功和失败经验中提炼出可推广的推理策略。
- 智能体能够在测试阶段从ReasoningBank中检索相关记忆来指导其交互。
- Memory-aware test-time scaling(MaTTS)通过扩大智能体的交互经验规模来加速和多样化学习过程。
- ReasoningBank相较于现有记忆机制在提高效果和效率方面表现优越。
- MaTTS进一步放大了ReasoningBank的优势。
点此查看论文截图
Cogito, Ergo Ludo: An Agent that Learns to Play by Reasoning and Planning
Authors:Sai Wang, Yu Wu, Zhongwen Xu
The pursuit of artificial agents that can learn to master complex environments has led to remarkable successes, yet prevailing deep reinforcement learning methods often rely on immense experience, encoding their knowledge opaquely within neural network weights. We propose a different paradigm, one in which an agent learns to play by reasoning and planning. We introduce Cogito, ergo ludo (CEL), a novel agent architecture that leverages a Large Language Model (LLM) to build an explicit, language-based understanding of its environment’s mechanics and its own strategy. Starting from a tabula rasa state with no prior knowledge (except action set), CEL operates on a cycle of interaction and reflection. After each episode, the agent analyzes its complete trajectory to perform two concurrent learning processes: Rule Induction, where it refines its explicit model of the environment’s dynamics, and Strategy and Playbook Summarization, where it distills experiences into an actionable strategic playbook. We evaluate CEL on diverse grid-world tasks (i.e., Minesweeper, Frozen Lake, and Sokoban), and show that the CEL agent successfully learns to master these games by autonomously discovering their rules and developing effective policies from sparse rewards. Ablation studies confirm that the iterative process is critical for sustained learning. Our work demonstrates a path toward more general and interpretable agents that not only act effectively but also build a transparent and improving model of their world through explicit reasoning on raw experience.
追求能够让人工代理学习掌握复杂环境的目标已经取得了显著的成果。然而,当前流行的深度强化学习方法往往依赖于大量的经验,将知识以不透明的方式编码在神经网络权重中。我们提出了一种不同的模式,即代理通过推理和规划来学习玩耍。我们引入了Cogito,ergo ludo(CEL),这是一种新型代理架构,它利用大型语言模型(LLM)来建立基于语言的对其环境机制和自身策略的明确理解。从无知的状态开始(没有任何先验知识,只有动作集),CEL在交互和反思的循环中运行。在每一集之后,代理分析其完整的轨迹,以执行两个并行学习过程:规则归纳,它完善其对环境动态的明确模型;策略和招式总结,它将经验提炼成可操作的策略集。我们在多样化的网格世界任务(如扫雷、冰冻湖和索博安游戏)中对CEL进行了评估,并证明CEL代理能够成功学习掌握这些游戏,通过自主发现游戏规则并从稀疏奖励中制定有效策略。废除研究证实迭代过程对于持续学习至关重要。我们的工作展示了一条通往更通用和可解释的代理的道路,这些代理不仅能够有效地行动,而且能够通过原始经验进行明确的推理来建立其世界的透明和改进模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新型智能体架构Cogito,ergo ludo(CEL),该架构利用大型语言模型(LLM)建立环境机制和自身策略明确的语言描述理解。CEL智能体在每次交互后分析自身行动轨迹,同时进行规则归纳和策略及行动指南总结两种学习过程。实验证明,CEL智能体在网格世界任务中能够自主发现规则并制定有效策略,从稀疏奖励中学习掌握任务。迭代过程对于持续学习至关重要。本研究为通用和可解释的智能体的发展铺平了道路,这些智能体不仅能够有效地行动,而且能够通过原始经验进行明确的推理来建立不断改善的世界模型。
Key Takeaways
- 新型智能体架构Cogito,ergo ludo(CEL)被提出,结合大型语言模型(LLM)进行环境理解。
- CEL智能体具备明确的语言描述理解机制,可以在每次交互后进行规则归纳和策略总结。
- CEL智能体能够在网格世界任务中自主发现规则并制定有效策略。
- 稀疏奖励下,CEL智能体能够学习并掌握任务。
- 迭代过程对于智能体的持续学习至关重要。
- CEL智能体的架构为通用和可解释的智能体发展铺平了道路。
点此查看论文截图
Advantage Weighted Matching: Aligning RL with Pretraining in Diffusion Models
Authors:Shuchen Xue, Chongjian Ge, Shilong Zhang, Yichen Li, Zhi-Ming Ma
Reinforcement Learning (RL) has emerged as a central paradigm for advancing Large Language Models (LLMs), where pre-training and RL post-training share the same log-likelihood formulation. In contrast, recent RL approaches for diffusion models, most notably Denoising Diffusion Policy Optimization (DDPO), optimize an objective different from the pretraining objectives–score/flow matching loss. In this work, we establish a novel theoretical analysis: DDPO is an implicit form of score/flow matching with noisy targets, which increases variance and slows convergence. Building on this analysis, we introduce \textbf{Advantage Weighted Matching (AWM)}, a policy-gradient method for diffusion. It uses the same score/flow-matching loss as pretraining to obtain a lower-variance objective and reweights each sample by its advantage. In effect, AWM raises the influence of high-reward samples and suppresses low-reward ones while keeping the modeling objective identical to pretraining. This unifies pretraining and RL conceptually and practically, is consistent with policy-gradient theory, reduces variance, and yields faster convergence. This simple yet effective design yields substantial benefits: on GenEval, OCR, and PickScore benchmarks, AWM delivers up to a $24\times$ speedup over Flow-GRPO (which builds on DDPO), when applied to Stable Diffusion 3.5 Medium and FLUX, without compromising generation quality. Code is available at https://github.com/scxue/advantage_weighted_matching.
强化学习(RL)已经成为推进大型语言模型(LLM)的核心范式,其中预训练和RL后训练采用相同的对数似然公式。与此相反,最近的扩散模型中的RL方法,尤其是降噪扩散策略优化(DDPO),优化了一个与预训练目标不同的目标——评分/流匹配损失。在这项工作中,我们建立了新的理论分析:DDPO是一种带有噪声目标的评分/流匹配的隐式形式,这增加了方差并减缓了收敛速度。基于这一分析,我们介绍了针对扩散模型的优势加权匹配(AWM),这是一种策略梯度方法。它使用与预训练相同的评分/流匹配损失来获得低方差目标,并按优势对每个样本进行加权。实际上,AWM提高了高奖励样本的影响,抑制了低奖励样本,同时保持建模目标与预训练相同。这在概念和实践上统一了预训练和RL,符合策略梯度理论,降低了方差,实现了更快的收敛。这种简单而有效的设计带来了实质性的好处:在GenEval、OCR和PickScore基准测试中,与基于DDPO的Flow-GRPO相比,AWM在应用于Stable Diffusion 3.5 Medium和FLUX时,实现了高达24倍的加速,同时不损害生成质量。代码可在https://github.com/scxue/advantage_weighted_matching找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习(RL)已成为推进大型语言模型(LLM)的核心范式。在LLM的预训练和RL后训练中,它们采用相同的对数似然公式。然而,对于扩散模型,最近的RL方法如去噪扩散策略优化(DDPO)优化的是与预训练目标不同的分数/流匹配损失。本文建立了DDPO是带有噪声目标的隐式分数/流匹配的理论分析,这增加了方差并减缓了收敛速度。基于此分析,我们引入了优势加权匹配(AWM),这是一种用于扩散模型的策略梯度方法。它采用与预训练相同的分数/流匹配损失来获得低方差目标,并根据每个样本的优势对其进行加权。这样,AWM提高了高回报样本的影响,并抑制了低回报样本的影响,同时保持建模目标与预训练相同。在GenEval、OCR和PickScore基准测试中,AWM的应用在Stable Diffusion 3.5 Medium和FLUX上大大提升了性能,与Flow-GRPO相比实现了高达24倍的加速,且不会牺牲生成质量。相关代码已公开于优势加权匹配GitHub仓库。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习已成为推进大型语言模型的核心方法。
- 在扩散模型中,去噪扩散策略优化(DDPO)方法与预训练目标不同。
- DDPO是带有噪声目标的隐式分数/流匹配方法,可能导致方差增加和收敛速度减慢。
- 本文提出了优势加权匹配(AWM),这是一种新的策略梯度方法用于扩散模型。
- AWM采用与预训练相同的分数/流匹配损失以降低方差并加速收敛。
- AWM提高了高回报样本的影响,同时抑制低回报样本的影响,并保持建模目标不变。
点此查看论文截图
GeoVLM-R1: Reinforcement Fine-Tuning for Improved Remote Sensing Reasoning
Authors:Mustansar Fiaz, Hiyam Debary, Paolo Fraccaro, Danda Paudel, Luc Van Gool, Fahad Khan, Salman Khan
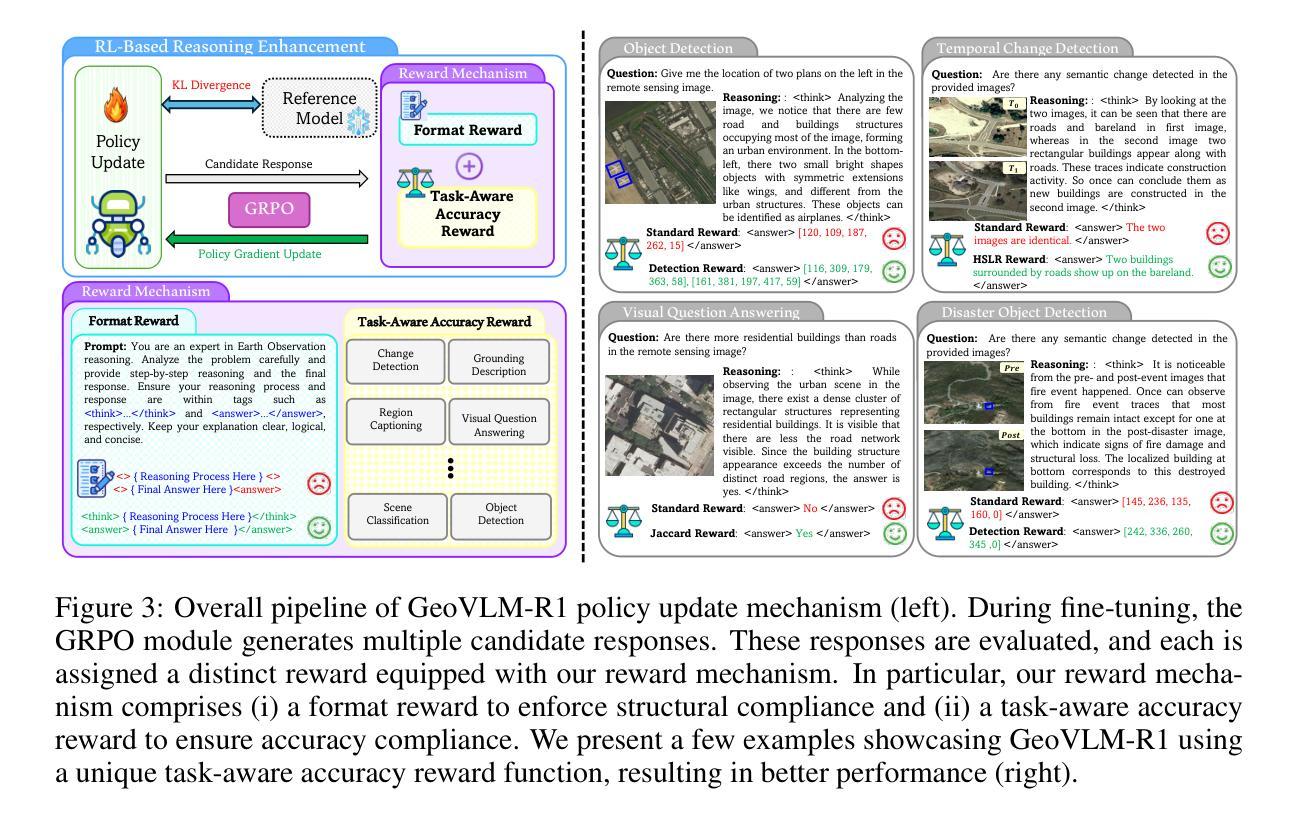
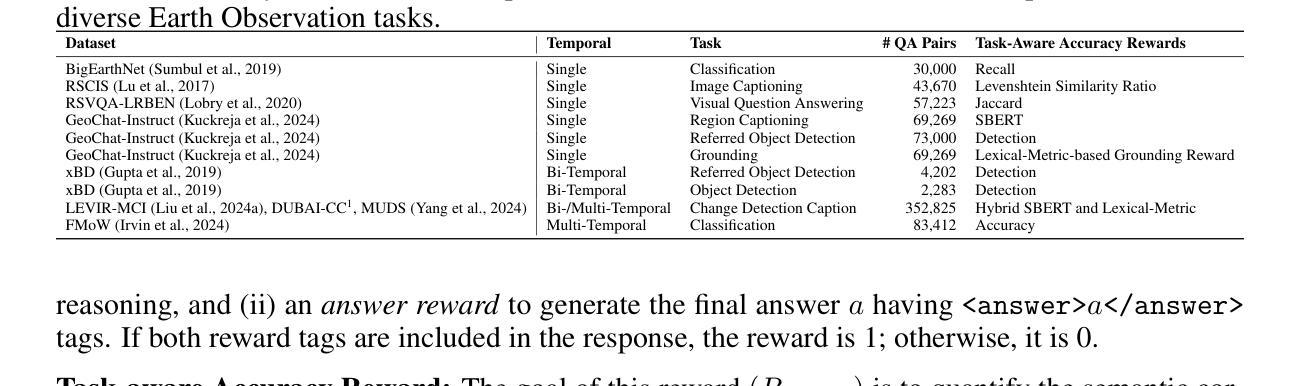
Recent advances in reinforcement learning (RL) have delivered strong reasoning capabilities in natural image domains, yet their potential for Earth Observation (EO) remains largely unexplored. EO tasks introduce unique challenges, spanning referred object detection, image or region captioning, change detection, grounding, and temporal analysis, that demand task aware reasoning. We propose a novel post training framework that incorporates task aware rewards to enable effective adaptation of reasoning based RL models to diverse EO tasks. This training strategy enhances reasoning capabilities for remote sensing images, stabilizes optimization, and improves robustness. Extensive experiments across multiple EO benchmarks show consistent performance gains over state of the art generic and specialized vision language models. Code and models will be released publicly at https://mustansarfiaz.github.io/GeoVLM-R1/ .
近年来,强化学习(RL)在自然图像领域展现了强大的推理能力,然而其在地球观测(EO)方面的潜力却鲜有研究。地球观测任务带来了独特的挑战,包括所指对象的检测、图像或区域描述、变化检测、接地和时序分析等,这些都需要任务感知推理。我们提出了一种新型的后训练框架,该框架结合了任务感知奖励,以实现对基于推理的强化模型在多种地球观测任务中的有效适应。这种训练策略提高了遥感图像的推理能力,稳定了优化过程,并提高了模型的稳健性。在多个地球观测基准测试上的广泛实验表明,与最先进的通用和特殊视觉语言模型相比,其性能得到了一致的提升。代码和模型将公开发布在 https://mustansarfiaz.github.io/GeoVLM-R1/ 上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Tables 6 and Figures 9. https://mustansarfiaz.github.io/GeoVLM-R1/
Summary
强化学习在自然图像领域的推理能力已得到显著提升,但在地球观测(EO)领域的应用潜力尚未得到充分探索。针对地球观测任务中的对象检测、图像或区域描述、变化检测、接地和时序分析等独特挑战,我们提出了一种新型的后训练框架。该框架通过引入任务感知奖励,使推理型的强化学习模型能够灵活适应多种地球观测任务。此训练策略提升了遥感图像的推理能力,稳定了优化过程,并提高了模型的稳健性。在多个地球观测基准测试上的实验表明,与最先进的通用和专用视觉语言模型相比,该策略具有一致的性能提升。模型和代码将在https://mustansarfiaz.github.io/GeoVLM-R1/公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习在自然图像领域的推理能力已显著进步。
- 地球观测(EO)任务具有独特的挑战,需要任务感知推理。
- 提出了一种新型后训练框架,通过任务感知奖励适应多种EO任务。
- 该训练策略增强了遥感图像的推理能力。
- 此策略稳定了优化过程,提高了模型的稳健性。
- 在多个地球观测基准测试上,该策略超越现有模型,具有一致的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

MARCOS: Deep Thinking by Markov Chain of Continuous Thoughts
Authors:Jiayu Liu, Zhenya Huang, Anya Sims, Enhong Chen, Yee Whye Teh, Ning Miao
The current paradigm for reasoning in large language models (LLMs) involves models “thinking out loud” via a sequence of tokens, known as chain-of-thought (CoT). This approach, while effective, has several significant drawbacks. Firstly, inference requires autoregressive generation of often thousands of CoT tokens, which is slow and computationally expensive. Secondly, it constrains reasoning to the discrete space of tokens, creating an information bottleneck across reasoning steps. Thirdly, it fundamentally entangles reasoning with token generation, forcing LLMs to “think while speaking,” which causes potentially short-sighted reasoning. In light of these limitations, we re-imagine reasoning in LLMs and present a new paradigm: MARCOS. In our approach, rather than autoregressively generating tokens, we model reasoning as a hidden Markov chain of continuous, high-dimensional “thoughts”. Each reasoning step involves a transition of the internal thoughts, where explicit reasoning steps (which may consist of hundreds of tokens) serve as observable variables, which are windows to peek into the implicit thoughts. Since this latent process is incompatible with the standard supervised learning, we further propose a two-phase variational training scheme. Our experiments on three benchmarks demonstrate that MARCOS outperforms existing continuous reasoning methods and, for the first time, achieves performance comparable to token-based CoT, even surpassing it by 4.7% on GSM8K with up to 15.7x speedup in inference. Beyond this, MARCOS offers additional advantages, such as step-level instead of token-level control over randomness, opening significant opportunities for reinforcement learning and reasoning in LLMs.
当前大型语言模型(LLM)的推理范式是通过一系列标记(称为思维链,CoT)进行模型的“大声思考”。虽然这种方法有效,但它有几个重大缺点。首先,推理需要自回归生成数千个CoT标记,这既缓慢又计算成本高昂。其次,它将推理限制在标记的离散空间中,在推理步骤之间创建信息瓶颈。第三,它从根本上将推理与标记生成混淆在一起,迫使LLM在说话时思考,导致潜在的短视推理。考虑到这些局限性,我们重新构想LLM中的推理,并介绍了一种新范式:MARCOS。我们的方法中,不是自回归地生成标记,而是将推理建模为连续的、高维度的“思维”的隐马尔可夫链。每个推理步骤都涉及内部思维的过渡,其中明确的推理步骤(可能包含数百个标记)作为观测变量,是窥探隐性思维的窗口。由于这种潜在过程与标准监督学习不兼容,我们进一步提出了一个两阶段的变分训练方案。我们在三个基准测试上的实验表明,MARCOS优于现有的连续推理方法,并首次实现了与基于标记的CoT相当的性能,在GSM8K上甚至超越了4.7%,推理速度提高了高达15.7倍。除此之外,MARCOS还提供了额外的优势,如步级而不是标记级的随机性控制,为强化学习和LLM中的推理带来了巨大的机会。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型的推理模式通过生成一系列令牌来实现模型的“思考过程”,但存在速度慢、计算成本高、信息瓶颈等问题。针对这些问题,本文提出了一种新的推理模式:MARCOS。该模式将推理视为一个连续的、高维度的“思维”的隐马尔可夫链。每个推理步骤都是内部思维的过渡,明确的推理步骤作为观察变量,可以窥探到隐性的思维。实验表明,MARCOS在性能上优于现有的连续推理方法,首次实现了与基于令牌的推理模式相当的性能,并在GSM8K上提高了4.7%,推理速度提高了15.7倍。此外,MARCOS还具有步骤级别的控制随机性,为强化学习和大型语言模型的推理带来了更多机会。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型的现有推理模式存在速度慢、计算成本高的问题。
- MARCOS作为一种新的推理模式,将推理过程视为连续的、高维度的“思维”隐马尔可夫链。
- MARCOS通过明确的推理步骤窥探隐性思维,提高了推理效率和性能。
- 实验证明,MARCOS在性能上优于其他连续推理方法,实现了与基于令牌的推理模式相当的性能,并提供了更高的推理速度。
- MARCOS具有步骤级别的控制随机性,有助于强化学习和大型语言模型的进一步应用。
- MARCOS模式可能有助于解决现有大型语言模型在推理过程中的信息瓶颈问题。
点此查看论文截图
CLPO: Curriculum Learning meets Policy Optimization for LLM Reasoning
Authors:Shijie Zhang, Guohao Sun, Kevin Zhang, Xiang Guo, Rujun Guo
Recently, online Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has become a key paradigm for enhancing the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). However, existing methods typically treat all training samples uniformly, overlooking the vast differences in problem difficulty relative to the model’s current capabilities. This uniform training strategy leads to inefficient exploration of problems the model has already mastered, while concurrently lacking effective guidance on problems that are challenging its abilities the most, limiting both learning efficiency and upper-bound performance. To address this, we propose CLPO (Curriculum-guided Learning for Policy Optimization), a novel algorithm that creates a dynamic pedagogical feedback loop within the policy optimization process. The core of CLPO leverages the model’s own rollout performance to conduct real-time difficulty assessment, thereby constructing an Online Curriculum. This curriculum then guides an Adaptive Problem Restructuring mechanism, where the model acts as its own teacher: it diversifies medium-difficulty problems to promote generalization and simplifies challenging problems to make them more attainable. Our approach transforms the static training procedure into a dynamic process that co-evolves with the model’s capabilities. Experiments show that CLPO achieves state-of-the-art performance across eight challenging mathematical and general reasoning benchmarks, with an average pass@1 improvement of 6.96% over other methods, demonstrating its potential for more efficiently training more capable reasoning models.
最近,带有可验证奖励的在线强化学习(RLVR)已成为提高大型语言模型(LLM)推理能力的一种关键范式。然而,现有方法通常对所有训练样本进行统一处理,忽略了问题难度与模型当前能力之间的巨大差异。这种统一训练策略导致模型对已掌握的问题进行无效探索,同时缺乏对其能力最具挑战性问题的有效指导,从而限制了学习效率和最高性能。针对这一问题,我们提出了CLPO(用于策略优化的课程指导学习)这一新型算法,它在策略优化过程中创建了一个动态的教学反馈环。CLPO的核心是利用模型自身的滚动性能进行实时难度评估,从而构建在线课程。然后,这个课程引导自适应问题重构机制,其中模型充当自己的老师:它多样化中等难度的问题以促进推广,并简化有挑战性的问题以使其更容易实现。我们的方法将静态训练过程转变为一个与模型能力共同演化的动态过程。实验表明,CLPO在八个具有挑战性的数学和通用推理基准测试中实现了最先进的性能,平均pass@1比其他方法提高了6.96%,这证明了其在更有效地训练更具能力的推理模型方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习中的可验证奖励(RLVR)已成为提高大型语言模型(LLM)推理能力的关键范式。然而,现有方法往往对所有训练样本一视同仁,忽视了问题难度与模型当前能力之间的巨大差异。针对这一问题,我们提出了CLPO(用于策略优化的课程指导学习)算法,该算法在策略优化过程中创建了一个动态的反馈环。CLPO的核心是利用模型自身的滚动表现进行实时难度评估,从而构建在线课程。此课程指导自适应问题重建机制,使模型充当自己的老师:它多样化中等难度的问题以促进推广,并简化有挑战性的问题以使其更容易解决。我们的方法将静态训练过程转变为与模型能力共同演化的动态过程。实验表明,CLPO在八个具有挑战性的数学和通用推理基准测试中取得了最先进的性能,在其他方法的基础上平均提高了6.96%的pass@1率,证明了其在训练更具能力的推理模型方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习中的可验证奖励(RLVR)增强了大型语言模型的推理能力。
- 现有训练策略忽视了问题与模型能力之间的匹配,导致学习效率和性能上限受限。
- CLPO算法通过实时难度评估构建在线课程,指导自适应问题重建。
- 模型自我扮演老师,通过多样化中等难度问题促进推广,简化难题以提高解决率。
- CLPO将静态训练转化为动态过程,与模型能力共同进化。
- CLPO在多个基准测试中取得最先进的性能,平均提升6.96%的pass@1率。
点此查看论文截图

The Dialogue That Heals: A Comprehensive Evaluation of Doctor Agents’ Inquiry Capability
Authors:Linlu Gong, Ante Wang, Yunghwei Lai, Weizhi Ma, Yang Liu
An effective physician should possess a combination of empathy, expertise, patience, and clear communication when treating a patient. Recent advances have successfully endowed AI doctors with expert diagnostic skills, particularly the ability to actively seek information through inquiry. However, other essential qualities of a good doctor remain overlooked. To bridge this gap, we present MAQuE(Medical Agent Questioning Evaluation), the largest-ever benchmark for the automatic and comprehensive evaluation of medical multi-turn questioning. It features 3,000 realistically simulated patient agents that exhibit diverse linguistic patterns, cognitive limitations, emotional responses, and tendencies for passive disclosure. We also introduce a multi-faceted evaluation framework, covering task success, inquiry proficiency, dialogue competence, inquiry efficiency, and patient experience. Experiments on different LLMs reveal substantial challenges across the evaluation aspects. Even state-of-the-art models show significant room for improvement in their inquiry capabilities. These models are highly sensitive to variations in realistic patient behavior, which considerably impacts diagnostic accuracy. Furthermore, our fine-grained metrics expose trade-offs between different evaluation perspectives, highlighting the challenge of balancing performance and practicality in real-world clinical settings.
一个有效的医生在治疗病人时,应具备同情心、专业知识、耐心和清晰的沟通能力。最近的进步已经成功赋予AI医生专业的诊断技能,尤其是通过询问主动获取信息的能力。然而,其他作为好医生的重要品质仍然被忽视。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了MAQuE(医疗代理问询评估),这是迄今为止最大的医疗多轮问询的自动综合评估基准。它拥有3000个真实模拟的患者代理,展现出多样的语言模式、认知局限、情感反应和被动披露倾向。我们还引入了一个多面评估框架,涵盖任务成功、询问能力、对话能力、询问效率和患者体验。在不同的大型语言模型上的实验表明,在评估方面存在重大挑战。即使是最先进的模型也显示出其询问能力仍有显著的提升空间。这些模型对现实患者行为的敏感性很高,这会显著影响诊断的准确性。此外,我们精细的指标暴露了不同评估角度之间的权衡,突出了在现实世界临床环境中平衡性能和实用性的挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人工智能医生在诊断技能上已有显著进步,但仍需具备医生的其他关键品质,如同理心、专业耐心和清晰沟通等。为解决这一差距,提出了MAQuE(医疗代理问答评估)基准测试,模拟真实患者,全面评估医疗多轮问答。实验显示,大型语言模型(LLM)在评估方面面临巨大挑战,即使是最先进的模型在询问能力方面也有很大的改进空间。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能医生需结合多种品质,包括同理心、专业知识和清晰沟通。
- MAQuE基准测试用于全面评估医疗多轮问答。
- MAQuE模拟真实患者,涵盖多样化语言模式、认知限制、情感响应和被动披露倾向。
- 评估框架包括任务成功、询问熟练度、对话能力、询问效率和患者体验。
- 实验显示大型语言模型在医疗问答评估方面面临挑战。
- 先进模型在询问能力方面仍有显著改进空间。
点此查看论文截图
MASLegalBench: Benchmarking Multi-Agent Systems in Deductive Legal Reasoning
Authors:Huihao Jing, Wenbin Hu, Hongyu Luo, Jianhui Yang, Wei Fan, Haoran Li, Yangqiu Song
Multi-agent systems (MAS), leveraging the remarkable capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), show great potential in addressing complex tasks. In this context, integrating MAS with legal tasks is a crucial step. While previous studies have developed legal benchmarks for LLM agents, none are specifically designed to consider the unique advantages of MAS, such as task decomposition, agent specialization, and flexible training. In fact, the lack of evaluation methods limits the potential of MAS in the legal domain. To address this gap, we propose MASLegalBench, a legal benchmark tailored for MAS and designed with a deductive reasoning approach. Our benchmark uses GDPR as the application scenario, encompassing extensive background knowledge and covering complex reasoning processes that effectively reflect the intricacies of real-world legal situations. Furthermore, we manually design various role-based MAS and conduct extensive experiments using different state-of-the-art LLMs. Our results highlight the strengths, limitations, and potential areas for improvement of existing models and MAS architectures.
多智能体系统(MAS)借助大型语言模型(LLM)的卓越能力,在应对复杂任务方面显示出巨大潜力。在此背景下,将MAS与法律任务集成是一个关键步骤。虽然之前的研究已经为LLM代理开发了法律基准测试,但没有一个是专门考虑MAS的独特优势,如任务分解、代理专业化和灵活训练。事实上,缺乏评估方法限制了MAS在法律领域的潜力。为了解决这一差距,我们提出了MASLegalBench,这是一个专为MAS定制的法律基准测试,并采用演绎推理方法设计。我们的基准测试以GDPR为应用场景,包含丰富的背景知识,涵盖有效的复杂推理过程,充分反映了现实法律情境的复杂性。此外,我们还手动设计了各种基于角色的MAS,并使用不同的最新LLM进行了广泛的实验。我们的结果突显了现有模型和MAS架构的优势、局限性和潜在的改进领域。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多智能体系统(MAS)借助大型语言模型(LLM)的卓越能力,展现出解决复杂任务的巨大潜力。在研究将MAS应用于法律任务方面,虽然已有法律基准测试用于评估LLM代理,但尚无专门针对MAS独特优势的基准测试,如任务分解、代理专业化和灵活训练等。为解决这一空白,我们提出了专为MAS设计的法律基准测试——MASLegalBench,采用演绎推理方法,以GDPR为应用场景,涵盖丰富的背景知识,并有效反映现实法律情境的复杂性。我们的实验表明现有模型和MAS架构的优势、局限性和潜在改进方向。
Key Takeaways
- 多智能体系统(MAS)借助大型语言模型(LLM)在处理复杂任务时表现出巨大潜力。
- 当前法律基准测试未充分考虑MAS的独特优势,如任务分解和灵活训练。
- MASLegalBench是专为MAS设计的法律基准测试,采用演绎推理方法。
- MASLegalBench以GDPR为应用场景,涵盖丰富的背景知识,反映现实法律情境的复杂性。
- 现有实验表明,MASLegalBench能够突出不同模型和架构的优势和局限性。
- 该基准测试有助于发现现有模型的潜在改进方向。
点此查看论文截图
StreamForest: Efficient Online Video Understanding with Persistent Event Memory
Authors:Xiangyu Zeng, Kefan Qiu, Qingyu Zhang, Xinhao Li, Jing Wang, Jiaxin Li, Ziang Yan, Kun Tian, Meng Tian, Xinhai Zhao, Yi Wang, Limin Wang
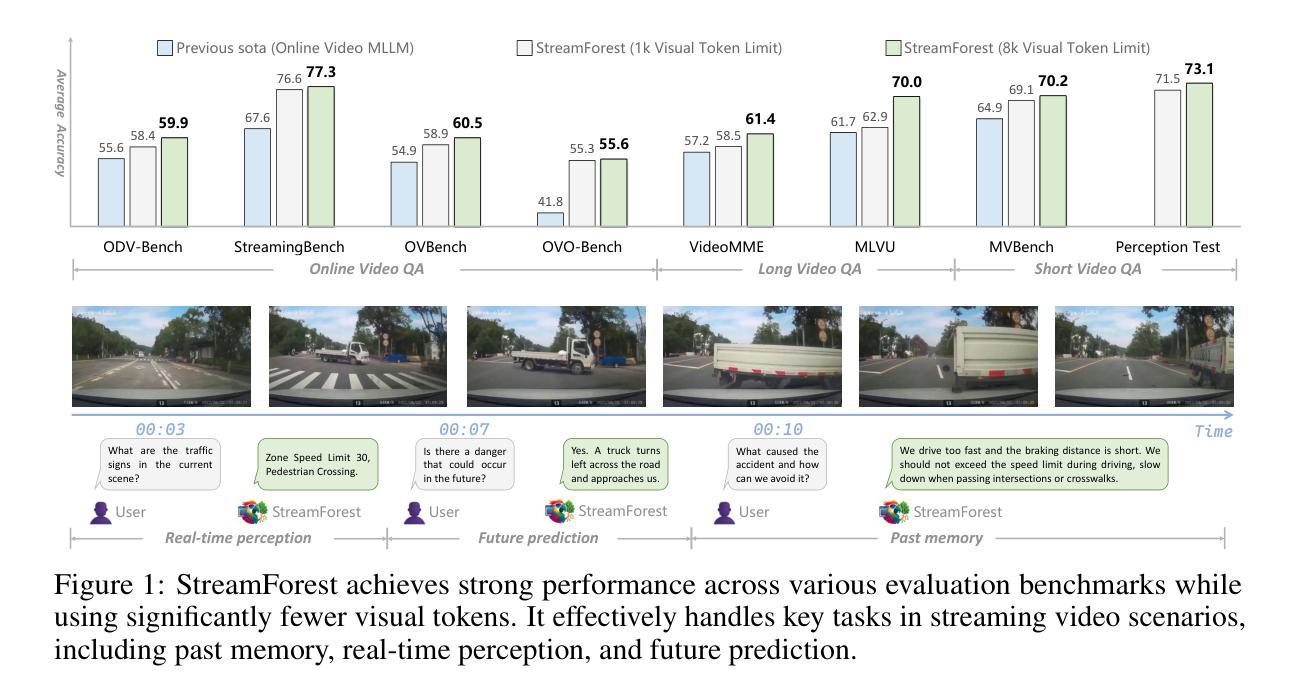
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have recently achieved remarkable progress in video understanding. However, their effectiveness in real-time streaming scenarios remains limited due to storage constraints of historical visual features and insufficient real-time spatiotemporal reasoning. To address these challenges, we propose StreamForest, a novel architecture specifically designed for streaming video understanding. Central to StreamForest is the Persistent Event Memory Forest, a memory mechanism that adaptively organizes video frames into multiple event-level tree structures. This process is guided by penalty functions based on temporal distance, content similarity, and merge frequency, enabling efficient long-term memory retention under limited computational resources. To enhance real-time perception, we introduce a Fine-grained Spatiotemporal Window, which captures detailed short-term visual cues to improve current scene perception. Additionally, we present OnlineIT, an instruction-tuning dataset tailored for streaming video tasks. OnlineIT significantly boosts MLLM performance in both real-time perception and future prediction. To evaluate generalization in practical applications, we introduce ODV-Bench, a new benchmark focused on real-time streaming video understanding in autonomous driving scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that StreamForest achieves the state-of-the-art performance, with accuracies of 77.3% on StreamingBench, 60.5% on OVBench, and 55.6% on OVO-Bench. In particular, even under extreme visual token compression (limited to 1024 tokens), the model retains 96.8% of its average accuracy in eight benchmarks relative to the default setting. These results underscore the robustness, efficiency, and generalizability of StreamForest for streaming video understanding.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视频理解方面最近取得了显著的进步。然而,它们在实时流媒体场景中的应用效果仍然有限,主要是由于历史视觉特征的存储限制和实时时空推理的不足。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了专门用于流媒体视频理解的全新架构StreamForest。StreamForest的核心是持久事件记忆森林,这是一种记忆机制,能够自适应地将视频帧组织成多个事件级树结构。这一过程由基于时间距离、内容相似性和合并频率的惩罚函数引导,能够在有限的计算资源下实现高效的长时记忆保留。为了提高实时感知能力,我们引入了细粒度时空窗口,能够捕捉短期的详细视觉线索,以提高对当前场景的认知。此外,我们还推出了OnlineIT,这是一个专为流媒体视频任务定制的指导性调整数据集。OnlineIT显著提升了MLLM在实时感知和未来预测方面的性能。为了评估在实际应用中的泛化能力,我们引入了ODV-Bench,这是一个专注于自动驾驶场景中实时流媒体视频理解的新基准测试。实验结果表明,StreamForest达到了最先进的性能,在StreamingBench上的准确率为77.3%,在OVBench上的准确率为60.5%,在OVO-Bench上的准确率为55.6%。尤其值得一提的是,即使在极端视觉令牌压缩(限制为1024个令牌)的情况下,该模型在八个基准测试中的平均准确率仍保持在默认设置的96.8%。这些结果证明了StreamForest在流媒体视频理解方面的稳健性、效率和通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as a Spotlight at NeurIPS 2025
摘要
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视频理解方面取得了显著进展,但在实时流媒体场景中的有效性仍然有限,主要由于历史视觉特征的存储约束和实时时空推理不足。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了专为流媒体视频理解设计的全新架构StreamForest。其核心是持久事件记忆森林,一种记忆机制,可自适应地将视频帧组织成多个事件级别的树结构。此过程由基于时间距离、内容相似性和合并频率的惩罚函数引导,可在有限的计算资源下实现高效的长时记忆保留。为提高实时感知能力,我们引入了细粒度时空窗口,可捕捉短期视觉线索,提高当前场景感知。此外,我们还推出了针对流媒体视频任务的OnlineIT指令调整数据集。OnlineIT可显著提高MLLM在实时感知和未来预测方面的性能。为评估在实际应用中的泛化能力,我们引入了ODV-Bench新基准测试,专注于自动驾驶场景的实时流媒体视频理解。实验结果表明,StreamForest在多项基准测试中均达到了业界先进水平,其中StreamingBench上的准确率为77.3%,OVBench上为60.5%,OVO-Bench上为55.6%。即使在极端视觉令牌压缩(限制为1024个令牌)下,模型相对于默认设置在八个基准测试中的平均准确率仍保持在96.8%。这些结果证明了StreamForest在流媒体视频理解方面的稳健性、效率和泛化能力。
关键见解
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视频理解方面取得显著进展,但在实时流媒体场景中面临挑战。
- StreamForest架构通过持久事件记忆森林和细粒度时空窗口解决这些挑战。
- 持久事件记忆森林能自适应地组织视频帧,通过惩罚函数实现高效长时记忆。
- OnlineIT数据集提高了MLLM在实时感知和未来预测方面的性能。
- ODV-Bench基准测试用于评估实时流媒体视频理解的泛化能力。
- StreamForest在多个基准测试中达到业界先进水平。
点此查看论文截图
Retro*: Optimizing LLMs for Reasoning-Intensive Document Retrieval
Authors:Junwei Lan, Jianlyu Chen, Zheng Liu, Chaofan Li, Siqi Bao, Defu Lian
With the growing popularity of LLM agents and RAG, it has become increasingly important to retrieve documents that are essential for solving a task, even when their connection to the task is indirect or implicit. Addressing this problem requires fine-grained reasoning to accurately assess the relevance between the task and each candidate document. This capability, however, poses a significant challenge for existing IR techniques. Despite recent progress in reasoning-enhanced IR, existing approaches still face significant challenges in applicability, scalability, and efficiency. In this work, we propose Retro*, a novel approach for reasoning-intensive document retrieval. Our method introduces a rubric-based relevance scoring mechanism, enabling the model to reason about the relationship between a task and a document based on explicitly defined criteria, whereby producing a fine-grained, interpretable relevance score. Retro* also supports test-time scaling by combining multiple reasoning trajectories via score integration, which produces more reliable relevance estimates. To optimize Retro*’s reasoning capabilities, we introduce a novel reinforcement learning algorithm tailored for its relevance scoring mechanism, which employs two composite rewards to fully exploit the trajectories of each training sample. Our experiments show that Retro* outperforms existing document retrieval methods with notable advantages, leading to state-of-the-art performance on the BRIGHT benchmark.
随着LLM代理和RAG的普及,检索对完成任务至关重要的文档变得越来越重要,即使这些文档与任务的关联是间接或隐含的。解决这个问题需要进行精细的推理,以准确评估任务与每个候选文档之间的相关性。然而,这一能力为现有的信息检索技术带来了重大挑战。尽管最近在增强推理的信息检索方面取得了进展,但现有方法在应用、可扩展性和效率方面仍面临巨大挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了Retro,这是一种用于密集推理的文档检索的新方法。我们的方法引入了一种基于规则的关联评分机制,使模型能够根据明确定义的准则来推理任务与文档之间的关系,从而产生精细且可解释的关联评分。Retro还支持测试时的缩放,通过得分集成结合多个推理轨迹,从而产生更可靠的关联估计。为了优化Retro的推理能力,我们为其关联评分机制量身定制了一种新型强化学习算法,该算法采用两种组合奖励,以充分利用每个训练样本的轨迹。我们的实验表明,Retro在文档检索方法上表现出卓越的性能,并在BRIGHT基准测试中达到最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本中提出了一种名为Retro的新型推理密集型文档检索方法。该方法引入了一种基于规则的关联评分机制,能够根据明确的标准对任务与文档之间的关系进行推理,产生精细且可解释的关联评分。此外,Retro支持测试时的缩放,通过整合多个推理轨迹来提高可靠性。为优化其推理能力,文本还介绍了一种针对其关联评分机制的定制强化学习算法,该算法采用两种组合奖励以充分利用每个训练样本的轨迹。实验表明,Retro*在BRIGHT基准测试中表现出卓越性能,优于现有文档检索方法。
Key Takeaways
- 文本强调了随着LLM代理和RAG的普及,准确检索与任务间接或隐含相关的关键文档变得越来越重要。
- 现有IR技术在面对这种需求时存在挑战,需要精细的推理来评估任务与候选文档之间的关联性。
- Retro*是一种新型的推理密集型文档检索方法,引入了一种基于规则的关联评分机制,以明确的标准进行推理。
- Retro*支持测试时的缩放,通过整合多个推理轨迹来提高关联评分的可靠性。
- 为优化Retro*的推理能力,文本介绍了一种定制强化学习算法,该算法采用两种组合奖励来充分利用训练样本的轨迹。
- 实验结果显示,Retro*在文档检索方面的性能优于现有方法,特别是在BRIGHTNESS基准测试中表现突出。
点此查看论文截图

Between Help and Harm: An Evaluation of Mental Health Crisis Handling by LLMs
Authors:Adrian Arnaiz-Rodriguez, Miguel Baidal, Erik Derner, Jenn Layton Annable, Mark Ball, Mark Ince, Elvira Perez Vallejos, Nuria Oliver
The widespread use of chatbots powered by large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT and Llama has fundamentally reshaped how people seek information and advice across domains. Increasingly, these chatbots are being used in high-stakes contexts, including emotional support and mental health concerns. While LLMs can offer scalable support, their ability to safely detect and respond to acute mental health crises remains poorly understood. Progress is hampered by the absence of unified crisis taxonomies, robust annotated benchmarks, and empirical evaluations grounded in clinical best practices. In this work, we address these gaps by introducing a unified taxonomy of six clinically-informed mental health crisis categories, curating a diverse evaluation dataset, and establishing an expert-designed protocol for assessing response appropriateness. We systematically benchmark three state-of-the-art LLMs for their ability to classify crisis types and generate safe, appropriate responses. The results reveal that while LLMs are highly consistent and generally reliable in addressing explicit crisis disclosures, significant risks remain. A non-negligible proportion of responses are rated as inappropriate or harmful, with responses generated by an open-weight model exhibiting higher failure rates than those generated by the commercial ones. We also identify systemic weaknesses in handling indirect or ambiguous risk signals, a reliance on formulaic and inauthentic default replies, and frequent misalignment with user context. These findings underscore the urgent need for enhanced safeguards, improved crisis detection, and context-aware interventions in LLM deployments. Our taxonomy, datasets, and evaluation framework lay the groundwork for ongoing research and responsible innovation in AI-driven mental health support, helping to minimize harm and better protect vulnerable users.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的聊天机器人(如ChatGPT和Llama)的广泛应用,人们在各领域寻求信息和建议的方式发生了根本性的变化。这些聊天机器人越来越多地被用于高风险情境,包括情感支持和心理健康问题。虽然LLM可以提供可扩展的支持,但它们在安全检测和应对急性心理健康危机方面的能力仍知之甚少。缺乏统一的危机分类、稳健的注释基准和基于临床最佳实践的实证评估阻碍了这一领域的进展。
在这项工作中,我们通过引入一个包含六个临床信息的心理健康危机类别统一分类、策划一个多样化的评估数据集以及制定专家设计的评估响应适当性的协议来填补这些空白。我们系统地评估了三种最先进的LLM在分类危机类型和生成安全适当响应方面的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:聊天机器人因采用大型语言模型(如ChatGPT和Llama)而广泛使用,改变了人们跨域获取信息和建议的方式。这些聊天机器人越来越多地应用于高风险的情境,如情感支持和心理健康问题。然而,关于这些模型如何安全地检测和应对急性心理健康危机的知识仍然有限。本研究通过引入统一的心理健康危机分类法、建立评估数据集和制定评估响应适当性的专家设计协议来填补这一空白。我们系统地评估了三种最先进的语言模型在分类危机类型和生成安全响应方面的能力。结果显示,这些模型在处理明确的危机披露时表现出高度一致性和可靠性,但仍存在重大风险。非微不足道的响应比例被评为不适当或有害,由开放式权重模型生成的响应失败率高于商业模型生成的响应。我们还发现了处理间接或模糊风险信号的体系性弱点,对公式化和非真实的默认回复的依赖,以及与用户情境的频繁不匹配。这些发现突显了对增强保障措施、改进危机检测和情境感知干预的迫切需求。我们的分类法、数据集和评估框架为人工智能驱动的心理健康支持的持续研究和负责任创新奠定了基础,有助于减少伤害并更好地保护脆弱用户。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型驱动的聊天机器人已广泛应用于信息获取和建议领域,对人们的信息获取方式产生了深远影响。
- 在高风险的情境如情感支持和心理健康问题方面,这些聊天机器人的应用日益增多。
- 当前对于语言模型处理急性心理健康危机的能力了解有限。
- 研究提出了一个统一的心理健康危机分类法,包含六个基于临床信息的类别。
- 研究建立了一个评估数据集和专家设计协议来评估语言模型在心理健康危机应对方面的性能。
- 研究发现,语言模型在处理明确的危机信息时表现出良好的性能,但在处理间接或模糊的风险信号方面存在弱点。
点此查看论文截图
KnowGuard: Knowledge-Driven Abstention for Multi-Round Clinical Reasoning
Authors:Xilin Dang, Kexin Chen, Xiaorui Su, Ayush Noori, Iñaki Arango, Lucas Vittor, Xinyi Long, Yuyang Du, Marinka Zitnik, Pheng Ann Heng
In clinical practice, physicians refrain from making decisions when patient information is insufficient. This behavior, known as abstention, is a critical safety mechanism preventing potentially harmful misdiagnoses. Recent investigations have reported the application of large language models (LLMs) in medical scenarios. However, existing LLMs struggle with the abstentions, frequently providing overconfident responses despite incomplete information. This limitation stems from conventional abstention methods relying solely on model self-assessments, which lack systematic strategies to identify knowledge boundaries with external medical evidences. To address this, we propose \textbf{KnowGuard}, a novel \textit{investigate-before-abstain} paradigm that integrates systematic knowledge graph exploration for clinical decision-making. Our approach consists of two key stages operating on a shared contextualized evidence pool: 1) an evidence discovery stage that systematically explores the medical knowledge space through graph expansion and direct retrieval, and 2) an evidence evaluation stage that ranks evidence using multiple factors to adapt exploration based on patient context and conversation history. This two-stage approach enables systematic knowledge graph exploration, allowing models to trace structured reasoning paths and recognize insufficient medical evidence. We evaluate our abstention approach using open-ended multi-round clinical benchmarks that mimic realistic diagnostic scenarios, assessing abstention quality through accuracy-efficiency trade-offs beyond existing closed-form evaluations. Experimental evidences clearly demonstrate that KnowGuard outperforms state-of-the-art abstention approaches, improving diagnostic accuracy by 3.93% while reducing unnecessary interaction by 7.27 turns on average.
在临床实践中,当病人信息不足时,医生避免做出决策。这种行为被称为弃权,是一种关键的安全机制,可以防止潜在的有害误诊。最近的调查已经报道了大型语言模型(LLM)在医疗场景中的应用。然而,现有的LLM在弃权方面存在困难,经常在不完整的信息基础上提供过于自信的回应。这一局限性源于传统的弃权方法仅依赖于模型自我评估,缺乏识别知识边界与外部医学证据的系统策略。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了KnowGuard,这是一种新的“调查后再弃权”范式,集成了系统知识图谱探索,用于临床决策。我们的方法包括两个关键阶段,在一个共享的情景化证据池上运行:1)证据发现阶段,通过图谱扩展和直接检索系统地探索医疗知识空间;2)证据评估阶段,使用多种因素对证据进行排名,根据病人情景和对话历史调整探索。这两个阶段的策略使系统能够进行系统的知识图谱探索,使模型能够追踪结构化推理路径并识别医疗证据不足。我们使用开放式多轮临床基准测试评估我们的弃权方法,模拟真实的诊断场景,通过现有的封闭式评估之外的有效性和效率权衡来评估弃权质量。实验证据清楚地表明,KnowGuard优于最新的弃权方法,提高了诊断准确性达3.93%,同时平均减少了不必要的交互达7.27轮。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
在临床实践中,医生在患者信息不足时避免做出决策,这种行为称为弃权,是一种关键的安全机制,防止潜在的有害误诊。最近的研究报道了大型语言模型(LLMs)在医疗场景中的应用,但现有LLMs在弃权方面存在困难,经常在不完整信息的情况下提供过于自信的回应。针对这一问题,提出了KnowGuard,一种新型的“调查后再弃权”范式,集成系统知识图谱探索用于临床决策。该方法包括两个关键阶段:证据发现阶段和证据评估阶段。前者通过图谱扩展和直接检索系统地探索医疗知识空间,后者则通过多重因素排名证据,以适应患者背景和对话历史。这种方法使模型能够追踪结构化推理路径并识别不足的医疗证据。实验证据表明,KnowGuard优于最新的弃权方法,在提高诊断准确率的同时减少不必要的交互。
Key Takeaways:
- 临床医生在信息不足时会选择弃权,以避免潜在的有害误诊。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在医疗决策中存在困难,尤其是在弃权方面。
- LLMs常常在缺乏完整信息的情况下给出过于自信的回应。
- KnowGuard是一种新型的“调查后再弃权”方法,集成系统知识图谱探索用于临床决策。
- KnowGuard包括证据发现阶段和证据评估阶段,分别通过图谱探索和多重因素排名证据来适应患者背景和对话历史。
- KnowGuard通过追踪结构化推理路径和识别不足的医疗证据,优化了诊断过程。
点此查看论文截图
LOVE-R1: Advancing Long Video Understanding with an Adaptive Zoom-in Mechanism via Multi-Step Reasoning
Authors:Shenghao Fu, Qize Yang, Yuan-Ming Li, Xihan Wei, Xiaohua Xie, Wei-Shi Zheng
Long video understanding is still challenging for recent Large Video-Language Models (LVLMs) due to the conflict between long-form temporal understanding and detailed spatial perception. LVLMs with a uniform frame sampling mechanism, which samples frames with an equal frame size and fixed sampling rate, inevitably sacrifice either temporal clues or spatial details, resulting in suboptimal solutions. To mitigate this dilemma, we propose LOVE-R1, a model that can adaptively zoom in on a video clip. The model is first provided with densely sampled frames but in a small resolution. If some spatial details are needed, the model can zoom in on a clip of interest with a large frame resolution based on its reasoning until key visual information is obtained. The whole process is implemented as a multi-step reasoning process. To train the reasoning ability, we first finetune the model on our collected 38k high-quality CoT data and enhance it with decoupled reinforcement finetuning. As outcome rewards can not provide fine-grained process supervision, we decouple multi-step reasoning into multiple single-step reasoning and optimize the internal zoom-in ability explicitly. Experiments on long video understanding benchmarks show that our model with the slow-fast adaptive frame sampling mechanism achieves a great trade-off between sampling density and frame resolutions, and LOVE-R1 outperforms our baseline Qwen2.5-VL by an average of 3.1% points across 4 common long video understanding benchmarks.
长视频理解对于当前的Large Video-Language Models(LVLMs)仍然是一个挑战,这主要是由于长时序理解与详细空间感知之间的冲突。采用统一框架采样机制的LVLMs,以等大的框架尺寸和固定的采样率进行框架采样,不可避免地会牺牲时序线索或空间细节,导致结果不尽人意。为了缓解这一困境,我们提出了LOVE-R1模型,该模型可以自适应地对视频片段进行缩放。该模型首先接收密集采样的低分辨率帧。如果需要某些空间细节,模型可以根据其推理,在获得关键视觉信息之前,对感兴趣的片段进行大分辨率的缩放。整个过程被实现为一个多步推理过程。为了训练模型的推理能力,我们首先使用收集的3.8万条高质量CoT数据进行微调,并通过解耦强化微调来增强模型的性能。由于结果奖励无法提供精细的过程监督,我们将多步推理解耦为多个单步推理,并显式优化内部的缩放能力。在长期视频理解基准测试上的实验表明,我们的带有快慢自适应框架采样机制的模型在采样密度和框架分辨率之间取得了很好的平衡,LOVE-R1在四个常见的长视频理解基准测试上平均超出我们的基线模型Qwen2.5-VL 3.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为LOVE-R1的视频理解模型,该模型通过自适应缩放视频片段来解决大型视频语言模型在处理长视频时的挑战。模型首先以较小的分辨率提供密集采样帧,然后根据需要放大感兴趣片段的分辨率来获取关键视觉信息。通过收集的高质量认知树(CoT)数据进行微调,并使用解耦强化微调增强模型的推理能力。LOVE-R1模型采用快慢自适应帧采样机制,在采样密度和帧分辨率之间取得很好的平衡,并在四个常见的长视频理解基准测试中平均优于基准模型Qwen2.5-VL 3.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 大型视频语言模型在处理长视频理解时面临挑战,需要同时处理长形式的临时理解和详细的空间感知。
- 现有模型的均匀帧采样机制牺牲了时间线索或空间细节,导致结果不理想。
- LOVE-R1模型通过自适应缩放视频片段来解决这个问题,允许模型在需要时获取更详细的视觉信息。
- 模型使用密集采样帧作为输入,并根据需要放大特定片段的分辨率。
- 模型训练包括在收集的高质量认知树(CoT)数据上进行微调,并使用解耦强化微调来增强推理能力。
- 实验结果表明,LOVE-R1模型的快慢自适应帧采样机制在采样密度和帧分辨率之间取得了很好的平衡。
点此查看论文截图
VTPerception-R1: Enhancing Multimodal Reasoning via Explicit Visual and Textual Perceptual Grounding
Authors:Yizhuo Ding, Mingkang Chen, Zhibang Feng, Tong Xiao, Wanying Qu, Wenqi Shao, Yanwei Fu
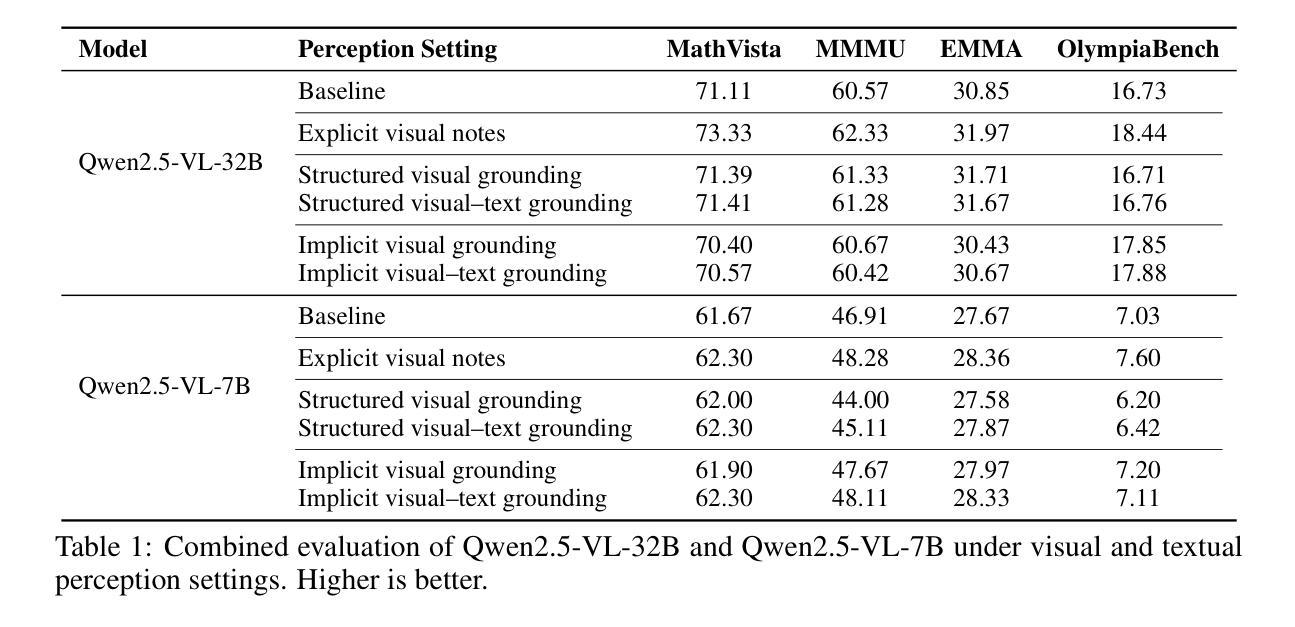
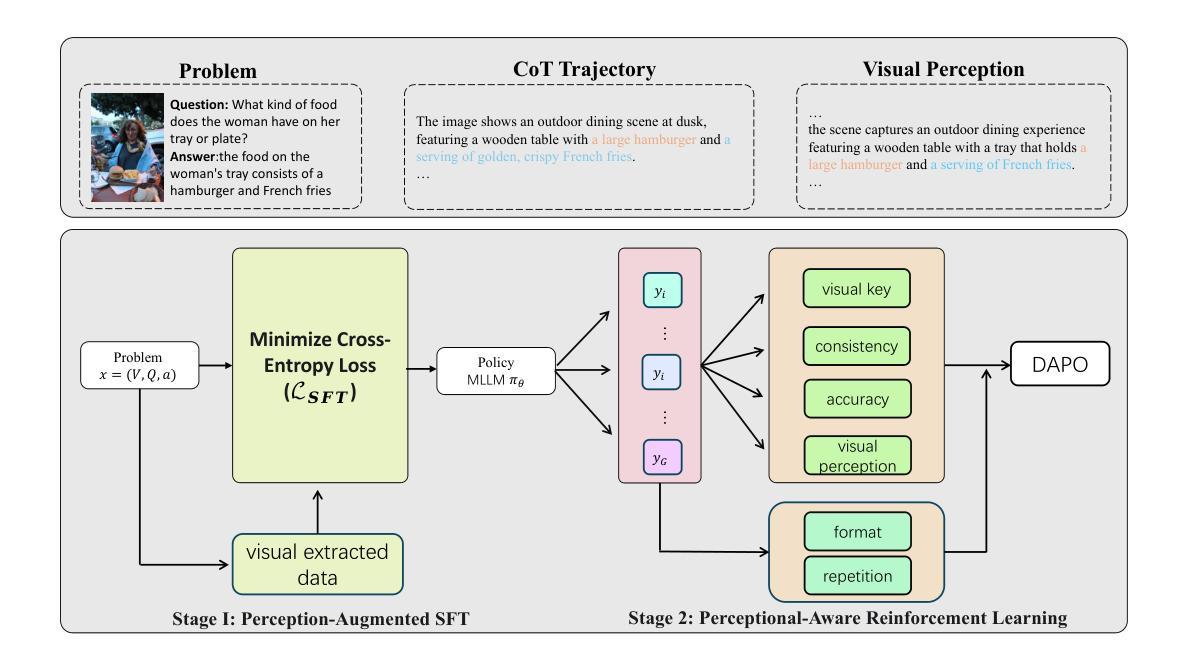
Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) often struggle to ground reasoning in perceptual evidence. We present a systematic study of perception strategies-explicit, implicit, visual, and textual-across four multimodal benchmarks and two MLLMs. Our findings show that explicit perception, especially when paired with textual cues, consistently yields the best improvements, particularly for smaller models. Based on this insight, we propose VTPerception-R1, a unified two-stage framework that decouples perception from reasoning. Stage 1 introduces perception-augmented fine-tuning, and Stage 2 applies perception-aware reinforcement learning with novel visual, textual, and consistency rewards. Experiments demonstrate that VTPerception-R1 significantly improves reasoning accuracy and robustness across diverse tasks, offering a scalable and auditable solution for perception-grounded multimodal reasoning. Our code is available at: https://github.com/yizhuoDi/VTPerceprion-R1.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)往往难以在感知证据中推理。我们进行了四项多模态基准测试和两项MLLM的感知策略系统研究,包括显式、隐式、视觉和文本感知策略。我们的研究发现,显式感知,特别是与文本线索相结合时,可以持续取得最佳改进,尤其是对于较小的模型。基于这一发现,我们提出了VTPerception-R1,这是一个将感知与推理解耦的统一两阶段框架。第一阶段引入感知增强微调,第二阶段应用感知强化学习,包括新型视觉、文本和一致性奖励。实验表明,VTPerception-R1在不同任务中显著提高了推理准确性和稳健性,为基于感知的多模态推理提供了可伸缩和可审核的解决方案。我们的代码位于:https://github.com/yizhuoDi/VTPerceprion-R1。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在感知证据中的推理能力。文章系统地探讨了明确、隐含、视觉和文本感知策略在四种多模态基准测试中的表现。研究结果表明,特别是与文本线索相结合时,明确的感知策略为小型模型提供了最好的改进。基于此,文章提出了一个统一的两个阶段框架VTPerception-R1,它将感知与推理分离。第一阶段引入感知增强微调,第二阶段应用感知增强强化学习,包括新型视觉、文本和一致性奖励。实验证明,VTPerception-R1在不同任务中显著提高了推理准确性和稳健性,为感知接地多模态推理提供了可伸缩和可审计的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在感知证据中的推理存在困难。
- 研究涉及四种多模态基准测试,探讨了明确、隐含、视觉和文本感知策略的表现。
- 明确感知策略与文本线索结合时表现最佳,对小型模型尤为如此。
- 提出VTPerception-R1框架,分为两个阶段:感知增强微调阶段和感知增强强化学习阶段。
- VTPerception-R1引入新型视觉、文本和一致性奖励机制。
- 实验证明VTPerception-R1提高了推理准确性和稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

From Ambiguity to Verdict: A Semiotic-Grounded Multi-Perspective Agent for LLM Logical Reasoning
Authors:Yunyao Zhang, Xinglang Zhang, Junxi Sheng, Wenbing Li, Junqing Yu, Wei Yang, Zikai Song
Logical reasoning is a fundamental capability of large language models (LLMs). However, existing studies largely overlook the interplay between logical complexity and semantic complexity, resulting in methods that struggle to address challenging scenarios involving abstract propositions, ambiguous contexts, and conflicting stances, which are central to human reasoning. For this gap, we propose LogicAgent, a semiotic-square-guided framework designed to jointly address logical complexity and semantic complexity. LogicAgent explicitly performs multi-perspective deduction in first-order logic (FOL), while mitigating vacuous reasoning through existential import checks that incorporate a three-valued decision scheme (True, False, Uncertain) to handle boundary cases more faithfully. Furthermore, to overcome the semantic simplicity and low logical complexity of existing datasets, we introduce RepublicQA, a benchmark that reaches college-level difficulty (FKGL = 11.94) and exhibits substantially greater lexical and structural diversity than prior benchmarks. RepublicQA is grounded in philosophical concepts, featuring abstract propositions and systematically organized contrary and contradictory relations, making it the most semantically rich resource for evaluating logical reasoning. Experiments demonstrate that LogicAgent achieves state-of-the-art performance on RepublicQA, with a 6.25% average gain over strong baselines, and generalizes effectively to mainstream logical reasoning benchmarks including ProntoQA, ProofWriter, FOLIO, and ProverQA, achieving an additional 7.05% average gain. These results highlight the strong effectiveness of our semiotic-grounded multi-perspective reasoning in boosting LLMs’ logical performance.
逻辑推理是大型语言模型(LLM)的基本能力。然而,现有研究大多忽视了逻辑复杂性与语义复杂性之间的相互作用,导致它们在处理涉及抽象命题、模糊上下文和冲突立场的挑战性场景时表现挣扎,而这些场景是人类推理的核心。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了LogicAgent,这是一个以符号平方为指导的框架,旨在共同解决逻辑复杂性和语义复杂性。LogicAgent显式执行一阶逻辑(FOL)中的多视角推理,同时通过存在性导入检查缓解空洞推理,采用三值决策方案(真、假、不确定)来处理边界情况,使其更加忠实。此外,为了克服现有数据集语义简单、逻辑复杂性低的问题,我们引入了RepublicQA,这是一个难度达到大学水平(FKGL=11.94)的基准测试,其词汇和结构多样性显著高于以前的基准测试。RepublicQA以哲学概念为基础,包含抽象命题,以及系统组织的相反和矛盾关系,成为评估逻辑推理方面最语义丰富的资源。实验表明,LogicAgent在RepublicQA上达到了最先进的性能,比强基线平均提高了6.25%,并在主流的逻辑推理基准测试(包括ProntoQA、ProofWriter、FOLIO和ProverQA)上实现了额外的7.05%的平均增幅。这些结果凸显了我们基于符号的多视角推理的强烈有效性,提升了LLM的逻辑性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
该文探讨了大型语言模型在逻辑推理方面的一个基本能力缺失问题。现有研究忽略了逻辑复杂性和语义复杂性之间的相互作用,导致在处理涉及抽象命题、模糊上下文和冲突立场等挑战场景时效果不佳。为此,提出了一种名为LogicAgent的框架,旨在联合解决逻辑复杂性和语义复杂性。LogicAgent在一阶逻辑中进行了多视角演绎,并通过存在性检查来减轻空洞推理,采用三值决策方案(真、假、不确定)以更准确地处理边界情况。此外,为了克服现有数据集语义简单、逻辑复杂度低的问题,引入了RepublicQA数据集,其难度达到大学水平,词汇和结构更加多样。实验表明,LogicAgent在RepublicQA上取得了最佳性能,平均优于强基线6.25%,并在主流逻辑推理基准测试上实现了额外的7.05%的平均增益。这证明了基于符号的多视角推理在提升语言模型的逻辑性能方面的强大效果。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型在处理逻辑推理时面临挑战,尤其是涉及抽象命题、模糊上下文和冲突立场的场景。
- LogicAgent框架旨在联合解决逻辑复杂性和语义复杂性,通过多视角演绎和存在性检查来增强推理能力。
- 现有数据集在语义和逻辑复杂度方面存在不足,因此引入了RepublicQA数据集,其难度更高、词汇和结构更加多样。
- LogicAgent在RepublicQA等基准测试上取得了显著成果,平均优于其他方法6.25%,且在主流逻辑推理基准测试上也有良好表现。
- LogicAgent采用的三值决策方案(真、假、不确定)有助于更准确地处理边界情况,提高推理的精准度。
- 该研究强调了逻辑复杂性和语义复杂性在逻辑推理中的重要性,以及它们之间的相互作用。
点此查看论文截图

Socratic-Zero : Bootstrapping Reasoning via Data-Free Agent Co-evolution
Authors:Shaobo Wang, Zhengbo Jiao, Zifan Zhang, Yilang Peng, Xu Ze, Boyu Yang, Wei Wang, Hu Wei, Linfeng Zhang
Recent breakthroughs in large language models (LLMs) on reasoning tasks rely heavily on massive, high-quality datasets-typically human-annotated and thus difficult to scale. While data synthesis or distillation offers a promising alternative, existing methods struggle with inconsistent data quality and an inability to dynamically adapt to the evolving capabilities of the model, leading to suboptimal training signals. To address these limitations, we introduce Socratic-Zero, a fully autonomous framework that generates high-quality training data from minimal seed examples through the co-evolution of three agents: the Teacher, the Solver, and the Generator. The Solver continuously refines its reasoning by learning from preference feedback on both successful and failed trajectories; the Teacher adaptively crafts increasingly challenging questions based on the Solver’s weaknesses; and the Generator distills the Teacher’s question-design strategy to enable scalable, high-fidelity curriculum generation. This closed-loop system produces a self-improving curriculum-requiring no pre-existing tasks or labels. Remarkably, starting from only 100 seed questions, our Socratic-Solver-8B achieves an average gain of +20.2 percentage points over prior data synthesis methods across seven mathematical reasoning benchmarks (AMC23, AIME24-25, Olympiad, MATH-500, Minerva, and GSM8K), with consistent gains on both Qwen3 and GLM4 series models. Even more surprisingly, synthetic data from Socratic-Generator-32B enables student LLMs to achieve superior performance compared to other state-of-the-art (SOTA) commercial LLMs on these benchmarks, including Qwen3-235B-A22B, DeepSeek-V3.1-671B, GPT-5, Gemini-2.5-Pro, Grok-4, and Claude-4.1-Opus.
最近,大型语言模型(LLM)在推理任务上的突破严重依赖于大规模的高质量数据集,通常是人工标注的,因此难以扩展。虽然数据合成或蒸馏提供了有前景的替代方案,但现有方法在数据质量不一致和无法动态适应模型不断发展的能力方面存在困难,导致训练信号不佳。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了Socratic-Zero,一个完全自主的框架,它通过教师、求解器和生成器三个代理的协同进化,从少量种子示例生成高质量的训练数据。求解器通过成功和失败轨迹的偏好反馈不断精进其推理能力;教师根据求解器的弱点自适应地构建越来越具挑战性的问题;生成器提炼教师的问题设计策略,实现可扩展的高保真课程生成。这个闭环系统产生了一个自我改进的课程,不需要预先存在的任务或标签。值得注意的是,仅从100个种子问题开始,我们的Socratic-Solver-8B在七个数学推理基准测试(AMC23、AIME24-25、Olympiad、MATH-500、Minerva和GSM8K)上的表现比先前的数据合成方法有平均+20.2个百分点的提升,在Qwen3和GLM4系列模型上也有持续的收益。更令人惊讶的是,来自Socratic-Generator-32B的合成数据使学生LLM在这些基准测试上的表现优于其他先进(SOTA)的商业LLM,包括Qwen3-235B-A22B、DeepSeek-V3.1-671B、GPT-5、Gemini-2.5-Pro、Grok-4和Claude-4.1-Opus。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 3 figures
Summary
大规模语言模型在推理任务上的最新突破严重依赖于大量高质量数据集,通常这些数据集需要人工标注,因此难以扩展。为解决此问题,我们推出了Socratic-Zero框架,该框架通过教师、求解器和生成器三个代理的协同进化,从少量种子示例中生成高质量训练数据。框架自主工作,无需预先存在的任务或标签,可产生自我改进的课程。通过仅使用100个种子问题,我们的Socratic-Solver-8B在七个数学推理基准测试上的表现优于先前的数据合成方法,平均提高了20.2个百分点。此外,来自Socratic-Generator-32B的合成数据使学生LLM在这些基准测试上的表现优于其他先进商业LLM。
Key Takeaways
- Socratic-Zero框架解决了大规模语言模型在推理任务中数据集难以扩展的问题。
- 框架包含教师、求解器和生成器三个代理,协同进化以生成高质量训练数据。
- 该框架能自主工作,无需预先存在的任务或标签,可产生自我改进的课程。
- Socratic-Solver-8B仅使用100个种子问题,在七个数学推理基准测试上的表现显著优于其他数据合成方法。
- Socratic-Generator-32B生成的合成数据使学生LLM的表现优于其他先进商业LLM。
- 教师代理根据求解器的弱点制定更具挑战性的问题。
点此查看论文截图

Identity Bridge: Enabling Implicit Reasoning via Shared Latent Memory
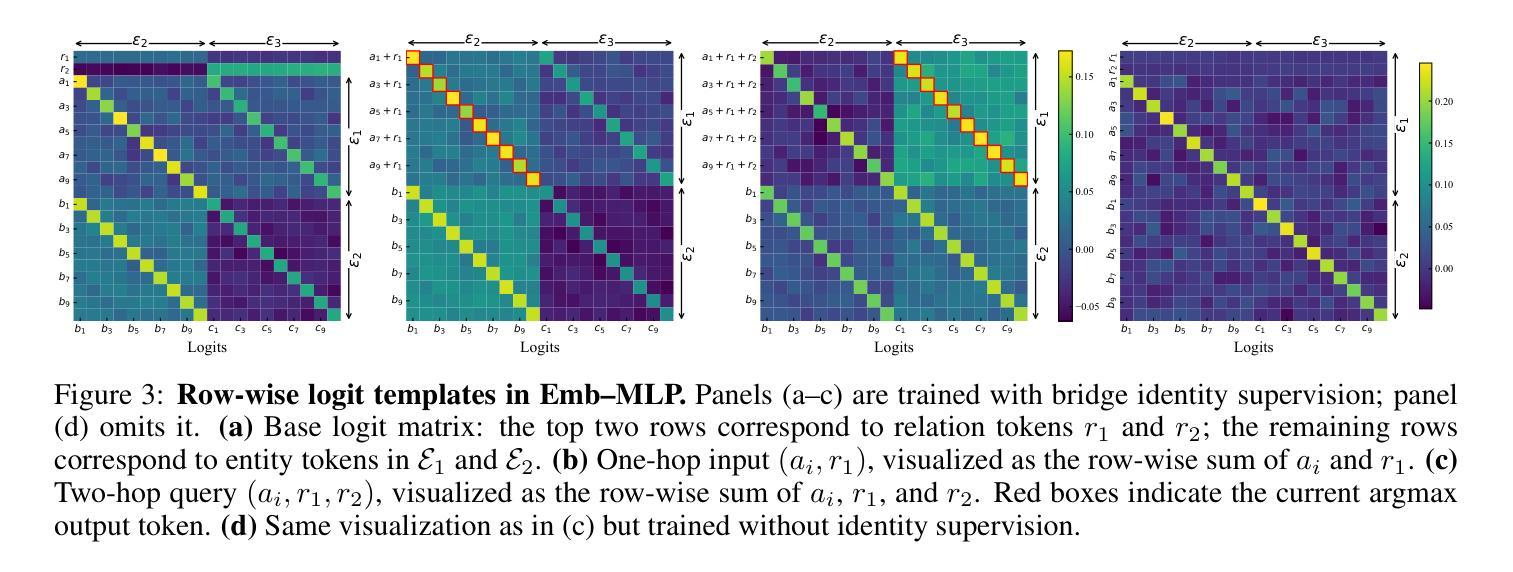
Authors:Pengxiao Lin, Zheng-An Chen, Zhi-Qin John Xu
Despite remarkable advances, large language models often fail at compositional reasoning tasks, a phenomenon exemplified by the ``curse of two-hop reasoning’’. This paper introduces the Identity Bridge, a simple yet powerful mechanism that resolves this compositionality gap by supervising the model on a zero-hop identity task. We demonstrate empirically that this addition enables models to successfully perform out-of-distribution two-hop reasoning, a task they otherwise completely fail. To explain this phenomenon, we provide a theoretical analysis using a simplified Emb-MLP model, proving that identity supervision reshapes the model’s latent geometry. We show this alignment is induced by an implicit nuclear-norm regularization during optimization, which favors low-rank solutions that share structure across tasks. For complex tasks, we use small initialization or weight decay to enhance the regularization effect, which enhances the latent space alignment effect and slows down the generalization decay. Finally, we extend our investigation to large-scale models, observing that they still achieve two-hop reasoning through the latent memory, which provides crucial inspiration for enhancing their implicit reasoning abilities.
尽管取得了显著的进步,大型语言模型在组合推理任务中常常表现不佳,这一现象被“两跳推理的诅咒”所例证。本文介绍了Identity Bridge,这是一种简单而强大的机制,通过监督模型进行零跳身份任务来解决组合性差距。我们实证证明,这一补充使得模型能够成功执行超出分布的两跳推理任务,否则这些任务会完全失败。为了解释这一现象,我们使用简化的Emb-MLP模型进行理论分析,证明身份监督会重塑模型的潜在几何结构。我们表明这种对齐是由优化过程中的隐式核范数正则化引起的,它有利于共享任务结构的低秩解。对于复杂任务,我们通过微调初始化或小权重衰减来增强正则化效果,这增强了潜在空间对齐效果并减缓了泛化衰减。最后,我们将调查扩展到大规模模型,观察到它们仍然通过潜在记忆实现两跳推理,这为增强它们的隐式推理能力提供了关键启示。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Identity Bridge机制,该机制通过监督模型进行零跳身份任务,解决了大型语言模型在组合推理任务上的不足。实验证明,该机制的引入使得模型能够成功进行跨分布的两跳推理,这是它们之前无法完成的任务。理论分析表明,身份监督重塑了模型的潜在几何结构,并通过优化过程中的隐式核范数正则化来实现。对于复杂任务,通过小初始化或权重衰减增强正则化效果,提高潜在空间对齐效果并减缓泛化衰减。最后,对大型模型的调查表明,它们仍通过潜在记忆实现两跳推理,这为增强它们的隐式推理能力提供了关键启示。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在组合推理任务上存在问题,如“两跳推理的诅咒”。
- Identity Bridge机制通过监督模型进行零跳身份任务来解决这一难题。
- 零跳身份任务的引入使模型能够成功进行跨分布的两跳推理。
- 理论分析表明,身份监督重塑了模型的潜在几何结构。
- 隐式核范数正则化在优化过程中起到关键作用。
- 对于复杂任务,通过小初始化或权重衰减增强正则化效果,提高模型性能。
点此查看论文截图
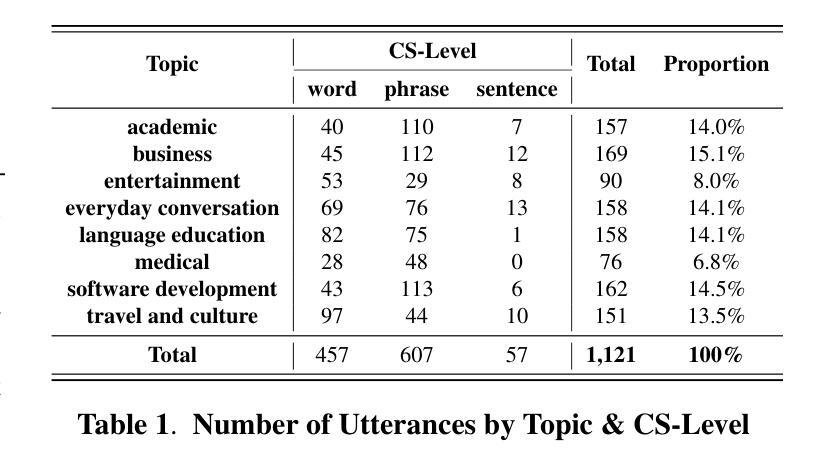
HiKE: Hierarchical Evaluation Framework for Korean-English Code-Switching Speech Recognition
Authors:Gio Paik, Yongbeom Kim, Soungmin Lee, Sangmin Ahn, Chanwoo Kim
Despite advances in multilingual automatic speech recognition (ASR), code-switching (CS), the mixing of languages within an utterance common in daily speech, remains a severely underexplored challenge. In this paper, we introduce HiKE: the Hierarchical Korean-English code-switching benchmark, the first globally accessible evaluation framework for Korean-English CS, aiming to provide a means for the precise evaluation of multilingual ASR models and to foster research in the field. The proposed framework not only consists of high-quality, natural CS data across various topics, but also provides meticulous loanword labels and a hierarchical CS-level labeling scheme (word, phrase, and sentence) that together enable a systematic evaluation of a model’s ability to handle each distinct level of code-switching. Through evaluations of diverse multilingual ASR models and fine-tuning experiments, this paper demonstrates that while most multilingual ASR models initially struggle with CS-ASR, this capability can be enabled through fine-tuning with CS data. HiKE will be available at https://github.com/ThetaOne-AI/HiKE.
尽管多语种自动语音识别(ASR)技术有所进步,但语言切换(CS)在日常对话中普遍存在,即在一句话中混合使用多种语言的情况仍然是一个被严重忽视的挑战。在本文中,我们介绍了HiKE:分层韩英语言切换基准测试,这是首个面向全球的韩英CS评估框架,旨在提供一种精确评估多语种ASR模型的手段,并推动该领域的研究。所提出的框架不仅包括高质量的自然CS数据,涵盖各种主题,还包括细致的借词标签和分层级的CS级别标签方案(单词、短语和句子),这些共同使模型能够系统地处理每个独特的语言切换级别。通过对各种多语种ASR模型的评估和微调实验,本文证明,虽然大多数多语种ASR模型最初对CS-ASR感到困惑,但通过CS数据进行微调可以具备此功能。HiKE将在https://github.com/ThetaOne-AI/HiKE上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 2 figures, Submitted to ICASSP2026
Summary
本文介绍了HiKE:一个面向韩语-英语转换的层次化代码切换基准测试平台。该平台旨在提供精确评估多语种语音识别模型的能力,并推动相关领域研究。该平台不仅包含高质量的自然转换数据,还有各种主题的细致借词标签和层次化的代码切换级别标签方案。实验证明,通过精细调整数据,大多数多语种语音识别模型都能应对代码切换挑战。HiKE将在GitHub上开放使用。
Key Takeaways
- 代码切换(CS)在日常语言中混合不同语言的现象在多语种自动语音识别(ASR)中仍然是一个严重未被充分研究的挑战。
- HiKE是首个面向韩语-英语转换的代码切换基准测试平台,旨在提供精确评估多语种ASR模型的工具,并推动相关研究。
- 该平台包含高质量的自然转换数据,涵盖各种主题。
- HiKE提供了详细的借词标签和层次化的代码切换级别标签方案(词、短语和句子)。
- 实验显示,大多数多语种ASR模型在最初面对代码切换时会遇到困难,但可以通过精细调整数据来提高应对能力。
- HiKE平台将在GitHub上开放使用,便于公众访问和使用。
点此查看论文截图

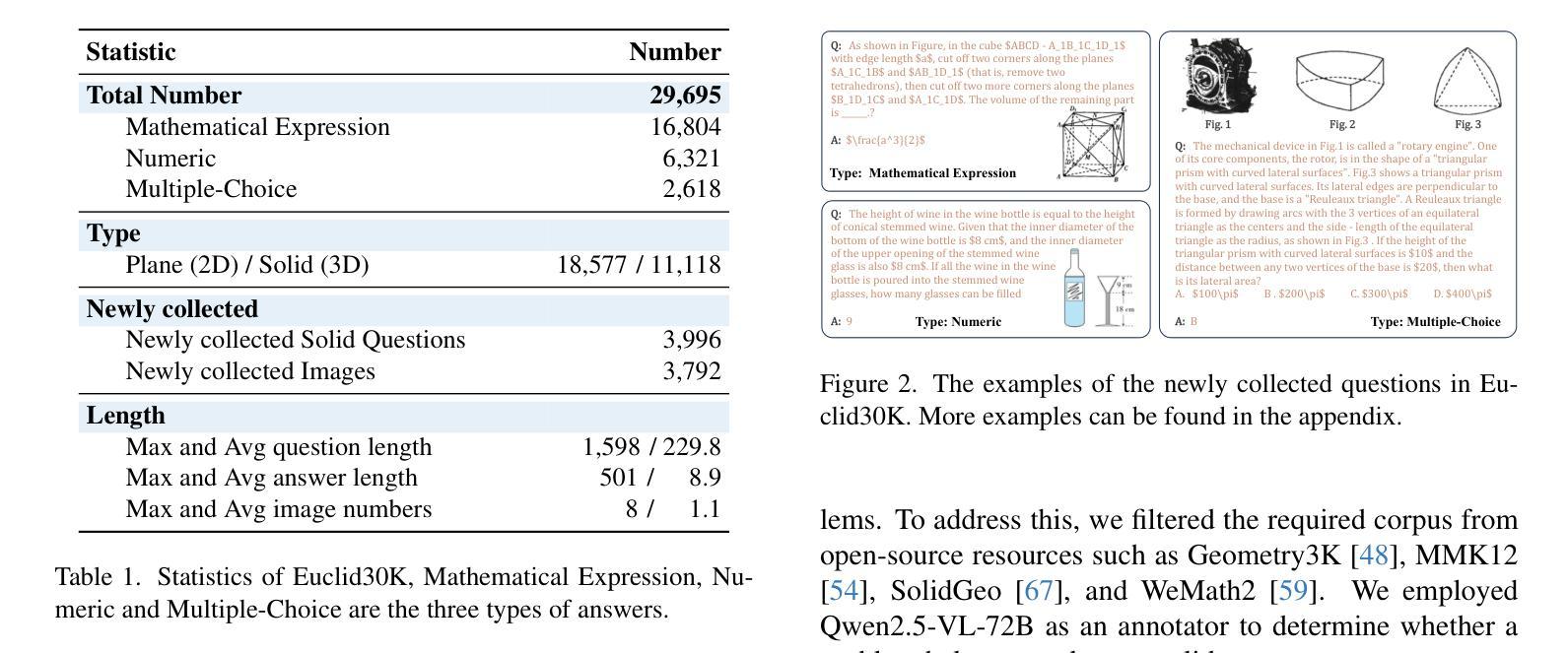
Euclid’s Gift: Enhancing Spatial Perception and Reasoning in Vision-Language Models via Geometric Surrogate Tasks
Authors:Shijie Lian, Changti Wu, Laurence Tianruo Yang, Hang Yuan, Bin Yu, Lei Zhang, Kai Chen
Spatial intelligence spans a rich suite of abilities, including visualising and transforming shapes, mentally rotating objects, judging relational positions and containment, and estimating numerosity. However, it still remains a critical unresolved challenge for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs).To fill this gap, we propose to treat Euclidean geometry problem-solving as a surrogate task. Specifically, we meticulously constructed a curated multimodal dataset, called Euclid30K, comprising approximately 30K plane and solid geometry problems. To enable the model to acquire and apply Euclidean principles from these geometry problems, we employed Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to finetune the Qwen2.5VL family and RoboBrain2.0 family, inspiring the models to identify shapes, count, and relate entities, and perform multi-step deductive reasoning using Euclidean principles. Our experiments demonstrate that the resulting models achieve substantial zero-shot gains across four spatial reasoning benchmarks (Super-CLEVR, Omni3DBench, VSI-Bench, and MindCube) without any task-specific adaptations. Notably, after training on the Euclid30K, the mean VSI-Bench accuracy of all evaluated models rose from 34.5% to 40.5%, improving by 5.5 percentage points. Among them, RoboBrain2.0-Euclid-7B achieves 49.6% accuracy, surpassing the previous state-of-the-art model, Spatial-MLLM.To our knowledge, this is the first systematic study showing that geometry-centric fine-tuning can confer vision-language models with broadly transferable spatial skills. Code and Euclid30K dataset can be found in https://zgca-ai4edu.github.io/Euclids_Gift.
空间智能涵盖了一系列丰富的能力,包括可视化并转换形状、在脑海中旋转物体、判断相对位置和包含关系,以及估计数量。然而,对于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)来说,这仍然是一个尚未解决的关键挑战。为了填补这一空白,我们提议将欧几里得几何问题解决作为替代任务。具体来说,我们精心构建了一个名为Euclid30K的多模态数据集,包含约30000个平面和立体几何问题。为了让模型从这些几何问题中学习并应用欧几里得原理,我们采用了集团相对策略优化(GRPO)来对Qwen2.5VL家族和RoboBrain2.0家族进行微调,激励模型识别形状、计数和关联实体,并使用欧几里得原理进行多步骤的推理。我们的实验表明,所得模型在四个空间推理基准测试(Super-CLEVR、Omni3DBench、VSI-Bench和MindCube)上实现了显著的零样本增益,无需任何针对特定任务的适应。值得注意的是,在Euclid30K训练后,所有评估模型的VSI-Bench平均准确率从34.5%提高到40.5%,提高了5.5个百分点。其中,RoboBrain2.0-Euclid-7B的准确率达到49.6%,超越了之前的先进模型Spatial-MLLM。据我们所知,这是第一项系统研究,表明以几何为中心的微调可以赋予视觉语言模型广泛可转移的空间技能。代码和Euclid30K数据集可在https://zgca-ai4edu.github.io/Euclids_Gift中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨空间智能在多模态大型语言模型中的重要性及其挑战。为填补这一空白,研究团队构建了一个名为Euclid30K的多模态数据集,并通过Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)对语言模型进行微调,使其掌握和应用欧几里得原理。实验表明,模型在四个空间推理基准测试上的表现得到了显著提升,且训练后的模型泛化能力更强。该研究显示了几何中心微调赋予语言模型广泛可转移的空间技能的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 空间智能包含多种能力,如形状可视化、物体旋转、关系定位、包含性判断及数量估算等,对于多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)仍是一个挑战。
- 为提高模型的空间智能,研究团队构建了Euclid30K多模态数据集,包含约30K的平面和立体几何问题。
- 采用Group Relative Policy Optimization(GRPO)对语言模型进行微调,使其能从几何问题中学习并应用欧几里得原理。
- 模型在四个空间推理基准测试上的表现显著,且在Euclid30K数据集训练后,VSI-Bench准确率从34.5%提升至40.5%,提升了5.5个百分点。
- RoboBrain2.0-Euclid-7B模型的准确率达到了49.6%,超越了现有的先进模型Spatial-MLLM。
- 此研究是首次系统研究证明几何中心微调能够使视觉语言模型获得广泛可转移的空间技能。
点此查看论文截图

CDT: A Comprehensive Capability Framework for Large Language Models Across Cognition, Domain, and Task
Authors:Haosi Mo, Xinyu Ma, Xuebo Liu, Derek F. Wong, Yu Li, Jie Liu, Min Zhang
Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced their capabilities, highlighting the need for comprehensive evaluation frameworks that extend beyond task-specific benchmarks. However, existing benchmarks often focus on isolated abilities, lacking a holistic framework for assessing LLM capabilities. To address this gap, we propose the Cognition-Domain-Task (CDT) framework, which comprehensively measures a model’s capabilities across three dimensions. We expand the scope of model capability definitions at the cognitive level by incorporating the Cattell-Horn-Carroll cognitive theory, refining the categorization of model capabilities. We apply CDT in two directions: dataset capability evaluation and data selection. Experiments show that our capability metrics correlate well with downstream performance and can support effective dataset analysis and construction. The experiments on data selection also show significant improvements in both general and specific benchmarks, achieving scores of 44.3 and 45.4, with an increase of 1.6 and 2.2 points over the baselines, respectively. These results validate the effectiveness and practicality of CDT. Source code and models are available at https://github.com/Alessa-mo/CDT.
近年来,大型语言模型(LLM)的进步显著增强了其能力,这突显了需要超越特定任务基准测试的综合评估框架。然而,现有的基准测试通常侧重于孤立的能力,缺乏评估LLM能力的整体框架。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了认知域任务(CDT)框架,该框架从三个维度全面衡量模型的能力。我们通过结合卡特尔-霍恩-卡罗尔认知理论来扩展模型能力定义的认知层面,对模型能力进行分类的细化。我们在两个方向应用CDT:数据集能力评估和数据处理选择。实验表明,我们的能力指标与下游性能密切相关,并支持有效的数据集分析和构建。在数据选择方面的实验也显示,在通用和特定基准测试中都有显著改善,得分分别为44.3和45.4,相较于基线分别提高了1.6和2.2分。这些结果验证了CDT的有效性和实用性。源代码和模型可在https://github.com/Alessa-mo/CDT上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 5 figures, EMNLP2025 Findings
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展显著增强了其能力,凸显出需要超越任务特定基准测试的综合评估框架。针对现有基准测试通常关注孤立能力、缺乏评估LLM能力的整体框架的问题,我们提出了认知域任务(CDT)框架,该框架能够全面衡量模型在三个维度上的能力。我们通过融合Cattell-Horn-Carroll认知理论来扩展模型能力定义的范畴,精细化了模型能力的分类。我们在数据集能力评估和数据选择两个方面应用了CDT。实验表明,我们的能力指标与下游性能密切相关,并支持有效的数据集分析和构建。数据选择实验在通用和特定基准测试上均显示出显著改进,得分分别为44.3和45.4,较基线分别提高了1.6和2.2分。实验结果验证了CDT的有效性和实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的能力评估需要更全面的框架,超越任务特定基准测试。
- 现有基准测试缺乏整体性,通常只关注模型孤立的能力。
- CDT框架全面衡量模型在三个维度上的能力:认知域任务框架涵盖了模型的广泛能力。
- 结合Cattell-Horn-Carroll认知理论扩展了模型能力定义,更精细地分类了模型能力。
- CDT框架应用于数据集能力评估和数据选择,实验证明其与下游性能密切相关。
- 数据选择实验在通用和特定基准测试上均显示出显著改进。