⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-01 更新
VT-FSL: Bridging Vision and Text with LLMs for Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Wenhao Li, Qiangchang Wang, Xianjing Meng, Zhibin Wu, Yilong Yin
Few-shot learning (FSL) aims to recognize novel concepts from only a few labeled support samples. Recent studies enhance support features by incorporating additional semantic information or designing complex semantic fusion modules. However, they still suffer from hallucinating semantics that contradict the visual evidence due to the lack of grounding in actual instances, resulting in noisy guidance and costly corrections. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework, bridging Vision and Text with LLMs for Few-Shot Learning (VT-FSL), which constructs precise cross-modal prompts conditioned on Large Language Models (LLMs) and support images, seamlessly integrating them through a geometry-aware alignment. It mainly consists of Cross-modal Iterative Prompting (CIP) and Cross-modal Geometric Alignment (CGA). Specifically, the CIP conditions an LLM on both class names and support images to generate precise class descriptions iteratively in a single structured reasoning pass. These descriptions not only enrich the semantic understanding of novel classes but also enable the zero-shot synthesis of semantically consistent images. The descriptions and synthetic images act respectively as complementary textual and visual prompts, providing high-level class semantics and low-level intra-class diversity to compensate for limited support data. Furthermore, the CGA jointly aligns the fused textual, support, and synthetic visual representations by minimizing the kernelized volume of the 3-dimensional parallelotope they span. It captures global and nonlinear relationships among all representations, enabling structured and consistent multimodal integration. The proposed VT-FSL method establishes new state-of-the-art performance across ten diverse benchmarks, including standard, cross-domain, and fine-grained few-shot learning scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/peacelwh/VT-FSL.
少量学习(FSL)旨在从仅有的少量标记样本中识别出新概念。最近的研究通过融入额外的语义信息或设计复杂的语义融合模块来提升支撑特征。然而,由于缺乏在实际实例中的定位,它们仍然会出现与视觉证据相矛盾的幻觉语义,导致产生嘈杂的指导和昂贵的修正。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新的框架——基于大型语言模型(LLM)的视觉与文本桥接少量学习(VT-FSL),它构建精确的跨模态提示,结合大型语言模型和支撑图像,通过几何感知对齐无缝集成它们。它主要由跨模态迭代提示(CIP)和跨模态几何对齐(CGA)组成。具体来说,CIP以类名和支撑图像为条件来引导大型语言模型,在一次单一的结构化推理过程中迭代生成精确的类描述。这些描述不仅丰富了对新颖类的语义理解,还实现了语义一致图像的零样本合成。这些描述和合成图像分别作为补充的文本和视觉提示,提供高级别的类语义和低级别的类内多样性,以弥补有限的支撑数据。此外,CGA通过最小化它们所跨越的3维平行四边形的内核体积来联合对齐融合的文本、支撑和合成视觉表示。它捕捉了所有表示之间的全局和非线性关系,实现了结构化且一致的多模态集成。所提出的VT-FSL方法在包括标准、跨域和细粒度少量学习场景在内的十个不同基准测试上达到了新的最先进的性能。代码可在https://github.com/peacelwh/VT-FSL找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NeurIPS 2025
摘要
针对仅由少量标记样本支撑识别新概念的few-shot学习(FSL)任务,提出一种融合视觉与文本的大模型辅助的少量样本学习框架(VT-FSL)。通过跨模态迭代提示和几何对齐机制,构建精确的跨模态提示,并利用大语言模型(LLM)和支撑图像实现无缝集成。框架实现了单一结构推理过程中对类别名称和支撑图像的迭代精确类描述生成。这些描述既丰富了新类别的语义理解,也实现了语义一致的图像零样本合成。描述和合成图像分别作为文本和视觉提示,提供高级类别语义和低级类别内多样性,以弥补有限的支撑数据。同时,通过最小化张量空间中多维度对齐文本、支撑图像及合成图像的方式捕捉不同元素之间的全局非线性关系。该方法在涵盖标准、跨域及精细粒度的少量样本学习场景中都实现了前所未有的优异性能。具体信息见https://github.com/peacelwh/VT-FSL。
关键发现
- 提出的VT-FSL框架结合了视觉和文本信息,利用大语言模型(LLM)和支撑图像进行few-shot学习。
- 通过跨模态迭代提示(CIP)生成精确类描述,既丰富新类别的语义理解,也实现语义一致的图像零样本合成。
- 跨模态几何对齐(CGA)机制能够捕捉文本、支撑图像及合成图像之间的全局非线性关系。
- CIP和CGA共同提高了模型的性能,使得VT-FSL在多种few-shot学习基准测试中表现领先。
- 该方法能够无缝集成不同的信息源,如类名、支撑图像以及合成图像等,提升了模型的泛化能力。
- VT-FSL框架在多种场景下都表现出强大的性能,包括标准、跨域以及精细粒度的few-shot学习场景。
点此查看论文截图
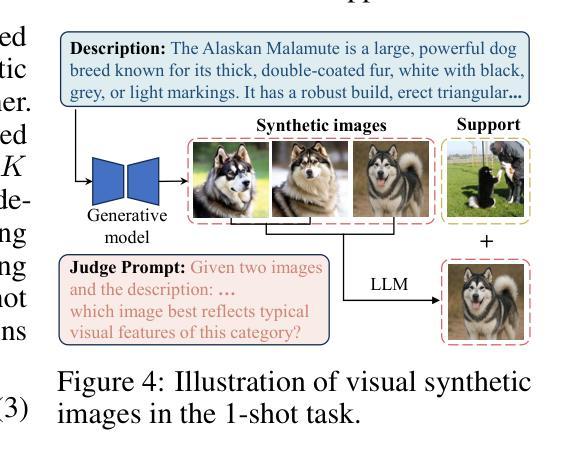
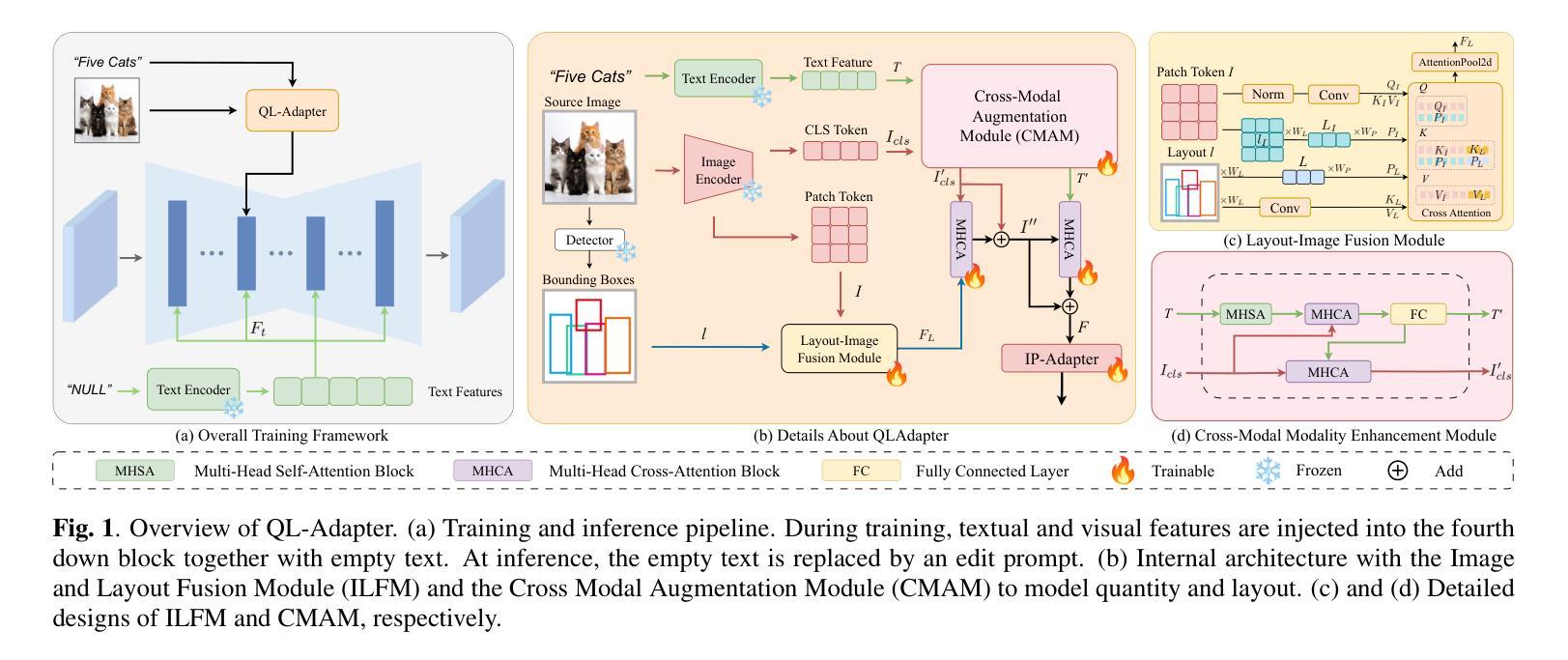
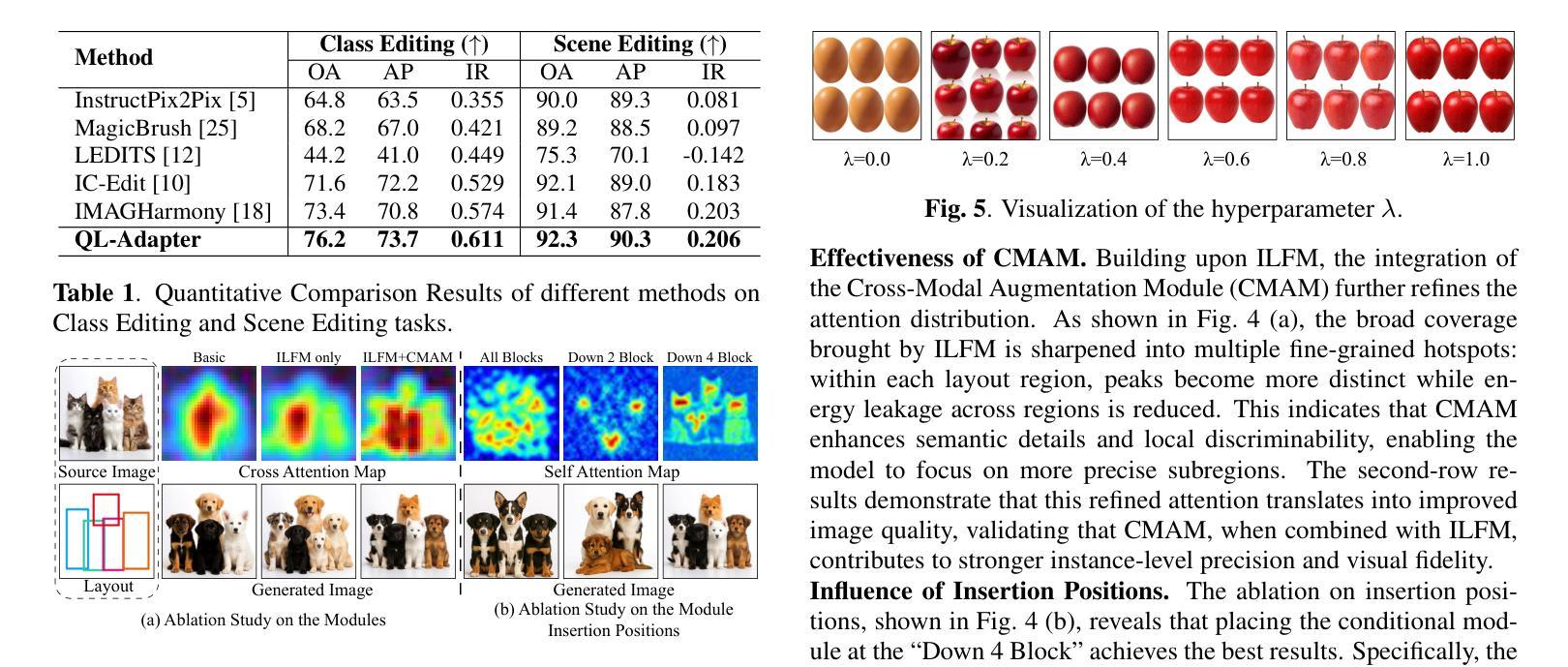
Instruction Guided Multi Object Image Editing with Quantity and Layout Consistency
Authors:Jiaqi Tan, Fangyu Li, Yang Liu
Instruction driven image editing with standard CLIP text encoders often fails in complex scenes with many objects. We present QL-Adapter, a framework for multiple object editing that tackles two challenges: enforcing object counts and spatial layouts, and accommodating diverse categories. QL-Adapter consists of two core modules: the Image-Layout Fusion Module (ILFM) and the Cross-Modal Augmentation Module (CMAM). ILFM fuses layout priors with ViT patch tokens from the CLIP image encoder to strengthen spatial structure understanding. CMAM injects image features into the text branch to enrich textual embeddings and improve instruction following. We further build QL-Dataset, a benchmark that spans broad category, layout, and count variations, and define the task of quantity and layout consistent image editing (QL-Edit). Extensive experiments show that QL-Adapter achieves state of the art performance on QL-Edit and significantly outperforms existing models.
在具有多个对象的复杂场景中,使用标准CLIP文本编码器的指令驱动图像编辑往往会失败。我们提出了QL-Adapter,这是一个用于多个对象编辑的框架,解决了两个挑战:强制对象计数和空间布局,并适应各种类别。QL-Adapter包含两个核心模块:图像布局融合模块(ILFM)和跨模态增强模块(CMAM)。ILFM将布局先验与CLIP图像编码器的ViT补丁标记融合,以加强空间结构理解。CMAM将图像特征注入文本分支,以丰富文本嵌入并改善指令遵循。我们进一步构建了QL-Dataset,这是一个涵盖广泛类别、布局和计数变化的基准测试,并定义了数量布局一致图像编辑的任务(QL-Edit)。大量实验表明,QL-Adapter在QL-Edit上达到了最先进的性能,并显著优于现有模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
点此查看论文截图

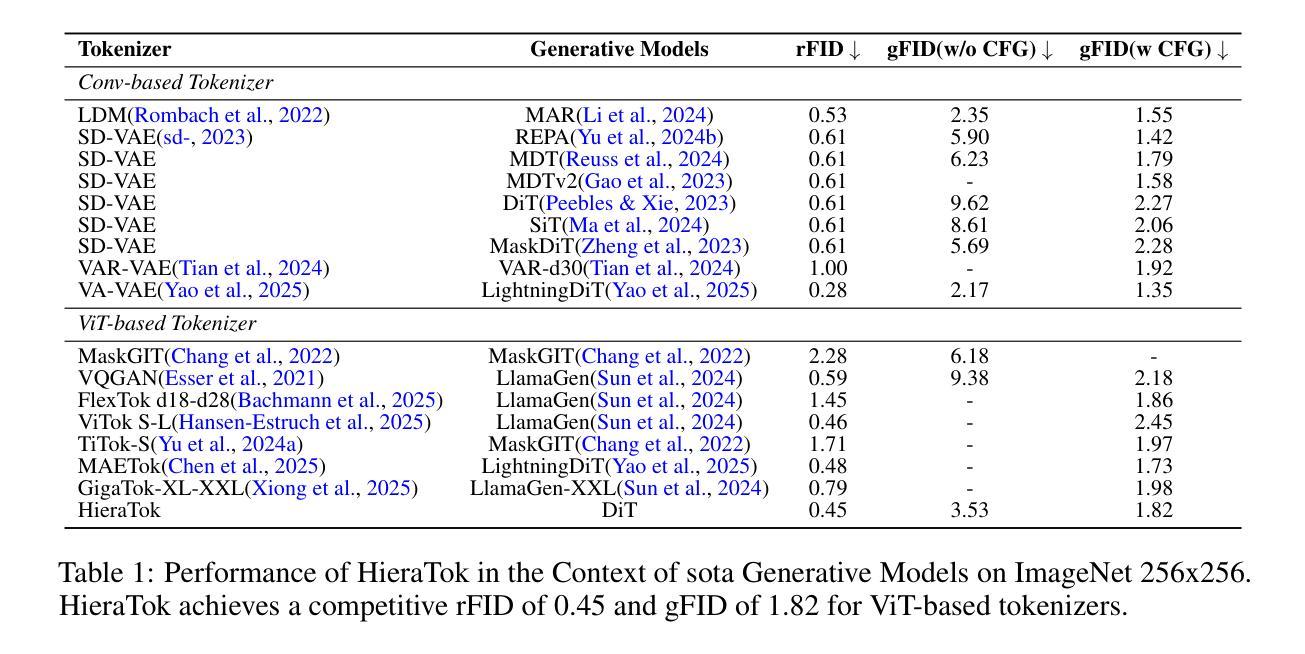
HieraTok: Multi-Scale Visual Tokenizer Improves Image Reconstruction and Generation
Authors:Cong Chen, Ziyuan Huang, Cheng Zou, Muzhi Zhu, Kaixiang Ji, Jiajia Liu, Jingdong Chen, Hao Chen, Chunhua Shen
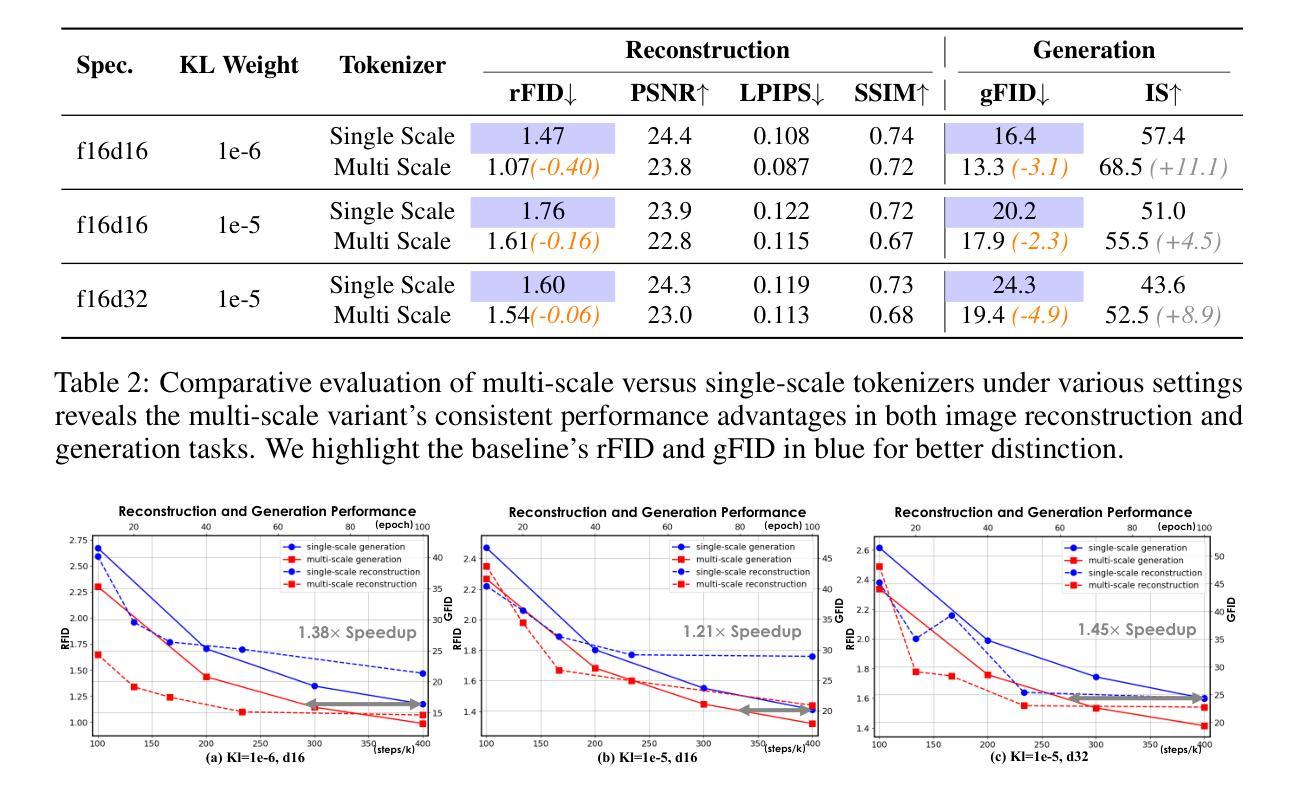
In this work, we present HieraTok, a novel multi-scale Vision Transformer (ViT)-based tokenizer that overcomes the inherent limitation of modeling single-scale representations. This is realized through two key designs: (1) multi-scale downsampling applied to the token map generated by the tokenizer encoder, producing a sequence of multi-scale tokens, and (2) a scale-causal attention mechanism that enables the progressive flow of information from low-resolution global semantic features to high-resolution structural details. Coupling these designs, HieraTok achieves significant improvements in both image reconstruction and generation tasks. Under identical settings, the multi-scale visual tokenizer outperforms its single-scale counterpart by a 27.2% improvement in rFID ($1.47 \rightarrow 1.07$). When integrated into downstream generation frameworks, it achieves a $1.38\times$ faster convergence rate and an 18.9% boost in gFID ($16.4 \rightarrow 13.3$), which may be attributed to the smoother and more uniformly distributed latent space. Furthermore, by scaling up the tokenizer’s training, we demonstrate its potential by a sota rFID of 0.45 and a gFID of 1.82 among ViT tokenizers. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to introduce multi-scale ViT-based tokenizer in image reconstruction and image generation. We hope our findings and designs advance the ViT-based tokenizers in visual generation tasks.
在这项工作中,我们提出了HieraTok,这是一种新型的多尺度Vision Transformer(ViT)基于的令牌化器,克服了建模单尺度表示的固有局限性。这是通过两个关键设计实现的:(1)对令牌映射进行多尺度降采样,生成一系列多尺度令牌;(2)一种尺度因果注意力机制,使信息从低分辨率全局语义特征流向高分辨率结构细节。通过结合这些设计,HieraTok在图像重建和生成任务中都取得了显著的改进。在相同设置下,多尺度视觉令牌化器在rFID指标上超过了其单尺度对应物(从1.47提高到1.07,改进了27.2%)。当集成到下游生成框架中时,它实现了1.38倍的更快收敛率,并在gFID上提高了18.9%(从16.4降至13.3)。这可能是归因于更平滑且分布更均匀的潜在空间。此外,通过扩大令牌化器的训练规模,我们在ViT令牌化器中实现了最先进的rFID为0.45和gFID为1.82。据我们所知,我们首次在图像重建和图像生成中引入了多尺度ViT基于的令牌化器。我们希望我们的发现和设计能推动ViT在视觉生成任务中的令牌化器的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于ViT的HieraTok多尺度视觉令牌器首次亮相。通过两个核心设计:对令牌图的多尺度降采样以生成多尺度令牌序列和规模因果注意力机制,实现信息从低分辨率全局语义特征到高分辨率结构细节的渐进流动。这改进了图像重建和生成任务,改善了rFID指标和生成框架的收敛速度。经过训练后,其展现出潜在的高性能。这项创新有望提升ViT在视觉生成任务中的令牌化技术。
Key Takeaways
- HieraTok是一个基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的多尺度视觉令牌器。
- 通过多尺度降采样和规模因果注意力机制,实现了信息从全局语义特征到结构细节的渐进流动。
- HieraTok在图像重建和生成任务上表现出显著优势,改善了rFID指标,提高了生成框架的收敛速度和gFID指标。
- 通过训练提升,HieraTok展现出高性能潜力。
点此查看论文截图
Patch Rebirth: Toward Fast and Transferable Model Inversion of Vision Transformers
Authors:Seongsoo Heo, Dong-Wan Choi
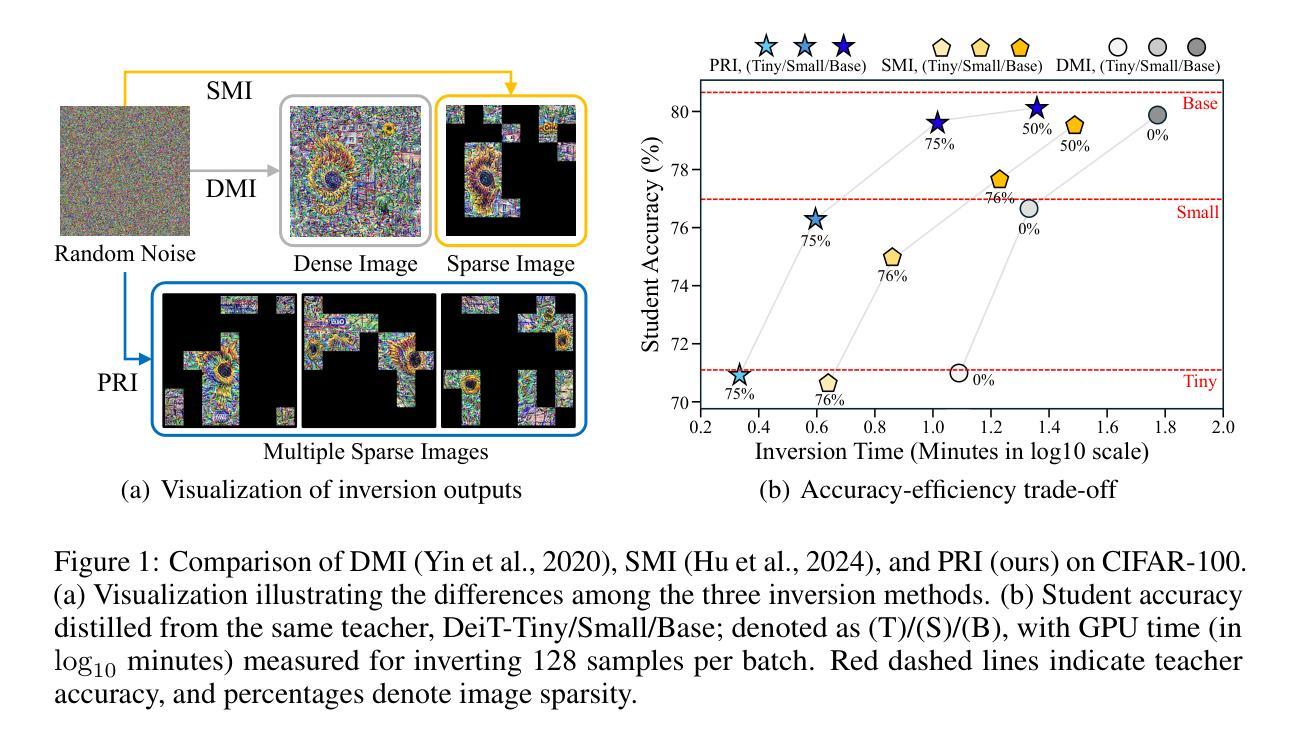
Model inversion is a widely adopted technique in data-free learning that reconstructs synthetic inputs from a pretrained model through iterative optimization, without access to original training data. Unfortunately, its application to state-of-the-art Vision Transformers (ViTs) poses a major computational challenge, due to their expensive self-attention mechanisms. To address this, Sparse Model Inversion (SMI) was proposed to improve efficiency by pruning and discarding seemingly unimportant patches, which were even claimed to be obstacles to knowledge transfer. However, our empirical findings suggest the opposite: even randomly selected patches can eventually acquire transferable knowledge through continued inversion. This reveals that discarding any prematurely inverted patches is inefficient, as it suppresses the extraction of class-agnostic features essential for knowledge transfer, along with class-specific features. In this paper, we propose Patch Rebirth Inversion (PRI), a novel approach that incrementally detaches the most important patches during the inversion process to construct sparse synthetic images, while allowing the remaining patches to continue evolving for future selection. This progressive strategy not only improves efficiency, but also encourages initially less informative patches to gradually accumulate more class-relevant knowledge, a phenomenon we refer to as the Re-Birth effect, thereby effectively balancing class-agnostic and class-specific knowledge. Experimental results show that PRI achieves up to 10x faster inversion than standard Dense Model Inversion (DMI) and 2x faster than SMI, while consistently outperforming SMI in accuracy and matching the performance of DMI.
模型反转是一种无数据学习的广泛采用的技术,它通过迭代优化从预训练模型中重建合成输入,无需访问原始训练数据。然而,将其应用于最先进的视觉变压器(ViT)带来了巨大的计算挑战,因为它们的自注意力机制非常昂贵。为了解决这一问题,提出了稀疏模型反转(SMI)来提高效率,通过修剪和丢弃似乎不重要的补丁,这些补丁甚至被声称是知识转移的障碍。然而,我们的实证发现恰恰相反:即使随机选择的补丁也可以通过持续的反转最终获得可转移的知识。这表明,提前丢弃任何反转的补丁都是低效的,因为它会抑制类无关特征和类特定特征的提取,这对于知识转移至关重要。在本文中,我们提出了Patch重生反转(PRI)这一新方法,它在反转过程中逐步剥离最重要的补丁来构建稀疏合成图像,同时允许剩余补丁继续演化以供未来选择。这种渐进的策略不仅提高了效率,还鼓励最初信息较少的补丁逐渐积累更多与类别相关的知识,我们将这一现象称为“重生效应”,从而有效地平衡了类无关和类特定的知识。实验结果表明,PRI的反转速度比标准的Dense Model Inversion(DMI)快10倍,比SMI快2倍,同时在准确性方面始终优于SMI,并匹配DMI的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文介绍了针对Vision Transformer模型的Sparse Model Inversion(SMI)方法面临的挑战,并提出了新的解决方案Patch Rebirth Inversion(PRI)。PRI通过增量地分离最重要的patches来构建稀疏合成图像,同时允许剩余的patches继续演化以供未来选择。这种方法不仅提高了效率,而且实现了最初信息量较少的patches逐渐积累与类别相关的知识,我们称之为“Re-Birth效应”,从而有效地平衡了类别无关和类别特定的知识。实验结果表明,PRI相较于标准Dense Model Inversion(DMI)实现了高达10倍的快速反转,并且相较于SMI有更高的准确率和更快的速度。
Key Takeaways
- 模型反转是一种在无数据学习中广泛采用的技术,可从预训练模型中重建合成输入,无需访问原始训练数据。但应用在Vision Transformer(ViT)模型上计算成本高。
- Sparse Model Inversion(SMI)方法试图通过丢弃看似不重要的patches来提高效率,但实证研究结果显示丢弃任何提前反转的patches是不高效的。
- 新方法Patch Rebirth Inversion(PRI)通过增量地分离最重要的patches构建稀疏合成图像,允许剩余patches继续演化以供未来选择,提高了效率并实现了类别知识的有效平衡。
- PRI实现了更高的反转速度和准确率,相较于标准Dense Model Inversion(DMI)达到10倍加速,相较于SMI则实现了更快的速度和更高的准确率。
- PRI方法鼓励最初信息量较少的patches逐渐积累与类别相关的知识,这种现象被称为“Re-Birth效应”。
- 丢弃不重要的patches会抑制类别无关特征的知识提取。
点此查看论文截图

Towards Comprehensive Interactive Change Understanding in Remote Sensing: A Large-scale Dataset and Dual-granularity Enhanced VLM
Authors:Junxiao Xue, Quan Deng, Xuecheng Wu, Kelu Yao, Xinyi Yin, Fei Yu, Wei Zhou, Yanfei Zhong, Yang Liu, Dingkang Yang
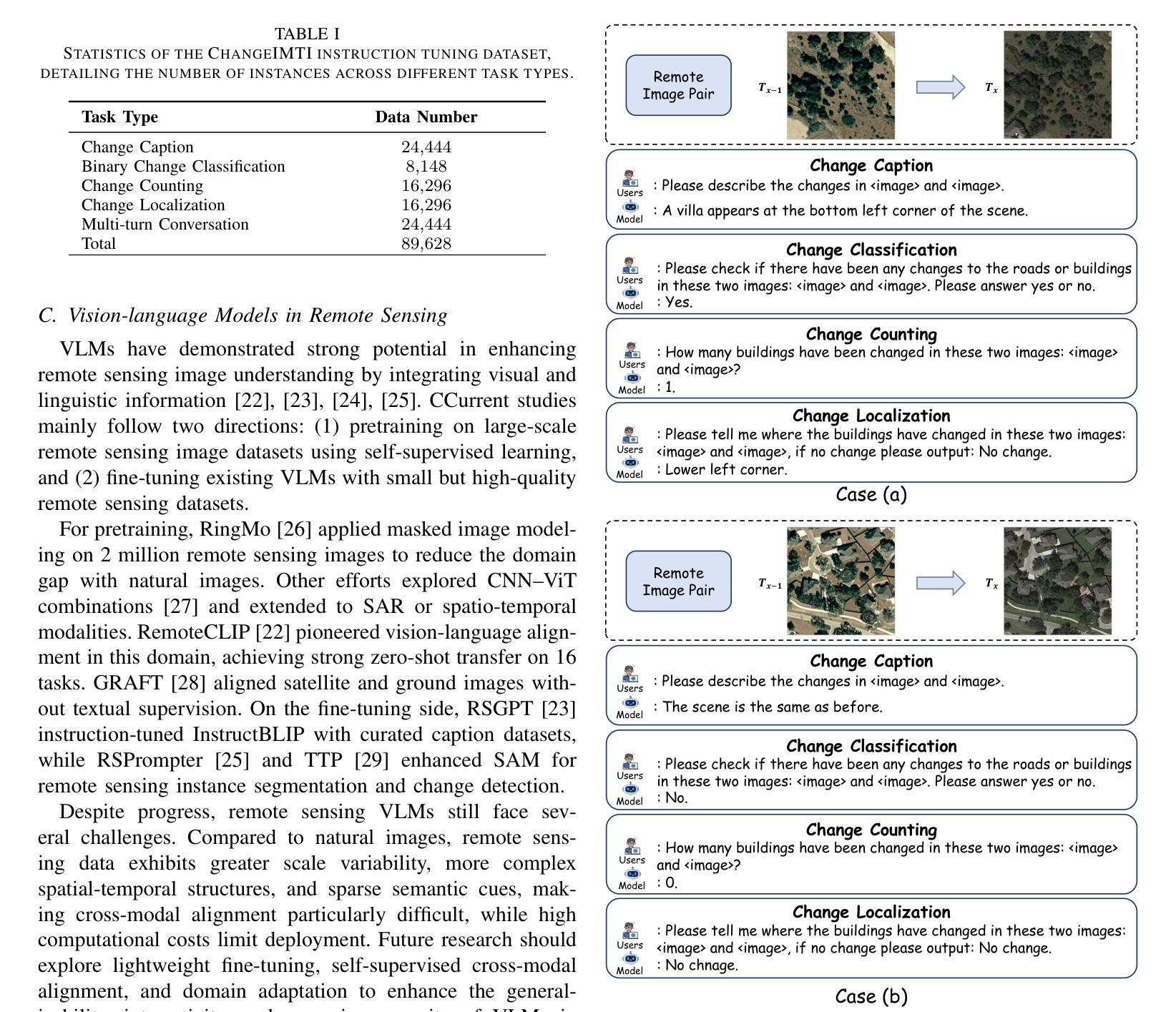
Remote sensing change understanding (RSCU) is essential for analyzing remote sensing images and understanding how human activities affect the environment. However, existing datasets lack deep understanding and interactions in the diverse change captioning, counting, and localization tasks. To tackle these gaps, we construct ChangeIMTI, a new large-scale interactive multi-task instruction dataset that encompasses four complementary tasks including change captioning, binary change classification, change counting, and change localization. Building upon this new dataset, we further design a novel vision-guided vision-language model (ChangeVG) with dual-granularity awareness for bi-temporal remote sensing images (i.e., two remote sensing images of the same area at different times). The introduced vision-guided module is a dual-branch architecture that synergistically combines fine-grained spatial feature extraction with high-level semantic summarization. These enriched representations further serve as the auxiliary prompts to guide large vision-language models (VLMs) (e.g., Qwen2.5-VL-7B) during instruction tuning, thereby facilitating the hierarchical cross-modal learning. We extensively conduct experiments across four tasks to demonstrate the superiority of our approach. Remarkably, on the change captioning task, our method outperforms the strongest method Semantic-CC by 1.39 points on the comprehensive S*m metric, which integrates the semantic similarity and descriptive accuracy to provide an overall evaluation of change caption. Moreover, we also perform a series of ablation studies to examine the critical components of our method.
遥感变化理解(RSCU)在分析遥感图像以及了解人类活动如何影响环境方面至关重要。然而,现有数据集在多样化的变化描述、计数和定位任务中缺乏深度理解和交互。为了弥补这些不足,我们构建了ChangeIMTI,这是一个新的大型交互式多任务指令数据集,包含四个互补任务,包括变化描述、二元变化分类、变化计数和变化定位。基于这个新数据集,我们进一步设计了一种新型视觉引导的视觉语言模型(ChangeVG),该模型具有双粒度意识,适用于双时态遥感图像(即同一区域在不同时间的两张遥感图像)。引入的视觉引导模块是一个双分支架构,协同结合了精细的的空间特征提取和高层次语义摘要。这些丰富的表示形式进一步作为辅助提示,用于指导大型视觉语言模型(VLMs)(例如Qwen2.5-VL-7B)在指令调整过程中的学习,从而促进分层跨模态学习。我们在四个任务上进行了广泛的实验,以证明我们的方法优越性。值得一提的是,在变化描述任务上,我们的方法在综合S*m指标上超越了最强方法Semantic-CC 1.39分,该指标结合了语义相似性和描述准确性,以提供对变化描述的总体评价。此外,我们还进行了一系列消融研究来检验我们方法的关键组成部分。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
该文本介绍了远程感应变化理解的重要性以及现有数据集的不足。为弥补这些不足,构建了一个大型交互式多任务指令数据集ChangeIMTI,并设计了一种新型视觉引导视觉语言模型ChangeVG,具有双粒度感知能力,用于处理双时态遥感图像。该模型通过结合精细空间特征提取与高级语义摘要,丰富了表示形式,并作为辅助提示引导大型视觉语言模型在指令调整期间进行分层跨模态学习。实验证明,该方法在四项任务上的表现均优于其他方法,特别是在变化描述任务上,其性能较最强方法Semantic-CC高出1.39个百分点。
Key Takeaways:
- 远程感应变化理解(RSCU)在分析遥感图像和了解人类活动对环境影响方面至关重要。
- 现有数据集在多样变化描述、计数和定位任务中缺乏深度理解和交互。
- 构建了ChangeIMTI大型交互式多任务指令数据集,包含四种互补任务:变化描述、二元变化分类、变化计数和变化定位。
- 设计了具有双粒度感知能力的视觉引导视觉语言模型ChangeVG,用于处理双时态遥感图像。
- ChangeVG模型结合了精细空间特征提取和高级语义摘要,丰富了表示形式。
- 使用大型视觉语言模型进行分层跨模态学习,通过辅助提示引导模型进行指令调整。
点此查看论文截图

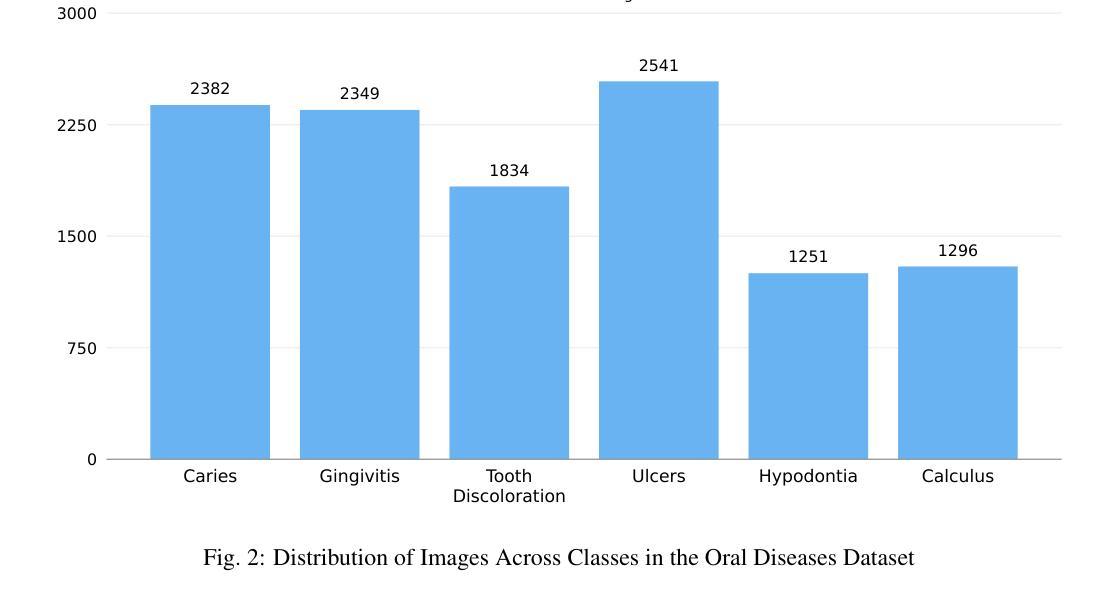
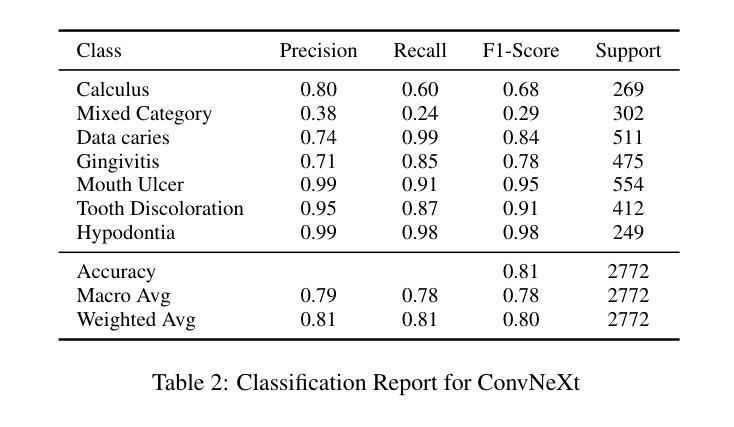
Deep Learning for Oral Health: Benchmarking ViT, DeiT, BEiT, ConvNeXt, and Swin Transformer
Authors:Ajo Babu George, Sadhvik Bathini, Niranjana S R
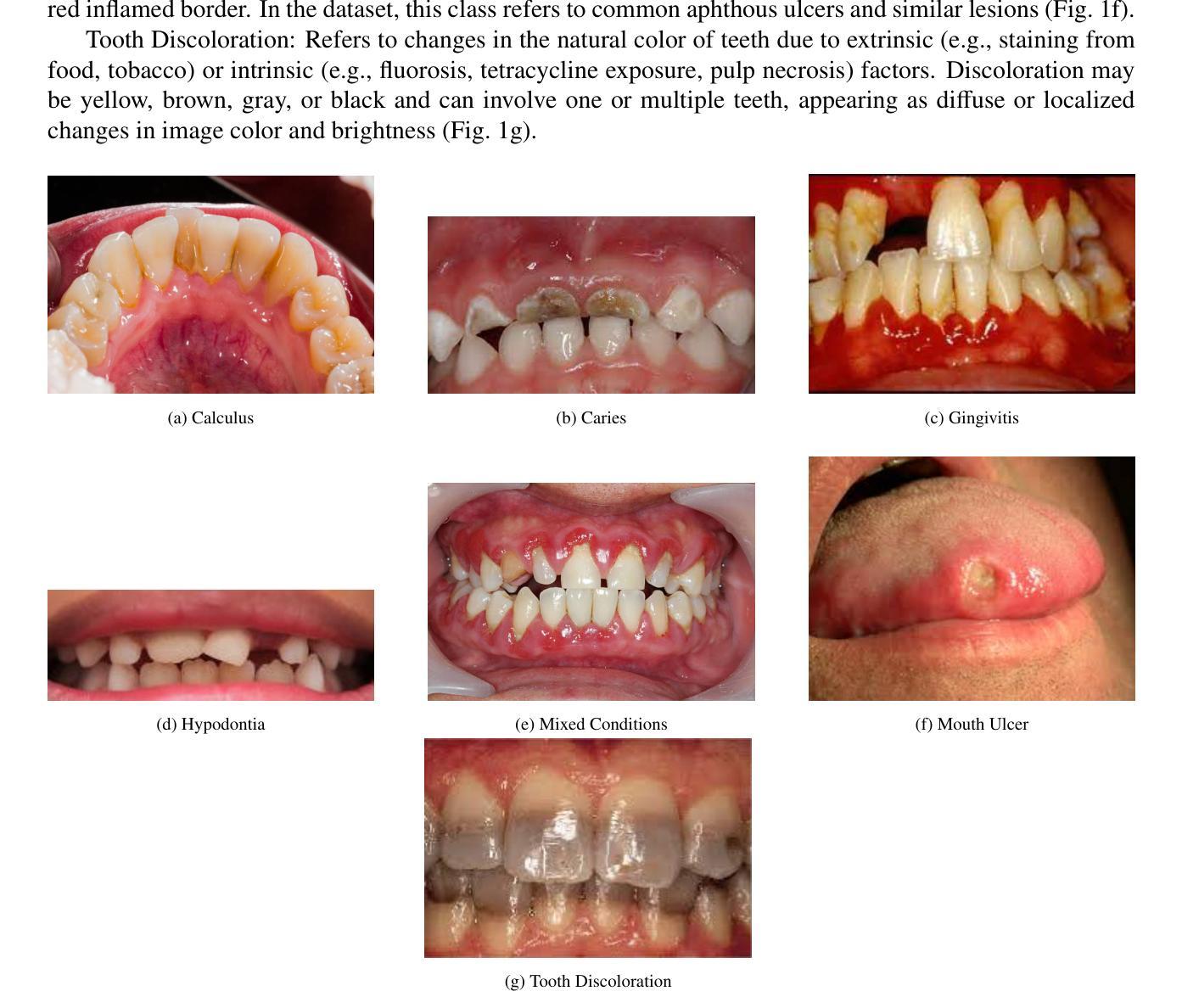
Objective: The aim of this study was to systematically evaluate and compare the performance of five state-of-the-art transformer-based architectures - Vision Transformer (ViT), Data-efficient Image Transformer (DeiT), ConvNeXt, Swin Transformer, and Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Image Transformers (BEiT) - for multi-class dental disease classification. The study specifically focused on addressing real-world challenges such as data imbalance, which is often overlooked in existing literature. Study Design: The Oral Diseases dataset was used to train and validate the selected models. Performance metrics, including validation accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score, were measured, with special emphasis on how well each architecture managed imbalanced classes. Results: ConvNeXt achieved the highest validation accuracy at 81.06, followed by BEiT at 80.00 and Swin Transformer at 79.73, all demonstrating strong F1-scores. ViT and DeiT achieved accuracies of 79.37 and 78.79, respectively, but both struggled particularly with Caries-related classes. Conclusions: ConvNeXt, Swin Transformer, and BEiT showed reliable diagnostic performance, making them promising candidates for clinical application in dental imaging. These findings provide guidance for model selection in future AI-driven oral disease diagnostic tools and highlight the importance of addressing data imbalance in real-world scenarios
目标:本研究旨在系统评估并比较五种最新基于transformer架构(包括Vision Transformer(ViT)、Data-efficient Image Transformer(DeiT)、ConvNeXt、Swin Transformer和Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Image Transformers(BEiT))在多类别牙科疾病分类中的表现。研究特别关注解决现实世界中的挑战,如数据不平衡问题,这在现有文献中经常被忽视。
研究设计:使用口腔疾病数据集对所选模型进行训练和验证。测量性能指标,包括验证准确率、精确度、召回率和F1分数,特别关注每种架构如何管理不平衡类别。
结果:ConvNeXt在验证准确率方面表现最佳,达到81.06%,其次是BEiT(80.00%)和Swin Transformer(79.73%),三者均表现出较高的F1分数。ViT和DeiT的准确率分别为79.37%和78.79%,但两者在处理与龋齿相关的类别时尤其困难。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages,3 figures
Summary
本文研究了五种先进的基于Transformer的架构(Vision Transformer、Data-efficient Image Transformer、ConvNeXt、Swin Transformer和Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Image Transformers)在多类牙科疾病分类中的性能表现。该研究着重解决数据不平衡等现实挑战,使用口腔疾病数据集进行训练和验证,并评估各架构在解决数据不平衡问题上的表现。结果显示,ConvNeXt、BEiT和Swin Transformer表现较好,其中ConvNeXt获得最高验证准确率。
Key Takeaways
- 研究旨在评估五种先进的基于Transformer的架构在多类牙科疾病分类中的性能。
- 研究关注现实挑战,如数据不平衡问题。
- 使用口腔疾病数据集进行训练和验证。
- ConvNeXt在验证准确率方面表现最佳,达到81.06%。
- BEiT和Swin Transformer也表现出良好的性能。
- ViT和DeiT在某些类别(如Caries)上的表现较差。
- ConvNeXt、Swin Transformer和BEiT在牙科影像临床应用中具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图
Mask What Matters: Controllable Text-Guided Masking for Self-Supervised Medical Image Analysis
Authors:Ruilang Wang, Shuotong Xu, Bowen Liu, Runlin Huang, Donglong Chen, Weifeng Su
The scarcity of annotated data in specialized domains such as medical imaging presents significant challenges to training robust vision models. While self-supervised masked image modeling (MIM) offers a promising solution, existing approaches largely rely on random high-ratio masking, leading to inefficiency and poor semantic alignment. Moreover, region-aware variants typically depend on reconstruction heuristics or supervised signals, limiting their adaptability across tasks and modalities. We propose Mask What Matters, a controllable text-guided masking framework for self-supervised medical image analysis. By leveraging vision-language models for prompt-based region localization, our method flexibly applies differentiated masking to emphasize diagnostically relevant regions while reducing redundancy in background areas. This controllable design enables better semantic alignment, improved representation learning, and stronger cross-task generalizability. Comprehensive evaluation across multiple medical imaging modalities, including brain MRI, chest CT, and lung X-ray, shows that Mask What Matters consistently outperforms existing MIM methods (e.g., SparK), achieving gains of up to +3.1 percentage points in classification accuracy, +1.3 in box average precision (BoxAP), and +1.1 in mask average precision (MaskAP) for detection. Notably, it achieves these improvements with substantially lower overall masking ratios (e.g., 40% vs. 70%). This work demonstrates that controllable, text-driven masking can enable semantically aligned self-supervised learning, advancing the development of robust vision models for medical image analysis.
在医疗成像等专业化领域,标注数据的稀缺性为训练稳健的视觉模型带来了重大挑战。虽然自监督的掩码图像建模(MIM)提供了有前景的解决方案,但现有方法大多依赖于随机的高比例掩码,导致效率低下和语义对齐不佳。此外,区域感知变体通常依赖于重建启发式或监督信号,这限制了它们在任务和模态之间的适应性。我们提出了“Mask What Matters”(掩码关键部分),这是一种可控的文本引导型掩码框架,用于自监督医疗图像分析。通过利用视觉语言模型进行基于提示的区域定位,我们的方法灵活地应用差异化掩码,以强调诊断相关区域,同时减少背景区域的冗余。这种可控的设计实现了更好的语义对齐、改进的表示学习和更强的跨任务泛化能力。在多种医疗成像模态的全面评估中,包括脑部MRI、胸部CT和肺部X射线,结果显示Mask What Matters始终优于现有的MIM方法(例如SparK),在分类精度上提高了高达+3.1个百分点,框平均精度(BoxAP)提高了+1.3,掩膜平均精度(MaskAP)在检测方面提高了+1.1。值得注意的是,它在实现这些改进的同时,总体掩码比例大幅降低(例如,40%对70%)。这项工作表明,可控的、文本驱动的掩码可以实现语义对齐的自监督学习,推动医疗图像分析领域稳健视觉模型的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对医学成像等特定领域标注数据稀缺的问题,自监督的掩膜图像建模(MIM)提供了一种有前途的解决方案。然而,现有方法大多依赖于随机高比例掩膜,导致效率低下和语义对齐不佳。本文提出Mask What Matters,一种可控的文本引导掩膜框架,用于自监督医学图像分析。通过利用视觉语言模型进行基于提示的区域定位,我们的方法能够灵活地应用差异化掩膜,以强调诊断相关区域,同时减少背景区域的冗余。该可控设计实现了更好的语义对齐、改进了表征学习和更强的跨任务泛化能力。在多个医学成像模态上的综合评估,包括脑MRI、胸部CT和肺部X射线,表明Mask What Matters在分类精度上较现有MIM方法平均提高了+3.1个百分点,框平均精度(BoxAP)提高了+1.3,掩膜平均精度(MaskAP)提高了+1.1。值得注意的是,它在实现这些改进的同时,整体掩膜比率大幅降低(例如,40%对70%)。这项工作表明,可控的、文本驱动的掩膜能够实现语义对齐的自监督学习,推动医学图像分析领域稳健视觉模型的发展。
关键见解
- 医学成像领域标注数据的稀缺性对训练稳健的视觉模型构成挑战。
- 自监督的掩膜图像建模(MIM)为这一问题提供了有前途的解决方案。
- 现有MIM方法主要依赖随机高比例掩膜,导致效率低下和语义对齐不佳。
- Mask What Matters框架通过文本引导的掩膜实现可控自监督学习。
- 该方法利用视觉语言模型进行基于提示的区域定位,强调诊断相关区域。
- Mask What Matters在多个医学成像模态上的表现优于现有MIM方法。
- 该方法在实现高性能的同时,降低了整体掩膜比率,展现了更强的效率和实用性。
点此查看论文截图
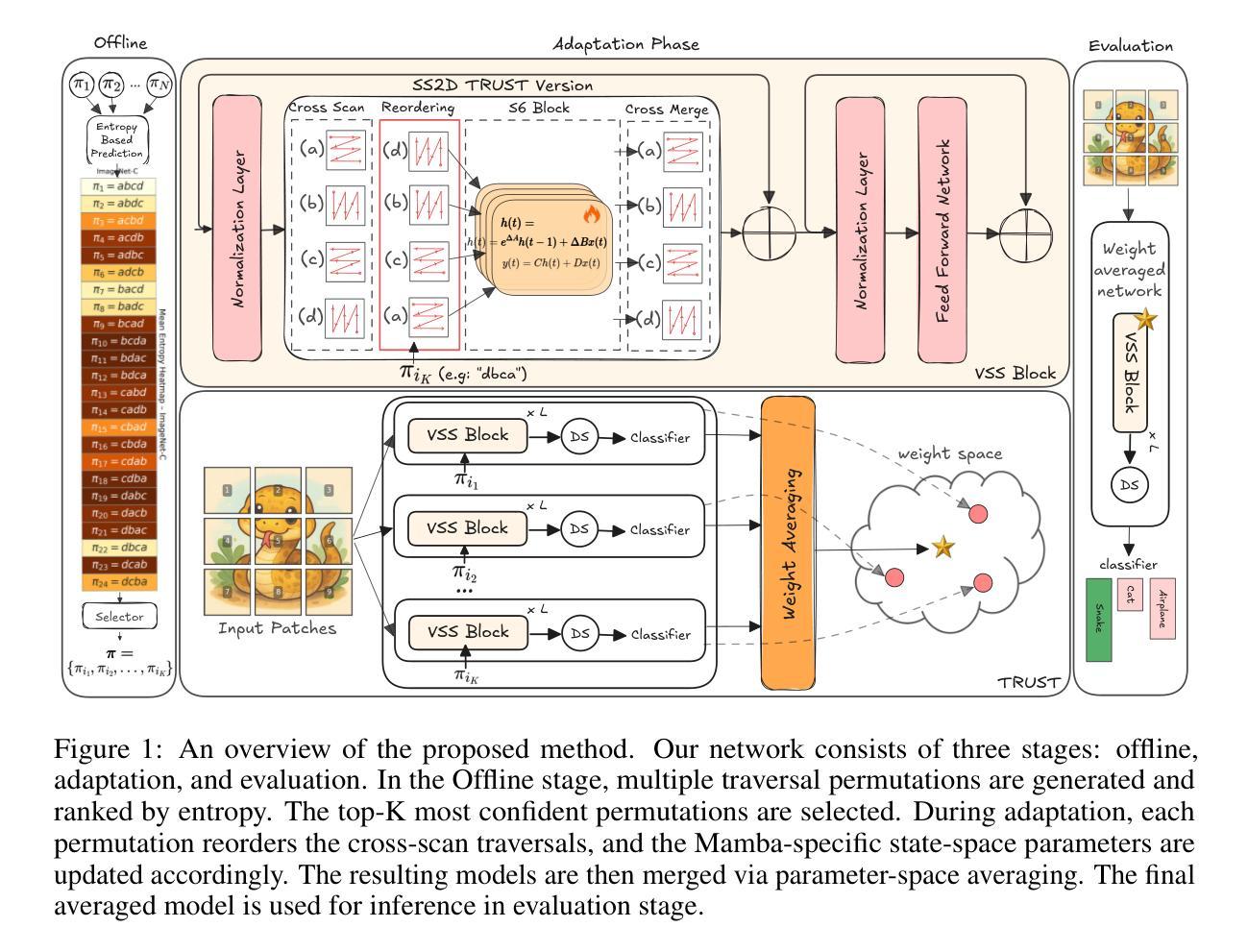
TRUST: Test-Time Refinement using Uncertainty-Guided SSM Traverses
Authors:Sahar Dastani, Ali Bahri, Gustavo Adolfo Vargas Hakim, Moslem Yazdanpanah, Mehrdad Noori, David Osowiechi, Samuel Barbeau, Ismail Ben Ayed, Herve Lombaert, Christian Desrosiers
State Space Models (SSMs) have emerged as efficient alternatives to Vision Transformers (ViTs), with VMamba standing out as a pioneering architecture designed for vision tasks. However, their generalization performance degrades significantly under distribution shifts. To address this limitation, we propose TRUST (Test-Time Refinement using Uncertainty-Guided SSM Traverses), a novel test-time adaptation (TTA) method that leverages diverse traversal permutations to generate multiple causal perspectives of the input image. Model predictions serve as pseudo-labels to guide updates of the Mamba-specific parameters, and the adapted weights are averaged to integrate the learned information across traversal scans. Altogether, TRUST is the first approach that explicitly leverages the unique architectural properties of SSMs for adaptation. Experiments on seven benchmarks show that TRUST consistently improves robustness and outperforms existing TTA methods.
状态空间模型(SSMs)作为视觉转换器(ViTs)的有效替代方案已经出现,其中VMamba作为一种针对视觉任务设计的开创性架构尤为突出。然而,它们在分布变化下的泛化性能会显著下降。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了名为TRUST(使用不确定性引导SSM遍历的测试时间细化)的新型测试时间适应(TTA)方法,该方法利用不同的遍历排列来生成输入图像的多个因果视角。模型预测作为伪标签来指导Mamba特定参数的更新,并且适应的权重被平均化以整合多次遍历扫描中所学习的信息。总体而言,TRUST是第一个明确利用SSMs的独特架构属性进行适应的方法。在七个基准测试上的实验表明,TRUST持续提高了稳健性并在测试中超越了现有的TTA方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
状态空间模型(SSMs)作为高效的视觉转换器(ViTs)替代方案已崭露头角,其中VMamba是为视觉任务设计的开创性架构。然而,它们在分布转移下的泛化性能显著下降。为解决这一局限性,我们提出了名为TRUST的新型测试时间适应(TTA)方法,该方法利用不同的遍历排列生成输入图像的多个因果视角。模型预测作为伪标签指导Mamba特定参数的更新,并平均适应权重以整合遍历扫描中的学习信息。总体而言,TRUST是第一个明确利用SSMs独特架构属性进行适应的方法。在七个基准测试上的实验表明,TRUST在提升稳健性方面表现稳定,并优于现有的TTA方法。
Key Takeaways
- 状态空间模型(SSMs)已成为Vision Transformers(ViTs)的有效替代方案。
- VMamba是一种专为视觉任务设计的开创性架构。
- SSMs在分布转移下的泛化性能存在显著下降。
- TRUST是一种新型的测试时间适应(TTA)方法,利用不同的遍历排列生成输入图像的多个因果视角。
- 模型预测作为伪标签指导Mamba特定参数的更新。
- TRUST通过平均适应权重整合遍历扫描中的学习信息。
点此查看论文截图
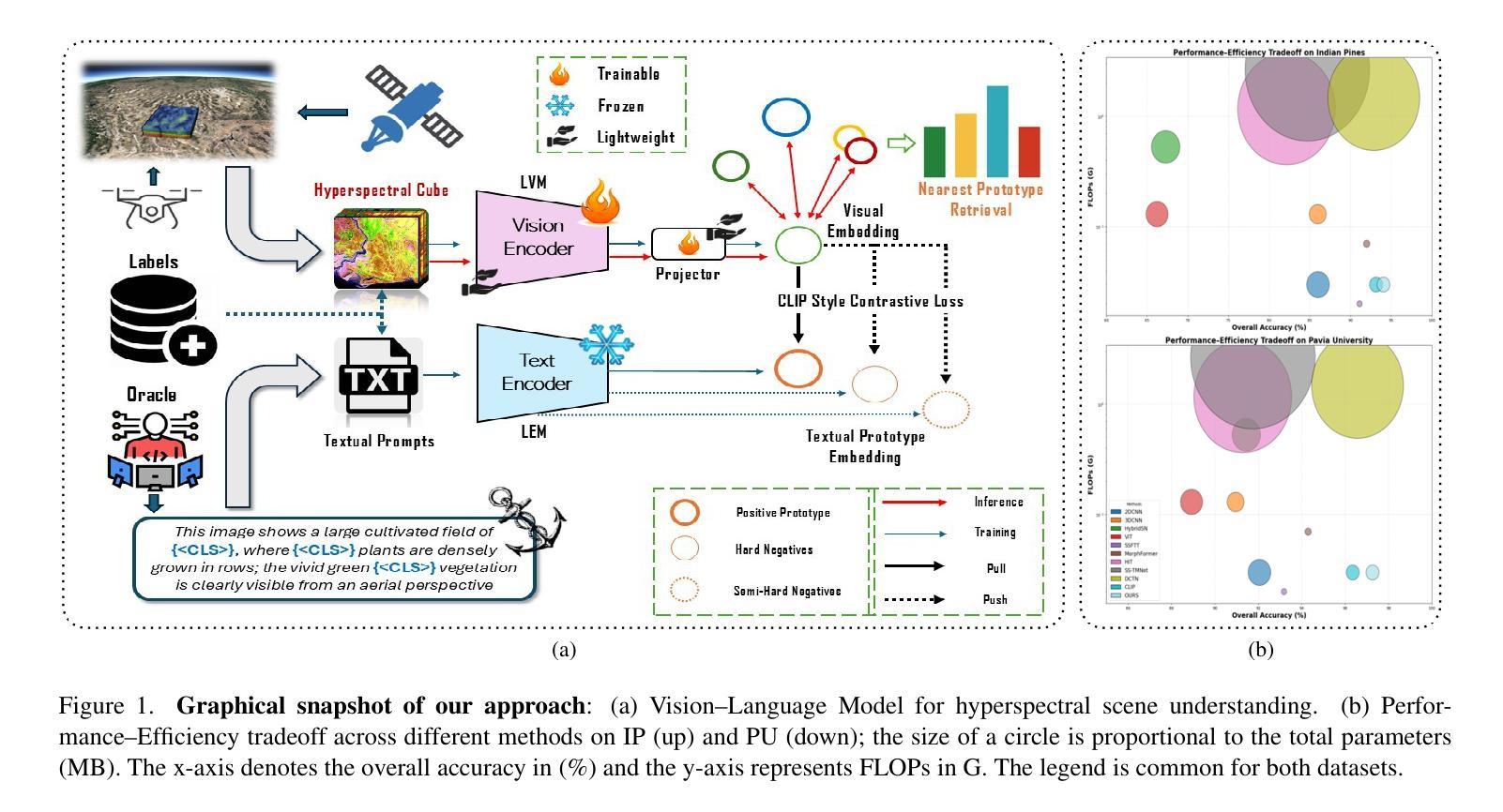
Learning Hyperspectral Images with Curated Text Prompts for Efficient Multimodal Alignment
Authors:Abhiroop Chatterjee, Susmita Ghosh
As data requirements continue to grow, efficient learning increasingly depends on the curation and distillation of high-value data rather than brute-force scaling of model sizes. In the case of a hyperspectral image (HSI), the challenge is amplified by the high-dimensional 3D voxel structure, where each spatial location is associated with hundreds of contiguous spectral channels. While vision and language models have been optimized effectively for natural image or text tasks, their cross-modal alignment in the hyperspectral domain remains an open and underexplored problem. In this article, we make an attempt to optimize a Vision-Language Model (VLM) for hyperspectral scene understanding by exploiting a CLIP-style contrastive training framework. Our framework maps voxel-level embeddings from a vision backbone onto the latent space of a frozen large embedding model (LEM), where a trainable probe aligns vision features with the model’s textual token representations. The two modalities are aligned via a contrastive loss restricted to a curated set of hard (closest wrong classes) and semi-hard (random distractors) negatives, along with positive pairs. To further enhance alignment, descriptive prompts that encode class semantics are introduced and act as structured anchors for the HSI embeddings. It is seen that the proposed method updates only 0.07 percent of the total parameters, yet yields state-of-the-art performance. For example, on Indian Pines (IP) the model produces better results over unimodal and multimodal baselines by +0.92 Overall Accuracy (OA) and +1.60 Kappa ($\kappa$), while on Pavia University (PU) data it provides gains of +0.69 OA and +0.90 $\kappa$. Moreover, this is achieved with the set of parameters, nearly 50$\times$ smaller than DCTN and 90$\times$ smaller than SS-TMNet.
随着数据需求的持续增长,高效学习越来越依赖于高价值数据的筛选和提炼,而不是粗暴地扩大模型规模。对于高光谱图像(HSI)而言,由于每个空间位置都与数百个连续光谱通道相关联的高维三维体素结构,挑战被放大了。虽然视觉和语言模型已针对自然图像或文本任务进行了有效优化,但它们在超光谱域中的跨模态对齐仍然是一个开放且尚未充分探索的问题。在本文中,我们尝试利用CLIP风格的对比训练框架来优化用于超光谱场景理解的视觉语言模型(VLM)。我们的框架将从视觉主干中提取的体素级嵌入映射到冻结的大型嵌入模型(LEM)的潜在空间上,其中可训练探针将视觉特征与模型的文本令牌表示进行对齐。两种模态通过对比损失与精选的硬(最接近的错类)和半硬(随机干扰项)负样本以及正样本对进行对齐。为了进一步增强对齐效果,引入了编码类语义的描述性提示,这些提示充当超光谱图像嵌入的结构锚点。可以看到,该方法仅更新总参数的0.07%,但取得了最新性能。例如,在印第安松(IP)上,该模型相对于单模态和多模态基线提高了+0.92的整体精度(OA)和+1.60的卡帕系数(κ),而在帕维亚大学(PU)数据集上,它提供了+0.69的OA和+0.90的卡帕系数增益。此外,这是通过使用参数集实现的,几乎是DCTN的50倍小,并且是SS-TMNet的90倍小。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV 2025), Workshop on Curated Data for Efficient Learning
Summary
本文探讨了随着数据量增长,高效学习越来越依赖于高质量数据的筛选和提炼,而非模型规模的简单扩展。针对高光谱图像(HSI)的特殊挑战,文章尝试优化跨模态对齐的视语言模型(VLM),利用CLIP风格的对比训练框架进行高光谱场景理解。通过映射视觉骨干的像素级嵌入到预训练的大型嵌入模型的潜在空间,并用可训练探头对齐视觉特征与模型文本符号表示来实现模型对齐。利用精选的硬(最接近的错误类别)和半硬(随机干扰项)负样本以及正样本对进行对比损失的限制,同时引入编码类别语义的描述性提示作为结构化锚点以增强对齐效果。此方法仅更新总参数的0.07%,却在印度松树和帕维亚大学数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 高效学习更注重高质量数据的筛选和提炼,而非模型规模的简单扩展。
- 针对高光谱图像的特殊挑战,优化视语言模型(VLM)在超光谱场景理解中的表现是一个关键课题。
- 利用CLIP风格的对比训练框架实现模型的跨模态对齐。
- 模型通过对视觉嵌入与预训练的大型嵌入模型对齐,以增强模型性能。
- 对比损失利用精选的负样本和正样本对进行训练,提高了模型的对齐精度。
- 描述性提示被引入作为结构化锚点,进一步增强模型的对齐效果。
- 该方法实现了在特定数据集上的先进性能,且参数规模相对较小。
点此查看论文截图
ViSpec: Accelerating Vision-Language Models with Vision-Aware Speculative Decoding
Authors:Jialiang Kang, Han Shu, Wenshuo Li, Yingjie Zhai, Xinghao Chen
Speculative decoding is a widely adopted technique for accelerating inference in large language models (LLMs), yet its application to vision-language models (VLMs) remains underexplored, with existing methods achieving only modest speedups (<1.5x). This gap is increasingly significant as multimodal capabilities become central to large-scale models. We hypothesize that large VLMs can effectively filter redundant image information layer by layer without compromising textual comprehension, whereas smaller draft models struggle to do so. To address this, we introduce Vision-Aware Speculative Decoding (ViSpec), a novel framework tailored for VLMs. ViSpec employs a lightweight vision adaptor module to compress image tokens into a compact representation, which is seamlessly integrated into the draft model’s attention mechanism while preserving original image positional information. Additionally, we extract a global feature vector for each input image and augment all subsequent text tokens with this feature to enhance multimodal coherence. To overcome the scarcity of multimodal datasets with long assistant responses, we curate a specialized training dataset by repurposing existing datasets and generating extended outputs using the target VLM with modified prompts. Our training strategy mitigates the risk of the draft model exploiting direct access to the target model’s hidden states, which could otherwise lead to shortcut learning when training solely on target model outputs. Extensive experiments validate ViSpec, achieving, to our knowledge, the first substantial speedup in VLM speculative decoding. Code is available at https://github.com/KangJialiang/ViSpec.
推测解码是加速大型语言模型(LLM)推理的广泛采用的技术,然而它在视觉语言模型(VLM)中的应用仍然被探索得不够深入,现有方法只实现了适中的加速(<1.5倍)。随着多模态能力成为大规模模型的核心,这一差距越来越显著。我们假设大型VLM可以逐层有效地过滤掉冗余的图像信息,而不损害文本理解,而较小的草稿模型则很难做到这一点。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了专为VLM定制的Vision-Aware Speculative Decoding(ViSpec)新型框架。ViSpec采用轻量级的视觉适配器模块,将图像令牌压缩成紧凑的表示形式,无缝集成到草稿模型的注意力机制中,同时保留原始图像的位置信息。此外,我们为每个输入图像提取全局特征向量,并将其增强到所有后续的文本令牌中,以提高多模态一致性。为了克服缺乏带有长辅助响应的多模态数据集的问题,我们通过重新利用现有数据集并使用目标VLM生成扩展输出,来制作一个专门用于训练的数据集。我们的训练策略减轻了草稿模型直接访问目标模型的隐藏状态的风险,因为如果仅在目标模型输出上进行训练,可能会导致走捷径学习。大量实验验证了ViSpec的有效性,据我们所知,这是VLM推测解码中的首次实质性加速。代码可在https://github.com/KangJialiang/ViSpec获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2025
Summary:
针对视觉语言模型(VLMs)的推测解码技术尚未得到充分研究,现有方法的速度提升有限(小于1.5倍)。为解决这一问题,本文提出一种针对VLMs量身定制的新型框架——Vision-Aware Speculative Decoding(ViSpec)。它通过轻量级视觉适配器模块压缩图像标记为紧凑表示形式,无缝集成到草案模型的注意力机制中,同时保留原始图像的位置信息。此外,本文还通过重新利用现有数据集并生成扩展输出,创建了一种特殊训练数据集。实验证明,ViSpec实现了对VLM推测解码的首次实质性加速。
Key Takeaways:
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)的推测解码技术应用不足,现有方法提速有限。
- 大型VLMs能有效过滤冗余图像信息层,而小型模型则难以做到。
- 引入新型框架Vision-Aware Speculative Decoding(ViSpec),专为VLMs设计。
- ViSpec使用轻量级视觉适配器模块压缩图像标记,并集成到模型的注意力机制中。
- ViSpec保留原始图像的位置信息,增强多模态连贯性。
- 通过重新利用现有数据集并生成扩展输出,创建特殊训练数据集。
- ViSpec实现了对VLM推测解码的首次实质性加速,代码已公开。
点此查看论文截图

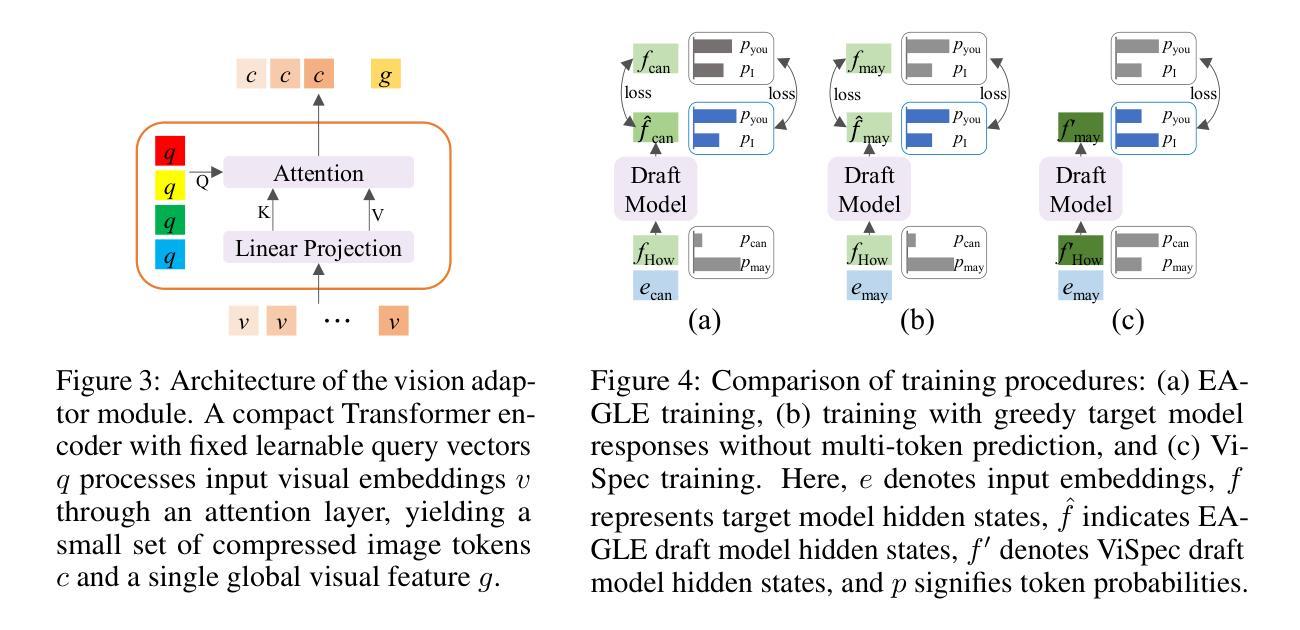
Power Battery Detection
Authors:Xiaoqi Zhao, Peiqian Cao, Chenyang Yu, Zonglei Feng, Lihe Zhang, Hanqi Liu, Jiaming Zuo, Youwei Pang, Jinsong Ouyang, Weisi Lin, Georges El Fakhri, Huchuan Lu, Xiaofeng Liu
Power batteries are essential components in electric vehicles, where internal structural defects can pose serious safety risks. We conduct a comprehensive study on a new task, power battery detection (PBD), which aims to localize the dense endpoints of cathode and anode plates from industrial X-ray images for quality inspection. Manual inspection is inefficient and error-prone, while traditional vision algorithms struggle with densely packed plates, low contrast, scale variation, and imaging artifacts. To address this issue and drive more attention into this meaningful task, we present PBD5K, the first large-scale benchmark for this task, consisting of 5,000 X-ray images from nine battery types with fine-grained annotations and eight types of real-world visual interference. To support scalable and consistent labeling, we develop an intelligent annotation pipeline that combines image filtering, model-assisted pre-labeling, cross-verification, and layered quality evaluation. We formulate PBD as a point-level segmentation problem and propose MDCNeXt, a model designed to extract and integrate multi-dimensional structure clues including point, line, and count information from the plate itself. To improve discrimination between plates and suppress visual interference, MDCNeXt incorporates two state space modules. The first is a prompt-filtered module that learns contrastive relationships guided by task-specific prompts. The second is a density-aware reordering module that refines segmentation in regions with high plate density. In addition, we propose a distance-adaptive mask generation strategy to provide robust supervision under varying spatial distributions of anode and cathode positions. The source code and datasets will be publicly available at \href{https://github.com/Xiaoqi-Zhao-DLUT/X-ray-PBD}{PBD5K}.
动力电池是电动汽车中的重要组成部分,其内部结构性缺陷可能带来严重的安全风险。我们对一项新任务——动力电池检测(PBD)进行了深入研究,该任务旨在从工业X射线图像中定位阴极和阳极板的密集端点,以进行质量检测。人工检测效率低下且易出错,而传统视觉算法在密集排列的板材、低对比度、尺度变化和图像伪影方面表现挣扎。为了解决这个问题并吸引更多注意力关注这项有意义的任务,我们推出了PBD5K,这是该任务的首个大规模基准测试,包含来自九种电池类型的5000张X射线图像,具有细粒度注释和八种现实世界中的视觉干扰类型。为了支持可扩展和一致的标注,我们开发了一个智能标注管道,该管道结合了图像过滤、模型辅助预标注、交叉验证和分层质量评估。我们将PBD制定为点级分割问题,并提出MDCNeXt模型,该模型旨在提取和整合包括点、线和计数信息在内的多维结构线索。为了提高板之间的辨别力并抑制视觉干扰,MDCNeXt结合了两种状态空间模块。第一个是提示过滤模块,它学习在任务特定提示的指导下对比关系。第二个是密度感知重排序模块,该模块可以细化高板密度区域的分割。此外,我们提出了一种距离自适应掩膜生成策略,以在阳极和阴极位置空间分布变化的情况下提供稳健的监督。源代码和数据集将在https://github.com/Xiaoqi-Zhao-DLUT/X-ray-PBD公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under submission to International Journal of Computer Vision (IJCV)
Summary
针对动力电池检测(PBD)任务,本研究提出PBD5K数据集和MDCNeXt模型。数据集包含五千张X射线图像和精细标注,旨在解决传统视觉算法在电池板密集排列、低对比度、尺度变化和成像伪影上的挑战。MDCNeXt能提取和整合多维结构线索,采用双态空间模块抑制视觉干扰并提高区分度。研究促进了技术进步和资源共享。详情请参见数据集及代码链接(https://github.com/Xiaoqi-Zhao-DLUT/X-ray-PBD)。
Key Takeaways
- 动力蓄电池检测(PBD)旨在从工业X射线图像中定位阴极和阳极板的密集端点进行质量检测。
- 手动检测效率低下且易出错,传统视觉算法面临多项挑战。
- 提出PBD5K数据集,包含五千张图像和精细标注,用于推动该任务的研究。
- 开发智能标注管道,支持可扩展和一致的标注工作。
- 将PBD定义为点级别分割问题,并提出MDCNeXt模型来解决这一问题。
- MDCNeXt通过两个态空间模块提高板间区分度和抑制视觉干扰。
- 采用自适应距离掩膜生成策略,适应不同空间分布的阳极和阴极位置标注问题。
点此查看论文截图
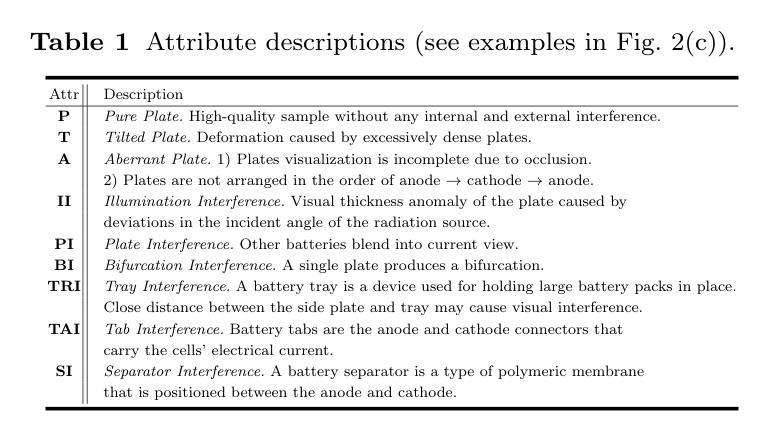
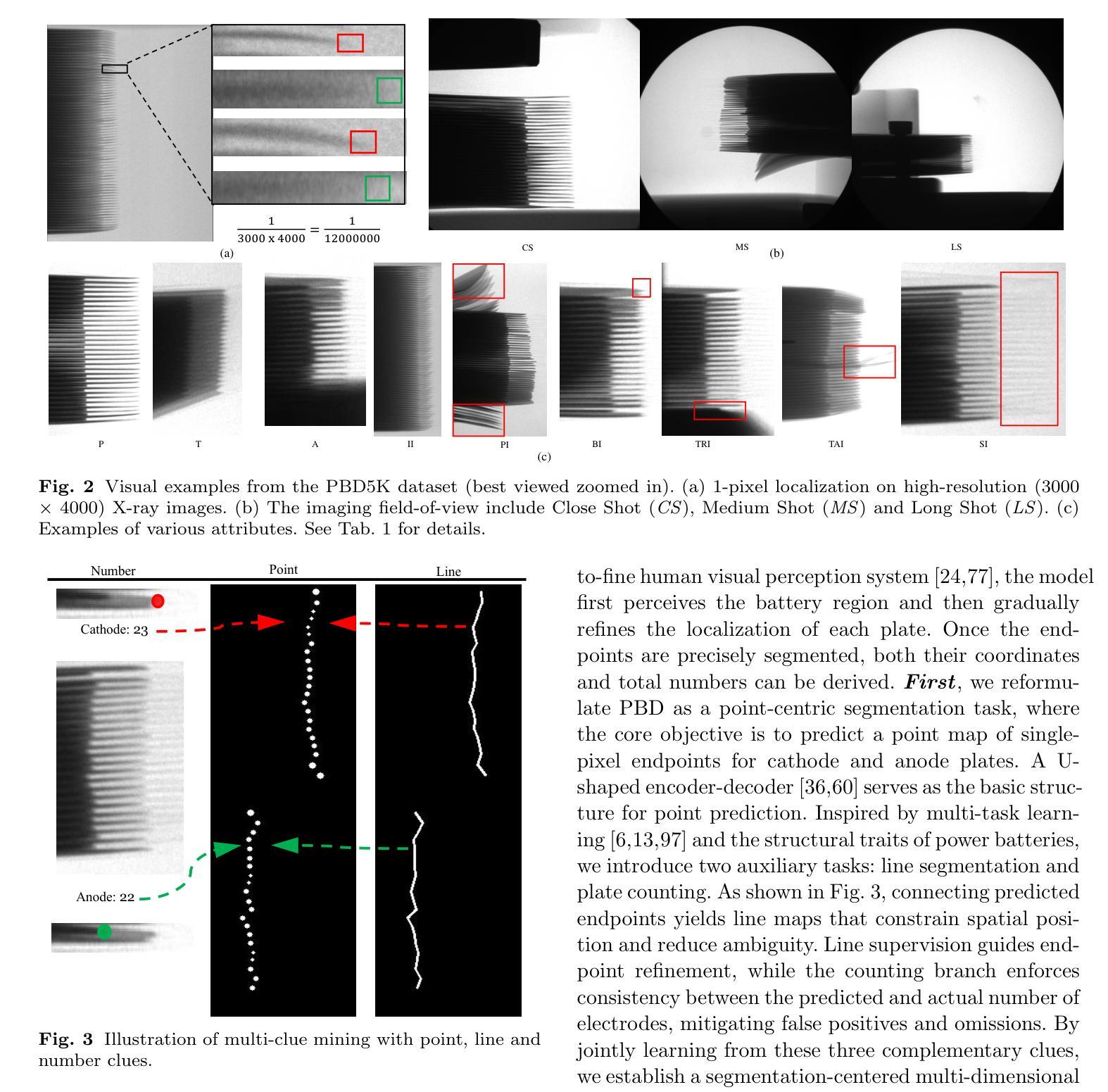
FA: Forced Prompt Learning of Vision-Language Models for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Authors:Xinhua Lu, Runhe Lai, Yanqi Wu, Kanghao Chen, Wei-Shi Zheng, Ruixuan Wang
Pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) have advanced out-of-distribution (OOD) detection recently. However, existing CLIP-based methods often focus on learning OOD-related knowledge to improve OOD detection, showing limited generalization or reliance on external large-scale auxiliary datasets. In this study, instead of delving into the intricate OOD-related knowledge, we propose an innovative CLIP-based framework based on Forced prompt leArning (FA), designed to make full use of the In-Distribution (ID) knowledge and ultimately boost the effectiveness of OOD detection. Our key insight is to learn a prompt (i.e., forced prompt) that contains more diversified and richer descriptions of the ID classes beyond the textual semantics of class labels. Specifically, it promotes better discernment for ID images, by forcing more notable semantic similarity between ID images and the learnable forced prompt. Moreover, we introduce a forced coefficient, encouraging the forced prompt to learn more comprehensive and nuanced descriptions of the ID classes. In this way, FA is capable of achieving notable improvements in OOD detection, even when trained without any external auxiliary datasets, while maintaining an identical number of trainable parameters as CoOp. Extensive empirical evaluations confirm our method consistently outperforms current state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at https://github.com/0xFAFA/FA.
预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)最近在异常分布(OOD)检测方面取得了进展。然而,现有的基于CLIP的方法往往侧重于学习OOD相关知识以提高OOD检测能力,表现出有限的泛化能力或对外部大规模辅助数据集的依赖。本研究中,我们并未深入研究复杂的OOD相关知识,而是提出了一种基于强制提示学习(FA)的CLIP模型框架,旨在充分利用内分布(ID)知识,并最终提高OOD检测的有效性。我们的关键见解是学习一种提示(即强制提示),其中包含超越类别标签文本语义的ID类别的更多样化和丰富的描述。具体来说,它通过强制ID图像和可学习的强制提示之间更显著的语义相似性,促进了对ID图像的更佳辨别力。此外,我们引入了一个强制系数,鼓励强制提示学习更全面、更微妙的ID类别描述。通过这种方式,即使在没有任何外部辅助数据集的情况下进行训练,FA也能在OOD检测方面实现显著的改进,同时保持与CoOp相同的可训练参数数量。大量的实证研究证实,我们的方法始终优于当前最先进的方法。代码可在https://github.com/0xFAFA/FA找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 4 figures, Accepted by ICCV2025
Summary
本文提出了一种基于CLIP的强制提示学习(FA)框架,旨在充分利用分布内(ID)知识,提高异常检测效果。通过强制提示学习,模型能够学习包含超过类别标签文本语义的更多样化和丰富的描述,促进对分布内图像的更好辨别。引入强制系数,鼓励强制提示学习更全面、更微妙的分布内类别描述,无需任何外部辅助数据集即可实现显著的异常检测改进。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种基于CLIP的强制提示学习(FA)框架,旨在提高异常检测效果。
- FA框架利用分布内(ID)知识,通过强制提示学习更多样化和丰富的描述。
- 强制提示学习能够促进对分布内图像的更好辨别。
- 引入强制系数,鼓励强制提示学习更全面、更微妙的分布内类别描述。
- FA框架无需任何外部辅助数据集即可实现显著的异常检测改进。
- 广泛实验评估表明,FA框架的性能持续超越当前先进方法。
点此查看论文截图
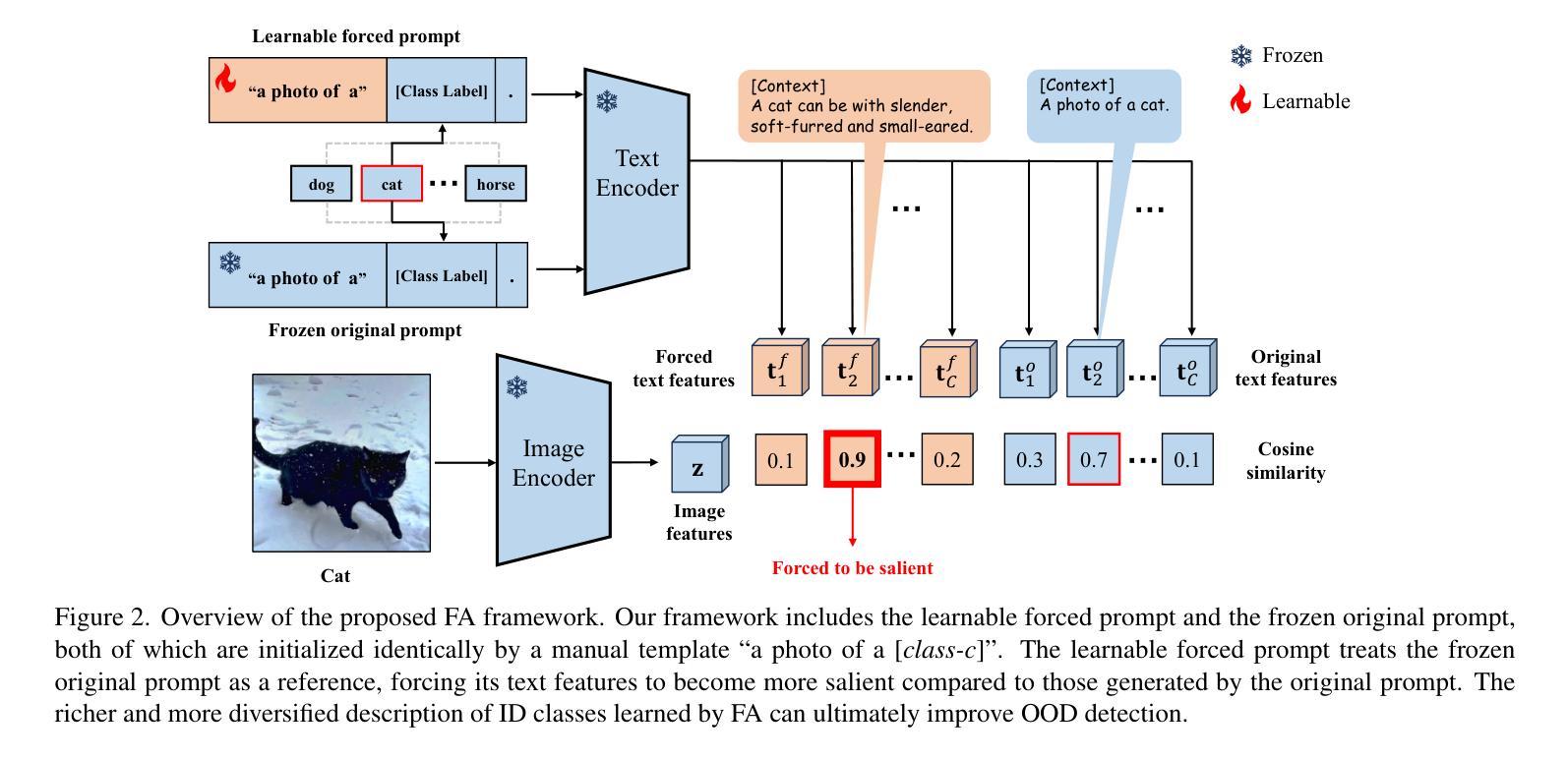
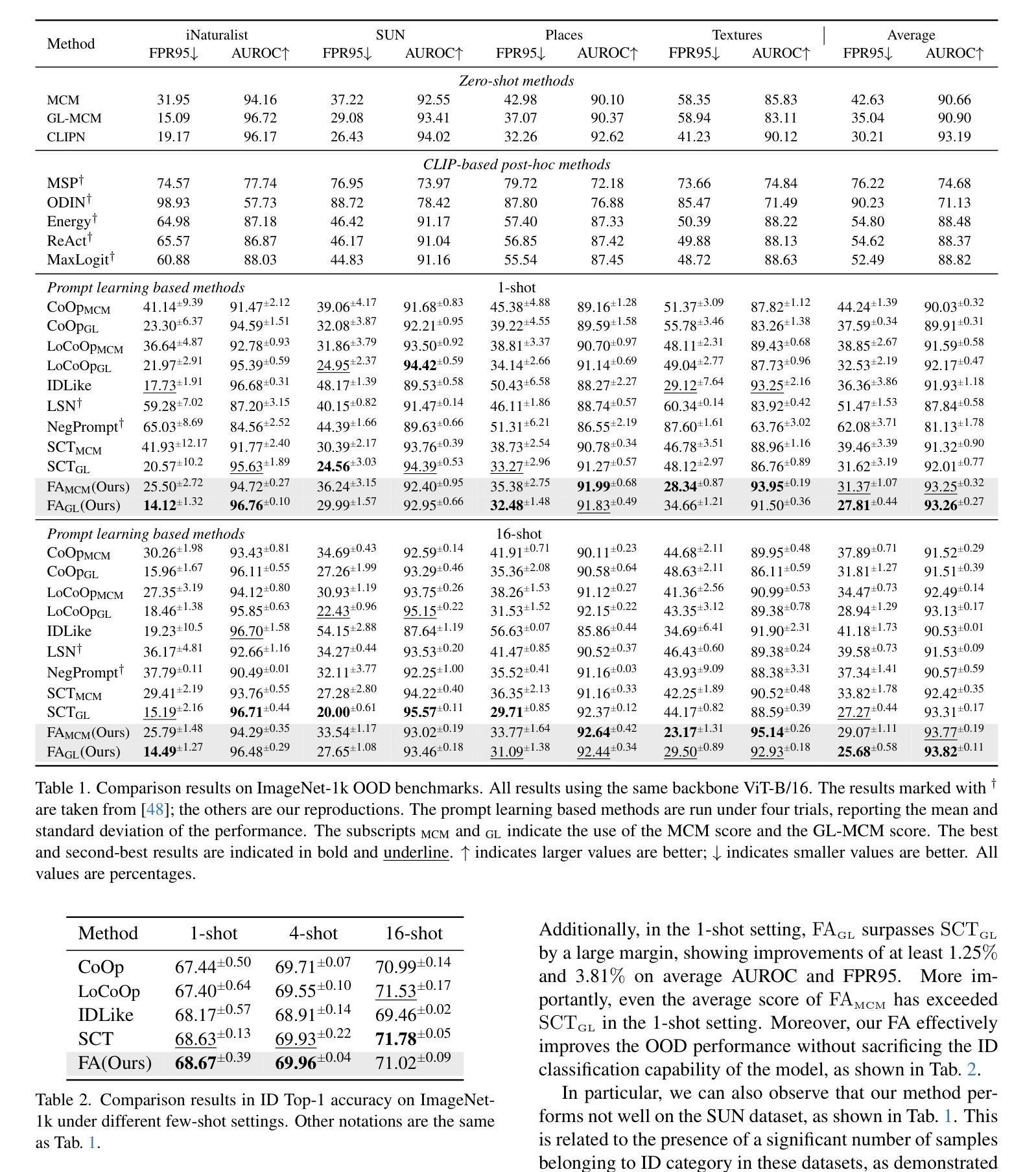
Advancing Marine Research: UWSAM Framework and UIIS10K Dataset for Precise Underwater Instance Segmentation
Authors:Hua Li, Shijie Lian, Zhiyuan Li, Runmin Cong, Chongyi Li, Laurence T. Yang, Weidong Zhang, Sam Kwong
With recent breakthroughs in large-scale modeling, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has demonstrated significant potential in a variety of visual applications. However, due to the lack of underwater domain expertise, SAM and its variants face performance limitations in end-to-end underwater instance segmentation tasks, while their higher computational requirements further hinder their application in underwater scenarios. To address this challenge, we propose a large-scale underwater instance segmentation dataset, UIIS10K, which includes 10,048 images with pixel-level annotations for 10 categories. Then, we introduce UWSAM, an efficient model designed for automatic and accurate segmentation of underwater instances. UWSAM efficiently distills knowledge from the SAM ViT-Huge image encoder into the smaller ViT-Small image encoder via the Mask GAT-based Underwater Knowledge Distillation (MG-UKD) method for effective visual representation learning. Furthermore, we design an End-to-end Underwater Prompt Generator (EUPG) for UWSAM, which automatically generates underwater prompts instead of explicitly providing foreground points or boxes as prompts, thus enabling the network to locate underwater instances accurately for efficient segmentation. Comprehensive experimental results show that our model is effective, achieving significant performance improvements over state-of-the-art methods on multiple underwater instance datasets. Datasets and codes are available at https://github.com/LiamLian0727/UIIS10K.
随着大规模建模的最新突破,Segment Anything Model(SAM)在各种视觉应用中显示出巨大的潜力。然而,由于缺乏水下领域的专业知识,SAM及其变体在端到端的水下实例分割任务中面临性能局限,而它们较高的计算要求进一步阻碍了在水下场景中的应用。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一个大规模的水下实例分割数据集UIIS10K,其中包括10,048张具有10类像素级注释的图像。接着,我们介绍了UWSAM,这是一个为水下实例自动准确分割而设计的高效模型。UWSAM通过基于Mask GAT的水下知识蒸馏(MG-UKD)方法,有效地从SAM的ViT-Huge图像编码器蒸馏知识到较小的ViT-Small图像编码器,从而实现有效的视觉表示学习。此外,我们为UWSAM设计了端到端的水下提示生成器(EUPG),它会自动生成水下提示,而不是显式提供前景点或框作为提示,从而使网络能够准确定位水下实例,以实现高效的分割。综合实验结果表明,我们的模型非常有效,在多个水下实例数据集上实现了对最先进方法的大幅性能提升。数据集和代码可通过https://github.com/LiamLian0727/UIIS10K获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
SAM模型在多种视觉应用中显示出巨大潜力,但在水下实例分割任务中表现受限。为应对挑战,我们提出了大规模水下实例分割数据集UIIS10K,包含10,048张带像素级标注的图像。同时,我们引入了专为水下实例自动准确分割设计的UWSAM模型。该模型通过Mask GAT基础水下知识蒸馏方法,从SAM的ViT-Huge图像编码器提炼知识,用于有效视觉表征学习。我们还为UWSAM设计了端到端水下提示生成器(EUPG),可自动生成水下提示,无需明确提供前景点或框,从而提高网络在水下实例定位的准确性。实验结果表明,我们的模型在多个水下实例数据集上实现了显著的性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- SAM模型在视觉应用中有巨大潜力,但在水下实例分割任务中表现受限,缺乏水下领域专业知识。
- 提出了大规模水下实例分割数据集UIIS10K,包含10,048张带像素级标注的图像,为水下实例分割研究提供数据支持。
- 引入了UWSAM模型,专为水下实例自动准确分割设计。
- UWSAM通过Mask GAT基础水下知识蒸馏方法提炼知识,提高视觉表征学习效果。
- 端到端水下提示生成器(EUPG)的引入,能够自动生成水下提示,提高网络在水下实例定位的准确性。
- UWSAM模型在多个水下实例数据集上实现了显著的性能提升。
- 数据集和代码已公开,便于研究使用。
点此查看论文截图
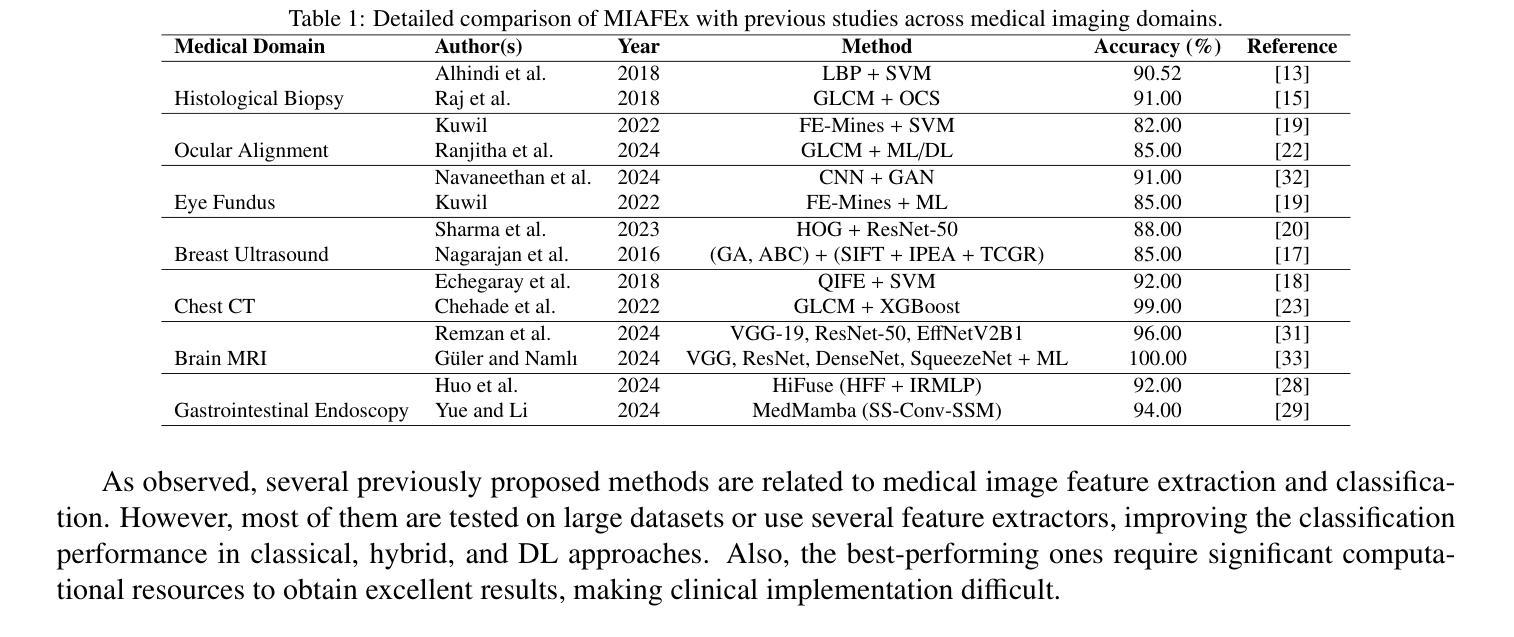
MIAFEx: An Attention-based Feature Extraction Method for Medical Image Classification
Authors:Oscar Ramos-Soto, Jorge Ramos-Frutos, Ezequiel Perez-Zarate, Diego Oliva, Sandra E. Balderas-Mata
Feature extraction techniques are crucial in medical image classification; however, classical feature extractors, in addition to traditional machine learning classifiers, often exhibit significant limitations in providing sufficient discriminative information for complex image sets. While Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformer (ViT) have shown promise in feature extraction, they are prone to overfitting due to the inherent characteristics of medical imaging data, including small sample sizes or high intra-class variance. In this work, the Medical Image Attention-based Feature Extractor (MIAFEx) is proposed, a novel method that employs a learnable refinement mechanism to enhance the classification token within the Transformer encoder architecture. This mechanism adjusts the token based on learned weights, improving the extraction of salient features and enhancing the model’s adaptability to the challenges presented by medical imaging data. The MIAFEx output feature quality is compared against classical feature extractors using traditional and hybrid classifiers. Also, the performance of these features is compared against modern CNN and ViT models in classification tasks, demonstrating their superiority in accuracy and robustness across multiple complex medical imaging datasets. This advantage is particularly pronounced in scenarios with limited training data, where traditional and modern models often struggle to generalize effectively. The source code of this proposal can be found at https://github.com/Oscar-RamosS/Medical-Image-Attention-based-Feature-Extractor-MIAFEx
特征提取技术在医学图像分类中至关重要;然而,除了传统的机器学习分类器外,经典的特征提取器在处理复杂图像集时,在提供足够的判别信息方面往往存在显著局限性。卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)在特征提取方面已显示出潜力,但由于医学成像数据内在的特性(如样本量小或类内方差高),它们容易发生过拟合。在本研究中,提出了一种医学图像注意力特征提取器(MIAFEx),这是一种新型方法,采用可学习的细化机制来增强转换器编码器架构中的分类标记。该机制根据学习到的权重调整标记,提高显著特征的提取能力,增强模型对医学成像数据所呈现挑战的适应性。将MIAFEx的输出特征质量与使用传统和混合分类器的经典特征提取器进行比较。此外,还比较了这些特征在现代CNN和ViT模型中的分类任务性能,在多个复杂的医学成像数据集上证明了其在准确性和稳健性方面的优越性。这一优势在训练数据有限的情况下尤为突出,传统和现代模型在这种情况下往往难以有效地推广。该提案的源代码可在https://github.com/Oscar-RamosS/Medical-Image-Attention-based-Feature-Extractor-MIAFEx找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This is the preprint version of an article that has been accepted for publication in Knowledge-Based Systems
Summary
本文介绍了在医疗图像分类中特征提取技术的重要性。针对传统特征提取器和机器学习分类器在处理复杂图像集时提供的判别信息不足的问题,提出了基于注意力的医疗图像特征提取器(MIAFEx)。该方法采用可学习的细化机制,根据学习到的权重调整分类令牌,提高了显著特征的提取能力,并增强了模型对医疗图像数据挑战的适应性。MIAFEx的特征输出质量在多个复杂的医疗图像数据集上被评估,并展示了相较于传统和现代模型的准确性和鲁棒性的优势,特别是在训练数据有限的情况下。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像分类中特征提取技术至关重要,但传统特征提取器和机器学习分类器存在局限性。
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) 和 Vision Transformer (ViT) 在特征提取方面展现出潜力,但仍存在过拟合风险。
- 提出的 Medical Image Attention-based Feature Extractor (MIAFEx) 采用可学习细化机制,改进分类令牌的提取。
- MIAFEx 能提高显著特征的提取能力,并增强模型对医疗图像数据挑战的适应性。
- MIAFEx 特征输出质量在多个医疗图像数据集上得到评估,表现出优于传统和现代模型的准确性和鲁棒性。
- 特别在训练数据有限的情况下,MIAFEx 的优势更为明显。
点此查看论文截图