⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-02 更新
MLA: A Multisensory Language-Action Model for Multimodal Understanding and Forecasting in Robotic Manipulation
Authors:Zhuoyang Liu, Jiaming Liu, Jiadong Xu, Nuowei Han, Chenyang Gu, Hao Chen, Kaichen Zhou, Renrui Zhang, Kai Chin Hsieh, Kun Wu, Zhengping Che, Jian Tang, Shanghang Zhang
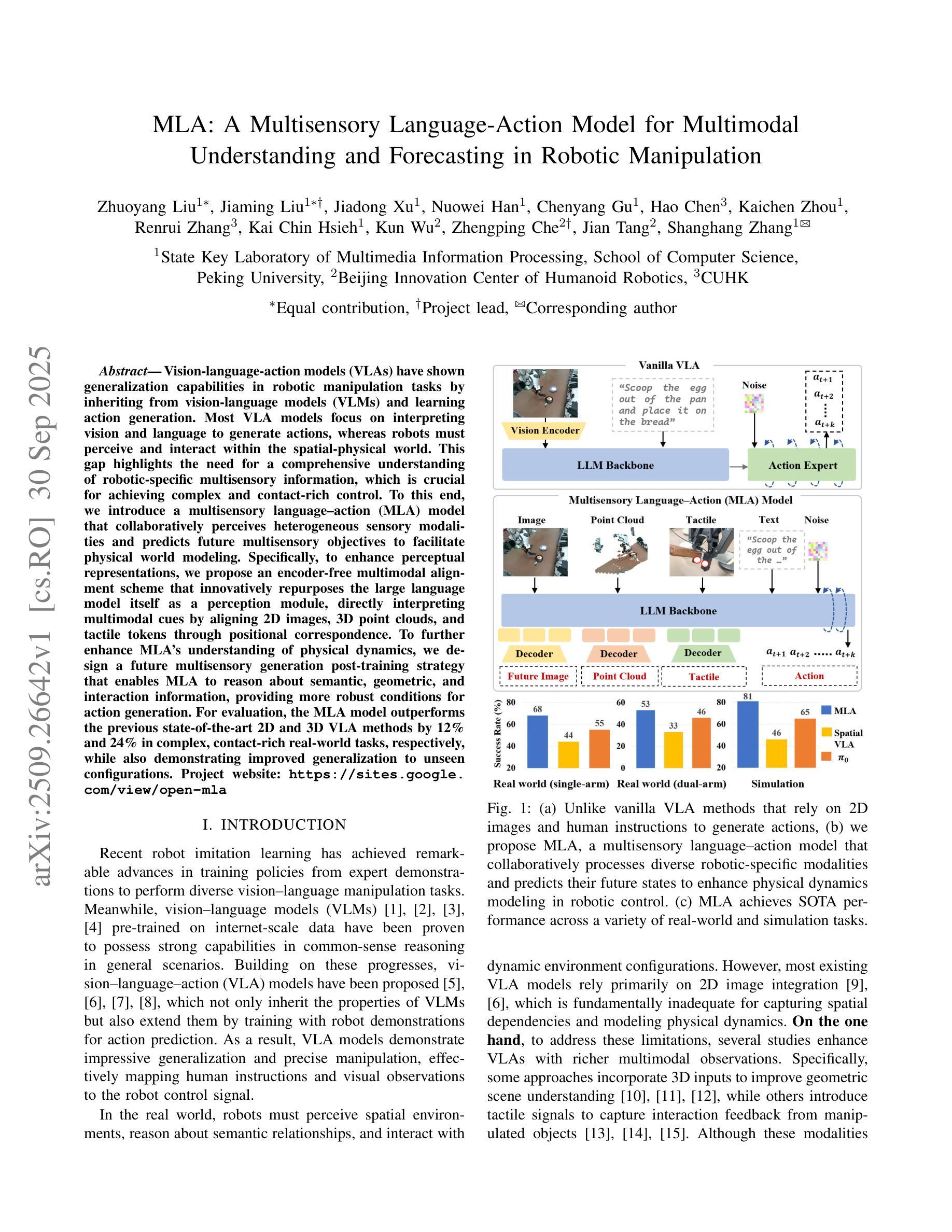
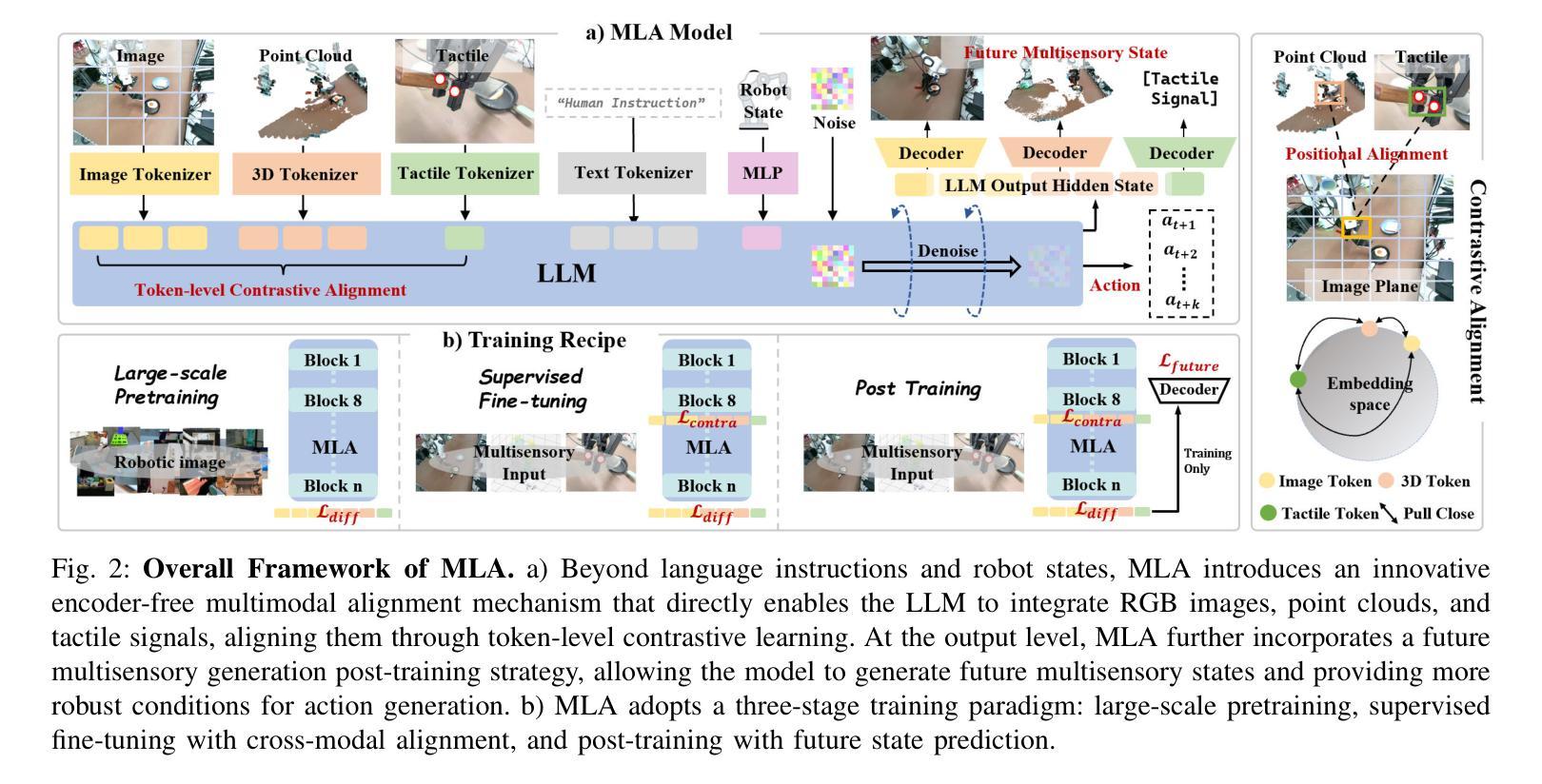
Vision-language-action models (VLAs) have shown generalization capabilities in robotic manipulation tasks by inheriting from vision-language models (VLMs) and learning action generation. Most VLA models focus on interpreting vision and language to generate actions, whereas robots must perceive and interact within the spatial-physical world. This gap highlights the need for a comprehensive understanding of robotic-specific multisensory information, which is crucial for achieving complex and contact-rich control. To this end, we introduce a multisensory language-action (MLA) model that collaboratively perceives heterogeneous sensory modalities and predicts future multisensory objectives to facilitate physical world modeling. Specifically, to enhance perceptual representations, we propose an encoder-free multimodal alignment scheme that innovatively repurposes the large language model itself as a perception module, directly interpreting multimodal cues by aligning 2D images, 3D point clouds, and tactile tokens through positional correspondence. To further enhance MLA’s understanding of physical dynamics, we design a future multisensory generation post-training strategy that enables MLA to reason about semantic, geometric, and interaction information, providing more robust conditions for action generation. For evaluation, the MLA model outperforms the previous state-of-the-art 2D and 3D VLA methods by 12% and 24% in complex, contact-rich real-world tasks, respectively, while also demonstrating improved generalization to unseen configurations. Project website: https://sites.google.com/view/open-mla
视觉语言行动模型(VLAs)通过继承视觉语言模型(VLMs)并学习行动生成,在机器人操作任务中表现出了泛化能力。大多数VLA模型侧重于解释视觉和语言以生成行动,而机器人必须在空间物理世界中进行感知和交互。这一差距凸显了对机器人特定多感官信息的全面理解的需求,这对于实现复杂且接触丰富的控制至关重要。为此,我们引入了一种多感官语言行动(MLA)模型,该模型可以协同感知不同的感官模式,并预测未来的多感官目标,以促进物理世界建模。具体来说,为了增强感知表示,我们提出了一种无编码器多模态对齐方案,该方案创新地将大型语言模型本身重新用作感知模块,通过位置对应关系直接解释多模态线索,对齐2D图像、3D点云和触觉标记。为了进一步增强MLA对物理动态的理解,我们设计了一种未来多感官生成后训练策略,使MLA能够推理语义、几何和交互信息,为行动生成提供更稳健的条件。在评估中,MLA模型在复杂、接触丰富的真实世界任务中分别比最新的2D和3DVLA方法高出12%和24%,同时显示出对未见配置的改进泛化能力。项目网站:https://sites.google.com/view/open-mla
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对机器人操作任务的多感官语言动作(MLA)模型。该模型融合了视觉、语言和多感官信息,旨在提高机器人对复杂、接触丰富的控制任务的通用性。通过引入编码器免费的跨模态对齐方案,以及未来多感官生成的后训练策略,MLA模型在真实世界的复杂任务中表现出优越的性能,并超越了现有的二维和三维VLA方法。
Key Takeaways
- MLA模型具备多感官融合能力,可提高对机器人操作任务的通用性。
- 编码器免费的跨模态对齐方案将大型语言模型直接用作感知模块,实现对多模态信号的直接解读。
- MLA模型通过跨模态对齐,能够融合2D图像、3D点云和触觉标记。
- 未来多感官生成的后训练策略增强了MLA对物理动态的理解,使其能够推理语义、几何和交互信息。
- MLA模型在复杂、接触丰富的真实世界任务中表现出优越性能,相对于现有的VLA方法有明显的提升。
- MLA模型在未见过的配置中具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图
Query-Kontext: An Unified Multimodal Model for Image Generation and Editing
Authors:Yuxin Song, Wenkai Dong, Shizun Wang, Qi Zhang, Song Xue, Tao Yuan, Hu Yang, Haocheng Feng, Hang Zhou, Xinyan Xiao, Jingdong Wang
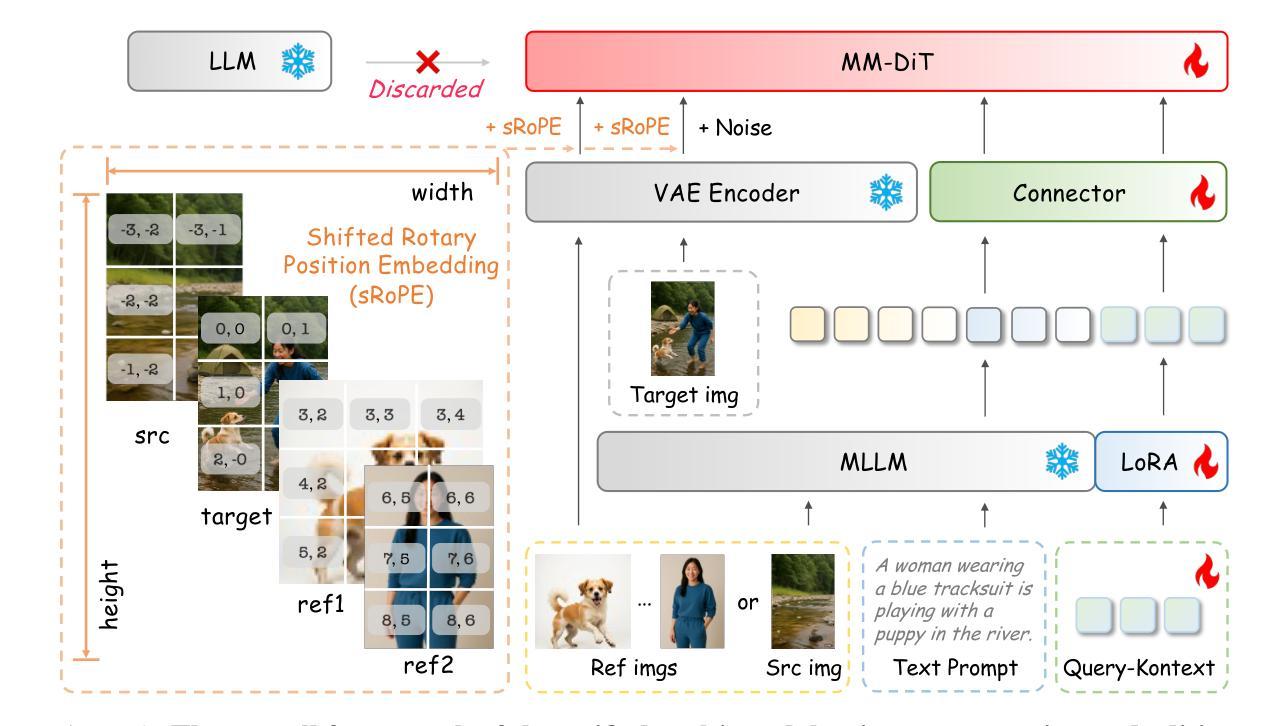
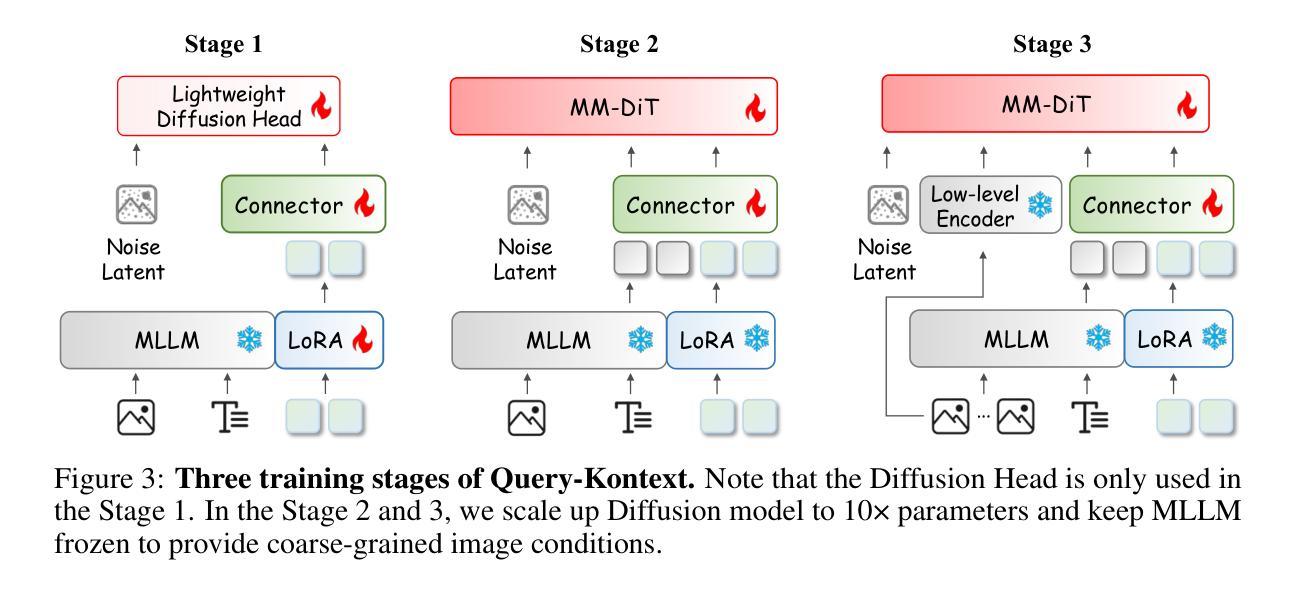
Unified Multimodal Models (UMMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance in text-to-image generation (T2I) and editing (TI2I), whether instantiated as assembled unified frameworks which couple powerful vision-language model (VLM) with diffusion-based generator, or as naive Unified Multimodal Models with an early fusion of understanding and generation modalities. We contend that in current unified frameworks, the crucial capability of multimodal generative reasoning which encompasses instruction understanding, grounding, and image referring for identity preservation and faithful reconstruction, is intrinsically entangled with high-fidelity synthesis. In this work, we introduce Query-Kontext, a novel approach that bridges the VLM and diffusion model via a multimodal ``kontext’’ composed of semantic cues and coarse-grained image conditions encoded from multimodal inputs. This design delegates the complex ability of multimodal generative reasoning to powerful VLM while reserving diffusion model’s role for high-quality visual synthesis. To achieve this, we propose a three-stage progressive training strategy. First, we connect the VLM to a lightweight diffusion head via multimodal kontext tokens to unleash the VLM’s generative reasoning ability. Second, we scale this head to a large, pre-trained diffusion model to enhance visual detail and realism. Finally, we introduce a low-level image encoder to improve image fidelity and perform instruction tuning on downstream tasks. Furthermore, we build a comprehensive data pipeline integrating real, synthetic, and open-source datasets, covering diverse multimodal reference-to-image scenarios, including image generation, instruction-driven editing, customized generation, and multi-subject composition. Experiments show that our approach matches strong unified baselines and even outperforms task-specific state-of-the-art methods in several cases.
统一多模态模型(UMMs)在文本到图像生成(T2I)和编辑(TI2I)方面表现出了卓越的性能,无论是作为集成了强大视觉语言模型(VLM)和基于扩散的生成器的统一框架,还是作为早期理解和生成模式融合的简单统一多模态模型。我们认为,在当前统一框架中,涵盖指令理解、接地和图像引用以进行身份保留和忠实重建的多模态生成推理的关键能力,与高保真合成紧密相连。在这项工作中,我们引入了Query-Kontext,这是一种通过由来自多模态输入的语义线索和粗粒度图像条件组成的多模态“kontext”来桥梁VLM和扩散模型的新型方法。这种设计将复杂的多模态生成推理能力委托给强大的VLM,同时保留扩散模型进行高质量视觉合成的作用。为了实现这一点,我们提出了一种三阶段渐进训练策略。首先,我们通过多模态kontext令牌将VLM连接到轻量级扩散头,以释放VLM的生成推理能力。其次,我们将此头扩展到大型预训练扩散模型,以提高视觉细节和逼真度。最后,我们引入低级图像编码器,以提高图像保真度,并对下游任务进行指令调整。此外,我们建立了一个综合数据管道,整合真实、合成和开源数据集,涵盖多样化的多模态参考到图像场景,包括图像生成、指令驱动编辑、定制生成和多主体组合。实验表明,我们的方法与强大的统一基线相匹配,甚至在某些情况下超越了任务特定的最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文介绍了统一多模态模型(UMMs)在文本到图像生成(T2I)和编辑(TI2I)中的卓越性能。提出了一种名为Query-Kontext的新型方法,通过多模态上下文将视觉语言模型(VLM)和扩散模型相结合,以实现多模态生成推理和高保真合成。通过三阶段渐进训练策略,Query-Kontext在统一多模态框架下实现了强大的生成能力。实验表明,该方法与强大的统一基线相匹配,并在某些情况下甚至超过了任务特定的最新技术方法。
Key Takeaways
- UMMs在文本到图像生成和编辑领域表现出卓越性能。
- Query-Kontext方法通过多模态上下文融合视觉语言模型(VLM)和扩散模型。
- Query-Kontext实现了强大的多模态生成推理能力。
- 三阶段渐进训练策略提高了模型的生成能力和视觉合成的质量。
- 该方法匹配强大的统一基线并在某些情况下超过任务特定方法。
- Query-Kontext建立了综合数据管道,涵盖多种多模态参考到图像的场景。
点此查看论文截图

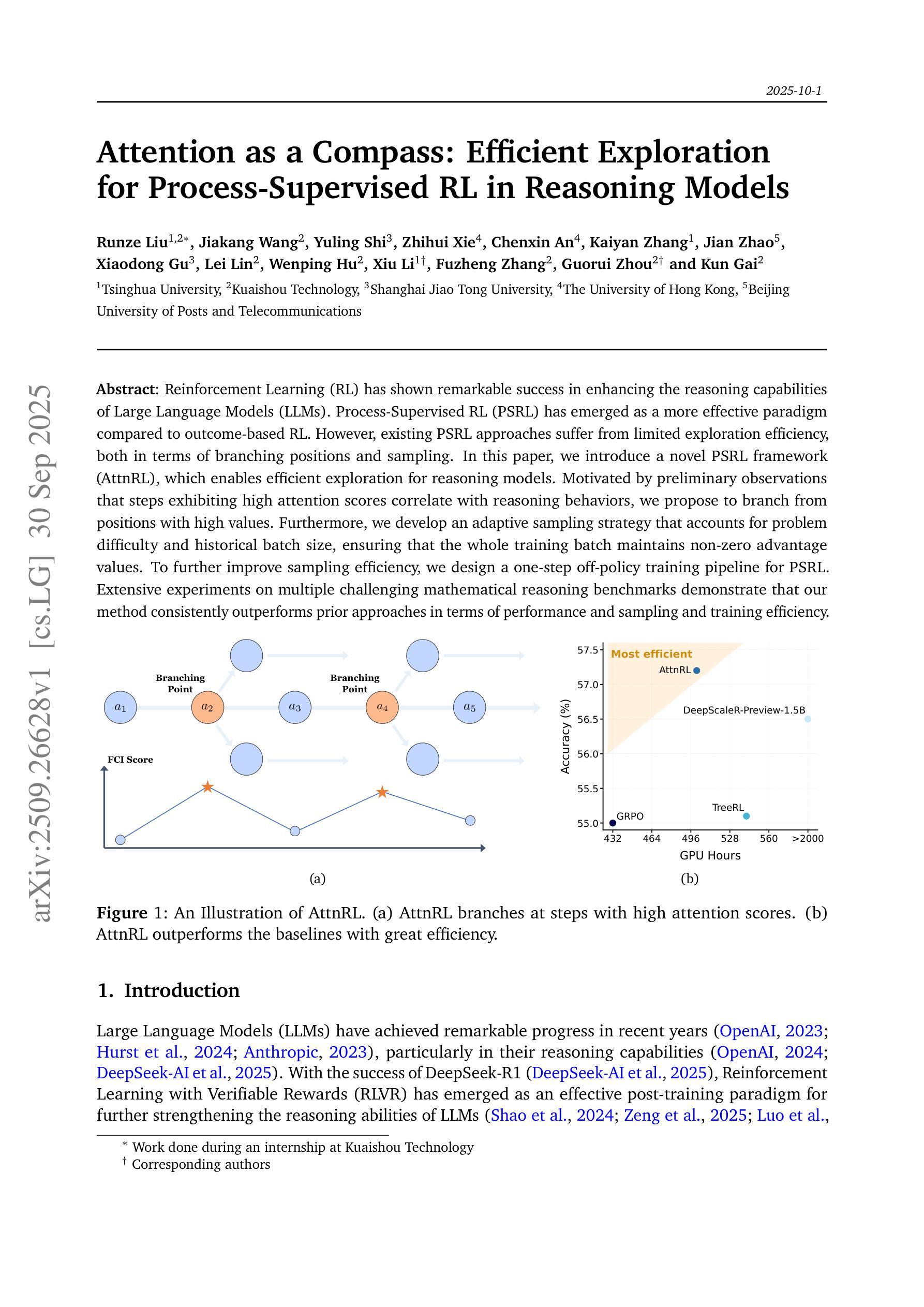
Attention as a Compass: Efficient Exploration for Process-Supervised RL in Reasoning Models
Authors:Runze Liu, Jiakang Wang, Yuling Shi, Zhihui Xie, Chenxin An, Kaiyan Zhang, Jian Zhao, Xiaodong Gu, Lei Lin, Wenping Hu, Xiu Li, Fuzheng Zhang, Guorui Zhou, Kun Gai
Reinforcement Learning (RL) has shown remarkable success in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). Process-Supervised RL (PSRL) has emerged as a more effective paradigm compared to outcome-based RL. However, existing PSRL approaches suffer from limited exploration efficiency, both in terms of branching positions and sampling. In this paper, we introduce a novel PSRL framework (AttnRL), which enables efficient exploration for reasoning models. Motivated by preliminary observations that steps exhibiting high attention scores correlate with reasoning behaviors, we propose to branch from positions with high values. Furthermore, we develop an adaptive sampling strategy that accounts for problem difficulty and historical batch size, ensuring that the whole training batch maintains non-zero advantage values. To further improve sampling efficiency, we design a one-step off-policy training pipeline for PSRL. Extensive experiments on multiple challenging mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms prior approaches in terms of performance and sampling and training efficiency.
强化学习(RL)在提高大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力方面取得了显著的成功。与基于结果的RL相比,过程监督RL(PSRL)作为一种更有效的范式已经出现。然而,现有的PSRL方法存在探索效率低下的问题,无论是在分支位置还是在采样方面。在本文中,我们引入了一种新型的PSRL框架(AttnRL),为推理模型实现高效探索。受初步观察启发,高注意力得分的步骤与推理行为相关,我们提出从高值位置进行分支。此外,我们开发了一种适应性问题难度和历史批处理大小的采样策略,确保整个训练批次保持非零优势值。为了进一步提高采样效率,我们为PSRL设计了一个一步离线训练管道。在多个具有挑战性的数学推理基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在性能和采样以及训练效率方面始终优于先前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习在提升大型语言模型的推理能力方面取得了显著的成功。过程监督强化学习(PSRL)相较于结果导向的强化学习范式展现出更大的效果。然而,现有的PSRL方法存在探索效率低下的问题,表现在分支位置和采样两个方面。本文提出一种新型的PSRL框架(AttnRL),为推理模型实现高效探索。基于初步观察,我们提出从高关注度得分的位置进行分支。此外,我们开发了一种适应性问题难度和历史批次大小的采样策略,确保整个训练批次保持非零优势值。为提高采样效率,我们设计了一个一步离线训练管道用于PSRL。在多个挑战性的数学推理基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法不仅在性能上持续超越先前的方法,而且在采样和训练效率方面也表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习显著提升了大型语言模型的推理能力。
- 过程监督强化学习(PSRL)相比传统结果导向的强化学习更为有效。
- 现有PSRL方法在探索效率上存在问题,体现在分支位置和采样两个方面。
- 新型PSRL框架(AttnRL)通过高效探索提升推理模型的性能。
- AttnRL基于高关注度得分的位置进行分支,与推理行为高度相关。
- 开发出适应性问题难度和历史批次大小的采样策略,确保训练批次的优势值。
- 一步离线训练管道提高了PSRL的采样效率。
点此查看论文截图
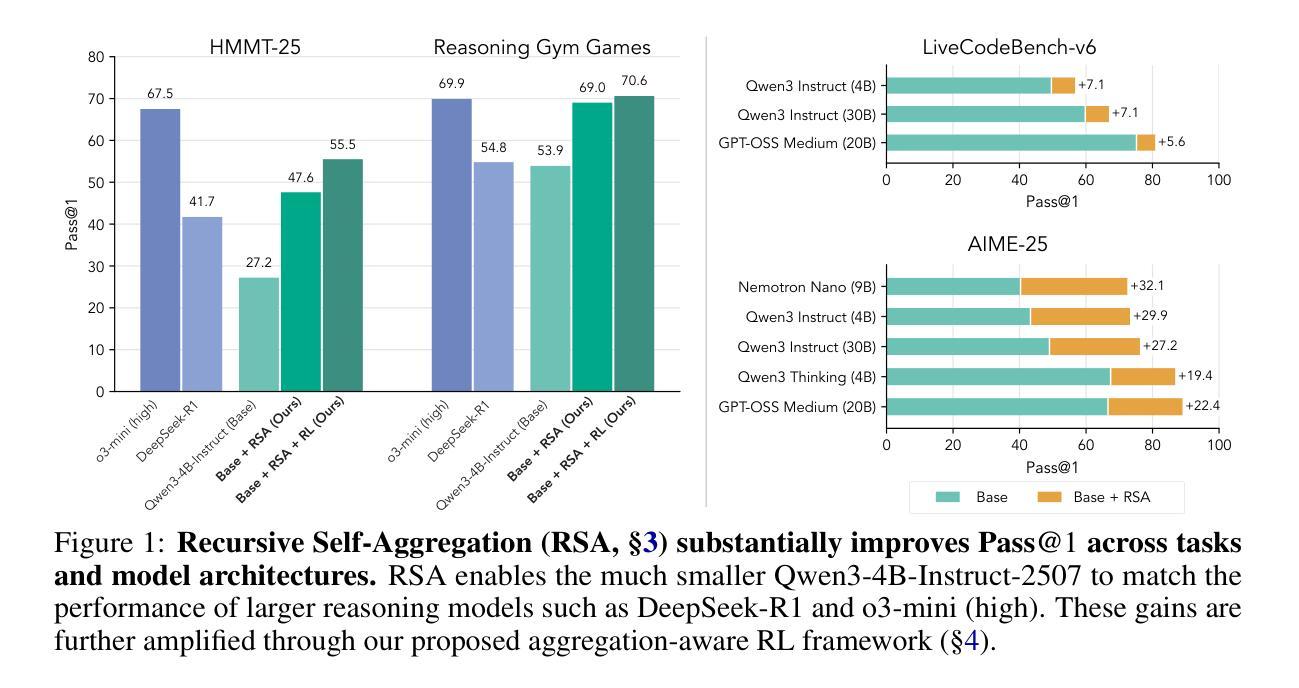
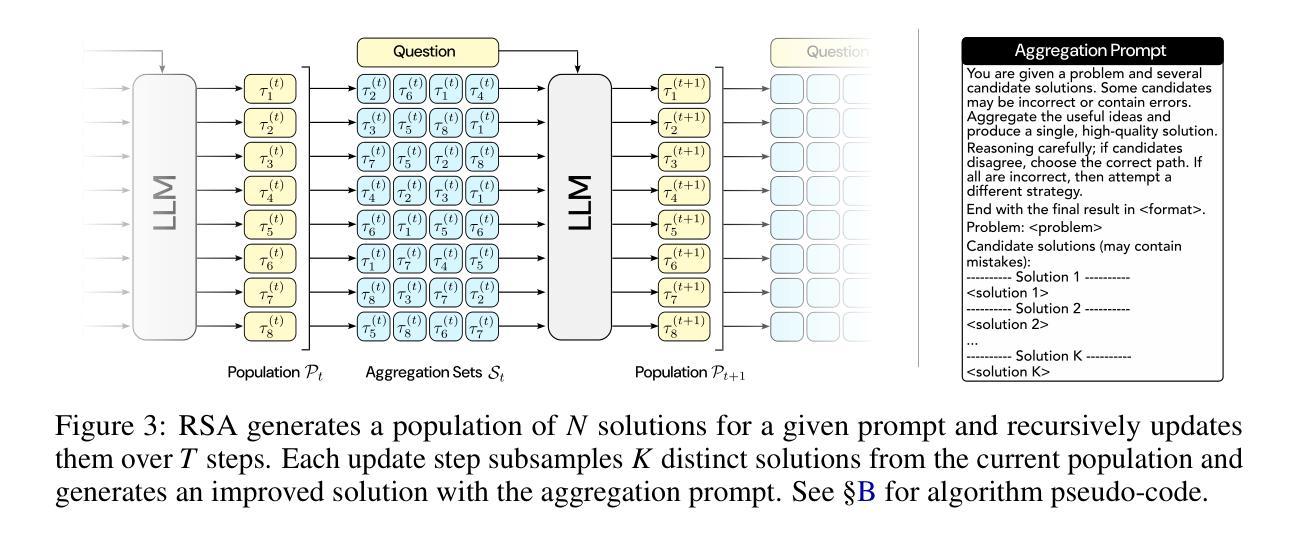
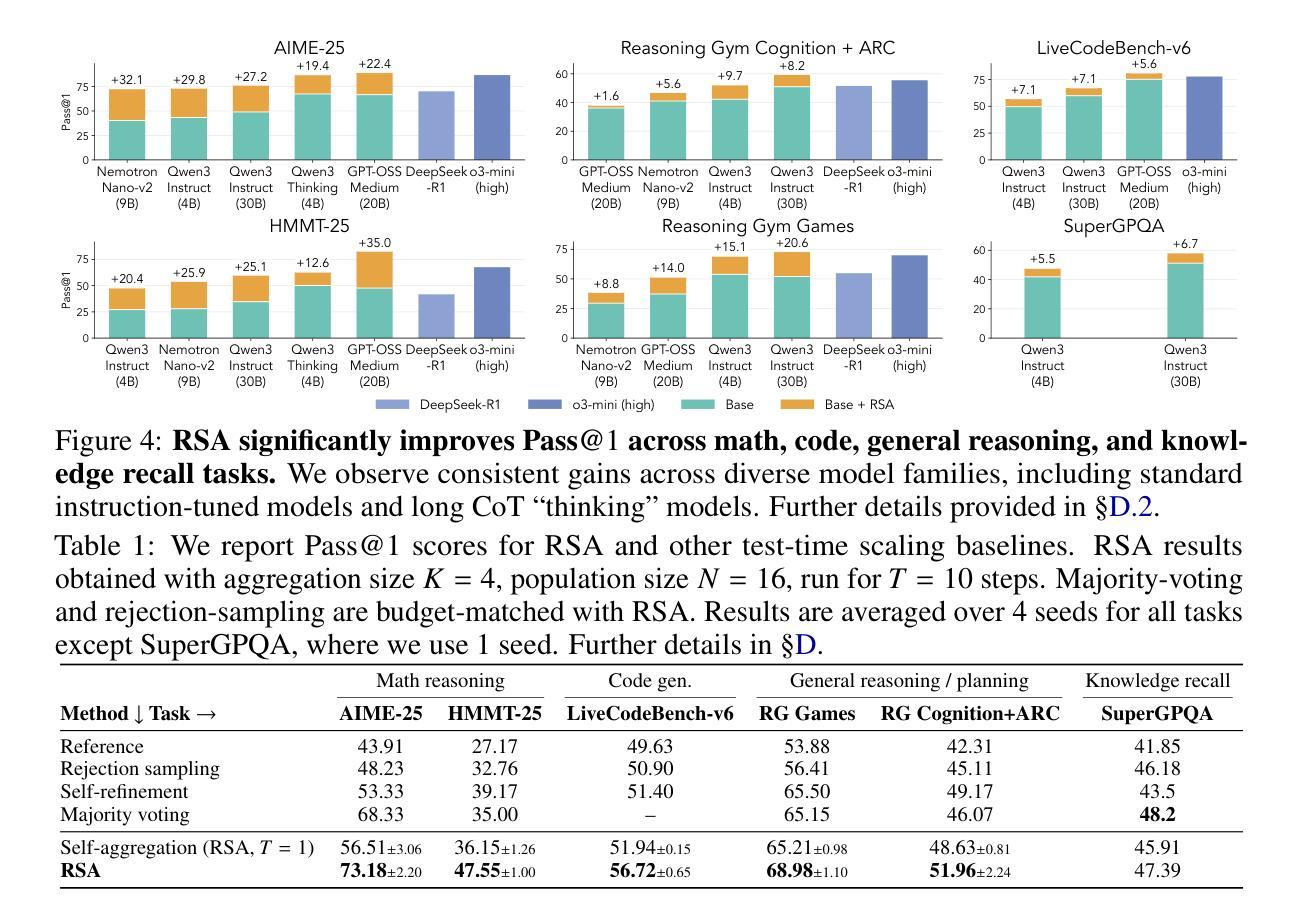
Recursive Self-Aggregation Unlocks Deep Thinking in Large Language Models
Authors:Siddarth Venkatraman, Vineet Jain, Sarthak Mittal, Vedant Shah, Johan Obando-Ceron, Yoshua Bengio, Brian R. Bartoldson, Bhavya Kailkhura, Guillaume Lajoie, Glen Berseth, Nikolay Malkin, Moksh Jain
Test-time scaling methods improve the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by increasing the amount of compute used during inference to make a prediction. Inference-time compute can be scaled in parallel by choosing among multiple independent solutions or sequentially through self-refinement. We propose Recursive Self-Aggregation (RSA), a test-time scaling method inspired by evolutionary methods that combines the benefits of both parallel and sequential scaling. Each step of RSA refines a population of candidate reasoning chains through aggregation of subsets to yield a population of improved solutions, which are then used as the candidate pool for the next iteration. RSA exploits the rich information embedded in the reasoning chains – not just the final answers – and enables bootstrapping from partially correct intermediate steps within different chains of thought. Empirically, RSA delivers substantial performance gains with increasing compute budgets across diverse tasks, model families and sizes. Notably, RSA enables Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507 to achieve competitive performance with larger reasoning models, including DeepSeek-R1 and o3-mini (high), while outperforming purely parallel and sequential scaling strategies across AIME-25, HMMT-25, Reasoning Gym, LiveCodeBench-v6, and SuperGPQA. We further demonstrate that training the model to combine solutions via a novel aggregation-aware reinforcement learning approach yields significant performance gains. Code available at https://github.com/HyperPotatoNeo/RSA.
测试时缩放方法通过增加用于推断的计算量来提高大型语言模型(LLM)的能力,以进行预测。推断时的计算量可以通过选择多个独立解决方案来并行缩放或通过自我完善来顺序缩放。我们提出递归自聚合(RSA)是一种受进化方法启发的测试时缩放方法,它结合了并行和顺序缩放的优势。RSA的每一步都会通过子集的聚合来完善候选推理链的种群,从而产生一批改进后的解决方案,这些解决方案然后被用作下一轮的候选池。RSA利用推理链中嵌入的丰富信息——不仅仅是最终答案——并能够从不同思维链条中部分正确的中间步骤进行启动。经验上,RSA在增加计算预算的情况下,在多种任务、模型家族和规模上实现了显著的性能提升。值得注意的是,RSA使Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507在包括DeepSeek-R1和o3-mini(高级)等大型推理模型中实现具有竞争力的性能,同时在AIME-25、HMMT-25、Reasoning Gym、LiveCodeBench-v6和SuperGPQA上超越了纯粹的并行和顺序缩放策略。我们进一步证明,通过一种新型聚合感知强化学习方法训练模型来组合解决方案,可以获得显著的性能提升。代码可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/HyperPotatoNeo/RSA 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 9 figures
Summary:提出的测试时缩放方法——递归自聚合(RSA)能够利用推理链中的丰富信息,在多个任务上实现性能的大幅提升。通过利用递归自聚合的优势,RSA在推理时能够将不同的解决方案通过逐步精炼并结合起来,以产生更好的预测结果。这种方法在多种任务、模型家族和规模上表现出显著的优势,特别是在计算预算增加的情况下。此外,RSA还通过一种新型的聚合感知强化学习方法来训练模型组合解决方案,进一步提高了性能。
Key Takeaways:
- RSA是一种测试时缩放方法,结合了并行和顺序缩放的优势。
- RSA利用推理链中的丰富信息,通过精炼候选推理链来产生更好的解决方案。
- RSA能够在多种任务上实现显著的性能提升,特别是在计算预算增加的情况下。
- RSA在不同规模、不同家族的模型上都表现出优势。
- RSA通过与大型推理模型比较展现出竞争力,例如DeepSeek-R1和o3-mini。
- RSA的性能优于纯粹的并行和顺序缩放策略。
点此查看论文截图

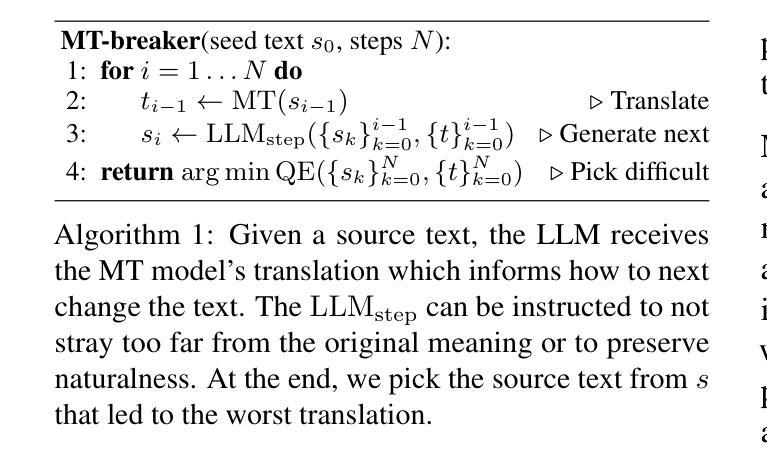
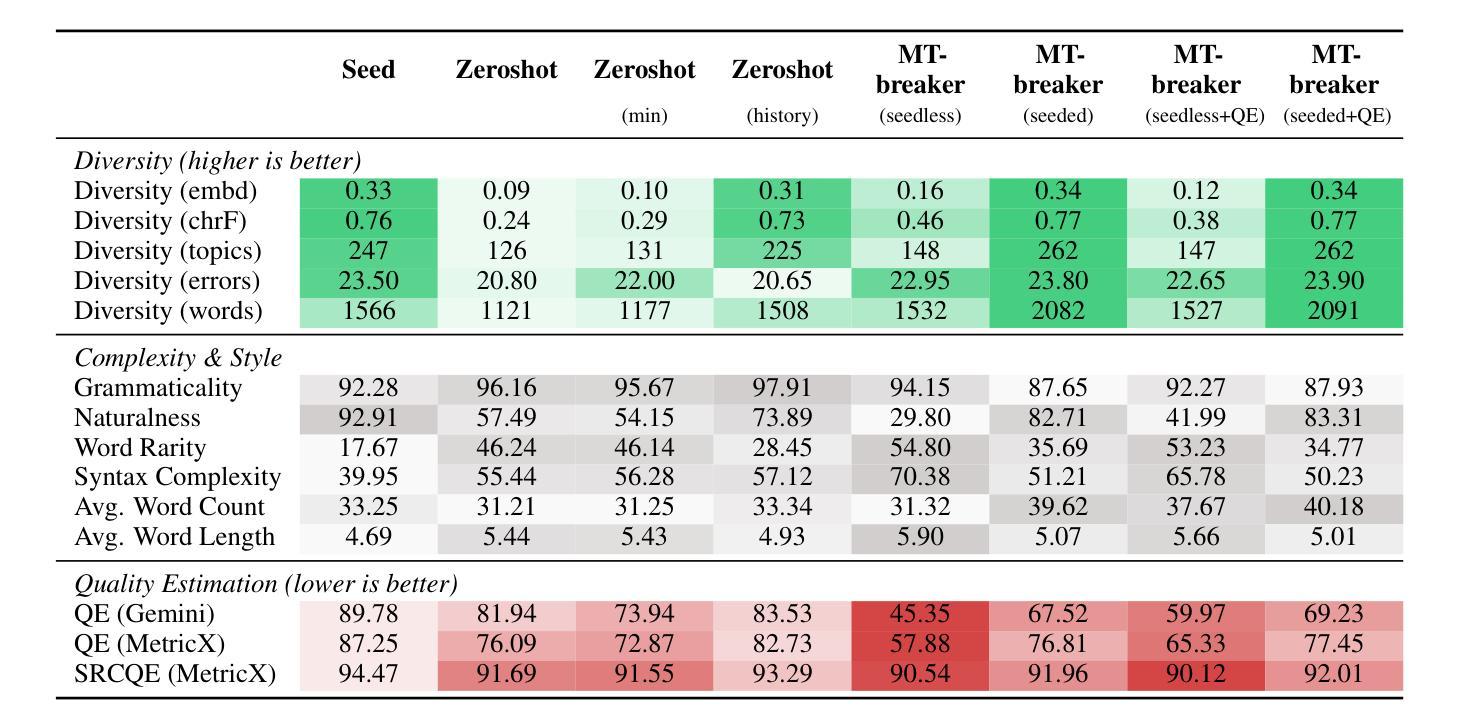
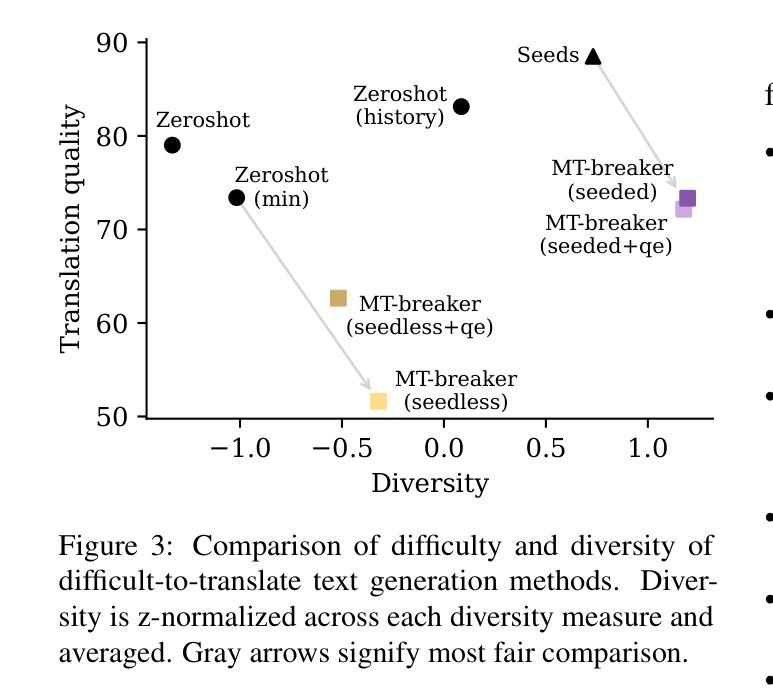
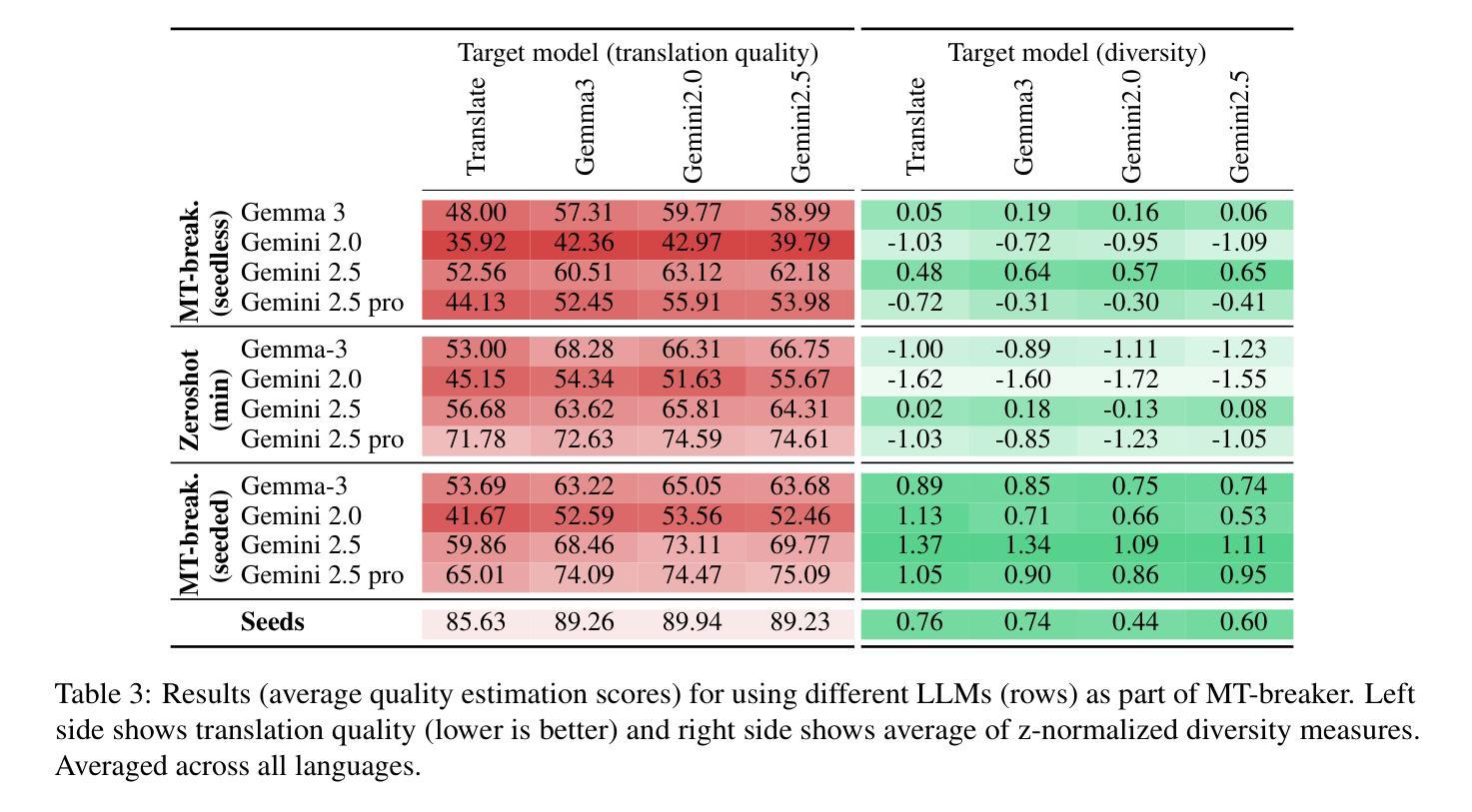
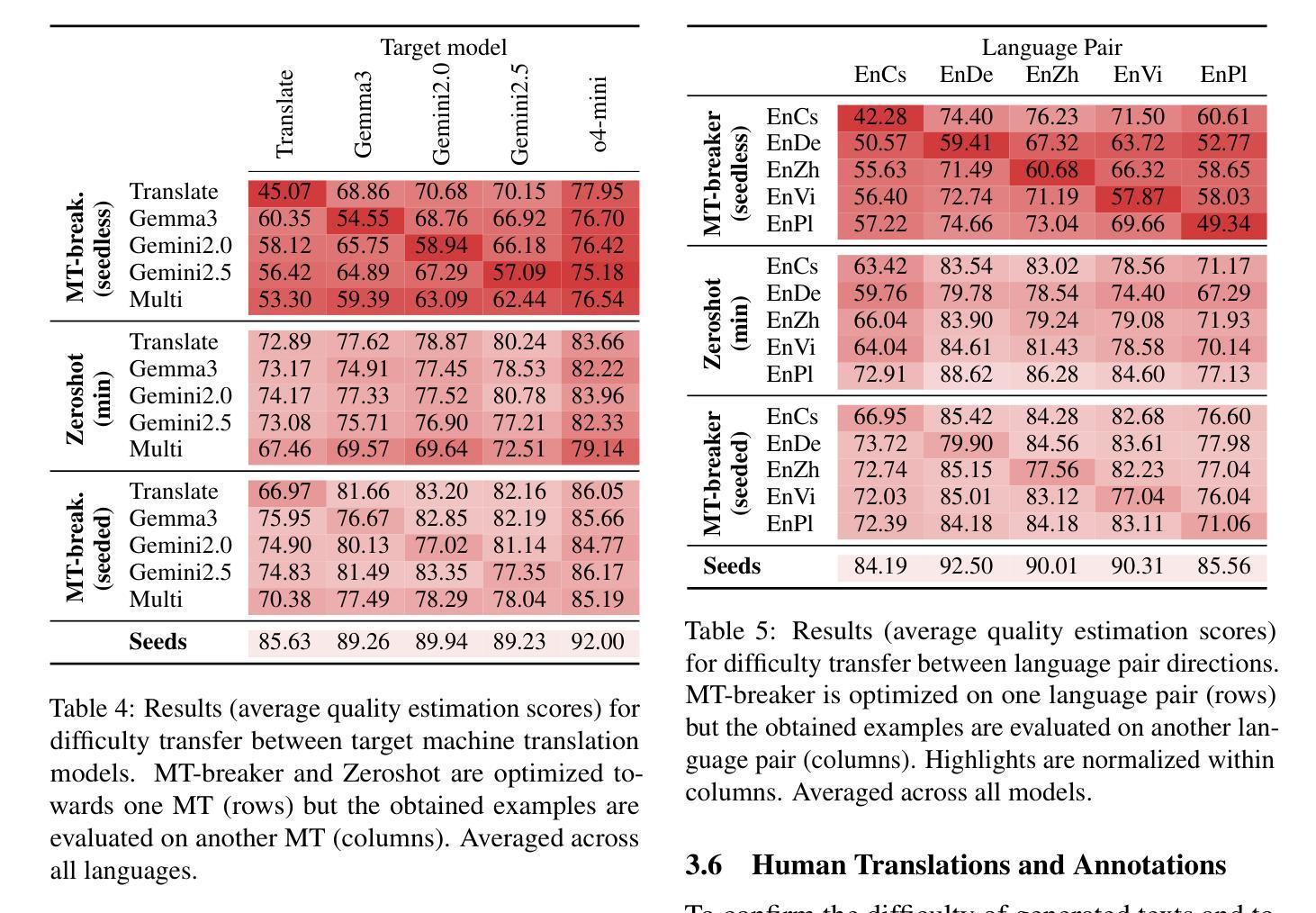
Generating Difficult-to-Translate Texts
Authors:Vilém Zouhar, Wenda Xu, Parker Riley, Juraj Juraska, Mara Finkelstein, Markus Freitag, Dan Deutsch
Machine translation benchmarks sourced from the real world are quickly obsoleted, due to most examples being easy for state-of-the-art translation models. This limits the benchmark’s ability to distinguish which model is better or to reveal models’ weaknesses. Current methods for creating difficult test cases, such as subsampling or from-scratch synthesis, either fall short of identifying difficult examples or suffer from a lack of diversity and naturalness. Inspired by the iterative process of human experts probing for model failures, we propose MT-breaker, a method where a large language model iteratively refines a source text to increase its translation difficulty. The LLM iteratively queries a target machine translation model to guide its generation of difficult examples. Our approach generates examples that are more challenging for the target MT model while preserving the diversity of natural texts. While the examples are tailored to a particular machine translation model during the generation, the difficulty also transfers to other models and languages.
现实世界来源的机器翻译基准测试由于大多数实例对于最先进的翻译模型来说过于简单而很快被淘汰。这限制了基准测试区分哪个模型更好或揭示模型弱点的能力。当前创建困难测试用例的方法,如子采样或从头开始合成,要么不能识别出困难的例子,要么缺乏多样性和自然性。受人类专家探测模型失败过程的启发,我们提出MT-breaker方法,这是一种大型语言模型通过迭代优化源文本来增加其翻译难度的方法。大型语言模型迭代地查询目标机器翻译模型,以指导其生成困难的例子。我们的方法为目标机器翻译模型生成更具挑战性的例子,同时保持自然文本的多样性。虽然这些例子是在生成过程中针对特定的机器翻译模型定制的,但难度也会转移到其他模型和语言上。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出机器翻译基准测试的局限性,因为大多数来自真实世界的例子对于当前最先进的翻译模型来说过于简单,无法区分模型优劣或揭示其弱点。现有的创建困难测试用例的方法,如子抽样或从头合成,要么无法识别困难的例子,要么缺乏多样性和自然性。受人类专家探查模型失败过程的启发,我们提出了MT-breaker方法,使用大型语言模型迭代地改进源文本以增加其翻译难度。该方法通过迭代查询目标机器翻译模型来指导困难例子的生成。我们的方法生成对目标翻译模型更具挑战性的例子,同时保持了自然文本的多样性。虽然这些例子是在生成过程中针对特定的机器翻译模型定制的,但其难度也适用于其他模型和语言。
Key Takeaways
- 机器翻译基准测试因大多数实例过于简单而迅速被淘汰。
- 现有创建困难测试用例的方法存在缺陷,无法有效识别困难例子或缺乏多样性和自然性。
- 提出了一种新的方法MT-breaker,使用大型语言模型迭代改进源文本,增加翻译难度。
- MT-breaker通过查询目标机器翻译模型来指导困难例子的生成。
- 该方法生成的例子对目标翻译模型更具挑战性。
- MT-breaker保留自然文本的多样性。
点此查看论文截图
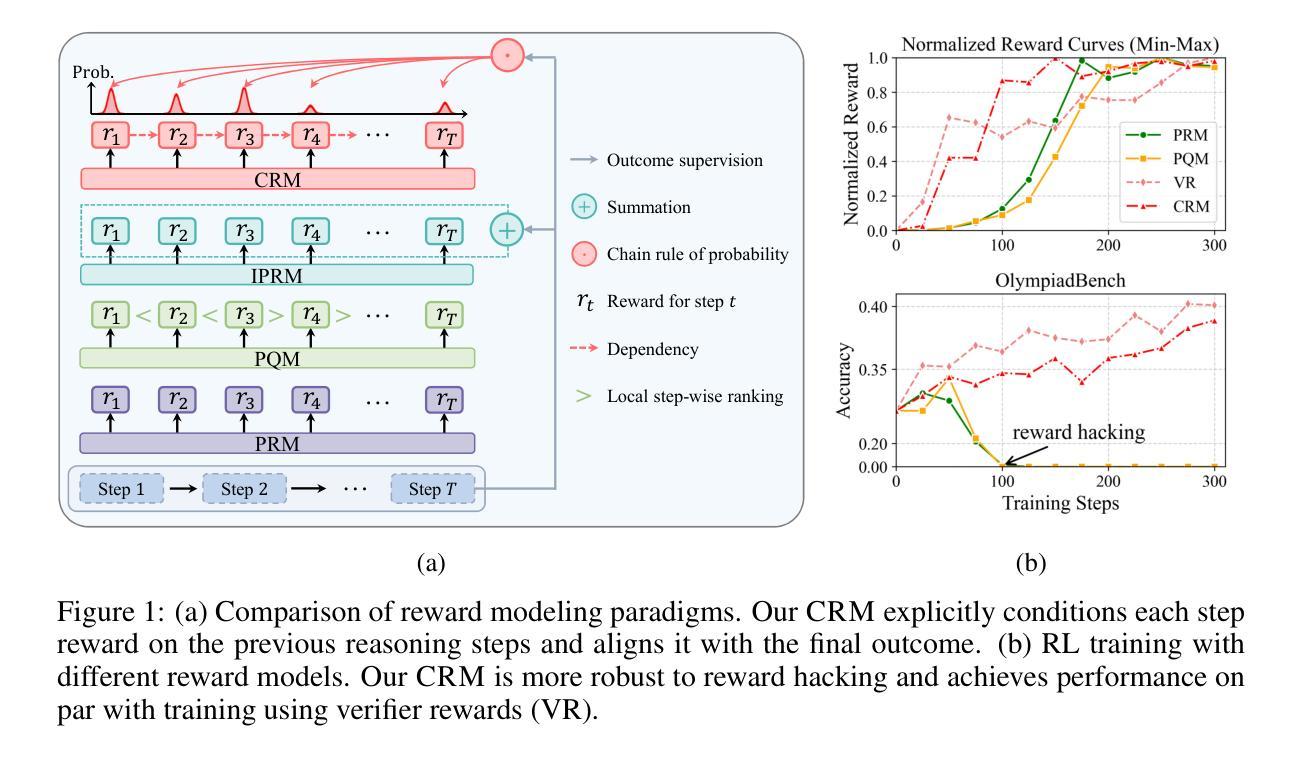
Linking Process to Outcome: Conditional Reward Modeling for LLM Reasoning
Authors:Zheng Zhang, Ziwei Shan, Kaitao Song, Yexin Li, Kan Ren
Process Reward Models (PRMs) have emerged as a promising approach to enhance the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by guiding their step-by-step reasoning toward a final answer. However, existing PRMs either treat each reasoning step in isolation, failing to capture inter-step dependencies, or struggle to align process rewards with the final outcome. Consequently, the reward signal fails to respect temporal causality in sequential reasoning and faces ambiguous credit assignment. These limitations make downstream models vulnerable to reward hacking and lead to suboptimal performance. In this work, we propose Conditional Reward Modeling (CRM) that frames LLM reasoning as a temporal process leading to a correct answer. The reward of each reasoning step is not only conditioned on the preceding steps but also explicitly linked to the final outcome of the reasoning trajectory. By enforcing conditional probability rules, our design captures the causal relationships among reasoning steps, with the link to the outcome allowing precise attribution of each intermediate step, thereby resolving credit assignment ambiguity. Further, through this consistent probabilistic modeling, the rewards produced by CRM enable more reliable cross-sample comparison. Experiments across Best-of-N sampling, beam search and reinforcement learning demonstrate that CRM consistently outperforms existing reward models, offering a principled framework for enhancing LLM reasoning. In particular, CRM is more robust to reward hacking and delivers stable downstream improvements without relying on verifiable rewards derived from ground truth.
流程奖励模型(PRM)作为一种新兴方法,通过指导大型语言模型(LLM)逐步推理以得出最终答案,增强了其推理能力。然而,现有的PRM要么孤立地处理每个推理步骤,无法捕捉步骤间的依赖关系,要么在将流程奖励与最终结果对齐时遇到困难。因此,奖励信号无法尊重序列推理中的时间因果关系,并面临模糊的信用分配问题。这些局限性使下游模型容易受到奖励破解的影响,导致性能不佳。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于过程奖励模型(PRM)在提升大型语言模型(LLM)推理能力方面的潜力,现有PRM方法存在局限性,如忽视推理步骤间的依赖关系、难以将过程奖励与最终成果对齐等。为解决这些问题,本文提出条件奖励建模(CRM),将LLM推理视为一个通向正确答案的时空过程。CRM的奖励不仅以前一步骤为条件,还与推理轨迹的最终结果有明确联系。通过执行条件概率规则,CRM捕捉推理步骤间的因果关系,解决信用分配模糊问题。实验表明,CRM在Best-of-N采样、集束搜索和强化学习等方面均表现出优于现有奖励模型的效果,为提升LLM推理能力提供了有力框架。
Key Takeaways
- 过程奖励模型(PRM)旨在增强大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。
- 现有PRM方法存在忽略推理步骤间依赖和对齐过程奖励与最终结果的问题。
- 条件奖励建模(CRM)将LLM推理视为一个过程,强调每一步的奖励与最终结果的联系。
- CRM通过执行条件概率规则捕捉推理步骤间的因果关系,解决信用分配模糊问题。
- CRM在多种实验设置中表现出优越性能,包括Best-of-N采样、集束搜索和强化学习。
- CRM框架更稳健,能有效抵抗奖励操纵,并在不依赖真实验证奖励的情况下实现稳定的下游改进。
点此查看论文截图
Probing the Critical Point (CritPt) of AI Reasoning: a Frontier Physics Research Benchmark
Authors:Minhui Zhu, Minyang Tian, Xiaocheng Yang, Tianci Zhou, Penghao Zhu, Eli Chertkov, Shengyan Liu, Yufeng Du, Lifan Yuan, Ziming Ji, Indranil Das, Junyi Cao, Yufeng Du, Jinchen He, Yifan Su, Jiabin Yu, Yikun Jiang, Yujie Zhang, Chang Liu, Ze-Min Huang, Weizhen Jia, Xinan Chen, Peixue Wu, Yunkai Wang, Juntai Zhou, Yong Zhao, Farshid Jafarpour, Jessie Shelton, Aaron Young, John Bartolotta, Wenchao Xu, Yue Sun, Anjun Chu, Victor Colussi, Chris Akers, Nathan Brooks, Wenbo Fu, Christopher Wilson, Jinchao Zhao, Marvin Qi, Anqi Mu, Yubo Yang, Allen Zang, Yang Lyu, Peizhi Mai, Xuefei Guo, Luyu Gao, Ze Yang, Chi Xue, Dmytro Bandak, Yaïr Hein, Yonatan Kahn, Kevin Zhou, John Drew Wilson Jarrod T. Reilly, Di Luo, Daniel Inafuku, Hao Tong, Liang Yang, Ruixing Zhang, Xueying Wang, Ofir Press, Nicolas Chia, Eliu Huerta, Hao Peng
While large language models (LLMs) with reasoning capabilities are progressing rapidly on high-school math competitions and coding, can they reason effectively through complex, open-ended challenges found in frontier physics research? And crucially, what kinds of reasoning tasks do physicists want LLMs to assist with? To address these questions, we present the CritPt (Complex Research using Integrated Thinking - Physics Test, pronounced “critical point”), the first benchmark designed to test LLMs on unpublished, research-level reasoning tasks that broadly covers modern physics research areas, including condensed matter, quantum physics, atomic, molecular & optical physics, astrophysics, high energy physics, mathematical physics, statistical physics, nuclear physics, nonlinear dynamics, fluid dynamics and biophysics. CritPt consists of 71 composite research challenges designed to simulate full-scale research projects at the entry level, which are also decomposed to 190 simpler checkpoint tasks for more fine-grained insights. All problems are newly created by 50+ active physics researchers based on their own research. Every problem is hand-curated to admit a guess-resistant and machine-verifiable answer and is evaluated by an automated grading pipeline heavily customized for advanced physics-specific output formats. We find that while current state-of-the-art LLMs show early promise on isolated checkpoints, they remain far from being able to reliably solve full research-scale challenges: the best average accuracy among base models is only 4.0% , achieved by GPT-5 (high), moderately rising to around 10% when equipped with coding tools. Through the realistic yet standardized evaluation offered by CritPt, we highlight a large disconnect between current model capabilities and realistic physics research demands, offering a foundation to guide the development of scientifically grounded AI tools.
随着具有推理能力的大型语言模型(LLM)在高中数学竞赛和编程方面取得快速发展,它们能否有效应对前沿物理研究中遇到的复杂、开放性的挑战?至关重要的一点是,物理学家希望LLM辅助完成哪些推理任务?为了解答这些问题,我们推出了CritPt(复杂研究综合思维物理测试),这是首个针对未发表的、研究级推理任务的基准测试。该测试广泛覆盖了现代物理研究领域,包括凝聚态物理、量子力学、原子、分子和光学物理、天体物理、高能物理、数学物理、统计物理、核物理、非线性动力学、流体力学和生物物理学等。CritPt由71个组合的研究挑战构成,旨在模拟入门级别的全面研究项目,同时分解为190个更简单的检查点任务,以获取更精细的见解。所有问题均由50多名活跃的物理研究者根据自己的研究全新创建。每个问题都经过手工筛选,以得出经得起猜测且可机器验证的答案,并由针对高级物理特定输出格式进行大量自定义的自动评分管道进行评估。我们发现,虽然当前最先进的大型语言模型在单独的检查点上显示出早期潜力,但它们仍然远远不能可靠地解决全面的研究规模挑战:基础模型中最好的平均准确率仅为4.0%,由GPT-5(高级)实现,配备编码工具时适度提升至约10%。通过CritPt提供的现实且标准化的评估,我们突出了当前模型能力与现实物理研究需求之间的巨大差距,为科学基础的人工智能工具的发展提供了指导基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 39 pages, 6 figures, 6 tables
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力在高中数学竞赛和编程方面迅速发展的背景下,其在前沿物理研究中的复杂、开放性的挑战中的有效推理能力如何?针对这一问题,提出了CritPt(Complex Research using Integrated Thinking - Physics Test)基准测试,用于测试LLM在未公布的研究级推理任务上的表现。研究发现,当前最先进的LLM在孤立的检查点上有早期承诺,但在解决全面的研究规模挑战方面仍有很大差距。
Key Takeaways
- CritPt基准测试旨在测试LLM在前沿物理研究领域的推理能力。
- 涵盖现代物理研究领域,包括凝聚态物理、量子力学、原子、分子与光学物理等。
- 由50多名活跃的物理研究者基于自身研究创作的问题,用于模拟完整的研究项目。
- 当前最先进的LLM在解决全面的研究规模挑战方面仍有较大差距,平均准确率仅为4.0%。
- GPT-5(高级)模型的平均准确率略有提高,达到约10%,但仅限于配备编程工具时。
- 当前模型能力与实际物理研究需求之间存在较大断层。
点此查看论文截图
Towards Verified Code Reasoning by LLMs
Authors:Meghana Sistla, Gogul Balakrishnan, Pat Rondon, José Cambronero, Michele Tufano, Satish Chandra
While LLM-based agents are able to tackle a wide variety of code reasoning questions, the answers are not always correct. This prevents the agent from being useful in situations where high precision is desired: (1) helping a software engineer understand a new code base, (2) helping a software engineer during code review sessions, and (3) ensuring that the code generated by an automated code generation system meets certain requirements (e.g. fixes a bug, improves readability, implements a feature). As a result of this lack of trustworthiness, the agent’s answers need to be manually verified before they can be trusted. Manually confirming responses from a code reasoning agent requires human effort and can result in slower developer productivity, which weakens the assistance benefits of the agent. In this paper, we describe a method to automatically validate the answers provided by a code reasoning agent by verifying its reasoning steps. At a very high level, the method consists of extracting a formal representation of the agent’s response and, subsequently, using formal verification and program analysis tools to verify the agent’s reasoning steps. We applied this approach to a benchmark set of 20 uninitialized variable errors detected by sanitizers and 20 program equivalence queries. For the uninitialized variable errors, the formal verification step was able to validate the agent’s reasoning on 13/20 examples, and for the program equivalence queries, the formal verification step successfully caught 6/8 incorrect judgments made by the agent.
虽然基于LLM的代理能够处理各种代码推理问题,但答案并不总是正确的。这导致在需要高精度的情境下,代理无法发挥用处,例如在以下场景:(1)帮助软件工程师理解新的代码库,(2)在代码审查会话期间帮助软件工程师,(3)确保由自动化代码生成系统生成的代码满足某些要求(例如修复错误、提高可读性、实现功能)。由于这种缺乏可信度的情况,代理的答案需要在手动确认后才能被信任。手动确认来自代码推理代理的响应需要人力,可能导致开发人员生产率降低,从而削弱了代理的助理效益。在本文中,我们描述了一种通过验证其推理步骤来自动验证代码推理代理提供的答案的方法。在很高的层次上,该方法由提取代理响应的形式表示开始,随后使用形式化验证和程序分析工具来验证代理的推理步骤。我们将这种方法应用到了由检查器检测到的20个未初始化变量错误和程序等价查询的基准测试集上。对于未初始化变量错误,形式化验证步骤能够验证代理在其中的13/20个例子上的推理过程;而对于程序等价查询,形式化验证步骤成功捕获了代理作出的错误的6/8个判断。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 43 pages
Summary:基于LLM的代理能够处理各种代码推理问题,但答案并不总是正确。这限制了其在需要高精度的场景(如帮助软件工程师理解新代码库、参与代码审查会话以及确保自动化代码生成系统生成的代码符合要求)中的应用价值。为解决信任问题,需要对代理的答案进行手动验证,这会消耗人力并降低开发者的工作效率,削弱了代理的辅助作用。本文介绍了一种通过验证其推理步骤来自动验证代码推理代理答案的方法。此方法包括提取代理响应的形式表示,并使用形式化验证和程序分析工具来验证代理的推理步骤。应用于一组未初始化变量错误和程序等价查询的基准测试集,该方法在验证未初始化变量错误时对代理推理进行了13/20的有效验证,在程序等价查询中成功捕捉到了代理作出的8/6次错误判断。
Key Takeaways:
- 基于LLM的代理在处理代码推理问题时存在答案不总是正确的问题。
- 这限制了代理在需要高精度的应用场景中的价值,如软件工程师的代码理解和审查以及自动化代码生成系统的验证。
- 手动验证代理答案会增加人力消耗,降低开发者效率,削弱代理的辅助作用。
- 本文介绍了一种自动验证代码推理代理答案的方法,通过验证其推理步骤来解决信任问题。
- 该方法包括提取代理响应的形式表示,并使用形式化验证和程序分析工具来进行验证。
- 在基准测试集上,该方法对代理推理的验证效果有限,但仍能在一定程度上提高验证效率和准确性。
点此查看论文截图

TASP: Topology-aware Sequence Parallelism
Authors:Yida Wang, Ke Hong, Xiuhong Li, Yuanchao Xu, Wenxun Wang, Guohao Dai, Yu Wang
Long-context large language models (LLMs) face constraints due to the quadratic complexity of the self-attention mechanism. The mainstream sequence parallelism (SP) method, Ring Attention, attempts to solve this by distributing the query into multiple query chunks across accelerators and enable each Q tensor to access all KV tensors from other accelerators via the Ring AllGather communication primitive. However, it exhibits low communication efficiency, restricting its practical applicability. This inefficiency stems from the mismatch between the Ring AllGather communication primitive it adopts and the AlltoAll topology of modern accelerators. A Ring AllGather primitive is composed of iterations of ring-styled data transfer, which can only utilize a very limited fraction of an AlltoAll topology. Inspired by the Hamiltonian decomposition of complete directed graphs, we identify that modern accelerator topology can be decomposed into multiple orthogonal ring datapaths which can concurrently transfer data without interference. Based on this, we further observe that the Ring AllGather primitive can also be decomposed into the same number of concurrent ring-styled data transfer at every iteration. Based on these insights, we propose TASP, a topology-aware SP method for long-context LLMs that fully utilizes the communication capacity of modern accelerators via topology decomposition and primitive decomposition. Experimental results on both single-node and multi-node NVIDIA H100 systems and a single-node AMD MI300X system demonstrate that TASP achieves higher communication efficiency than Ring Attention on these modern accelerator topologies and achieves up to 3.58 speedup than Ring Attention and its variant Zigzag-Ring Attention. The code is available at https://github.com/infinigence/HamiltonAttention.
长上下文大型语言模型(LLM)由于自注意力机制的二次复杂性而面临约束。主流的序列并行(SP)方法——环形注意力,试图通过将在加速器间分布的查询分成多个查询块来解决这个问题,并允许每个Q张量通过环形全收集通信原语访问其他加速器的所有KV张量。然而,它表现出较低的通信效率,限制了其实用性。这种低效率源于其采用的环形全收集通信原语与现代加速器的所有到所有拓扑结构之间的不匹配。环形全收集原语由环形数据转移的迭代组成,只能利用到所有到所有拓扑的一个很小部分。受完全有向图的哈密顿分解的启发,我们发现现代加速器拓扑可以分解成多个正交环形数据路径,这些路径可以并发传输数据而不会相互干扰。基于此,我们进一步观察到环形全收集原语也可以分解为同样数量的并发环形数据转移,每次迭代时都是如此。基于这些见解,我们提出了针对长上下文LLM的拓扑感知SP方法TASP,它通过对现代加速器的拓扑结构和原始结构进行分解来充分利用其通信能力。在单节点和多节点的NVIDIA H100系统以及单节点的AMD MI300X系统上的实验结果表明,TASP在现代加速器拓扑上实现了比环形注意力更高的通信效率,并且相对于环形注意力和其变体Zigzag-Ring Attention实现了最高达3.58的加速。代码可在https://github.com/infinigence/HamiltonAttention上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文探讨了长语境大型语言模型(LLM)面临的自注意力机制二次复杂度约束问题。主流序列并行(SP)方法,即Ring Attention,通过分布式查询来尝试解决此问题,但存在通信效率低下的问题,限制了其实际应用。作者基于现代加速器的AlltoAll拓扑与Ring AllGather通信原始组件的不匹配问题,提出一种全新的拓扑感知序列并行方法TASP。通过分解现代加速器的拓扑结构和通信原始组件,TASP能充分利用现代加速器的通信容量。实验结果表明,在单节点和多节点的NVIDIA H100系统以及单节点的AMD MI300X系统上,TASP在通信效率上优于Ring Attention,并对其进行了最高达3.58倍的性能加速。相关代码已公开在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 长语境大型语言模型(LLM)面临自注意力机制的二次复杂度约束挑战。
- 主流序列并行(SP)方法,如Ring Attention,虽能解决部分问题,但通信效率低下。
- 通信效率低下源于Ring AllGather通信原始组件与现代加速器AlltoAll拓扑结构的不匹配。
- 通过分解现代加速器的拓扑结构和通信原始组件,提出一种新的拓扑感知序列并行方法TASP。
- TASP能充分利用现代加速器的通信容量,提高通信效率。
- 在不同系统上的实验表明,TASP相较于Ring Attention有显著性能提升。
点此查看论文截图
OceanGym: A Benchmark Environment for Underwater Embodied Agents
Authors:Yida Xue, Mingjun Mao, Xiangyuan Ru, Yuqi Zhu, Baochang Ren, Shuofei Qiao, Mengru Wang, Shumin Deng, Xinyu An, Ningyu Zhang, Ying Chen, Huajun Chen
We introduce OceanGym, the first comprehensive benchmark for ocean underwater embodied agents, designed to advance AI in one of the most demanding real-world environments. Unlike terrestrial or aerial domains, underwater settings present extreme perceptual and decision-making challenges, including low visibility, dynamic ocean currents, making effective agent deployment exceptionally difficult. OceanGym encompasses eight realistic task domains and a unified agent framework driven by Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs), which integrates perception, memory, and sequential decision-making. Agents are required to comprehend optical and sonar data, autonomously explore complex environments, and accomplish long-horizon objectives under these harsh conditions. Extensive experiments reveal substantial gaps between state-of-the-art MLLM-driven agents and human experts, highlighting the persistent difficulty of perception, planning, and adaptability in ocean underwater environments. By providing a high-fidelity, rigorously designed platform, OceanGym establishes a testbed for developing robust embodied AI and transferring these capabilities to real-world autonomous ocean underwater vehicles, marking a decisive step toward intelligent agents capable of operating in one of Earth’s last unexplored frontiers. The code and data are available at https://github.com/OceanGPT/OceanGym.
我们介绍了OceanGym,这是针对海洋水下实体智能体设计的首个综合基准测试平台,旨在推动人工智能在最苛刻的现实环境之一中的应用。与陆地或空中领域不同,水下环境带来了极端的感知和决策挑战,包括低能见度、动态海洋水流,使得有效部署智能体变得异常困难。OceanGym包含八个现实的任务领域和一个由多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)驱动的统一智能体框架,该框架融合了感知、记忆和序列决策。智能体需要理解光学和声纳数据,自主探索复杂环境,并在这些恶劣条件下完成长期目标。大量实验表明,最先进的MLLM驱动的智能体与人类专家之间存在明显差距,凸显了海洋水下环境中感知、规划和适应性的持久性难题。通过提供高保真、严格设计的平台,OceanGym为开发稳健的实体人工智能并将这些能力转移到现实世界的自主海洋水下车辆建立了测试床,这是朝着能够操作地球最后一个未开发前沿之一的智能实体迈出的决定性一步。代码和数据可在https://github.com/OceanGPT/OceanGym找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
OceanGym是首个针对海洋水下智能主体的全面基准测试平台,旨在推进人工智能在最具挑战性的现实环境之一中的应用。该平台涵盖八个真实任务领域,采用多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)驱动的统一主体框架,面临低能见度、动态洋流等极端感知和决策挑战。OceanGym要求智能主体理解光学和声纳数据,自主探索复杂环境,并在这些恶劣条件下完成长期目标。实验表明,现有MLLM驱动的智能主体与人类专家之间仍存在巨大差距,凸显了海洋水下环境中的感知、规划和适应能力的持久挑战。OceanGym为开发稳健的嵌入式人工智能提供了一个高保真、严谨设计的平台,并将这些能力转移到现实世界的自主海洋水下车辆中,标志着朝着智能主体在地球最后的前沿之一中运行的重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- OceanGym是首个针对海洋水下智能主体的全面基准测试平台。
- 平台旨在推进人工智能在海洋环境下的应用,这是一个极具挑战性的现实环境。
- OceanGym包含八个真实任务领域,并采用了多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)驱动的统一主体框架。
- 智能主体需要面对低能见度、动态洋流等极端感知和决策挑战。
- 智能主体需要理解光学和声纳数据,自主探索复杂环境,完成长期目标。
- 实验显示,现有MLLM驱动的智能主体与人类专家之间在感知、规划和适应方面存在巨大差距。
点此查看论文截图
The Dragon Hatchling: The Missing Link between the Transformer and Models of the Brain
Authors:Adrian Kosowski, Przemysław Uznański, Jan Chorowski, Zuzanna Stamirowska, Michał Bartoszkiewicz
The relationship between computing systems and the brain has served as motivation for pioneering theoreticians since John von Neumann and Alan Turing. Uniform, scale-free biological networks, such as the brain, have powerful properties, including generalizing over time, which is the main barrier for Machine Learning on the path to Universal Reasoning Models. We introduce `Dragon Hatchling’ (BDH), a new Large Language Model architecture based on a scale-free biologically inspired network of $n$ locally-interacting neuron particles. BDH couples strong theoretical foundations and inherent interpretability without sacrificing Transformer-like performance. BDH is a practical, performant state-of-the-art attention-based state space sequence learning architecture. In addition to being a graph model, BDH admits a GPU-friendly formulation. It exhibits Transformer-like scaling laws: empirically BDH rivals GPT2 performance on language and translation tasks, at the same number of parameters (10M to 1B), for the same training data. BDH can be represented as a brain model. The working memory of BDH during inference entirely relies on synaptic plasticity with Hebbian learning using spiking neurons. We confirm empirically that specific, individual synapses strengthen connection whenever BDH hears or reasons about a specific concept while processing language inputs. The neuron interaction network of BDH is a graph of high modularity with heavy-tailed degree distribution. The BDH model is biologically plausible, explaining one possible mechanism which human neurons could use to achieve speech. BDH is designed for interpretability. Activation vectors of BDH are sparse and positive. We demonstrate monosemanticity in BDH on language tasks. Interpretability of state, which goes beyond interpretability of neurons and model parameters, is an inherent feature of the BDH architecture.
计算系统与大脑之间的关系自约翰·冯·诺依曼和艾伦·图灵以来一直激励着理论先驱者。均匀、无标度的生物网络,如大脑,具有强大的功能属性,包括随着时间的推移进行概括,这是机器通用推理模型路径上机器学习所面临的主要障碍。我们引入了名为“龙孵化器”(BDH)的大型语言模型架构,该架构基于无标度生物灵感网络,由n个局部交互神经元粒子组成。BDH结合了强大的理论基础和固有的可解释性,同时不牺牲类似Transformer的性能。BDH是一种实用、高效的基于注意力状态空间的序列学习架构。除了作为图形模型之外,BDH还采用了一种适用于GPU的公式。它表现出类似Transformer的扩展定律:在相同的参数数量(从10M到1B)和相同的训练数据下,实证中BDH在语言翻译任务上的性能与GPT2相媲美。BDH可以被表示为一种大脑模型。BDH在推理过程中的工作内存完全依赖于利用脉冲神经元的赫布学习来加强突触可塑性。我们实证证实,每当BDH处理语言输入时听到或推理特定概念时,特定单个突触会加强连接。BDH的神经元交互网络是一个高模块化、重尾分布程度的图。BDH模型在生物学上是合理的,解释了人类神经元实现语言的一种可能机制。BDH旨在实现可解释性。BDH的激活向量是稀疏且正向的。我们在语言任务上展示了BDH的单语义性。除了神经元和模型参数的可解释性之外,状态的可解释性是BDH架构的固有特征。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code available at: https://github.com/pathwaycom/bdh Accompanying blog: https://pathway.com/research/bdh
摘要
该文本探讨了计算系统和人脑的关系以及对于实现通用推理模型的重要启示。文中提出了一种基于无尺度生物网络的新型大规模语言模型架构——“龙孵化器”(BDH)。该架构具有强大的理论基础和固有的可解释性,同时不牺牲类似Transformer的性能。BDH是一个实用、高性能的状态空间序列学习架构,既是一个图形模型,也支持GPU友好型公式。它表现出类似Transformer的规模效应,在语言和翻译任务上的性能可与GPT-2相提并论。此外,BDH可以作为一种大脑模型来表示,其工作记忆在推理过程中完全依赖于突触可塑性,采用赫布学习规则通过脉冲神经元实现。经验证实,BDH处理语言输入时,特定的突触会在听到或推理特定概念时加强连接。最后,BDH的设计旨在实现可解释性,其激活向量稀疏且呈阳性。在任务语言方面展示了单语义性,即状态的可解释性不仅是神经元和模型参数的可解释性,而是BDH架构的固有特性。
关键见解
- 计算系统与大脑的关联为理论学者提供了动力,无尺度生物网络如大脑具有强大的属性,如随时间概括化,这对机器学习实现通用推理模型是主要障碍。
- 引入了一种新型大规模语言模型架构“龙孵化器”(BDH),基于无尺度生物网络启发设计。
- BDH结合了强大的理论基础和固有的可解释性,同时保持了类似Transformer的性能。
- BDH是一个高效、实用的状态空间序列学习架构,既作为图形模型也兼容GPU。
- BDH展现出类似Transformer的规模效应,能在语言和翻译任务上达到与GPT-2相当的性能水平。
- BDH可视为一种大脑模型,其工作记忆基于突触可塑性,并采用赫布学习规则通过脉冲神经元实现。
点此查看论文截图
Revealing the Power of Post-Training for Small Language Models via Knowledge Distillation
Authors:Miao Rang, Zhenni Bi, Hang Zhou, Hanting Chen, An Xiao, Tianyu Guo, Kai Han, Xinghao Chen, Yunhe Wang
The rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) has significantly advanced the capabilities of artificial intelligence across various domains. However, their massive scale and high computational costs render them unsuitable for direct deployment in resource-constrained edge environments. This creates a critical need for high-performance small models that can operate efficiently at the edge. Yet, after pre-training alone, these smaller models often fail to meet the performance requirements of complex tasks. To bridge this gap, we introduce a systematic post-training pipeline that efficiently enhances small model accuracy. Our post training pipeline consists of curriculum-based supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and offline on-policy knowledge distillation. The resulting instruction-tuned model achieves state-of-the-art performance among billion-parameter models, demonstrating strong generalization under strict hardware constraints while maintaining competitive accuracy across a variety of tasks. This work provides a practical and efficient solution for developing high-performance language models on Ascend edge devices.
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展已在各个领域显著提高了人工智能的能力。然而,由于其庞大的规模和较高的计算成本,它们不适合在资源受限的边缘环境中直接部署。这为能在边缘高效运行的高性能小型模型带来了迫切需求。然而,仅通过预训练,这些较小的模型往往难以满足复杂任务的性能要求。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了一种系统的后训练管道,该管道可以有效地提高小模型的准确性。我们的后训练管道包括基于课程的监督微调(SFT)和离线在线策略知识蒸馏。所得指令调整模型在百亿参数模型中实现最佳性能,在严格的硬件约束下表现出强大的泛化能力,同时在各种任务中保持竞争力。这项工作为在Ascend边缘设备上开发高性能语言模型提供了实用且高效的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展极大地推动了人工智能在多个领域的能力提升。然而,其庞大的规模和较高的计算成本使其不适合在资源受限的边缘环境中直接部署。因此,需要高性能的小型模型在边缘进行高效运行。然而,仅通过预训练,这些小型模型往往难以满足复杂任务的性能要求。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了一种系统的后训练管道,有效提高小型模型的准确性。我们的后训练管道包括基于课程表的监督微调(SFT)和离线在线政策知识蒸馏。结果得到的指令调整模型在亿级参数模型中实现最佳性能,在严格的硬件约束下表现出强大的泛化能力,同时在各种任务中保持竞争力准确性。本工作在为Ascend边缘设备开发高性能语言模型方面提供了实用且高效的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展推动了人工智能的进步,但在资源受限的边缘环境下部署存在挑战。
- 需要高性能小型模型在边缘进行高效运行。
- 仅有预训练的模型难以满足复杂任务的需求。
- 提出了一种系统的后训练管道,包括监督微调(SFT)和知识蒸馏。
- 该管道提高了小型模型的准确性,实现了亿级参数模型中的最佳性能。
- 模型在严格的硬件约束下表现出强大的泛化能力,同时在各种任务中保持高准确性。
点此查看论文截图
LaTo: Landmark-tokenized Diffusion Transformer for Fine-grained Human Face Editing
Authors:Zhenghao Zhang, Ziying Zhang, Junchao Liao, Xiangyu Meng, Qiang Hu, Siyu Zhu, Xiaoyun Zhang, Long Qin, Weizhi Wang
Recent multimodal models for instruction-based face editing enable semantic manipulation but still struggle with precise attribute control and identity preservation. Structural facial representations such as landmarks are effective for intermediate supervision, yet most existing methods treat them as rigid geometric constraints, which can degrade identity when conditional landmarks deviate significantly from the source (e.g., large expression or pose changes, inaccurate landmark estimates). To address these limitations, we propose LaTo, a landmark-tokenized diffusion transformer for fine-grained, identity-preserving face editing. Our key innovations include: (1) a landmark tokenizer that directly quantizes raw landmark coordinates into discrete facial tokens, obviating the need for dense pixel-wise correspondence; (2) a location-mapping positional encoding that integrates facial and image tokens for unified processing, enabling flexible yet decoupled geometry-appearance interactions with high efficiency and strong identity preservation; and (3) a landmark predictor that leverages vision-language models to infer target landmarks from instructions and source images, whose structured chain-of-thought improves estimation accuracy and interactive control. To mitigate data scarcity, we curate HFL-150K, to our knowledge the largest benchmark for this task, containing over 150K real face pairs with fine-grained instructions. Extensive experiments show that LaTo outperforms state-of-the-art methods by 7.8% in identity preservation and 4.6% in semantic consistency. Code and dataset will be made publicly available upon acceptance.
最近的多模态指令式人脸编辑模型能够实现语义操作,但在精确属性控制和身份保留方面仍存在困难。面部结构表示(如地标)对于中间监督是有效的,但大多数现有方法将其视为刚性的几何约束,当条件地标与源面部(例如,大幅度表情或姿态变化、地标估计不准确)存在显著差异时,会导致身份降级。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了LaTo,一种用于精细粒度、身份保留的人脸编辑的基于地标符号化的扩散转换器。我们的关键创新包括:(1)地标分词器,它直接将原始地标坐标量化成离散面部符号,无需密集像素级的对应关系;(2)位置映射位置编码,将面部和图像符号集成进行统一处理,实现灵活但解耦的几何外观交互,具有高效率强身份保留能力;(3)地标预测器利用视觉语言模型从指令和源图像推断目标地标,其结构化思维链提高了估计精度和交互控制。为了缓解数据稀缺问题,我们整理了HFL-150K数据集,据我们所知,这是该任务最大的基准测试数据集,包含超过150,000个精细指令的真实人脸对。大量实验表明,在身份保留和语义一致性方面,LaTo优于最新技术方法,分别提高了7.8%和4.6%。接受后将公开代码和数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为LaTo的里程碑标记化扩散转换器,用于精细粒度的身份保留面部编辑。通过引入里程碑标记化、位置映射位置编码和里程碑预测器等技术,实现了灵活的几何与外观交互、高效的身份保留以及精确的语义控制。为解决数据稀缺问题,还推出了HFL-150K数据集,包含超过15万对真实面部图像和精细指令。实验表明,LaTo在身份保留和语义一致性方面优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- LaTo通过引入里程碑标记化技术,将原始面部编辑中的几何约束转化为离散面部标记,提高了模型的灵活性。
- 位置映射位置编码技术实现了面部和图像标记的集成处理,提高了效率并增强了身份保留能力。
- LaTo利用视觉语言模型来推断目标里程碑,从而提高估算准确性和交互控制性。
- HFL-150K数据集的推出解决了面部编辑任务中数据稀缺的问题,为相关研究提供了丰富的资源。
- LaTo在身份保留和语义一致性方面显著优于现有技术,实验结果表明其有效性。
- LaTo通过精细的里程碑预测和高效的模型结构,实现了灵活的几何与外观交互。
点此查看论文截图
MASLegalBench: Benchmarking Multi-Agent Systems in Deductive Legal Reasoning
Authors:Huihao Jing, Wenbin Hu, Hongyu Luo, Jianhui Yang, Wei Fan, Haoran Li, Yangqiu Song
Multi-agent systems (MAS), leveraging the remarkable capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), show great potential in addressing complex tasks. In this context, integrating MAS with legal tasks is a crucial step. While previous studies have developed legal benchmarks for LLM agents, none are specifically designed to consider the unique advantages of MAS, such as task decomposition, agent specialization, and flexible training. In fact, the lack of evaluation methods limits the potential of MAS in the legal domain. To address this gap, we propose MASLegalBench, a legal benchmark tailored for MAS and designed with a deductive reasoning approach. Our benchmark uses GDPR as the application scenario, encompassing extensive background knowledge and covering complex reasoning processes that effectively reflect the intricacies of real-world legal situations. Furthermore, we manually design various role-based MAS and conduct extensive experiments using different state-of-the-art LLMs. Our results highlight the strengths, limitations, and potential areas for improvement of existing models and MAS architectures.
多智能体系统(MAS)利用大型语言模型(LLM)的卓越能力,在解决复杂任务方面显示出巨大潜力。在此背景下,将MAS与法律任务集成是一个关键步骤。虽然之前的研究已经为LLM代理开发了法律基准,但没有一个是专门考虑MAS的独特优势,如任务分解、代理专业化和灵活的训练。事实上,缺乏评估方法限制了MAS在法律领域的潜力。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了MASLegalBench,这是一个专为MAS定制的法律基准,采用演绎推理方法设计。我们的基准以GDPR为应用场景,包含丰富的背景知识,涵盖有效的复杂推理过程,反映了现实法律情况的复杂性。此外,我们还手动设计了各种基于角色的MAS,并使用不同的最新LLM进行了广泛的实验。我们的结果突显了现有模型和MAS架构的优势、局限性和潜在的改进领域。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于多代理系统(MAS)和大型语言模型(LLM)的融合技术,为解决复杂任务展现了巨大潜力。针对法律任务集成MAS的重要性,当前缺乏专门考虑MAS独特优势的法律基准。为解决此空白,提出MASLegalBench,一个专为MAS设计的法律基准,采用演绎推理方法,以GDPR为应用场景,涵盖广泛背景知识,有效反映现实法律情境的复杂性。
Key Takeaways
- 多代理系统(MAS)与大型语言模型(LLM)融合,为解决复杂任务提供巨大潜力。
- 当前法律任务集成MAS至关重要,但需考虑MAS的独特优势,如任务分解、代理专业化和灵活训练。
- 缺乏专门考虑MAS优势的法律基准限制其在法律领域的应用潜力。
- MASLegalBench是一个为MAS设计的法律基准,采用演绎推理方法。
- MASLegalBench以GDPR为应用场景,涵盖广泛背景知识,反映现实法律情境的复杂性。
- 通过实验发现,现有模型和MAS架构的优势、局限性和改进潜力。
点此查看论文截图
MaskSQL: Safeguarding Privacy for LLM-Based Text-to-SQL via Abstraction
Authors:Sepideh Abedini, Shubhankar Mohapatra, D. B. Emerson, Masoumeh Shafieinejad, Jesse C. Cresswell, Xi He
Large language models (LLMs) have shown promising performance on tasks that require reasoning, such as text-to-SQL, code generation, and debugging. However, regulatory frameworks with strict privacy requirements constrain their integration into sensitive systems. State-of-the-art LLMs are also proprietary, costly, and resource-intensive, making local deployment impractical. Consequently, utilizing such LLMs often requires sharing data with third-party providers, raising privacy concerns and risking noncompliance with regulations. Although fine-tuned small language models (SLMs) can outperform LLMs on certain tasks and be deployed locally to mitigate privacy concerns, they underperform on more complex tasks such as text-to-SQL translation. In this work, we introduce MaskSQL, a text-to-SQL framework that utilizes abstraction as a privacy protection mechanism to mask sensitive information in LLM prompts. Unlike redaction, which removes content entirely, or generalization, which broadens tokens, abstraction retains essential information while discarding unnecessary details, striking an effective privacy-utility balance for the text-to-SQL task. Moreover, by providing mechanisms to control the privacy-utility tradeoff, MaskSQL facilitates adoption across a broader range of use cases. Our experimental results show that MaskSQL outperforms leading SLM-based text-to-SQL models and achieves performance approaching state-of-the-art LLM-based models, while preserving privacy.
大型语言模型(LLM)在需要推理的任务中表现出有前景的性能,如文本到SQL、代码生成和调试。然而,具有严格隐私要求的监管框架限制了它们融入敏感系统。当前先进的大型语言模型也是专有化的,成本高昂且资源密集,使得本地部署不切实际。因此,利用这些大型语言模型通常需要与第三方提供商共享数据,这引发了隐私担忧并可能违反法规。虽然经过微调的小型语言模型(SLM)可以在某些任务上优于大型语言模型并可在本地部署以缓解隐私担忧,但它们在处理更复杂的任务(如文本到SQL翻译)时表现较差。在这项工作中,我们介绍了MaskSQL,这是一个文本到SQL的框架,它利用抽象作为隐私保护机制来掩盖大型语言模型提示中的敏感信息。与完全删除内容的删除或扩大范围的泛化不同,抽象保留了必要信息同时丢弃了不必要的细节,为文本到SQL任务实现了有效的隐私效用平衡。此外,通过提供控制隐私效用权衡的机制,MaskSQL促进了其在更广泛的使用案例中的应用。我们的实验结果表明,MaskSQL优于领先的小型语言模型基础的文本到SQL模型,其性能接近先进的大型语言模型基础模型,同时保护了隐私。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the 3rd Workshop on Regulatable ML at NeurIPS 2025
Summary
LLMs在需要推理的任务上表现优异,如文本到SQL、代码生成和调试。但严格隐私要求的监管框架限制了它们在某些敏感系统的集成。LLMs通常是专有、昂贵且资源密集型的,难以进行本地部署。为解决隐私担忧与合规风险,我们提出MaskSQL框架,利用抽象作为隐私保护机制,在LLM提示中隐藏敏感信息。抽象既保留了必要信息又剔除了不必要的细节,为文本到SQL任务实现了有效的隐私效用平衡。MaskSQL还提供控制隐私效用的机制,适用于更广泛的使用场景。实验结果显示,MaskSQL优于领先的SLM-based文本到SQL模型,性能接近先进的LLM-based模型,同时保护隐私。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在需要推理的任务上表现良好,但在隐私敏感系统的集成中受到监管和部署挑战。
- 现有LLMs是专有、昂贵且资源密集型的,本地部署不切实际。
- MaskSQL框架使用抽象作为隐私保护机制,隐藏LLM提示中的敏感信息。
- 抽象方法有效平衡了隐私和效用,优于简单的删除或泛化方法。
- MaskSQL提供了控制隐私效用平衡的机制,适用于多种使用场景。
- MaskSQL在文本到SQL任务上的性能接近或优于先进的LLM模型。
点此查看论文截图
Critique to Verify: Accurate and Honest Test-Time Scaling with RL-Trained Verifiers
Authors:Zhicheng Yang, Zhijiang Guo, Yinya Huang, Yongxin Wang, Yiwei Wang, Xiaodan Liang, Jing Tang
Test-time scaling via solution sampling and aggregation has become a key paradigm for improving the reasoning performance of Large Language Models (LLMs). While reward model selection is commonly employed in this approach, it often fails to identify minority-yet-correct answers, which limits its effectiveness beyond that of simple majority voting. We argue that this limitation stems from a lack of informative critique signals during verifier training. To bridge this gap, we introduce Mirror-Critique, a framework that trains a verifier with informative critiques. Our key insight is to leverage the rich critique signal by contrasting model-generated solutions with ground-truth solutions. We deploy a small instruction-tuned model to synthesize high-quality critique data with rejection sampling that teaches the verifier not only what is wrong, but also why. The synthetic data is used to cold-start the LLMs in the RLVR process to further improve the verification ability. The resulting Mirror-Verifier is deployed to evaluate candidate solutions by generating multiple critiques per solution, aggregating them into a verify score used for weighted voting or selective abstention. The experimental results show that our Mirror-Verifier significantly outperforms majority voting in terms of solution accuracy and also improves the solver’s honesty to recognize and abstain from answering beyond its capability boundaries.
通过解决方案采样和聚合进行测试时缩放已成为提高大型语言模型(LLM)推理性能的关键范式。虽然奖励模型选择在这种方法中经常被使用,但它通常无法识别出少数但正确的答案,这限制了其效果,超过了简单的多数投票制。我们认为,这一局限性源于验证器训练期间缺乏信息性批判信号。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了Mirror-Critique框架,该框架训练了一个具有信息性批判的验证器。我们的关键见解是通过对比模型生成的解决方案与真实解决方案,利用丰富的批判信号。我们部署了一个小型指令调整模型,通过拒绝采样合成高质量的批判数据,这不仅教会验证器什么是错误的,还教会它为什么错误。合成数据用于在RLVR过程中启动LLM,以进一步提高验证能力。所得的Mirror-Verifier被用来评估候选解决方案,通过为每个解决方案生成多个批判并将其聚合为验证分数,用于加权投票或选择性弃权。实验结果表明,我们的Mirror-Verifier在解决方案的准确性方面显著优于多数投票制,并提高了求解者的诚实度,使其能够识别和避免超出其能力边界的答案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文介绍了通过解决方案采样和聚合的测试时间缩放方法,已成为提高大型语言模型(LLM)推理性能的关键范式。文章指出,虽然奖励模型选择是这一方法中的常用手段,但它往往无法识别出少数正确的答案,这限制了其效果,超越简单的多数投票制。为解决这一问题,文章提出了Mirror-Critique框架,通过训练携带信息丰富的评论信号的验证器来弥补这一差距。该框架利用对比模型生成解决方案与真实解决方案的方式,生成高质量的评论数据。这些数据用于在RLVR过程中启动LLM,以提高验证能力。实验结果表明,Mirror-Verifier在解决方案准确性和求解器诚实度方面显著优于多数投票制。
Key Takeaways
- 测试时间缩放通过解决方案采样和聚合已成为改善大型语言模型(LLM)推理性能的关键方法。
- 奖励模型选择虽然常用,但难以识别少数正确答案,限制了其效果。
- Mirror-Critique框架旨在通过训练携带信息丰富的评论信号的验证器来解决此问题。
- 该框架通过对比模型生成解决方案与真实解决方案的方式生成高质量的评论数据。
- 利用这些评论数据冷启动LLM以提高验证能力。
- Mirror-Verifier显著提高解决方案准确性和求解器诚实度。
点此查看论文截图
Towards Comprehensive Interactive Change Understanding in Remote Sensing: A Large-scale Dataset and Dual-granularity Enhanced VLM
Authors:Junxiao Xue, Quan Deng, Xuecheng Wu, Kelu Yao, Xinyi Yin, Fei Yu, Wei Zhou, Yanfei Zhong, Yang Liu, Dingkang Yang
Remote sensing change understanding (RSCU) is essential for analyzing remote sensing images and understanding how human activities affect the environment. However, existing datasets lack deep understanding and interactions in the diverse change captioning, counting, and localization tasks. To tackle these gaps, we construct ChangeIMTI, a new large-scale interactive multi-task instruction dataset that encompasses four complementary tasks including change captioning, binary change classification, change counting, and change localization. Building upon this new dataset, we further design a novel vision-guided vision-language model (ChangeVG) with dual-granularity awareness for bi-temporal remote sensing images (i.e., two remote sensing images of the same area at different times). The introduced vision-guided module is a dual-branch architecture that synergistically combines fine-grained spatial feature extraction with high-level semantic summarization. These enriched representations further serve as the auxiliary prompts to guide large vision-language models (VLMs) (e.g., Qwen2.5-VL-7B) during instruction tuning, thereby facilitating the hierarchical cross-modal learning. We extensively conduct experiments across four tasks to demonstrate the superiority of our approach. Remarkably, on the change captioning task, our method outperforms the strongest method Semantic-CC by 1.39 points on the comprehensive S*m metric, which integrates the semantic similarity and descriptive accuracy to provide an overall evaluation of change caption. Moreover, we also perform a series of ablation studies to examine the critical components of our method.
遥感变化理解(RSCU)在分析遥感图像以及了解人类活动如何影响环境方面至关重要。然而,现有数据集在多样化的变化描述、计数和定位任务中缺乏深入的理解和交互。为了弥补这些空白,我们构建了ChangeIMTI,这是一个新的大型交互式多任务指令数据集,包含四个互补任务,包括变化描述、二元变化分类、变化计数和变化定位。基于这个新数据集,我们进一步设计了一种新型视觉引导的视觉语言模型(ChangeVG),该模型具有双粒度意识,适用于双时序遥感图像(即同一地区不同时间的两张遥感图像)。引入的视觉引导模块是一个双分支架构,协同结合了精细的空间特征提取和高层次语义摘要。这些丰富的表示形式进一步作为辅助提示,在指令微调过程中引导大型视觉语言模型(VLMs)(例如Qwen2.5-VL-7B),从而促进分层跨模态学习。我们通过四个任务的实验来展示我们方法的优越性。值得一提的是,在变化描述任务上,我们的方法在综合S*m指标上超越了最强方法Semantic-CC(高出1.39分),该指标结合了语义相似性和描述准确性,为变化描述提供了整体评价。此外,我们还进行了一系列消融研究来检验我们方法的关键组成部分。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了远程感应变化理解(RSCU)的重要性,并指出了现有数据集在多样变化描述、计数和定位任务中的不足。为弥补这些不足,构建了ChangeIMTI这一大型多任务互动指令数据集,包含变化描述、二元变化分类、变化计数和变化定位四个互补任务。基于该新数据集,设计了一种具有双粒度意识的视觉引导视觉语言模型(ChangeVG),用于处理双时态遥感图像。该模型通过精细的空间特征提取和高层次语义总结的结合,丰富了表示形式,作为辅助提示引导大型视觉语言模型(VLMs)进行指令微调,促进了分层跨模态学习。实验证明,该方法在变化描述任务上优于最强方法Semantic-CC,综合S*m指标提高了1.39点。
Key Takeaways
- 远程感应变化理解(RSCU)在分析遥感图像和了解人类活动对环境影响方面至关重要。
- 现有数据集在变化描述、计数和定位任务中缺乏深度理解和互动。
- 构建了ChangeIMTI这一大型多任务互动指令数据集,包含四个互补任务。
- 设计了具有双粒度意识的视觉引导视觉语言模型(ChangeVG),适用于双时态遥感图像。
- 视觉引导模块采用双分支架构,结合了精细的空间特征提取和高层次语义总结。
- ChangeVG方法在变化描述任务上表现优越,综合S*m指标优于最强方法Semantic-CC。
点此查看论文截图
The Geometry of Creative Variability: How Credal Sets Expose Calibration Gaps in Language Models
Authors:Esteban Garces Arias, Julian Rodemann, Christian Heumann
Understanding uncertainty in large language models remains a fundamental challenge, particularly in creative tasks where multiple valid outputs exist. We present a geometric framework using credal sets - convex hulls of probability distributions - to quantify and decompose uncertainty in neural text generation, calibrated against human creative variation. Analyzing 500 creative writing prompts from the WritingPrompts dataset with 10 unique human continuations each, we evaluate four language models across five decoding strategies, generating 100,000 stories. Our credal set analysis reveals substantial gaps in capturing human creative variation, with the best model-human calibration reaching only 0.434 (Gemma-2B with temperature 0.7). We decompose total uncertainty into epistemic and aleatoric components, finding that the choice of decoding strategy contributes 39.4% to 72.0% of total epistemic uncertainty. Model scale shows weak correlation with calibration quality and no significant difference exists between base and instruction-tuned models in calibration quality. Our geometric framework provides actionable insights for improving generation systems for human-AI creative alignment. We release our complete experimental framework.
理解大型语言模型中的不确定性仍然是一个基本挑战,特别是在存在多个有效输出的创造性任务中。我们提出了一个几何框架,使用可信集(概率分布凸包)来量化和分解神经文本生成中的不确定性,并与人类创造性变化进行校准。我们分析了WritingPrompts数据集中的500个创造性写作提示,每个提示有10个独特的人类续写,我们评估了四个语言模型的五种解码策略,生成了10万个故事。我们的可信集分析显示,在捕捉人类创造性变化方面存在巨大差距,最佳模型与人类的校准仅为0.434(Gemma-2B,温度为0.7)。我们将总不确定性分解为认知不确定性和偶然不确定性成分,发现解码策略的选择对总认知不确定性的贡献在39.4%至72.0%之间。模型规模与校准质量呈弱相关性,基础模型和指令调整模型在校准质量上不存在显著差异。我们的几何框架为改进人类-人工智能创造性对齐的生成系统提供了可操作性的见解。我们发布了完整的实验框架。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the 2nd UncertaiNLP Workshop @ EMNLP 2025
摘要
大语言模型的确定性问题是一大挑战,尤其是在存在多个有效输出的创造性任务中更是如此。本文提出一种基于几何框架的算法,使用可信集(概率分布凸包)来量化并分解神经文本生成中的不确定性,并与人类创造性变化进行校准。通过对WritingPrompts数据集500个创意写作提示的分析,每个提示有10个不同的人为延续,我们评估了四个语言模型的五种解码策略,生成了十万个故事。我们的可信集分析显示,在捕捉人类创造性变化方面存在巨大差距,最好的模型与人类校准仅达到0.434(Gemma-2B模型,温度为0.7)。我们将总不确定性分解为知识性和偶然性成分,发现解码策略的选择对总知识不确定性的贡献在39.4%~72.0%之间。模型规模与校准质量呈弱相关性,基础模型和指令调整模型在校准质量上无显著差异。我们的几何框架为改进人类-人工智能创造性对齐的生成系统提供了可操作性的见解。我们公开了完整的实验框架。
关键见解
- 神经文本生成中存在不确定性问题,特别是在创造性任务中。
- 提出使用几何框架和可信集来量化并分解不确定性。
- 通过分析WritingPrompts数据集,发现捕捉人类创造性变化方面存在巨大差距。
- 最佳模型与人类的校准程度有限。
- 解码策略对总知识不确定性的贡献显著。
- 模型规模与校准质量之间呈弱相关性。
点此查看论文截图
DiTraj: training-free trajectory control for video diffusion transformer
Authors:Cheng Lei, Jiayu Zhang, Yue Ma, Xinyu Wang, Long Chen, Liang Tang, Yiqiang Yan, Fei Su, Zhicheng Zhao
Diffusion Transformers (DiT)-based video generation models with 3D full attention exhibit strong generative capabilities. Trajectory control represents a user-friendly task in the field of controllable video generation. However, existing methods either require substantial training resources or are specifically designed for U-Net, do not take advantage of the superior performance of DiT. To address these issues, we propose DiTraj, a simple but effective training-free framework for trajectory control in text-to-video generation, tailored for DiT. Specifically, first, to inject the object’s trajectory, we propose foreground-background separation guidance: we use the Large Language Model (LLM) to convert user-provided prompts into foreground and background prompts, which respectively guide the generation of foreground and background regions in the video. Then, we analyze 3D full attention and explore the tight correlation between inter-token attention scores and position embedding. Based on this, we propose inter-frame Spatial-Temporal Decoupled 3D-RoPE (STD-RoPE). By modifying only foreground tokens’ position embedding, STD-RoPE eliminates their cross-frame spatial discrepancies, strengthening cross-frame attention among them and thus enhancing trajectory control. Additionally, we achieve 3D-aware trajectory control by regulating the density of position embedding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms previous methods in both video quality and trajectory controllability.
基于扩散转换器(DiT)的视频生成模型具有强大的生成能力,且拥有3D全注意力。轨迹控制代表了可控视频生成领域的一项友好任务。然而,现有方法要么需要大量训练资源,要么专为U-Net设计,并未充分利用DiT的卓越性能。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了DiTraj,这是一个简单有效的无需训练的轨迹控制框架,适用于文本到视频的生成,并为DiT量身定制。具体来说,首先,为了注入物体的轨迹,我们提出前景背景分离指导:我们使用大型语言模型(LLM)将用户提供的提示转化为前景和背景提示,分别指导视频中的前景和背景区域的生成。接着,我们分析了3D全注意力,并探索了令牌间注意力得分与位置嵌入之间的紧密关系。基于此,我们提出了跨帧时空解耦的3D-RoPE(STD-RoPE)。通过仅修改前景令牌的位置嵌入,STD-RoPE消除了跨帧的空间差异,增强了它们之间的跨帧注意力,从而提高了轨迹控制。此外,我们通过调整位置嵌入的密度实现了3D感知轨迹控制。大量实验表明,我们的方法在视频质量和轨迹可控性方面都优于以前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于扩散转换器(DiT)的视频生成模型,借助3D全注意力表现出强大的生成能力。轨迹控制是可控视频生成领域的一个用户友好型任务。然而,现有方法要么需要大量训练资源,要么专为U-Net设计,没有充分利用DiT的卓越性能。为解决这些问题,我们提出DiTraj,一个用于文本到视频生成的轨迹控制的简单有效且无需训练框架,专为DiT设计。通过前景背景分离指导注入物体轨迹,使用大型语言模型(LLM)将用户提示转换为前景和背景提示,分别指导视频中的前景和背景区域的生成。我们分析了3D全注意力,并发现令牌间注意力得分与位置嵌入之间存在紧密关联。基于此,我们提出跨帧时空解耦的3D-RoPE(STD-RoPE)。通过仅修改前景令牌的位置嵌入,STD-RoPE消除了跨帧空间差异,增强了它们之间的跨帧注意力,从而提高了轨迹控制。此外,我们通过调节位置嵌入的密度实现了3D感知轨迹控制。大量实验表明,我们的方法在视频质量和轨迹可控性方面都优于以前的方法。
关键见解
- 基于扩散转换器(DiT)的视频生成模型展现出强大的生成能力。
- 现有轨迹控制在视频生成中存在资源需求大或特定于U-Net设计的问题。
- 提出DiTraj框架,一个针对DiT设计的文本到视频生成轨迹控制的无训练框架。
- 通过前景背景分离指导注入物体轨迹。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLM)转换用户提示,指导视频的前景和背景生成。
- 分析3D全注意力,发现令牌间注意力与位置嵌入的关联。
点此查看论文截图
Code2MCP: Transforming Code Repositories into MCP Services
Authors:Chaoqian Ouyang, Ling Yue, Shimin Di, Libin Zheng, Linan Yue, Shaowu Pan, Jian Yin, Min-Ling Zhang
The Model Context Protocol (MCP) aims to create a standard for how Large Language Models use tools. However, most current research focuses on selecting tools from an existing pool. A more fundamental, yet largely overlooked, problem is how to populate this pool by converting the vast number of existing software projects into MCP-compatible services. To bridge this gap, we introduce Code2MCP, an agent-based framework that automatically transforms a GitHub repository into a functional MCP service with minimal human intervention. Code2MCP employs a multi-agent workflow for code analysis, environment setup, tool function design, and service generation, enhanced by a self-correcting loop to ensure reliability. We demonstrate that Code2MCP successfully transforms open-source computing libraries in scientific fields such as bioinformatics, mathematics, and fluid dynamics that are not available in existing MCP servers. By providing a novel automated pathway to unlock GitHub, the world’s largest code repository, for the MCP ecosystem, Code2MCP serves as a catalyst to significantly accelerate the protocol’s adoption and practical application. The code is public at https://github.com/DEFENSE-SEU/Code2MCP.
模型上下文协议(MCP)旨在创建大型语言模型使用工具的标准。然而,目前大多数研究都集中在从现有工具池中选工具。一个更为基础但常被忽视的问题是,如何通过将大量现有软件项目转化为MCP兼容服务来填充这个工具池。为了填补这一空白,我们引入了Code2MCP,这是一个基于代理的框架,能够自动将GitHub仓库转化为功能型的MCP服务,并且只需极少的人工干预。Code2MCP采用多代理工作流程进行代码分析、环境设置、工具功能设计和服务生成,并通过自我修正循环增强可靠性。我们证明Code2MCP能够成功转化科学领域中的开源计算库,如生物信息学、数学和流体动力学等领域中那些在现有MCP服务器中无法获得的库。通过为MCP生态系统解锁世界上最大的代码仓库GitHub提供新型自动化途径,Code2MCP成为加速该协议采用和实际应用的催化剂。代码公开在https://github.com/DEFENSE-SEU/Code2MCP。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型的工具使用标准化问题受到关注,当前研究多聚焦于从现有工具池中筛选工具。然而,一个更基础但常被忽视的问题是,如何将大量现有软件项目转化为适用于模型上下文协议(MCP)的服务以填充工具池。为解决此问题,我们提出了Code2MCP框架,它能将GitHub仓库自动转化为功能性的MCP服务,只需极少的人工干预。Code2MCP采用多智能体工作流程进行代码分析、环境设置、工具功能设计和服务生成,并通过自我修正循环确保可靠性。Code2MCP成功转化了科学领域如生物信息学、数学和流体动力学的开源计算库,这些库在现有的MCP服务器中并不可用。Code2MCP为MCP生态系统解锁了世界上最大的代码仓库GitHub,从而促进了该协议的采用和实际应用的加速。
Key Takeaways
- Model Context Protocol (MCP) 旨在标准化大型语言模型使用工具的方式。
- 当前研究主要关注从现有工具池中筛选工具,但如何填充这个工具池的问题被忽视。
- Code2MCP 是一个基于智能体的框架,旨在自动将GitHub仓库转化为功能性的MCP服务。
- Code2MCP 采用多智能体工作流程,包括代码分析、环境设置、工具功能设计和服务生成。
- Code2MCP 具有自我修正功能,确保可靠性。
- Code2MCP 成功转化了科学领域的开源计算库,如生物信息学、数学和流体动力学。
- Code2MCP 为解锁GitHub作为MCP生态系统的资源提供了新型自动化途径,加速了MCP的采用和实际应用。
