⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-02 更新
Query-Kontext: An Unified Multimodal Model for Image Generation and Editing
Authors:Yuxin Song, Wenkai Dong, Shizun Wang, Qi Zhang, Song Xue, Tao Yuan, Hu Yang, Haocheng Feng, Hang Zhou, Xinyan Xiao, Jingdong Wang
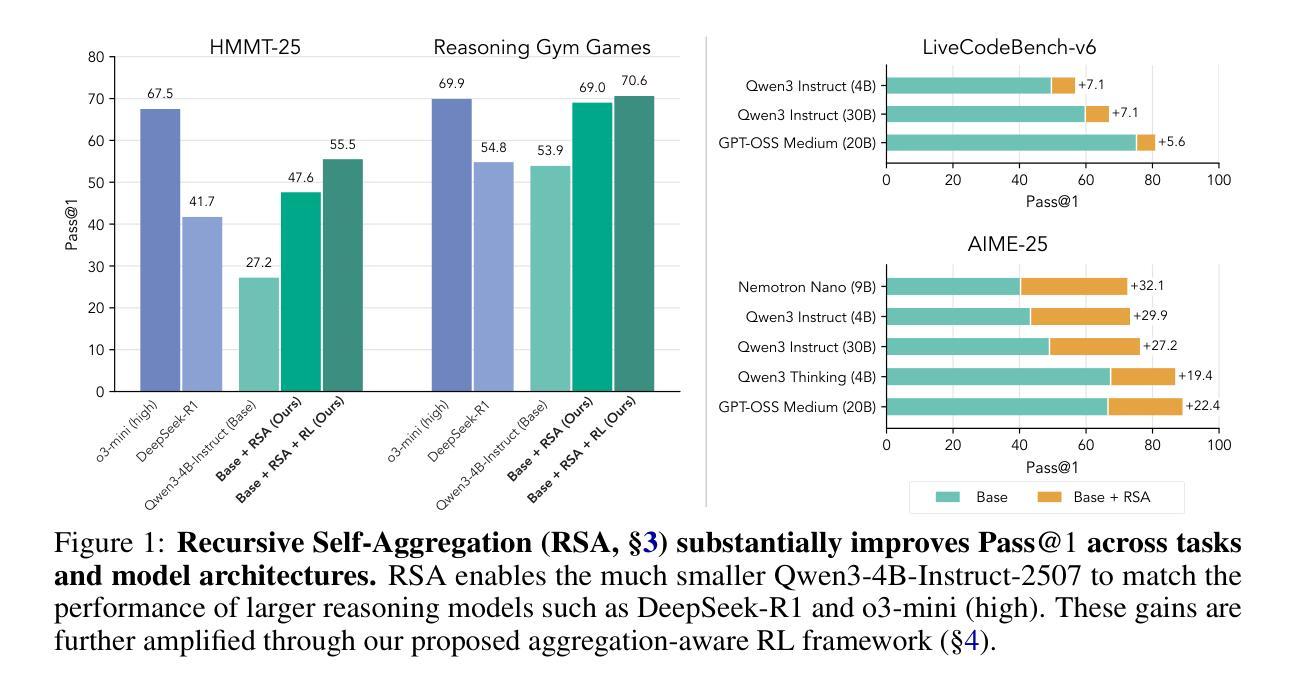
Unified Multimodal Models (UMMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance in text-to-image generation (T2I) and editing (TI2I), whether instantiated as assembled unified frameworks which couple powerful vision-language model (VLM) with diffusion-based generator, or as naive Unified Multimodal Models with an early fusion of understanding and generation modalities. We contend that in current unified frameworks, the crucial capability of multimodal generative reasoning which encompasses instruction understanding, grounding, and image referring for identity preservation and faithful reconstruction, is intrinsically entangled with high-fidelity synthesis. In this work, we introduce Query-Kontext, a novel approach that bridges the VLM and diffusion model via a multimodal ``kontext’’ composed of semantic cues and coarse-grained image conditions encoded from multimodal inputs. This design delegates the complex ability of multimodal generative reasoning to powerful VLM while reserving diffusion model’s role for high-quality visual synthesis. To achieve this, we propose a three-stage progressive training strategy. First, we connect the VLM to a lightweight diffusion head via multimodal kontext tokens to unleash the VLM’s generative reasoning ability. Second, we scale this head to a large, pre-trained diffusion model to enhance visual detail and realism. Finally, we introduce a low-level image encoder to improve image fidelity and perform instruction tuning on downstream tasks. Furthermore, we build a comprehensive data pipeline integrating real, synthetic, and open-source datasets, covering diverse multimodal reference-to-image scenarios, including image generation, instruction-driven editing, customized generation, and multi-subject composition. Experiments show that our approach matches strong unified baselines and even outperforms task-specific state-of-the-art methods in several cases.
统一多模态模型(UMMs)在文本到图像生成(T2I)和编辑(TI2I)方面表现出了显著的性能,无论是作为集成了强大视觉语言模型(VLM)和基于扩散的生成器的统一框架,还是作为早期理解和生成模态融合的简单统一多模态模型。我们认为,在当前统一框架中,包含指令理解、接地和图像引用在内的多模态生成推理的关键能力,对于身份保留和忠实重建以及与高保真合成有着本质的联系。在这项工作中,我们引入了Query-Kontext,这是一种通过由来自多模态输入的语义线索和粗粒度图像条件组成的多模态``kontext’’来桥梁VLM和扩散模型的新型方法。这种设计将复杂的多模态生成推理能力委托给强大的VLM,同时保留扩散模型进行高质量视觉合成的作用。为了实现这一点,我们提出了一种分三阶段的渐进训练策略。首先,我们通过多模态kontext令牌将VLM连接到轻量级的扩散头,以释放VLM的生成推理能力。其次,我们将此头扩展到大型预训练扩散模型,以提高视觉细节和逼真度。最后,我们引入一个低级图像编码器,以提高图像保真度并对下游任务进行指令调整。此外,我们建立了一个综合数据管道,融合了真实、合成和开源数据集,涵盖了多样化的多模态参考到图像场景,包括图像生成、指令驱动编辑、定制生成和多主体组合。实验表明,我们的方法与强大的统一基线相匹配,甚至在某些情况下超过了任务特定的最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 10 figures
Summary
多媒体融合模型在文本转图像生成和编辑任务中展现出卓越性能。本研究提出Query-Kontext方法,通过语义线索和粗粒度图像条件的多模态上下文桥接视觉语言模型与扩散模型。采用三阶段渐进训练策略,释放VLM的生成推理能力,增强视觉细节和真实感,并引入低级别图像编码器提高图像保真度。建立综合数据管道,涵盖多种多媒体参考转图像场景。实验显示,该方法匹配强大统一基线,并在某些情况下超越特定任务的最先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- UMMs在文本转图像生成和编辑任务中表现优异,通过强大的VLM与扩散模型结合实现高性能。
- Query-Kontext方法通过多模态上下文桥接VLM和扩散模型,包含语义线索和图像条件的编码。
- 采用三阶段渐进训练策略,以释放VLM的生成推理能力,并增强视觉质量和图像保真度。
- 综合数据管道的建立涵盖了多种多媒体参考转图像场景,包括图像生成、指令驱动编辑、自定义生成和多主体组合。
- 实验结果表明,Query-Kontext方法性能强大,与现有先进方法相比具有竞争力。
- 该方法强调语义理解和生成模态的融合,为实现更真实的图像生成和编辑提供了新思路。
点此查看论文截图


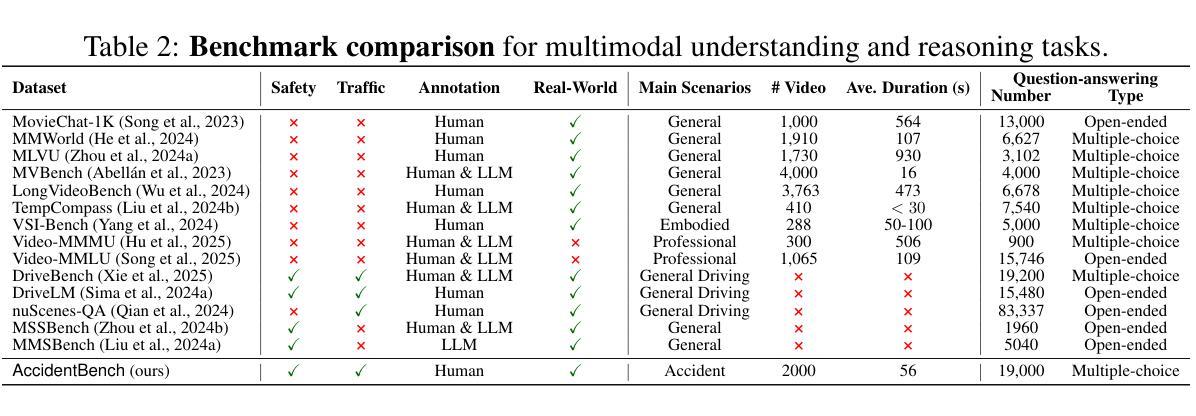
AccidentBench: Benchmarking Multimodal Understanding and Reasoning in Vehicle Accidents and Beyond
Authors:Shangding Gu, Xiaohan Wang, Donghao Ying, Haoyu Zhao, Runing Yang, Ming Jin, Boyi Li, Marco Pavone, Serena Yeung-Levy, Jun Wang, Dawn Song, Costas Spanos
Rapid advances in multimodal models demand benchmarks that rigorously evaluate understanding and reasoning in safety-critical, dynamic real-world settings. We present AccidentBench, a large-scale benchmark that combines vehicle accident scenarios with Beyond domains, safety-critical settings in air and water that emphasize spatial and temporal reasoning (e.g., navigation, orientation, multi-vehicle motion). The benchmark contains approximately 2000 videos and over 19000 human-annotated question–answer pairs spanning multiple video lengths (short/medium/long) and difficulty levels (easy/medium/hard). Tasks systematically probe core capabilities: temporal, spatial, and intent understanding and reasoning. By unifying accident-centric traffic scenes with broader safety-critical scenarios in air and water, AccidentBench offers a comprehensive, physically grounded testbed for evaluating models under real-world variability. Evaluations of state-of-the-art models (e.g., Gemini-2.5 Pro and GPT-5) show that even the strongest models achieve only about 18% accuracy on the hardest tasks and longest videos, revealing substantial gaps in real-world temporal, spatial, and intent reasoning. AccidentBench is designed to expose these critical gaps and drive the development of multimodal models that are safer, more robust, and better aligned with real-world safety-critical challenges. The code and dataset are available at: https://github.com/SafeRL-Lab/AccidentBench
随着多模态模型的快速发展,我们需要基准测试来严格评估其在安全关键、动态现实环境中的理解和推理能力。我们推出了AccidentBench,这是一个大规模基准测试,结合了车辆事故场景和Beyond域(强调空间和时间推理的航空和水上安全关键设置,如导航、定位、多车辆运动)。该基准测试包含大约2000个视频和超过19000个人工标注的问题答案对,涵盖多种视频长度(短/中/长)和难度级别(容易/中等/困难)。任务系统地检测核心能力:时间、空间和意图的理解和推理。通过以事故为中心的场景与更广泛的航空和水上安全关键场景的融合,AccidentBench为在现实世界的多变环境下评估模型提供了一个全面且物理基础的测试平台。对最新模型(如Gemini-2.5 Pro和GPT-5)的评估显示,即使在面对最困难的任务和最长视频时,最先进的模型也仅达到约18%的准确率,这揭示了在实际世界的时间、空间和意图推理方面仍存在巨大差距。AccidentBench旨在揭示这些关键差距,并推动开发更安全、更稳健、更好地适应现实安全挑战的多模态模型。代码和数据集可在:https://github.com/SafeRL-Lab/AccidentBench 获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
事故基准(AccidentBench)是一个大规模基准测试,结合了车辆事故场景与其他安全关键领域(如空中和水上),强调时空推理和意图理解。它包含大约2000个视频和超过1万9千个人类标注的问题答案对,旨在评估模型在现实世界的复杂多变环境中的理解和推理能力。该基准测试通过设计复杂的任务来评估模型的核心能力,如时间、空间和意图推理。尽管最强的模型在测试中的准确率只有约18%,但事故基准设计旨在揭示模型在现实世界的推理能力上的差距,并推动开发更安全、更稳健且更符合现实安全挑战的多模态模型。数据集和代码可在GitHub上获取。
Key Takeaways
- AccidentBench是一个评估多模态模型在现实世界环境中理解和推理能力的基准测试。
- 它结合了车辆事故场景以及其他安全关键领域(如空中和水上),强调时空推理和意图理解的重要性。
- 该基准包含大量视频和标注的问题答案对,涵盖不同视频长度和难度级别。
- 事故基准设计旨在评估模型的核心能力,如时间、空间和意图推理。
- 最先进的模型在事故基准上的准确率较低,揭示了模型在现实世界的推理能力上的差距。
- AccidentBench的目标是推动开发更安全、更稳健的多模态模型,更好地应对现实安全挑战。
点此查看论文截图


Attention as a Compass: Efficient Exploration for Process-Supervised RL in Reasoning Models
Authors:Runze Liu, Jiakang Wang, Yuling Shi, Zhihui Xie, Chenxin An, Kaiyan Zhang, Jian Zhao, Xiaodong Gu, Lei Lin, Wenping Hu, Xiu Li, Fuzheng Zhang, Guorui Zhou, Kun Gai
Reinforcement Learning (RL) has shown remarkable success in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). Process-Supervised RL (PSRL) has emerged as a more effective paradigm compared to outcome-based RL. However, existing PSRL approaches suffer from limited exploration efficiency, both in terms of branching positions and sampling. In this paper, we introduce a novel PSRL framework (AttnRL), which enables efficient exploration for reasoning models. Motivated by preliminary observations that steps exhibiting high attention scores correlate with reasoning behaviors, we propose to branch from positions with high values. Furthermore, we develop an adaptive sampling strategy that accounts for problem difficulty and historical batch size, ensuring that the whole training batch maintains non-zero advantage values. To further improve sampling efficiency, we design a one-step off-policy training pipeline for PSRL. Extensive experiments on multiple challenging mathematical reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms prior approaches in terms of performance and sampling and training efficiency.
强化学习(RL)在提升大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力方面取得了显著的成就。与基于结果的RL相比,过程监督RL(PSRL)作为一种更有效的范式而出现。然而,现有的PSRL方法存在探索效率低下的问题,无论是在分支位置还是在采样方面。在本文中,我们引入了一种新型的PSRL框架(AttnRL),为推理模型实现高效探索。受初步观察启发,表现高注意力得分的步骤与推理行为相关,我们建议在高位值的位置进行分支。此外,我们制定了一种自适应采样策略,该策略考虑了问题的难度和历史批次大小,确保整个训练批次保持非零优势值。为了进一步改善采样效率,我们为PSRL设计了一个一步离线训练管道。在多个具有挑战性的数学推理基准测试上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在性能和采样以及训练效率方面始终优于先前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
强化学习(RL)在提升大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力方面取得了显著的成功。相较于结果导向的RL,过程监督强化学习(PSRL)展现出更优越的模式。然而,现有的PSRL方法存在探索效率有限的问题,涉及分支位置和采样两个方面。本文引入了一种新型PSRL框架——AttnRL,为推理模型提供高效探索能力。根据初步观察,高注意力分数的步骤与推理行为相关,我们从高价值位置进行分支。此外,我们开发了一种适应性问题难度和历史批次大小的采样策略,确保整个训练批次保持非零优势值。为提高采样效率,我们还设计了一步离线策略训练管道。在多个具有挑战性的数学推理基准测试上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的方法性能和采样及训练效率方面均持续超越先前方法。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习在提升大型语言模型的推理能力上具有显著成功。
- 过程监督强化学习(PSRL)相比结果导向的RL展现出更优越的模式。
- 现有PSRL方法存在探索效率有限的问题,涉及分支位置和采样。
- 新型PSRL框架——AttnRL被引入,该框架从高价值位置进行分支,提高探索效率。
- AttnRL考虑了问题难度和历史批次大小来开发采样策略。
- AttnRL设计了一步离线策略训练管道,以提高采样效率。
点此查看论文截图
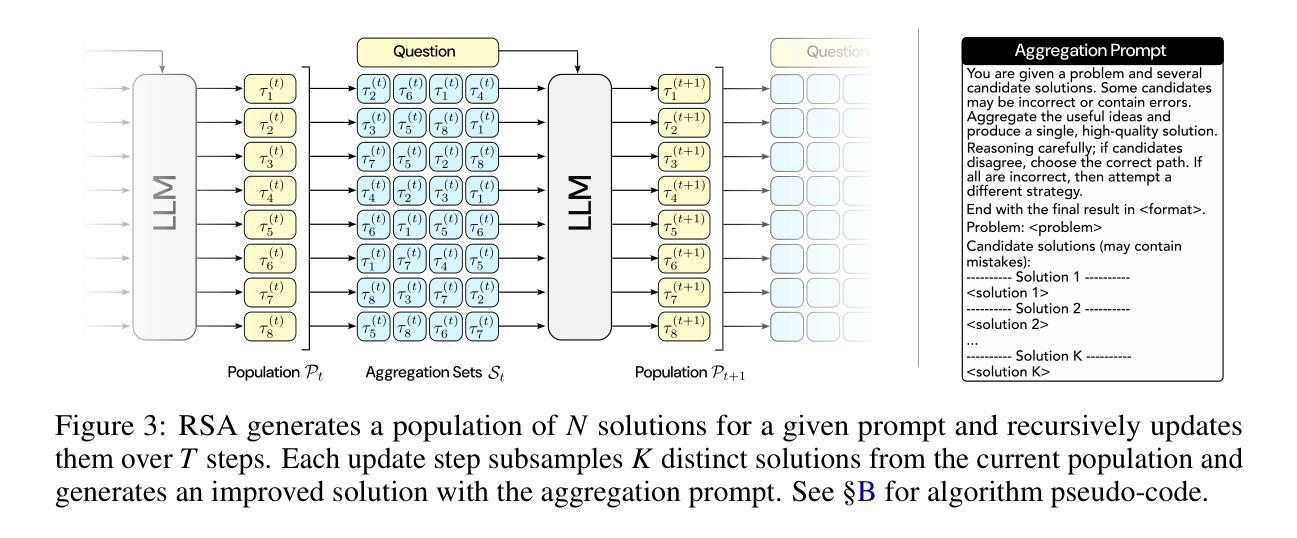
Recursive Self-Aggregation Unlocks Deep Thinking in Large Language Models
Authors:Siddarth Venkatraman, Vineet Jain, Sarthak Mittal, Vedant Shah, Johan Obando-Ceron, Yoshua Bengio, Brian R. Bartoldson, Bhavya Kailkhura, Guillaume Lajoie, Glen Berseth, Nikolay Malkin, Moksh Jain
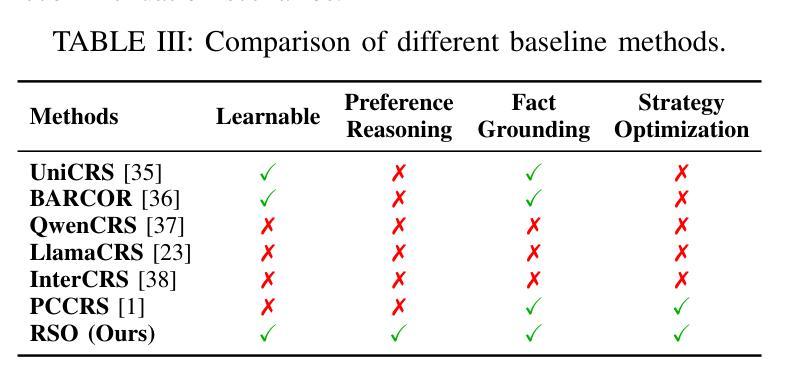
Test-time scaling methods improve the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by increasing the amount of compute used during inference to make a prediction. Inference-time compute can be scaled in parallel by choosing among multiple independent solutions or sequentially through self-refinement. We propose Recursive Self-Aggregation (RSA), a test-time scaling method inspired by evolutionary methods that combines the benefits of both parallel and sequential scaling. Each step of RSA refines a population of candidate reasoning chains through aggregation of subsets to yield a population of improved solutions, which are then used as the candidate pool for the next iteration. RSA exploits the rich information embedded in the reasoning chains – not just the final answers – and enables bootstrapping from partially correct intermediate steps within different chains of thought. Empirically, RSA delivers substantial performance gains with increasing compute budgets across diverse tasks, model families and sizes. Notably, RSA enables Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507 to achieve competitive performance with larger reasoning models, including DeepSeek-R1 and o3-mini (high), while outperforming purely parallel and sequential scaling strategies across AIME-25, HMMT-25, Reasoning Gym, LiveCodeBench-v6, and SuperGPQA. We further demonstrate that training the model to combine solutions via a novel aggregation-aware reinforcement learning approach yields significant performance gains. Code available at https://github.com/HyperPotatoNeo/RSA.
测试时缩放方法通过增加用于预测的推理过程中的计算量,提高了大型语言模型(LLM)的能力。推理时间的计算可以通过选择多个独立解决方案进行并行缩放,或通过自我完善进行顺序缩放。我们提出了递归自聚合(RSA)这一测试时缩放方法,它受到进化方法的启发,结合了并行和顺序缩放的优点。RSA的每一步都通过对候选推理链的子集进行聚合来优化一个候选群体,从而产生一组改进的解决方案,这些解决方案然后被用作下一轮的候选池。RSA利用推理链中嵌入的丰富信息——不仅仅是最终的答案——并利用从不同思考链中部分正确的中间步骤进行引导。经验表明,RSA在增加计算预算的情况下,在多种任务、模型家族和规模上实现了显著的性能提升。值得注意的是,RSA使Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507能够在大型推理模型(包括DeepSeek-R1和o3-mini(高级))中取得具有竞争力的表现,同时在AIME-25、HMMT-25、Reasoning Gym、LiveCodeBench-v6和SuperGPQA上超越了纯粹的并行和顺序缩放策略。我们进一步证明,通过一种新型聚合感知强化学习方法训练模型来组合解决方案,可以获得显著的性能提升。代码可访问:https://github.com/HyperPotatoNeo/RSA。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 9 figures
Summary
RSA(递归自聚合)是一种测试时缩放方法,它通过结合并行和顺序缩放的优势,提高大型语言模型(LLMs)的能力。该方法通过精炼候选推理链并利用推理链中的丰富信息来提高性能,使不同思维链中的部分正确中间步骤能够互相引导。实证结果表明,RSA在增加计算预算的情况下,在多种任务、模型家族和规模上实现了显著的性能提升。RSA使Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507能够在性能上与大得多的推理模型竞争,同时在一些特定任务上超越了纯并行和顺序缩放策略。通过引入一种新型聚合感知强化学习方法来训练模型组合解决方案,RSA取得了显著的性能提升。更多详情可通过访问公开代码链接获得。
Key Takeaways
- RSA是一种基于进化方法的测试时缩放策略,结合了并行和顺序缩放的优势。
- RSA通过精炼候选推理链并利用其中的丰富信息来提高性能。
- RSA允许部分正确的中间步骤在不同思维链中互相引导,实现自我改进。
- 在多种任务、模型家族和规模上,RSA显著提高了大型语言模型的性能。
- RSA使得较小规模的模型如Qwen3-4B-Instruct-2507能够在性能上与大得多的推理模型竞争。
- RSA在某些特定任务上的性能超过了纯并行和顺序缩放策略。
点此查看论文截图
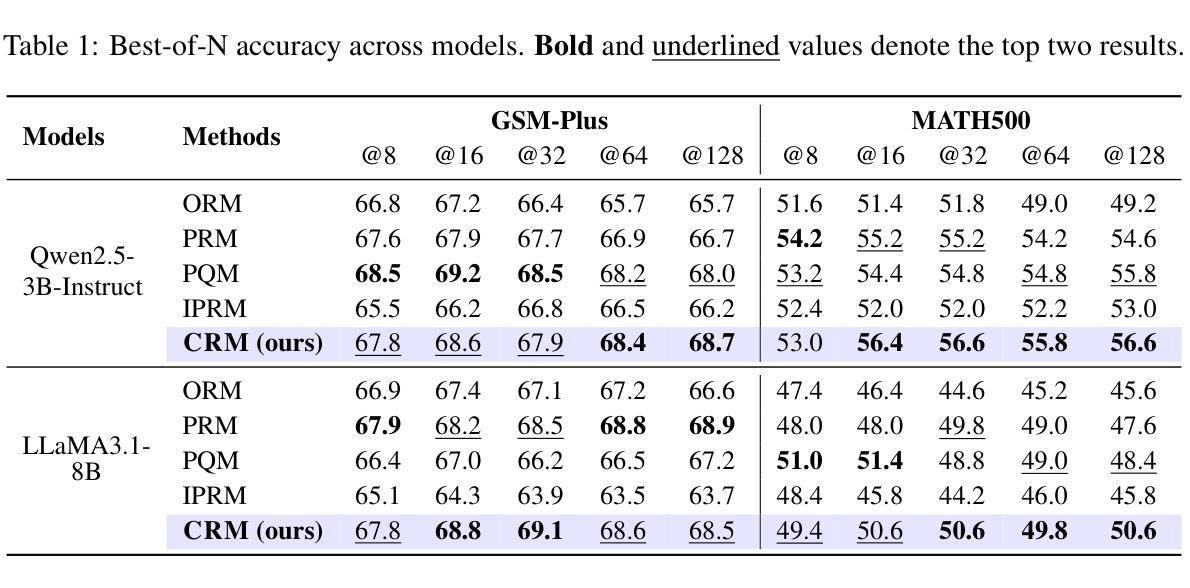
Linking Process to Outcome: Conditional Reward Modeling for LLM Reasoning
Authors:Zheng Zhang, Ziwei Shan, Kaitao Song, Yexin Li, Kan Ren
Process Reward Models (PRMs) have emerged as a promising approach to enhance the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by guiding their step-by-step reasoning toward a final answer. However, existing PRMs either treat each reasoning step in isolation, failing to capture inter-step dependencies, or struggle to align process rewards with the final outcome. Consequently, the reward signal fails to respect temporal causality in sequential reasoning and faces ambiguous credit assignment. These limitations make downstream models vulnerable to reward hacking and lead to suboptimal performance. In this work, we propose Conditional Reward Modeling (CRM) that frames LLM reasoning as a temporal process leading to a correct answer. The reward of each reasoning step is not only conditioned on the preceding steps but also explicitly linked to the final outcome of the reasoning trajectory. By enforcing conditional probability rules, our design captures the causal relationships among reasoning steps, with the link to the outcome allowing precise attribution of each intermediate step, thereby resolving credit assignment ambiguity. Further, through this consistent probabilistic modeling, the rewards produced by CRM enable more reliable cross-sample comparison. Experiments across Best-of-N sampling, beam search and reinforcement learning demonstrate that CRM consistently outperforms existing reward models, offering a principled framework for enhancing LLM reasoning. In particular, CRM is more robust to reward hacking and delivers stable downstream improvements without relying on verifiable rewards derived from ground truth.
过程奖励模型(PRMs)作为一种有前景的方法,通过指导大型语言模型(LLMs)的逐步推理以获取最终答案,增强了其推理能力。然而,现有的PRM要么孤立地处理每个推理步骤,无法捕捉步骤间的依赖关系,要么在将过程奖励与最终结果对齐方面遇到困难。因此,奖励信号不尊重序列推理中的时间因果关系,并面临模糊的信用分配问题。这些局限性使得下游模型容易受到奖励破解的影响,导致性能不佳。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于过程奖励模型(PRM)在增强大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力方面展现出巨大潜力,但现有PRM在处理推理步骤间的依赖关系和对最终结果的奖励对齐方面存在局限。本研究提出条件奖励建模(CRM),将LLM推理视为导向正确答案的暂时过程。CRM的奖励不仅取决于先前的步骤,还明确与推理轨迹的最终结果相关联,从而捕捉推理步骤之间的因果关系,解决信用分配模糊问题。实验表明,CRM在多种采样方法和强化学习下均表现优异,更稳健且能稳定提升下游任务性能。
Key Takeaways
- 过程奖励模型(PRM)有助于增强大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力。
- 现有PRM在处理推理步骤间的依赖关系和对最终结果的奖励对齐方面存在局限。
- 条件奖励建模(CRM)将LLM推理视为导向正确答案的暂时过程。
- CRM通过条件概率规则捕捉推理步骤间的因果关系,并解决信用分配模糊问题。
- CRM通过一致的概率建模,使奖励更可靠地进行跨样本比较。
- 实验表明,CRM在多种采样方法和强化学习下表现优异,且更稳健。
点此查看论文截图
Probing the Critical Point (CritPt) of AI Reasoning: a Frontier Physics Research Benchmark
Authors:Minhui Zhu, Minyang Tian, Xiaocheng Yang, Tianci Zhou, Penghao Zhu, Eli Chertkov, Shengyan Liu, Yufeng Du, Lifan Yuan, Ziming Ji, Indranil Das, Junyi Cao, Yufeng Du, Jinchen He, Yifan Su, Jiabin Yu, Yikun Jiang, Yujie Zhang, Chang Liu, Ze-Min Huang, Weizhen Jia, Xinan Chen, Peixue Wu, Yunkai Wang, Juntai Zhou, Yong Zhao, Farshid Jafarpour, Jessie Shelton, Aaron Young, John Bartolotta, Wenchao Xu, Yue Sun, Anjun Chu, Victor Colussi, Chris Akers, Nathan Brooks, Wenbo Fu, Christopher Wilson, Jinchao Zhao, Marvin Qi, Anqi Mu, Yubo Yang, Allen Zang, Yang Lyu, Peizhi Mai, Xuefei Guo, Luyu Gao, Ze Yang, Chi Xue, Dmytro Bandak, Yaïr Hein, Yonatan Kahn, Kevin Zhou, John Drew Wilson Jarrod T. Reilly, Di Luo, Daniel Inafuku, Hao Tong, Liang Yang, Ruixing Zhang, Xueying Wang, Ofir Press, Nicolas Chia, Eliu Huerta, Hao Peng
While large language models (LLMs) with reasoning capabilities are progressing rapidly on high-school math competitions and coding, can they reason effectively through complex, open-ended challenges found in frontier physics research? And crucially, what kinds of reasoning tasks do physicists want LLMs to assist with? To address these questions, we present the CritPt (Complex Research using Integrated Thinking - Physics Test, pronounced “critical point”), the first benchmark designed to test LLMs on unpublished, research-level reasoning tasks that broadly covers modern physics research areas, including condensed matter, quantum physics, atomic, molecular & optical physics, astrophysics, high energy physics, mathematical physics, statistical physics, nuclear physics, nonlinear dynamics, fluid dynamics and biophysics. CritPt consists of 71 composite research challenges designed to simulate full-scale research projects at the entry level, which are also decomposed to 190 simpler checkpoint tasks for more fine-grained insights. All problems are newly created by 50+ active physics researchers based on their own research. Every problem is hand-curated to admit a guess-resistant and machine-verifiable answer and is evaluated by an automated grading pipeline heavily customized for advanced physics-specific output formats. We find that while current state-of-the-art LLMs show early promise on isolated checkpoints, they remain far from being able to reliably solve full research-scale challenges: the best average accuracy among base models is only 4.0% , achieved by GPT-5 (high), moderately rising to around 10% when equipped with coding tools. Through the realistic yet standardized evaluation offered by CritPt, we highlight a large disconnect between current model capabilities and realistic physics research demands, offering a foundation to guide the development of scientifically grounded AI tools.
随着拥有推理能力的大型语言模型(LLMs)在高中数学竞赛和编程方面取得快速发展,它们能否有效应对前沿物理研究中遇到的复杂、开放性的挑战?关键的是,物理学家希望LLMs辅助完成哪些推理任务?为了解答这些问题,我们推出了CritPt(利用综合思维进行复杂研究——物理测试,简称“临界点”),这是第一个针对未发表的、研究级别的推理任务设计的基准测试,广泛覆盖了现代物理研究领域,包括凝聚态物理、量子力学、原子、分子与光学物理、天体物理、高能物理、数学物理、统计物理、核物理、非线性动力学、流体力学和生物物理学。CritPt由71个复合研究挑战构成,旨在模拟入门级别的全尺寸研究项目,同时分解为190个更简单的检查点任务,以获取更精细的见解。所有问题均由50多名活跃的物理研究者根据他们自己的研究全新创作。每个问题都经过手工筛选,以得出不易猜测且可机器验证的答案,并由针对高级物理特定输出格式进行大量定制的自动评分管道进行评估。我们发现,虽然当前最先进的LLMs在单独的检查点上显示出初步的希望,但它们仍然远远不能可靠地解决全尺寸的研究挑战:基础模型中的最佳平均准确率仅为GPT-5(高级版)达到的4.0%,配备编码工具时准确率适度上升至约10%。通过CritPt提供的现实且标准化的评估,我们突出了当前模型能力与现实物理研究需求之间的巨大差距,为开发科学基础的AI工具提供了指导基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 39 pages, 6 figures, 6 tables
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在解决高中数学竞赛和编程方面的能力已经得到迅速提升,但它们在处理复杂、开放性的物理研究挑战方面能否进行有效推理仍存在疑问。为此,研究者推出了CritPt基准测试,该测试包含71个模拟完整研究项目的复合挑战,旨在测试LLMs在未公开的、研究级别的推理任务中的表现。尽管当前最先进的LLMs在孤立的检查点上有早期表现,但在解决全面的研究规模挑战方面仍有很大差距。因此,当前模型的能力与真实的物理研究需求之间存在巨大差距。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs已显示出在高中数学竞赛和编程方面的快速进步。
- CritPt是首个针对LLMs的测试基准,旨在测试其在未发表的研究级别物理推理任务中的能力。
- CritPt包含模拟完整研究项目的复合挑战和更精细的检查点任务。
- 当前最先进的LLMs在解决全面的物理研究挑战方面仍有限,平均准确率仅为4%。
- CritPt提供了一个评估和引导AI工具科学发展的基础。
点此查看论文截图

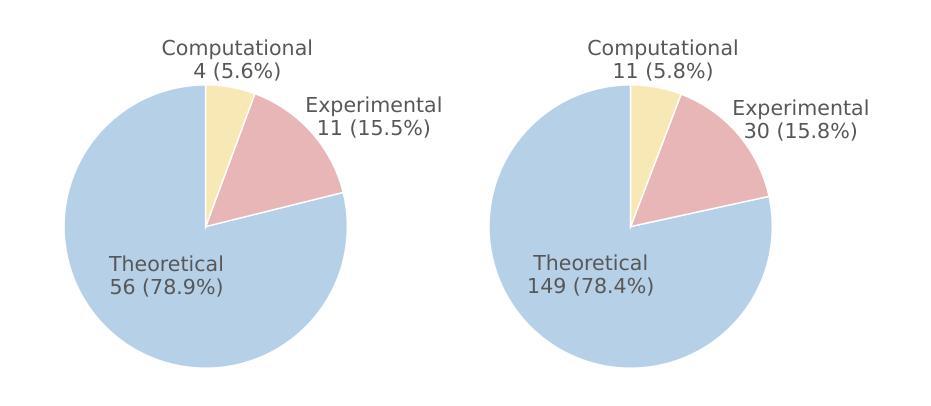
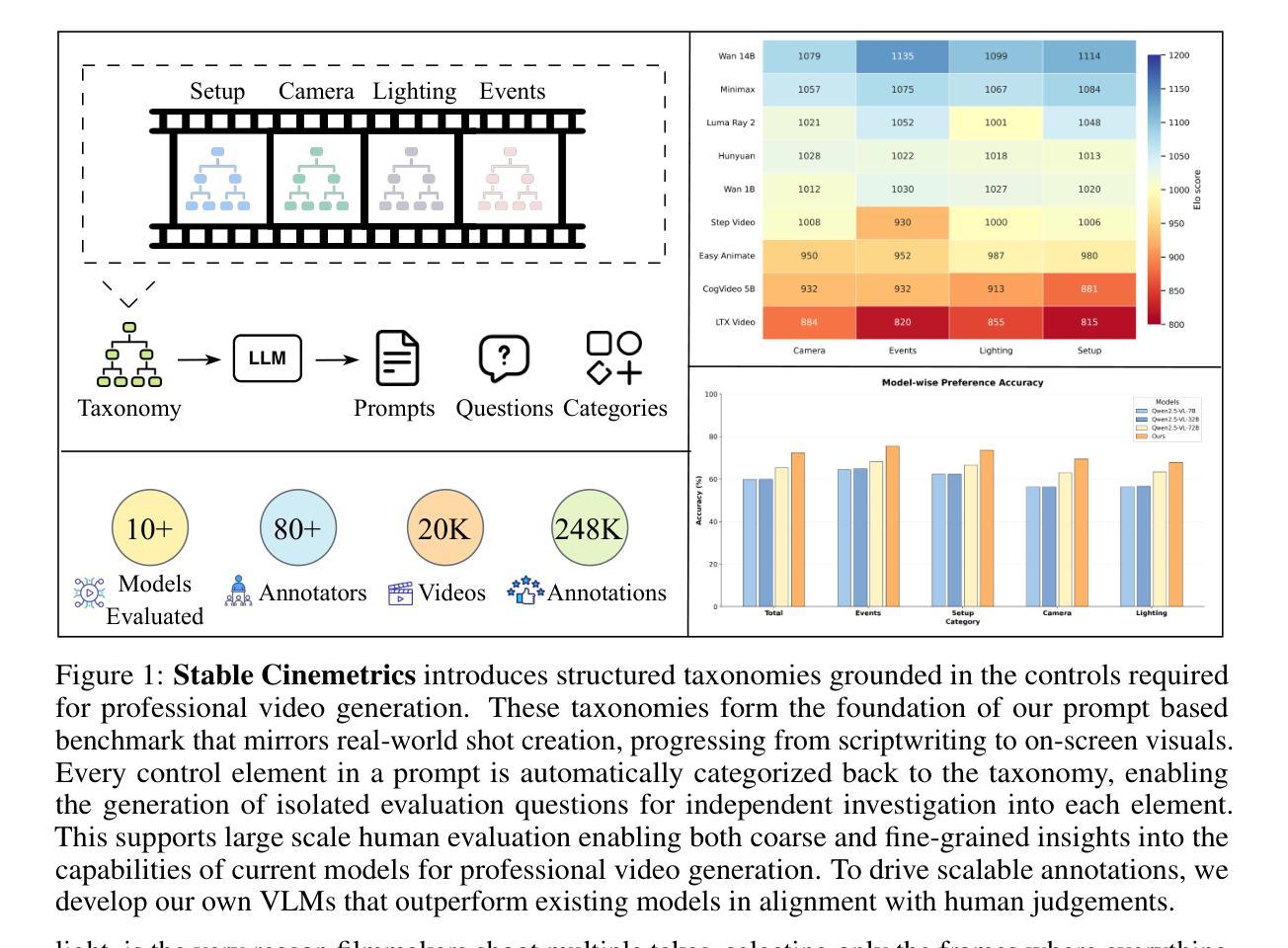
Stable Cinemetrics : Structured Taxonomy and Evaluation for Professional Video Generation
Authors:Agneet Chatterjee, Rahim Entezari, Maksym Zhuravinskyi, Maksim Lapin, Reshinth Adithyan, Amit Raj, Chitta Baral, Yezhou Yang, Varun Jampani
Recent advances in video generation have enabled high-fidelity video synthesis from user provided prompts. However, existing models and benchmarks fail to capture the complexity and requirements of professional video generation. Towards that goal, we introduce Stable Cinemetrics, a structured evaluation framework that formalizes filmmaking controls into four disentangled, hierarchical taxonomies: Setup, Event, Lighting, and Camera. Together, these taxonomies define 76 fine-grained control nodes grounded in industry practices. Using these taxonomies, we construct a benchmark of prompts aligned with professional use cases and develop an automated pipeline for prompt categorization and question generation, enabling independent evaluation of each control dimension. We conduct a large-scale human study spanning 10+ models and 20K videos, annotated by a pool of 80+ film professionals. Our analysis, both coarse and fine-grained reveal that even the strongest current models exhibit significant gaps, particularly in Events and Camera-related controls. To enable scalable evaluation, we train an automatic evaluator, a vision-language model aligned with expert annotations that outperforms existing zero-shot baselines. SCINE is the first approach to situate professional video generation within the landscape of video generative models, introducing taxonomies centered around cinematic controls and supporting them with structured evaluation pipelines and detailed analyses to guide future research.
近年来,视频生成技术的进展使用户可以根据提示进行高保真视频合成。然而,现有模型和基准测试无法捕捉专业视频生成的复杂性和要求。为此,我们引入了稳定电影指标(Stable Cinemetrics),这是一个结构化的评估框架,它将电影制作的控制正规化为四个分离、分层的分类法:设置、事件、照明和摄像机。这些分类法共同定义了76个基于行业实践的精细控制节点。使用这些分类法,我们构建了与专业用例对齐的提示基准测试,并开发了用于提示分类和问题生成的自动化管道,能够对每个控制维度进行独立评估。我们进行了一项大规模的人类研究,涉及10多个模型和2万多个视频,由80多名电影专业人士进行标注。我们的分析,无论是粗略的还是精细的,都表明即使是最强大的当前模型也表现出明显的差距,特别是在事件和与摄像机相关的控制方面。为了进行可评估的评估,我们训练了一个自动评估器,这是一个与专家注释对齐的视听语言模型,它超越了现有的零样本基线。SCINE是首次在专业视频生成领域定位视频生成模型的方法,引入以电影控制为中心的分类法,并通过结构化评估管道和详细分析来支持它们,以指导未来的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2025. Project Page : https://stable-cinemetrics.github.io/
Summary
本文主要介绍了Stable Cinemetrics这一结构化评估框架的推出,该框架正式将电影制作控制分解成四个独立、分层的分类:设置、事件、照明和摄像机。通过这四大分类,定义了基于行业实践的76个精细控制节点。同时构建了对齐专业用例的基准提示,并开发了一个自动化的提示分类和问题生成管道,能够独立评估每个控制维度。进行了一项涵盖超过八万名专业影视人员的超过十万个视频的大规模人类研究。分析表明,即使在事件和摄像机相关控制方面,最先进的模型也存在明显差距。为了进行可评估的评估,训练了一种与专家注释对齐的视觉语言模型,并超过了现有的零样本基线。总体而言,该文率先将专业视频生成定位在视频生成模型的大背景下,推出了围绕电影控制的分类支持它们并具有结构化的评估流程和详细分析以指导未来研究。
Key Takeaways
- Stable Cinemetrics框架为专业视频生成提供了一个结构化评估方法,涵盖设置、事件、照明和摄像机四大层次分类。
- 定义了一个包含76个控制节点的基准提示集,反映了行业实践。
- 构建了一个自动化管道来独立评估每个控制维度并进行提示分类和问题生成。
- 进行的大规模人类研究表明现有模型在专业视频生成领域存在明显差距,特别是在事件和摄像机相关控制方面。
- 训练了一种视觉语言模型作为自动评估器,与专家注释对齐并超越了现有的零样本基线。
- SCINE是首个将专业视频生成定位在视频生成模型背景下的方法,推出了一系列基于电影控制的分类。
点此查看论文截图
Towards Verified Code Reasoning by LLMs
Authors:Meghana Sistla, Gogul Balakrishnan, Pat Rondon, José Cambronero, Michele Tufano, Satish Chandra
While LLM-based agents are able to tackle a wide variety of code reasoning questions, the answers are not always correct. This prevents the agent from being useful in situations where high precision is desired: (1) helping a software engineer understand a new code base, (2) helping a software engineer during code review sessions, and (3) ensuring that the code generated by an automated code generation system meets certain requirements (e.g. fixes a bug, improves readability, implements a feature). As a result of this lack of trustworthiness, the agent’s answers need to be manually verified before they can be trusted. Manually confirming responses from a code reasoning agent requires human effort and can result in slower developer productivity, which weakens the assistance benefits of the agent. In this paper, we describe a method to automatically validate the answers provided by a code reasoning agent by verifying its reasoning steps. At a very high level, the method consists of extracting a formal representation of the agent’s response and, subsequently, using formal verification and program analysis tools to verify the agent’s reasoning steps. We applied this approach to a benchmark set of 20 uninitialized variable errors detected by sanitizers and 20 program equivalence queries. For the uninitialized variable errors, the formal verification step was able to validate the agent’s reasoning on 13/20 examples, and for the program equivalence queries, the formal verification step successfully caught 6/8 incorrect judgments made by the agent.
基于大模型的智能代理虽然能够应对各种代码推理问题,但答案并不总是正确。这导致在需要高精度的场景中,智能代理无法发挥应有的作用,例如在(1)帮助软件工程师理解新的代码库、(2)在代码审查期间帮助软件工程师以及在(3)确保由自动化代码生成系统生成的代码满足某些要求(例如修复错误、提高可读性、实现功能)。由于这种缺乏可信度的问题,需要在信任智能代理的答案之前手动验证它们。手动确认来自代码推理代理的响应需要人力,并可能导致开发人员生产率降低,从而削弱了代理的辅助效益。在本文中,我们描述了一种通过验证其推理步骤来自动验证代码推理代理提供的答案的方法。在很高的层次上,该方法由提取代理响应的正式表示形式开始,随后使用形式化验证和程序分析工具来验证代理的推理步骤。我们将此方法应用于一组基准测试集,包括由检查器检测到的20个未初始化变量错误和20个程序等价查询。对于未初始化变量错误,形式化验证步骤能够验证代理对其中13个案例的推理;而对于程序等价查询,形式化验证步骤成功捕捉到了代理作出的8个案例中不正确的判断中的6个。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 43 pages
Summary:
基于大型语言模型的代理能够处理多种代码推理问题,但答案并不总是正确。这限制了代理在需要高精确度场景的应用,如帮助软件工程师理解新代码基础、参与代码审查会话以及确保自动化代码生成系统生成的代码符合要求。因此,需要对代理的答案进行手动验证,这会消耗人力并可能导致开发效率降低,削弱代理的协助效益。本文描述了一种通过验证其推理步骤来自动验证代码推理代理答案的方法。该方法包括提取代理响应的形式表示,然后使用形式化验证和程序分析工具来验证代理的推理步骤。我们将其应用于一组未初始化变量错误的基准测试集和一组程序等价查询。对于未初始化变量错误,形式化验证步骤能够在13/20的示例中验证代理的推理;对于程序等价查询,形式化验证步骤成功捕获了代理做出的6/8个错误判断。
Key Takeaways:
- LLM-based agents can handle various code reasoning questions but answers may not always be accurate.
- Inaccuracy in agent answers requires manual verification, leading to reduced developer productivity.
- This paper proposes a method to automatically validate the answers of a code reasoning agent by verifying its reasoning steps.
- Formal verification and program analysis tools are used in this method.
- The method was tested on a benchmark set of uninitialized variable errors and program equivalence queries.
- For uninitialized variable errors, the method successfully validated the agent’s reasoning for 13/20 examples.
点此查看论文截图


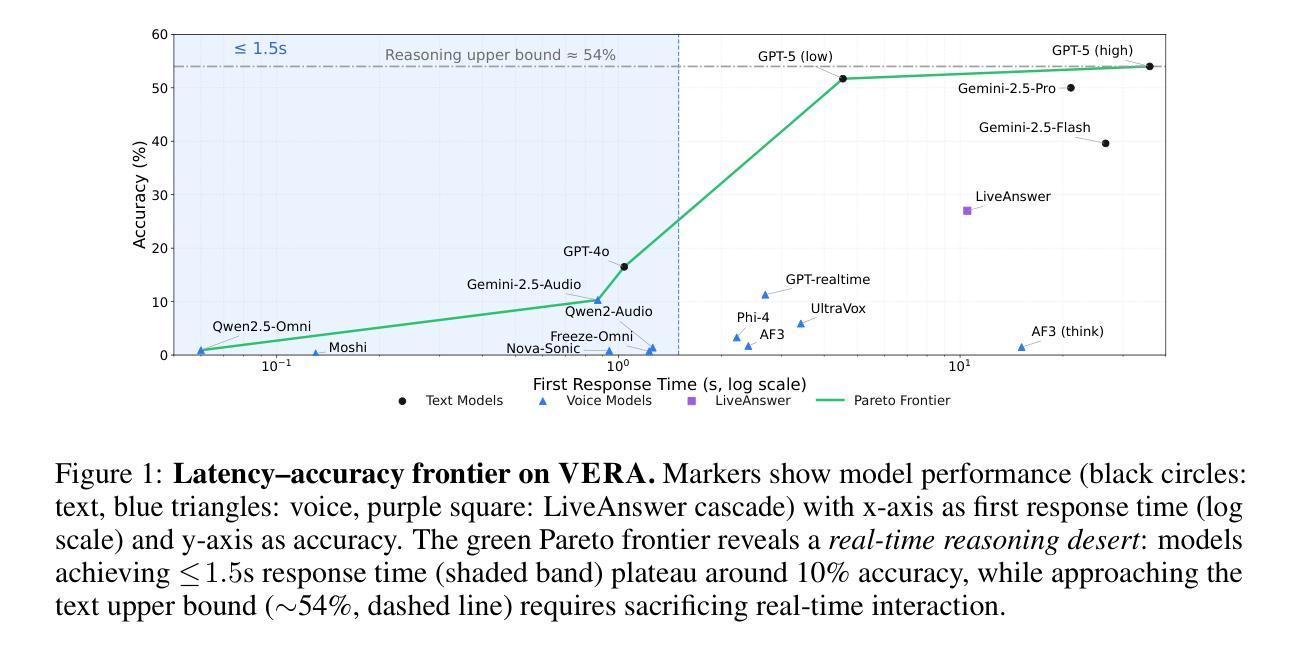
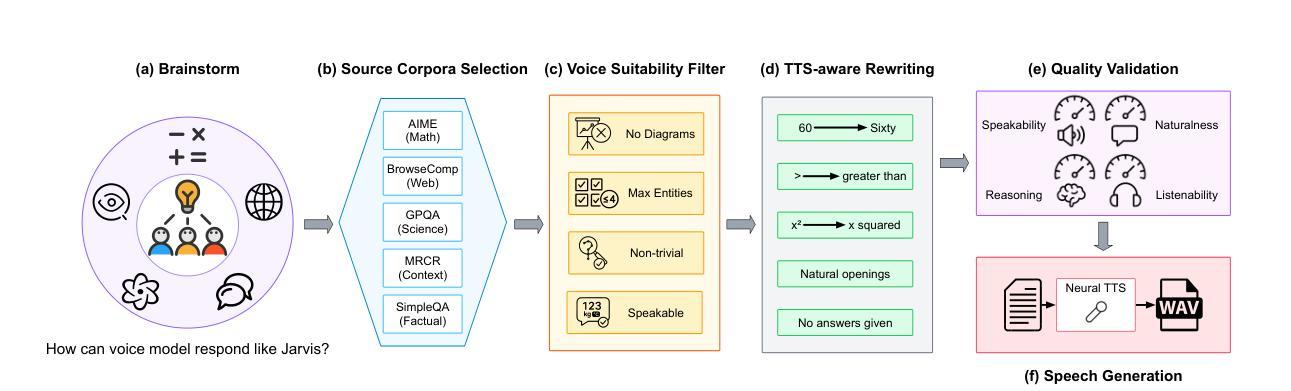
Voice Evaluation of Reasoning Ability: Diagnosing the Modality-Induced Performance Gap
Authors:Yueqian Lin, Zhengmian Hu, Qinsi Wang, Yudong Liu, Hengfan Zhang, Jayakumar Subramanian, Nikos Vlassis, Hai Helen Li, Yiran Chen
We present Voice Evaluation of Reasoning Ability (VERA), a benchmark for evaluating reasoning ability in voice-interactive systems under real-time conversational constraints. VERA comprises 2,931 voice-native episodes derived from established text benchmarks and organized into five tracks (Math, Web, Science, Long-Context, Factual). Each item is adapted for speech interaction while preserving reasoning difficulty. VERA enables direct text-voice comparison within model families and supports analysis of how architectural choices affect reliability. We assess 12 contemporary voice systems alongside strong text baselines and observe large, consistent modality gaps: on competition mathematics a leading text model attains 74.8% accuracy while its voice counterpart reaches 6.1%; macro-averaged across tracks the best text models achieve 54.0% versus 11.3% for voice. Latency-accuracy analyses reveal a low-latency plateau, where fast voice systems cluster around ~10% accuracy, while approaching text performance requires sacrificing real-time interaction. Diagnostic experiments indicate that common mitigations are insufficient. Increasing “thinking time” yields negligible gains; a decoupled cascade that separates reasoning from narration improves accuracy but still falls well short of text and introduces characteristic grounding/consistency errors. Failure analyses further show distinct error signatures across native streaming, end-to-end, and cascade designs. VERA provides a reproducible testbed and targeted diagnostics for architectures that decouple thinking from speaking, offering a principled way to measure progress toward real-time voice assistants that are both fluent and reliably reasoned.
我们推出了语音推理能力评估(VERA),这是一个基准测试,用于评估实时对话约束下语音交互系统中的推理能力。VERA包含2931个本地语音片段,这些片段取自既定的文本基准测试,并分为五个赛道(数学、网络、科学、长文本、事实)。每个项目都适应语音交互,同时保持推理难度。VERA能够在模型家族内进行直接文本语音比较,并支持分析架构选择如何影响可靠性。我们评估了12个当代语音系统以及强大的文本基准测试,并观察到了一致且显著的模态差距:在数学竞赛中,领先的文本模型达到74.8%的准确率,而其语音对应模型的准确率仅为6.1%;跨赛道宏观平均,最佳文本模型达到54.0%,而语音模型仅为11.3%。延迟-准确性分析显示了一个低延迟平台,在此平台上快速语音系统的准确率约为10%,而要达到文本性能则需要牺牲实时交互。诊断实验表明,常见的缓解措施并不足够。增加“思考时间”只会带来微不足道的收益;一个分离的级联系统,将推理与叙述分开,可以提高准确性,但仍远远落后于文本,并引入典型的接地/一致性错误。失败分析进一步显示了原生流媒体、端到端和级联设计之间的不同错误特征。VERA为从思考到说话解耦的架构提供了一个可重复的测试平台和有针对性的诊断工具,为向既流畅又可靠推理的实时语音助手发展提供了有原则的衡量方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code and data available at https://github.com/linyueqian/VERA
Summary
在实时对话的限制下,本文提出了一种名为VERA的语音推理能力评估基准测试。它包含了五大领域、共两千九百三十一集的语音原始片段,可以用于评估语音交互系统中的推理能力。文章分析了12种现代语音系统及其与顶尖文本模型的差距,发现语音模型的推理能力普遍较差。同时,文章还探讨了不同架构选择对可靠性的影响,并提供了针对架构优化的建议和诊断方法。总体而言,VERA提供了一个可重复使用的测试平台,为开发既流畅又具备实时推理能力的语音助手提供了方向。
Key Takeaways
- VERA是一个用于评估语音交互系统中推理能力的基准测试。
- VERA包含五大领域、共两千九百三十一集的语音原始片段。
- 语音系统的推理能力普遍较差,与顶尖文本模型存在显著差距。
- 不同架构选择会影响语音系统的可靠性。
- 增加“思考时间”对提升语音系统性能作用甚微。
- 分离推理和叙述的架构能提高准确性,但仍未能达到文本性能水平。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient and Transferable Agentic Knowledge Graph RAG via Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Jinyeop Song, Song Wang, Julian Shun, Yada Zhu
Knowledge-graph retrieval-augmented generation (KG-RAG) couples large language models (LLMs) with structured, verifiable knowledge graphs (KGs) to reduce hallucinations and expose reasoning traces. However, many KG-RAG systems compose multiple LLM modules (e.g planning, reasoning, and responding), inflating inference cost and binding behavior to a specific target KG. To address this, we introduce KG-R1, an agentic KG retrieval-augmented generation (KG-RAG) framework through reinforcement learning (RL). KG-R1 utilizes a single agent that interacts with KGs as its environment, learning to retrieve at each step and incorporating the retrieved information into its reasoning and generation. The process is optimized through end-to-end RL. In controlled experiments across Knowledge-Graph Question Answering (KGQA) benchmarks, our method demonstrates both efficiency and transferability: Using Qwen-2.5-3B, KG-R1 improves answer accuracy with fewer generation tokens than prior multi-module workflow methods that use larger foundation or fine-tuned models. Furthermore, KG-R1 enables plug and play: after training, it maintains strong accuracy on new KGs without modification. These properties make KG-R1 a promising KG-RAG framework for real-world deployment. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/Jinyeop3110/KG-R1.
知识图谱检索增强生成(KG-RAG)技术将大型语言模型(LLM)与结构化的、可验证的知识图谱(KGs)相结合,以减少幻觉并暴露推理痕迹。然而,许多KG-RAG系统组合了多个LLM模块(例如规划、推理和响应),增加了推理成本并与特定的目标知识图谱绑定行为。为解决这一问题,我们引入了通过强化学习(RL)的代理知识图谱检索增强生成(KG-R1)框架。KG-R1利用单个代理与知识图谱作为环境进行交互,学习在每一步进行检索,并将检索到的信息融入其推理和生成中。该过程通过端到端的RL进行优化。在知识图谱问答(KGQA)基准测试上的受控实验表明,我们的方法既有效率也有可转移性:使用Qwen-2.5-3B,KG-R1在提高答案准确性的同时,生成标记的数量少于之前使用更大基础模型或微调模型的多模块工作流程方法。此外,KG-R1即插即用:训练后,它在新的知识图谱上无需修改就能保持高度的准确性。这些特性使KG-R1成为现实世界部署中颇有前途的KG-RAG框架。我们的代码可公开访问 https://github.com/Jinyeop3110/KG-R1。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 5 figures. Submitted to ICLR 2026
Summary
基于知识图谱的检索增强生成(KG-RAG)技术结合了大型语言模型(LLM)和可验证的知识图谱(KG),旨在减少虚构内容并展示推理轨迹。针对现有KG-RAG系统存在多模块、推理成本高以及与特定知识图谱绑定的问题,我们提出了通过强化学习(RL)的KG-R1代理框架。KG-R1利用单个代理与知识图谱环境进行交互,学习在每一步进行检索,并将其纳入推理和生成过程中。该过程通过端到端的RL进行优化。在知识图谱问答(KGQA)基准测试上的实验表明,KG-R1既高效又具可迁移性,使用Qwen-2.5-3B模型提高了答案准确性,且生成令牌少于使用更大基础或微调模型的多模块工作流程方法。此外,KG-R1实现了即插即用:训练后,它在新的知识图谱上无需修改就能保持高度的准确性。这些特性使KG-R1成为现实世界部署的有前途的KG-RAG框架。
Key Takeaways
- KG-RAG结合了大型语言模型和知识图谱,旨在提高准确性并展示推理轨迹。
- 现有KG-RAG系统存在多模块、高推理成本和特定知识图谱绑定的问题。
- KG-R1是一个通过强化学习优化的代理框架,用于知识图谱检索增强生成。
- KG-R1利用单个代理与知识图谱交互,在每一步进行检索并纳入推理和生成过程。
- KG-R1在知识图谱问答基准测试上表现出高效性和可迁移性。
- KG-R1提高了答案准确性,并生成较少的令牌。
点此查看论文截图

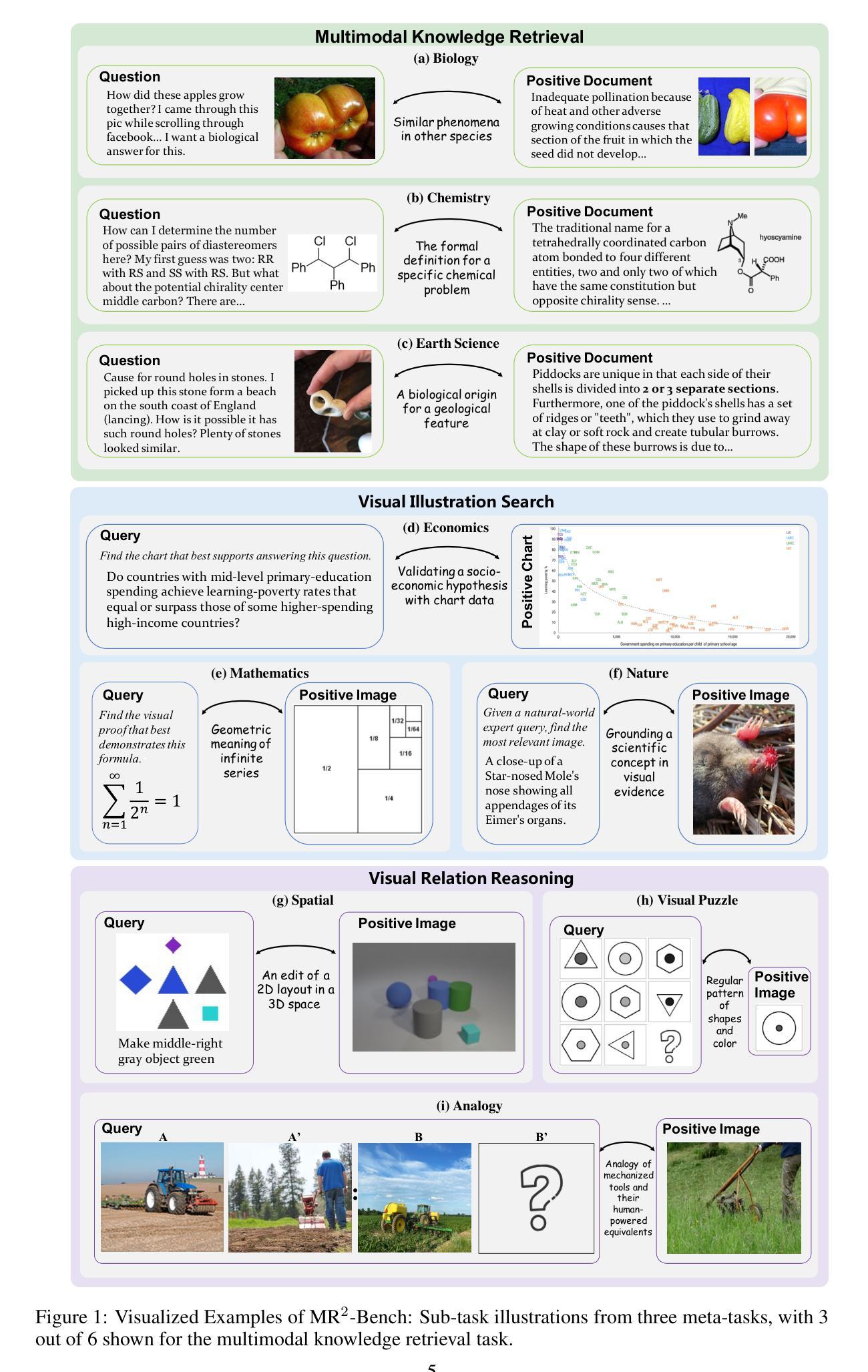
MR$^2$-Bench: Going Beyond Matching to Reasoning in Multimodal Retrieval
Authors:Junjie Zhou, Ze Liu, Lei Xiong, Jin-Ge Yao, Yueze Wang, Shitao Xiao, Fenfen Lin, Miguel Hu Chen, Zhicheng Dou, Siqi Bao, Defu Lian, Yongping Xiong, Zheng Liu
Multimodal retrieval is becoming a crucial component of modern AI applications, yet its evaluation lags behind the demands of more realistic and challenging scenarios. Existing benchmarks primarily probe surface-level semantic correspondence (e.g., object-text matching) while failing to assess the deeper reasoning required to capture complex relationships between visual and textual information. To address this gap, we introduce MR$^2$-Bench, a reasoning-intensive benchmark for multimodal retrieval. MR$^2$-Bench presents the following critical values: 1) all tasks are reasoning-driven, going beyond shallow matching to effectively assess models’ capacity for logical, spatial, and causal inference; 2) it features diverse multimodal data, such as natural images, diagrams, and visual puzzles, enabling comprehensive evaluation across content types; 3) it supports complex queries and documents containing multiple images and covers diverse retrieval scenarios, more accurately reflecting real-world applications. Our benchmark contains 1,309 curated queries, derived either from manual collection and annotation or from selective consolidation of public datasets. Despite achieving strong results on existing benchmarks, current state-of-the-art models still struggle on MR$^2$-Bench: for example, the leading Seed1.6-Embedding model attains a Recall@1 of 77.78 on MMEB, but only 9.91 on MR$^2$-Bench. This substantial performance gap highlights both the increased challenge posed by our benchmark and the pressing need for further advances in reasoning-intensive multimodal retrieval. The dataset and evaluation code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/VectorSpaceLab/MR2-Bench.
多模态检索已成为现代人工智能应用的重要组成部分,但其评估却落后于更现实和有挑战性的场景的需求。现有基准测试主要探索表面级的语义对应关系(例如,对象文本匹配),而无法评估捕获视觉和文本信息之间复杂关系所需的更深层次推理。为了解决这一差距,我们引入了MR$^2$-Bench,这是一个用于多模态检索的推理密集型基准测试。MR$^2$-Bench具有以下关键价值:1)所有任务均基于推理驱动,超越浅层匹配,有效评估模型在逻辑、空间和因果推理方面的能力;2)它拥有多样化的多模态数据,如自然图像、图表和视觉谜题,能够全面评估各种内容类型的检索;3)它支持复杂的查询和包含多个图像的文档,并覆盖各种检索场景,更能准确反映实际应用。我们的基准测试包含1309个精选查询,这些查询来自手动收集和注释,或是从公共数据集的精选整合。尽管在现有基准测试上取得了强劲的结果,但当前最先进的模型在MR$^2$-Bench上仍面临挑战:例如,领先的Seed1.6-Embedding模型在MMEB上的Recall@1为77.78,但在MR$^2$-Bench上仅为9.91。这一显著的性能差距突显了我们的基准测试所带来的增加挑战,以及推理密集型多模态检索的迫切需求。数据集和评估代码将在https://github.com/VectorSpaceLab/MR2-Bench上公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:多媒体检索在现代AI应用中成为至关重要的部分,然而其评估方式却落后于实际需求。现有的基准测试主要测试表面级别的语义对应关系,如物体与文本匹配等,而无法评估深度推理捕捉视觉和文本信息之间复杂关系的能力。为了解决这个问题,引入了MR$^2$-Bench,一个用于多媒体检索的推理密集型基准测试。它超越浅层次的匹配任务,专注于逻辑、空间和因果推理的测试;涵盖多种多媒体数据如自然图像、图表和视觉谜题等;支持复杂查询和包含多个图像的文档检索场景,更准确地反映实际应用情况。虽然当前最先进模型在现有基准测试中表现良好,但在MR$^2$-Bench上表现挣扎。巨大性能差距凸显了测试需求提升与多媒体检索进步之间的差距。Key Takeaways:
- MR$^2$-Bench是首个针对多媒体检索的推理密集型基准测试。
- 它超越了传统的表面级别语义对应测试,着重于评估模型捕捉复杂关系的能力。
- MR$^2$-Bench包含多种类型的多媒体数据,如自然图像、图表和视觉谜题等。
- 该测试支持复杂查询和包含多个图像的文档检索场景,反映真实应用需求。
- 当前最先进的模型在MR$^2$-Bench上的表现表明推理能力还有巨大的提升空间。
- MR$^2$-Bench提供了一个全新的评估标准来比较和优化多媒体检索模型在实际应用中的性能。
点此查看论文截图
SafeBehavior: Simulating Human-Like Multistage Reasoning to Mitigate Jailbreak Attacks in Large Language Models
Authors:Qinjian Zhao, Jiaqi Wang, Zhiqiang Gao, Zhihao Dou, Belal Abuhaija, Kaizhu Huang
Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved impressive performance across diverse natural language processing tasks, but their growing power also amplifies potential risks such as jailbreak attacks that circumvent built-in safety mechanisms. Existing defenses including input paraphrasing, multi step evaluation, and safety expert models often suffer from high computational costs, limited generalization, or rigid workflows that fail to detect subtle malicious intent embedded in complex contexts. Inspired by cognitive science findings on human decision making, we propose SafeBehavior, a novel hierarchical jailbreak defense mechanism that simulates the adaptive multistage reasoning process of humans. SafeBehavior decomposes safety evaluation into three stages: intention inference to detect obvious input risks, self introspection to assess generated responses and assign confidence based judgments, and self revision to adaptively rewrite uncertain outputs while preserving user intent and enforcing safety constraints. We extensively evaluate SafeBehavior against five representative jailbreak attack types including optimization based, contextual manipulation, and prompt based attacks and compare it with seven state of the art defense baselines. Experimental results show that SafeBehavior significantly improves robustness and adaptability across diverse threat scenarios, offering an efficient and human inspired approach to safeguarding LLMs against jailbreak attempts.
大型语言模型(LLM)在不同种类的自然语言处理任务中取得了令人印象深刻的性能表现,但它们日益增强的能力也放大了潜在风险,比如绕过内置安全机制的越狱攻击。现有防御措施,包括输入同义替换、多步评估和安全专家模型等,常常面临高计算成本、有限的泛化能力或僵硬的工作流程等问题,无法检测到复杂语境中嵌入的微妙恶意意图。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 5 figure
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在处理自然语言处理任务时表现出强大的性能,但也带来了潜在风险,如越狱攻击等,可能会绕过内置的安全机制。现有的防御策略存在计算成本高、通用性有限或工作流程僵化等问题,无法检测复杂上下文中的微妙恶意意图。受认知科学关于人类决策制定的发现的启发,我们提出了SafeBehavior,这是一种模拟人类自适应多阶段推理过程的新型层次化越狱防御机制。SafeBehavior将安全评估分解为三个阶段:意图推断,检测明显的输入风险;自我反思,评估生成的响应并根据判断分配信心;自我修订,自适应重写不确定的输出,同时保留用户意图并强制执行安全约束。实验结果表明,SafeBehavior在多种威胁场景下显著提高了鲁棒性和适应性,为防范LLMs的越狱攻击提供了一种高效且受人类启发的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)虽然在自然语言处理任务中表现出强大的性能,但存在潜在风险,如越狱攻击。
- 现有防御策略面临计算成本高、通用性有限及工作流程僵化等问题。
- SafeBehavior是一种模拟人类多阶段推理过程的层次化越狱防御机制。
- SafeBehavior将安全评估分为三个主要阶段:意图推断、自我反思和自我修订。
- SafeBehavior通过这三个阶段提高LLMs对多种越狱攻击的鲁棒性和适应性。
- SafeBehavior能够在保留用户意图的同时强制执行安全约束。
点此查看论文截图
Memory-Driven Self-Improvement for Decision Making with Large Language Models
Authors:Xue Yan, Zijing Ou, Mengyue Yang, Yan Song, Haifeng Zhang, Yingzhen Li, Jun Wang
Large language models (LLMs) have emerged as effective action policies for sequential decision-making (SDM) tasks due to their extensive prior knowledge. However, this broad yet general knowledge is often insufficient for specific decision-making tasks with limited task-related data, making it challenging to efficiently adapt LLMs to specific SDM tasks. To address this challenge, we propose a memory-driven self-improvement framework that combines LLM general prior knowledge with a compact memory of domain-specific experiences. Memory retains past interactions and associated Q-values, thereby capturing decision-relevant knowledge that facilitates accurate value estimation and informs the LLM prior refinement. The refined LLM prior, in turn, generates higher-reward trajectories that further enrich memory, forming a natural self-improvement framework where memory and LLM prior mutually reinforce each other. Experiments show that our memory-driven approach significantly outperforms both traditional RL and LLM-based baselines, e.g., improving performance by over 40% on in-distribution tasks and over 75% when generalized to unseen tasks in ALFWorld.
大型语言模型(LLM)由于其丰富的先验知识,已成为序列决策(SDM)任务的有效行动策略。然而,这种广泛但通用的知识对于具有有限任务相关数据的具体决策任务往往是不够的,使得将LLM有效地适应特定的SDM任务具有挑战性。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种记忆驱动的自改进框架,该框架结合了LLM的通用先验知识与特定领域经验的紧凑记忆。记忆保留了过去的交互和相关的Q值,从而捕获与决策相关的知识,有助于准确的价值评估并优化LLM的先验知识。反过来,优化后的LLM先验知识会产生更高回报的轨迹,进一步丰富记忆,形成了一种自然的自改进框架,其中记忆和LLM先验知识相互加强。实验表明,我们的记忆驱动方法显著优于传统的强化学习和基于LLM的基线方法,例如在ALFWorld中的内部任务上性能提高超过40%,在未见过的任务上性能提高超过75%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在序列决策(SDM)任务中展现出有效的行动策略,得益于其丰富的先验知识。然而,对于特定决策任务,尤其是数据有限的情境下,这种泛化知识常显不足,导致LLMs难以高效适应特定SDM任务。为应对这一挑战,我们提出一种以记忆驱动的自提升框架,结合LLM的通用先验知识与领域特定经验的紧凑记忆。记忆保留过去交互与关联Q值,从而捕获决策相关知识,促进准确价值估计并优化LLM先验。优化后的LLM先验生成更高奖励轨迹,进一步丰富记忆,形成自然自提升框架,其中记忆与LLM先验相互强化。实验显示,我们的记忆驱动方法显著优于传统强化学习与LLM基线方法,如在ALFWorld环境中,对已知任务的性能提升超过40%,对未知任务的性能提升超过75%。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在序列决策(SDM)任务中表现出强大的效能,主要得益于其广泛的先验知识。
- 在数据有限的情况下,LLMs的泛化知识常常不足以应对特定决策任务。
- 提出一种记忆驱动的自提升框架,结合LLM的通用先验知识与领域特定经验。
- 记忆系统能够保留过去的交互和关联的Q值,从而获取决策相关知识。
- 该框架能够促进准确的价值估计并优化LLM的先验知识。
- 优化后的LLM能够生成更高奖励的轨迹,进一步丰富记忆。
点此查看论文截图


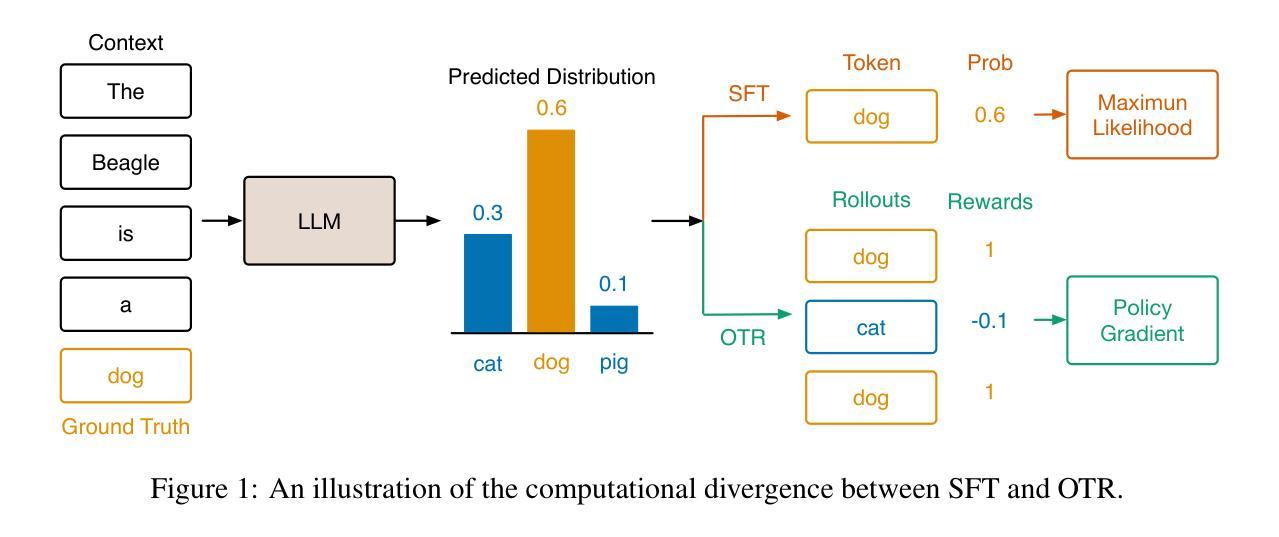
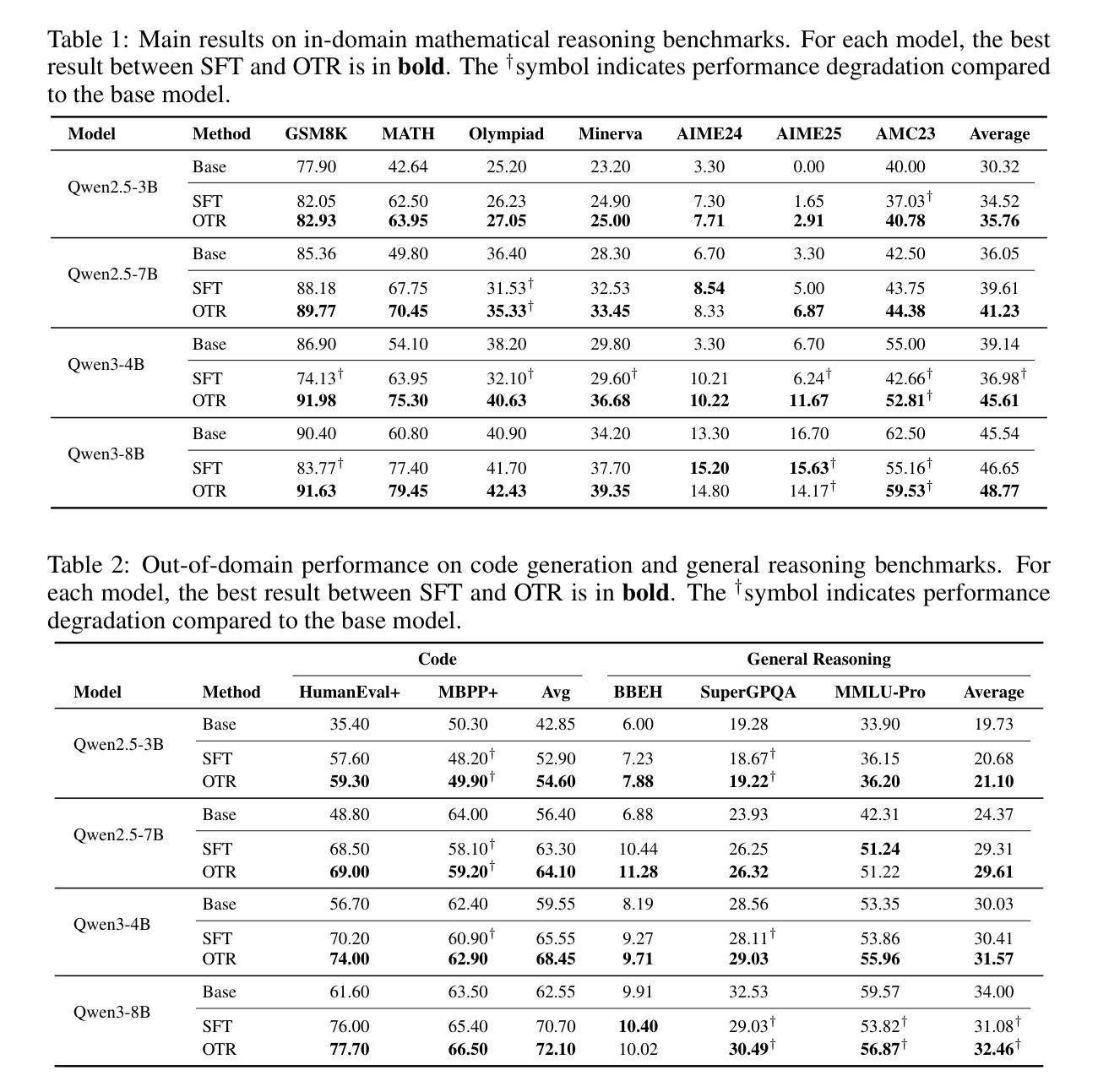
One-Token Rollout: Guiding Supervised Fine-Tuning of LLMs with Policy Gradient
Authors:Rui Ming, Haoyuan Wu, Shoubo Hu, Zhuolun He, Bei Yu
Supervised fine-tuning (SFT) is the predominant method for adapting large language models (LLMs), yet it often struggles with generalization compared to reinforcement learning (RL). In this work, we posit that this performance disparity stems not just from the loss function, but from a more fundamental difference: SFT learns from a fixed, pre-collected dataset, whereas RL utilizes on-policy data sampled from the current policy. Building on this hypothesis, we introduce one-token rollout (OTR), a novel fine-tuning algorithm that guides SFT with the policy gradient method. OTR reframes the autoregressive learning process by treating each token generation as a single-step reinforcement learning trajectory. At each step, it performs a Monte Carlo ``rollout’’ by sampling multiple candidate tokens from the current policy’s distribution. The ground-truth token from the supervised data is then used to provide a reward signal to these samples. Guided by policy gradient, our algorithm repurposes static, off-policy supervised data into a dynamic, on-policy signal at the token level, capturing the generalization benefits of on-policy learning while bypassing the costly overhead of full sentence generation. Through extensive experiments on a diverse suite of challenging benchmarks spanning mathematical reasoning, code generation, and general domain reasoning, we demonstrate that OTR consistently outperforms standard SFT. Our findings establish OTR as a powerful and practical alternative for fine-tuning LLMs and provide compelling evidence that the on-policy nature of data is a critical driver of generalization, offering a promising new direction for fine-tuning LLMs.
监督微调(SFT)是适应大型语言模型(LLM)的主要方法,但在与强化学习(RL)的对比中,它往往面临泛化能力不足的问题。在此工作中,我们认为这种性能差异不仅仅源于损失函数,更源于一个根本性的不同:SFT是从预先收集好的固定数据集中学习,而RL则是利用当前策略的在线数据进行采样。基于这一假设,我们引入了单令牌滚动(OTR),这是一种新型的微调算法,采用策略梯度方法来指导SFT。OTR通过把每个令牌的生成视为一个单独的强化学习轨迹,从而重新构建了自回归学习过程。在每一步中,它通过对当前政策分布进行多个候选令牌的采样,来执行Monte Carlo“滚动”。然后,来自监督数据的真实令牌被用来为这些样本提供奖励信号。在我们的算法中,策略梯度的引导使得静态的离线监督数据变为动态的在线信号,在令牌级别上捕获在线学习的泛化优势,同时避免了全句生成的昂贵开销。通过在涵盖数学推理、代码生成和通用领域推理的一系列具有挑战性的基准测试中进行大量实验,我们证明了OTR始终优于标准SFT。我们的研究结果确立了OTR作为强大且实用的LLM微调替代方案,并有力证明数据的在线性质是推动泛化的关键因素,为LLM的微调提供了有前景的新方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为“One-Token Rollout (OTR)”的新型监督微调算法,该算法结合了监督学习和强化学习的优势。它通过对每个生成的令牌进行蒙特卡洛模拟来模拟强化学习过程,利用监督数据中的真实令牌作为奖励信号,从而引导微调过程。实验表明,OTR在多个挑战性基准测试中表现优于标准监督微调方法,具有强大的泛化能力。这表明数据在策略决策中的即时性是提高泛化的关键要素。这为微调大型语言模型提供了新思路。
Key Takeaways
- 监督微调(SFT)和强化学习在大型语言模型应用上的表现差异,源自数据使用的差异,而非仅仅损失函数的不同。
- SFT使用固定的预收集数据集,而强化学习则利用当前策略的即时数据。
- One-Token Rollout (OTR)是一种新型的监督微调算法,它通过蒙特卡洛模拟将强化学习引入监督微调过程。
- OTR在每个步骤中模拟生成令牌的强化学习过程,并使用监督数据中的真实令牌作为奖励信号。
- OTR算法通过利用即时策略数据来提高泛化能力,且在多种基准测试中表现优于标准监督微调方法。
点此查看论文截图

Interactive Learning for LLM Reasoning
Authors:Hehai Lin, Shilei Cao, Minzhi Li, Sudong Wang, Haotian Wu, Linyi Yang, Juepeng Zheng, Chengwei Qin
Existing multi-agent learning approaches have developed interactive training environments to explicitly promote collaboration among multiple Large Language Models (LLMs), thereby constructing stronger multi-agent systems (MAS). However, during inference, they require re-executing the MAS to obtain final solutions, which diverges from human cognition that individuals can enhance their reasoning capabilities through interactions with others and resolve questions independently in the future. To investigate whether multi-agent interaction can enhance LLMs’ independent problem-solving ability, we introduce ILR, a novel co-learning framework for MAS that integrates two key components: Dynamic Interaction and Perception Calibration. Specifically, Dynamic Interaction first adaptively selects either cooperative or competitive strategies depending on question difficulty and model ability. LLMs then exchange information through Idea3 (Idea Sharing, Idea Analysis, and Idea Fusion), an innovative interaction paradigm designed to mimic human discussion, before deriving their respective final answers. In Perception Calibration, ILR employs Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to train LLMs while integrating one LLM’s reward distribution characteristics into another’s reward function, thereby enhancing the cohesion of multi-agent interactions. We validate ILR on three LLMs across two model families of varying scales, evaluating performance on five mathematical benchmarks and one coding benchmark. Experimental results show that ILR consistently outperforms single-agent learning, yielding an improvement of up to 5% over the strongest baseline. We further discover that Idea3 can enhance the robustness of stronger LLMs during multi-agent inference, and dynamic interaction types can boost multi-agent learning compared to pure cooperative or competitive strategies.
现有的多智能体学习方法已经构建了交互式训练环境,以明确促进多个大型语言模型(LLM)之间的协作,从而构建更强大的多智能体系统(MAS)。然而,在推理过程中,它们需要重新执行MAS才能获得最终解决方案,这与人类认知不符——人类可以通过与他人的互动来增强自己的推理能力,并在未来独立解决问题。为了研究多智能体交互是否能增强LLM的独立解决问题的能力,我们引入了ILR,这是一种新型的多智能体协同学习框架,它集成了两个关键组件:动态交互和感知校准。具体而言,动态交互首先根据问题的难度和模型能力自适应地选择合作或竞争策略。然后,LLM通过思想共享(Idea Sharing)、思想分析(Idea Analysis)和融合(Idea Fusion)进行信息交换,这是一种模仿人类讨论的创新交互模式,然后得出各自的最终答案。在感知校准中,ILR采用群组相对策略优化(GRPO)训练LLM,同时将一个LLM的奖励分布特征集成到另一个的奖励函数中,从而提高多智能体交互的凝聚力。我们在两个不同规模的模型家族中的三个LLM上验证了ILR的有效性,并在五个数学基准测试和一个编码基准测试上评估其性能。实验结果表明,ILR始终优于单智能体学习,比最强基线提高了高达5%。我们还发现思想共享可以在多智能体推理过程中增强强大LLM的稳健性,并且与纯粹的合作或竞争策略相比,动态交互类型可以促进多智能体学习。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The code will be released later
摘要
现有多智能体学习的方法通过构建交互式训练环境来促进多个大型语言模型(LLM)之间的协作,从而构建更强大的多智能体系统(MAS)。然而,在推理过程中,它们需要重新执行MAS来获得最终解决方案,这与人类认知不同,人类可以通过与他人互动增强自身推理能力,并在未来独立解决问题。为了研究多智能体交互是否能增强LLM的独立问题解决能力,我们提出了ILR,这是一种新型的多智能体系统协同学习框架,它包括两个关键组成部分:动态交互和感知校准。具体而言,动态交互根据问题的难度和模型能力自适应地选择合作或竞争策略。LLM通过模仿人类讨论的创新交互模式Idea3(思想共享、思想分析和思想融合)交换信息,然后得出各自的最终答案。在感知校准中,ILR采用群体相对策略优化(GRPO)训练LLM,同时将一个LLM的奖励分布特性集成到另一个LLM的奖励函数中,从而提高多智能体交互的凝聚力。我们在两个模型家族中的三个不同规模的LLM上验证了ILR的有效性,并在五个数学基准测试和一个编码基准测试上评估其性能。实验结果表明,ILR在各方面均优于单智能体学习,与最强基线相比提高了高达5%。我们还发现Idea3可以增强强LLM在多智能体推理中的稳健性,而动态交互类型相对于纯粹的合作或竞争策略可以促进多智能体学习。
关键见解
- 多智能体学习通过构建交互式训练环境促进LLM间的协作。
- ILR框架引入动态交互和感知校准以增强多智能体系统的性能。
- 动态交互根据问题难度和模型能力自适应选择合作或竞争策略。
- Idea3交互模式模仿人类讨论,有助于LLM交换信息并得出最终答案。
- 感知校准通过GRPO训练LLM,提高多智能体交互的凝聚力。
- ILR在多个LLM上验证有效,并在数学和编码基准测试中表现优于单智能体学习。
点此查看论文截图

PRPO: Paragraph-level Policy Optimization for Vision-Language Deepfake Detection
Authors:Tuan Nguyen, Naseem Khan, Khang Tran, NhatHai Phan, Issa Khalil
The rapid rise of synthetic media has made deepfake detection a critical challenge for online safety and trust. Progress remains constrained by the scarcity of large, high-quality datasets. Although multimodal large language models (LLMs) exhibit strong reasoning capabilities, their performance on deepfake detection is poor, often producing explanations that are misaligned with visual evidence or hallucinatory. To address this limitation, we introduce a reasoning-annotated dataset for deepfake detection and propose Paragraph-level Relative Policy Optimization (PRPO), a reinforcement learning algorithm that aligns LLM reasoning with image content at the paragraph level. Experiments show that PRPO improves detection accuracy by a wide margin and achieves the highest reasoning score of 4.55/5.0. Ablation studies further demonstrate that PRPO significantly outperforms GRPO under test-time conditions. These results underscore the importance of grounding multimodal reasoning in visual evidence to enable more reliable and interpretable deepfake detection.
合成媒体的迅速崛起使得深度伪造检测成为网络安全和信任的关键挑战。由于大型高质量数据集的稀缺,进展仍然受到限制。尽管多模态大型语言模型(LLM)展现出强大的推理能力,但它们对深度伪造检测的表现却不尽人意,往往产生与视觉证据不符或臆想的解释。为解决此限制,我们引入用于深度伪造检测的推理注释数据集,并提出段落级相对策略优化(PRPO),这是一种强化学习算法,能够在段落级别将LLM推理与图像内容对齐。实验表明,PRPO在检测准确率上有显著提高,并获得了最高推理评分4.55/5.0。进一步的消融研究表明,在测试条件下,PRPO显著优于GRPO。这些结果强调了在视觉证据的基础上实现多模态推理的重要性,以实现更可靠、更可解释的深度伪造检测。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
合成媒体的迅速崛起使得深度伪造检测成为网络安全与信任的关键挑战。由于缺乏大规模高质量数据集,进展仍然受限。尽管多模态大型语言模型展现出强大的推理能力,但在深度伪造检测方面的表现不佳,往往产生与视觉证据不符或虚幻的解释。为解决此问题,我们引入深度伪造检测推理注释数据集并提出段落级相对策略优化(PRPO),一种强化学习算法,可在段落级别将LLM推理与图像内容对齐。实验表明,PRPO大幅提高了检测精度并获得了最高推理分数4.55/5.0。消融研究进一步证明,在测试条件下PRPO显著优于GRPO。这些结果强调了在视觉证据的基础上实现多模态推理的重要性,以进行更可靠和可解释的深度伪造检测。
Key Takeaways
- 合成媒体的普及使得深度伪造检测成为网络安全的重要挑战。
- 当前深度伪造检测面临缺乏大规模高质量数据集的制约。
- 多模态大型语言模型在深度伪造检测方面的表现有待提高。
- 引入了一个针对深度伪造检测的推理注释数据集。
- 提出了段落级相对策略优化(PRPO)强化学习算法,以提高检测精度和推理能力。
- 实验结果显示PRPO在深度伪造检测方面表现出优异的性能。
点此查看论文截图
EnScale: Temporally-consistent multivariate generative downscaling via proper scoring rules
Authors:Maybritt Schillinger, Maxim Samarin, Xinwei Shen, Reto Knutti, Nicolai Meinshausen
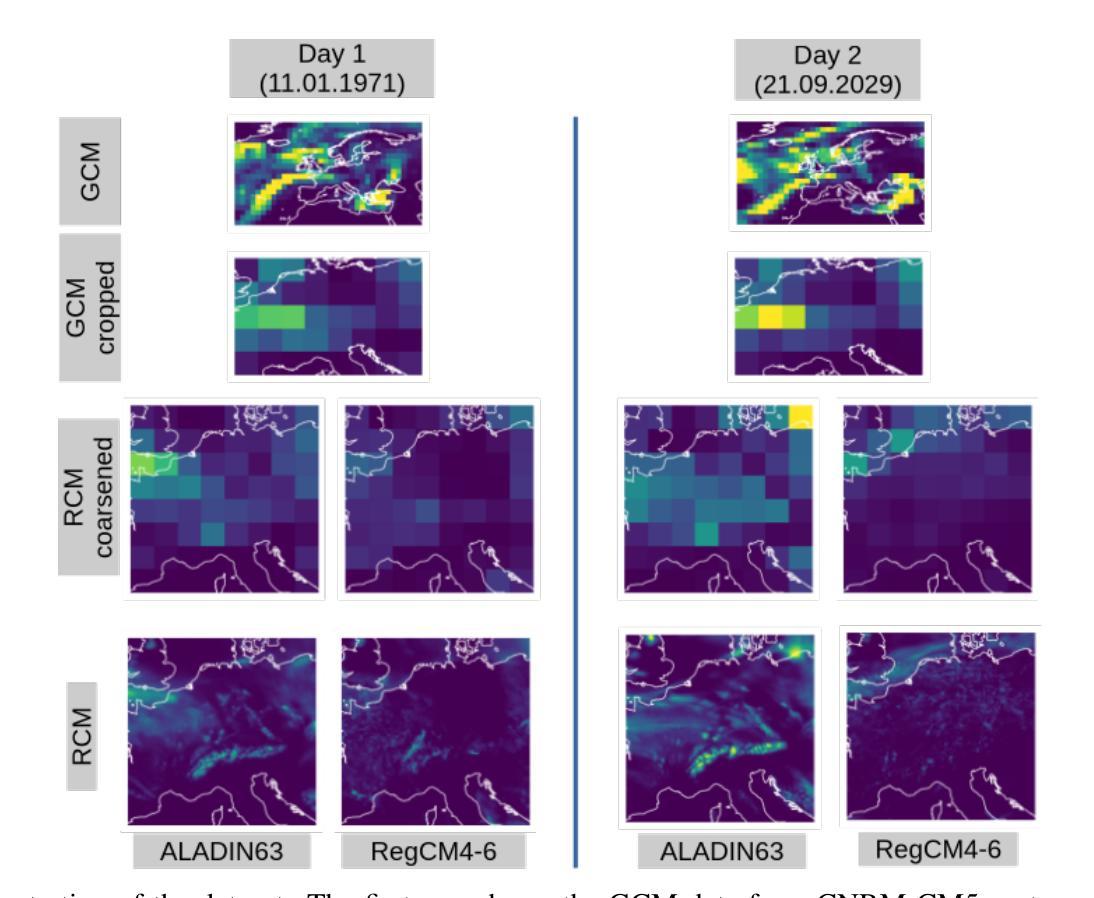
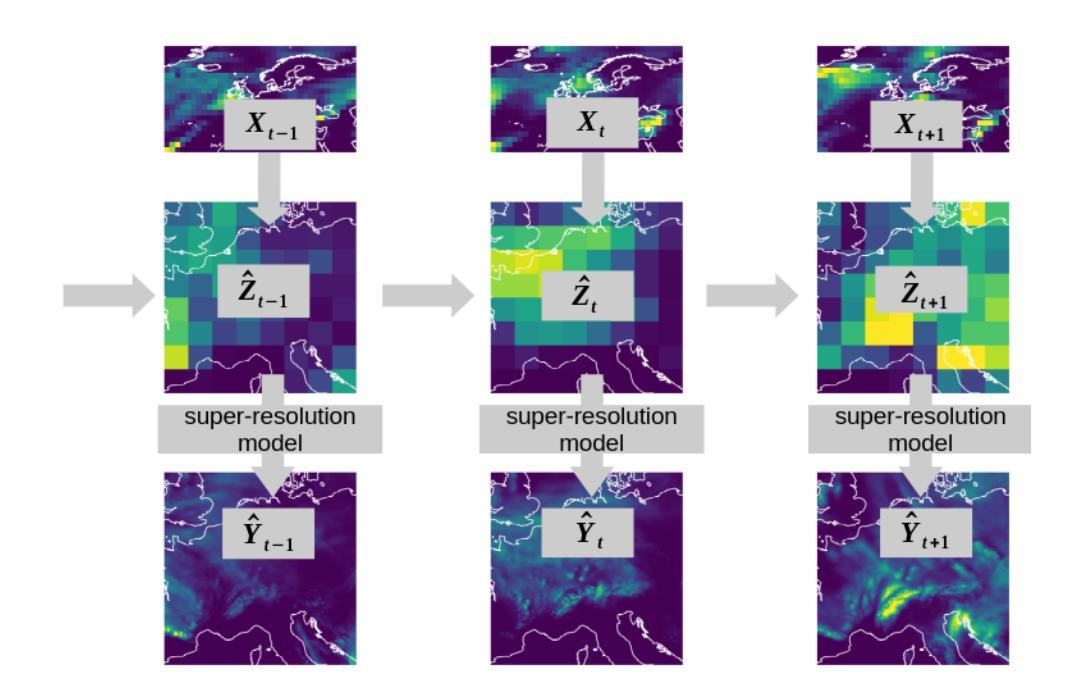
The practical use of future climate projections from global circulation models (GCMs) is often limited by their coarse spatial resolution, requiring downscaling to generate high-resolution data. Regional climate models (RCMs) provide this refinement, but are computationally expensive. To address this issue, machine learning models can learn the downscaling function, mapping coarse GCM outputs to high-resolution fields. Among these, generative approaches aim to capture the full conditional distribution of RCM data given coarse-scale GCM data, which is characterized by large variability and thus challenging to model accurately. We introduce EnScale, a generative machine learning framework that emulates the full GCM-to-RCM map by training on multiple pairs of GCM and corresponding RCM data. It first adjusts large-scale mismatches between GCM and coarsened RCM data, followed by a super-resolution step to generate high-resolution fields. Both steps employ generative models optimized with the energy score, a proper scoring rule. Compared to state-of-the-art ML downscaling approaches, our setup reduces computational cost by about one order of magnitude. EnScale jointly emulates multiple variables – temperature, precipitation, solar radiation, and wind – spatially consistent over an area in Central Europe. In addition, we propose a variant EnScale-t that enables temporally consistent downscaling. We establish a comprehensive evaluation framework across various categories including calibration, spatial structure, extremes, and multivariate dependencies. Comparison with diverse benchmarks demonstrates EnScale’s strong performance and computational efficiency. EnScale offers a promising approach for accurate and temporally consistent RCM emulation.
实际应用中,全球环流模型(GCMs)的未来气候预测常常受到其空间分辨率较低的限制,需要降尺度生成高分辨率数据。区域气候模型(RCMs)可以提供这种精细化的数据,但计算成本较高。为了解决这一问题,机器学习模型可以学习降尺度函数,将粗分辨率的GCM输出映射到高分辨率场。其中,生成式方法旨在捕捉给定粗尺度GCM数据的RCM数据的全条件分布。由于RCM数据具有较大的变异性,因此准确建模具有挑战性。我们引入了EnScale,这是一个生成式机器学习框架,通过训练多对GCM和相应的RCM数据来模拟完整的GCM到RCM的映射。它首先调整GCM和简化RCM数据之间的宏观不匹配,然后通过超分辨率步骤生成高分辨率场。这两个步骤都使用以能量评分优化过的生成模型,这是一种适当的评分规则。与最先进的ML降尺度方法相比,我们的设置将计算成本降低了大约一个数量级。EnScale可以同时模拟多个变量——温度、降水、太阳辐射和风力——在空间上一致覆盖中欧地区。此外,我们提出了一种EnScale-t变体,能够实现时间一致的降尺度。我们建立了全面的评估框架,包括校准、空间结构、极端事件和多元依赖等各个类别。与各种基准的比较表明,EnScale具有强大的性能和计算效率。EnScale为准确和时间上一致的RCM模拟提供了有前景的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
使用全球环流模型(GCMs)的未来气候预测在实际应用中常受限于其较低的空间分辨率,需要降尺度以生成高分辨率数据。区域气候模型(RCMs)虽能提供这一细化,但计算成本较高。为解决这一问题,机器学习模型可学习降尺度函数,将粗糙的GCM输出映射到高分辨率场。本文介绍了一种名为EnScale的生成式机器学习框架,它通过多对GCM和相应RCM数据的训练来模拟完整的GCM到RCM的映射。它首先调整GCM和简化RCM数据之间的大尺度不匹配,然后通过超分辨率步骤生成高分辨率场。这两个步骤都使用以能量分数为优化目标的生成模型。与最先进的ML降尺度方法相比,我们的设置将计算成本降低了大约一个数量级。EnScale可联合模拟温度、降水、太阳辐射和风力等多个变量,并在中欧地区实现空间一致性。此外,我们提出了EnScale-t变体以实现时间一致的降尺度。我们建立了包括校准、空间结构、极端事件和多元依赖在内的全面评估框架。与多种基准的比较表明,EnScale具有强大的性能和计算效率。EnScale为准确和时间一致的RCM模拟提供了有前景的方法。
关键见解
- EnScale是一个生成式机器学习框架,能够模拟GCM到RCM的完整映射。
- 该框架通过调整大尺度不匹配和超级分辨率生成步骤,以生成高分辨率数据。
- 与其他先进的ML降尺度方法相比,EnScale的计算成本降低了大约一个数量级。
- EnScale能够联合模拟多个气候变量,如温度、降水、太阳辐射和风力,并在中欧地区实现空间一致性。
- EnScale-t变体实现了时间一致的降尺度。
- 建立了包括校准、空间结构、极端事件和多元依赖的全面评估框架。
点此查看论文截图
Diversity-Incentivized Exploration for Versatile Reasoning
Authors:Zican Hu, Shilin Zhang, Yafu Li, Jianhao Yan, Xuyang Hu, Leyang Cui, Xiaoye Qu, Chunlin Chen, Yu Cheng, Zhi Wang
Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has emerged as a crucial paradigm for incentivizing reasoning capabilities in Large Language Models (LLMs). Due to vast state-action spaces and reward sparsity in reasoning tasks, existing methods often struggle with deficient exploration and poor sample efficiency. In the paper, we propose \textbf{DIVER} (\textbf{D}iversity-\textbf{I}ncentivized Exploration for \textbf{V}ersatil\textbf{E} \textbf{R}easoning), an innovative framework that highlights the pivotal role of global sequence-level diversity to incentivize deep exploration for versatile reasoning. We first conduct a primary empirical study to reveal a strong positive correlation between global diversity and reasoning capacity. Building on this insight, we introduce global diversity incentives as an intrinsic reward to promote deep exploration in a semantically structured space. Incorporating the intrinsic reward, we develop a potential-based reward shaping mechanism to preserve optimal policy invariance and design simple heuristics to mitigate possible reward hacking. Experimental results show that DIVER outperforms competitive RLVR baselines with various exploration strategies on both in-domain and out-of-domain tasks, excelling in both Pass@1 and Pass@k evaluations. Our code is available at https://github.com/NJU-RL/DIVER.
强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)已成为激励大型语言模型(LLM)中的推理能力的重要范式。由于推理任务中的状态动作空间庞大和奖励稀疏,现有方法往往面临探索不足和样本效率低的问题。在论文中,我们提出了DIVER(多样激励探索促进推理),这是一个创新框架,强调全局序列水平多样性在激励深度探索以促进多样化推理中的关键作用。我们首先进行了一项初步实证研究,揭示了全局多样性与推理能力之间的强烈正相关关系。在此基础上,我们引入全局多样性激励作为内在奖励,以促进语义结构空间中的深度探索。结合这种内在奖励,我们开发了一种基于潜力的奖励塑造机制,以保持最优策略的不变性,并设计简单的启发式方法来缓解可能的奖励黑客攻击。实验结果表明,无论是在域内还是域外任务上,DIVER在各种探索策略方面的表现都优于RLVR基线,在Pass@1和Pass@k评估中都表现出色。我们的代码可在https://github.com/NJU-RL/DIVER找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 26 pages, 10 figures
Summary
强化学习可验证奖励(RLVR)已成为激励大型语言模型(LLM)推理能力的重要范式。现有方法由于推理任务中的状态动作空间庞大和奖励稀疏,常常面临探索不足和样本效率不高的问题。本文提出DIVER(针对多样化激励的探索以促进通用推理),强调全局序列级别多样性在激励深度探索中的关键作用。我们首先进行了一项实证研究,揭示了全局多样性与推理能力之间的强正相关关系。在此基础上,我们引入全局多样性激励作为内在奖励,以促进语义结构化空间中的深度探索。结合这一内在奖励,我们开发了一种基于潜力的奖励塑造机制,以保持最优策略的不变性,并设计简单的启发式方法来防止可能的奖励操纵。实验结果表明,在域内和域外任务上,DIVER在Pass@1和Pass@k评估中都优于其他RLVR基线方法。我们的代码可在https://github.com/NJU-RL/DIVER找到。
Key Takeaways
- 强化学习可验证奖励(RLVR)是激励大型语言模型(LLM)推理能力的重要方法。
- 现有方法在推理任务中面临探索不足和样本效率不高的问题。
- DIVER框架强调全局序列级别多样性在激励深度探索中的关键作用。
- 实证研究表明全局多样性与推理能力之间存在强正相关关系。
- 引入全局多样性激励作为内在奖励,促进语义结构化空间中的深度探索。
- 开发基于潜力的奖励塑造机制,保持最优策略的不变性。
点此查看论文截图
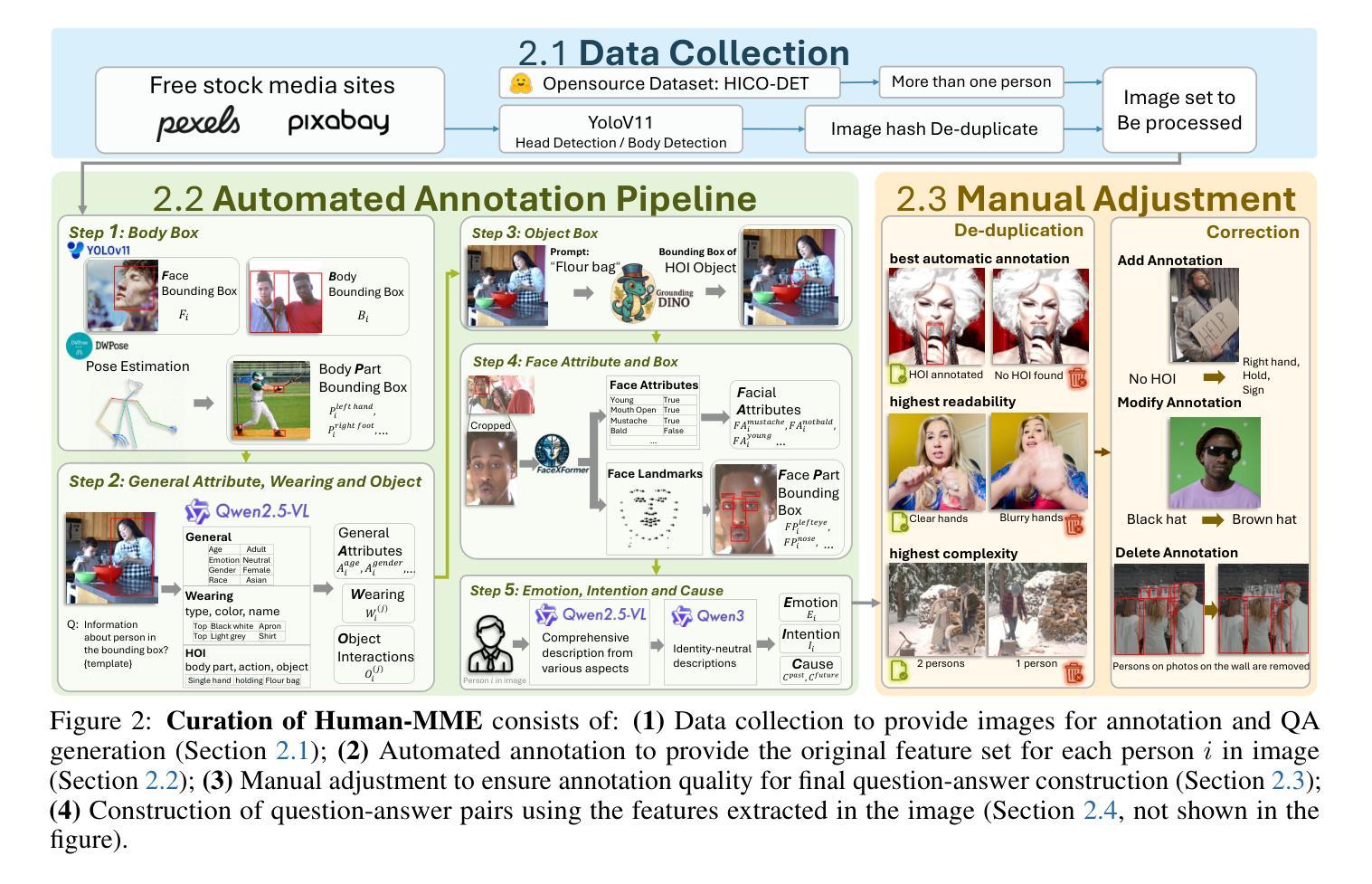
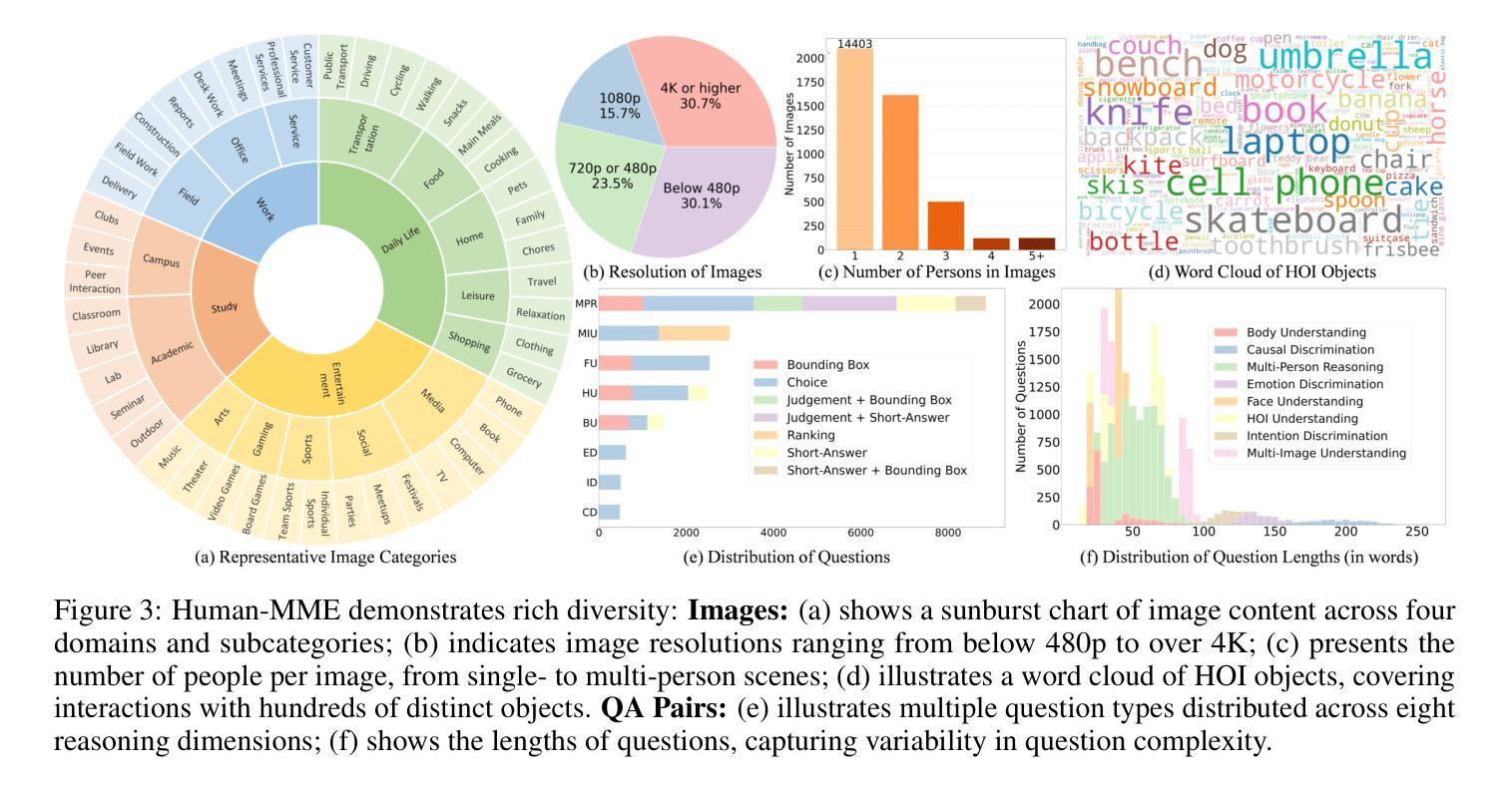
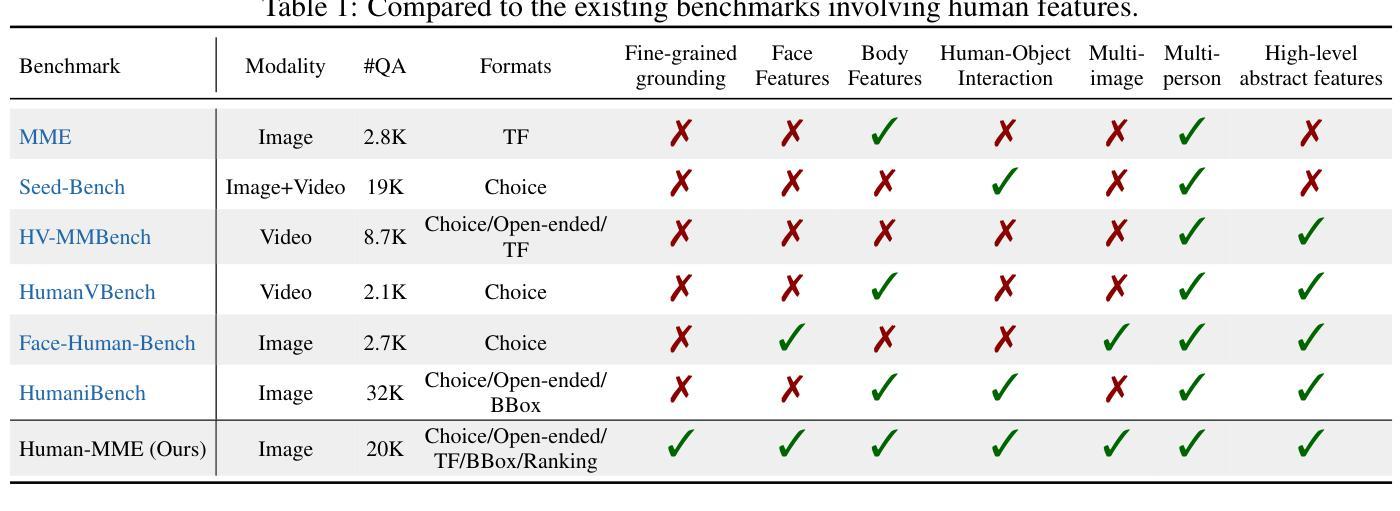
Human-MME: A Holistic Evaluation Benchmark for Human-Centric Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Yuansen Liu, Haiming Tang, Jinlong Peng, Jiangning Zhang, Xiaozhong Ji, Qingdong He, Donghao Luo, Zhenye Gan, Junwei Zhu, Yunhang Shen, Chaoyou Fu, Chengjie Wang, Xiaobin Hu, Shuicheng Yan
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated significant advances in visual understanding tasks. However, their capacity to comprehend human-centric scenes has rarely been explored, primarily due to the absence of comprehensive evaluation benchmarks that take into account both the human-oriented granular level and higher-dimensional causal reasoning ability. Such high-quality evaluation benchmarks face tough obstacles, given the physical complexity of the human body and the difficulty of annotating granular structures. In this paper, we propose Human-MME, a curated benchmark designed to provide a more holistic evaluation of MLLMs in human-centric scene understanding. Compared with other existing benchmarks, our work provides three key features: 1. Diversity in human scene, spanning 4 primary visual domains with 15 secondary domains and 43 sub-fields to ensure broad scenario coverage. 2. Progressive and diverse evaluation dimensions, evaluating the human-based activities progressively from the human-oriented granular perception to the higher-dimensional reasoning, consisting of eight dimensions with 19,945 real-world image question pairs and an evaluation suite. 3. High-quality annotations with rich data paradigms, constructing the automated annotation pipeline and human-annotation platform, supporting rigorous manual labeling to facilitate precise and reliable model assessment. Our benchmark extends the single-target understanding to the multi-person and multi-image mutual understanding by constructing the choice, short-answer, grounding, ranking and judgment question components, and complex questions of their combination. The extensive experiments on 17 state-of-the-art MLLMs effectively expose the limitations and guide future MLLMs research toward better human-centric image understanding. All data and code are available at https://github.com/Yuan-Hou/Human-MME.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视觉理解任务中取得了显著进展。然而,它们在理解以人类为中心的场景方面的能力很少被探索,这主要是因为缺乏综合考虑人类导向的颗粒度和高维因果推理能力的全面评估基准。鉴于人体物理结构的复杂性以及颗粒结构标注的困难,高质量评估基准面临着艰巨的障碍。在本文中,我们提出了Human-MME,这是一个精心设计的基准,旨在更全面地对MLLMs在以人类为中心的场景理解进行评估。与其他现有基准相比,我们的工作提供了三个关键特点:
人类场景的多样性,涵盖4个主要视觉领域,包括15个次级领域和43个子领域,以确保广泛的场景覆盖。
渐进且多样的评估维度,从以人为基础的活动进行渐进评估,从人类导向的颗粒感知到高维推理,包括八个维度,包含19945个真实世界图像问题对和一个评估套件。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种针对多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在人类为中心的场景理解能力的评估基准——Human-MME。相较于其他基准,Human-MME具备三大特点:涵盖多种人类场景、渐进且多样的评估维度以及高质量的数据标注。Human-MME的构建促进了多目标理解向多人、多图像相互理解的转变,为MLLMs的未来发展提供了指导。
Key Takeaways
- Human-MME是一个针对MLLMs在人类为中心的场景理解能力的评估基准。
- Human-MME涵盖了多种人类场景,包括4个主要视觉领域和15个次级领域,确保了广泛的场景覆盖。
- 该基准具有渐进和多样的评估维度,从人类导向的颗粒度感知到更高维度的推理。
- Human-MME提供了高质量的数据标注,支持严格的手动标注,促进了精确和可靠的模型评估。
- Human-MME从单目标理解扩展到多人和多图像的相互理解。
- 通过大量实验,Human-MME揭示了当前MLLMs的局限性,并为未来的研究提供了指导。
点此查看论文截图
Reinforced Strategy Optimization for Conversational Recommender Systems via Network-of-Experts
Authors:Xiaoyan Zhao
Conversational Recommender Systems (CRSs) provide personalized recommendations through multi-turn interactions. With the strong reasoning abilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), applying them to CRSs has become promising. Yet, existing methods often lack explicit optimization of interaction strategies, relying instead on unified prompts, which can yield suboptimal outcomes. We propose Reinforced Strategy Optimization (RSO), a hierarchical framework that decomposes response generation into macro-level strategy planning and micro-level adaptation within a network-of-experts. A Planner selects strategies (e.g., recommend, explain, encourage), while an Actor generates responses guided by auxiliary experts for preferences and factual grounding. This disentanglement enables more tractable learning. To address limited multi-turn data, we model strategy learning as reinforcement learning with an LLM-based reward for exploration. Experiments show RSO outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, validating the effectiveness of hierarchical strategy optimization.
对话推荐系统(CRSs)通过多轮交互提供个性化推荐。利用大型语言模型(LLM)的强大推理能力,将其应用于CRSs已经显示出巨大的潜力。然而,现有方法往往缺乏明确的优化交互策略,而是依赖于统一的提示,这可能导致次优结果。我们提出了强化策略优化(RSO),这是一个层次框架,将响应生成分解为宏观层面的策略规划和微观层面的专家网络内的适应。规划器选择策略(例如推荐、解释、鼓励),而行为者根据辅助专家生成偏好和事实基础的响应。这种分解使得学习更容易进行。为了解决有限的多轮数据问题,我们将策略学习建模为强化学习,利用基于LLM的奖励进行探索。实验表明,RSO优于最新的基线方法,验证了层次策略优化的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:对话推荐系统(CRSs)通过多轮交互提供个性化推荐。将大型语言模型(LLMs)的推理能力应用于CRSs具有广阔前景。然而,现有方法缺乏明确的交互策略优化,依赖于统一提示,可能导致次优结果。本文提出强化策略优化(RSO)的分层框架,将响应生成分解为宏观策略规划和微观层面的专家网络内的适应。规划器选择策略(如推荐、解释、鼓励),而Actor根据辅助专家生成响应以实现偏好和事实依据。实验证明RSO优于最新技术基线,验证了分层策略优化的有效性。
Key Takeaways:
- 对话推荐系统通过多轮交互提供个性化推荐。
- 大型语言模型在对话推荐系统中的应用具有广阔前景。
- 现有方法缺乏明确的交互策略优化,可能导致次优结果。
- 提出强化策略优化(RSO)的分层框架,包括策略规划和响应生成。
- 策略学习被建模为强化学习,使用大型语言模型作为奖励进行探索。
- 实验证明RSO优于现有方法,验证了分层策略优化的有效性。
点此查看论文截图