⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-04 更新
Touching the tumor boundary: A pilot study on ultrasound based virtual fixtures for breast-conserving surgery
Authors:Laura Connolly, Tamas Ungi, Adnan Munawar, Anton Deguet, Chris Yeung, Russell H. Taylor, Parvin Mousavi, Gabor Fichtinger Keyvan Hashtrudi-Zaad
Purpose: Delineating tumor boundaries during breast-conserving surgery is challenging as tumors are often highly mobile, non-palpable, and have irregularly shaped borders. To address these challenges, we introduce a cooperative robotic guidance system that applies haptic feedback for tumor localization. In this pilot study, we aim to assess if and how this system can be successfully integrated into breast cancer care. Methods: A small haptic robot is retrofitted with an electrocautery blade to operate as a cooperatively controlled surgical tool. Ultrasound and electromagnetic navigation are used to identify the tumor boundaries and position. A forbidden region virtual fixture is imposed when the surgical tool collides with the tumor boundary. We conducted a study where users were asked to resect tumors from breast simulants both with and without the haptic guidance. We then assess the results of these simulated resections both qualitatively and quantitatively. Results: Virtual fixture guidance is shown to improve resection margins. On average, users find the task to be less mentally demanding, frustrating, and effort intensive when haptic feedback is available. We also discovered some unanticipated impacts on surgical workflow that will guide design adjustments and training protocol moving forward. Conclusion: Our results suggest that virtual fixtures can help localize tumor boundaries in simulated breast-conserving surgery. Future work will include an extensive user study to further validate these results and fine-tune our guidance system.
目的:在保乳手术中划定肿瘤边界是一项挑战,因为肿瘤经常活动度高、不可触及,并且边界形状不规则。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了一种合作型机器人引导系统,该系统采用触觉反馈来进行肿瘤定位。在本试点研究中,我们的目标是评估这一系统能否成功整合到乳腺癌护理中。
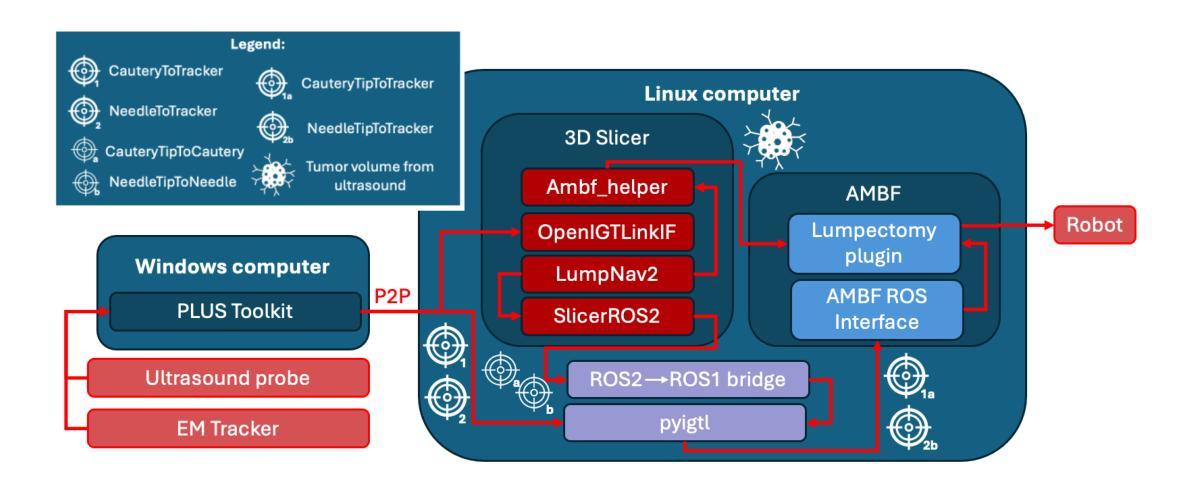
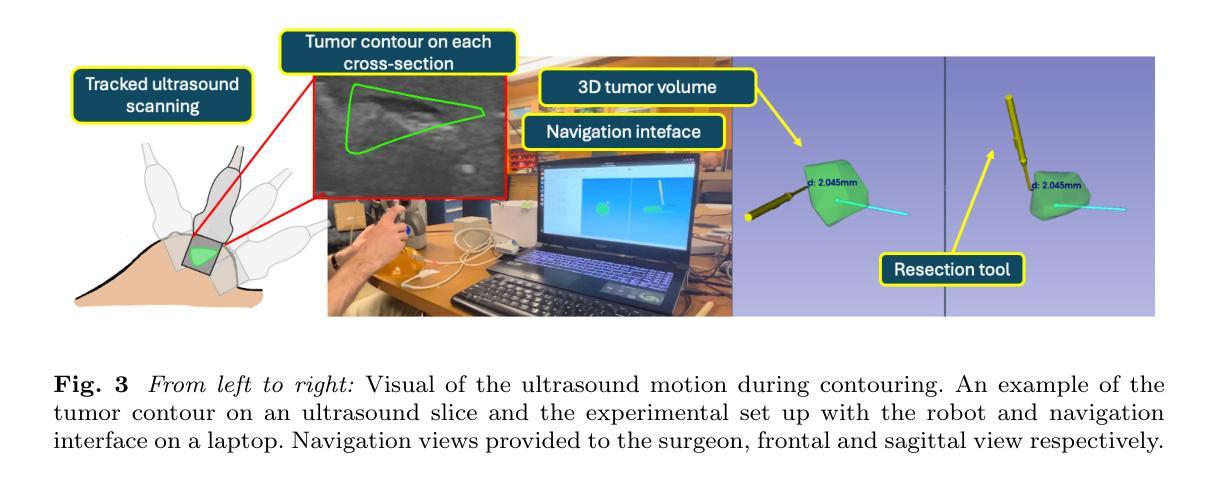
方法:小型触觉机器人被改装成带有电灼刀的手术工具,以实现合作控制。超声和电磁导航被用来识别肿瘤边界和位置。当手术工具碰到肿瘤边界时,系统会实施一个禁止区域虚拟装置。我们进行了一项研究,要求参与者在带有和不带触觉引导的条件下,从乳房模拟物中切除肿瘤。然后,我们定性和定量地评估这些模拟切除的结果。
结果:虚拟装置引导显示可以改善切除边缘。平均而言,当提供触觉反馈时,参与者认为任务在精神需求、挫败感和努力程度上都较低。我们还发现了一些对手术工作流程的意外影响,这将指导我们未来的设计调整和培训协议。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于乳腺癌保乳手术中的合作机器人引导系统,该系统采用触觉反馈来定位肿瘤。在一项试点研究中,作者评估了该系统在模拟乳房切除手术中的表现,发现虚拟夹具指导可以改善切除边界,并降低了用户的心理需求和操作难度。尽管存在一些未预见的影响,但作者认为该系统的引入具有潜力,未来还需进行更多的用户研究来验证并优化该系统。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌保乳手术中肿瘤定位具有挑战性,因为肿瘤具有移动性高、不可触及和边界不规则等特点。
- 介绍了一种合作机器人引导系统,该系统使用触觉反馈来解决这些挑战。
- 在模拟乳房切除手术中评估了该系统的表现。
- 虚拟夹具指导可以改善切除边界。
- 该系统的引入降低了用户完成手术时的心理需求和操作难度。
- 在应用该系统的过程中出现了一些未预见的影响,需要进一步设计和训练上的调整。
点此查看论文截图