⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-04 更新
AortaDiff: A Unified Multitask Diffusion Framework For Contrast-Free AAA Imaging
Authors:Yuxuan Ou, Ning Bi, Jiazhen Pan, Jiancheng Yang, Boliang Yu, Usama Zidan, Regent Lee, Vicente Grau
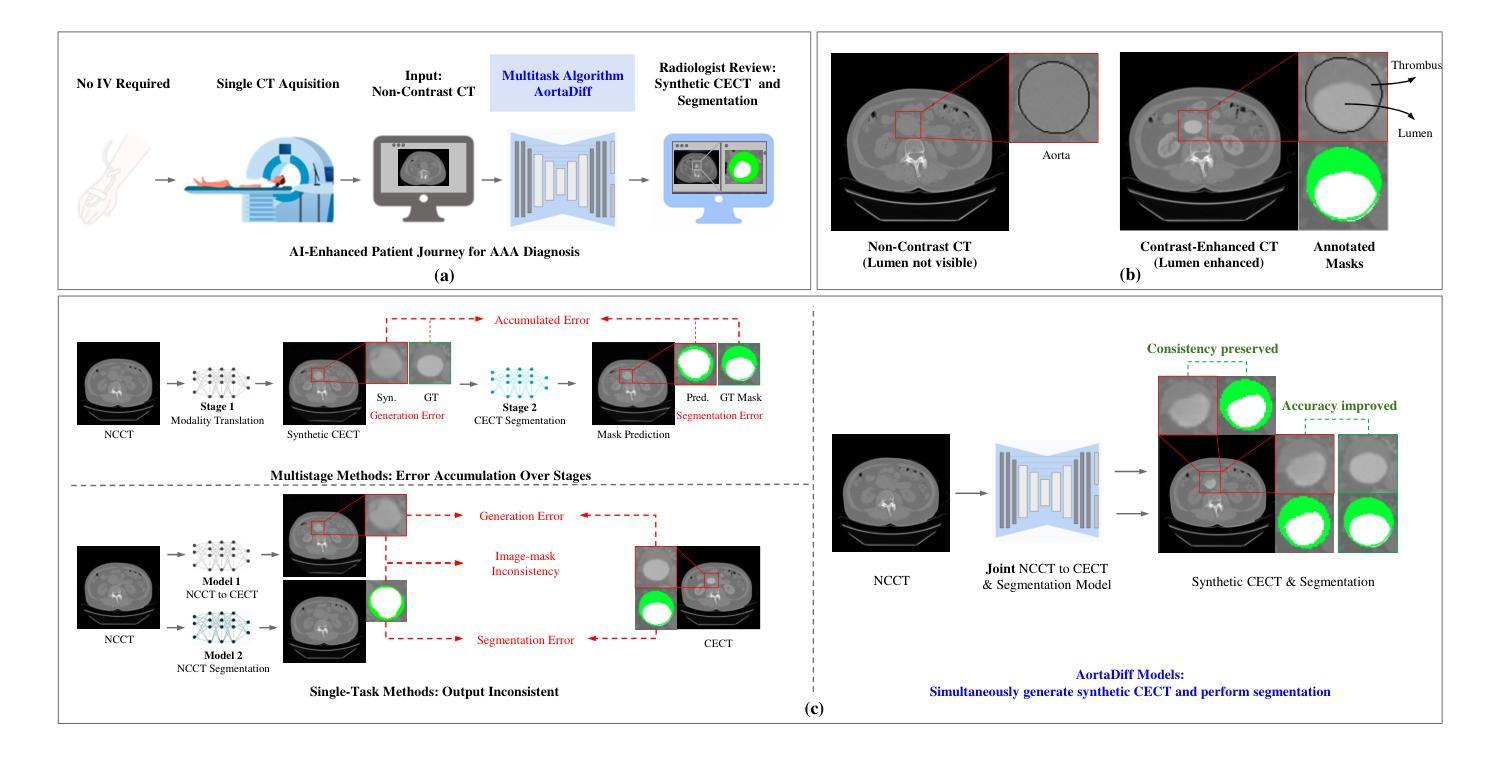
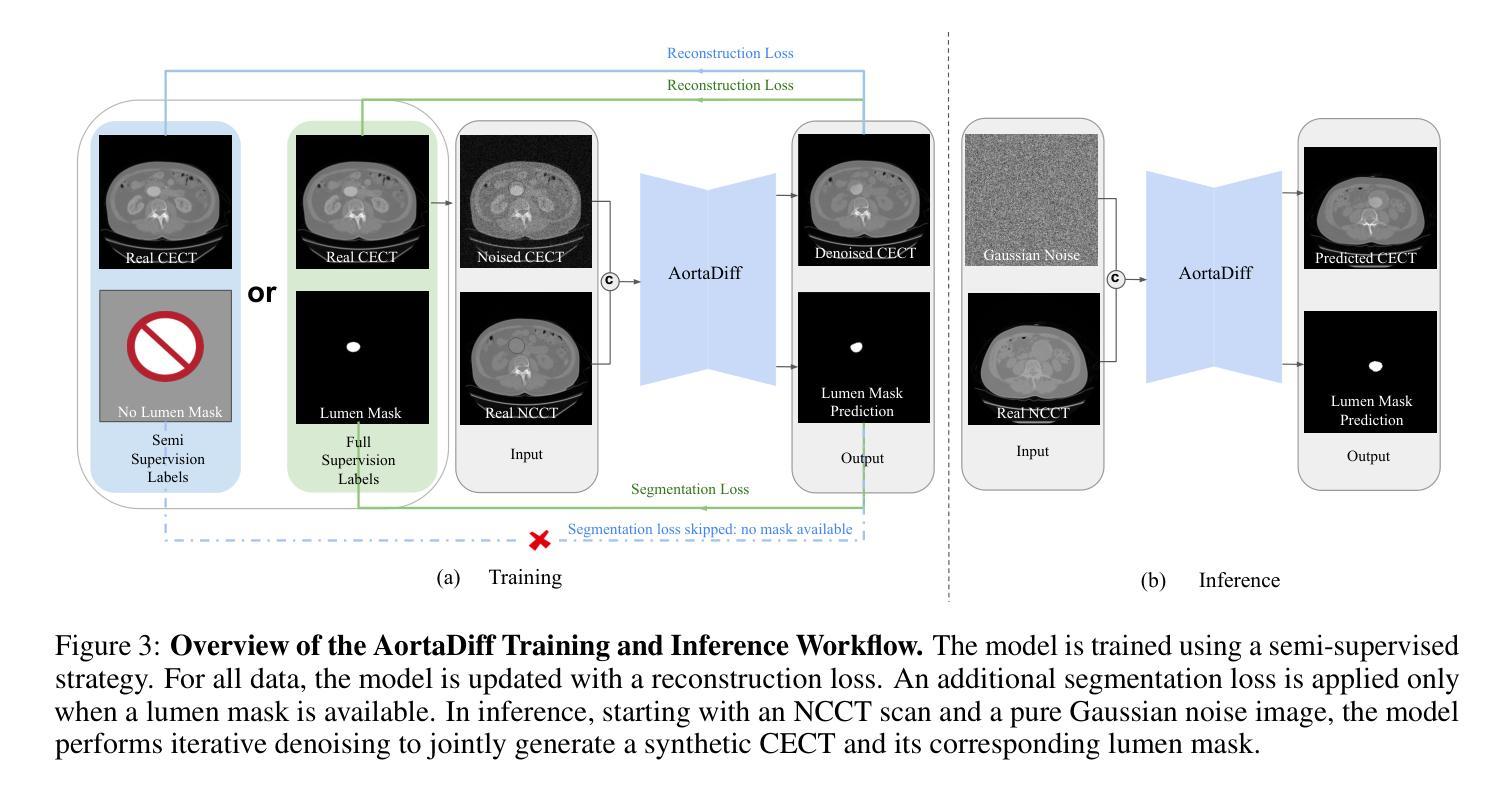
While contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) is standard for assessing abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA), the required iodinated contrast agents pose significant risks, including nephrotoxicity, patient allergies, and environmental harm. To reduce contrast agent use, recent deep learning methods have focused on generating synthetic CECT from non-contrast CT (NCCT) scans. However, most adopt a multi-stage pipeline that first generates images and then performs segmentation, which leads to error accumulation and fails to leverage shared semantic and anatomical structures. To address this, we propose a unified deep learning framework that generates synthetic CECT images from NCCT scans while simultaneously segmenting the aortic lumen and thrombus. Our approach integrates conditional diffusion models (CDM) with multi-task learning, enabling end-to-end joint optimization of image synthesis and anatomical segmentation. Unlike previous multitask diffusion models, our approach requires no initial predictions (e.g., a coarse segmentation mask), shares both encoder and decoder parameters across tasks, and employs a semi-supervised training strategy to learn from scans with missing segmentation labels, a common constraint in real-world clinical data. We evaluated our method on a cohort of 264 patients, where it consistently outperformed state-of-the-art single-task and multi-stage models. For image synthesis, our model achieved a PSNR of 25.61 dB, compared to 23.80 dB from a single-task CDM. For anatomical segmentation, it improved the lumen Dice score to 0.89 from 0.87 and the challenging thrombus Dice score to 0.53 from 0.48 (nnU-Net). These segmentation enhancements led to more accurate clinical measurements, reducing the lumen diameter MAE to 4.19 mm from 5.78 mm and the thrombus area error to 33.85% from 41.45% when compared to nnU-Net. Code is available at https://github.com/yuxuanou623/AortaDiff.git.
在评估腹部主动脉瘤(AAA)时,虽然增强CT(CECT)是标准方法,但所需的碘造影剂存在重大风险,包括肾毒性、患者过敏和环境损害。为了减少造影剂的使用,最近的深度学习方法专注于从非对比CT(NCCT)扫描生成合成CECT。然而,大多数方法采用多阶段流程,先生成图像,然后进行分割,这会导致误差累积,并且未能充分利用共享语义和解剖结构。针对这一问题,我们提出了一种统一的深度学习框架,可以从NCCT扫描生成合成CECT图像,同时分割主动脉腔和血栓。我们的方法将条件扩散模型(CDM)与多任务学习相结合,实现对图像合成和解剖结构分割的端到端联合优化。与之前的多任务扩散模型不同,我们的方法无需进行初步预测(例如粗略分割掩膜),在任务之间共享编码器和解码器参数,并采用半监督训练策略来学习缺失分割标签的扫描数据,这在现实的临床数据中是很常见的约束。我们在一组264名患者身上评估了我们的方法,它始终优于最新的单任务和多阶段模型。在图像合成方面,我们的模型达到了25.61分贝的峰值信噪比(PSNR),高于单任务CDM的23.80分贝。在解剖结构分割方面,它将腔的Dice系数从0.87提高到0.89,并将具有挑战性的血栓Dice系数从0.48提高到0.53(与nnU-Net相比)。这些分割改进带来了更准确的临床测量值,将腔直径的平均绝对误差从5.78毫米减少到4.19毫米,并将血栓面积误差从41.45%减少到33.85%,与nnU-Net相比有明显改善。相关代码可在https://github.com/yuxuanou623/AortaDiff.git上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究采用深度学习技术,从非对比增强CT扫描生成合成对比增强CT图像,同时分割主动脉腔和血栓。该研究采用一体化深度学习框架,结合条件扩散模型和多任务学习,实现图像合成与解剖分割的联合优化。该方法无需初始预测,共享编码器和解码器参数,并采用半监督训练策略学习缺失分割标签的扫描数据。在264例患者中评估,该方法优于单任务和多阶段模型。
关键见解
- 碘化对比剂在腹部主动脉瘤评估中存在风险,包括肾毒性、患者过敏和环境危害。
- 深度学习技术可用于从非对比增强CT扫描生成合成对比增强CT图像,减少对比剂使用。
- 提出的一体化深度学习框架可同时进行图像合成和解剖分割,实现端对端联合优化。
- 方法结合条件扩散模型和多任务学习,无需初始预测,并共享编码器和解码器参数。
- 采用半监督训练策略,能学习缺失分割标签的扫描数据,适应现实临床数据常见约束。
- 在264例患者中的评估结果显示,该方法在图像合成和解剖分割方面均优于现有模型。
- 该方法能提高临床测量的准确性,降低主动脉腔直径和血栓面积的错误率。
点此查看论文截图

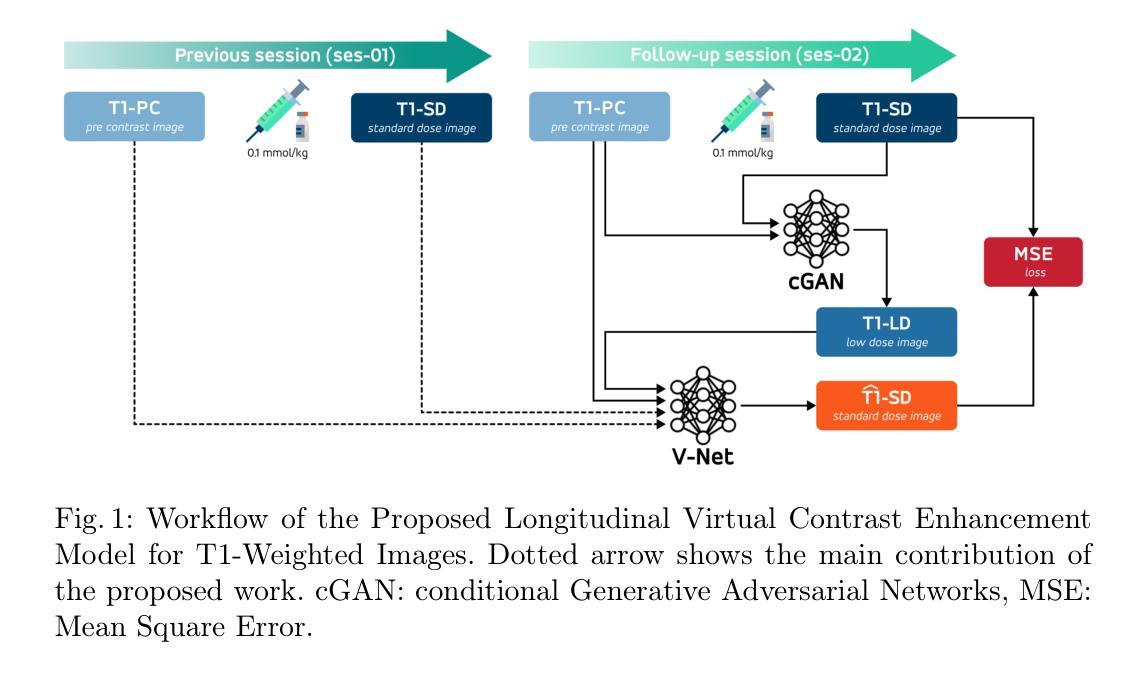
Improving Virtual Contrast Enhancement using Longitudinal Data
Authors:Pierre Fayolle, Alexandre Bône, Noëlie Debs, Philippe Robert, Pascal Bourdon, Remy Guillevin, David Helbert
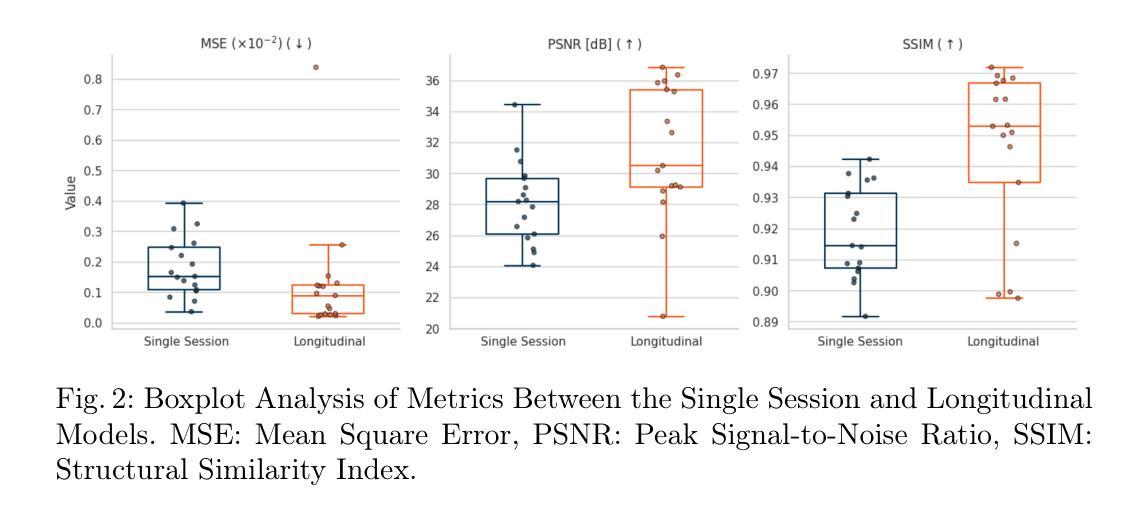
Gadolinium-based contrast agents (GBCAs) are widely used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to enhance lesion detection and characterisation, particularly in the field of neuro-oncology. Nevertheless, concerns regarding gadolinium retention and accumulation in brain and body tissues, most notably for diseases that require close monitoring and frequent GBCA injection, have led to the need for strategies to reduce dosage. In this study, a deep learning framework is proposed for the virtual contrast enhancement of full-dose post-contrast T1-weighted MRI images from corresponding low-dose acquisitions. The contribution of the presented model is its utilisation of longitudinal information, which is achieved by incorporating a prior full-dose MRI examination from the same patient. A comparative evaluation against a non-longitudinal single session model demonstrated that the longitudinal approach significantly improves image quality across multiple reconstruction metrics. Furthermore, experiments with varying simulated contrast doses confirmed the robustness of the proposed method. These results emphasize the potential of integrating prior imaging history into deep learning-based virtual contrast enhancement pipelines to reduce GBCA usage without compromising diagnostic utility, thus paving the way for safer, more sustainable longitudinal monitoring in clinical MRI practice.
钆基造影剂(GBCAs)在磁共振成像(MRI)中广泛应用于病变的检测和特征描述,特别是在神经肿瘤学领域。然而,关于钆在大脑和身体组织中的滞留和积累问题的担忧,特别是在需要密切监测和频繁注射GBCA的疾病中,已经引发了对减少剂量的需求。本研究提出了一种深度学习框架,用于从相应的低剂量采集中对全剂量对比后的T1加权MRI图像进行虚拟对比增强。所提出模型的贡献在于其利用了纵向信息,这是通过融入来自同一病人的先前全剂量MRI检查实现的。与横向单会话模型的比较评估表明,纵向方法在多重建指标方面显著提高图像质量。此外,不同模拟对比度的实验验证了所提出方法的稳健性。这些结果强调了将先前成像历史融入基于深度学习的虚拟对比增强流程中的潜力,可以在不损害诊断价值的情况下减少GBCA的使用,从而为临床MRI实践中更安全、更可持续的纵向监测铺平道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 figures, Workshop MICCAI 2025 - Learning with Longitudinal Medical Images and Data
Summary
该研究利用深度学习框架对低剂量获取的T1加权MRI图像进行虚拟对比增强,实现对全剂量对比后图像的质量提升。研究引入纵向信息,通过融入同一患者的先前全剂量MRI检查数据,提高了图像质量。相较于非纵向的单次会话模型,该方法的图像重建效果更佳。此外,模拟不同对比剂量的实验验证了该方法的稳健性。此研究展示了将前期影像资料融入深度学习虚拟对比增强流程减少GBCA使用量且不影响诊断效用,为临床MRI实践中更安全、可持续的纵向监测开辟了新路径。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注于使用深度学习技术改善低剂量对比剂MRI图像质量,以替代全剂量对比剂。
- 研究利用了纵向信息,即结合患者的先前全剂量MRI检查数据,以提高图像质量评估。
- 与非纵向的单次会话模型相比,引入纵向信息的模型能显著提高图像质量。
- 通过模拟不同对比剂剂量的实验验证了模型的稳健性。
- 此方法可减少对比剂的使用量,降低患者体内钆的滞留和积累风险。
- 集成前期影像资料的深度学习技术可提高诊断效用,为临床MRI实践带来更好的可持续性。
点此查看论文截图