⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-04 更新
FSDENet: A Frequency and Spatial Domains based Detail Enhancement Network for Remote Sensing Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Jiahao Fu, Yinfeng Yu, Liejun Wang
To fully leverage spatial information for remote sensing image segmentation and address semantic edge ambiguities caused by grayscale variations (e.g., shadows and low-contrast regions), we propose the Frequency and Spatial Domains based Detail Enhancement Network (FSDENet). Our framework employs spatial processing methods to extract rich multi-scale spatial features and fine-grained semantic details. By effectively integrating global and frequency-domain information through the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) in global mappings, the model’s capability to discern global representations under grayscale variations is significantly strengthened. Additionally, we utilize Haar wavelet transform to decompose features into high- and low-frequency components, leveraging their distinct sensitivity to edge information to refine boundary segmentation. The model achieves dual-domain synergy by integrating spatial granularity with frequency-domain edge sensitivity, substantially improving segmentation accuracy in boundary regions and grayscale transition zones. Comprehensive experimental results demonstrate that FSDENet achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on four widely adopted datasets: LoveDA, Vaihingen, Potsdam, and iSAID.
为了充分利用遥感图像分割中的空间信息,并解决由灰度变化(如阴影和低对比度区域)引起的语义边缘模糊问题,我们提出了基于频率和空间域的细节增强网络(FSDENet)。我们的框架采用空间处理方法来提取丰富的多尺度空间特征和精细的语义细节。通过全局映射中的快速傅里叶变换(FFT)有效整合全局和频域信息,模型在灰度变化下辨别全局表示的能力得到显著增强。此外,我们利用Haar小波变换将特征分解为高频和低频成分,利用其对不同边缘信息的不同敏感性来优化边界分割。该模型通过整合空间粒度和频域边缘敏感性,实现了双域协同,极大地提高了边界区域和灰度过渡区的分割精度。全面的实验结果表明,FSDENet在四个广泛采用的数据集LoveDA、Vaihingen、Potsdam和iSAID上达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication by IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing
Summary
基于空间信息和频率域技术的细节增强网络(FSDENet)能有效解决遥感图像分割中的语义边缘模糊问题。通过提取丰富的多尺度空间特征和精细语义细节,并结合全局和频率域信息,强化模型在灰度变化下的全局表示能力。利用哈尔小波变换对特征进行高低频分解,提高边界分割的精度。实现空间粒度和频率域边缘敏感性的协同,显著提高边界区域和灰度过渡区的分割精度。在四大数据集上的表现均达到领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- FSDENet网络结合空间信息和频率域技术用于遥感图像分割。
- 提取丰富的多尺度空间特征和精细语义细节,解决语义边缘模糊问题。
- 通过快速傅里叶变换(FFT)融合全局和频率域信息,增强模型在灰度变化下的表示能力。
- 利用哈尔小波变换进行特征分解,提高边界分割精度。
- 实现空间粒度和频率域边缘敏感性的协同,提高分割准确性。
- 在多个数据集上的表现均达到领先水平。
- FSDENet模型对于处理遥感图像的语义分割问题具有实际应用价值。
点此查看论文截图
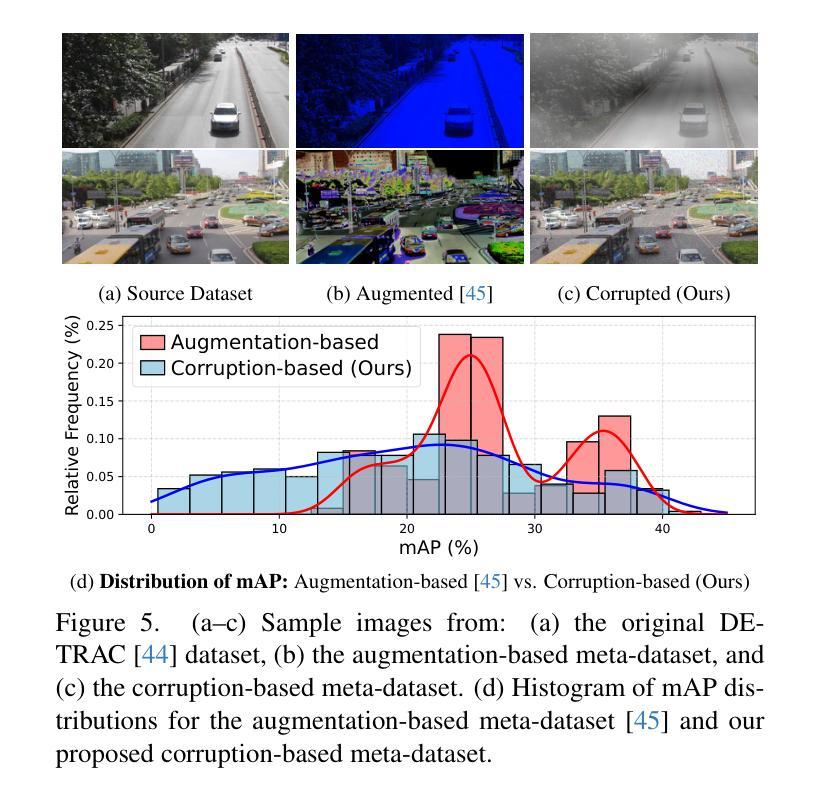
Automated Model Evaluation for Object Detection via Prediction Consistency and Reliability
Authors:Seungju Yoo, Hyuk Kwon, Joong-Won Hwang, Kibok Lee
Recent advances in computer vision have made training object detectors more efficient and effective; however, assessing their performance in real-world applications still relies on costly manual annotation. To address this limitation, we develop an automated model evaluation (AutoEval) framework for object detection. We propose Prediction Consistency and Reliability (PCR), which leverages the multiple candidate bounding boxes that conventional detectors generate before non-maximum suppression (NMS). PCR estimates detection performance without ground-truth labels by jointly measuring 1) the spatial consistency between boxes before and after NMS, and 2) the reliability of the retained boxes via the confidence scores of overlapping boxes. For a more realistic and scalable evaluation, we construct a meta-dataset by applying image corruptions of varying severity. Experimental results demonstrate that PCR yields more accurate performance estimates than existing AutoEval methods, and the proposed meta-dataset covers a wider range of detection performance. The code is available at https://github.com/YonseiML/autoeval-det.
计算机视觉的最新进展使得训练目标检测器更加高效和有效;然而,评估其在现实世界应用中的性能仍然依赖于成本高昂的人工标注。为了解决这个问题,我们为对象检测开发了一个自动化模型评估(AutoEval)框架。我们提出了预测一致性及可靠性(PCR),它利用传统检测器在非最大抑制(NMS)之前生成的多个候选边界框。PCR通过联合测量1)NMS前后框之间的空间一致性,以及2)通过重叠框的置信度得分评估保留框的可靠性,从而估计无真实标签情况下的检测性能。为了进行更真实和可扩展的评估,我们通过应用不同严重程度的图像腐蚀来构建一个元数据集。实验结果表明,PCR产生的性能估计比现有的AutoEval方法更准确,并且所提出的元数据集涵盖了更广泛的检测性能。代码可在https://github.com/YonseiML/autoeval-det找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025 Oral; v2: fixed a typo in the title and updated experimental results
Summary
为应对计算机视觉中目标检测器在现实世界应用性能评估上依赖昂贵人工标注的问题,研究团队提出了自动化模型评估框架(AutoEval)。该框架引入预测一致性及可靠性(PCR),利用常规检测器在进行非极大值抑制(NMS)前产生的多个候选边界框来评估检测性能。PCR通过联合测量1)NMS前后的空间一致性,以及2)保留框的可靠性(通过重叠框的置信度得分),在不依赖真实标签的情况下估算检测性能。为实现更真实、可扩展的评估,研究团队通过应用不同严重程度的图像腐蚀构建了一个元数据集。实验结果表明,PCR较现有的AutoEval方法能更准确地估计性能,且所提元数据集涵盖更广泛的检测性能。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 近期计算机视觉的进步提高了目标检测器的效率和效果。
- 评估目标检测器在现实世界应用中的性能通常依赖昂贵的人工标注,存在局限性。
- 研究团队提出了自动化模型评估框架(AutoEval)来解决这一问题。
- AutoEval中的PCR方法利用边界框的预测一致性和可靠性来评估检测性能,无需真实标签。
- PCR通过测量NMS前后的空间一致性和保留框的可靠性来进行评估。
- 为提高评估的真实性和可扩展性,研究团队构建了元数据集,涵盖不同严重程度的图像腐蚀。
点此查看论文截图

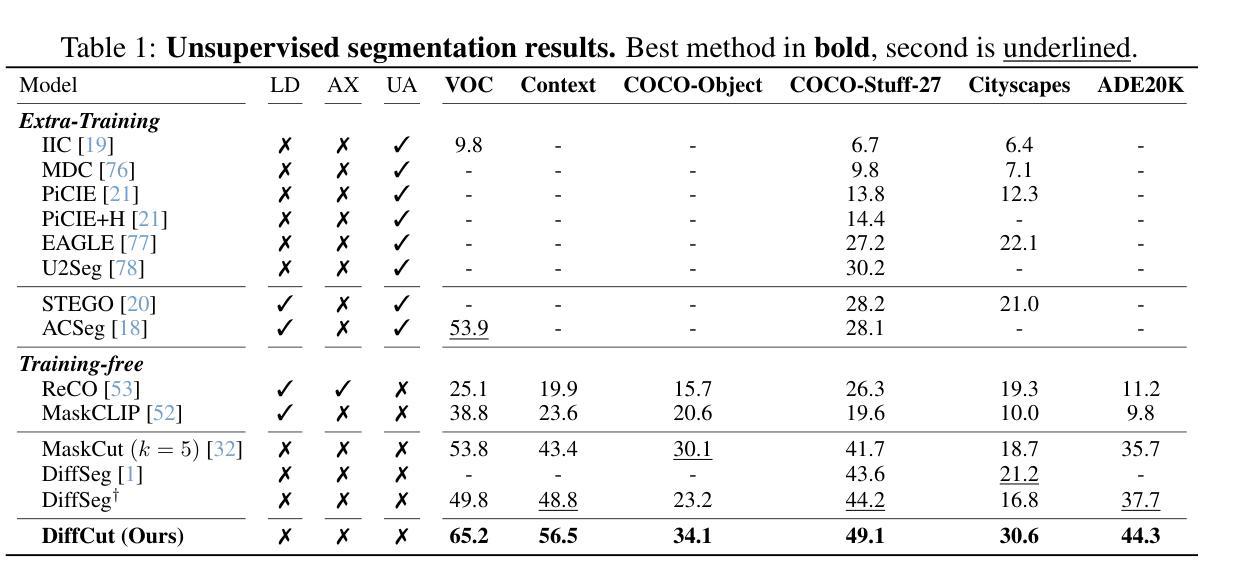
DiffCut: Catalyzing Zero-Shot Semantic Segmentation with Diffusion Features and Recursive Normalized Cut
Authors:Paul Couairon, Mustafa Shukor, Jean-Emmanuel Haugeard, Matthieu Cord, Nicolas Thome
Foundation models have emerged as powerful tools across various domains including language, vision, and multimodal tasks. While prior works have addressed unsupervised image segmentation, they significantly lag behind supervised models. In this paper, we use a diffusion UNet encoder as a foundation vision encoder and introduce DiffCut, an unsupervised zero-shot segmentation method that solely harnesses the output features from the final self-attention block. Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrate that the utilization of these diffusion features in a graph based segmentation algorithm, significantly outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods on zero-shot segmentation. Specifically, we leverage a recursive Normalized Cut algorithm that softly regulates the granularity of detected objects and produces well-defined segmentation maps that precisely capture intricate image details. Our work highlights the remarkably accurate semantic knowledge embedded within diffusion UNet encoders that could then serve as foundation vision encoders for downstream tasks. Project page at https://diffcut-segmentation.github.io
跨语言、视觉和多模态任务等多个领域,基础模型已成为强大的工具。虽然先前的研究已经解决了无监督图像分割的问题,但它们显著落后于监督模型。在本文中,我们使用扩散UNet编码器作为基础视觉编码器,并引入了DiffCut,这是一种无监督零样本分割方法,它仅利用最终自注意块输出的特征。通过广泛的实验,我们证明了在基于图的分割算法中使用这些扩散特征,在零样本分割方面显著优于以前的最先进方法。具体来说,我们利用递归规范化切割算法,该算法可以轻柔地调节检测到的对象的粒度,并产生定义明确的分割图,能够精确捕捉图像细节。我们的工作突出了扩散UNet编码器中嵌入的非常精确语义知识,然后可以作为下游任务的基础视觉编码器。项目页面为:https://diffcut-segmentation.github.io 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024. Project page at https://diffcut-segmentation.github.io. Code at https://github.com/PaulCouairon/DiffCut
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于扩散UNet编码器的新方法——DiffCut,用于零样本图像分割。该方法仅利用最终自注意力块的输出特征,通过基于图的分割算法实现显著优于先前最新技术的方法。通过递归归一化切割算法,可以精细控制检测对象的粒度,并生成精确捕捉图像细节的清晰分割图。本文强调了扩散UNet编码器中嵌入的精确语义知识,可为下游任务提供有力的基础视觉编码器。
Key Takeaways
- 使用扩散UNet编码器作为基础视觉编码器,用于零样本图像分割任务。
- 引入DiffCut方法,结合扩散特征和基于图的分割算法,实现显著优于先前技术的性能。
- 采用递归归一化切割算法,可控制检测对象的粒度。
- 生成精确捕捉图像细节的清晰分割图。
- 强调扩散UNet编码器中嵌入的精确语义知识的重要性。
- 为下游任务提供了有力的基础视觉编码器。
点此查看论文截图