⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-04 更新
InfoMosaic-Bench: Evaluating Multi-Source Information Seeking in Tool-Augmented Agents
Authors:Yaxin Du, Yuanshuo Zhang, Xiyuan Yang, Yifan Zhou, Cheng Wang, Gongyi Zou, Xianghe Pang, Wenhao Wang, Menglan Chen, Shuo Tang, Zhiyu Li, Siheng Chen
Information seeking is a fundamental requirement for humans. However, existing LLM agents rely heavily on open-web search, which exposes two fundamental weaknesses: online content is noisy and unreliable, and many real-world tasks require precise, domain-specific knowledge unavailable from the web. The emergence of the Model Context Protocol (MCP) now allows agents to interface with thousands of specialized tools, seemingly resolving this limitation. Yet it remains unclear whether agents can effectively leverage such tools – and more importantly, whether they can integrate them with general-purpose search to solve complex tasks. Therefore, we introduce InfoMosaic-Bench, the first benchmark dedicated to multi-source information seeking in tool-augmented agents. Covering six representative domains (medicine, finance, maps, video, web, and multi-domain integration), InfoMosaic-Bench requires agents to combine general-purpose search with domain-specific tools. Tasks are synthesized with InfoMosaic-Flow, a scalable pipeline that grounds task conditions in verified tool outputs, enforces cross-source dependencies, and filters out shortcut cases solvable by trivial lookup. This design guarantees both reliability and non-triviality. Experiments with 14 state-of-the-art LLM agents reveal three findings: (i) web information alone is insufficient, with GPT-5 achieving only 38.2% accuracy and 67.5% pass rate; (ii) domain tools provide selective but inconsistent benefits, improving some domains while degrading others; and (iii) 22.4% of failures arise from incorrect tool usage or selection, highlighting that current LLMs still struggle with even basic tool handling.
信息检索是人类的基本需求之一。然而,现有的大型语言模型(LLM)代理主要依赖于开放网页搜索,这暴露了两个基本弱点:在线内容嘈杂且不可靠,许多现实世界的任务需要精确、特定的领域知识,这些在网页上无法获取。模型上下文协议(MCP)的出现现在允许代理与数千种专业工具进行交互,似乎解决了这一限制。然而,仍然不清楚代理是否能有效地利用这些工具——更重要的是,它们是否能将这些工具与通用搜索整合,以解决复杂的任务。因此,我们推出了InfoMosaic-Bench,这是第一个专门为工具增强型代理中的多源信息检索而设计的基准测试。它涵盖了六个代表性领域(医学、金融、地图、视频、网页和多领域集成),要求代理将通用搜索与领域特定工具相结合。任务是通过InfoMosaic-Flow合成的,这是一个可扩展的管道,它以经过验证的工具输出来设定任务条件,强制实施跨源依赖性,并过滤出可以通过简单查找解决的快捷方式案例。这种设计保证了可靠性和非易处理性。与14个最新大型语言模型代理的实验表明,有三个发现:(i)仅依靠网络信息是不够的,GPT-5的准确率和通过率仅为38.2%和67.5%;(ii)领域工具提供了选择性的但不一贯的好处,可以改善某些领域的同时恶化其他领域;(iii)22.4%的失败是由于工具使用或选择不正确造成的,这表明当前的大型语言模型即使在基本工具处理方面仍存在困难。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
信息寻求是人类的基本需求,但现有大型语言模型(LLM)代理主要依赖于开放网页搜索,存在噪声大、可靠性低的问题。为解决此局限性,出现了模型上下文协议(MCP),允许代理与数千种专业工具接口。然而,尚不清楚代理是否能有效利用这些工具,特别是在结合通用搜索解决复杂任务方面。为解决这一问题,引入了InfoMosaic-Bench基准测试,该测试致力于工具增强型代理的多源信息寻求能力。覆盖六个代表性领域,InfoMosaic-Bench要求代理结合通用搜索与领域特定工具。实验表明,仅依赖网络信息不足,GPT-5的准确率和通过率分别仅为38.2%和67.5%;领域工具提供选择性但收益不一,部分领域有所提升而部分则下降;22.4%的失败源于工具使用或选择的错误,表明当前LLM在工具处理方面仍有困难。
Key Takeaways
- 信息寻求对人类至关重要,但LLM在信息获取方面存在局限性。
- LLM依赖开放网页搜索存在噪声和可靠性问题。
- 模型上下文协议(MCP)允许代理与多种专业工具接口,解决了部分局限性。
- InfoMosaic-Bench基准测试是衡量工具增强型代理多源信息寻求能力的关键。
- InfoMosaic-Bench涵盖多个领域,要求结合通用搜索和特定工具。
- 仅依赖网络信息不足,GPT-5表现有限。
点此查看论文截图
The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Scaling Agents for Computer Use
Authors:Gonzalo Gonzalez-Pumariega, Vincent Tu, Chih-Lun Lee, Jiachen Yang, Ang Li, Xin Eric Wang
Computer-use agents (CUAs) hold promise for automating everyday digital tasks, but their unreliability and high variance hinder their application to long-horizon, complex tasks. We introduce Behavior Best-of-N (bBoN), a method that scales over agents by generating multiple rollouts and selecting among them using behavior narratives that describe the agents’ rollouts. It enables both wide exploration and principled trajectory selection, substantially improving robustness and success rates. On OSWorld, our bBoN scaling method establishes a new state of the art (SoTA) at 69.9%, significantly outperforming prior methods and approaching human-level performance at 72%, with comprehensive ablations validating key design choices. We further demonstrate strong generalization results to different operating systems on WindowsAgentArena and AndroidWorld. Crucially, our results highlight the unreasonable effectiveness of scaling CUAs, when you do it right: effective scaling requires structured trajectory understanding and selection, and bBoN provides a practical framework to achieve this.
自动化日常数字任务具有潜力,但计算机使用代理(CUAs)存在不可靠和高方差的问题,阻碍了其在长期复杂任务中的应用。我们引入了行为最佳N(bBoN)方法,它通过生成多个回归来扩展代理选择,并使用描述代理回归的行为叙事来选择它们。它能够实现广泛的探索和有原则的轨迹选择,从而显著提高鲁棒性和成功率。在OSWorld上,我们的bBoN扩展方法建立了新的最新技术状态(SoTA),达到69.9%,显著优于先前的方法并接近人类水平的性能(达到72%),综合全面消除验证了关键的设计选择。我们在WindowsAgentArena和AndroidWorld的不同操作系统上进一步展示出色的泛化结果。重要的是,我们的结果强调了正确扩展CUAs时的不合理有效性:有效的扩展需要结构化轨迹理解和选择,而bBoN提供了一个实现此目标的实用框架。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 7 figures, 10 tables
Summary
计算机使用代理(CUAs)在自动化日常数字任务上具有潜力,但其可靠性和高方差的问题限制了它们在长期复杂任务中的应用。我们引入了行为最佳N(bBoN)方法,它通过生成多个回滚并选择描述代理回滚的行为叙事来扩展多个代理。它实现了广泛的探索和原则性的轨迹选择,显著提高了鲁棒性和成功率。在OSWorld上,我们的bBoN扩展方法建立了新的最佳状态,达到69.9%,显著优于以前的方法并接近人类水平的性能72%,全面的局部研究验证了关键设计选择。我们进一步展示了对不同操作系统的强泛化结果,如在WindowsAgentArena和AndroidWorld上。结果强调了正确扩展CUA的不合理有效性:有效的扩展需要结构化的轨迹理解和选择,而bBoN提供了一个实现这一目标的实用框架。
Key Takeaways
- 计算机使用代理(CUAs)在自动化日常数字任务上具有潜力,但需要解决可靠性和高方差问题以应对长期复杂任务。
- 引入行为最佳N(bBoN)方法,通过生成多个回滚并选择最佳行为叙事来扩展代理性能。
- bBoN方法实现了广泛的探索和原则性的轨迹选择,提高了鲁棒性和成功率。
- 在OSWorld上,bBoN方法达到新的最佳性能,接近人类水平。
- bBoN方法在不同操作系统上展现出强大的泛化能力。
- 有效扩展CUAs需要理解并选择合适的行为轨迹。
点此查看论文截图

StockBench: Can LLM Agents Trade Stocks Profitably In Real-world Markets?
Authors:Yanxu Chen, Zijun Yao, Yantao Liu, Jin Ye, Jianing Yu, Lei Hou, Juanzi Li
Large language models (LLMs) have recently demonstrated strong capabilities as autonomous agents, showing promise in reasoning, tool use, and sequential decision-making. While prior benchmarks have evaluated LLM agents in domains such as software engineering and scientific discovery, the finance domain remains underexplored, despite its direct relevance to economic value and high-stakes decision-making. Existing financial benchmarks primarily test static knowledge through question answering, but they fall short of capturing the dynamic and iterative nature of trading. To address this gap, we introduce StockBench, a contamination-free benchmark designed to evaluate LLM agents in realistic, multi-month stock trading environments. Agents receive daily market signals – including prices, fundamentals, and news – and must make sequential buy, sell, or hold decisions. Performance is assessed using financial metrics such as cumulative return, maximum drawdown, and the Sortino ratio. Our evaluation of state-of-the-art proprietary (e.g., GPT-5, Claude-4) and open-weight (e.g., Qwen3, Kimi-K2, GLM-4.5) models shows that while most LLM agents struggle to outperform the simple buy-and-hold baseline, several models demonstrate the potential to deliver higher returns and manage risk more effectively. These findings highlight both the challenges and opportunities in developing LLM-powered financial agents, showing that excelling at static financial knowledge tasks does not necessarily translate into successful trading strategies. We release StockBench as an open-source resource to support reproducibility and advance future research in this domain.
大型语言模型(LLM)最近作为自主代理展现出了强大的能力,在推理、工具使用和序列决策等方面展现出潜力。虽然先前的基准测试已在软件工程和科学发现等领域评估了LLM代理,但金融领域仍然未被充分探索,尽管它与经济价值和高风险决策直接相关。现有的金融基准测试主要通过问答来测试静态知识,但它们无法捕捉交易的动态和迭代性质。为了弥补这一空白,我们推出了StockBench,这是一个无污染基准测试,旨在评估代理在真实、多月的股票交易环境中的表现。代理每天接收市场信号,包括价格、基本面和新闻,并必须做出连续的买入、卖出或持有决策。性能评估使用金融指标,如累计回报、最大回撤和索提诺比率。我们对最先进的专有(例如GPT-5、Claude-4)和开放权重(例如Qwen3、Kimi-K2、GLM-4.5)模型的评估表明,虽然大多数LLM代理难以超越简单的买入并持有基准线,但一些模型显示出实现更高回报和更有效地管理风险的潜力。这些发现突出了开发LLM驱动的金融代理的挑战和机遇,表明在静态金融知识任务上表现出色并不一定转化为成功的交易策略。我们将StockBench作为开源资源发布,以支持可重复性并推动该领域未来的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在自主代理方面展现出强大的能力,包括推理、工具使用和序列决策。尽管已有基准测试了LLM代理在软件工程和科学发现等领域的应用,但金融领域仍被忽视。为此,我们推出StockBench基准测试,旨在评估LLM代理在真实、多月的股票交易环境中的表现。评估结果显示,虽然大多数LLM代理难以超越简单的买入并持有策略,但一些模型展现出更高的回报和更有效的风险管理潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自主代理方面表现出强大的能力,涵盖推理、工具使用和序列决策。
- 金融领域在LLM研究中被忽视,尽管金融决策具有高价值和高风险。
- 现有金融基准测试主要通过问答评估静态知识,无法捕捉交易的动态和迭代特性。
- 推出StockBench基准测试,评估LLM代理在真实股票交易环境中的表现。
- 评估结果显示,大多数LLM代理难以超越简单买入并持有策略。
- 部分LLM模型展现出更高的回报和更有效的风险管理潜力。
点此查看论文截图
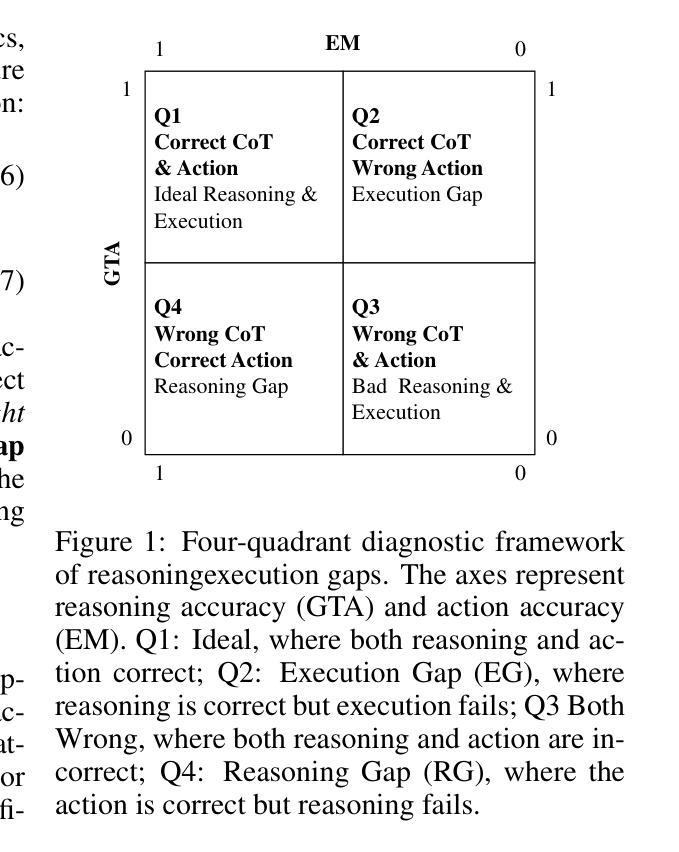
Say One Thing, Do Another? Diagnosing Reasoning-Execution Gaps in VLM-Powered Mobile-Use Agents
Authors:Lingzhong Dong, Ziqi Zhou, Shuaibo Yang, Haiyue Sheng, Pengzhou Cheng, Zongru Wu, Zheng Wu, Gongshen Liu, Zhuosheng Zhang
Mobile-use agents powered by vision-language models (VLMs) have shown great potential in interpreting natural language instructions and generating corresponding actions based on mobile graphical user interface. Recent studies suggest that incorporating chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning tends to improve the execution accuracy. However, existing evaluations emphasize execution accuracy while neglecting whether CoT reasoning aligns with ground-truth actions. This oversight fails to assess potential reasoning-execution gaps, which in turn foster over-trust: users relying on seemingly plausible CoTs may unknowingly authorize harmful actions, potentially resulting in financial loss or trust crisis. In this work, we introduce a new evaluation framework to diagnose reasoning-execution gaps. At its core lies Ground-Truth Alignment (GTA), which measures whether the action implied by a CoT matches the ground-truth action. By combining GTA with the standard Exact Match (EM) metric, we jointly assess both the reasoning accuracy and execution accuracy. This joint perspective reveals two types of reasoning-execution gaps: (i) Execution Gap (EG), where the reasoning correctly identifies the correct action but execution fails, and (ii) Reasoning Gap (RG), where execution succeeds but reasoning process conflicts with the actual execution. Experimental results across a wide range of mobile interaction tasks reveal that reasoning-execution gaps are prevalent, with execution gaps occurring more frequently than reasoning gaps. Moreover, while scaling up model size reduces the overall gap, sizable execution gaps persist even in the largest models. Further analysis shows that our framework reliably reflects systematic EG/RG patterns in state-of-the-art models. These findings offer concrete diagnostics and support the development of more trustworthy mobile-use agents.
由视觉语言模型(VLMs)驱动的使用代理(agent)在手机图形用户界面上解释自然语言指令并生成相应的行动方面显示出巨大的潜力。最近的研究表明,融入思维链(CoT)推理可以提高执行准确性。然而,现有的评估强调执行准确性,却忽略了CoT推理是否与真实行动一致。这种忽视无法评估潜在的推理执行差距,这反过来又可能导致过度信任:用户可能会依赖看似合理的CoT而无意中授权有害行为,可能导致财务损失或信任危机。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个新的评估框架来诊断推理执行差距。其核心在于地面真实对齐(GTA),它衡量的是由CoT暗示的行动是否与地面真实行动相符。通过将GTA与标准的精确匹配(EM)指标相结合,我们共同评估了推理准确性和执行准确性。这种联合视角揭示了两种类型的推理执行差距:(i)执行差距(EG),即推理正确地识别了正确的行动,但执行失败;(ii)推理差距(RG),即执行成功但推理过程与实际执行相冲突。在广泛的移动交互任务上的实验结果表明,推理执行差距普遍存在,执行差距比推理差距更频繁地发生。而且,虽然扩大模型规模会减少总体差距,但在大型模型中仍然存在相当大的执行差距。进一步的分析表明,我们的框架可靠地反映了最先进模型中的系统性EG/RG模式。这些发现提供了具体的诊断支持,并有助于开发更值得信赖的移动使用代理。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了移动使用代理(基于视觉语言模型)在解释自然语言指令和根据移动图形用户界面生成相应动作方面的潜力。研究指出,引入思维链(CoT)推理可以提高执行准确性,但现有评估主要关注执行准确性,忽视CoT推理是否与真实动作一致。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一个新的评估框架,用于诊断推理与执行之间的鸿沟,其中包括对动作一致性进行衡量的“地面真实对齐”(GTA)方法。联合评估结果表明,存在推理与执行鸿沟,其中执行鸿沟(EG)比推理鸿沟(RG)更为常见。尽管扩大模型规模有助于减少总体差距,但执行鸿沟仍然存在。该框架为现有模型提供了可靠的EG/RG模式诊断。
Key Takeaways
- 移动使用代理具有基于视觉语言模型(VLMs)解释自然语言指令和生成相应动作的潜力。
- 引入思维链(CoT)推理能提高执行准确性。
- 现有评估主要关注执行准确性,忽视了推理与实际动作的一致性。
- 提出新的评估框架以诊断推理与执行鸿沟,包括“地面真实对齐”(GTA)方法。
- 存在两种类型的推理与执行鸿沟:执行鸿沟(EG)和推理鸿沟(RG)。
- 执行鸿沟比推理鸿沟更常见,即使模型规模扩大,执行鸿沟仍然存在。
点此查看论文截图
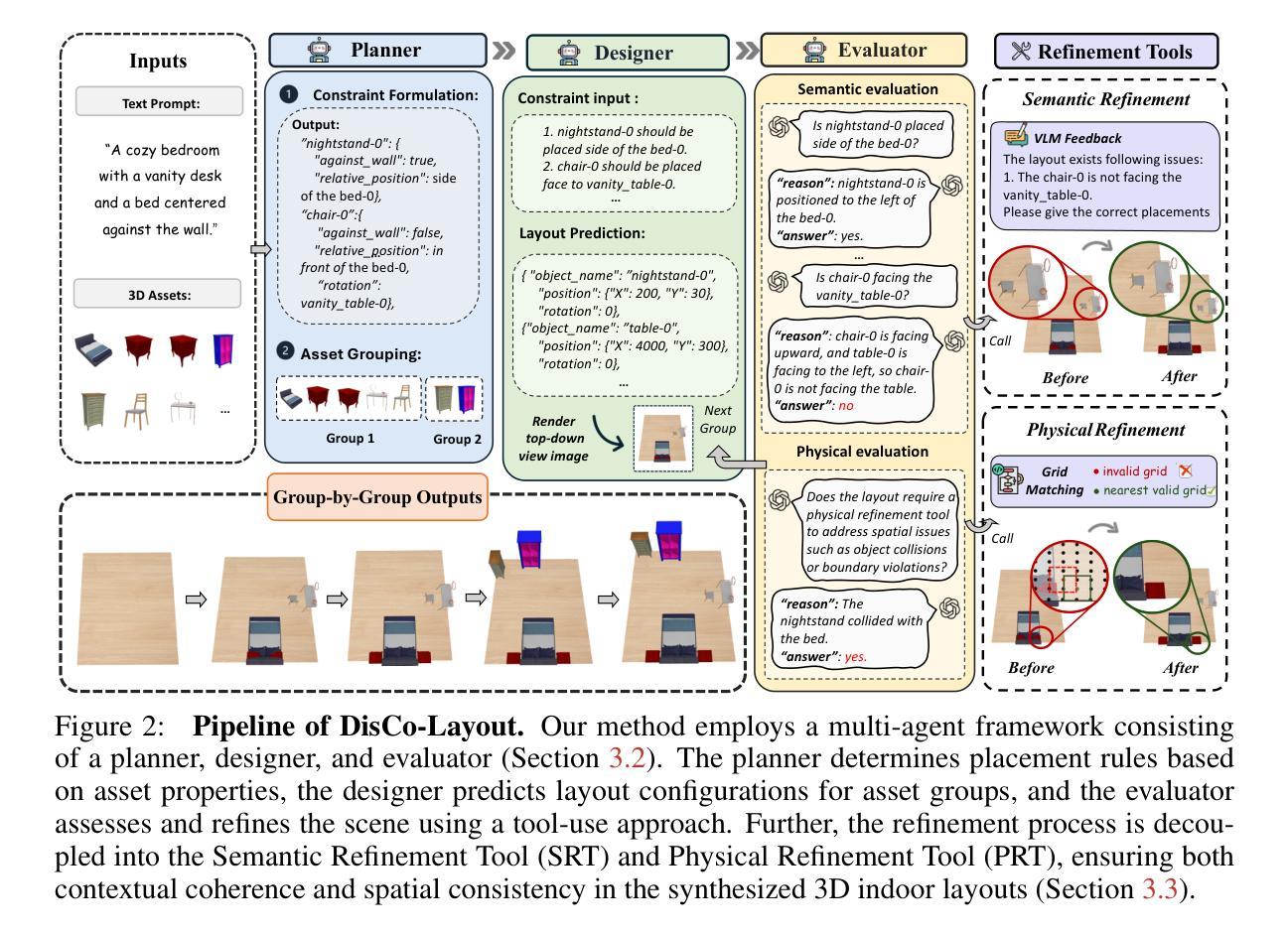
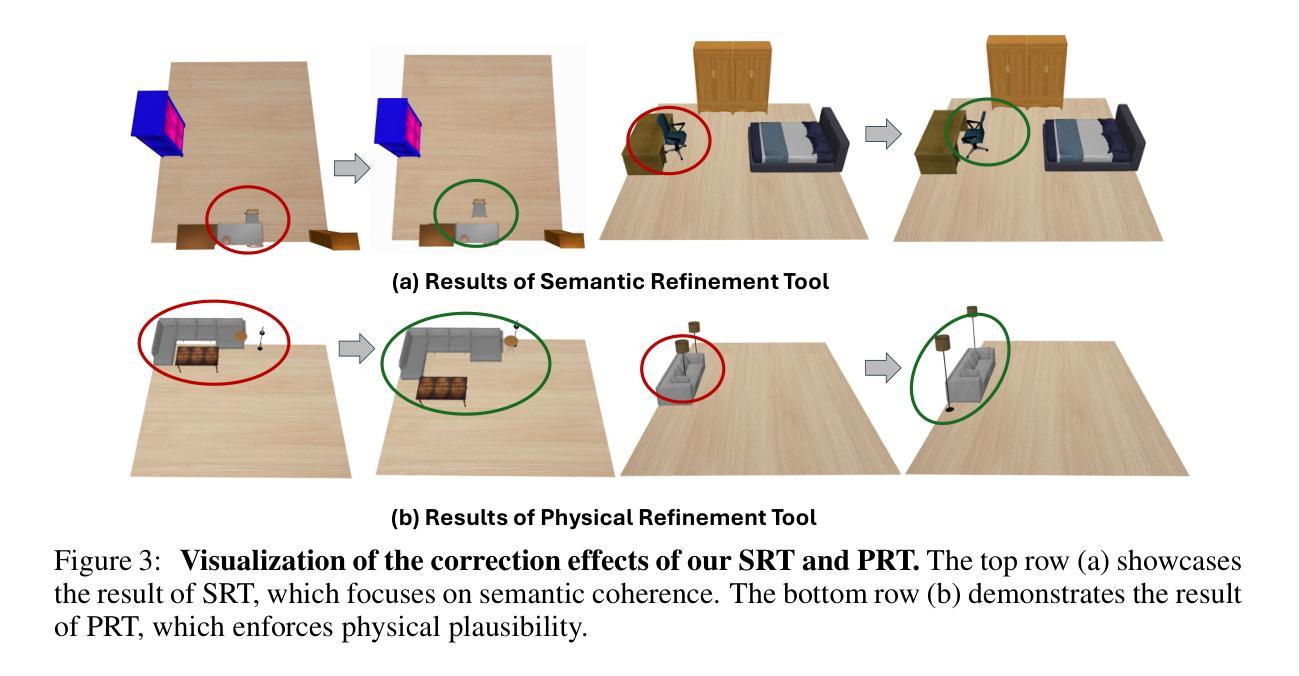
DisCo-Layout: Disentangling and Coordinating Semantic and Physical Refinement in a Multi-Agent Framework for 3D Indoor Layout Synthesis
Authors:Jialin Gao, Donghao Zhou, Mingjian Liang, Lihao Liu, Chi-Wing Fu, Xiaowei Hu, Pheng-Ann Heng
3D indoor layout synthesis is crucial for creating virtual environments. Traditional methods struggle with generalization due to fixed datasets. While recent LLM and VLM-based approaches offer improved semantic richness, they often lack robust and flexible refinement, resulting in suboptimal layouts. We develop DisCo-Layout, a novel framework that disentangles and coordinates physical and semantic refinement. For independent refinement, our Semantic Refinement Tool (SRT) corrects abstract object relationships, while the Physical Refinement Tool (PRT) resolves concrete spatial issues via a grid-matching algorithm. For collaborative refinement, a multi-agent framework intelligently orchestrates these tools, featuring a planner for placement rules, a designer for initial layouts, and an evaluator for assessment. Experiments demonstrate DisCo-Layout’s state-of-the-art performance, generating realistic, coherent, and generalizable 3D indoor layouts. Our code will be publicly available.
三维室内布局合成在创建虚拟环境中起着至关重要的作用。传统的方法由于固定数据集的问题而难以实现普及。虽然最近的LLM和VLM方法提供了更丰富的语义,但它们往往缺乏稳健性和灵活的细化,导致布局不佳。我们开发了DisCo-Layout这一新型框架,可以解开并协调物理和语义细化。对于独立细化,我们的语义细化工具(SRT)可以纠正抽象对象关系,而物理细化工具(PRT)则通过网格匹配算法解决具体的空间问题。对于协作细化,多智能体框架智能地协调这些工具,包括放置规则的规划器、初始布局的的设计师和评估的评估器。实验表明,DisCo-Layout处于领先水平,能够生成现实、连贯和通用的三维室内布局。我们的代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了室内三维布局合成的重要性及其对虚拟环境创建的影响。传统的合成方法受限于固定数据集,难以实现泛化。最近基于LLM和VLM的方法虽然提高了语义丰富性,但在灵活性和鲁棒性方面存在不足,导致布局结果不尽人意。本文提出了一种新型框架DisCo-Layout,该框架能够分离和协调物理和语义的修正,包括独立的修正和协作的修正。独立的修正通过语义修正工具(SRT)和物理修正工具(PRT)实现,分别负责纠正抽象对象关系和解决具体的空间问题。协作修正则通过一个多智能体框架进行工具的智能编排,包括放置规则规划器、初始布局设计师和评估器。实验证明,DisCo-Layout在生成真实、连贯、泛化的室内三维布局方面具有领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 室内三维布局合成在虚拟环境创建中具有重要作用。
- 传统布局合成方法受限于固定数据集,难以实现泛化。
- 基于LLM和VLM的方法虽然提高了语义丰富性,但在灵活性和鲁棒性方面有待提高。
- DisCo-Layout框架能够分离和协调物理和语义的修正。
- DisCo-Layout包括独立的修正(语义修正工具SRT和物理修正工具PRT)和协作的修正(多智能体框架)。
- DisCo-Layout在生成真实、连贯、泛化的室内三维布局方面具有领先水平。
点此查看论文截图
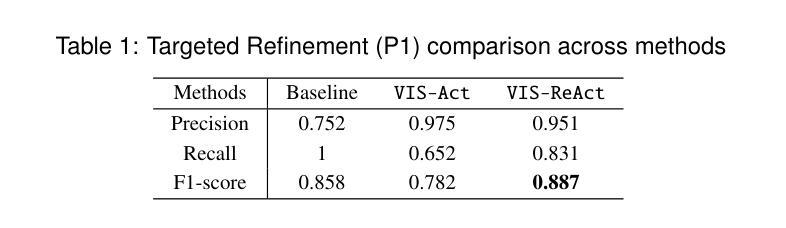
Agentic Reasoning and Refinement through Semantic Interaction
Authors:Xuxin Tang, Rehema Abulikemu, Eric Krokos, Kirsten Whitley, Xuan Wang, Chris North
Sensemaking report writing often requires multiple refinements in the iterative process. While Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in generating initial reports based on human visual workspace representations, they struggle to precisely incorporate sequential semantic interactions during the refinement process. We introduce VIS-ReAct, a framework that reasons about newly-added semantic interactions in visual workspaces to steer the LLM for report refinement. VIS-ReAct is a two-agent framework: a primary LLM analysis agent interprets new semantic interactions to infer user intentions and generate refinement planning, followed by an LLM refinement agent that updates reports accordingly. Through case study, VIS-ReAct outperforms baseline and VIS-ReAct (without LLM analysis) on targeted refinement, semantic fidelity, and transparent inference. Results demonstrate that VIS-ReAct better handles various interaction types and granularities while enhancing the transparency of human-LLM collaboration.
感知报告写作往往需要多次迭代和细化过程。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在基于人类视觉工作空间表示生成初步报告方面显示出潜力,但它们难以在细化过程中精确地融入连续的语义交互。我们引入了VIS-ReAct框架,该框架能够推理视觉工作空间中新增的语义交互,以引导LLM进行报告细化。VIS-ReAct是一个两agent框架:主要LLM分析agent解释新的语义交互来推断用户意图并生成细化计划,然后是相应的LLM细化agent更新报告。通过案例研究,VIS-ReAct在目标细化、语义保真和透明推理方面优于基准和VIS-ReAct(无LLM分析)。结果表明,VIS-ReAct更好地处理了各种交互类型和粒度,同时提高了人-LLM合作的透明度。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
本文介绍了一种名为VIS-ReAct的框架,该框架利用视觉工作空间中的新语义交互来指导大型语言模型(LLM)进行报告改进。VIS-ReAct是一个两阶段的框架,其中包括一个主要的LLM分析代理来解析新语义交互以推断用户意图并生成改进计划,随后是一个LLM改进代理来相应地更新报告。通过案例研究,VIS-ReAct在目标改进、语义保真和透明推理方面优于基线以及没有LLM分析的VIS-ReAct。结果表明,VIS-ReAct能更好地处理各种交互类型和粒度,同时提高了人机协作的透明度。
关键见解
- VIS-ReAct框架结合了视觉工作空间中的新语义交互来指导大型语言模型(LLM)进行报告改进。
- VIS-ReAct是一个两阶段的框架,包括LLM分析代理和LLM改进代理。
- LLM分析代理解析新语义交互以推断用户意图并生成改进计划。
- LLM改进代理根据改进计划更新报告。
- 案例研究表明,VIS-ReAct在目标改进、语义保真和透明推理方面优于基线。
- VIS-ReAct能够处理各种交互类型和粒度。
- VIS-ReAct提高了人机协作的透明度。
点此查看论文截图

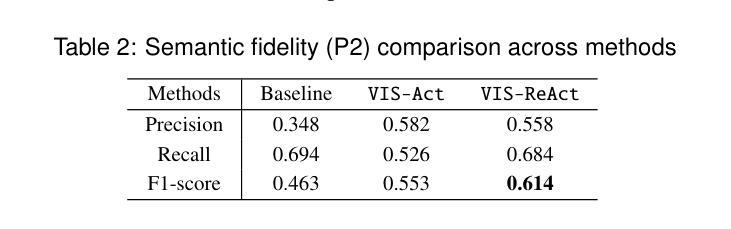
BioinfoMCP: A Unified Platform Enabling MCP Interfaces in Agentic Bioinformatics
Authors:Florensia Widjaja, Zhangtianyi Chen, Juexiao Zhou
Bioinformatics tools are essential for complex computational biology tasks, yet their integration with emerging AI-agent frameworks is hindered by incompatible interfaces, heterogeneous input-output formats, and inconsistent parameter conventions. The Model Context Protocol (MCP) provides a standardized framework for tool-AI communication, but manually converting hundreds of existing and rapidly growing specialized bioinformatics tools into MCP-compliant servers is labor-intensive and unsustainable. Here, we present BioinfoMCP, a unified platform comprising two components: BioinfoMCP Converter, which automatically generates robust MCP servers from tool documentation using large language models, and BioinfoMCP Benchmark, which systematically validates the reliability and versatility of converted tools across diverse computational tasks. We present a platform of 38 MCP-converted bioinformatics tools, extensively validated to show that 94.7% successfully executed complex workflows across three widely used AI-agent platforms. By removing technical barriers to AI automation, BioinfoMCP enables natural-language interaction with sophisticated bioinformatics analyses without requiring extensive programming expertise, offering a scalable path to intelligent, interoperable computational biology.
生物信息学工具对于复杂的计算生物学任务至关重要,然而,它们与新兴的AI代理框架的集成受到不兼容接口、不同的输入输出格式和不一致的参数约定的阻碍。模型上下文协议(MCP)为工具与AI之间的通信提供了标准化的框架,但是将数百个现有的和快速增长的专业生物信息学工具手动转换为符合MCP的服务器是一项劳动密集型且不可持续的任务。在这里,我们提出了BioinfoMCP,一个统一平台,包括两个组件:BioinfoMCP转换器,它使用大型语言模型根据工具文档自动生成可靠的MCP服务器;BioinfoMCP基准测试,它在各种计算任务上系统地验证转换工具的可靠性和通用性。我们展示了一个包含38个由MCP转换的生物信息学工具的平台,经过广泛验证表明,这些工具在三个广泛使用的AI代理平台上成功执行了复杂工作流程的94.7%。通过消除AI自动化的技术障碍,BioinfoMCP实现了与复杂的生物信息学分析的自然语言交互,无需广泛的编程专业知识,为智能、可互操作的计算生物学提供了一条可扩展的道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 8 figures, 3 tables
Summary:
生物信息学工具对于复杂的计算生物学任务至关重要,但其与新兴的AI代理框架的集成受到不兼容接口、异构的输入输出格式和参数约定不一致的阻碍。模型上下文协议(MCP)为工具与人工智能之间的通信提供了标准化框架,但手动将大量现有的和快速增长的专业生物信息学工具转换为MCP兼容服务器是劳动密集型的,且不可持续。本文介绍BioinfoMCP统一平台,包括两个组件:BioinfoMCP转换器,利用大型语言模型自动从工具文档中生成稳健的MCP服务器;BioinfoMCP基准测试系统,系统地验证转换工具在不同计算任务中的可靠性和通用性。本文展示了38个MCP转换的生物信息学工具平台,广泛验证表明,94.7%的工具成功地在三个广泛使用的AI代理平台上执行了复杂的工作流。通过消除人工智能自动化的技术障碍,BioinfoMCP实现了与高级生物信息学分析的自然语言交互,无需广泛的编程专业知识,为智能、可互操作的计算生物学提供了可扩展的路径。
Key Takeaways:
- 生物信息学工具与AI代理框架集成面临挑战,包括接口不兼容、输入输出格式异构和参数约定不一致。
- Model Context Protocol (MCP) 提供工具与AI之间的通信标准化框架。
- BioinfoMCP是一个统一平台,包括BioinfoMCP转换器和BioinfoMCP基准测试系统两个组件。
- BioinfoMCP转换器可自动从工具文档生成稳健的MCP服务器。
- BioinfoMCP基准测试系统验证了转换工具在不同计算任务中的可靠性和通用性。
- 展示了38个MCP转换的生物信息学工具平台,其中94.7%的工具可在三个广泛使用的AI代理平台上成功执行复杂工作流。
点此查看论文截图
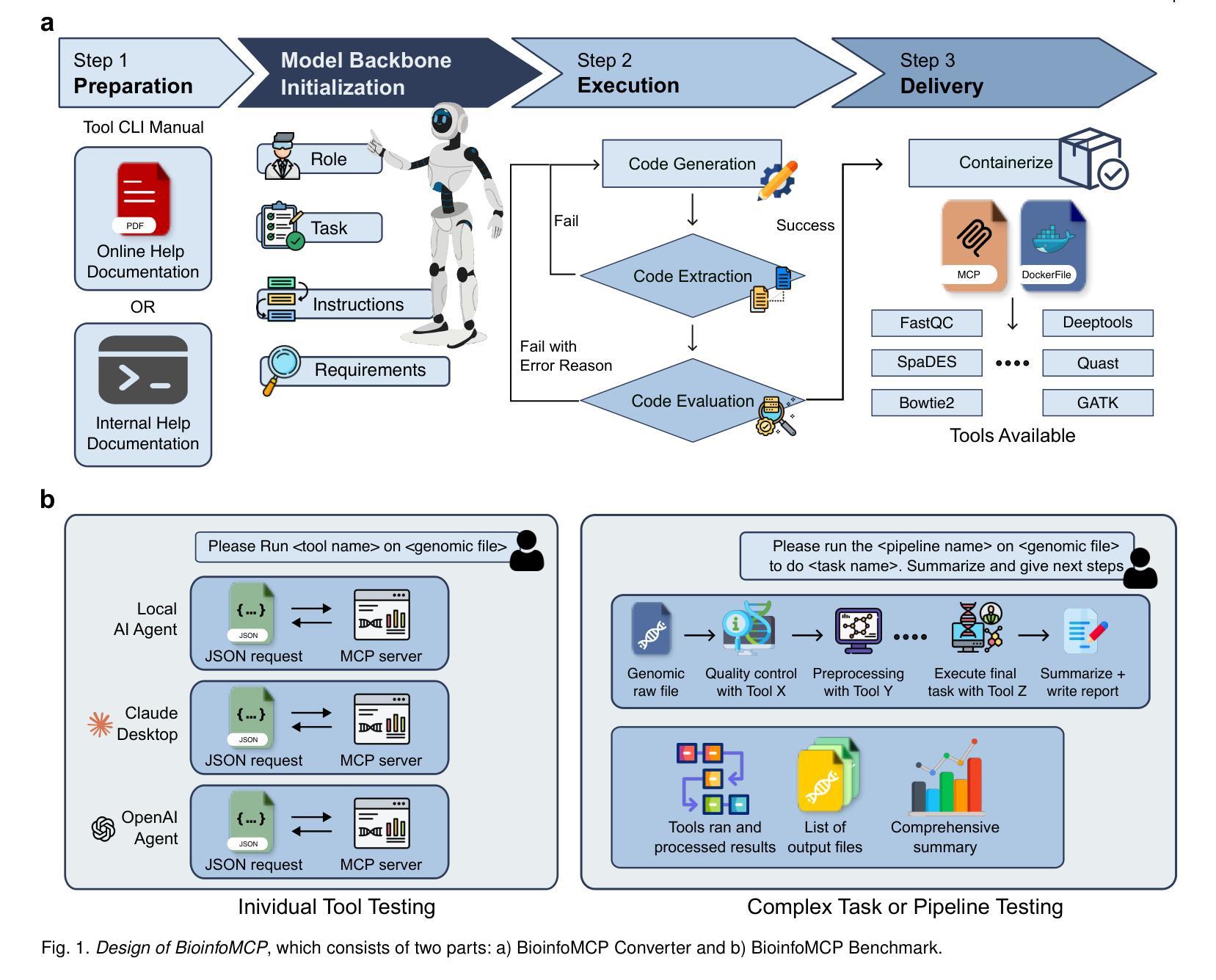
A cybersecurity AI agent selection and decision support framework
Authors:Masike Malatji
This paper presents a novel, structured decision support framework that systematically aligns diverse artificial intelligence (AI) agent architectures, reactive, cognitive, hybrid, and learning, with the comprehensive National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) 2.0. By integrating agent theory with industry guidelines, this framework provides a transparent and stepwise methodology for selecting and deploying AI solutions to address contemporary cyber threats. Employing a granular decomposition of NIST CSF 2.0 functions into specific tasks, the study links essential AI agent properties such as autonomy, adaptive learning, and real-time responsiveness to each subcategory’s security requirements. In addition, it outlines graduated levels of autonomy (assisted, augmented, and fully autonomous) to accommodate organisations at varying stages of cybersecurity maturity. This holistic approach transcends isolated AI applications, providing a unified detection, incident response, and governance strategy. Through conceptual validation, the framework demonstrates how tailored AI agent deployments can align with real-world constraints and risk profiles, enhancing situational awareness, accelerating response times, and fortifying long-term resilience via adaptive risk management. Ultimately, this research bridges the gap between theoretical AI constructs and operational cybersecurity demands, establishing a foundation for robust, empirically validated multi-agent systems that adhere to industry standards.
本文提出一个新的结构化决策支持框架,该框架系统地整合了多种人工智能(AI)代理架构,包括反应型、认知型、混合型和学习型,与全面的国家仪器标准技术研究所(NIST)网络安全框架(CSF)2.0。通过整合代理理论与行业标准,该框架提供了一种透明且分步骤的方法,用于选择和实施AI解决方案,以应对当前的网络安全威胁。通过对NISTCSF 2.0功能的精细分解,研究将AI代理的关键属性(如自主性、自适应学习和实时响应能力)与每个子类的安全要求联系起来。此外,它还概述了不同层次的自主性(辅助型、增强型和完全自主型),以适应处于不同网络安全成熟阶段的组织。这种整体方法超越了孤立的人工智能应用程序,提供了一个统一的检测、事件响应和治理策略。通过概念验证,该框架展示了如何根据现实世界中的约束和风险概况定制AI代理部署,从而提高态势感知能力,加快响应时间,并通过自适应风险管理加强长期韧性。最终,这项研究缩小了理论人工智能和操作网络安全需求之间的差距,为符合行业标准的稳健、实证验证的多代理系统奠定了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 figures, 6 tables, AI agents decision support framework
Summary:
该论文提出了一种新的结构化决策支持框架,该框架系统地整合了多种人工智能(AI)代理架构(反应性、认知性、混合性和学习性)与NIST网络安全框架(CSF 2.0)。通过整合代理理论与行业标准,该框架提供了一种透明且分步的方法,用于选择并部署AI解决方案来应对当前的网络安全威胁。研究将NISTCSF 2.0的功能细化分解为特定任务,并将AI代理的关键属性(如自主性、适应性学习和实时响应能力)与每个子类别的安全要求相关联。此外,它概述了不同层次的自主性(辅助、增强和完全自主),以适应处于不同网络安全成熟阶段的组织。该研究超越了孤立的人工智能应用程序,提供了一种统一的检测、事件响应和治理策略。该框架通过概念验证,展示了如何根据现实世界的约束和风险配置文件定制AI代理部署,增强态势感知,加快响应时间,并通过适应性风险管理加强长期恢复能力。最终,该研究建立了连接理论上的AI结构与实际操作中的网络安全需求之间的桥梁,为遵循行业标准的稳健、经验验证的多代理系统奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways:
- 论文提出了一个结合多种AI代理架构与NIST网络安全框架(CSF 2.0)的新结构化决策支持框架。
- 该框架通过整合代理理论与行业标准,提供了一种选择并部署AI解决方案以应对网络安全威胁的透明且分步的方法。
- 研究将AI代理的关键属性与NISTCSF 2.0的子类别安全要求相关联。
- 框架内包含了不同层次的自主性,以适应不同网络安全成熟阶段的组织。
- 该框架超越了孤立的人工智能应用程序,提供了统一的检测、事件响应和治理策略。
- 通过概念验证,展示了AI代理部署如何增强态势感知,加快响应时间,并通过适应性风险管理加强长期恢复能力。
点此查看论文截图
MetaboT: AI-based agent for natural language-based interaction with metabolomics knowledge graphs
Authors:Madina Bekbergenova, Lucas Pradi, Benjamin Navet, Emma Tysinger, Franck Michel, Matthieu Feraud, Yousouf Taghzouti, Yan Zhou Chen, Olivier Kirchhoffer, Florence Mehl, Martin Legrand, Tao Jiang, Marco Pagni, Soha Hassoun, Jean-Luc Wolfender, Wout Bittremieux, Fabien Gandon, Louis-Félix Nothias
Mass spectrometry metabolomics generates vast amounts of data requiring advanced methods for interpretation. Knowledge graphs address these challenges by structuring mass spectrometry data, metabolite information, and their relationships into a connected network (Gaudry et al. 2024). However, effective use of a knowledge graph demands an in-depth understanding of its ontology and its query language syntax. To overcome this, we designed MetaboT, an AI system utilizing large language models (LLMs) to translate user questions into SPARQL semantic query language for operating on knowledge graphs (Steve Harris 2013). We demonstrate its effectiveness using the Experimental Natural Products Knowledge Graph (ENPKG), a large-scale public knowledge graph for plant natural products (Gaudry et al. 2024).MetaboT employs specialized AI agents for handling user queries and interacting with the knowledge graph by breaking down complex tasks into discrete components, each managed by a specialised agent (Fig. 1a). The multi-agent system is constructed using the LangChain and LangGraph libraries, which facilitate the integration of LLMs with external tools and information sources (LangChain, n.d.). The query generation process follows a structured workflow. First, the Entry Agent determines if the question is new or a follow-up to previous interactions. New questions are forwarded to the Validator Agent, which verifies if the question is related to the knowledge graph. Then, the valid question is sent to the Supervisor Agent, which identifies if the question requires chemical conversions or standardized identifiers. In this case it delegates the question to the Knowledge Graph Agent, which can use tools to extract necessary details, such as URIs or taxonomies of chemical names, from the user query. Finally, an agent responsible for crafting the SPARQL queries equipped with the ontology of the knowledge graph uses the provided identifiers to generate the query. Then, the system executes the generated query against the metabolomics knowledge graph and returns structured results to the user (Fig. 1b). To assess the performance of MetaboT we have curated 50 metabolomics-related questions and their expected answers. In addition to submitting these questions to MetaboT, we evaluated a baseline by submitting them to a standard LLM (GPT-4o) with a prompt that incorporated the knowledge graph ontology but did not provide specific entity IDs. This baseline achieved only 8.16% accuracy, compared to MetaboT’s 83.67%, underscoring the necessity of our multi-agent system for accurately retrieving entities and generating correct SPARQL queries. MetaboT demonstrates promising performance as a conversational question-answering assistant, enabling researchers to retrieve structured metabolomics data through natural language queries. By automating the generation and execution of SPARQL queries, it removes technical barriers that have traditionally hindered access to knowledge graphs. Importantly, MetaboT leverages the capabilities of LLMs while maintaining experimentally grounded query generation, ensuring that outputs remain aligned with domain-specific standards and data structures. This approach facilitates data-driven discoveries by bridging the gap between complex semantic technologies and user-friendly interaction. MetaboT is accessible at [https://metabot.holobiomicslab.eu/], and its source code is available at [https://github.com/HolobiomicsLab/MetaboT].
代谢组学质谱生成大量数据,需要高级方法进行解释。知识图谱通过构建质谱数据、代谢物信息及其关联网络来应对这些挑战(Gaudry等人,2024)。然而,有效利用知识图谱需要对其本体和查询语言语法有深入了解。为了克服这一问题,我们设计了MetaboT,这是一个利用大型语言模型(LLM)将用户问题翻译成SPARQL语义查询语言的AI系统,用于操作知识图谱(Steve Harris,2013)。我们使用实验天然产物知识图谱(ENPKG)演示了其有效性,这是一个用于植物天然产物的大规模公共知识图谱(Gaudry等人,2024)。
MetaboT采用专门的AI代理来处理用户查询并与知识图谱互动,通过将复杂任务分解为离散组件来运作,每个组件由专门的代理管理(图1a)。多代理系统使用LangChain和LangGraph库构建,这些库便于LLM与外部工具和信息资源整合(LangChain,n.d.)。查询生成过程遵循结构化工作流程。首先,入口代理确定问题是新的还是之前的交互的跟进。新问题会转发给验证代理,该代理验证问题是否与知识图谱相关。然后,有效的问题被发送到监督代理,该代理确定问题是否需要化学转换或标准化标识符。在这种情况下,它会将问题委托给知识图谱代理,该代理可以使用工具提取用户查询中的必要细节,如URI或化学名称的分类。最后,一个负责根据知识图谱本体构建SPARQL查询的代理使用提供的标识符来生成查询。然后,系统执行针对代谢组学知识图谱的生成查询并返回结构化结果给用户(图1b)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:知识图谱解决了质谱代谢组学产生的大规模数据解读难题,通过构建代谢物信息及其关系的网络结构。然而,有效使用知识图谱需要深入了解其本体和查询语言语法。为此,研究者设计了MetaboT系统,利用大型语言模型(LLMs)将用户问题翻译成SPARQL语义查询语言,用于操作知识图谱。该系统通过多代理系统实现复杂任务的分解和精细管理,提高了查询效率和准确性。评估显示,MetaboT在处理代谢组学相关问题时表现出高准确性,突出了其作为对话问答助手的潜力。目前MetaboT已公开发布并提供源代码供公众使用。
Key Takeaways:
- 知识图谱是解决质谱代谢组学数据解读难题的重要工具,它通过构建代谢物信息及其关系的网络结构来促进数据理解。
- MetaboT系统利用大型语言模型(LLMs)将用户问题转化为SPARQL查询语言,以操作知识图谱,从而提高查询效率和准确性。
- MetaboT采用多代理系统设计,可以处理复杂任务并精细管理每个任务组件,提高了系统的灵活性和效率。
- 与标准的大型语言模型相比,MetaboT在处理代谢组学相关问题时表现出更高的准确性。
- MetaboT系统有助于弥合了复杂语义技术和用户友好交互之间的鸿沟,促进了数据驱动的发现。
- MetaboT系统已公开发布并提供了源代码供公众使用,为研究人员提供了一个强大的工具来检索结构化代谢组学数据。
点此查看论文截图

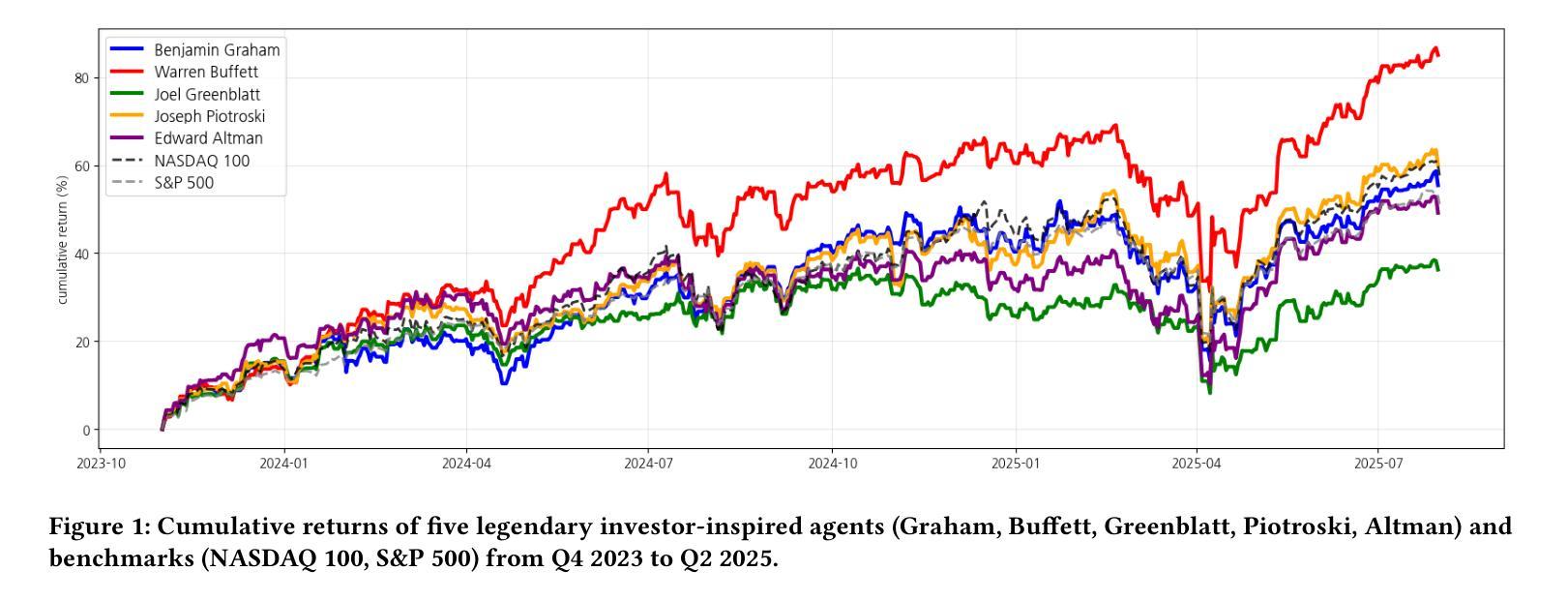
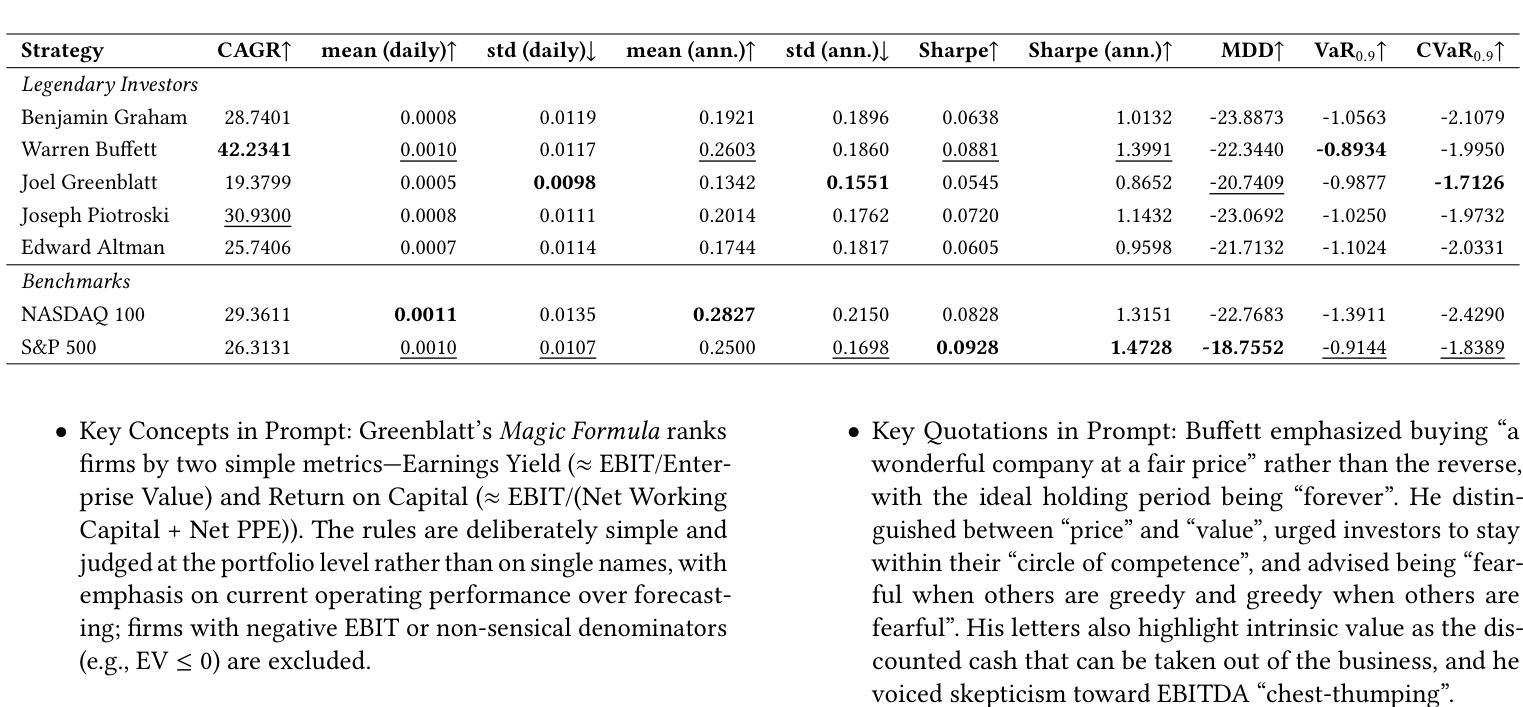
GuruAgents: Emulating Wise Investors with Prompt-Guided LLM Agents
Authors:Yejin Kim, Youngbin Lee, Juhyeong Kim, Yongjae Lee
This study demonstrates that GuruAgents, prompt-guided AI agents, can systematically operationalize the strategies of legendary investment gurus. We develop five distinct GuruAgents, each designed to emulate an iconic investor, by encoding their distinct philosophies into LLM prompts that integrate financial tools and a deterministic reasoning pipeline. In a backtest on NASDAQ-100 constituents from Q4 2023 to Q2 2025, the GuruAgents exhibit unique behaviors driven by their prompted personas. The Buffett GuruAgent achieves the highest performance, delivering a 42.2% CAGR that significantly outperforms benchmarks, while other agents show varied results. These findings confirm that prompt engineering can successfully translate the qualitative philosophies of investment gurus into reproducible, quantitative strategies, highlighting a novel direction for automated systematic investing. The source code and data are available at https://github.com/yejining99/GuruAgents.
本研究表明,GuruAgents(即时引导的人工智能代理)能够系统地实施传奇投资大师的策略。我们通过将他们的独特理念编码成结合金融工具和确定性推理管道的大型语言模型提示,开发出五个独特的GuruAgents,每个Agent旨在模仿标志性投资者。在针对纳斯达克100成分股的从2023年第四季度至2025年第二季度的回测中,GuruAgents展现出受其提示个性驱动的独特行为。巴菲特GuruAgent表现最佳,实现了42.2%的复合年增长率,显著优于基准指数,而其他代理表现各异。这些发现证实,提示工程能够成功地将投资大师们的定性理念转化为可复制的定量策略,为自动化系统化投资指明了新的方向。源代码和数据可在https://github.com/yejining99/GuruAgents找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 Pages, 2 figures
Summary
本文展示了GuruAgents(提示引导的人工智能代理)如何系统地运用传奇投资大师的策略。通过编码五位标志性投资者的独特哲学思想,开发出五个不同的GuruAgents。在一个关于纳斯达克100成分股的回测中,这些GuruAgents表现出了独特的行为特点,巴菲特GuruAgent表现最为出色,取得了高投资回报率,成功实现了预期的投资目标。这项研究证明了提示工程能够成功地将投资大师的定性哲学转化为可复制的定量策略,为自动化系统性投资提供了新颖的方向。源码和数据可在GitHub上找到。
Key Takeaways
- GuruAgents通过模拟五位著名投资者的策略,实现了系统化的投资方法。
- 每个GuruAgent都融合了特定的金融工具和确定性推理流程。
- 在纳斯达克成分股的回测中,GuruAgents表现出独特的行为特征。
- 巴菲特GuruAgent表现最佳,年化收益率显著超过基准水平。
- 提示工程能将投资大师的哲学思想转化为可量化的策略。
- GuruAgents的成功证明了自动化系统性投资的新方向。
点此查看论文截图
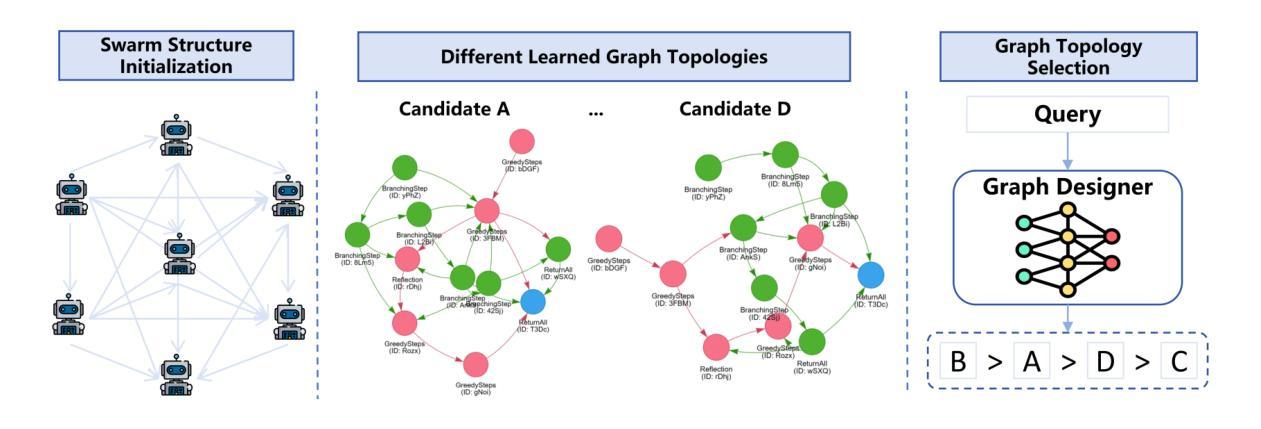
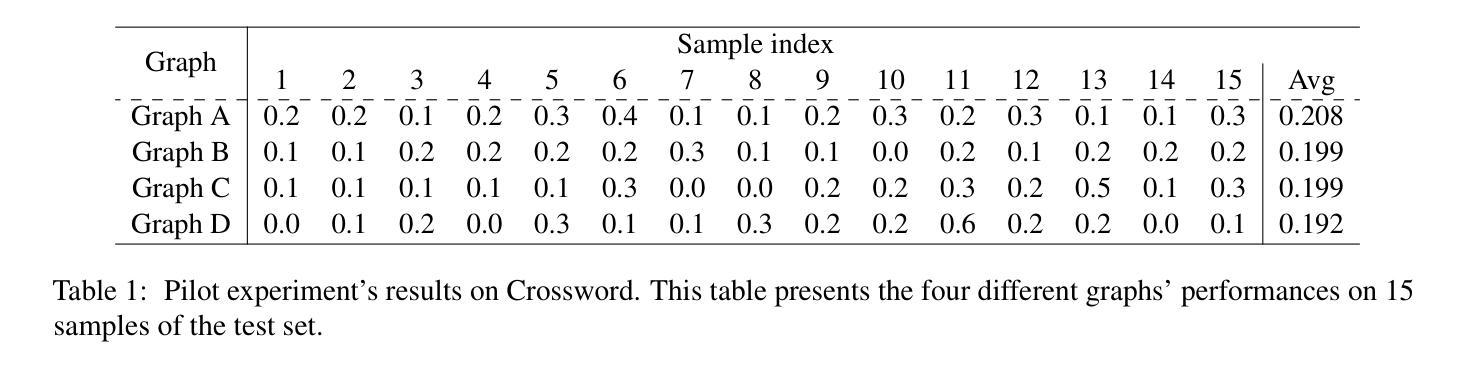
AMAS: Adaptively Determining Communication Topology for LLM-based Multi-Agent System
Authors:Hui Yi Leong, Yuheng Li, Yuqing Wu, Wenwen Ouyang, Wei Zhu, Jiechao Gao
Although large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing capabilities, their practical implementation as autonomous multi-agent systems (MAS) for industrial problem-solving encounters persistent barriers. Conventional MAS architectures are fundamentally restricted by inflexible, hand-crafted graph topologies that lack contextual responsiveness, resulting in diminished efficacy across varied academic and commercial workloads. To surmount these constraints, we introduce AMAS, a paradigm-shifting framework that redefines LLM-based MAS through a novel dynamic graph designer. This component autonomously identifies task-specific optimal graph configurations via lightweight LLM adaptation, eliminating the reliance on monolithic, universally applied structural templates. Instead, AMAS exploits the intrinsic properties of individual inputs to intelligently direct query trajectories through task-optimized agent pathways. Rigorous validation across question answering, mathematical deduction, and code generation benchmarks confirms that AMAS systematically exceeds state-of-the-art single-agent and multi-agent approaches across diverse LLM architectures. Our investigation establishes that context-sensitive structural adaptability constitutes a foundational requirement for high-performance LLM MAS deployments.
尽管大型语言模型(LLM)已经彻底改变了自然语言处理的能力,但它们在作为解决工业问题的自主多智能体系统(MAS)的实际应用中仍然面临持续存在的障碍。传统的MAS架构受到不灵活、手工制作的图形拓扑结构的根本限制,这些拓扑结构缺乏上下文响应能力,导致在多样化的学术和商业工作负载中的效率降低。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了AMAS,这是一个改变范式框架,它通过新型动态图形设计者重新定义了基于LLM的MAS。该组件通过轻量级LLM适配自主确定特定任务的优化图形配置,消除了对通用应用的单一结构模板的依赖。相反,AMAS利用单个输入的固有属性来智能地引导查询轨迹,通过任务优化的智能体路径。在问答、数学推理和代码生成基准测试上的严格验证证实,AMAS在多种LLM架构上系统地超越了最新的单智能体和多智能体方法。我们的调查表明,上下文敏感的结构适应性是高性能LLM MAS部署的基本要求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在自然语言处理方面带来了革命性的进步,但在工业问题解决的自主多智能体系统(MAS)实际应用中仍面临持续障碍。传统MAS架构受限于固定、手工设计的图形拓扑,缺乏上下文响应能力,导致在多种学术和商业工作负载中的效能降低。为克服这些限制,我们推出AMAS框架,通过新型动态图形设计重新定义LLM为基础的MAS。该组件通过轻量级LLM适应自主识别任务特定最优图形配置,消除了对通用结构模板的依赖。相反,AMAS利用个体输入的内在特性,智能引导查询轨迹,通过任务优化代理路径。严格验证表明,AMAS在问答、数学推理和代码生成基准测试中系统地超越了先进单智能体和多智能体方法,在不同LLM架构中表现优异。研究结果表明,高性能LLM MAS部署要求具备上下文敏感的结构适应性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在自主多智能体系统(MAS)实际应用中面临挑战。
- 传统MAS架构受限于固定图形拓扑,缺乏上下文响应能力。
- AMAS框架通过动态图形设计重新定义LLM为基础的MAS。
- AMAS自主识别任务特定最优图形配置,消除对通用结构模板的依赖。
- AMAS利用个体输入的内在特性,智能引导查询轨迹。
- AMAS在多项基准测试中表现超越先进方法,适应不同LLM架构。
- 高性能LLM MAS部署需要上下文敏感的结构适应性。
点此查看论文截图
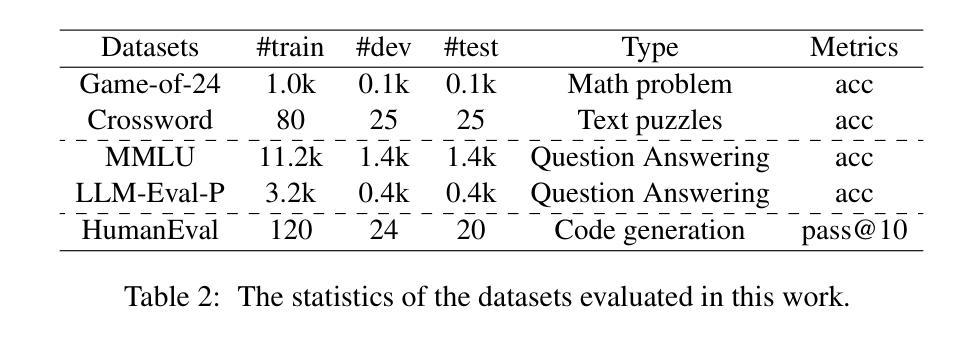
AgentRec: Next-Generation LLM-Powered Multi-Agent Collaborative Recommendation with Adaptive Intelligence
Authors:Bo Ma, Hang Li, ZeHua Hu, XiaoFan Gui, LuYao Liu, Simon Lau
Interactive conversational recommender systems have gained significant attention for their ability to capture user preferences through natural language interactions. However, existing approaches face substantial challenges in handling dynamic user preferences, maintaining conversation coherence, and balancing multiple ranking objectives simultaneously. This paper introduces AgentRec, a next-generation LLM-powered multi-agent collaborative recommendation framework that addresses these limitations through hierarchical agent networks with adaptive intelligence. Our approach employs specialized LLM-powered agents for conversation understanding, preference modeling, context awareness, and dynamic ranking, coordinated through an adaptive weighting mechanism that learns from interaction patterns. We propose a three-tier learning strategy combining rapid response for simple queries, intelligent reasoning for complex preferences, and deep collaboration for challenging scenarios. Extensive experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate that AgentRec achieves consistent improvements over state-of-the-art baselines, with 2.8% enhancement in conversation success rate, 1.9% improvement in recommendation accuracy (NDCG@10), and 3.2% better conversation efficiency while maintaining comparable computational costs through intelligent agent coordination.
交互式对话推荐系统因其通过自然语言交互捕捉用户偏好的能力而受到广泛关注。然而,现有方法在处理动态用户偏好、保持对话连贯性和同时平衡多个排名目标方面面临巨大挑战。本文介绍了AgentRec,一个由大型语言模型驱动的新一代多智能体协同推荐框架,它通过自适应智能的分层智能体网络来解决这些限制。我们的方法采用专门的大型语言模型驱动的智能体进行对话理解、偏好建模、上下文感知和动态排名,通过自适应加权机制进行协调,该机制从交互模式中学习。我们提出了一种三层学习策略,结合快速响应简单查询、智能推理复杂偏好和深度协作应对挑战场景。在三个真实世界数据集上的大量实验表明,AgentRec较最新基线技术实现了一致改进,对话成功率提高2.8%,推荐准确性(NDCG@10)提高1.9%,对话效率提高3.2%,同时通过智能智能体协调保持相当的计算成本。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
交互式对话推荐系统可通过自然语言交互捕捉用户偏好,备受关注。然而,现有方法在处理动态用户偏好、保持对话连贯性和平衡多个排名目标方面面临挑战。本文提出AgentRec,一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的多智能体协作推荐框架,通过分层智能体网络自适应智能解决这些问题。该方法采用专门的大型语言模型驱动的智能体进行对话理解、偏好建模、上下文感知和动态排名,通过自适应加权机制协调,该机制从交互模式中学习。我们提出了一种三层学习策略,结合快速响应简单查询、智能推理复杂偏好和深度协作应对挑战场景。在三个真实数据集上的广泛实验表明,AgentRec较最新基线技术实现了一致改进,对话成功率提高2.8%,推荐准确性(NDCG@10)提高1.9%,对话效率提高3.2%,同时通过智能协调保持相当的计算成本。
Key Takeaways
- 交互式对话推荐系统能够通过自然语言交互捕捉用户偏好。
- 现有方法在处理动态用户偏好、对话连贯性和平衡多个排名目标方面存在挑战。
- AgentRec是一个基于大型语言模型(LLM)的多智能体协作推荐框架,旨在解决上述问题。
- AgentRec通过分层智能体网络自适应智能进行工作,包括对话理解、偏好建模、上下文感知和动态排名等。
- AgentRec采用自适应加权机制进行协调,该机制从交互模式中学习。
- AgentRec采用三层学习策略,以提高处理效率并应对不同复杂度的查询和场景。
点此查看论文截图
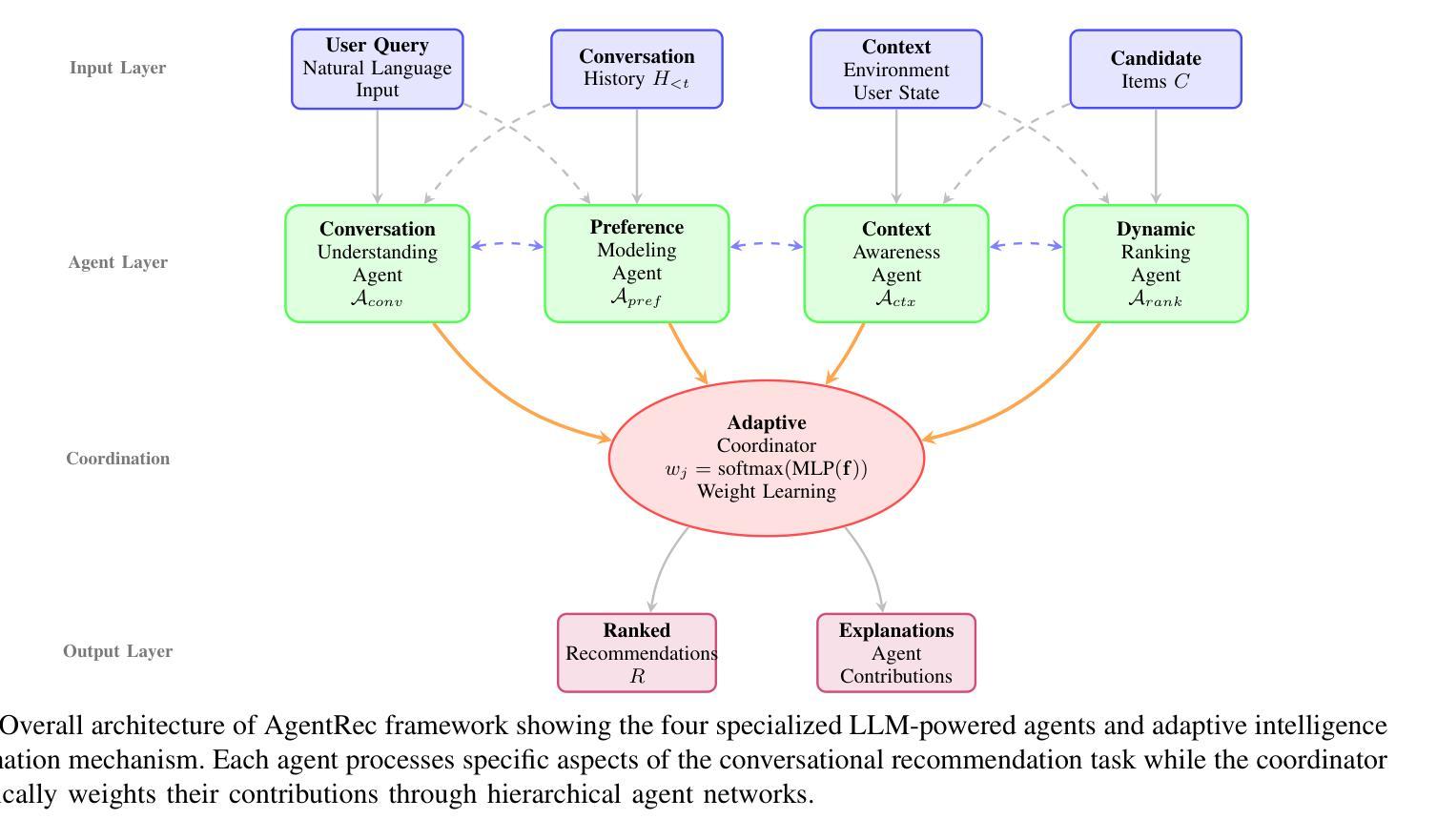
TimeSeriesScientist: A General-Purpose AI Agent for Time Series Analysis
Authors:Haokun Zhao, Xiang Zhang, Jiaqi Wei, Yiwei Xu, Yuting He, Siqi Sun, Chenyu You
Time series forecasting is central to decision-making in domains as diverse as energy, finance, climate, and public health. In practice, forecasters face thousands of short, noisy series that vary in frequency, quality, and horizon, where the dominant cost lies not in model fitting, but in the labor-intensive preprocessing, validation, and ensembling required to obtain reliable predictions. Prevailing statistical and deep learning models are tailored to specific datasets or domains and generalize poorly. A general, domain-agnostic framework that minimizes human intervention is urgently in demand. In this paper, we introduce TimeSeriesScientist (TSci), the first LLM-driven agentic framework for general time series forecasting. The framework comprises four specialized agents: Curator performs LLM-guided diagnostics augmented by external tools that reason over data statistics to choose targeted preprocessing; Planner narrows the hypothesis space of model choice by leveraging multi-modal diagnostics and self-planning over the input; Forecaster performs model fitting and validation and, based on the results, adaptively selects the best model configuration as well as ensemble strategy to make final predictions; and Reporter synthesizes the whole process into a comprehensive, transparent report. With transparent natural-language rationales and comprehensive reports, TSci transforms the forecasting workflow into a white-box system that is both interpretable and extensible across tasks. Empirical results on eight established benchmarks demonstrate that TSci consistently outperforms both statistical and LLM-based baselines, reducing forecast error by an average of 10.4% and 38.2%, respectively. Moreover, TSci produces a clear and rigorous report that makes the forecasting workflow more transparent and interpretable.
时间序列预测在能源、金融、气候和公共卫生等领域中的决策制定中占据核心地位。在实践中,预测人员面临成千上万短暂且嘈杂的时间序列数据,这些数据在频率、质量和范围上各不相同。主要的成本并不在于模型拟合,而在于为了获得可靠预测所需的劳动密集型的预处理、验证和集成。现有的统计和深度学习模型都是针对特定数据集或领域定制的,通用性较差。急需一种通用的、领域无关的框架,尽量减少人为干预。在本文中,我们介绍了TimeSeriesScientist(TSci),这是首个用于通用时间序列预测的LLM驱动的智能框架。该框架包含四个专业代理:Curator通过LLM指导的诊断和外部工具进行推理来选择有针对性的预处理;Planner通过多模式诊断和输入的自规划来缩小模型选择的假设空间;Forecaster执行模型拟合和验证,并根据结果自适应地选择最佳模型配置和集成策略来进行最终预测;Reporter将整个过程综合成全面、透明的报告。通过透明的自然语言理由和全面的报告,TSci将预测工作流程转变为一个既可在任务之间解释又可扩展的白盒系统。在八个既定基准测试上的实证结果表明,TSci在统计和LLM基准测试上表现一致,平均减少预测误差分别为10.4%和38.2%。此外,TSci生成的报告清晰严谨,使预测工作流程更加透明和可解释。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
时间序列预测在不同领域如能源、金融、气候和公共卫生中的决策制定中占据核心地位。在实践中,预测者面临成千上万短暂且嘈杂的数据序列,这些数据序列在频率、质量和时间范围上各不相同,主要成本不在于模型拟合,而在于获得可靠预测所需的劳动密集型的预处理、验证和集成过程。流行的统计和深度学习模型针对特定数据集或领域定制,其泛化能力较差。迫切需要一种通用的、独立于领域的框架,以最小化人工干预。本文介绍了一种名为TimeSeriesScientist(TSci)的LLM驱动的时间序列预测框架,该框架包含四个专门代理:Curator使用LLM引导的诊并在选择针对性预处理时运用外部工具来合理分析数据统计学;Planner通过利用多模式诊断和自我规划选择缩小模型选择假设空间;Forecaster进行模型拟合和验证并根据结果自适应地选择和最终预测的最佳模型配置和集成策略;Reporter将整个流程整合成综合的透明报告。TSci以透明的自然语言理由和全面的报告将预测工作流程转化为一个透明、可解释且可跨任务扩展的白盒系统。在八个基准测试上的实证结果表明,TSci在统计和LLM基准测试上表现优越,平均减少预测误差分别为10.4%和38.2%。此外,TSci生成清晰严格的报告使预测工作流程更加透明和可解释。
关键见解
- 时间序列预测在许多领域中都至关重要,例如能源、金融、气候和公共卫生。
- 当前预测过程中面临的主要挑战包括数据多样性、预处理需求以及模型的泛化能力问题。
- TimeSeriesScientist(TSci)是首个LLM驱动的时间序列预测框架,旨在解决上述问题。
- TSci包含四个专门代理:Curator、Planner、Forecaster和Reporter,分别负责数据诊断、模型选择、模型拟合验证和报告生成。
- TSci通过自然语言解释和全面报告使预测工作流程透明化。
- 在多个基准测试上,TSci表现出卓越的性能,显著优于统计和LLM基线方法。
点此查看论文截图
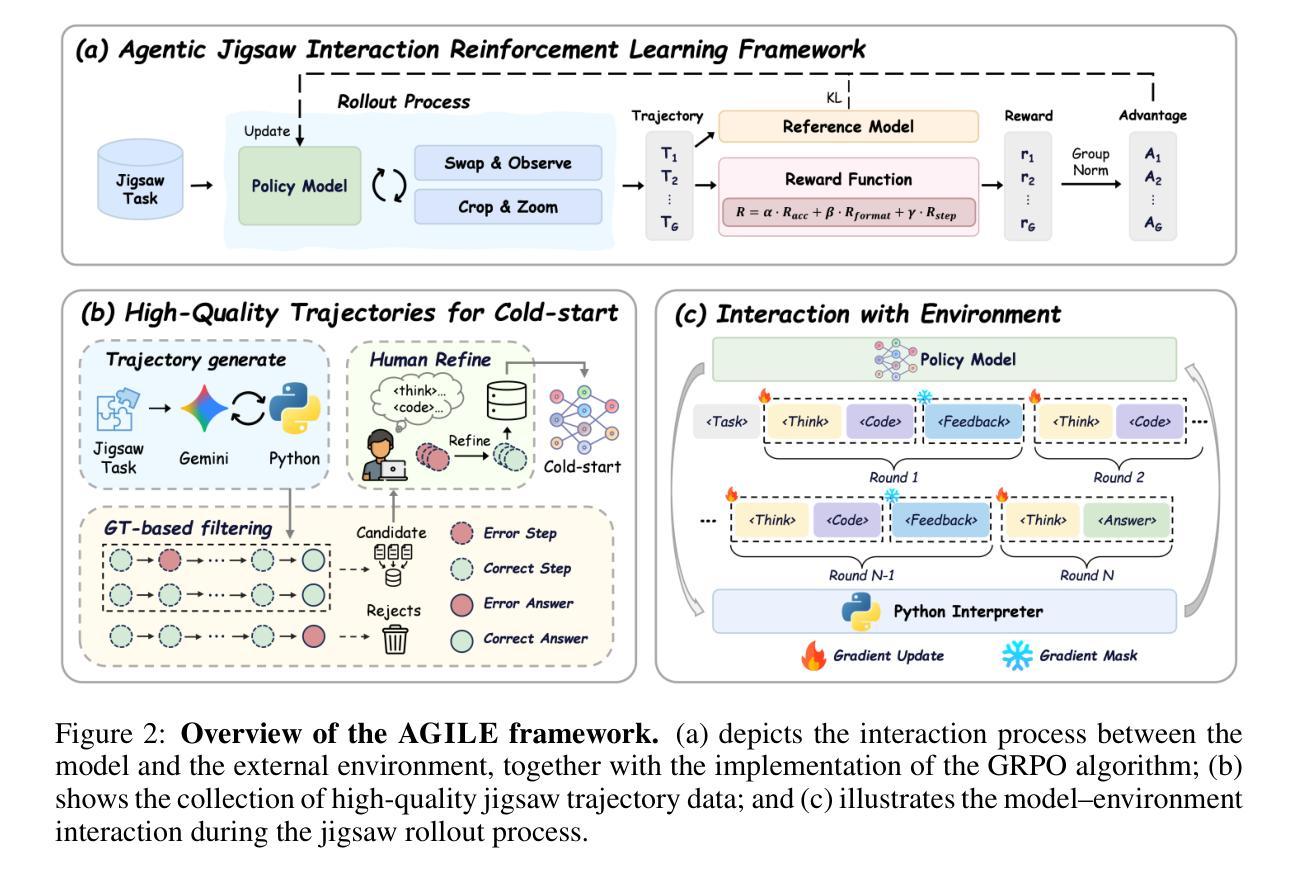
Agentic Jigsaw Interaction Learning for Enhancing Visual Perception and Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Authors:Yu Zeng, Wenxuan Huang, Shiting Huang, Xikun Bao, Yukun Qi, Yiming Zhao, Qiuchen Wang, Lin Chen, Zehui Chen, Huaian Chen, Wanli Ouyang, Feng Zhao
Although current large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have advanced in multimodal understanding and reasoning, their fundamental perceptual and reasoning abilities remain limited. Specifically, even on simple jigsaw tasks, existing VLMs perform near randomly, revealing deficiencies in core perception and reasoning capabilities. While high-quality vision-language data can enhance these capabilities, its scarcity and limited scalability impose significant constraints. To address this, we propose AGILE, an Agentic jiGsaw Interaction Learning for Enhancing visual perception and reasoning in VLMs. AGILE formulates jigsaw solving as an interactive process, enabling the model to progressively engage with the environment. At each step, the model generates executable code to perform an action based on the current state, while the environment provides fine-grained visual feedback to guide task completion. Through this iterative cycle of observation and interaction, the model incrementally improves its perceptual and reasoning capabilities via exploration and feedback. Experimental results show that AGILE not only substantially boosts performance on jigsaw tasks of varying complexity (e.g., increasing accuracy from 9.5% to 82.8% under the 2 $\times$ 2 setting) but also demonstrates strong generalization across 9 general vision tasks, achieving an average improvement of 3.1%. These results indicate notable enhancements in both perceptual and reasoning abilities. This work opens a new avenue for advancing reasoning and generalization in multimodal models and provides an efficient, scalable solution to the scarcity of multimodal reinforcement learning data. The code and datasets is available at https://github.com/yuzeng0-0/AGILE .
尽管当前的视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多模态理解和推理方面取得了进展,但它们的基本感知和推理能力仍然有限。具体来说,即使在简单的拼图任务中,现有的VLMs的表现也接近随机,这暴露了其在核心感知和推理能力上的不足。虽然高质量的视觉语言数据可以增强这些能力,但其稀缺性和有限的可扩展性带来了重大制约。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了AGILE,这是一种用于增强VLMs中视觉感知和推理的基于代理的拼图互动学习(Agentic jiGsaw Interaction Learning)。AGILE将拼图问题的解决过程公式化为一个互动过程,使模型能够逐步与环境进行交互。在每一步中,模型根据当前状态生成可执行代码以执行操作,而环境提供精细的视觉反馈来指导任务的完成。通过观察和互动的迭代循环,模型通过探索和反馈逐步提高其感知和推理能力。实验结果表明,AGILE不仅大大提高了不同复杂程度的拼图任务性能(例如,在2 × 2设置下将准确度从9.5%提高到82.8%),而且在9个通用视觉任务中表现出强大的泛化能力,平均提高了3.1%。这些结果表明感知和推理能力都有了显著的改进。这项工作为提高多模态模型中的推理和泛化能力开辟了新途径,并为解决多模态强化学习数据的稀缺性问题提供了高效、可扩展的解决方案。代码和数据集可在https://github.com/yuzeng0-0/AGILE找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在现有的大型视觉语言模型(VLMs)中,尽管它们在多模态理解和推理方面有所进步,但其基本的感知和推理能力仍然有限。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种名为AGILE的方法,通过拼图解决过程中的互动学习来提升模型的视觉感知和推理能力。AGILE将拼图解决过程转化为一个互动过程,使模型能够逐步与环境互动。实验结果显示,AGILE不仅能显著提升拼图任务的性能,还展现出了良好的泛化能力。代码和数据集已公开分享。
Key Takeaways
- 当前大型视觉语言模型在感知和推理方面存在局限性,即使在简单的拼图任务上也表现不佳。
- AGILE方法通过拼图解决过程中的互动学习来提升模型的视觉感知和推理能力。
- AGILE将拼图任务转化为一个互动过程,模型逐步与环境互动,逐步改进感知和推理能力。
- AGILE显著提升了拼图任务的性能,并在不同复杂度的任务中均表现出良好效果。
- AGILE在九个通用视觉任务上展现出强大的泛化能力。
- AGILE提供了一种解决多模态强化学习数据稀缺问题的有效、可扩展的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

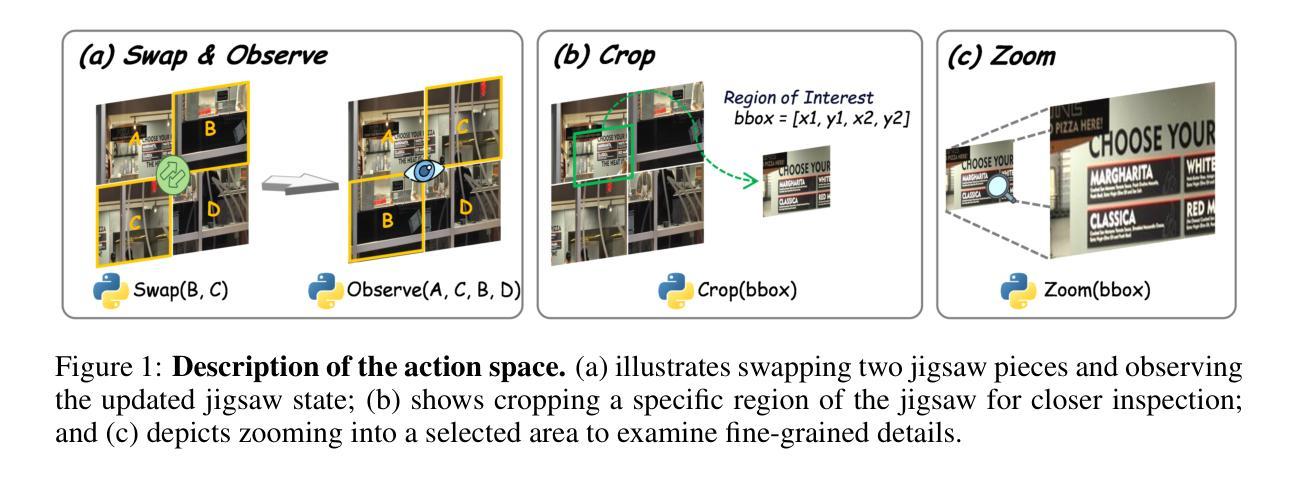
DS-STAR: Data Science Agent via Iterative Planning and Verification
Authors:Jaehyun Nam, Jinsung Yoon, Jiefeng Chen, Tomas Pfister
Data science, which transforms raw data into actionable insights, is critical for data-driven decision-making. However, these tasks are often complex, involving steps for exploring multiple data sources and synthesizing findings to deliver insightful answers. While large language models (LLMs) show significant promise in automating this process, they often struggle with heterogeneous data formats and generate sub-optimal analysis plans, as verifying plan sufficiency is inherently difficult without ground-truth labels for such open-ended tasks. To overcome these limitations, we introduce DS-STAR, a novel data science agent. Specifically, DS-STAR makes three key contributions: (1) a data file analysis module that automatically explores and extracts context from diverse data formats, including unstructured types; (2) a verification step where an LLM-based judge evaluates the sufficiency of the analysis plan at each stage; and (3) a sequential planning mechanism that starts with a simple, executable plan and iteratively refines it based on the DS-STAR’s feedback until its sufficiency is verified. This iterative refinement allows DS-STAR to reliably navigate complex analyses involving diverse data sources. Our experiments show that DS-STAR achieves state-of-the-art performance across three challenging benchmarks: DABStep, KramaBench, and DA-Code. Moreover, DS-STAR particularly outperforms baselines on hard tasks that require processing multiple data files with heterogeneous formats.
数据科学能够将原始数据转化为可操作的见解,对于数据驱动决策至关重要。然而,这些任务通常很复杂,需要探索多个数据源并综合发现以提供有洞察力的答案。虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在自动化此过程中显示出巨大的潜力,但它们经常面临处理异构数据格式的困难,并生成不理想的分析计划。由于没有为这种开放式任务提供真实标签,验证计划的有效性变得极为困难。为了克服这些局限性,我们引入了DS-STAR这一新型数据科学代理。具体来说,DS-STAR做出了三个关键贡献:(1)数据文件分析模块,能够自动探索和提取来自不同数据格式(包括非结构化类型)的上下文;(2)一个验证步骤,使用基于LLM的法官评估每个阶段分析计划的充分性;(3)一个顺序规划机制,它从简单的可执行计划开始,基于DS-STAR的反馈进行迭代优化,直至验证其充分性。这种迭代优化允许DS-STAR可靠地处理涉及多种数据源的复杂分析。我们的实验表明,DS-STAR在DABStep、KramaBench和DA-Code三个具有挑战性的基准测试中达到了最新技术水平。此外,在处理具有异构格式的多数据文件的任务中,DS-STAR尤其超越了基线水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
数据科学能够将原始数据转化为可操作的见解,对于数据驱动决策至关重要。然而,这一过程复杂,涉及探索多个数据源和合成发现以提供深刻答案的步骤。尽管大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动化此过程中显示出巨大潜力,但它们常常处理具有不同格式的数据时遇到困难,并产生次优的分析计划,因为验证计划的充分性对于此类开放任务而言,没有真实标签,本质上很难进行。为了克服这些限制,我们引入了DS-STAR这一新型数据科学代理。DS-STAR有三个主要贡献:一是数据文件分析模块,可自动探索和提取来自各种数据格式(包括非结构化类型)的上下文;二是验证步骤,采用LLM作为法官评估分析计划的充分性;三是顺序规划机制,从简单可执行的计划开始,根据DS-STAR的反馈逐步对其进行改进,直至验证其充分性。这种迭代优化使DS-STAR能够可靠地处理涉及多种数据源的复杂分析。实验表明,DS-STAR在DABStep、KramaBench和DA-Code三个具有挑战性的基准测试中取得了最新技术水平的性能表现。特别是在处理具有不同格式的多数据文件等困难任务时,DS-STAR表现尤为出色。
Key Takeaways
- 数据科学可将原始数据转化为操作建议,是数据驱动决策的核心。
- 大型语言模型在处理复杂数据任务时面临挑战,如处理多种格式的数据和生成最佳分析计划。
- DS-STAR是一个新型数据科学代理,可自动探索多种格式的数据并提取上下文。
- DS-STAR通过LLM法官评估分析计划的充分性。
- DS-STAR采用顺序规划机制,通过迭代优化处理复杂数据分析。
- 实验显示DS-STAR在多个基准测试中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图
Design and Evaluation of Generative Agent-based Platform for Human-Assistant Interaction Research: A Tale of 10 User Studies
Authors:Ziyi Xuan, Yiwen Wu, Xuhai Xu, Vinod Namboodiri, Mooi Choo Chuah, Yu Yang
Designing and evaluating personalized and proactive assistant agents remains challenging due to the time, cost, and ethical concerns associated with human-in-the-loop experimentation. Existing Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) methods often require extensive physical setup and human participation, which introduces privacy concerns and limits scalability. Simulated environments offer a partial solution but are typically constrained by rule-based scenarios and still depend heavily on human input to guide interactions and interpret results. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have introduced the possibility of generative agents that can simulate realistic human behavior, reasoning, and social dynamics. However, their effectiveness in modeling human-assistant interactions remains largely unexplored. To address this gap, we present a generative agent-based simulation platform designed to simulate human-assistant interactions. We identify ten prior studies on assistant agents that span different aspects of interaction design and replicate these studies using our simulation platform. Our results show that fully simulated experiments using generative agents can approximate key aspects of human-assistant interactions. Based on these simulations, we are able to replicate the core conclusions of the original studies. Our work provides a scalable and cost-effective approach for studying assistant agent design without requiring live human subjects. Additional resources and project materials are available at https://dash-gidea.github.io/
设计并评估个性化和主动性的助理代理仍然具有挑战性,因为涉及到人类参与的实验在时间、成本和道德方面的担忧。现有的人机交互(HCI)方法通常需要大量的物理设置和人类参与,这引发了隐私担忧并限制了可扩展性。模拟环境提供了部分解决方案,但通常受限于基于规则的场景,仍然严重依赖于人类输入来指导交互和解释结果。最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进步为能够模拟真实人类行为、推理和社会动态的生成代理的出现提供了可能。然而,它们在模拟人类助理交互方面的有效性尚未得到充分探索。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了一个基于生成代理的模拟平台,旨在模拟人类助理交互。我们确定了关于助理代理的十个早期研究,这些研究涵盖了互动设计的不同方面,并使用我们的模拟平台进行复制研究。结果表明,使用生成代理进行的完全模拟实验可以近似模拟人类助理交互的关键方面。基于这些模拟结果,我们能够复制原始研究的核心结论。我们的工作提供了一种可扩展且经济高效的方法,可以在没有实际人类受试者的情况下研究助理代理设计。有关更多资源和项目材料,请访问:[https://dash-gidea.github.io/]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于人机交互实验的时间、成本和伦理问题,设计并评估个性化主动助理代理仍面临挑战。现有方法需要大规模的物理设置和人类参与,引发隐私担忧并限制了可扩展性。大型语言模型的进步为模拟人类行为和社交动态提供了可能,但在模拟人助交互方面的有效性尚未得到深入研究。本文提出了一个基于生成代理的模拟平台来模拟人助交互,并通过该平台复制了十个关于助理代理的先前研究。结果显示,使用生成代理的完全模拟实验可以近似模拟人助交互的关键方面。基于这些模拟,我们能够复制原始研究的核心结论,提供了一种可扩展且经济高效的研究助理代理设计的方法,无需真人参与。
Key Takeaways
- 人机交互实验存在时间、成本和伦理挑战。
- 现有的人机交互方法需要大规模物理设置和人类参与,引发隐私担忧并限制可扩展性。
- 大型语言模型为模拟人类行为和社交动态提供了可能性。
- 生成代理模拟平台可用于模拟人助交互。
- 通过该平台复制了十个关于助理代理的先前研究,验证了模拟实验的有效性。
- 完全模拟实验可以近似模拟人助交互的关键方面。
点此查看论文截图
AgentDAM: Privacy Leakage Evaluation for Autonomous Web Agents
Authors:Arman Zharmagambetov, Chuan Guo, Ivan Evtimov, Maya Pavlova, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Kamalika Chaudhuri
Autonomous AI agents that can follow instructions and perform complex multi-step tasks have tremendous potential to boost human productivity. However, to perform many of these tasks, the agents need access to personal information from their users, raising the question of whether they are capable of using it appropriately. In this work, we introduce a new benchmark AgentDAM that measures if AI web-navigation agents follow the privacy principle of data minimization''. For the purposes of our benchmark, data minimization means that the agent uses a piece of potentially sensitive information only if it is necessary’’ to complete a particular task. Our benchmark simulates realistic web interaction scenarios end-to-end and is adaptable to all existing web navigation agents. We use AgentDAM to evaluate how well AI agents built on top of GPT-4, Llama-3 and Claude can limit processing of potentially private information, and show that they are prone to inadvertent use of unnecessary sensitive information. We also propose a prompting-based defense that reduces information leakage, and demonstrate that our end-to-end benchmarking provides a more realistic measure than probing LLMs about privacy. Our results highlight that further research is needed to develop AI agents that can prioritize data minimization at inference time.
具有遵循指令并执行复杂多步骤任务能力的自主人工智能代理,在提升人类生产力方面拥有巨大潜力。然而,为了执行这些任务中的许多任务,这些代理需要访问来自其用户的个人信息,这就引发了它们是否能够适当使用这些信息的问题。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个新的基准测试AgentDAM,用于衡量人工智能网络导航代理是否遵循“数据最小化”的隐私原则。在我们的基准测试中,“数据最小化”意味着代理仅在完成特定任务是“必要”时才使用可能敏感的信息。我们的基准测试模拟了端到端的现实网络交互场景,并且能够适应所有现有的网络导航代理。我们使用AgentDAM来评估基于GPT-4、Llama-3和Claude构建的人工智能代理在限制潜在私有信息处理方面的表现,并表明它们容易在不经意间使用不必要的敏感信息。我们还提出了一种基于提示的防御措施,以减少信息泄露,并证明我们的端到端基准测试提供了一种比询问大型语言模型关于隐私问题的更现实的衡量方法。我们的结果强调,需要进一步的研究来开发能够在推理过程中优先考虑数据最小化的代理。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NeurIPS 2025 (D&B track), project page: https://github.com/facebookresearch/ai-agent-privacy
Summary
人工智能代理人在遵循指令和执行复杂多步骤任务方面具有巨大潜力,这有助于提高人类生产力。然而,为了执行这些任务,这些代理人需要访问用户个人信息,引发了它们是否能适当使用这些信息的疑问。本文介绍了一个新的基准测试AgentDAM,用于衡量AI网页导航代理人是否符合“数据最小化”的隐私原则。在我们的基准测试中,数据最小化意味着代理人仅在完成特定任务“必需”时才使用可能敏感的信息。我们的基准测试模拟了端到端的现实网页互动场景,并适应所有现有的网页导航代理人。我们利用AgentDAM评估基于GPT-4、Llama-3和Claude构建的AI代理人在限制潜在私有信息的处理方面的表现,并指出他们容易在无意中使用了不必要的敏感信息。我们还提出了一种基于提示的防御手段来减少信息泄露,并证明我们的端到端基准测试比询问大型语言模型关于隐私的问题提供了更现实的衡量方法。我们的研究结果强调,需要进一步研发能在推理时优先考虑数据最小化的AI代理人。
Key Takeaways
- 自主AI代理人在提高人类生产力方面具有巨大潜力,特别是在遵循指令和执行复杂多步骤任务方面。
- AI代理人需要访问用户个人信息来执行许多任务,引发关于其是否能适当使用这些信息的疑问。
- 引入了一个新的基准测试AgentDAM,以衡量AI网页导航代理人是否符合“数据最小化”的隐私原则。
- 数据最小化意味着代理人仅在完成特定任务必需时才使用可能敏感的信息。
- AgentDAM模拟了端到端的现实网页互动场景,并适应所有现有的网页导航代理人。
- 基于GPT-4、Llama-3和Claude的AI代理人在限制潜在私有信息的处理方面存在不足,容易在无意中使用了不必要的敏感信息。
点此查看论文截图

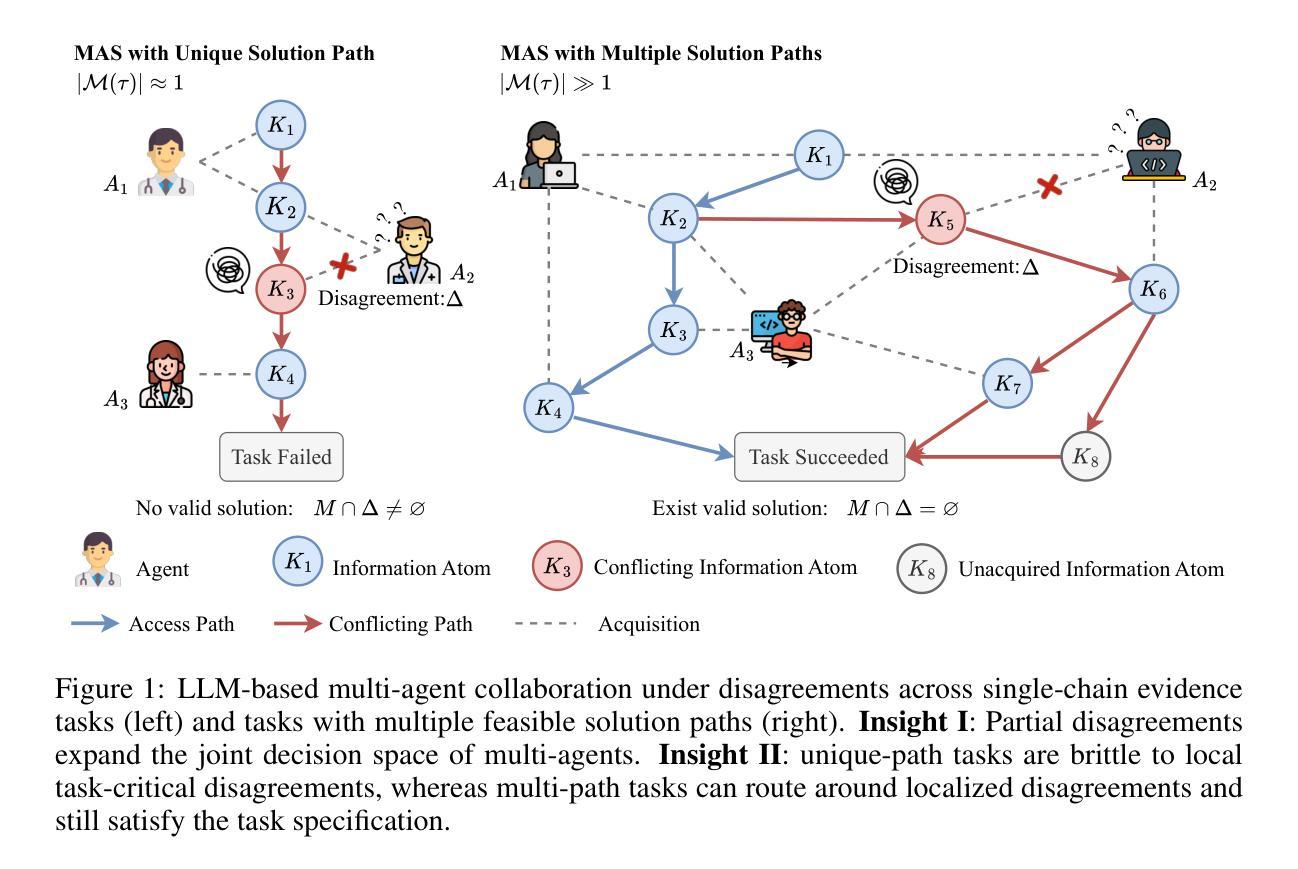
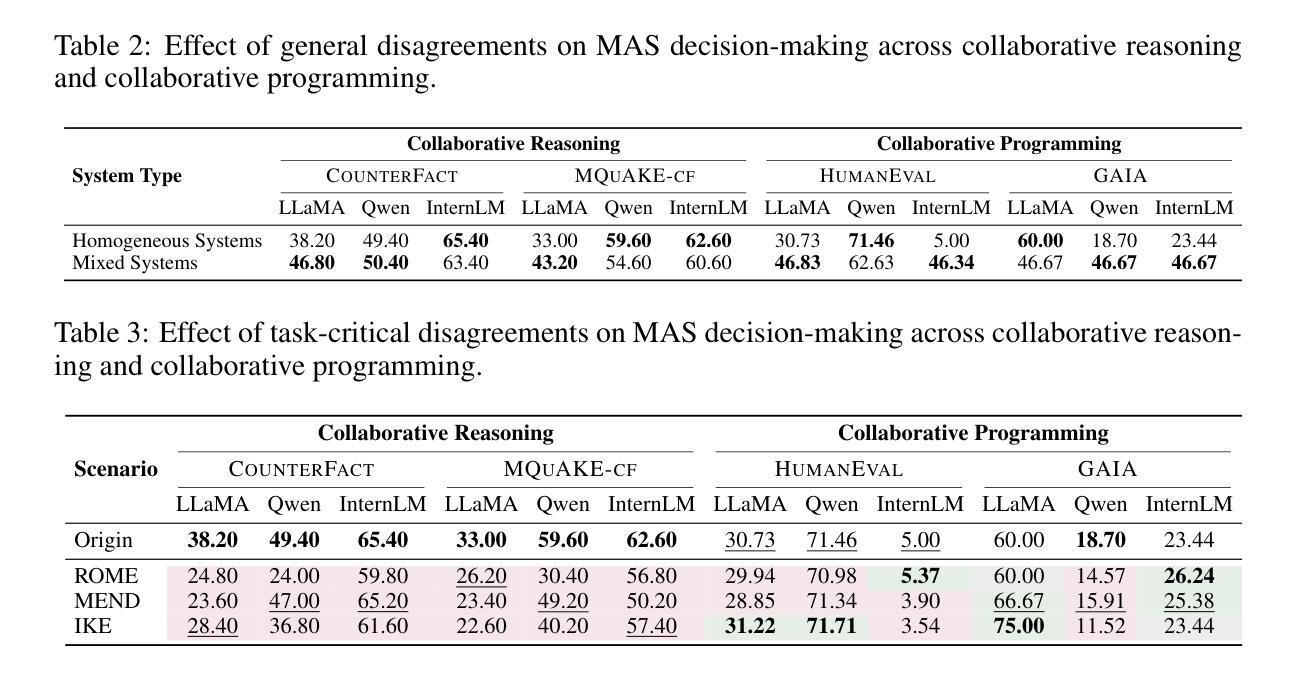
When Disagreements Elicit Robustness: Investigating Self-Repair Capabilities under LLM Multi-Agent Disagreements
Authors:Tianjie Ju, Bowen Wang, Hao Fei, Mong-Li Lee, Wynne Hsu, Yun Li, Qianren Wang, Pengzhou Cheng, Zongru Wu, Haodong Zhao, Zhuosheng Zhang, Gongshen Liu
Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have upgraded them from sophisticated text generators to autonomous agents capable of cooperation and tool use in multi-agent systems (MAS). However, it remains unclear how disagreements shape collective decision-making. In this paper, we revisit the role of disagreement and argue that general, partially overlapping disagreements prevent premature consensus and expand the explored solution space, while disagreements on task-critical steps can derail collaboration depending on the topology of solution paths. We investigate two collaborative settings with distinct path structures: collaborative reasoning (CounterFact, MQuAKE-cf), which typically follows a single evidential chain, whereas collaborative programming (HumanEval, GAIA) often adopts multiple valid implementations. Disagreements are instantiated as general heterogeneity among agents and as task-critical counterfactual knowledge edits injected into context or parameters. Experiments reveal that general disagreements consistently improve success by encouraging complementary exploration. By contrast, task-critical disagreements substantially reduce success on single-path reasoning, yet have a limited impact on programming, where agents can choose alternative solutions. Trace analyses show that MAS frequently bypasses the edited facts in programming but rarely does so in reasoning, revealing an emergent self-repair capability that depends on solution-path rather than scale alone. Our code is available at https://github.com/wbw625/MultiAgentRobustness.
最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进步使其从复杂的文本生成器升级为能够在多智能体系统(MAS)中进行合作和使用工具的自主动剂。然而,尚不清楚分歧如何影响集体决策。本文重新审视了分歧的作用,并认为普遍存在的部分重叠分歧能防止过早达成共识并扩大探索的解空间,而关于任务关键步骤的分歧可能会根据解决方案路径的拓扑结构阻碍协作。我们研究了两种具有不同路径结构的协作环境:通常遵循单一证据链的协作推理(CounterFact、MQuAKE-cf),以及通常采用多种有效实现的协作编程(HumanEval、GAIA)。分歧被实例化为智能体之间的普遍异质性,以及注入上下文或参数中的任务关键反事实知识编辑。实验表明,普遍的分歧通过鼓励互补探索来持续提高成功率。相比之下,任务关键的分歧会极大地减少单一路径推理的成功率,但对编程的影响有限,因为智能体可以选择替代解决方案。轨迹分析显示,MAS在编程中会经常绕过编辑的事实,但在推理中很少这样做,这表明出现了一种依赖解决方案路径而非单一规模的自我修复能力。我们的代码可从 https://github.com/wbw6e利用查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Working in progress
Summary
近期大型语言模型(LLM)的进步使其从高级文本生成器升级为具备协作和工具使用能力的多智能体系统(MAS)。本文探讨了分歧在集体决策中的角色,认为普遍性的部分重叠分歧能防止过早达成共识并扩大解决方案的探索空间,而针对任务关键步骤的分歧可能会破坏协作,这取决于解决方案路径的拓扑结构。实验表明,一般性分歧通过鼓励互补性探索来持续提高成功率。相比之下,任务关键分歧对单一路径推理的成功率产生较大负面影响,但对编程的影响有限。分析显示,MAS在编程时经常绕过修改的事实,而在推理时则很少这样做,显示出一种新兴的自我修复能力,这取决于解决方案路径而不是规模本身。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)已从文本生成器发展为多智能体系统(MAS)的自主代理。
- 普遍的部分重叠分歧能扩大解决方案的探索空间并防止过早达成共识。
- 任务关键步骤的分歧可能对协作产生负面影响,取决于解决方案路径的拓扑结构。
- 一般性分歧有助于提高成功率,通过鼓励互补性探索实现。
- 任务关键分歧对单一路径推理成功率影响较大,但对编程影响有限。
- 多智能体系统在编程时表现出新兴的自我修复能力,这取决于解决方案路径而非规模。
点此查看论文截图