⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-04 更新
VIRTUE: Visual-Interactive Text-Image Universal Embedder
Authors:Wei-Yao Wang, Kazuya Tateishi, Qiyu Wu, Shusuke Takahashi, Yuki Mitsufuji
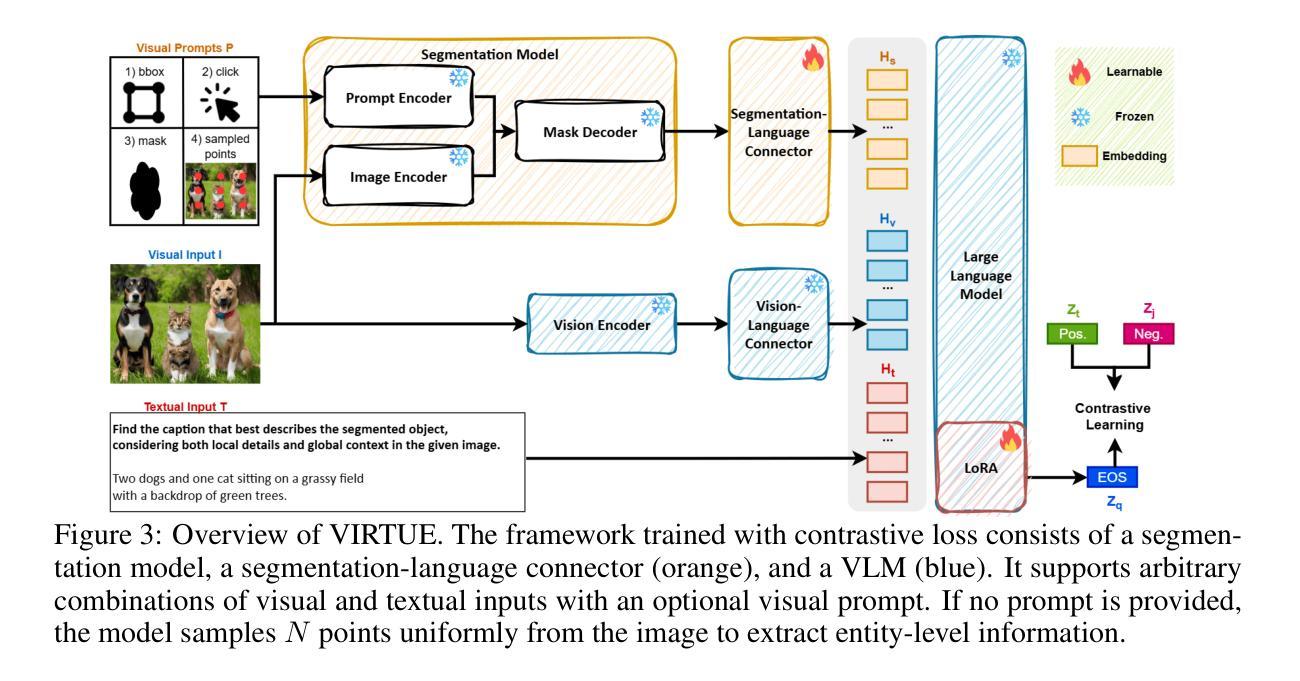
Multimodal representation learning models have demonstrated successful operation across complex tasks, and the integration of vision-language models (VLMs) has further enabled embedding models with instruction-following capabilities. However, existing embedding models lack visual-interactive capabilities to specify regions of interest from users (e.g., point, bounding box, mask), which have been explored in generative models to broaden their human-interactive applicability. Equipping embedding models with visual interactions not only would unlock new applications with localized grounding of user intent, which remains unexplored, but also enable the models to learn entity-level information within images to complement their global representations for conventional embedding tasks. In this paper, we propose a novel Visual-InteRactive Text-Image Universal Embedder (VIRTUE) that extends the capabilities of the segmentation model and the vision-language model to the realm of representation learning. In VIRTUE, the segmentation model can process visual prompts that pinpoint specific regions within an image, thereby enabling the embedder to handle complex and ambiguous scenarios more precisely. To evaluate the visual-interaction ability of VIRTUE, we introduce a large-scale Segmentation-and-Scene Caption Retrieval (SCaR) benchmark comprising 1M samples that aims to retrieve the text caption by jointly considering the entity with a specific object and image scene. VIRTUE consistently achieves a state-of-the-art performance with significant improvements across 36 universal MMEB (3.1%-8.5%) and five visual-interactive SCaR (15.2%-20.3%) tasks.
多模态表示学习模型已在复杂的任务中成功运行,视觉语言模型(VLMs)的集成进一步使嵌入模型具备指令执行能力。然而,现有的嵌入模型缺乏视觉交互能力来指定用户感兴趣的区域(例如点、边界框、蒙版),这在生成模型中已被探索以扩大其人机交互的适用性。为嵌入模型配备视觉交互功能不仅可以解锁新的应用,实现用户意图的本地化基础,这在以前尚未被探索,还可以使模型学习图像中的实体级信息,以补充其用于传统嵌入任务的全球表示。在本文中,我们提出了一种新颖的视觉交互式文本图像通用嵌入器(VIRTUE),它扩展了分割模型和视觉语言模型在表示学习领域的能力。在VIRTUE中,分割模型可以处理视觉提示,精确定位图像内的特定区域,从而使嵌入器能够更精确地处理复杂和模糊的场景。为了评估VIRTUE的视觉交互能力,我们引入了一个大规模的分割和场景字幕检索(SCaR)基准测试,包含100万个样本,旨在通过联合考虑特定实体对象和图像场景来检索文本字幕。VIRTUE在36项通用MMEB任务(提高3.1%-8.5%)和五项视觉交互SCaR任务(提高15.2%-20.3%)中均达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 25 pages
Summary
本文提出了一种名为VIRTUE的视觉交互式文本图像通用嵌入器,它将分割模型和视觉语言模型扩展到表示学习领域。VIRTUE能够通过处理视觉提示来定位图像中的特定区域,从而更精确地处理复杂和模糊的场景。为评估VIRTUE的视觉交互能力,引入了大规模的分割和场景字幕检索(SCaR)基准测试,旨在通过联合考虑特定对象和图像场景来检索文本字幕。VIRTUE在36个通用MMEB任务和五个视觉交互SCaR任务上均取得了最先进的性能,并实现了显著的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态表示学习模型在复杂任务中表现出成功的操作。
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)的整合使嵌入模型具备指令遵循能力。
- 现有嵌入模型缺乏从用户指定感兴趣区域(如点、边界框、掩膜)的视觉交互能力。
- VIRTUE模型扩展了分割模型和视觉语言模型的能力到表示学习领域。
- VIRTUE能够通过处理视觉提示来定位图像中的特定区域,以更精确地处理复杂和模糊的场景。
- 引入了SCaR基准测试来评估VIRTUE的视觉交互能力。
点此查看论文截图
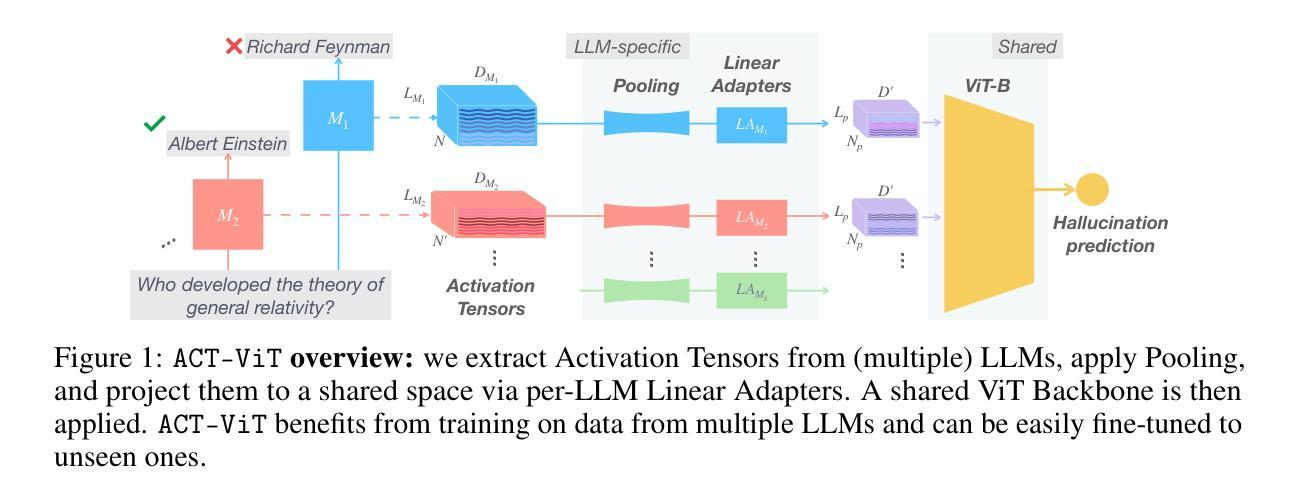
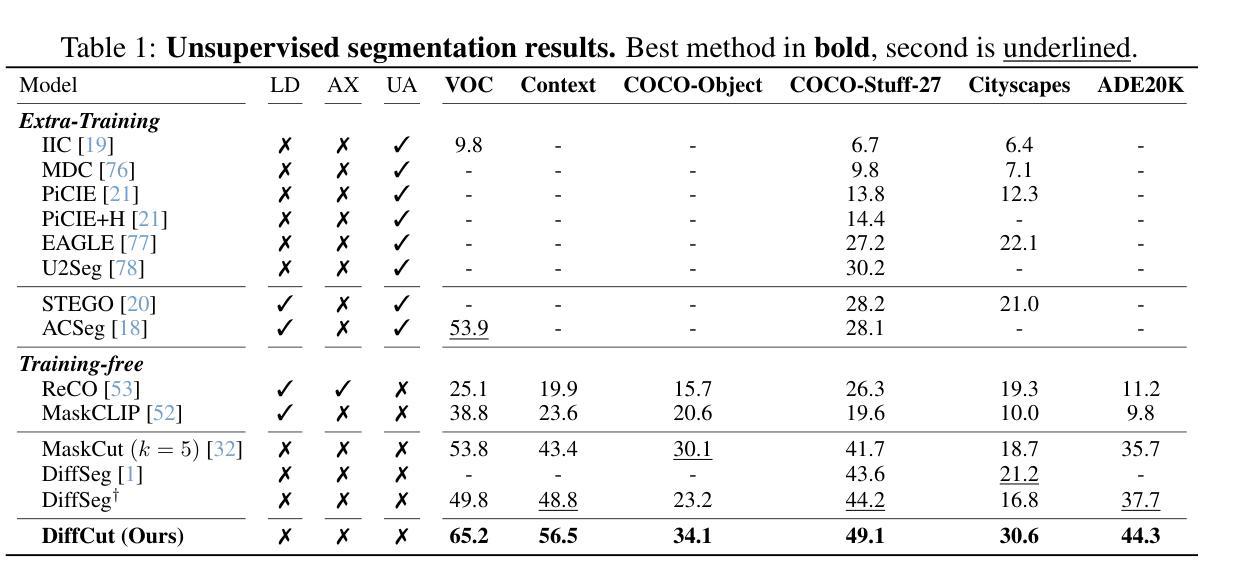
Beyond Token Probes: Hallucination Detection via Activation Tensors with ACT-ViT
Authors:Guy Bar-Shalom, Fabrizio Frasca, Yaniv Galron, Yftah Ziser, Haggai Maron
Detecting hallucinations in Large Language Model-generated text is crucial for their safe deployment. While probing classifiers show promise, they operate on isolated layer-token pairs and are LLM-specific, limiting their effectiveness and hindering cross-LLM applications. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach to address these shortcomings. We build on the natural sequential structure of activation data in both axes (layers $\times$ tokens) and advocate treating full activation tensors akin to images. We design ACT-ViT, a Vision Transformer-inspired model that can be effectively and efficiently applied to activation tensors and supports training on data from multiple LLMs simultaneously. Through comprehensive experiments encompassing diverse LLMs and datasets, we demonstrate that ACT-ViT consistently outperforms traditional probing techniques while remaining extremely efficient for deployment. In particular, we show that our architecture benefits substantially from multi-LLM training, achieves strong zero-shot performance on unseen datasets, and can be transferred effectively to new LLMs through fine-tuning. Full code is available at https://github.com/BarSGuy/ACT-ViT.
在大型语言模型生成的文本中检测幻觉对于其安全部署至关重要。虽然探测分类器显示出了一定的潜力,但它们作用于孤立的层令牌对,并且针对特定的大型语言模型,这限制了其有效性并阻碍了跨大型语言模型的应用。在本文中,我们介绍了一种解决这些不足的新方法。我们建立在两个轴(层x令牌)上激活数据的自然顺序结构,并提倡将完整的激活张量视为图像进行处理。我们设计了ACT-ViT,这是一个受视觉变压器启发的模型,可以有效地应用于激活张量,并支持同时从多个大型语言模型的数据进行训练。通过涵盖多个大型语言模型和数据集的综合实验,我们证明了ACT-ViT始终优于传统的探测技术,同时在部署时效率极高。尤其值得一提的是,我们的架构从多大型语言模型训练中受益匪浅,在未标记的数据集上实现了强大的零样本性能,并且可以通过微调有效地转移到新的大型语言模型上。完整的代码可以在 https://github.com/BarSGuy/ACT-ViT 上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in NeurIPS 2025
Summary
本论文针对大型语言模型生成文本中的幻觉检测问题,提出了一种新的方法。传统探查分类器在针对层令牌对时存在局限性,限制了其有效性和跨大型语言模型的应用。本研究利用激活数据的自然序列结构,提出将完整的激活张量视为图像进行处理。设计了一种基于视觉Transformer的ACT-ViT模型,可有效地应用于激活张量,并同时支持多个大型语言模型的数据训练。实验表明,ACT-ViT在多种大型语言模型和数据集上的性能优于传统探查技术,而且部署效率高。尤其是该架构从多大型语言模型训练中受益显著,在未见数据集上具有强大的零样本性能,并能通过微调有效迁移到新的大型语言模型。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型生成文本中的幻觉检测至关重要,影响模型的安全部署。
- 传统探查分类器存在局限性,需要新方法解决幻觉检测问题。
- 本研究提出将激活张量视为图像处理的新思路,利用其在两个轴上的自然序列结构。
- 引入ACT-ViT模型,灵感来源于视觉Transformer,适用于处理激活张量。
- ACT-ViT能同时处理多个大型语言模型的数据进行训练,提高效率和性能。
- 实验证明ACT-ViT在多种大型语言模型和数据集上的性能优于传统方法。
点此查看论文截图