⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-07 更新
Wave-GMS: Lightweight Multi-Scale Generative Model for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Talha Ahmed, Nehal Ahmed Shaikh, Hassan Mohy-ud-Din
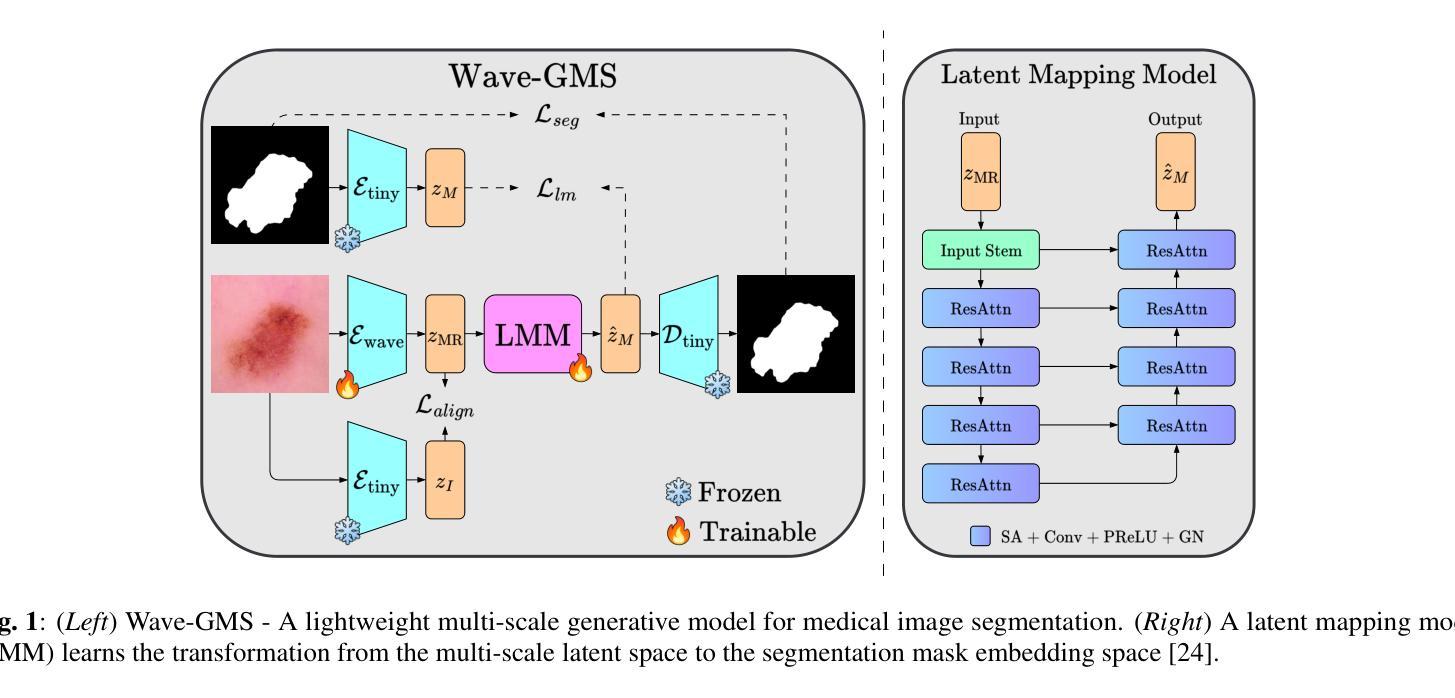
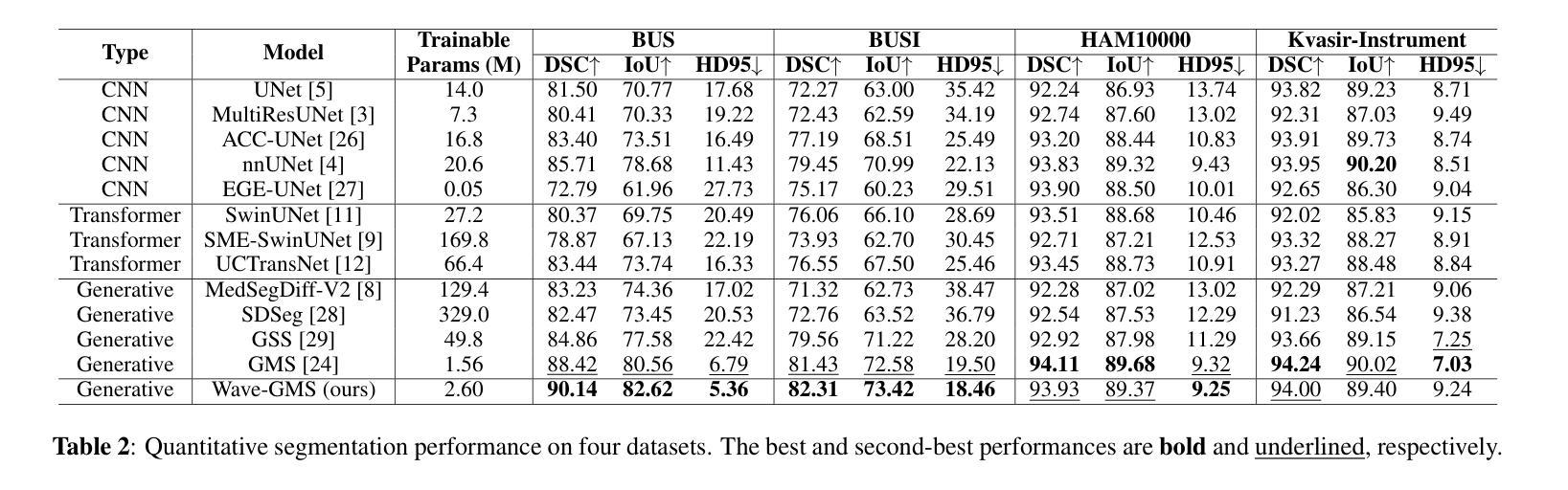
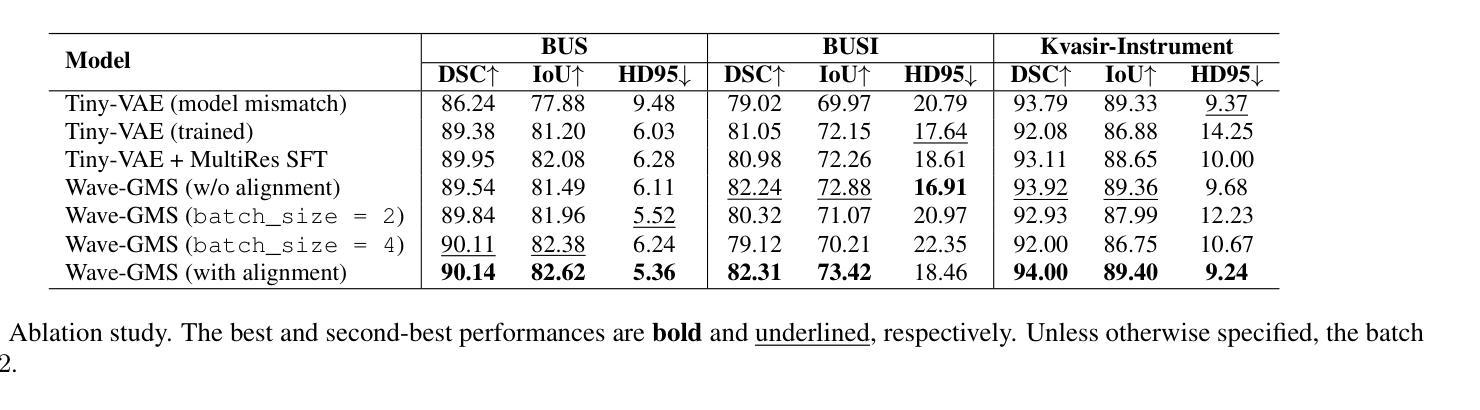
For equitable deployment of AI tools in hospitals and healthcare facilities, we need Deep Segmentation Networks that offer high performance and can be trained on cost-effective GPUs with limited memory and large batch sizes. In this work, we propose Wave-GMS, a lightweight and efficient multi-scale generative model for medical image segmentation. Wave-GMS has a substantially smaller number of trainable parameters, does not require loading memory-intensive pretrained vision foundation models, and supports training with large batch sizes on GPUs with limited memory. We conducted extensive experiments on four publicly available datasets (BUS, BUSI, Kvasir-Instrument, and HAM10000), demonstrating that Wave-GMS achieves state-of-the-art segmentation performance with superior cross-domain generalizability, while requiring only ~2.6M trainable parameters. Code is available at https://github.com/ATPLab-LUMS/Wave-GMS.
为了在医院和医疗保健设施中实现人工智能工具的公平部署,我们需要提供高性能的深度分割网络,它能够在具有有限内存和大批量数据的情况下,在成本效益高的GPU上进行训练。在这项工作中,我们提出了Wave-GMS,这是一种用于医学图像分割的轻量级、高效的多尺度生成模型。Wave-GMS具有大量的可训练参数,不需要加载内存密集型的预训练视觉基础模型,并且支持在具有有限内存的GPU上进行大批量训练。我们在四个公开可用数据集(BUS、BUSI、Kvasir-Instrument和HAM10000)上进行了大量实验,证明Wave-GMS达到了最先进的分割性能,具有出色的跨域泛化能力,同时只需要约2.6M的可训练参数。代码可在https://github.com/ATPLab-LUMS/Wave-GMS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 1 figure, 4 tables; Submitted to IEEE Conference for possible publication
摘要
提出一种高效且轻量级的医学图像分割网络Wave-GMS,用于在具有有限内存和大型批量的低成本GPU上训练并实现高水平的医疗图像分割性能。Wave-GMS具有较少的可训练参数,无需加载内存密集型预训练视觉基础模型,并支持在具有有限内存的GPU上进行大规模批量训练。在四个公开数据集上的实验表明,Wave-GMS实现了最先进的分割性能,具有出色的跨域泛化能力,并且只需要大约2.6M的可训练参数。相关代码可通过特定网址下载。
关键见解
- 提出了一种新的医学图像分割网络Wave-GMS,旨在实现均衡部署。该网络针对医院的公平需求而设计。它在性能高和内存有限的GPU上运行良好。
点此查看论文截图
SpineBench: A Clinically Salient, Level-Aware Benchmark Powered by the SpineMed-450k Corpus
Authors:Ming Zhao, Wenhui Dong, Yang Zhang, Xiang Zheng, Zhonghao Zhang, Zian Zhou, Yunzhi Guan, Liukun Xu, Wei Peng, Zhaoyang Gong, Zhicheng Zhang, Dachuan Li, Xiaosheng Ma, Yuli Ma, Jianing Ni, Changjiang Jiang, Lixia Tian, Qixin Chen, Kaishun Xia, Pingping Liu, Tongshun Zhang, Zhiqiang Liu, Zhongan Bi, Chenyang Si, Tiansheng Sun, Caifeng Shan
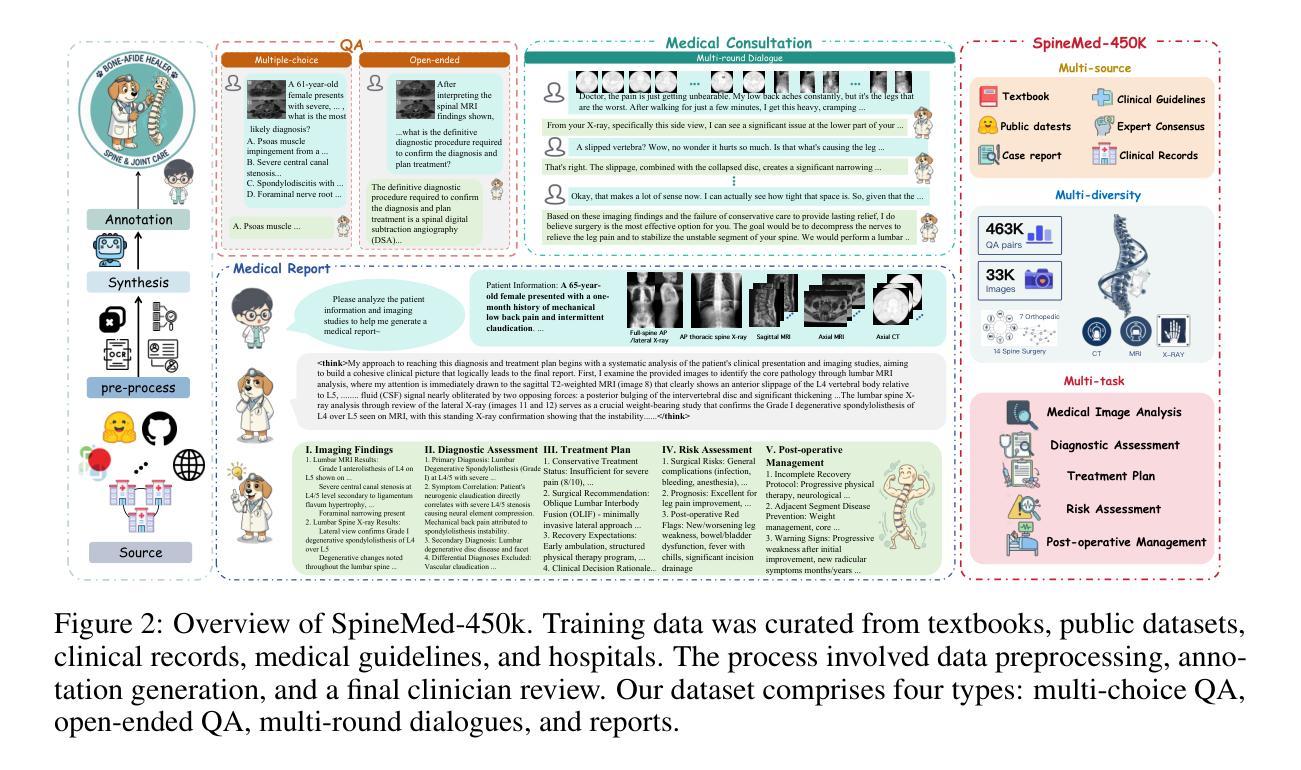
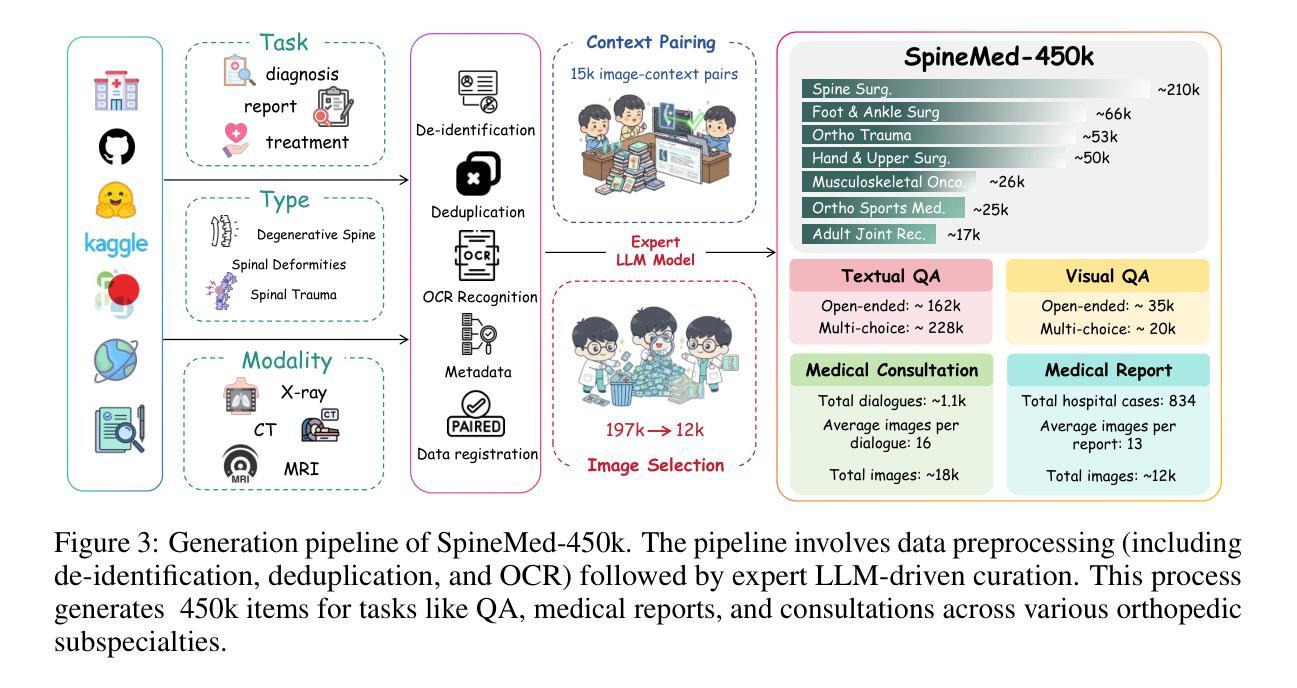
Spine disorders affect 619 million people globally and are a leading cause of disability, yet AI-assisted diagnosis remains limited by the lack of level-aware, multimodal datasets. Clinical decision-making for spine disorders requires sophisticated reasoning across X-ray, CT, and MRI at specific vertebral levels. However, progress has been constrained by the absence of traceable, clinically-grounded instruction data and standardized, spine-specific benchmarks. To address this, we introduce SpineMed, an ecosystem co-designed with practicing spine surgeons. It features SpineMed-450k, the first large-scale dataset explicitly designed for vertebral-level reasoning across imaging modalities with over 450,000 instruction instances, and SpineBench, a clinically-grounded evaluation framework. SpineMed-450k is curated from diverse sources, including textbooks, guidelines, open datasets, and ~1,000 de-identified hospital cases, using a clinician-in-the-loop pipeline with a two-stage LLM generation method (draft and revision) to ensure high-quality, traceable data for question-answering, multi-turn consultations, and report generation. SpineBench evaluates models on clinically salient axes, including level identification, pathology assessment, and surgical planning. Our comprehensive evaluation of several recently advanced large vision-language models (LVLMs) on SpineBench reveals systematic weaknesses in fine-grained, level-specific reasoning. In contrast, our model fine-tuned on SpineMed-450k demonstrates consistent and significant improvements across all tasks. Clinician assessments confirm the diagnostic clarity and practical utility of our model’s outputs.
脊椎疾病影响全球6.19亿人,是导致残疾的主要原因之一。然而,人工智能辅助诊断仍然受限于缺乏感知级别的多模态数据集。脊椎疾病的临床决策需要在特定的椎体水平上对X光、CT和MRI进行复杂推理。然而,由于缺乏可追溯的、以临床为基础的指令数据以及标准化的脊椎特定基准测试,进展一直受到限制。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了SpineMed,这是一个与执业脊椎外科医生共同设计生态系统。它包含SpineMed-450k和SpineBench两个特点。SpineMed-450k是专为椎体级别的跨成像模态推理设计的大规模数据集,包含超过45万个指令实例。这些数据集是从多样化的来源精心策划而成,包括教科书、指南、公开数据集以及大约1000个匿名医院病例,通过使用有临床医生参与的闭环管道和两阶段的LLM生成方法(草稿和修订)来确保高质量的可追溯数据可用于问答、多轮咨询和报告生成。SpineBench是一个以临床为基础的评价框架,用于评估模型在临床重要轴上的表现,包括水平识别、病理评估和手术规划等。我们对几个最近先进的视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在SpineBench上的全面评估表明,在精细粒度的水平特定推理方面存在系统性弱点。相比之下,我们的模型在SpineMed-450k上调优后,在所有任务上都表现出一致且显著的改进。临床医生评估证实了我们的模型输出的诊断清晰度和实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要基于医学图像领域的一项研究,该研究表明脊柱疾病是全球导致残疾的主要原因之一,影响人数高达6.19亿。然而,由于缺乏多模态数据集,人工智能辅助诊断的应用受到限制。为解决此问题,研究团队推出了SpineMed生态系统,其中包括SpineMed-450k数据集和SpineBench评估框架。SpineMed-450k数据集涵盖超过45万条指令实例,专为椎体级别的跨模态成像推理设计。研究团队通过一系列方法确保数据质量,并进行了全面的评估。结果显示,经过SpineMed-450k训练模型在所有任务中表现显著改进。临床医生评估也确认了模型的诊断清晰度和实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 脊柱疾病影响巨大,全球范围内有数亿人受影响,亟需高效准确的诊断方法。
- AI在医学诊断中的应用受限于缺乏多模态数据集,特别是针对特定椎体级别的数据。
- 推出SpineMed生态系统,包含SpineMed-450k数据集和SpineBench评估框架,以解决上述问题。
- SpineMed-450k数据集是专为椎体级别跨模态成像推理设计的大规模数据集,包含超过45万条指令实例。
- 数据集通过多元化来源及严格的数据质量管控流程进行构建。
- 对先进的视觉语言模型进行全面评估,结果显示经过SpineMed-450k训练的模型表现最佳。
点此查看论文截图
HAVIR: HierArchical Vision to Image Reconstruction using CLIP-Guided Versatile Diffusion
Authors:Shiyi Zhang, Dong Liang, Hairong Zheng, Yihang Zhou
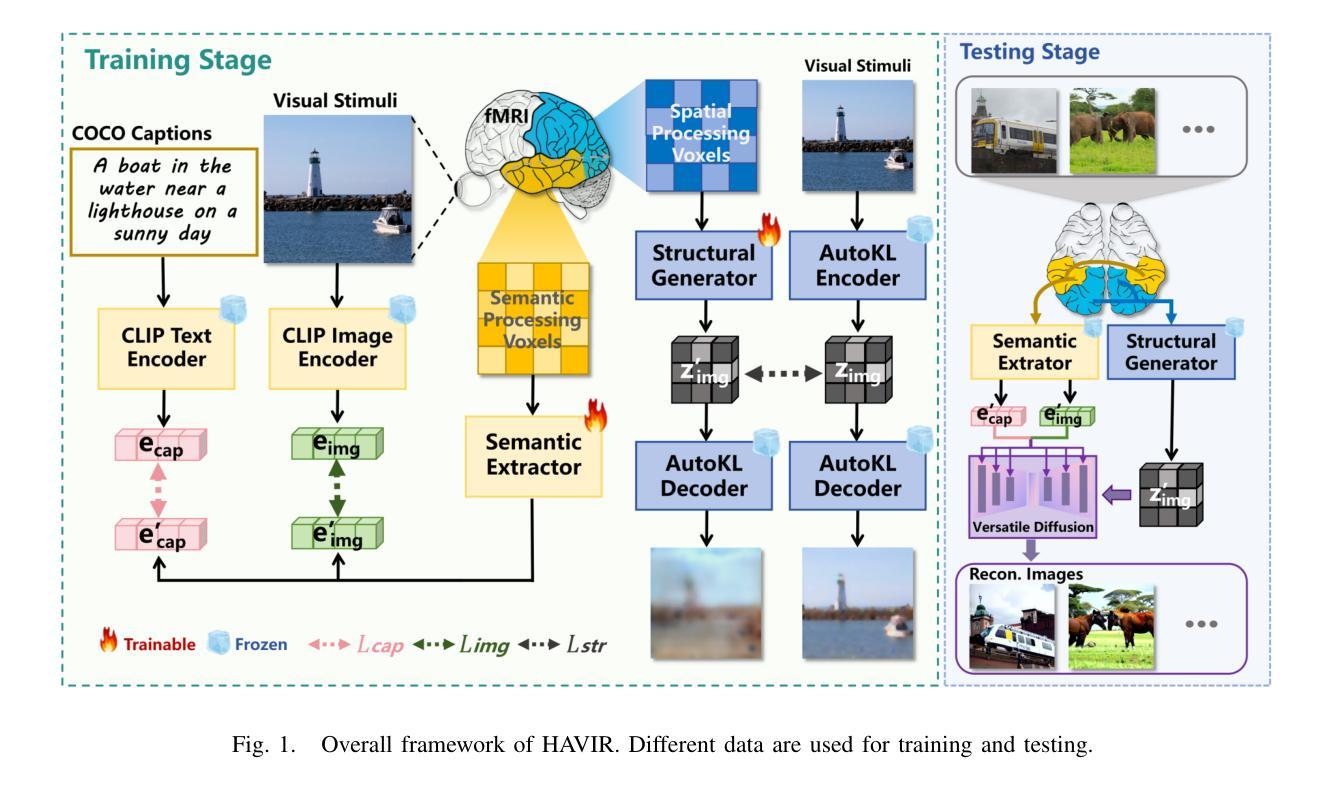
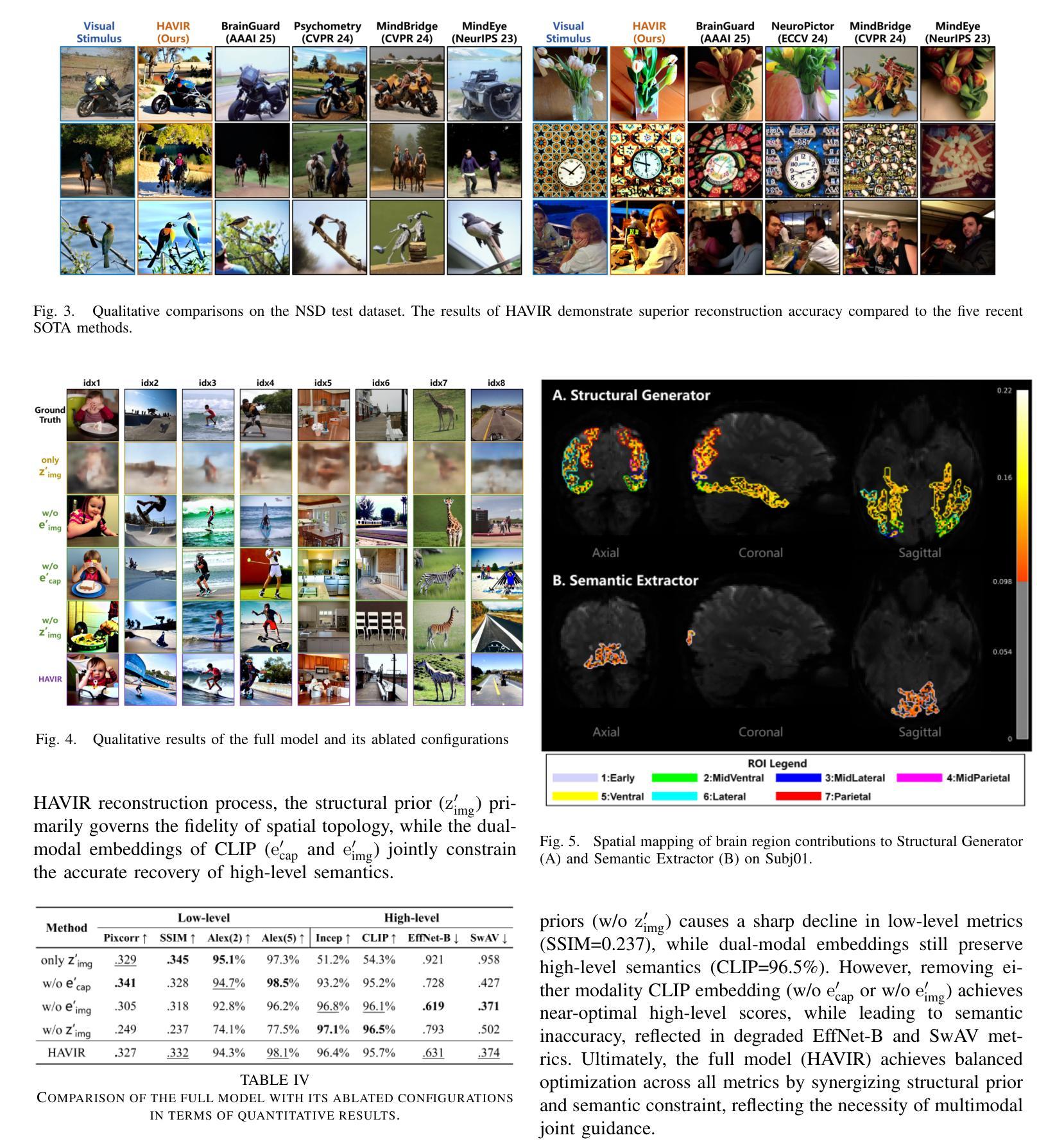
The reconstruction of visual information from brain activity fosters interdisciplinary integration between neuroscience and computer vision. However, existing methods still face challenges in accurately recovering highly complex visual stimuli. This difficulty stems from the characteristics of natural scenes: low-level features exhibit heterogeneity, while high-level features show semantic entanglement due to contextual overlaps. Inspired by the hierarchical representation theory of the visual cortex, we propose the HAVIR model, which separates the visual cortex into two hierarchical regions and extracts distinct features from each. Specifically, the Structural Generator extracts structural information from spatial processing voxels and converts it into latent diffusion priors, while the Semantic Extractor converts semantic processing voxels into CLIP embeddings. These components are integrated via the Versatile Diffusion model to synthesize the final image. Experimental results demonstrate that HAVIR enhances both the structural and semantic quality of reconstructions, even in complex scenes, and outperforms existing models.
从脑活动中重建视觉信息促进了神经科学与计算机视觉之间的跨学科整合。然而,现有方法仍然在准确恢复高度复杂的视觉刺激方面面临挑战。这一难题源于自然场景的特性:低级特征表现出异质性,而高级特征由于上下文重叠而表现出语义纠缠。受视觉皮层分层表示理论的启发,我们提出了HAVIR模型,该模型将视觉皮层分为两个层次区域,并从每个区域中提取不同的特征。具体而言,结构生成器从空间处理体素中提取结构信息,并将其转换为潜在扩散先验知识,而语义提取器将语义处理体素转换为CLIP嵌入。这些组件通过通用扩散模型集成,合成最终图像。实验结果表明,HAVIR即使在复杂场景中也能提高重建的结构和语义质量,并优于现有模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像重建过程中面临复杂视觉刺激恢复难题,源于自然场景的低层次特征异质性和高层次特征的语义纠缠。借鉴视觉皮层层次表示理论,提出HAVIR模型,分为结构生成器和语义提取器,分别提取空间处理体素的结构信息和语义处理体素的语义信息,并通过通用扩散模型合成最终图像。实验证明HAVIR能提高重建图像的结构和语义质量,优于现有模型。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像重建面临复杂视觉刺激恢复的挑战。
- 挑战源于自然场景的低层次特征异质性和高层次特征的语义纠缠。
- HAVIR模型借鉴视觉皮层层次表示理论,分为结构生成器和语义提取器。
- 结构生成器从空间处理体素中提取结构信息并转换为潜在扩散先验。
- 语义提取器将语义处理体素转换为CLIP嵌入。
- HAVIR模型通过通用扩散模型合成最终图像。
点此查看论文截图
Semantic Similarity in Radiology Reports via LLMs and NER
Authors:Beth Pearson, Ahmed Adnan, Zahraa Abdallah
Radiology report evaluation is a crucial part of radiologists’ training and plays a key role in ensuring diagnostic accuracy. As part of the standard reporting workflow, a junior radiologist typically prepares a preliminary report, which is then reviewed and edited by a senior radiologist to produce the final report. Identifying semantic differences between preliminary and final reports is essential for junior doctors, both as a training tool and to help uncover gaps in clinical knowledge. While AI in radiology is a rapidly growing field, the application of large language models (LLMs) remains challenging due to the need for specialised domain knowledge. In this paper, we explore the ability of LLMs to provide explainable and accurate comparisons of reports in the radiology domain. We begin by comparing the performance of several LLMs in comparing radiology reports. We then assess a more traditional approach based on Named-Entity-Recognition (NER). However, both approaches exhibit limitations in delivering accurate feedback on semantic similarity. To address this, we propose Llama-EntScore, a semantic similarity scoring method using a combination of Llama 3.1 and NER with tunable weights to emphasise or de-emphasise specific types of differences. Our approach generates a quantitative similarity score for tracking progress and also gives an interpretation of the score that aims to offer valuable guidance in reviewing and refining their reporting. We find our method achieves 67% exact-match accuracy and 93% accuracy within +/- 1 when compared to radiologist-provided ground truth scores - outperforming both LLMs and NER used independently. Code is available at: \href{https://github.com/otmive/llama_reports}{github.com/otmive/llama\_reports}
放射学报告评估是放射科医生培训的重要组成部分,对于确保诊断准确性起着关键作用。作为标准报告工作流程的一部分,初级放射科医生通常会编写初步报告,然后由高级放射科医生进行审查和编辑以产生最终报告。识别初步报告和最终报告之间的语义差异对于初级医生至关重要,既是训练工具,也有助于发现临床知识上的差距。尽管人工智能在放射学领域是一个快速发展的领域,但由于需要专业的领域知识,大型语言模型(LLM)的应用仍然具有挑战性。在本文中,我们探讨了LLM在放射学报告中提供可解释和准确比较的能力。我们首先比较了多个LLM在比较放射学报告方面的性能。然后,我们评估了基于命名实体识别(NER)的更传统的方法。然而,这两种方法在提供语义相似性准确反馈方面都存在局限性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了Llama-EntScore,一种语义相似性评分方法,结合了Llama 3.1和NER,使用可调权重来强调或淡化特定类型的差异。我们的方法生成一个量化的相似度分数,用于跟踪进度,并对分数进行解释,旨在提供有价值的指导,以审查和改进报告。我们发现,与放射科医生提供的真实分数相比,我们的方法达到了67%的精确匹配准确率和93%的±1内的准确率,超越了单独使用的LLMs和NER。相关代码可在:github.com/otmive/llama_reports找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了大型语言模型(LLMs)在放射学报告对比中的应用。研究对比了LLMs和传统命名实体识别(NER)方法的性能,发现两者在语义相似性反馈方面存在局限性。为此,研究提出了Llama-EntScore方法,结合Llama 3.1和NER,可量化放射学报告的相似性,并解释评分,为报告审查和精进提供指导。该方法较LLMs和NER独立使用表现更优,与放射科医生提供的真实评分相比,准确率高达93%。
Key Takeaways
- 放射学报告评估是放射科医生培训的关键环节,有助于确保诊断准确性。
- 初步报告与最终报告间的语义差异对初级医生而言是重要的训练工具。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在放射学报告对比中的应用具有挑战,需专业领域知识。
- LLMs和传统的命名实体识别(NER)方法在语义相似性反馈方面存在局限性。
- Llama-EntScore方法结合Llama 3.1和NER,提供量化相似度评分并解释,旨在指导报告审查和精进。
- Llama-EntScore方法较LLMs和NER独立使用表现更优,与放射科医生提供的真实评分相比,准确率较高。
- 代码已公开,可供进一步研究使用。
点此查看论文截图
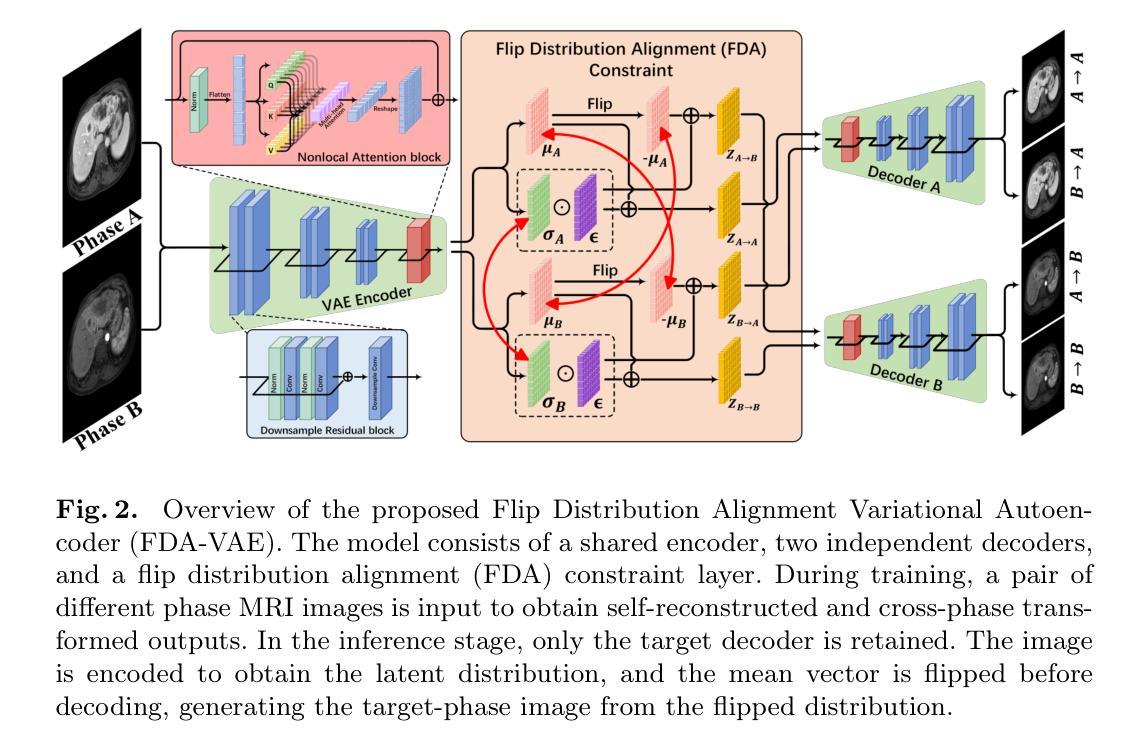
Flip Distribution Alignment VAE for Multi-Phase MRI Synthesis
Authors:Xiaoyan Kui, Qianmu Xiao, Qqinsong Li, Zexin Ji, JIelin Zhang, Beiji Zou
Separating shared and independent features is crucial for multi-phase contrast-enhanced (CE) MRI synthesis. However, existing methods use deep autoencoder generators with low parameter efficiency and lack interpretable training strategies. In this paper, we propose Flip Distribution Alignment Variational Autoencoder (FDA-VAE), a lightweight feature-decoupled VAE model for multi-phase CE MRI synthesis. Our method encodes input and target images into two latent distributions that are symmetric concerning a standard normal distribution, effectively separating shared and independent features. The Y-shaped bidirectional training strategy further enhances the interpretability of feature separation. Experimental results show that compared to existing deep autoencoder-based end-to-end synthesis methods, FDA-VAE significantly reduces model parameters and inference time while effectively improving synthesis quality. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/QianMuXiao/FDA-VAE.
在多阶段增强(CE)MRI合成中,分离共享和独立特征至关重要。然而,现有方法使用参数效率较低的深度自编码器生成器,并且缺乏可解释的训练策略。在本文中,我们提出了Flip分布对齐变分自编码器(FDA-VAE),这是一种用于多阶段CE MRI合成的轻量级特征解耦VAE模型。我们的方法将输入图像和目标图像编码为两个潜在分布,这两个分布关于标准正态分布是对称的,从而有效地分离了共享和独立特征。Y形双向训练策略进一步增强了特征分离的可解释性。实验结果表明,与现有的基于深度自编码器的端到端合成方法相比,FDA-VAE在减少模型参数和推理时间的同时,有效地提高了合成质量。源代码公开在https://github.com/QianMuXiao/FDA-VAE。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been early accept by MICCAI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为Flip Distribution Alignment Variational Autoencoder(FDA-VAE)的轻量级特征解耦变分自编码器模型,用于多阶段对比增强MRI合成。该方法能有效分离共享和独立特征,采用Y形双向训练策略进一步提高特征分离的可解释性。与现有基于深度自编码器的端到端合成方法相比,FDA-VAE在减少模型参数和推理时间的同时,有效提高合成质量。
Key Takeaways
- FDA-VAE模型用于多阶段对比增强MRI合成。
- 现有方法使用深度自编码器生成器,存在参数效率低和缺乏可解释训练策略的问题。
- FDA-VAE将输入和目标图像编码为两个关于标准正态分布的对称潜在分布,有效分离共享和独立特征。
- 采用Y形双向训练策略提高特征分离的可解释性。
- FDA-VAE显著减少模型参数和推理时间。
- 实验结果表明,FDA-VAE有效提高合成质量。
点此查看论文截图

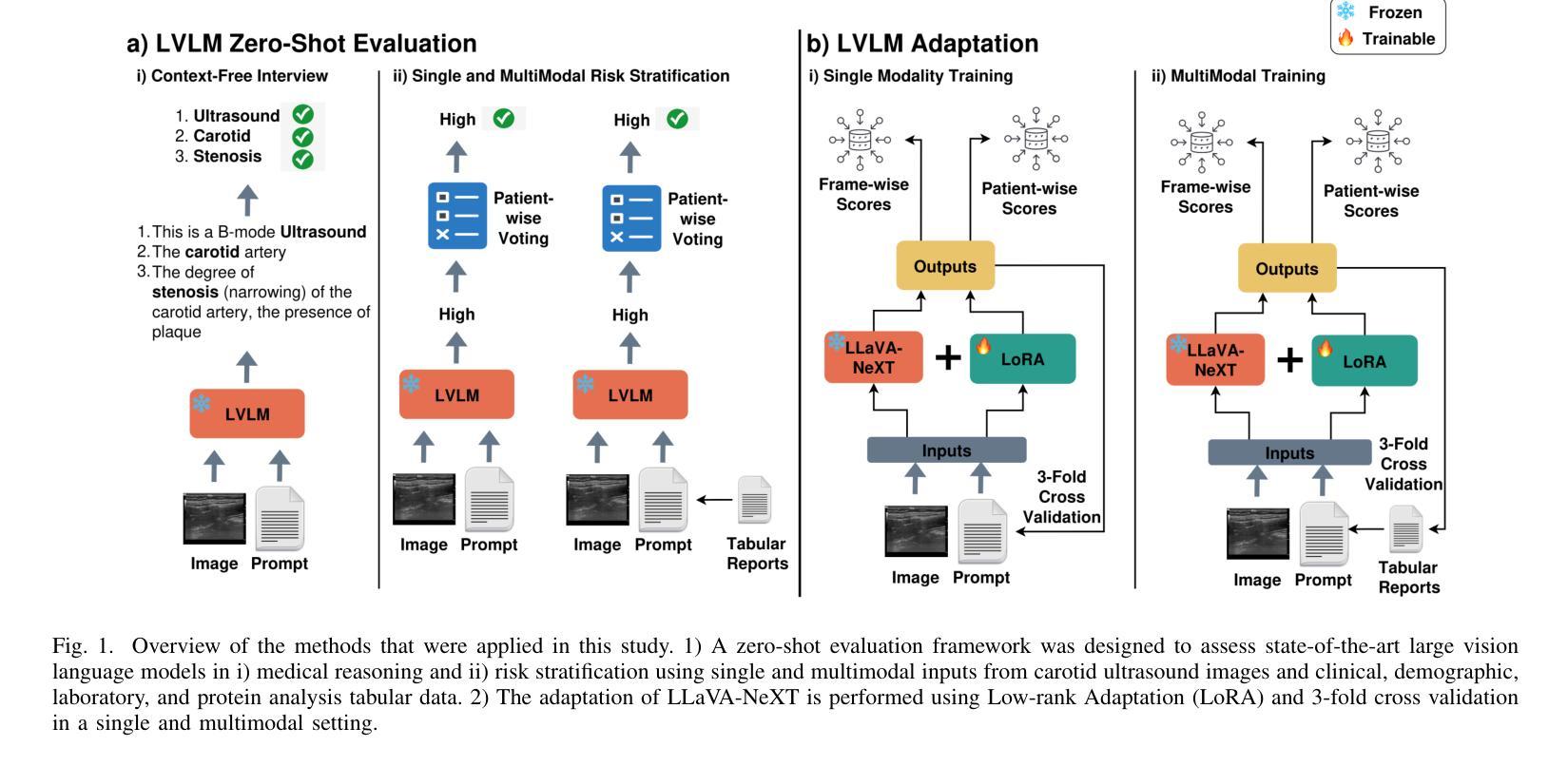
Multimodal Carotid Risk Stratification with Large Vision-Language Models: Benchmarking, Fine-Tuning, and Clinical Insights
Authors:Daphne Tsolissou, Theofanis Ganitidis, Konstantinos Mitsis, Stergios CHristodoulidis, Maria Vakalopoulou, Konstantina Nikita
Reliable risk assessment for carotid atheromatous disease remains a major clinical challenge, as it requires integrating diverse clinical and imaging information in a manner that is transparent and interpretable to clinicians. This study investigates the potential of state-of-the-art and recent large vision-language models (LVLMs) for multimodal carotid plaque assessment by integrating ultrasound imaging (USI) with structured clinical, demographic, laboratory, and protein biomarker data. A framework that simulates realistic diagnostic scenarios through interview-style question sequences is proposed, comparing a range of open-source LVLMs, including both general-purpose and medically tuned models. Zero-shot experiments reveal that even if they are very powerful, not all LVLMs can accurately identify imaging modality and anatomy, while all of them perform poorly in accurate risk classification. To address this limitation, LLaVa-NeXT-Vicuna is adapted to the ultrasound domain using low-rank adaptation (LoRA), resulting in substantial improvements in stroke risk stratification. The integration of multimodal tabular data in the form of text further enhances specificity and balanced accuracy, yielding competitive performance compared to prior convolutional neural network (CNN) baselines trained on the same dataset. Our findings highlight both the promise and limitations of LVLMs in ultrasound-based cardiovascular risk prediction, underscoring the importance of multimodal integration, model calibration, and domain adaptation for clinical translation.
对颈动脉粥样斑块疾病进行可靠的风险评估仍然是临床上的一个主要挑战,因为它需要以透明和临床医生可解释的方式整合各种临床和成像信息。本研究探讨了最先进的近期大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在多模态颈动脉斑块评估中的潜力,通过整合超声成像(USI)与结构化临床、人口统计、实验室和蛋白质生物标志物数据。提出了一种模拟现实诊断场景的框架,通过访谈式问题序列进行比较,包括一系列开源LVLMs,既包括通用模型也包括医学调优模型。零样本实验表明,即使它们非常强大,并非所有的LVLMs都能准确地识别成像模态和解剖学结构,而它们在准确的风险分类方面的表现都很差。为了解决这一局限性,使用低秩适应(LoRA)将LLaVa-NeXT-Vicuna适应于超声领域,从而极大地提高了中风风险分层的效果。以文本形式整合多模态表格数据进一步提高了特异性和平衡精度,与在相同数据集上训练的先前卷积神经网络(CNN)基准测试相比,表现出竞争力。我们的研究结果突出了LVLMs在超声心动图心血管风险预测中的潜力和局限性,强调了多模态整合、模型校准和领域适应对于临床转化的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了先进的大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在多模态颈动脉斑块评估中的潜力,通过整合超声成像与结构化临床、人口学、实验室和蛋白质生物标志物数据,模拟真实诊断场景。研究结果显示,LVLMs在识别成像模态和解剖结构方面存在局限性,且风险分类准确性较低。通过低秩适应(LoRA)适应超声领域后,性能有所提升。多模态表格数据的文本形式进一步提高了特异性和平衡精度,与基于同一数据集的卷积神经网络(CNN)基准测试相比具有竞争力。研究强调了多模态整合、模型校准和领域适应在超声心血管风险预测中的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 可靠的颈动脉粥样疾病风险评估是临床上的重大挑战,需要整合各种临床和成像信息,且这些信息必须透明且对临床医生具有可解释性。
- 本研究探讨了大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在多模态颈动脉斑块评估中的潜力,这些模型能够整合超声成像与多种临床数据。
- 零样本实验表明,并非所有LVLMs都能准确识别成像模态和解剖结构,且风险分类准确性普遍较低。
- 通过低秩适应(LoRA)技术,LVLMs在超声领域的适应性得到提高,特别是在卒中风险分层方面。
- 多模态表格数据的整合进一步提高了诊断的特异性和平衡精度。
- 与基于同一数据集的卷积神经网络(CNN)相比,LVLMs表现出竞争力。
点此查看论文截图


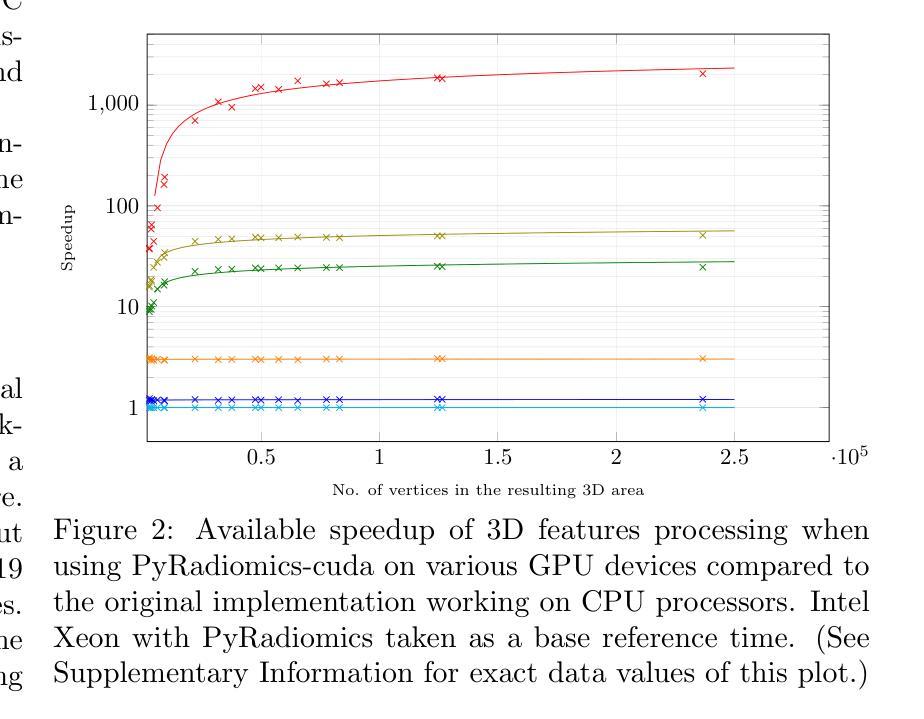
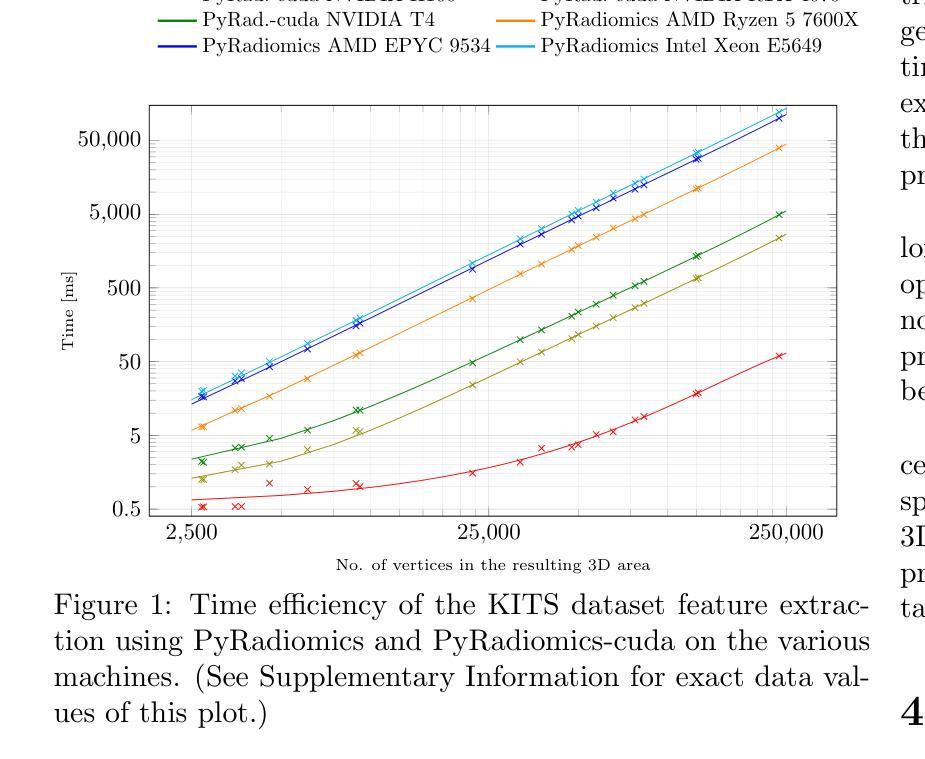
PyRadiomics-cuda: a GPU-accelerated 3D features extraction from medical images within PyRadiomics
Authors:Jakub Lisowski, Piotr Tyrakowski, Szymon Zyguła, Krzysztof Kaczmarski
PyRadiomics-cuda is a GPU-accelerated extension of the PyRadiomics library, designed to address the computational challenges of extracting three-dimensional shape features from medical images. By offloading key geometric computations to GPU hardware it dramatically reduces processing times for large volumetric datasets. The system maintains full compatibility with the original PyRadiomics API, enabling seamless integration into existing AI workflows without code modifications. This transparent acceleration facilitates efficient, scalable radiomics analysis, supporting rapid feature extraction essential for high-throughput AI pipeline. Tests performed on a typical computational cluster, budget and home devices prove usefulness in all scenarios. PyRadiomics-cuda is implemented in Python and C/CUDA and is freely available under the BSD license at https://github.com/mis-wut/pyradiomics-CUDA Additionally PyRadiomics-cuda test suite is available at https://github.com/mis-wut/pyradiomics-cuda-data-gen. It provides detailed handbook and sample scripts suited for different kinds of workflows plus detailed installation instructions. The dataset used for testing is available at Kaggle https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/sabahesaraki/kidney-tumor-segmentation-challengekits-19
PyRadiomics-cuda是PyRadiomics库的GPU加速扩展,旨在解决从医学图像中提取三维形状特征的计算挑战。通过将关键的几何计算任务转移到GPU硬件上,它极大地减少了处理大型体积数据集的处理时间。该系统与原始PyRadiomics API保持完全兼容性,无需修改代码即可无缝集成到现有的AI工作流程中。这种透明的加速促进了高效、可扩展的放射学分析,支持高速AI管道所需的关键特征提取。在典型的计算集群、预算和家庭设备上进行的测试证明了其在所有场景中的实用性。PyRadiomics-cuda使用Python和C/CUDA实现,可在BSD许可下免费使用,网址为:https://github.com/mis-wut/pyradiomics-CUDA。此外,PyRadiomics-cuda测试套件可在https://github.com/mis-wut/pyradiomics-cuda-data-gen上找到。它提供了针对不同类型工作流程的详细手册和样本脚本,以及详细的安装说明。用于测试的数据集可在Kaggle上找到:https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/sabahesaraki/kidney-tumor-segmentation-challengekits-19。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
PyRadiomics-cuda是PyRadiomics库的GPU加速扩展,旨在解决从医学图像中提取三维形状特征的计算挑战。它通过卸载关键几何计算到GPU硬件,显著减少了大型体积数据集的处理时间。该系统与原始PyRadiomics API完全兼容,可无缝集成到现有的人工智能工作流程中,无需进行代码修改。此透明的加速促进高效、可扩展的放射学分析,支持快速特征提取,对于高流量的人工智能管道至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- PyRadiomics-cuda是PyRadiomics库的扩展,专为加速医学图像中的三维形状特征提取计算而设计。
- 通过利用GPU硬件,PyRadiomics-cuda显著减少了大型数据集的处理时间。
- 系统与原始PyRadiomics API兼容,可轻松集成到现有的人工智能工作流程中。
- 透明的加速机制促进了高效、可扩展的放射学分析。
- PyRadiomics-cuda支持快速特征提取,对于高流量的人工智能管道至关重要。
- PyRadiomics-cuda在常规计算集群、经济型设备以及家用设备上均经过测试,证明了其在各种场景下的实用性。
- PyRadiomics-cuda提供详细手册、适用于不同工作流程的示例脚本以及详细的安装说明。测试数据集可在Kaggle上找到。
点此查看论文截图

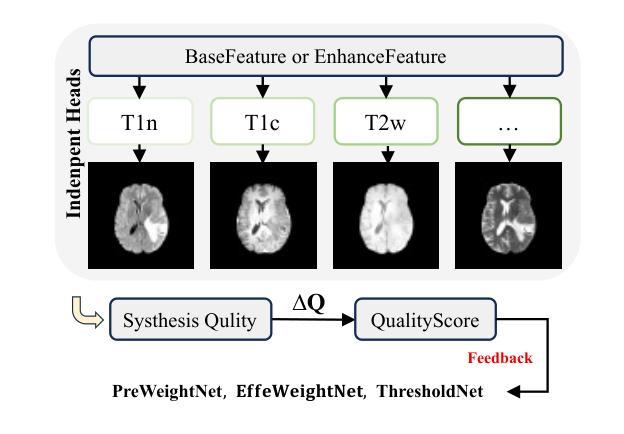
Med-K2N: Flexible K-to-N Modality Translation for Medical Image Synthesis
Authors:Feng Yuan, Yifan Gao, Yuehua Ye, Haoyue Li, Xin Gao
Cross-modal medical image synthesis research focuses on reconstructing missing imaging modalities from available ones to support clinical diagnosis. Driven by clinical necessities for flexible modality reconstruction, we explore K to N medical generation, where three critical challenges emerge: How can we model the heterogeneous contributions of different modalities to various target tasks? How can we ensure fusion quality control to prevent degradation from noisy information? How can we maintain modality identity consistency in multi-output generation? Driven by these clinical necessities, and drawing inspiration from SAM2’s sequential frame paradigm and clinicians’ progressive workflow of incrementally adding and selectively integrating multi-modal information, we treat multi-modal medical data as sequential frames with quality-driven selection mechanisms. Our key idea is to “learn” adaptive weights for each modality-task pair and “memorize” beneficial fusion patterns through progressive enhancement. To achieve this, we design three collaborative modules: PreWeightNet for global contribution assessment, ThresholdNet for adaptive filtering, and EffiWeightNet for effective weight computation. Meanwhile, to maintain modality identity consistency, we propose the Causal Modality Identity Module (CMIM) that establishes causal constraints between generated images and target modality descriptions using vision-language modeling. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our proposed Med-K2N outperforms state-of-the-art methods by significant margins on multiple benchmarks. Source code is available.
跨模态医学图像合成研究旨在利用现有成像模式重建缺失的成像模式,以支持临床诊断。受临床对灵活模态重建的需求驱动,我们探索了从K到N的医学图像生成方法,其中出现了三个关键挑战:我们如何建模不同模态对各项任务的异质贡献?我们如何确保融合质量控制,防止噪声信息的退化?我们如何在多输出生成中保持模态身份的一致性?受这些临床需求的驱动,并受到SAM2的顺序框架范式和临床医生逐步添加和选择性整合多模态信息的工作流程的启发,我们将多模态医学数据视为具有质量驱动选择机制的顺序帧。我们的核心思想是“学习”每个模态任务对的自适应权重,并通过逐步增强来“记忆”有益的融合模式。为此,我们设计了三个协作模块:用于全局贡献评估的PreWeightNet、用于自适应过滤的ThresholdNet、以及用于有效权重计算EffiWeightNet。同时,为了保持模态身份的一致性,我们提出了因果模态身份模块(CMIM),它使用视觉语言建模在生成的图像和目标模态描述之间建立因果约束。广泛的实验结果证明,我们提出的Med-K2N在多基准测试中显著优于最先进的方法。源代码已公开。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR2026 under review
Summary
本文研究了跨模态医学图像合成,旨在从已有的成像模态重建缺失的模态,以支持临床诊断。文章提出了Med-K2N方法,通过模拟多模态数据的顺序框架和临床医生逐步的工作流程,对多模态医学数据进行处理。通过设计PreWeightNet、ThresholdNet和EffiWeightNet三个协作模块以及Causal Modality Identity Module(CMIM)来优化合成过程并确保生成的图像保持目标模态的身份一致性。实验结果表明,所提出的方法在多个基准测试中显著优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 跨模态医学图像合成旨在从现有成像模态重建缺失的模态,以辅助临床诊断。
- Med-K2N方法基于临床需求驱动,模拟多模态数据的顺序框架和医生逐步集成多模态信息的流程。
- Med-K2N通过设计PreWeightNet、ThresholdNet和EffiWeightNet三个协作模块,实现自适应权重学习和融合模式的记忆。
- 为保持模态身份一致性,提出了Causal Modality Identity Module(CMIM)。
- CMIM利用视觉语言建模,在生成的图像和目标模态描述之间建立因果约束。
- 相较于其他先进方法,Med-K2N在多个基准测试中表现出显著优势。
点此查看论文截图
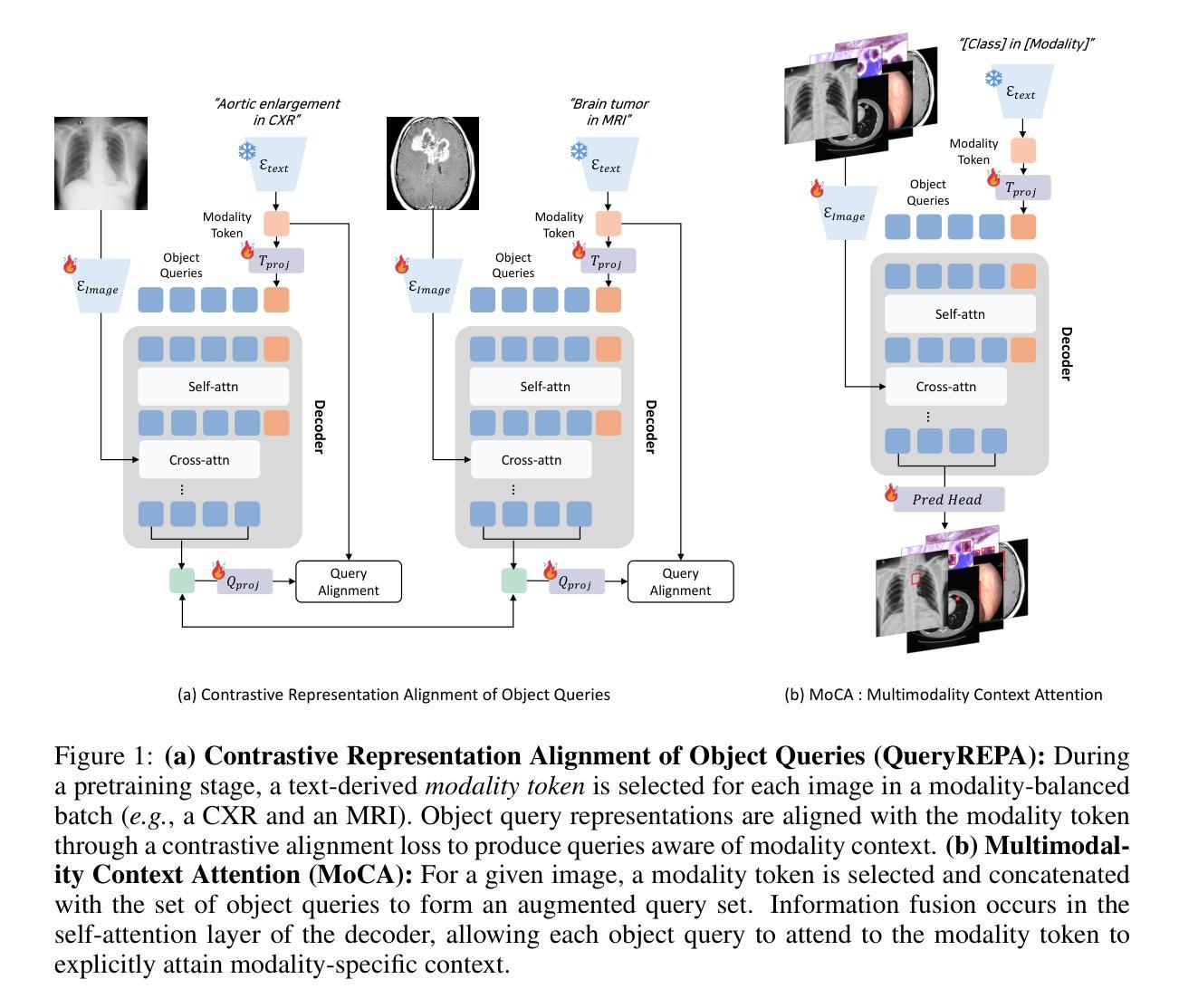
Align Your Query: Representation Alignment for Multimodality Medical Object Detection
Authors:Ara Seo, Bryan Sangwoo Kim, Hyungjin Chung, Jong Chul Ye
Medical object detection suffers when a single detector is trained on mixed medical modalities (e.g., CXR, CT, MRI) due to heterogeneous statistics and disjoint representation spaces. To address this challenge, we turn to representation alignment, an approach that has proven effective for bringing features from different sources into a shared space. Specifically, we target the representations of DETR-style object queries and propose a simple, detector-agnostic framework to align them with modality context. First, we define modality tokens: compact, text-derived embeddings encoding imaging modality that are lightweight and require no extra annotations. We integrate the modality tokens into the detection process via Multimodality Context Attention (MoCA), mixing object-query representations via self-attention to propagate modality context within the query set. This preserves DETR-style architectures and adds negligible latency while injecting modality cues into object queries. We further introduce QueryREPA, a short pretraining stage that aligns query representations to their modality tokens using a task-specific contrastive objective with modality-balanced batches. Together, MoCA and QueryREPA produce modality-aware, class-faithful queries that transfer effectively to downstream training. Across diverse modalities trained altogether, the proposed approach consistently improves AP with minimal overhead and no architectural modifications, offering a practical path toward robust multimodality medical object detection. Project page: https://araseo.github.io/alignyourquery/.
医学对象检测在单一检测器对混合医学模态(如CXR、CT、MRI)进行训练时会遇到困难,这是由于统计数据的异质性和表示空间的分离所导致的。为了应对这一挑战,我们转向表示对齐,这是一种已被证明可以将不同来源的特征带入共享空间的有效方法。具体来说,我们针对DETR风格的对象查询表示,提出一个简单、通用的框架,将其与模态上下文对齐。首先,我们定义模态令牌:紧凑、文本衍生的嵌入编码成像模态,它们轻便且无需额外注释。我们通过多模态上下文注意力(MoCA)将模态令牌集成到检测过程中,通过自注意力将对象查询表示混合,在查询集中传播模态上下文。这保留了DETR风格架构,增加了微不足道的延迟,同时将模态线索注入对象查询中。我们还引入了QueryREPA,这是一个简短的预训练阶段,通过任务特定的对比目标和模态平衡批次将查询表示与他们的模态令牌对齐。MoCA和QueryREPA共同作用,产生感知模态的类忠实查询,有效地转移到下游训练中。通过不同的模态共同训练,所提出的方法在平均准确度(AP)上实现了一致的改进,带来了最小的开销并且不需要修改架构。这为朝着稳健的多模态医学对象检测提供了一条实用途径。项目页面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://araseo.github.io/alignyourquery/
Summary
针对医学图像多模态检测中的异质统计和离散表示空间问题,提出一种基于表示对齐的方法,通过定义模态令牌并集成到检测过程中,实现对不同模态的共享空间表示。引入多模态上下文注意力(MoCA)和QueryREPA预训练阶段,有效提高多模态医学对象检测的鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学对象检测在混合医学模态(如CXR、CT、MRI)上的单一检测器训练会面临挑战,主要由于异质统计和离散表示空间造成。
- 提出使用表示对齐方法来解决此挑战,该方法可有效将不同来源的特征带入共享空间。
- 目标是针对DETR风格的对象查询表示,提出一个简单、检测器无关的框架来进行对齐,并与模态上下文集成。
- 定义模态令牌,这是一种紧凑的、基于文本的嵌入,编码成像模态,轻便且无需额外注释。
- 通过多模态上下文注意力(MoCA)将模态令牌集成到检测过程中,通过自注意力混合对象查询表示,在查询集中传播模态上下文。
- 引入QueryREPA预训练阶段,通过对查询表示与模态令牌进行对齐,使用具有模态平衡批次的任务特定对比目标。
点此查看论文截图

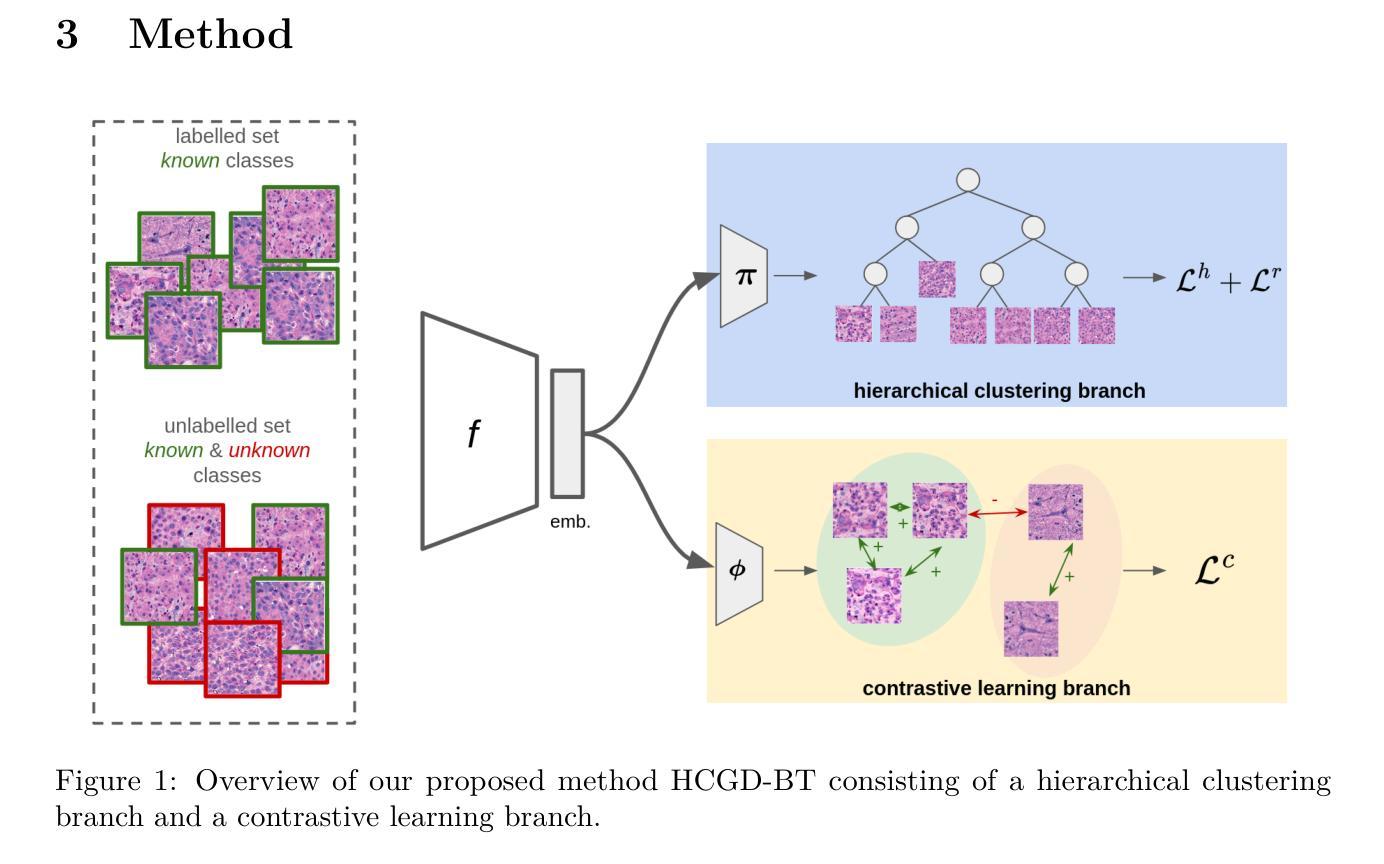
Hierarchical Generalized Category Discovery for Brain Tumor Classification in Digital Pathology
Authors:Matthias Perkonigg, Patrick Rockenschaub, Georg Göbel, Adelheid Wöhrer
Accurate brain tumor classification is critical for intra-operative decision making in neuro-oncological surgery. However, existing approaches are restricted to a fixed set of predefined classes and are therefore unable to capture patterns of tumor types not available during training. Unsupervised learning can extract general-purpose features, but it lacks the ability to incorporate prior knowledge from labelled data, and semi-supervised methods often assume that all potential classes are represented in the labelled data. Generalized Category Discovery (GCD) aims to bridge this gap by categorizing both known and unknown classes within unlabelled data. To reflect the hierarchical structure of brain tumor taxonomies, in this work, we introduce Hierarchical Generalized Category Discovery for Brain Tumor Classification (HGCD-BT), a novel approach that integrates hierarchical clustering with contrastive learning. Our method extends contrastive learning based GCD by incorporating a novel semi-supervised hierarchical clustering loss. We evaluate HGCD-BT on OpenSRH, a dataset of stimulated Raman histology brain tumor images, achieving a +28% improvement in accuracy over state-of-the-art GCD methods for patch-level classification, particularly in identifying previously unseen tumor categories. Furthermore, we demonstrate the generalizability of HGCD-BT on slide-level classification of hematoxylin and eosin stained whole-slide images from the Digital Brain Tumor Atlas, confirming its utility across imaging modalities.
精确的脑肿瘤分类对于神经肿瘤外科手术中的决策制定至关重要。然而,现有方法仅限于一组预定义的类别,因此无法捕获训练期间未出现的肿瘤类型模式。无监督学习可以提取通用特征,但它缺乏将先验知识融入标注数据的能力,而半监督方法通常假设所有潜在类别都在标注数据中有所体现。广义类别发现(GCD)旨在通过无标签数据中的已知和未知类别分类来缩小这一差距。为了反映脑肿瘤分类的层次结构,我们在本文中引入了用于脑肿瘤分类的分层广义类别发现(HGCD-BT)这一新方法,该方法将层次聚类与对比学习相结合。我们的方法通过融入一种新型半监督层次聚类损失扩展了基于对比学习的GCD。我们在OpenSRH(一个模拟拉曼组织脑肿瘤图像数据集)上对HGCD-BT进行了评估,与前沿的GCD方法在补丁级别分类上的准确率提高了+28%,特别是在识别先前未见过的肿瘤类别方面表现尤为出色。此外,我们在数字脑肿瘤图谱中的苏木精和伊红染色全片图像切片级别的分类上验证了HGCD-BT的通用性,证明了其在不同成像模式中的实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于脑肿瘤分类的新方法——分层广义类别发现(HGCD-BT),该方法结合了分层聚类和对比学习,旨在弥补现有方法对已知和未知类别分类的空白。在OpenSRH数据集上的实验表明,HGCD-BT在斑块级别分类的准确度比最新GCD方法提高了28%,特别是在识别先前未见过的肿瘤类别方面表现出色。此外,HGCD-BT在全脑肿瘤图谱中的HE染色全幻灯片图像幻灯片级别分类上的表现也证明了其跨成像模式的通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 脑肿瘤分类对于神经肿瘤外科手术中的决策至关重要。
- 现有方法受限于预设类别集,无法识别训练期间未涵盖的肿瘤类型模式。
- 分层广义类别发现(HGCD)旨在分类已知和未知类别,弥补这一缺陷。
- HGCD-BT是HGCD在脑肿瘤分类中的具体应用,结合了分层聚类和对比学习。
- HGCD-BT在OpenSRH数据集上的表现优于最新的GCD方法,尤其在识别先前未见的肿瘤类别方面。
- HGCD-BT在跨成像模式(如不同染色技术和图像类型)下具有良好的通用性。
点此查看论文截图
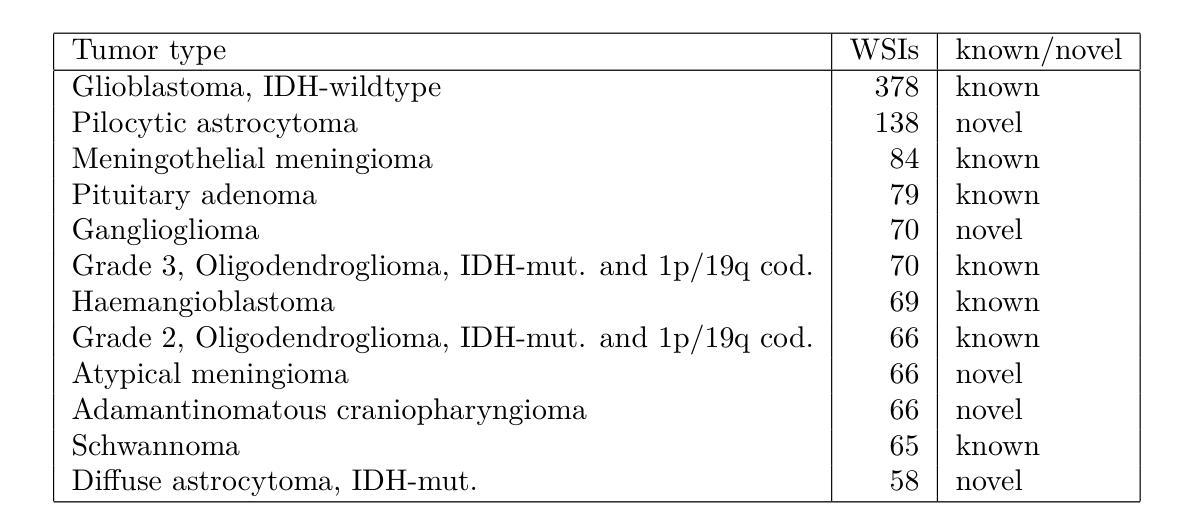
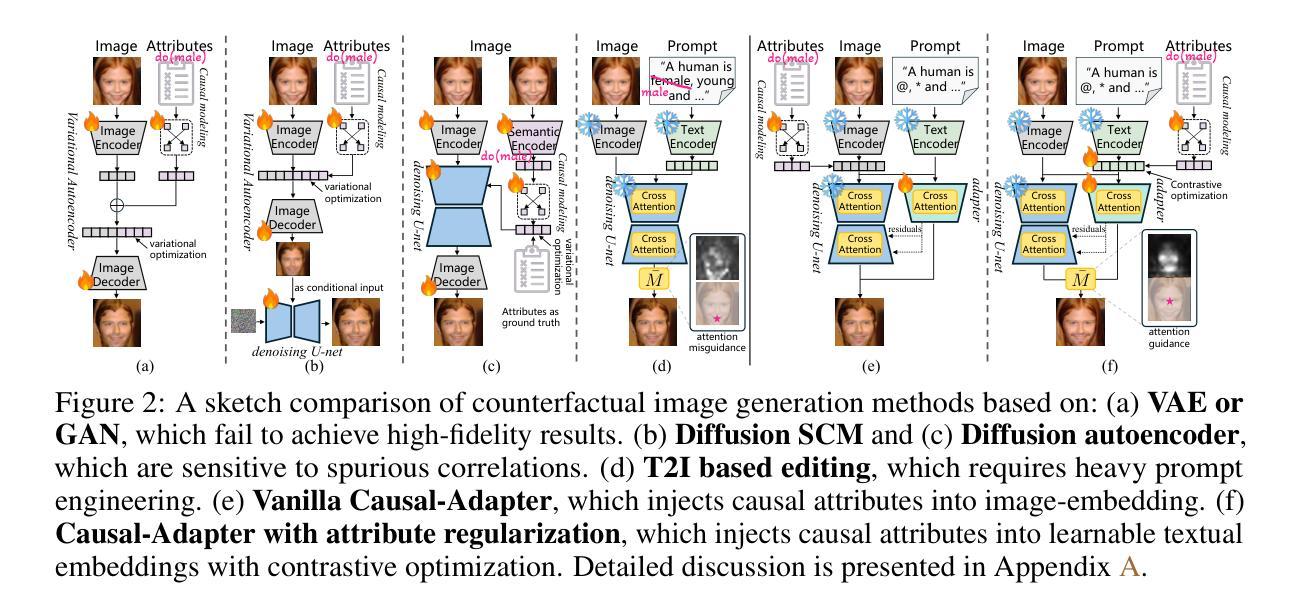
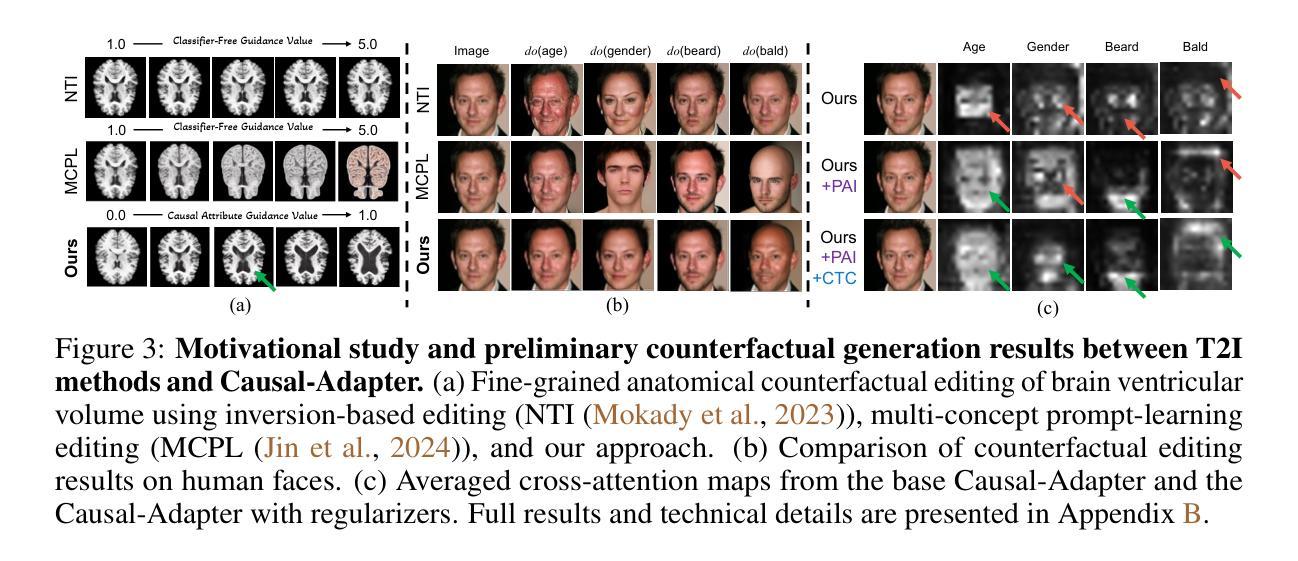
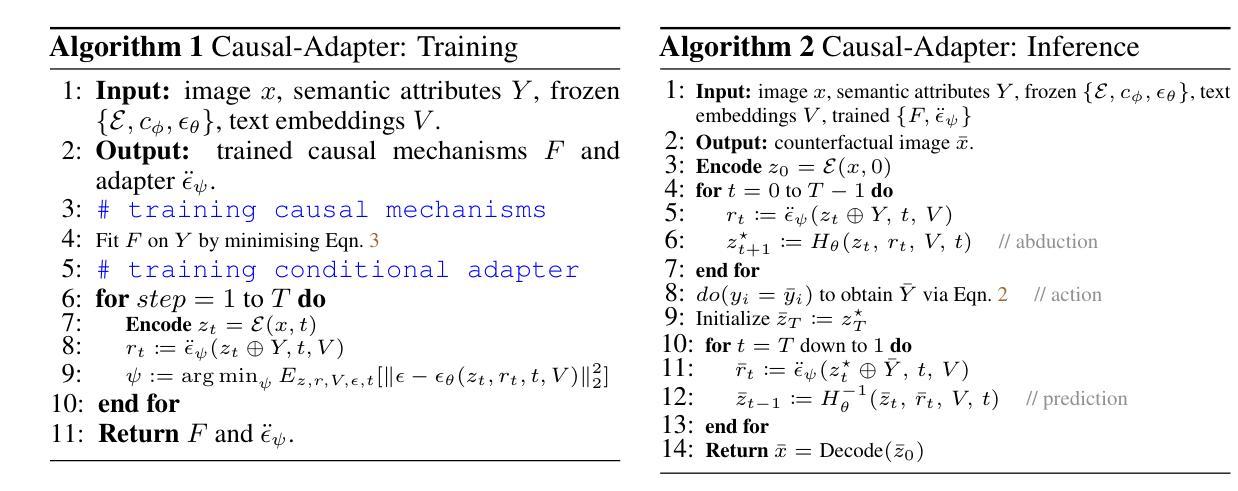
Causal-Adapter: Taming Text-to-Image Diffusion for Faithful Counterfactual Generation
Authors:Lei Tong, Zhihua Liu, Chaochao Lu, Dino Oglic, Tom Diethe, Philip Teare, Sotirios A. Tsaftaris, Chen Jin
We present Causal-Adapter, a modular framework that adapts frozen text-to-image diffusion backbones for counterfactual image generation. Our method enables causal interventions on target attributes, consistently propagating their effects to causal dependents without altering the core identity of the image. In contrast to prior approaches that rely on prompt engineering without explicit causal structure, Causal-Adapter leverages structural causal modeling augmented with two attribute regularization strategies: prompt-aligned injection, which aligns causal attributes with textual embeddings for precise semantic control, and a conditioned token contrastive loss to disentangle attribute factors and reduce spurious correlations. Causal-Adapter achieves state-of-the-art performance on both synthetic and real-world datasets, with up to 91% MAE reduction on Pendulum for accurate attribute control and 87% FID reduction on ADNI for high-fidelity MRI image generation. These results show that our approach enables robust, generalizable counterfactual editing with faithful attribute modification and strong identity preservation.
我们提出了因果适配器(Causal-Adapter)这一模块化框架,用于适应冻结的文本到图像扩散主干网络以进行反事实图像生成。我们的方法能够在目标属性上实施因果干预,并持续地将这些效应传播到因果依赖项上,而不会改变图像的核心身份。与以往依赖提示工程且没有明确的因果结构的方法相比,因果适配器利用结构因果建模并结合两种属性正则化策略:提示对齐注入,将因果属性与文本嵌入对齐以实现精确语义控制;条件令牌对比损失,以解开属性因素并减少虚假关联。因果适配器在合成和现实世界数据集上均达到了最先进的性能,在摆锤数据集上实现了高达91%的MAE降低以实现精确的属性控制,在ADNI数据集上实现了高达87%的FID降低以实现高保真MRI图像生成。这些结果表明,我们的方法能够实现稳健且可泛化的反事实编辑,具有可靠的属性修改和强大的身份保留功能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 26 figures
Summary
Causal-Adapter是一个模块化框架,用于适应冷冻文本到图像的扩散主干以进行反事实图像生成。通过因果干预目标属性,该方法能够在不改变图像核心身份的情况下,持续地将干预效果传播到因果依赖项。与依赖提示工程而没有明确因果结构的旧方法不同,Causal-Adapter利用结构因果建模,辅以两种属性正则化策略:提示对齐注入和条件令牌对比损失。前者将因果属性与文本嵌入对齐,以实现精确语义控制;后者用于分解属性因素并减少偶然关联。Causal-Adapter在合成和真实数据集上均达到领先水平,在Pendulum上实现高达91%的MAE减少,进行准确的属性控制,并在ADNI上实现87%的FID减少,用于高保真MRI图像生成。结果显示,该方法能够实现稳健、通用的反事实编辑,具有忠诚的属性修改和强大的身份保留。
Key Takeaways
- Causal-Adapter是一个适应文本到图像扩散模型的模块化框架,用于反事实图像生成。
- 该方法能够实现因果干预目标属性,并持续地将干预效果传播到因果依赖项,同时保持图像的核心身份不变。
- 与其他方法相比,Causal-Adapter利用结构因果建模,并辅以两种属性正则化策略:提示对齐注入和条件令牌对比损失。
- 提示对齐注入策略能够将因果属性与文本嵌入对齐,从而实现精确的语义控制。
- 条件令牌对比损失策略有助于分解属性因素并减少偶然关联。
- Causal-Adapter在多个数据集上达到了领先水平,包括在Pendulum上的MAE减少91%,以及在ADNI上的FID减少87%。
点此查看论文截图
Robust Pan-Cancer Mitotic Figure Detection with YOLOv12
Authors:Raphaël Bourgade, Guillaume Balezo, Thomas Walter
Mitotic figures represent a key histoprognostic feature in tumor pathology, providing crucial insights into tumor aggressiveness and proliferation. However, their identification remains challenging, subject to significant inter-observer variability, even among experienced pathologists. To address this issue, the MItosis DOmain Generalization (MIDOG) 2025 challenge marks the third edition of an international competition aiming to develop robust mitosis detection algorithms. In this paper, we present a mitotic figure detection approach based on the state-of-the-art YOLOv12 object detection architecture. Our method achieved an F1-score of 0.801 on the preliminary test set (hotspots only) and ranked second on the final test leaderboard with an F1-score of 0.7216 across complex and heterogeneous whole-slide regions, without relying on external data.
有丝分裂图像在肿瘤病理学中是一个关键的组织预后特征,为肿瘤侵袭性和增殖提供了重要见解。然而,它们的识别仍然具有挑战性,即使是经验丰富的病理学家之间也存在显著的观察者间变异。为了解决这一问题,有丝分裂域泛化(MIDOG)2025挑战标志着旨在开发稳健的有丝分裂检测算法的第三次国际竞赛。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于最新YOLOv12目标检测架构的有丝分裂图像检测方法。我们的方法在初步测试集(仅热点)上达到了0.801的F1分数,并在最终测试排行榜上以0.7216的F1分数排名第二,涵盖了复杂且异质的全幻灯片区域,且无需依赖外部数据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在肿瘤病理学中,有丝分裂图像作为关键的组织预后特征,对肿瘤侵袭性和增殖提供重要见解。然而,其识别仍然具有挑战性,存在显著的观察者间变异。为解决这一问题,MItosis DOmain Generalization(MIDOG)挑战是一个国际竞赛的第三版,旨在开发稳健的有丝分裂检测算法。本文提出了一种基于最新YOLOv12目标检测架构的有丝分裂图像检测方法,该方法在初步测试集上取得了F1分数为0.801(仅针对热点区域),并在最终测试排行榜上以F1分数为0.7216排名第二,覆盖了复杂且异质的整张幻灯片区域,且无需依赖外部数据。
Key Takeaways
- 有丝分裂图像是肿瘤病理学中重要的组织预后特征,能反映肿瘤的侵袭性和增殖情况。
- 有丝分裂图像的识别存在挑战,不同观察者之间存在显著的差异。
- MItosis DOmain Generalization (MIDOG) 挑战是国际上的竞赛,旨在开发稳健的有丝分裂检测算法。
- 本文采用基于YOLOv12目标检测架构的方法,进行有丝分裂图像检测。
- 该方法在初步测试集上取得了较高的F1分数(0.801)。
- 在最终测试中,该方法在复杂的整张幻灯片区域上取得了F1分数为0.7216,并排名第二。
点此查看论文截图

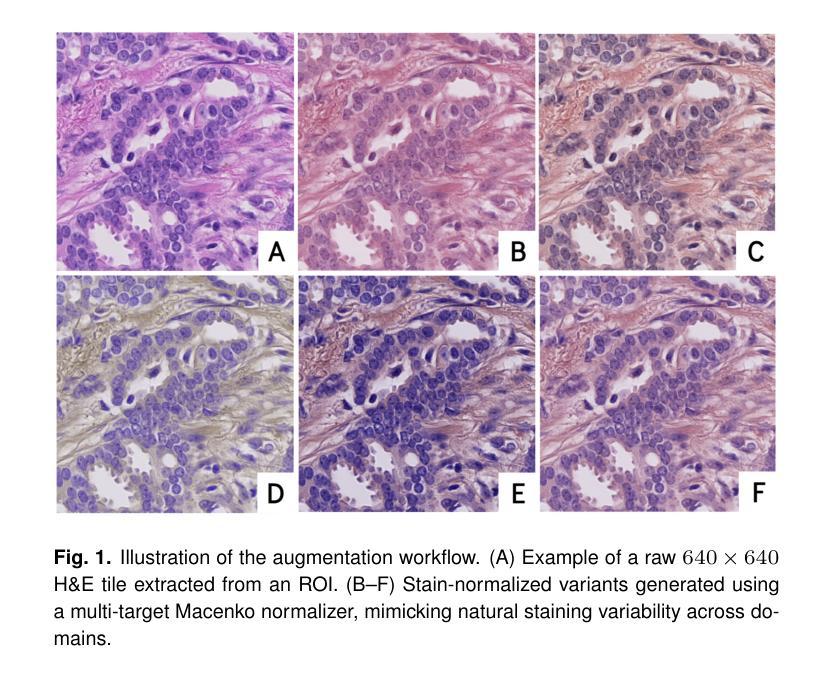
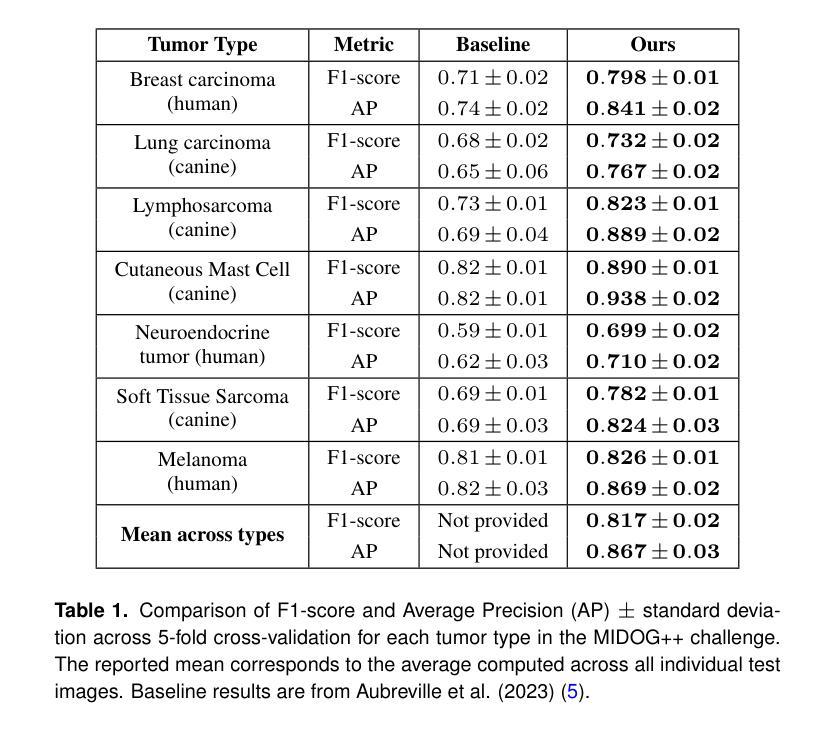
A Tutorial on MRI Reconstruction: From Modern Methods to Clinical Implications
Authors:Tolga Çukur, Salman U. H. Dar, Valiyeh Ansarian Nezhad, Yohan Jun, Tae Hyung Kim, Shohei Fujita, Berkin Bilgic
MRI is an indispensable clinical tool, offering a rich variety of tissue contrasts to support broad diagnostic and research applications. Clinical exams routinely acquire multiple structural sequences that provide complementary information for differential diagnosis, while research protocols often incorporate advanced functional, diffusion, spectroscopic, and relaxometry sequences to capture multidimensional insights into tissue structure and composition. However, these capabilities come at the cost of prolonged scan times, which reduce patient throughput, increase susceptibility to motion artifacts, and may require trade-offs in image quality or diagnostic scope. Over the last two decades, advances in image reconstruction algorithms–alongside improvements in hardware and pulse sequence design–have made it possible to accelerate acquisitions while preserving diagnostic quality. Central to this progress is the ability to incorporate prior information to regularize the solutions to the reconstruction problem. In this tutorial, we overview the basics of MRI reconstruction and highlight state-of-the-art approaches, beginning with classical methods that rely on explicit hand-crafted priors, and then turning to deep learning methods that leverage a combination of learned and crafted priors to further push the performance envelope. We also explore the translational aspects and eventual clinical implications of these methods. We conclude by discussing future directions to address remaining challenges in MRI reconstruction. The tutorial is accompanied by a Python toolbox (https://github.com/tutorial-MRI-recon/tutorial) to demonstrate select methods discussed in the article.
磁共振成像(MRI)是临床中不可或缺的工具,提供了丰富的组织对比度,支持广泛的诊断和医学研究应用。在临床检查中,通常获取多个结构序列,为鉴别诊断提供补充信息;而研究协议通常包含高级的功能、扩散、光谱和松弛序列,以捕捉关于组织结构和组成的多维度见解。然而,这些功能需要长时间的扫描,降低了患者通过率,增加了运动伪影的易感性,并可能需要牺牲图像质量或诊断范围。在过去的二十年中,随着图像重建算法的进步以及硬件和脉冲序列设计的改进,在加速采集的同时保持诊断质量成为可能。这种进步的核心是融入先验信息以规范化重建问题的解决方案。在本教程中,我们概述了磁共振成像重建的基础知识,并重点介绍了最新方法,首先从依赖显式手工先验的经典方法开始,然后转向利用学习和手工先验相结合深度学习方法,以进一步突破性能极限。我们还探讨了这些方法的翻译方面以及最终的临床影响。最后,我们讨论了解决磁共振成像重建中剩余挑战的未来方向。本教程还附带了一个Python工具箱(https://github.com/tutorial-MRI-recon/tutorial),以演示文章中讨论的选择性方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering. The final published version is available at https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2025.3617575
Summary
核磁共振成像(MRI)是临床不可或缺的工具,具有多种组织对比度,支持广泛的诊断和科研应用。临床检查经常获取多个结构序列,为鉴别诊断提供补充信息,而研究协议通常包含高级功能、扩散、光谱和松弛序列,以获取对组织结构和组成的多维度见解。然而,这些功能需要延长扫描时间,这降低了患者通过率,增加了运动伪影的易感性,并可能影响图像质量或诊断范围。过去二十年来,图像重建算法的进步以及硬件和脉冲序列设计的改进,能够在保持诊断质量的同时加速采集。本文概述了核磁共振成像重建的基础知识,并介绍了最新方法,包括依赖明确手工先验的经典方法,以及利用学习和手工先验结合的深度学习方法。我们还探讨了这些方法的临床转化方面及其最终的临床影响。
Key Takeaways
- MRI是临床不可或缺的工具,具有多种组织对比度,广泛应用于诊断和科研。
- 临床检查经常获取多个结构序列以支持诊断,而研究协议包含高级序列以获取多维度见解。
- 扫描时间延长会影响患者通过率、增加运动伪影风险并可能影响图像质量和诊断范围。
- 过去的二十年中,MRI图像重建算法取得了进步,可以加速采集过程并保持诊断质量。
- 最新方法包括使用明确手工先验的经典方法和结合学习和手工先验的深度学习方法。
- 这些图像重建方法的临床转化及其最终临床影响是被探讨的重要话题。
点此查看论文截图
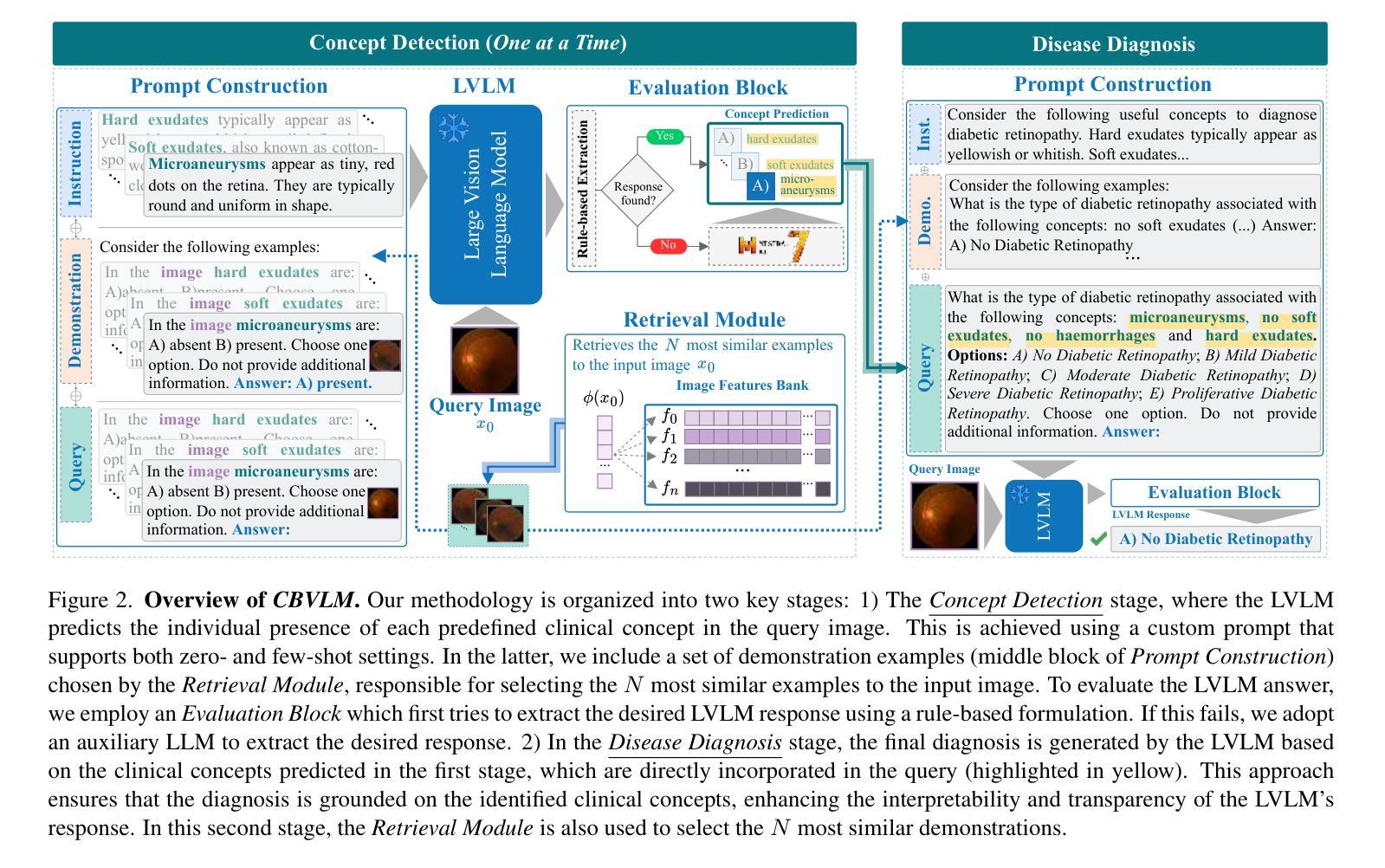
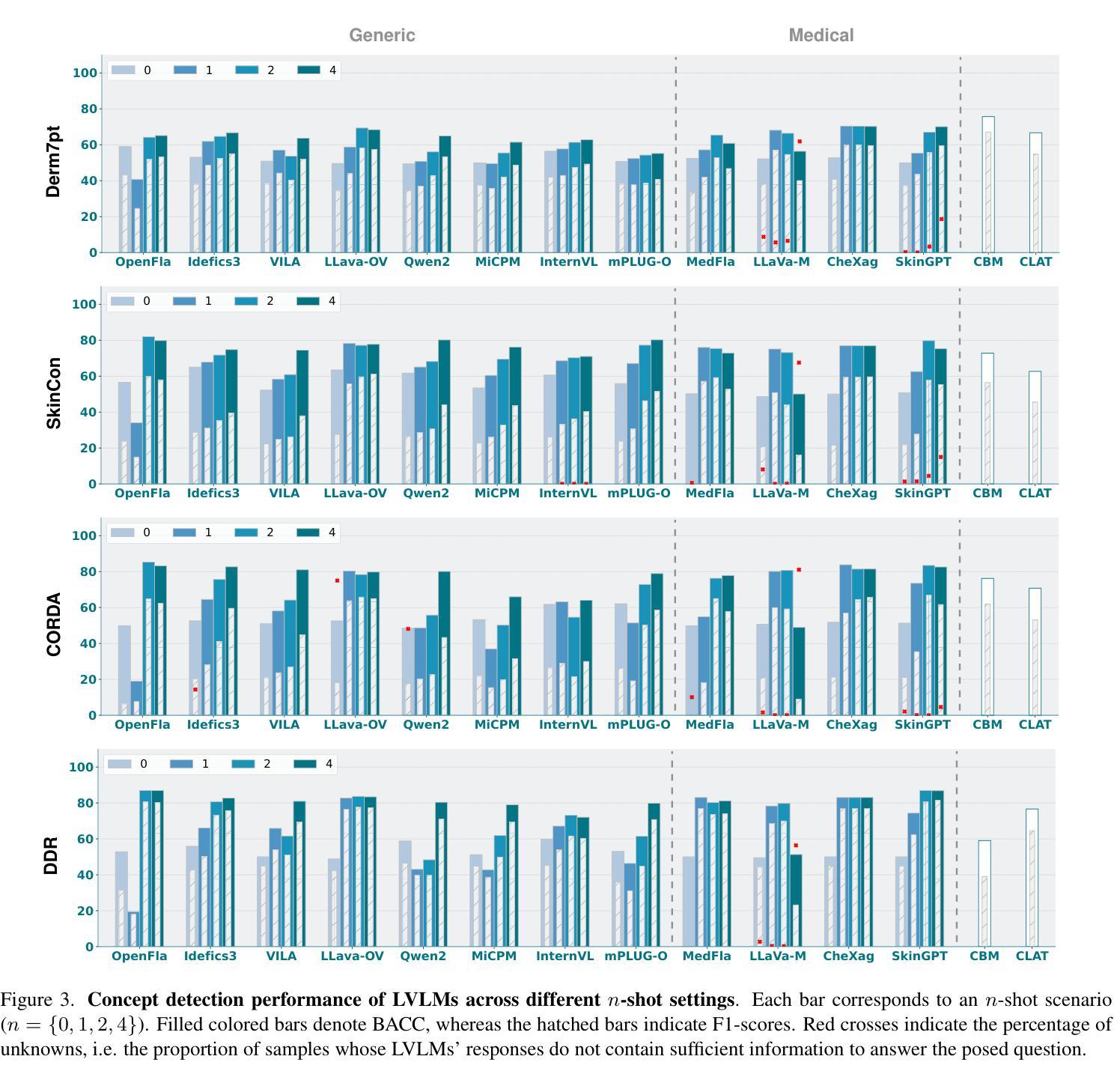
CBVLM: Training-free Explainable Concept-based Large Vision Language Models for Medical Image Classification
Authors:Cristiano Patrício, Isabel Rio-Torto, Jaime S. Cardoso, Luís F. Teixeira, João C. Neves
The main challenges limiting the adoption of deep learning-based solutions in medical workflows are the availability of annotated data and the lack of interpretability of such systems. Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs) tackle the latter by constraining the model output on a set of predefined and human-interpretable concepts. However, the increased interpretability achieved through these concept-based explanations implies a higher annotation burden. Moreover, if a new concept needs to be added, the whole system needs to be retrained. Inspired by the remarkable performance shown by Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) in few-shot settings, we propose a simple, yet effective, methodology, CBVLM, which tackles both of the aforementioned challenges. First, for each concept, we prompt the LVLM to answer if the concept is present in the input image. Then, we ask the LVLM to classify the image based on the previous concept predictions. Moreover, in both stages, we incorporate a retrieval module responsible for selecting the best examples for in-context learning. By grounding the final diagnosis on the predicted concepts, we ensure explainability, and by leveraging the few-shot capabilities of LVLMs, we drastically lower the annotation cost. We validate our approach with extensive experiments across four medical datasets and twelve LVLMs (both generic and medical) and show that CBVLM consistently outperforms CBMs and task-specific supervised methods without requiring any training and using just a few annotated examples. More information on our project page: https://cristianopatricio.github.io/CBVLM/.
在医学工作流中采用基于深度学习的解决方案的主要挑战是标注数据的可用性和系统解释性的缺乏。概念瓶颈模型(CBMs)通过约束模型输出在一组预定义和可人类解释的概念上来解决后者问题。然而,通过这些概念解释实现的增加的解释性意味着更高的标注负担。而且,如果需要添加新概念,整个系统需要重新训练。受大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在少量样本设置中的出色表现的启发,我们提出了一种简单而有效的方法论CBVLM,该方法解决了上述两个挑战。首先,对于每个概念,我们提示LVLM回答概念是否出现在输入图像中。然后,我们让LVLM基于之前的概念预测对图像进行分类。而且,在两个阶段中,我们融入了一个检索模块,负责选择最佳样本进行上下文学习。通过将最终诊断建立在预测的概念上,我们确保了可解释性,并通过利用LVLMs的少量样本能力,我们大大降低了标注成本。我们通过四个医学数据集和十二个(通用和医学)LVLM的广泛实验验证了我们的方法,并显示CBVLM持续优于CBMs和特定任务监督方法,而且无需任何训练,只需使用少数几个标注样本。更多关于我们项目页面的信息:https://cristianopatricio.github.io/CBVLM/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in Computers in Biology and Medicine
Summary
本文探讨了深度学习在医学工作流中应用的主要挑战,包括标注数据可用性和系统解释性缺乏的问题。提出一种名为CBVLM的新方法,通过利用大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的少样本学习能力,解决这两个问题。CBVLM能够通过预测概念并基于这些预测进行分类,确保诊断的合理性。通过简单的操作和几个标注例子,CBVLM能大幅度降低标注成本。实验结果证实CBVLM在四个医学数据集上持续优于概念瓶颈模型(CBMs)和任务特定监督方法。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医学工作流中面临标注数据可用性和系统解释性问题。
- 概念瓶颈模型(CBMs)解决了系统解释性问题,但增加了标注负担,且添加新概念需要整个系统重新训练。
- 本文提出CBVLM方法,利用大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)的少样本学习能力解决上述问题。
- CBVLM通过预测概念并基于这些预测对图像进行分类,确保诊断的合理性。
- CBVLM通过简单的操作和几个标注例子大幅度降低了标注成本。
- 实验结果证实CBVLM在多个医学数据集上的性能优于CBMs和任务特定监督方法。
点此查看论文截图
WaveNet-SF: A Hybrid Network for Retinal Disease Detection Based on Wavelet Transform in Spatial-Frequency Domain
Authors:Jilan Cheng, Guoli Long, Zeyu Zhang, Zhenjia Qi, Hanyu Wang, Libin Lu, Shuihua Wang, Yudong Zhang, Jin Hong
Retinal diseases are a leading cause of vision impairment and blindness, with timely diagnosis being critical for effective treatment. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) has become a standard imaging modality for retinal disease diagnosis, but OCT images often suffer from issues such as speckle noise, complex lesion shapes, and varying lesion sizes, making interpretation challenging. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, WaveNet-SF, to enhance retinal disease detection by integrating the spatial-domain and frequency-domain learning. The framework utilizes wavelet transforms to decompose OCT images into low- and high-frequency components, enabling the model to extract both global structural features and fine-grained details. To improve lesion detection, we introduce a Multi-Scale Wavelet Spatial Attention (MSW-SA) module, which enhances the model’s focus on regions of interest at multiple scales. Additionally, a High-Frequency Feature Compensation (HFFC) block is incorporated to recover edge information lost during wavelet decomposition, suppress noise, and preserve fine details crucial for lesion detection. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) classification accuracies of 97.82% and 99.58% on the OCT-C8 and OCT2017 datasets, respectively, surpassing existing methods. These results demonstrate the efficacy of WaveNet-SF in addressing the challenges of OCT image analysis and its potential as a powerful tool for retinal disease diagnosis.
视网膜疾病是导致视力和失明的主要原因之一,及时诊断对有效治疗至关重要。光学相干断层扫描(OCT)已成为视网膜疾病诊断的标准成像方式,但OCT图像常常存在斑点噪声、病变形状复杂、病变大小不一等问题,使得解读具有挑战性。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型框架WaveNet-SF,通过结合空间域和频率域学习,增强视网膜疾病的检测。该框架利用小波变换将OCT图像分解为低频和高频成分,使模型能够提取全局结构特征和细粒度细节。为了提高病变检测能力,我们引入了一种多尺度小波空间注意力(MSW-SA)模块,该模块能够在多个尺度上增强模型对感兴趣区域的关注。此外,还融入了一种高频特征补偿(HFFC)块,以恢复小波分解过程中丢失的边缘信息,抑制噪声,并保留对病变检测至关重要的细节。我们的方法在OCT-C8和OCT2017数据集上分别实现了最先进的分类准确率97.82%和99.58%,超越了现有方法。这些结果证明了WaveNet-SF在解决OCT图像分析挑战方面的有效性,以及其作为视网膜疾病诊断的强大工具潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为WaveNet-SF的新框架,用于增强视网膜疾病检测。该框架结合了空间域和频率域学习,利用小波变换将OCT图像分解为低频和高频成分,从而提取全局结构特征和精细细节。通过引入多尺度小波空间注意力模块和高频特征补偿块,提高了病变检测性能。WaveNet-SF在OCT-C8和OCT2017数据集上取得了最先进的分类准确率,分别为97.82%和99.58%,表现出对OCT图像分析的有效性,并有望成为视网膜疾病诊断的有力工具。
Key Takeaways
- 视网膜疾病是视力受损和失明的主要原因,及时诊断对有效治疗至关重要。
- OCT(光学相干断层扫描)是视网膜疾病诊断的标准成像技术,但OCT图像存在斑点噪声、病变形状复杂和病变大小不一等问题,使得解读具有挑战性。
- 提出了新的框架WaveNet-SF,结合空间域和频率域学习,以提高视网膜疾病的检测。
- 利用小波变换分解OCT图像为低频和高频成分,以便提取全局结构特征和精细细节。
- 引入多尺度小波空间注意力模块(MSW-SA),提高病变检测的准确性。
- 加入了高频特征补偿块(HFFC),以恢复丢失的边缘信息,抑制噪声,并保留对病变检测至关重要的精细细节。
点此查看论文截图
MIAFEx: An Attention-based Feature Extraction Method for Medical Image Classification
Authors:Oscar Ramos-Soto, Jorge Ramos-Frutos, Ezequiel Perez-Zarate, Diego Oliva, Sandra E. Balderas-Mata
Feature extraction techniques are crucial in medical image classification; however, classical feature extractors, in addition to traditional machine learning classifiers, often exhibit significant limitations in providing sufficient discriminative information for complex image sets. While Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Vision Transformer (ViT) have shown promise in feature extraction, they are prone to overfitting due to the inherent characteristics of medical imaging data, including small sample sizes or high intra-class variance. In this work, the Medical Image Attention-based Feature Extractor (MIAFEx) is proposed, a novel method that employs a learnable refinement mechanism to enhance the classification token within the Transformer encoder architecture. This mechanism adjusts the token based on learned weights, improving the extraction of salient features and enhancing the model’s adaptability to the challenges presented by medical imaging data. The MIAFEx output feature quality is compared against classical feature extractors using traditional and hybrid classifiers. Also, the performance of these features is compared against modern CNN and ViT models in classification tasks, demonstrating their superiority in accuracy and robustness across multiple complex medical imaging datasets. This advantage is particularly pronounced in scenarios with limited training data, where traditional and modern models often struggle to generalize effectively. The source code of this proposal can be found at https://github.com/Oscar-RamosS/Medical-Image-Attention-based-Feature-Extractor-MIAFEx
特征提取技术在医学图像分类中起着至关重要的作用;然而,除了传统的机器学习分类器外,经典的特征提取器在为复杂的图像集提供足够的判别信息时往往存在重大局限。卷积神经网络(CNNs)和视觉转换器(ViT)在特征提取方面显示出潜力,但由于医学成像数据固有的特性,包括样本量小或类内方差高,它们容易过度拟合。本文提出了基于医学图像注意力的特征提取器(MIAFEx),这是一种新方法,采用可学习的细化机制来提高Transformer编码器架构中的分类标记。该机制根据学习到的权重调整标记,提高了显著特征的提取能力,增强了模型对医学成像数据挑战的适应能力。MIAFEx的输出特征质量使用传统和混合分类器与经典特征提取器进行了比较。此外,这些特征在分类任务中的性能与现代CNN和ViT模型进行了比较,证明它们在多个复杂的医学成像数据集上的准确性和稳健性方面具有优势。这一优势在训练数据有限的情况下尤为突出,传统和现代模型往往难以有效地推广。该提案的源代码可在https://github.com/Oscar-RamosS/Medical-Image-Attention-based-Feature-Extractor-MIAFEx找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This is the preprint version of an article that has been accepted for publication in Knowledge-Based Systems
摘要
医学图像分类中特征提取技术至关重要。然而,传统特征提取器结合传统机器学习分类器在处理复杂图像集时,提供足够判别信息方面存在显著局限性。卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)在特征提取方面展现出潜力,但由于医学成像数据的小样本规模或高类内方差等固有特性,易出现过拟合。本文提出医学图像注意力特征提取器(MIAFEx),这是一种采用可学习细化机制的新方法,用于增强转换器编码器架构中的分类令牌。这种机制基于学习到的权重调整令牌,改进了显著特征的提取,增强了模型对医学成像数据挑战的适应性。MIAFEx的特征输出质量与经典特征提取器使用传统和混合分类器进行了比较。此外,这些特征与现代CNN和ViT模型在分类任务上的表现进行了比较,在多个复杂医学成像数据集上展示了其在准确性和稳健性方面的优越性。特别是在训练数据有限的情况下,传统和现代模型往往难以有效推广,而MIAFEx的优势更为突出。相关源代码可见:https://github.com/Oscar-RamosS/Medical-Image-Attention-based-Feature-Extractor-MIAFEx。
要点
- 医学图像分类中特征提取的重要性及其对传统方法的挑战。
- CNN和ViT在医学图像特征提取中的应用及其局限性。
- 提出了一种新的医学图像注意力特征提取器(MIAFEx),结合可学习细化机制,增强分类令牌。
- MIAFEx在多个复杂医学成像数据集上,与现代CNN和ViT模型相比,表现出优异的准确性和稳健性。
- MIAFEx在有限训练数据的情况下表现尤其出色。
- 源代码可在指定GitHub仓库找到。
点此查看论文截图

tCURLoRA: Tensor CUR Decomposition Based Low-Rank Parameter Adaptation and Its Application in Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Guanghua He, Wangang Cheng, Hancan Zhu, Xiaohao Cai, Gaohang Yu
Transfer learning, by leveraging knowledge from pre-trained models, has significantly enhanced the performance of target tasks. However, as deep neural networks scale up, full fine-tuning introduces substantial computational and storage challenges in resource-constrained environments, limiting its widespread adoption. To address this, parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods have been developed to reduce computational complexity and storage requirements by minimizing the number of updated parameters. While matrix decomposition-based PEFT methods, such as LoRA, show promise, they struggle to fully capture the high-dimensional structural characteristics of model weights. In contrast, high-dimensional tensors offer a more natural representation of neural network weights, allowing for a more comprehensive capture of higher-order features and multi-dimensional interactions. In this paper, we propose tCURLoRA, a novel fine-tuning method based on tensor CUR decomposition. By concatenating pre-trained weight matrices into a three-dimensional tensor and applying tensor CUR decomposition, we update only the lower-order tensor components during fine-tuning, effectively reducing computational and storage overhead. Experimental results demonstrate that tCURLoRA outperforms existing PEFT methods in medical image segmentation tasks.
借助预训练模型的知识进行迁移学习已显著提高目标任务的性能。然而,随着深度神经网络规模的扩大,完全微调在资源受限的环境中引发了巨大的计算和存储挑战,限制了其广泛应用。为了解决这一问题,开发了参数高效微调(PEFT)方法,通过最小化更新的参数数量来降低计算复杂性和存储要求。虽然基于矩阵分解的PEFT方法(如LoRA)显示出潜力,但它们难以完全捕获模型权重的高维结构特征。相反,高维张量提供了神经网络权重的更自然表示,能够更全面地捕获高阶特征和多维交互。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于张量CUR分解的新型微调方法tCURLoRA。我们将预训练的权重矩阵合并成一个三维张量,并应用张量CUR分解,在微调过程中只更新低阶张量组件,有效地降低了计算和存储开销。实验结果表明,在医学图像分割任务中,tCURLoRA优于现有的PEFT方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to MICCAI 2025. The final version of record is published in Springer LNCS
摘要
借助预训练模型的知识进行迁移学习已显著提高目标任务的性能。然而,随着深度神经网络规模的扩大,完全微调会在资源受限的环境中引入巨大的计算和存储挑战,限制了其广泛应用。为解决此问题,开发了参数效率高的微调(PEFT)方法,以减少计算和存储复杂性,并最小化更新的参数数量。虽然基于矩阵分解的PEFT方法(如LoRA)显示出潜力,但它们难以完全捕获模型权重的高维结构特征。相反,高维张量提供更自然的神经网络权重表示,能够更全面地捕获高阶特征和多维交互。本文提出一种基于张量CUR分解的新型微调方法tCURLoRA。通过将预训练权重矩阵连接成三维张量并应用张量CUR分解,我们只在微调时更新低阶张量组件,有效地减少计算和存储开销。实验结果表明,tCURLoRA在医学图像分割任务中的性能优于现有PEFT方法。
关键见解
- 迁移学习利用预训练模型知识提高了目标任务的性能。
- 完全微调在资源受限环境中面临巨大的计算和存储挑战。
- 参数效率高的微调(PEFT)方法旨在减少计算和存储复杂性。
- 现有PEFT方法如LoRA基于矩阵分解,难以捕获模型权重的所有高维结构特征。
- 高维张量为神经网络权重提供更自然的表示,能更全面地捕获高阶特征和交互。
- 本文提出的tCURLoRA方法基于张量CUR分解,有效减少计算和存储开销。
- 实验结果显示,tCURLoRA在医学图像分割任务中优于其他PEFT方法。
点此查看论文截图

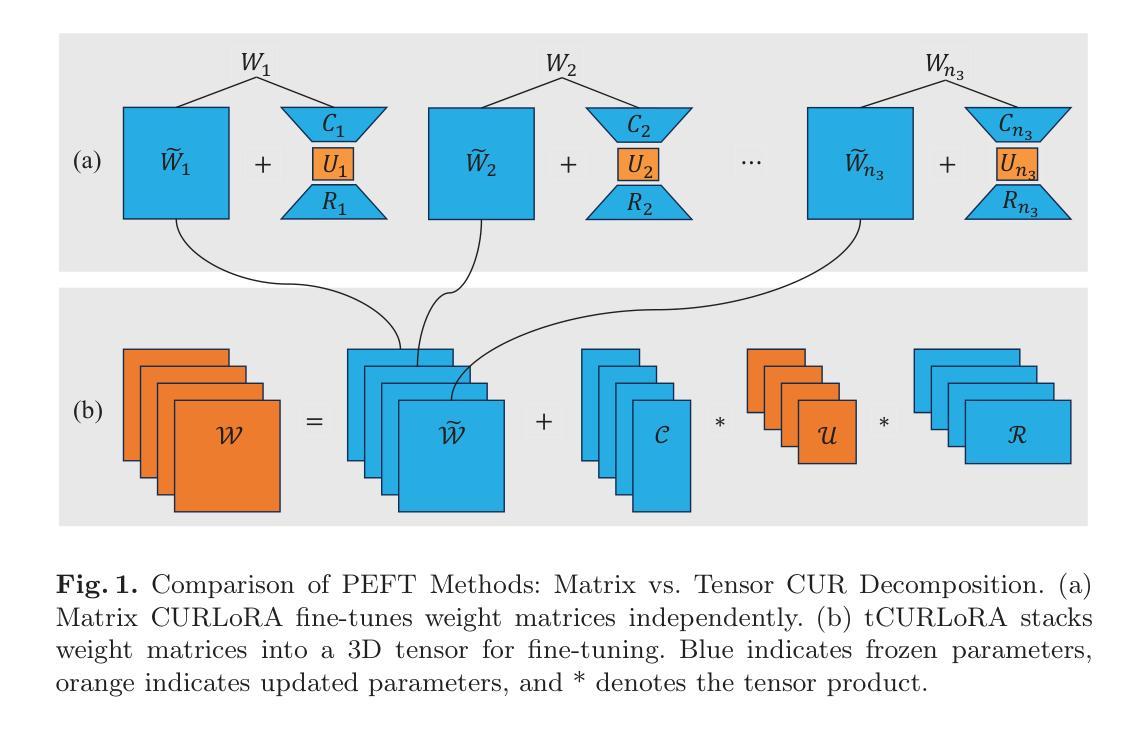
LoRA-PT: Low-Rank Adapting UNETR for Hippocampus Segmentation Using Principal Tensor Singular Values and Vectors
Authors:Guanghua He, Wangang Cheng, Hancan Zhu, Gaohang Yu
The hippocampus is an important brain structure involved in various psychiatric disorders, and its automatic and accurate segmentation is vital for studying these diseases. Recently, deep learning-based methods have made significant progress in hippocampus segmentation. However, training deep neural network models requires substantial computational resources, time, and a large amount of labeled training data, which is frequently scarce in medical image segmentation. To address these issues, we propose LoRA-PT, a novel parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) method that transfers the pre-trained UNETR model from the BraTS2021 dataset to the hippocampus segmentation task. Specifically, LoRA-PT divides the parameter matrix of the transformer structure into three distinct sizes, yielding three third-order tensors. These tensors are decomposed using tensor singular value decomposition to generate low-rank tensors consisting of the principal singular values and vectors, with the remaining singular values and vectors forming the residual tensor. During fine-tuning, only the low-rank tensors (i.e., the principal tensor singular values and vectors) are updated, while the residual tensors remain unchanged. We validated the proposed method on three public hippocampus datasets, and the experimental results show that LoRA-PT outperformed state-of-the-art PEFT methods in segmentation accuracy while significantly reducing the number of parameter updates. Our source code is available at https://github.com/WangangCheng/LoRA-PT/tree/LoRA-PT.
海马体是参与多种精神疾病的重要脑结构,其自动和准确的分割对于研究这些疾病至关重要。最近,基于深度学习的方法在海马体分割方面取得了显著进展。然而,训练深度神经网络模型需要大量的计算资源、时间和大量的标记训练数据,这在医学图像分割中经常是稀缺的。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了LoRA-PT,这是一种新型参数高效微调(PEFT)方法,它将BraTS2021数据集预训练的UNETR模型转移到海马体分割任务。具体来说,LoRA-PT将transformer结构的参数矩阵分成三种不同大小,产生三个三阶张量。这些张量通过张量奇异值分解进行分解,生成由主要奇异值和向量组成的低阶张量,其余的奇异值和向量形成残差张量。在微调过程中,只更新低阶张量(即主要张量的奇异值和向量),而残差张量保持不变。我们在三个公开的海马体数据集上验证了所提出的方法,实验结果表明,在分割精度上,LoRA-PT超越了最先进的PEFT方法,同时显著减少了参数更新的数量。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/WangangCheng/LoRA-PT/tree/LoRA-PT找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (2025). Final published version available online
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型的参数高效微调方法LoRA-PT,用于从BraTS2021数据集迁移至海马体分割任务。该方法通过分解变压器结构参数矩阵,仅更新主要奇异值向量,显著提高分割精度并减少参数更新数量,在公开海马体数据集上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 海马体在精神疾病的研究中的重要性及其自动准确分割的必要性。
- 深度学习在海马体分割中的最新进展及面临的挑战,如计算资源、时间和标注数据的稀缺性。
- 提出的LoRA-PT方法是一种参数高效微调方法,能够从BraTS2021数据集迁移至海马体分割任务。
- LoRA-PT方法通过分解变压器结构参数矩阵来提升性能。
- 在公开海马体数据集上,LoRA-PT方法相较于其他先进PEFT方法表现更优,具有较高的分割精度并显著减少参数更新数量。
- LoRA-PT方法的源代码已公开可供使用。
点此查看论文截图
DiffCut: Catalyzing Zero-Shot Semantic Segmentation with Diffusion Features and Recursive Normalized Cut
Authors:Paul Couairon, Mustafa Shukor, Jean-Emmanuel Haugeard, Matthieu Cord, Nicolas Thome
Foundation models have emerged as powerful tools across various domains including language, vision, and multimodal tasks. While prior works have addressed unsupervised image segmentation, they significantly lag behind supervised models. In this paper, we use a diffusion UNet encoder as a foundation vision encoder and introduce DiffCut, an unsupervised zero-shot segmentation method that solely harnesses the output features from the final self-attention block. Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrate that the utilization of these diffusion features in a graph based segmentation algorithm, significantly outperforms previous state-of-the-art methods on zero-shot segmentation. Specifically, we leverage a recursive Normalized Cut algorithm that softly regulates the granularity of detected objects and produces well-defined segmentation maps that precisely capture intricate image details. Our work highlights the remarkably accurate semantic knowledge embedded within diffusion UNet encoders that could then serve as foundation vision encoders for downstream tasks. Project page at https://diffcut-segmentation.github.io
跨语言、视觉和多模态任务等多个领域,基础模型已展现出强大的工具潜力。尽管早期的工作已经解决了无监督图像分割的问题,但它们显著落后于监督模型。在本文中,我们采用扩散UNet编码器作为基础视觉编码器,并引入DiffCut,一种无监督零分割方法,该方法仅利用最终自注意模块的输出特性。通过广泛的实验,我们证明在基于图的分割算法中使用这些扩散特征,在零分割方面显著优于以前的最先进方法。具体来说,我们采用递归归一化切割算法,该算法可以轻柔地调节检测对象的粒度,并产生定义明确的分割图,能够精确地捕获图像细节。我们的工作突出了扩散UNet编码器中嵌入的非常精确语义知识,之后可以作为下游任务的基础视觉编码器。项目页面:https://diffcutsegmentat ion.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024. Project page at https://diffcut-segmentation.github.io. Code at https://github.com/PaulCouairon/DiffCut
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散UNet编码器的基础视觉编码器,用于无监督零分割任务。通过引入扩散特征并利用基于图的分割算法,该模型在零分割任务上显著优于现有最先进的方法。采用递归归一化切割算法,能够精细检测对象粒度并生成精确的分割地图。该工作证明了扩散UNet编码器中嵌入的语义知识的准确性,可为下游任务提供基础视觉编码器。
Key Takeaways
- 引入扩散UNet编码器作为基础视觉编码器,适用于各种任务。
- 提出DiffCut方法,实现了无监督零分割任务的高效完成。
- 利用扩散特征并结合基于图的分割算法,性能超越现有先进方法。
- 采用递归归一化切割算法,能精准捕获图像细节。
- 该方法具有调节检测对象粒度的能力。
- 证明扩散UNet编码器中嵌入的语义知识的准确性。