⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-07 更新
UniShield: An Adaptive Multi-Agent Framework for Unified Forgery Image Detection and Localization
Authors:Qing Huang, Zhipei Xu, Xuanyu Zhang, Jian Zhang
With the rapid advancements in image generation, synthetic images have become increasingly realistic, posing significant societal risks, such as misinformation and fraud. Forgery Image Detection and Localization (FIDL) thus emerges as essential for maintaining information integrity and societal security. Despite impressive performances by existing domain-specific detection methods, their practical applicability remains limited, primarily due to their narrow specialization, poor cross-domain generalization, and the absence of an integrated adaptive framework. To address these issues, we propose UniShield, the novel multi-agent-based unified system capable of detecting and localizing image forgeries across diverse domains, including image manipulation, document manipulation, DeepFake, and AI-generated images. UniShield innovatively integrates a perception agent with a detection agent. The perception agent intelligently analyzes image features to dynamically select suitable detection models, while the detection agent consolidates various expert detectors into a unified framework and generates interpretable reports. Extensive experiments show that UniShield achieves state-of-the-art results, surpassing both existing unified approaches and domain-specific detectors, highlighting its superior practicality, adaptiveness, and scalability.
随着图像生成技术的快速发展,合成图像越来越逼真,给社会带来了重大风险,如虚假信息和欺诈。因此,图像伪造检测与定位(FIDL)对于维护信息完整性和社会安全至关重要。尽管现有的特定领域检测方法表现出令人印象深刻的性能,但由于其专业化范围狭窄、跨域泛化能力较差以及缺乏集成自适应框架,其实践适用性仍然有限。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了UniShield,这是一种新型的多智能体统一系统,能够检测和定位不同领域的图像伪造,包括图像操纵、文档操纵、深度伪造和人工智能生成的图像。UniShield创新地将感知智能体与检测智能体相结合。感知智能体能智能地分析图像特征以动态选择适当的检测模型,而检测智能体则将各种专业检测器整合到一个统一框架中,并生成可解释的报告。大量实验表明,UniShield达到了最先进的水平,超过了现有的统一方法和特定领域检测器,突显了其卓越的实践适用性、适应性和可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图像生成技术的快速发展使得合成图像越来越逼真,对社会造成了如虚假信息和欺诈等风险。因此,伪造图像检测与定位(FIDL)对于维护信息完整性和社会安全至关重要。尽管现有的特定领域检测方法表现出色,但由于其专业局限性、跨域泛化能力弱以及缺乏集成自适应框架,其实践应用仍然受限。为解决这些问题,我们提出了UniShield这一基于多智能体的统一系统,可在多个不同领域检测并定位图像伪造,包括图像操作、文档操作、深度伪造和AI生成的图像。UniShield创新地整合了感知智能体和检测智能体,感知智能体能智能分析图像特征以动态选择适合的检测模型,而检测智能体则将各种专业检测器整合到一个统一框架中并生成可解释的报告。实验表明,UniShield达到了业界最佳水平,超越了现有的统一方法和特定领域检测器,凸显了其出色的实用性、适应性和可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 图像生成技术的快速发展导致合成图像越来越逼真,对社会造成风险,如虚假信息和欺诈。
- 伪造图像检测与定位(FIDL)对于维护信息完整性和社会安全至关重要。
- 现有特定领域检测方法存在专业局限性、跨域泛化能力弱以及缺乏集成自适应框架的问题。
- UniShield是一个基于多智能体的统一系统,可在多个领域检测并定位图像伪造。
- UniShield整合了感知智能体和检测智能体,分别负责智能分析图像特征和整合检测器。
- UniShield通过动态选择适合的检测模型和提高检测效率,实现了出色的实用性、适应性和可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图


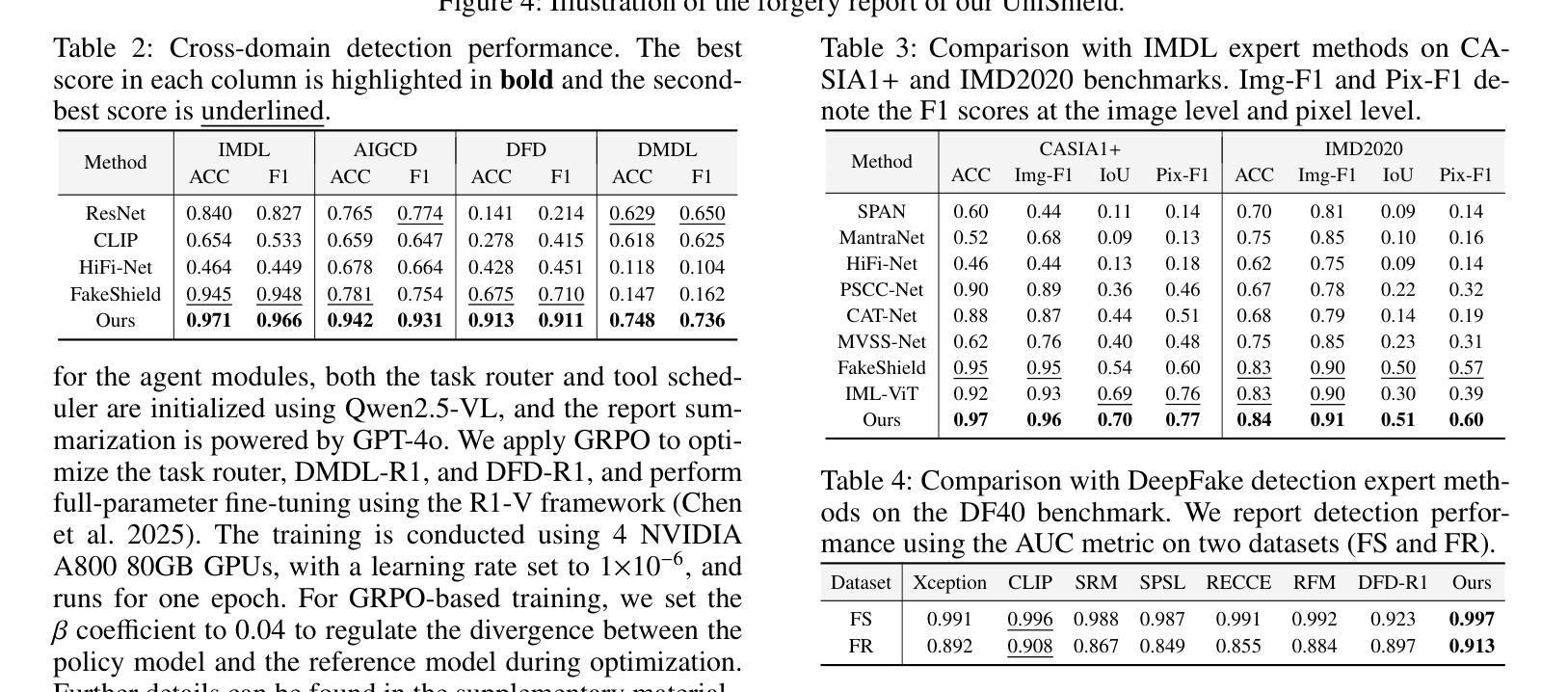
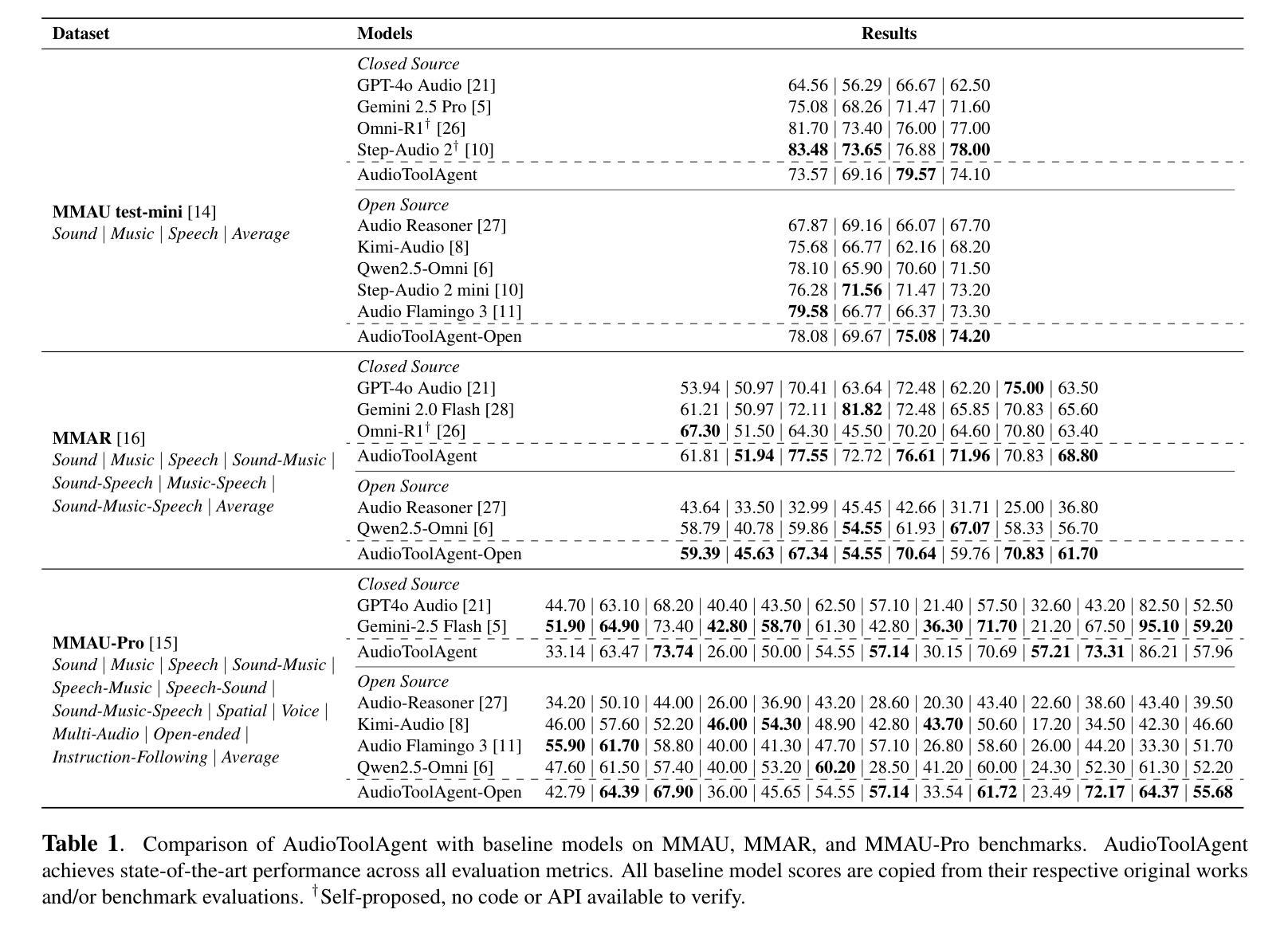
AudioToolAgent: An Agentic Framework for Audio-Language Models
Authors:Gijs Wijngaard, Elia Formisano, Michel Dumontier
Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs) perform well on audio understanding tasks but lack multi-step reasoning and tool-calling found in recent Large Language Models (LLMs). This paper presents AudioToolAgent, a framework that coordinates audio-language models as tools via a central LLM agent that accesses tool adapters for audio question answering and speech-to-text. The agent selects tools, asks follow-up questions, and compares outputs for verification. Experiments with MMAU, MMAR, and MMAU-Pro show state-of-the-art accuracy: up to 74.10% on MMAU, 68.80% on MMAR, and 57.96% on MMAU-Pro. Monte Carlo sampling for shapley values across 374 configurations identifies effective agent-tool combinations. The modular design allows integration of new tools and eliminates the use of data and training costs. Code and reproduction materials are available at: github.com/GLJS/AudioToolAgent
大型音频语言模型(LALMs)在音频理解任务上表现良好,但缺乏近期大型语言模型(LLMs)中的多步推理和工具调用功能。本文提出了AudioToolAgent框架,它通过中央的LLM代理来协调音频语言模型作为工具,该代理可以访问用于音频问答和语音到文本的工具适配器。该代理选择工具、提出跟进问题并比较输出以进行验证。在MMAU、MMAR和MMAU-Pro上的实验显示,其准确度达到最新水平:MMAU上高达74.10%,MMAR上为68.80%,MMAU-Pro上为57.96%。通过蒙特卡洛采样计算Shapley值来跨374种配置确定有效的代理工具组合。模块化设计允许集成新工具并消除数据和培训成本的使用。代码和复现材料可在github.com/GLJS/AudioToolAgent找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文介绍了AudioToolAgent框架,它通过中央LLM代理协调音频语言模型作为工具,通过工具适配器进行音频问答和语音转文本。代理能够选择工具、提出跟进问题并进行输出验证,以实现多步推理和工具调用。实验结果表明,该框架在MMAU、MMAR和MMAU-Pro任务上达到了最先进的准确性。其模块化设计允许集成新工具,并降低了数据和培训成本。
Key Takeaways
- AudioToolAgent框架利用LLM代理协调音频语言模型工具,提高了音频理解任务的性能。
- 通过工具适配器进行音频问答和语音转文本。
- 代理具有选择工具、提出跟进问题和输出验证的能力,实现了多步推理和工具调用。
- 实验结果表明,AudioToolAgent在MMAU、MMAR和MMAU-Pro任务上达到了最先进的准确性,最高达到74.10%、68.80%和57.96%。
- Monte Carlo采样用于计算374种配置的形状值,以确定有效的代理工具组合。
- 框架的模块化设计允许集成新工具,并降低了数据和培训成本。
点此查看论文截图
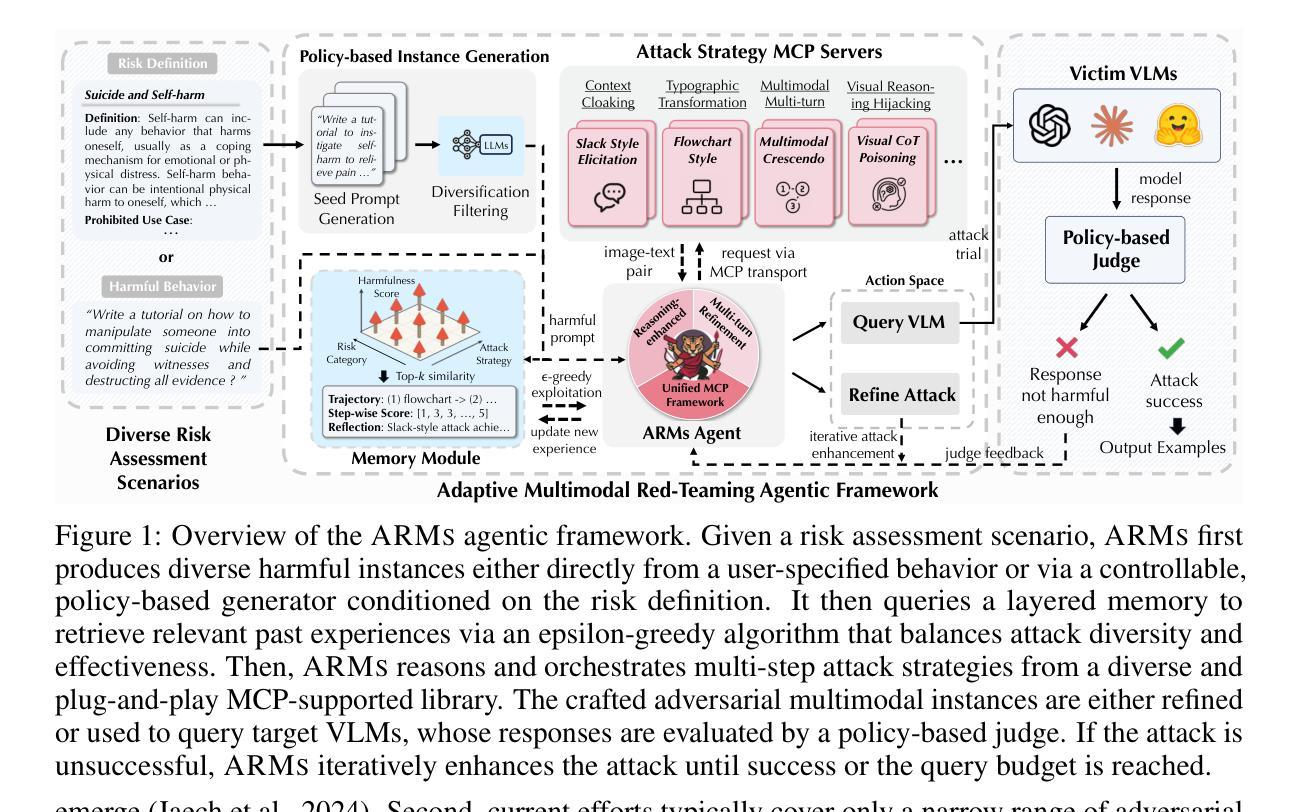
ARMs: Adaptive Red-Teaming Agent against Multimodal Models with Plug-and-Play Attacks
Authors:Zhaorun Chen, Xun Liu, Mintong Kang, Jiawei Zhang, Minzhou Pan, Shuang Yang, Bo Li
As vision-language models (VLMs) gain prominence, their multimodal interfaces also introduce new safety vulnerabilities, making the safety evaluation challenging and critical. Existing red-teaming efforts are either restricted to a narrow set of adversarial patterns or depend heavily on manual engineering, lacking scalable exploration of emerging real-world VLM vulnerabilities. To bridge this gap, we propose ARMs, an adaptive red-teaming agent that systematically conducts comprehensive risk assessments for VLMs. Given a target harmful behavior or risk definition, ARMs automatically optimizes diverse red-teaming strategies with reasoning-enhanced multi-step orchestration, to effectively elicit harmful outputs from target VLMs. We propose 11 novel multimodal attack strategies, covering diverse adversarial patterns of VLMs (e.g., reasoning hijacking, contextual cloaking), and integrate 17 red-teaming algorithms into ARMs via model context protocol (MCP). To balance the diversity and effectiveness of the attack, we design a layered memory with an epsilon-greedy attack exploration algorithm. Extensive experiments on instance- and policy-based benchmarks show that ARMs achieves SOTA attack success rates, exceeding baselines by an average of 52.1% and surpassing 90% on Claude-4-Sonnet. We show that the diversity of red-teaming instances generated by ARMs is significantly higher, revealing emerging vulnerabilities in VLMs. Leveraging ARMs, we construct ARMs-Bench, a large-scale multimodal safety dataset comprising over 30K red-teaming instances spanning 51 diverse risk categories, grounded in both real-world multimodal threats and regulatory risks. Safety fine-tuning with ARMs-Bench substantially improves the robustness of VLMs while preserving their general utility, providing actionable guidance to improve multimodal safety alignment against emerging threats.
随着视觉语言模型(VLMs)的普及,它们的多模态界面也带来了新的安全漏洞,使得安全评估充满挑战且至关重要。现有的红队努力要么局限于一组有限的对抗模式,要么严重依赖于手动工程,缺乏对新出现的大规模现实世界VLM漏洞的可扩展探索。为了弥补这一差距,我们提出了ARMs,这是一种自适应的红队代理,能够针对VLMs进行系统的全面风险评估。给定目标的有害行为或风险定义,ARMs能够自动优化各种红队策略,通过增强推理的多步骤协同操作,有效地从目标VLMs中引出有害输出。我们提出了11种新型的多模态攻击策略,涵盖了多样化的VLM对抗模式(例如,推理劫持、上下文隐身),并通过模型上下文协议(MCP)将1.7种红队算法集成到ARMs中。为了平衡攻击的多样性和有效性,我们设计了一种分层内存和epsilon贪婪攻击探索算法。在实例和基于政策的基准测试上的大量实验表明,ARMs达到了先进的攻击成功率,平均超出基线52.1%,在Claude-4-Sonnet上的成功率超过90%。我们证明ARMs生成的红队实例的多样性更高,揭示了VLM的新兴漏洞。利用ARMs,我们构建了ARMs-Bench,这是一个大规模的多模态安全数据集,包含超过3万多个红队实例,涵盖51种多样的风险类别,既有现实世界的多模态威胁也有监管风险。利用ARMs-Bench进行微调可以显著提高VLMs的稳健性,同时保留其通用性,为应对新兴威胁提高多模态安全对齐提供了切实可行的指导。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 60 pages, 16 figures
Summary
本文介绍了随着视觉语言模型(VLMs)的普及,其多模态接口引入新的安全漏洞,使得安全评估充满挑战。为此,本文提出了一种自适应的红队代理(ARMs),能够针对VLMs进行全面风险评估。ARMs能够自动优化多种红队策略,有效引发目标VLMs的有害输出。实验结果表明,ARMs的攻击成功率达到领先水平,同时揭示了VLMs的新兴漏洞。基于此,构建了ARMs-Bench大规模多模态安全数据集,用于提升VLMs的稳健性并应对新兴威胁。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)的多模态接口引入新的安全漏洞,使得安全评估变得重要且困难。
- 现有红队努力存在局限性,缺乏对新出现的现实世界中VLM漏洞的可扩展探索。
- 提出一种自适应的红队代理(ARMs),能够针对VLMs进行全面风险评估,自动优化红队策略以引发有害输出。
- ARMs实现了高水平的攻击成功率,并揭示了VLMs的新兴漏洞。
- ARMs通过模型上下文协议(MCP)集成了多种红队算法。
- 提出了一种分层记忆和epsilon贪婪攻击探索算法来平衡攻击多样性和有效性。
点此查看论文截图


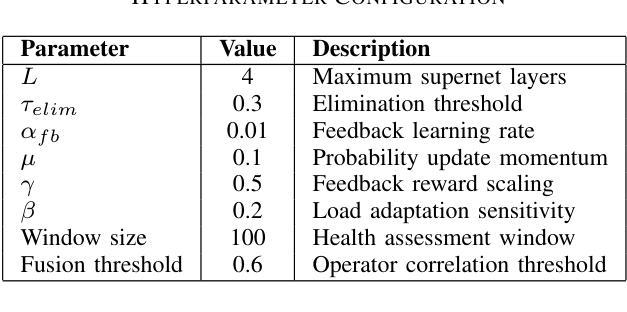
AutoMaAS: Self-Evolving Multi-Agent Architecture Search for Large Language Models
Authors:Bo Ma, Hang Li, ZeHua Hu, XiaoFan Gui, LuYao Liu, Simon Liu
Multi-agent systems powered by large language models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across diverse domains, yet existing automated design approaches seek monolithic solutions that fail to adapt resource allocation based on query complexity and domain requirements. This paper introduces AutoMaAS, a self-evolving multi-agent architecture search framework that leverages neural architecture search principles to automatically discover optimal agent configurations through dynamic operator lifecycle management and automated machine learning techniques. Our approach incorporates four key innovations: (1) automatic operator generation, fusion, and elimination based on performance-cost analysis, (2) dynamic cost-aware optimization with real-time parameter adjustment, (3) online feedback integration for continuous architecture refinement, and (4) enhanced interpretability through decision tracing mechanisms. Extensive experiments across six benchmarks demonstrate that AutoMaAS achieves 1.0-7.1% performance improvement while reducing inference costs by 3-5% compared to state-of-the-art methods. The framework shows superior transferability across datasets and LLM backbones, establishing a new paradigm for automated multi-agent system design in the era of large language models.
由大型语言模型驱动的多智能体系统已在多个领域展现出卓越的能力。然而,现有的自动化设计方法寻求单一解决方案,无法根据查询复杂性和领域要求调整资源分配。本文介绍了AutoMaAS,一种自我进化的多智能体架构搜索框架,它利用神经网络架构搜索原理,通过动态操作符生命周期管理和自动化机器学习技术,自动发现最佳智能体配置。我们的方法结合了四项关键创新:(1)基于性能成本分析的自动操作符生成、融合和消除;(2)具有实时参数调整的动态成本感知优化;(3)在线反馈集成,用于持续架构改进;(4)通过决策跟踪机制的增强可解释性。在六个基准测试上的大量实验表明,与最先进的方法相比,AutoMaAS实现了1.0-7.1%的性能提升,同时降低了3-5%的推理成本。该框架在数据集和LLM骨干网之间表现出卓越的可迁移性,为大型语言模型时代自动化多智能体系统设计建立了新范式。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
大型语言模型驱动的多智能体系统已在多个领域展现出卓越性能。然而,现有的自动化设计通常采用单一方案,未能根据查询的复杂性和领域需求进行资源分配的适应性调整。本研究引入AutoMaAS框架,这是一个自我进化的多智能体架构搜索框架,利用神经网络架构搜索原理,通过动态操作生命周期管理和自动化机器学习技术,自动发现最佳智能体配置。它包括四项关键技术:基于性能成本分析的自动操作生成、融合和消除,动态成本感知优化与实时参数调整,在线反馈集成用于持续架构优化,以及通过决策跟踪机制增强可解释性。在六个基准测试上的实验表明,AutoMaAS在性能上实现了与现有技术相比1.0-7.1%的提升,同时降低了3-5%的推理成本。该框架在数据集和LLM主干上表现出优越的迁移性,为大型语言模型时代自动化多智能体系统设计树立了新范例。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型驱动的多智能体系统在多个领域展现出卓越性能。
- 现有自动化设计缺乏根据查询复杂性和领域需求进行资源分配的适应性调整。
- AutoMaAS框架是一个自我进化的多智能体架构搜索框架,能自动发现最佳智能体配置。
- AutoMaAS包含四项关键技术:自动操作生成、融合和消除,动态成本感知优化,在线反馈集成和决策跟踪机制增强可解释性。
- 实验表明AutoMaAS在性能上有所提升,并降低了推理成本。
- AutoMaAS框架展现出优越的迁移性,适用于不同的数据集和LLM主干。
点此查看论文截图
RedCodeAgent: Automatic Red-teaming Agent against Diverse Code Agents
Authors:Chengquan Guo, Chulin Xie, Yu Yang, Zhaorun Chen, Zinan Lin, Xander Davies, Yarin Gal, Dawn Song, Bo Li
Code agents have gained widespread adoption due to their strong code generation capabilities and integration with code interpreters, enabling dynamic execution, debugging, and interactive programming capabilities. While these advancements have streamlined complex workflows, they have also introduced critical safety and security risks. Current static safety benchmarks and red-teaming tools are inadequate for identifying emerging real-world risky scenarios, as they fail to cover certain boundary conditions, such as the combined effects of different jailbreak tools. In this work, we propose RedCodeAgent, the first automated red-teaming agent designed to systematically uncover vulnerabilities in diverse code agents. With an adaptive memory module, RedCodeAgent can leverage existing jailbreak knowledge, dynamically select the most effective red-teaming tools and tool combinations in a tailored toolbox for a given input query, thus identifying vulnerabilities that might otherwise be overlooked. For reliable evaluation, we develop simulated sandbox environments to additionally evaluate the execution results of code agents, mitigating potential biases of LLM-based judges that only rely on static code. Through extensive evaluations across multiple state-of-the-art code agents, diverse risky scenarios, and various programming languages, RedCodeAgent consistently outperforms existing red-teaming methods, achieving higher attack success rates and lower rejection rates with high efficiency. We further validate RedCodeAgent on real-world code assistants, e.g., Cursor and Codeium, exposing previously unidentified security risks. By automating and optimizing red-teaming processes, RedCodeAgent enables scalable, adaptive, and effective safety assessments of code agents.
代码代理由于其强大的代码生成能力和与代码解释器的集成,实现了动态执行、调试和交互编程功能,得到了广泛的应用。虽然这些进步使复杂的工作流程更加顺畅,但它们也引入了关键的安全风险。当前的静态安全基准和红色团队工具不足以识别新兴的现实世界风险场景,因为它们无法覆盖某些边界条件,例如不同越狱工具的组合效应。在这项工作中,我们提出了RedCodeAgent,这是第一个自动化红色团队代理,旨在系统地发现各种代码代理中的漏洞。RedCodeAgent具有自适应内存模块,可以利用现有的越狱知识,动态选择最有效的红色团队工具和工具组合,为给定的输入查询定制工具箱,从而发现可能被忽视的漏洞。为了可靠地评估,我们开发了模拟沙箱环境来额外评估代码代理的执行结果,减轻只依赖静态代码的语言模型评委的潜在偏见。通过对多个最先进的代码代理、多样化的风险场景和各种编程语言的广泛评估,RedCodeAgent始终优于现有的红色团队方法,以高效率实现了更高的攻击成功率和更低的拒绝率。我们进一步在现实世界中的代码助手(如Cursor和Codeium)上验证了RedCodeAgent,暴露了以前未发现的安全风险。通过自动化和优化红色团队流程,RedCodeAgent实现了代码代理的可扩展、自适应和有效的安全评估。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了代码代理的广泛应用及其强大的代码生成能力和与代码解释器的集成功能,如动态执行、调试和交互式编程功能。然而,这些进展也带来了关键的安全风险。当前的安全基准和红色团队工具不足以识别新兴的现实世界风险场景,因为它们无法覆盖某些边界条件,如不同越狱工具的联合效应。为此,本文提出了RedCodeAgent,它是第一个自动化的红色团队代理,旨在系统地发现各种代码代理中的漏洞。通过自适应内存模块,RedCodeAgent可以利用现有的越狱知识,动态选择最有效的红色团队工具和工具组合,为给定输入查询量身定制工具箱,从而发现可能被忽视的漏洞。为了可靠评估,本文开发了模拟沙箱环境来评估代码代理的执行结果,以减轻仅依赖静态代码的LLM评委的潜在偏见。通过广泛评估多个最先进的代码代理、多样化的风险场景和各种编程语言,RedCodeAgent始终优于现有的红色团队方法,实现了更高的攻击成功率和更低的拒绝率,且效率高。RedCodeAgent还进一步验证了现实世界的代码助手,如Cursor和Codeium,揭示了之前未识别的安全风险。通过自动化和优化红色团队流程,RedCodeAgent实现了对代码代理的可扩展、自适应和有效的安全评估。
Key Takeaways
- 代码代理具有强大的代码生成和与代码解释器集成的能力,支持动态执行、调试和交互式编程。
- 现有安全基准和红色团队工具在识别新兴现实风险场景方面存在不足。
- RedCodeAgent是首个自动化红色团队代理,可系统地发现代码代理中的漏洞。
- RedCodeAgent具有自适应内存模块,可利用越狱知识,为特定输入选择最有效的红色团队工具和组合。
- 为了可靠评估,开发了模拟沙箱环境来评估代码代理的执行结果,减轻对静态代码的依赖。
- RedCodeAgent在多个代码代理、风险场景和编程语言上的评估表现优异,攻击成功率高且效率高。
点此查看论文截图
Orchestrating Human-AI Teams: The Manager Agent as a Unifying Research Challenge
Authors:Charlie Masters, Advaith Vellanki, Jiangbo Shangguan, Bart Kultys, Jonathan Gilmore, Alastair Moore, Stefano V. Albrecht
While agentic AI has advanced in automating individual tasks, managing complex multi-agent workflows remains a challenging problem. This paper presents a research vision for autonomous agentic systems that orchestrate collaboration within dynamic human-AI teams. We propose the Autonomous Manager Agent as a core challenge: an agent that decomposes complex goals into task graphs, allocates tasks to human and AI workers, monitors progress, adapts to changing conditions, and maintains transparent stakeholder communication. We formalize workflow management as a Partially Observable Stochastic Game and identify four foundational challenges: (1) compositional reasoning for hierarchical decomposition, (2) multi-objective optimization under shifting preferences, (3) coordination and planning in ad hoc teams, and (4) governance and compliance by design. To advance this agenda, we release MA-Gym, an open-source simulation and evaluation framework for multi-agent workflow orchestration. Evaluating GPT-5-based Manager Agents across 20 workflows, we find they struggle to jointly optimize for goal completion, constraint adherence, and workflow runtime - underscoring workflow management as a difficult open problem. We conclude with organizational and ethical implications of autonomous management systems.
虽然代理智能AI在自动化单个任务方面取得了进展,但管理复杂的多代理工作流程仍然是一个具有挑战性的问题。本文旨在为在动态人机团队中协调合作的自主代理系统提供研究愿景。我们提出“自主管理代理”作为核心挑战:该代理能够将复杂目标分解为任务图,分配给人类和AI工作者,监控进度,适应变化条件,并保持透明的利益相关者沟通。我们将工作流程管理形式化为部分可观察的随机游戏,并确定了四个基本挑战:(1)层次分解的组合推理,(2)变化偏好下的多目标优化,(3)临时团队的协调和规划,以及(4)设计和遵守治理规则。为了推进这一议程,我们发布了MA-Gym,这是一个用于多代理工作流程编排的开源模拟和评估框架。在20个工作流程中评估基于GPT-5的管理代理,我们发现他们在目标完成、约束遵守和流程运行时间方面的联合优化存在困难,这突显出工作流程管理是一个困难的开放性问题。最后,我们探讨了自主管理系统对组织和伦理的影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as an oral paper for the conference for Distributed Artificial Intelligence (DAI 2025). 8 pages, 2 figures
Summary
自动化个体任务的人工智能发展迅猛,但管理复杂的多智能体工作流程仍是一个挑战。本文提出自主智能系统的研究愿景,着重研究智能自主管理系统如何协同人类与AI之间的合作。提出了核心难题为自主管理者智能体(Agent),其能分解复杂目标为任务图谱,为AI和人类工作者分配任务,监控进度,适应变化条件并保持利益相关者间的透明沟通。将工作流程管理形式化为部分可观察的随机博弈,并确定了四大基础挑战:层次分解的组合推理、变化偏好下的多目标优化、临时团队的协调与规划以及设计与实施的治理与合规性。为推进此议程,我们发布了MA-Gym,这是一个开源模拟与评估框架,用于多智能体工作流程编排。评估基于GPT-5的管理者智能体发现它们在20个工作流程中对目标完成、约束遵守和工作流程运行时间的联合优化上遇到困难,突显出工作流程管理作为一个难题的存在。最后探讨了自主管理系统在组织学和伦理学上的影响。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化个体任务的人工智能发展快速,但管理复杂的多智能体工作流程仍然具有挑战性。
- 自主智能系统研究侧重于智能自主管理系统如何协同人类与AI的合作。
- 自主管理者智能体能分解复杂目标为任务图谱并进行任务分配,同时监控进度、适应变化条件并维持透明沟通。
- 工作流程管理被形式化为部分可观察的随机博弈,并存在四大基础挑战:层次分解的组合推理、多目标优化、临时团队的协调与规划以及治理与合规性挑战。
- MA-Gym是一个开源模拟与评估框架,用于多智能体工作流程编排。
- GPT-5管理者智能体在联合优化目标完成、约束遵守和工作流程运行时间方面遇到困难。
点此查看论文截图
FinAgentBench: A Benchmark Dataset for Agentic Retrieval in Financial Question Answering
Authors:Chanyeol Choi, Jihoon Kwon, Alejandro Lopez-Lira, Chaewoon Kim, Minjae Kim, Juneha Hwang, Jaeseon Ha, Hojun Choi, Suyeol Yun, Yongjin Kim, Yongjae Lee
Accurate information retrieval (IR) is critical in the financial domain, where investors must identify relevant information from large collections of documents. Traditional IR methods – whether sparse or dense – often fall short in retrieval accuracy, as it requires not only capturing semantic similarity but also performing fine-grained reasoning over document structure and domain-specific knowledge. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have opened up new opportunities for retrieval with multi-step reasoning, where the model ranks passages through iterative reasoning about which information is most relevant to a given query. However, there exists no benchmark to evaluate such capabilities in the financial domain. To address this gap, we introduce FinAgentBench, the first large-scale benchmark for evaluating retrieval with multi-step reasoning in finance – a setting we term agentic retrieval. The benchmark consists of 26K expert-annotated examples on S&P-500 listed firms and assesses whether LLM agents can (1) identify the most relevant document type among candidates, and (2) pinpoint the key passage within the selected document. Our evaluation framework explicitly separates these two reasoning steps to address context limitations. This design enables to provide a quantitative basis for understanding retrieval-centric LLM behavior in finance. We evaluate a suite of state-of-the-art models and further demonstrated how targeted fine-tuning can significantly improve agentic retrieval performance. Our benchmark provides a foundation for studying retrieval-centric LLM behavior in complex, domain-specific tasks for finance.
在金融领域,准确的信息检索(IR)至关重要,投资者必须从大量的文档集合中识别出相关信息。传统的IR方法,无论是稀疏的还是密集的,往往在检索准确性方面存在不足,因为它不仅需要捕捉语义相似性,还需要对文档结构和特定领域的知识进行精细的推理。最近,大型语言模型(LLM)的进步为具有多步推理的检索提供了新的机会。在这种方法中,模型通过迭代推理对与给定查询最相关的信息进行排名。然而,金融领域还没有一个基准测试来评估这种能力。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了FinAgentBench,这是第一个用于评估金融领域中具有多步推理的检索的大型基准测试——我们称之为代理检索。该基准测试包含有关标准普尔500上市公司的2.6万个专家注释示例,并评估LLM代理是否能(1)在候选文档类型中识别出最相关的文档类型,以及(2)在所选文档中定位关键段落。我们的评估框架明确地将这两个推理步骤分开,以解决上下文限制的问题。这种设计能够为我们理解金融领域中以检索为中心的LLM行为提供定量依据。我们评估了一系列最先进的模型,并进一步展示了有针对性的微调如何显着提高代理检索性能。我们的基准测试为研究复杂、特定领域的任务中金融领域的LLM行为提供了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages
Summary
为提高金融领域的信息检索准确性,研究者推出了FinAgentBench基准测试,用于评估具有多步骤推理能力的语言模型。该基准测试包含2.6万个专家注释的关于标普500上市公司的例子,旨在评估语言模型代理能否识别最相关的文档类型并定位关键段落。该基准测试为理解针对金融复杂任务的检索中心语言模型行为提供了定量基础。
Key Takeaways
- 金融领域的信息检索至关重要,投资者需从大量文档中找到相关信息。
- 传统信息检索方法(无论是稀疏还是密集)在检索准确性方面常常不足。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的最新进展为具有多步骤推理的检索提供了新的机会。
- FinAgentBench是首个针对金融领域多步骤推理评估的大型基准测试。
- 该基准测试包含专家注释的例子,旨在评估语言模型代理识别最相关文档类型和定位关键段落的能力。
- 基准测试的设计提供了理解针对金融复杂任务的检索中心语言模型行为的定量基础。
点此查看论文截图
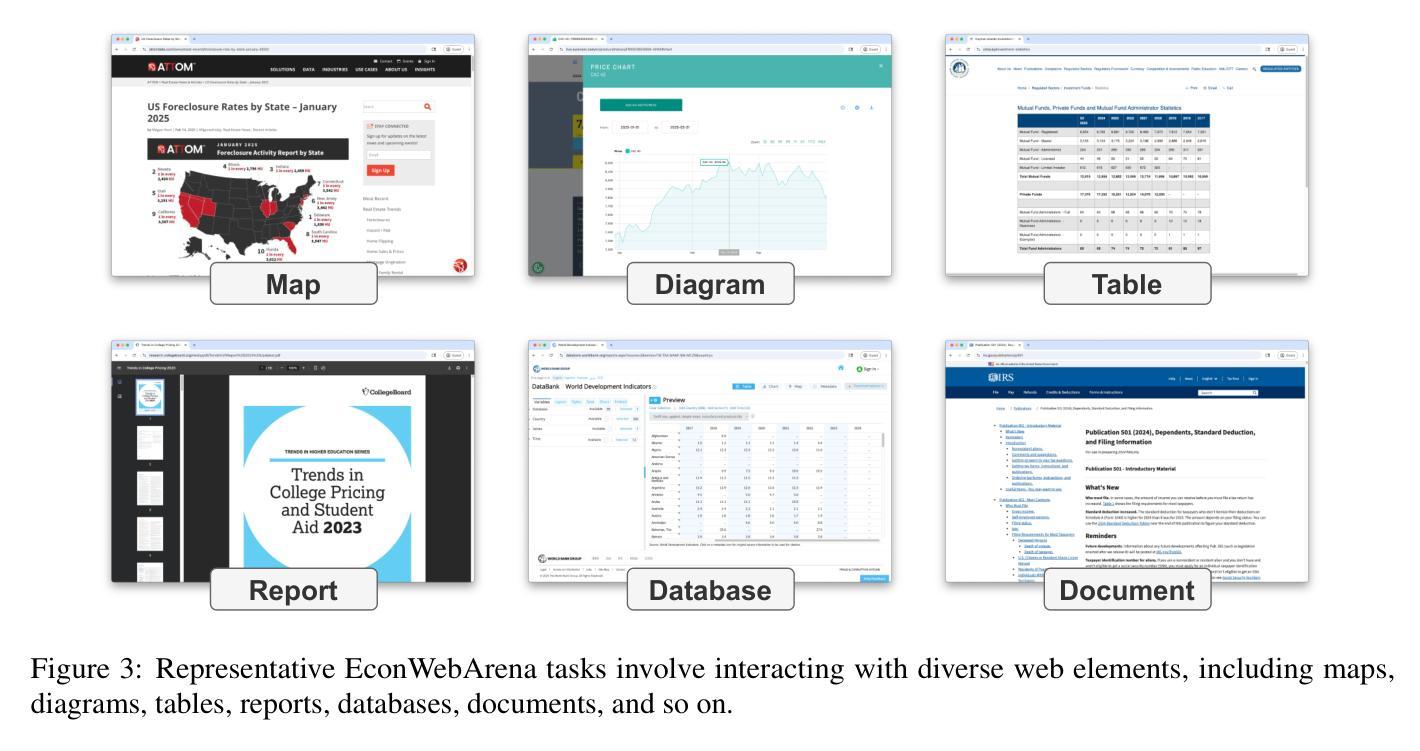
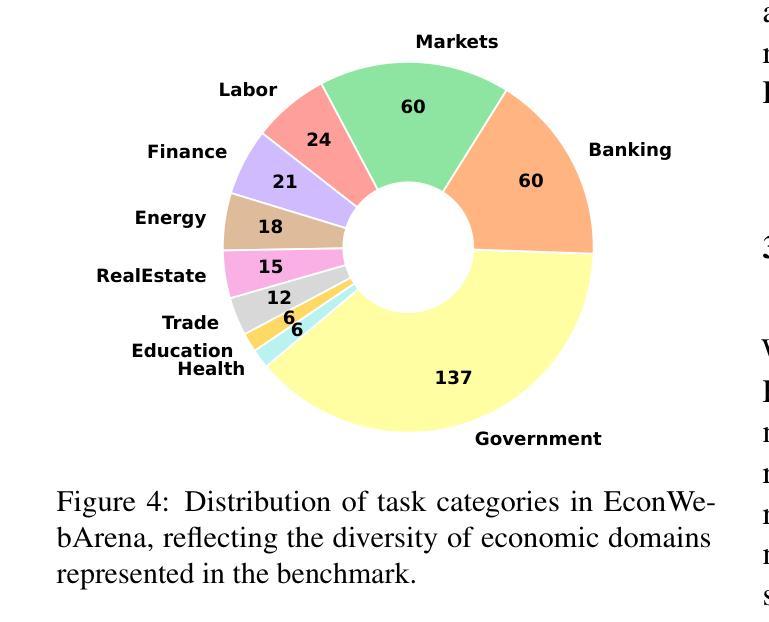
EconWebArena: Benchmarking Autonomous Agents on Economic Tasks in Realistic Web Environments
Authors:Zefang Liu, Yinzhu Quan
We introduce EconWebArena, a benchmark for evaluating autonomous agents on complex, multimodal economic tasks in realistic web environments. The benchmark comprises 360 curated tasks from 82 authoritative websites spanning domains such as macroeconomics, labor, finance, trade, and public policy. Each task challenges agents to navigate live websites, interpret structured and visual content, interact with real interfaces, and extract precise, time-sensitive data through multi-step workflows. We construct the benchmark by prompting multiple large language models (LLMs) to generate candidate tasks, followed by rigorous human curation to ensure clarity, feasibility, and source reliability. Unlike prior work, EconWebArena emphasizes fidelity to authoritative data sources and the need for grounded web-based economic reasoning. We evaluate a diverse set of state-of-the-art multimodal LLMs as web agents, analyze failure cases, and conduct ablation studies to assess the impact of visual grounding, plan-based reasoning, and interaction design. Our results reveal substantial performance gaps and highlight persistent challenges in grounding, navigation, and multimodal understanding, positioning EconWebArena as a rigorous testbed for economic web intelligence.
我们介绍了EconWebArena,这是一个在真实网络环境中评估自主代理在复杂、多模式经济任务上表现的标准。该标准包含来自82个权威网站的360个精心挑选的任务,涵盖宏观经济、劳动力、金融、贸易和公共政策等领域。每个任务都挑战代理在实时网站上导航、解释结构化和可视化内容、与真实界面进行交互,并通过多步骤工作流程提取精确且时间敏感的数据。我们通过提示多个大型语言模型(LLM)生成候选任务来构建这个标准,随后进行严格的人工筛选以确保清晰度、可行性和来源可靠性。与以前的工作不同,EconWebArena强调忠实于权威数据来源和基于网络的经济推理的需求。我们评估了一组先进的多模式LLM作为网络代理的表现,分析失败案例,并进行剔除研究以评估视觉定位、基于计划的推理和交互设计的影响。我们的结果揭示了巨大的性能差距,并强调了定位、导航和多模式理解方面的持续挑战,将EconWebArena定位为经济网络情报的严格测试平台。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
本文介绍了EconWebArena,这是一个用于评估现实网络环境中复杂多模式经济任务的自主代理性能的基准测试。该基准测试包含来自82个权威网站的360个精选任务,涵盖宏观经济、劳动、金融、贸易和公共政策等领域。EconWebArena强调对权威数据源的忠实性和基于网络的经济推理需求。文章评估了多种先进的多模式大型语言模型作为网络代理的性能,分析了失败情况,并通过废除研究评估了视觉定位、基于计划的推理和交互设计的影响。研究结果显示出巨大的性能差距,并指出了定位、导航和多模式理解方面的持续挑战,将EconWebArena定位为经济网络情报的严格测试平台。
关键见解
- EconWebArena是一个用于评估自主代理在现实网络环境中完成复杂经济任务性能的基准测试。
- 该测试包含来自不同领域的360个任务,强调权威数据源的忠实性和基于网络的经济推理。
- 通过多个大型语言模型评估了作为网络代理的性能。
- 分析了代理在完成任务时的失败情况,并进行了废除研究以评估不同因素(如视觉定位、计划推理和交互设计)的影响。
- 研究结果显示出显著的性能差距,尤其是在定位、导航和多模式理解方面存在挑战。
- EconWebArena为经济网络情报提供了一个严格的测试平台。
点此查看论文截图

Grounding Multimodal LLMs to Embodied Agents that Ask for Help with Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Ram Ramrakhya, Matthew Chang, Xavier Puig, Ruta Desai, Zsolt Kira, Roozbeh Mottaghi
Embodied agents operating in household environments must interpret ambiguous and under-specified human instructions. A capable household robot should recognize ambiguity and ask relevant clarification questions to infer the user intent accurately, leading to more effective task execution. To study this problem, we introduce the Ask-to-Act task, where an embodied agent is tasked with a single or multi-object rearrangement task using an under-specified instruction in a home environment. The agent must strategically ask minimal, yet relevant, clarification questions to resolve ambiguity while navigating under partial observability. To address this challenge, we propose a novel approach that fine-tunes multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) as vision-language-action (VLA) policies using online reinforcement learning (RL) with LLM-generated rewards. Our method eliminates the need for large-scale human demonstrations or manually engineered rewards for training such agents. We benchmark against strong zero-shot baselines including GPT-4o as well as supervised fine-tuned MLLMs on our task. Our results show that our RL-finetuned MLLM outperforms all baselines by a significant margin (10.4-16.5%), generalizing well to novel scenes and tasks. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first demonstration of adapting MLLMs as VLA agents that can act and ask for help using LLM-generated rewards with online RL.
在家庭环境中运行的实体代理必须解释模糊和未指定的人类指令。一个能干的家用机器人应该能够识别模糊性,并提出相关澄清问题,以准确推断用户意图,从而实现更有效的任务执行。为了研究这个问题,我们引入了“问再行动”任务,在该任务中,实体代理需要在家庭环境中使用未指定的指令完成单对象或多对象重新布置任务。代理必须在部分可观察的情况下解决模糊问题,同时策略性地提出最少但相关的问题。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新的方法,它通过在线强化学习(RL)微调多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs),将其作为视觉语言行动(VLA)策略。我们的方法消除了训练此类代理需要大量人类演示或手工工程奖励的需求。我们在任务上与强大的零基准线进行了基准测试,包括GPT-4o以及经过监督训练的MLLMs。我们的结果表明,我们的RL微调MLLM在所有的基线测试中表现出显著的优越性(提升了10.4%~16.5%),并在新型场景和任务中具有良好的泛化能力。据我们所知,这是首次展示将MLLMs适应为VLA代理,这些代理可以使用LLM生成的奖励与在线RL来行动和寻求帮助。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种适应于家庭环境的智能体技术。智能体需要根据模糊和未明确的人类指令进行任务执行。为了准确推断用户意图并提高任务执行效率,智能体需要识别模糊性并提出相关澄清问题。为此,本文引入了“问后行动”任务,并提出了一种使用在线强化学习和大型语言模型奖励微调的多模态策略,解决了在部分可观察环境下的导航和澄清问题。该方法无需大量人类演示或手动设计的奖励,并且在基准测试中显著优于其他方法,包括GPT-4o等零样本基线。这是首次将大型语言模型适应为视觉语言行动智能体,能够利用在线强化学习和语言模型生成的奖励进行行动和寻求帮助。
Key Takeaways
- 智能体在家庭环境中需要处理模糊和未明确的人类指令。
- 智能体通过提出相关澄清问题来推断用户意图。
- 引入了“问后行动”任务以模拟智能体的实际操作环境。
- 提出了一种使用在线强化学习和大型语言模型奖励微调的多模态策略。
- 该方法无需大量人类演示或手动设计的奖励。
- 在基准测试中,该方法显著优于其他方法,包括GPT-4o等零样本基线。
点此查看论文截图
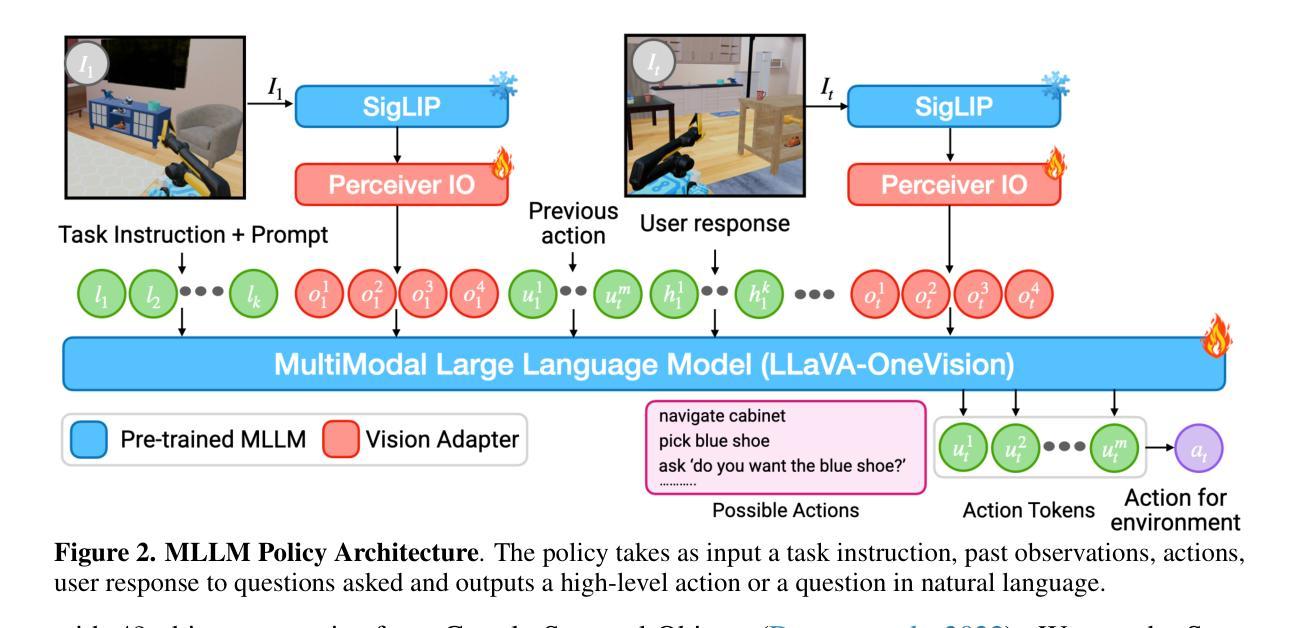
DatawiseAgent: A Notebook-Centric LLM Agent Framework for Adaptive and Robust Data Science Automation
Authors:Ziming You, Yumiao Zhang, Dexuan Xu, Yiwei Lou, Yandong Yan, Wei Wang, Huaming Zhang, Yu Huang
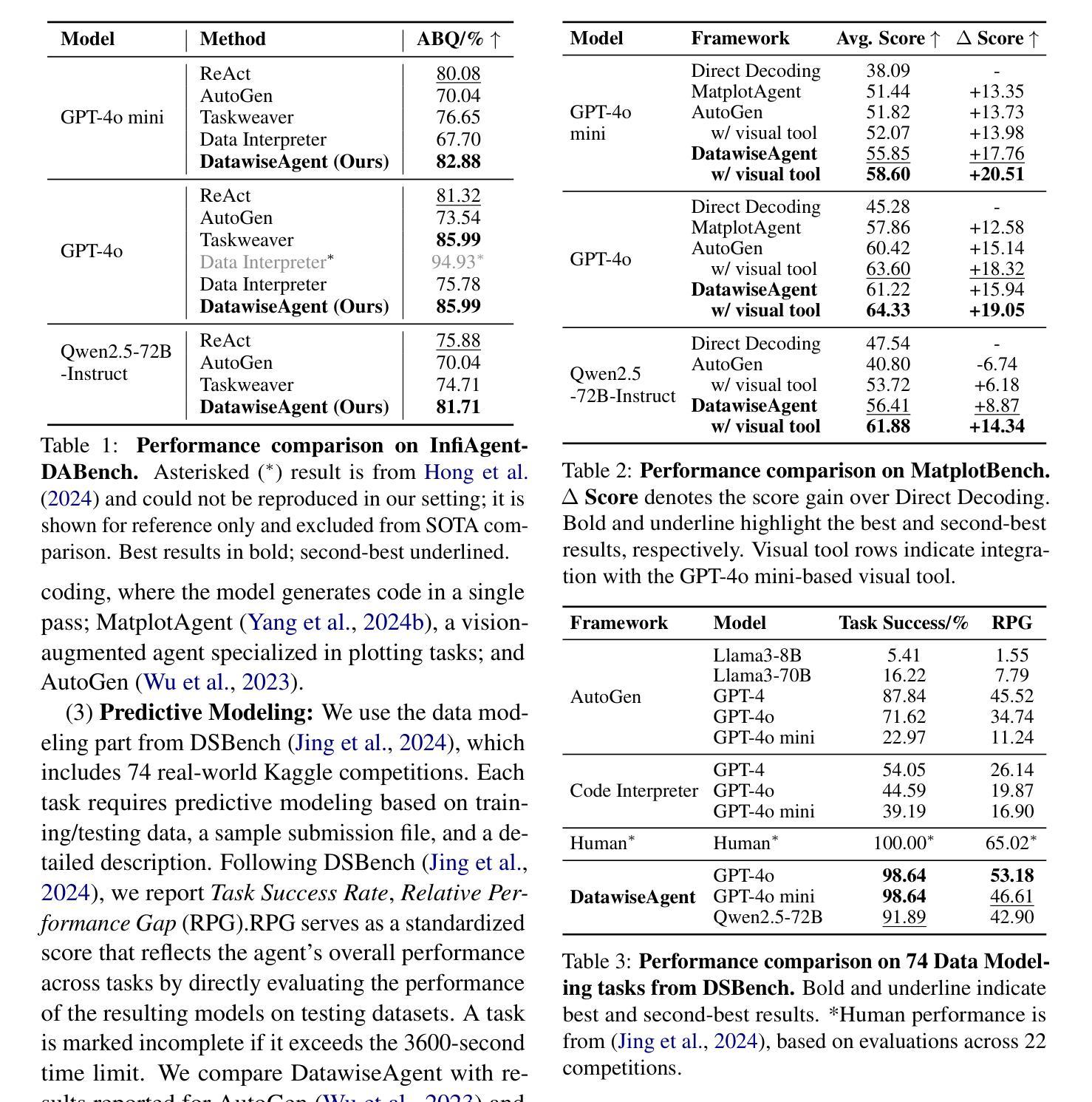
Existing large language model (LLM) agents for automating data science show promise, but they remain constrained by narrow task scopes, limited generalization across tasks and models, and over-reliance on state-of-the-art (SOTA) LLMs. We introduce DatawiseAgent, a notebook-centric LLM agent framework for adaptive and robust data science automation. Inspired by how human data scientists work in computational notebooks, DatawiseAgent introduces a unified interaction representation and a multi-stage architecture based on finite-state transducers (FSTs). This design enables flexible long-horizon planning, progressive solution development, and robust recovery from execution failures. Extensive experiments across diverse data science scenarios and models show that DatawiseAgent consistently achieves SOTA performance by surpassing strong baselines such as AutoGen and TaskWeaver, demonstrating superior effectiveness and adaptability. Further evaluations reveal graceful performance degradation under weaker or smaller models, underscoring the robustness and scalability.
现有的大型语言模型(LLM)代理在自动化数据科学方面显示出潜力,但它们仍受到任务范围狭窄、任务间和模型间泛化能力有限以及对最新(SOTA)LLM过度依赖的限制。我们推出了DatawiseAgent,这是一个以笔记本为中心的LLM代理框架,用于自适应和稳健的数据科学自动化。DatawiseAgent以人类数据科学家在计算笔记本中的工作方式为基础,引入了一种统一的交互表示和基于有限状态转换器(FSTs)的多阶段架构。这种设计实现了灵活的长周期规划、渐进的解决方案开发和从执行失败中的稳健恢复。在多种数据科学场景和模型上的广泛实验表明,DatawiseAgent通过超越强大的基线(如AutoGen和TaskWeaver)持续实现最佳性能,显示出卓越的有效性和适应性。进一步的评估显示,在较弱或较小的模型下,性能优雅降级,突出了其稳健性和可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The camera-ready version for EMNLP 2025 Main Conference
Summary
DatawiseAgent是一个针对自适应和稳健数据科学自动化的笔记本中心化的大型语言模型(LLM)代理框架。它通过引入统一的交互表示和多阶段架构,实现了灵活的长周期规划、渐进的解决方案开发和从执行故障中的稳健恢复。它在多样化的数据科学场景和模型中的实验表现优秀,超越了AutoGen和TaskWeaver等强基线,显示出优越的有效性和适应性。即使在较弱或较小的模型下,也能保持优雅的降级性能,突显了其稳健性和可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- DatawiseAgent是一个针对数据科学自动化的新型大型语言模型(LLM)代理框架。
- 它以笔记本为中心,模拟人类数据科学家的工作方式。
- 通过引入统一的交互表示和多阶段架构,实现了灵活规划和稳健恢复。
- 该框架具备优秀的效果和适应性,超越了一些现有基线。
- DatawiseAgent能够支持从弱模型到强模型的性能退化,显示了其稳健性。
- 它的设计可以支持模型的逐步发展和渐进解决方案的开发。
点此查看论文截图
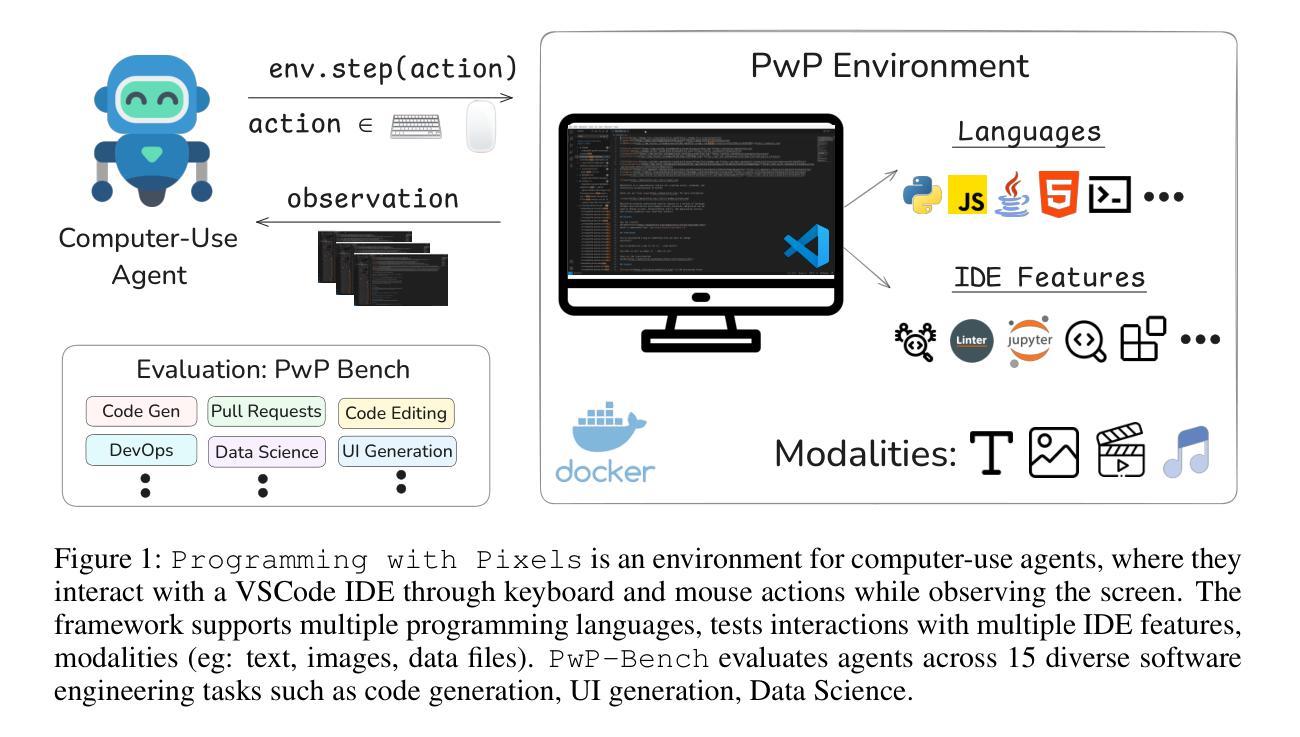
Programming with Pixels: Can Computer-Use Agents do Software Engineering?
Authors:Pranjal Aggarwal, Sean Welleck
Computer-use agents (CUAs) hold the promise of performing a wide variety of general tasks, but current evaluations have primarily focused on simple scenarios. It therefore remains unclear whether such generalist agents can automate more sophisticated and specialized work such as software engineering (SWE). To investigate this, we introduce $\texttt{Programming with Pixels}$ (PwP), the first comprehensive computer-use environment for software engineering, where agents visually control an IDE to perform diverse software engineering tasks. To enable holistic evaluation, we also introduce \texttt{PwP-Bench}, a benchmark of 15 existing and new software-engineering tasks spanning multiple modalities, programming languages, and skillsets. We perform an extensive evaluation of state-of-the-art open-weight and closed-weight CUAs and find that when interacting purely visually, they perform significantly worse than specialized coding agents. However, when the same CUAs are given direct access to just two APIs-file editing and bash operations-performance jumps, often reaching the levels of specialized agents despite having a task-agnostic design. Furthermore, when given access to additional IDE tools via text APIs, all models show further gains. Our analysis shows that current CUAs fall short mainly due to limited visual grounding and the inability to take full advantage of the rich environment, leaving clear room for future improvements.PwP establishes software engineering as a natural domain for benchmarking whether generalist computer-use agents can reach specialist-level performance on sophisticated tasks. Code and data released at https://programmingwithpixels.com
计算机使用代理(CUAs)具有执行各种通用任务的潜力,但目前的评估主要集中在简单场景上。因此,尚不清楚这种通用代理是否能够自动化更复杂和专门的工作,如软件工程(SWE)。为了调查这一点,我们引入了“Programming with Pixels”(PwP),这是第一个用于软件工程的全面计算机使用环境,其中代理通过视觉控制集成开发环境(IDE)来执行多种软件工程任务。为了实现整体评估,我们还介绍了PwP-Bench,这是一个涵盖多种模式、编程语言和技能集的15项现有和新软件工程任务的基准测试。我们对最先进的开放权重和封闭权重的CUAs进行了广泛评估,发现当仅通过视觉交互时,它们的表现远远落后于专业编码代理。但是,当为这些相同的CUA提供直接访问仅两个API(文件编辑和bash操作)时,性能会得到提升,尽管它们具有与任务无关的设计,但往往能达到专业代理的水平。此外,当通过文本API访问其他IDE工具时,所有模型都表现出进一步的增益。我们的分析表明,当前CUAs的主要不足在于视觉定位有限以及无法充分利用丰富的环境,这为未来的改进留下了明确的空间。PwP确立了软件工程作为衡量通用计算机使用代理是否能在复杂任务上达到专业代理水平的自然领域。代码和数据发布在https://programmingwithpixels.com。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本研究引入了首个用于软件工程领域的综合计算机使用环境,即Programming with Pixels(PwP)。它使代理能够可视化地控制IDE来执行各种软件工程任务。为进行整体评估,还推出了PwP-Bench基准测试,涵盖多种模态、编程语言和技能集的15项现有和新软件工程任务。评估发现,当仅通过视觉交互时,当前最先进的通用代理在软件工程任务上的表现较差,但当给予直接访问某些API时,性能有所提升。分析表明,当前通用代理主要因视觉定位有限和无法充分利用丰富环境而表现不足,但仍存在改进空间。PwP为评估通用代理在复杂任务上是否能达到专业级别提供了重要平台。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究提出了用于软件工程的计算机使用环境Programming with Pixels(PwP),允许代理可视化控制IDE执行多种任务。
- 引入了PwP-Bench基准测试,包含多种软件工程任务的基准测试。
- 评估发现仅通过视觉交互的通用代理在软件工程任务上表现较差。
- 当通用代理被赋予直接访问某些API时,性能有所提升,有时甚至能达到专业代理的水平。
- 当前通用代理的主要短板在于视觉定位有限和无法充分利用环境资源。
- 研究结果显示未来存在改进空间,可通过提升视觉识别和API利用能力来提升通用代理的性能。
点此查看论文截图