⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-07 更新
CBVLM: Training-free Explainable Concept-based Large Vision Language Models for Medical Image Classification
Authors:Cristiano Patrício, Isabel Rio-Torto, Jaime S. Cardoso, Luís F. Teixeira, João C. Neves
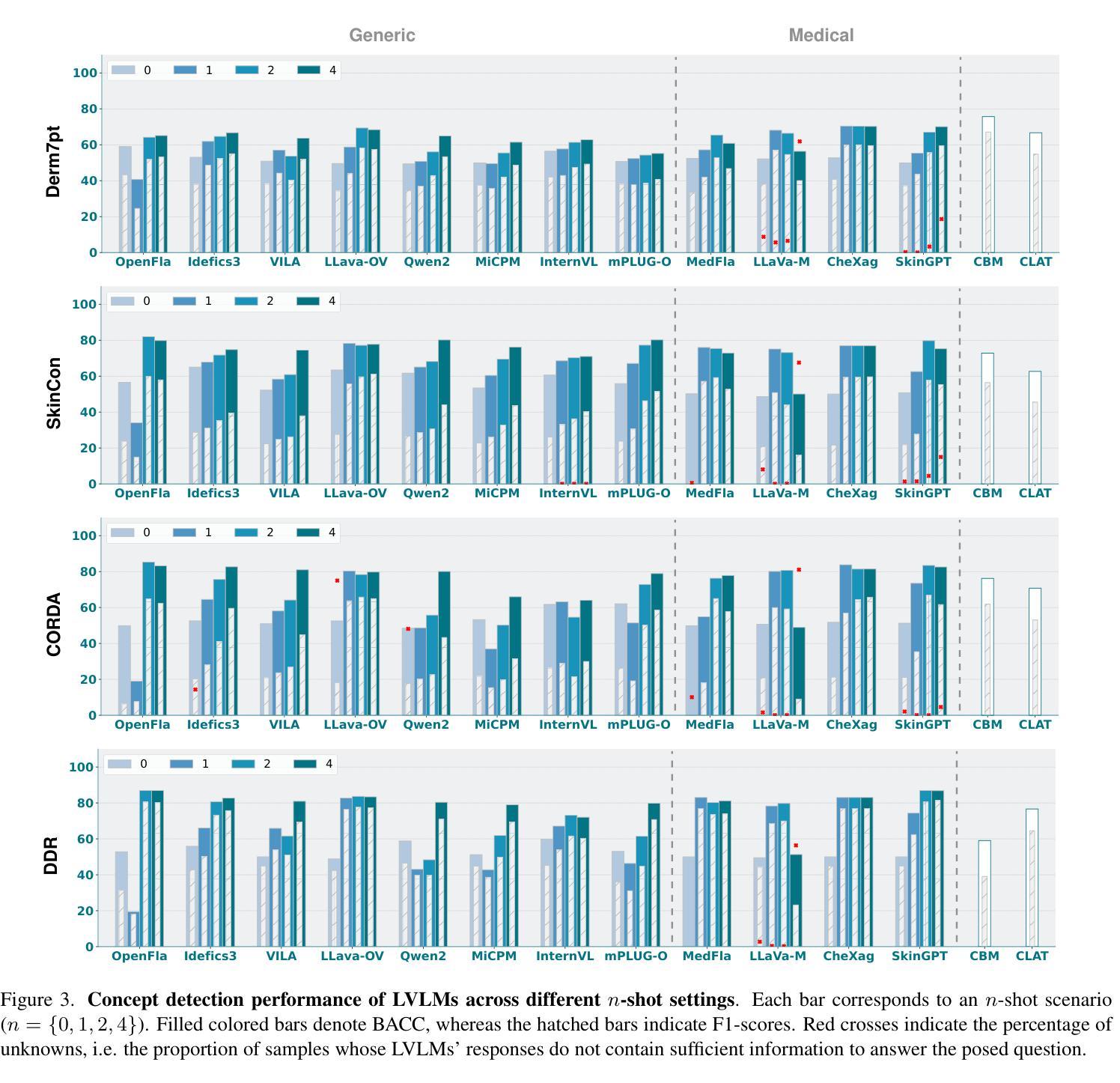
The main challenges limiting the adoption of deep learning-based solutions in medical workflows are the availability of annotated data and the lack of interpretability of such systems. Concept Bottleneck Models (CBMs) tackle the latter by constraining the model output on a set of predefined and human-interpretable concepts. However, the increased interpretability achieved through these concept-based explanations implies a higher annotation burden. Moreover, if a new concept needs to be added, the whole system needs to be retrained. Inspired by the remarkable performance shown by Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) in few-shot settings, we propose a simple, yet effective, methodology, CBVLM, which tackles both of the aforementioned challenges. First, for each concept, we prompt the LVLM to answer if the concept is present in the input image. Then, we ask the LVLM to classify the image based on the previous concept predictions. Moreover, in both stages, we incorporate a retrieval module responsible for selecting the best examples for in-context learning. By grounding the final diagnosis on the predicted concepts, we ensure explainability, and by leveraging the few-shot capabilities of LVLMs, we drastically lower the annotation cost. We validate our approach with extensive experiments across four medical datasets and twelve LVLMs (both generic and medical) and show that CBVLM consistently outperforms CBMs and task-specific supervised methods without requiring any training and using just a few annotated examples. More information on our project page: https://cristianopatricio.github.io/CBVLM/.
在医疗工作流中采用基于深度学习的解决方案的主要挑战是标注数据可用性和系统解释性的缺乏。概念瓶颈模型(CBMs)通过约束模型输出在一组预定义和可解释的概念上来解决后者的问题。然而,通过基于概念的解释来提高解释性意味着更高的标注负担。而且,如果要添加新概念,需要整个系统重新训练。受大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在少样本环境中的出色表现的启发,我们提出了一种简单而有效的方法,即CBVLM,它解决了上述两个挑战。首先,对于每个概念,我们提示LVLM回答概念是否出现在输入图像中。然后,我们让LVLM基于之前的概念预测对图像进行分类。而且,在两个阶段中,我们都融入了一个检索模块,负责选择最佳样本进行上下文学习。通过基于预测的概念做出最终诊断,我们确保了可解释性,并通过利用LVLMs的少样本能力,我们大大降低了标注成本。我们通过四个医疗数据集和十二个(通用和医疗)LVLMs的广泛实验验证了我们的方法,并显示CBVLM始终优于CBMs和特定任务监督方法,而且无需任何训练,只需使用少量标注样本即可。更多信息请参见我们的项目页面:https://cristianopatricio.github.io/CBVLM/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in Computers in Biology and Medicine
Summary
深度学习在医疗工作流程中的应用面临标注数据可用性和系统解释性的挑战。CBVLM方法通过利用大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)的少样本能力,解决这些问题。它能在图像中预测概念并进行分类,通过检索模块选择最佳示例进行上下文学习。通过基于预测概念的结果诊断确保了解释性,利用LVLMs的少样本能力降低了标注成本。CBVLM在四个医疗数据集上验证了其性能超越概念瓶颈模型和任务特定监督方法,而且无需训练即可使用少量的标注示例。详情请参阅我们的项目页面:https://cristianopatricio.github.io/CBVLM/。
Key Takeaways
- CBVLM解决了深度学习在医疗领域应用中遇到的标注数据可用性和系统解释性问题。
- CBVLM方法利用大型视觉语言模型(LVLM)进行概念预测和图像分类。
- CBVLM通过结合检索模块和基于预测概念的分类,提高模型的解释性和准确性。
- CBVLM利用LVLM的少样本学习能力,降低了标注成本。
- CBVLM在多个医疗数据集上的性能超越了概念瓶颈模型和任务特定监督方法。
点此查看论文截图