⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-07 更新
Test-Time Defense Against Adversarial Attacks via Stochastic Resonance of Latent Ensembles
Authors:Dong Lao, Yuxiang Zhang, Haniyeh Ehsani Oskouie, Yangchao Wu, Alex Wong, Stefano Soatto
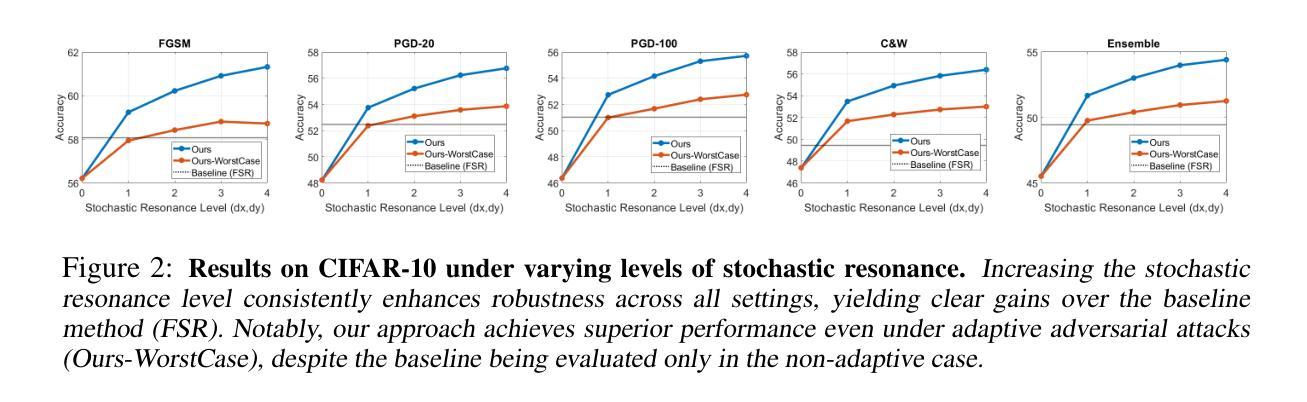
We propose a test-time defense mechanism against adversarial attacks: imperceptible image perturbations that significantly alter the predictions of a model. Unlike existing methods that rely on feature filtering or smoothing, which can lead to information loss, we propose to “combat noise with noise” by leveraging stochastic resonance to enhance robustness while minimizing information loss. Our approach introduces small translational perturbations to the input image, aligns the transformed feature embeddings, and aggregates them before mapping back to the original reference image. This can be expressed in a closed-form formula, which can be deployed on diverse existing network architectures without introducing additional network modules or fine-tuning for specific attack types. The resulting method is entirely training-free, architecture-agnostic, and attack-agnostic. Empirical results show state-of-the-art robustness on image classification and, for the first time, establish a generic test-time defense for dense prediction tasks, including stereo matching and optical flow, highlighting the method’s versatility and practicality. Specifically, relative to clean (unperturbed) performance, our method recovers up to 68.1% of the accuracy loss on image classification, 71.9% on stereo matching, and 29.2% on optical flow under various types of adversarial attacks.
我们提出了一种针对对抗性攻击的测试时防御机制:即对图像进行细微的、难以察觉的扰动,从而显著改变模型的预测结果。与依赖特征过滤或平滑的现有方法不同,这些方法可能导致信息丢失,我们提出通过利用随机共振来增强鲁棒性,同时尽量减少信息损失,以“以噪声对抗噪声”的方式应对。我们的方法在输入图像上引入微小的平移扰动,对齐变换后的特征嵌入,将它们聚合,然后映射回原始参考图像。这可以用封闭形式的公式来表示,可以在各种现有的网络架构上部署,而无需引入额外的网络模块或为特定的攻击类型进行微调。所得方法完全无需训练、不受架构限制,且不受攻击影响。经验结果表明,该方法在图像分类方面达到了最先进的稳健性,并且首次为密集预测任务建立了通用的测试时防御机制,包括立体匹配和光流,这突出了该方法的通用性和实用性。具体来说,相对于清洁(无扰动)的性能,我们的方法在图像分类上恢复了高达68.1%的精度损失,在立体匹配上恢复了71.9%,在光流上恢复了29.2%,在各种类型的对抗性攻击下表现良好。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种针对对抗攻击的测试时防御机制:通过引入几乎不可察觉的图像扰动来显著改变模型的预测结果。不同于依赖特征过滤或平滑的现有方法,可能导致信息损失,本文采用“以噪声对抗噪声”的策略,利用随机共振增强稳健性并尽量减少信息损失。方法通过在输入图像上引入微小平移扰动、对齐变换后的特征嵌入并对其进行聚合,再映射回原始参考图像。该方法以封闭形式公式表达,可部署在各种现有网络架构上,无需针对特定攻击类型引入额外的网络模块或微调。该方法完全无需训练,具有架构无关性和攻击无关性,并在图像分类方面取得了最先进的稳健性成果。此外,本文首次为密集预测任务(包括立体匹配和光流)建立了通用的测试时防御,突显了方法的通用性和实用性。在不同类型的对抗攻击下,相较于干净(无扰动)的性能,该方法在图像分类、立体匹配和光流方面分别恢复了高达68.1%、71.9%和29.2%的精度损失。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种新型测试时防御机制对抗对抗攻击。
- 通过微小平移扰动来增强模型稳健性,并尽量减少信息损失。
- 利用随机共振的策略——“以噪声对抗噪声”。
- 该方法可在多种网络架构上部署,无需额外的网络模块或针对特定攻击的微调。
- 完全无需训练,具有架构无关性和攻击无关性。
- 在图像分类方面取得最先进的稳健性成果。
- 首次为密集预测任务建立通用测试时防御,包括立体匹配和光流任务。
点此查看论文截图

Multimodal Carotid Risk Stratification with Large Vision-Language Models: Benchmarking, Fine-Tuning, and Clinical Insights
Authors:Daphne Tsolissou, Theofanis Ganitidis, Konstantinos Mitsis, Stergios CHristodoulidis, Maria Vakalopoulou, Konstantina Nikita
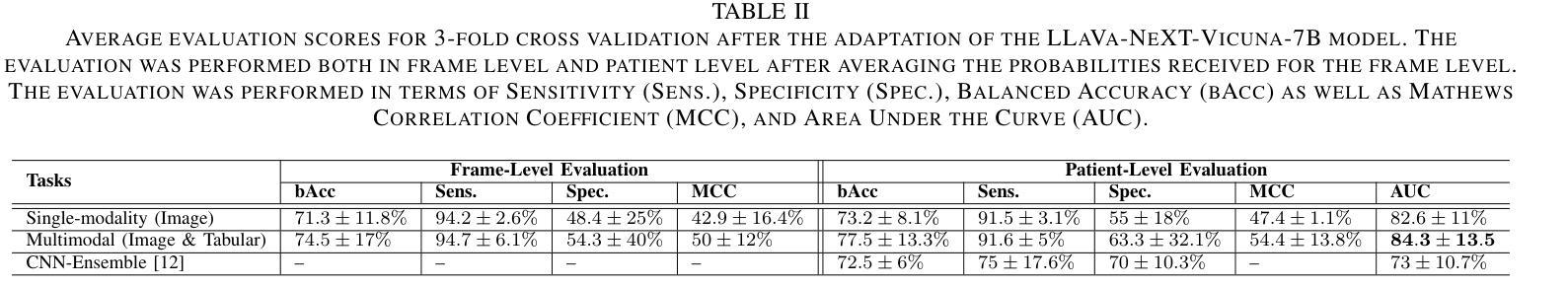
Reliable risk assessment for carotid atheromatous disease remains a major clinical challenge, as it requires integrating diverse clinical and imaging information in a manner that is transparent and interpretable to clinicians. This study investigates the potential of state-of-the-art and recent large vision-language models (LVLMs) for multimodal carotid plaque assessment by integrating ultrasound imaging (USI) with structured clinical, demographic, laboratory, and protein biomarker data. A framework that simulates realistic diagnostic scenarios through interview-style question sequences is proposed, comparing a range of open-source LVLMs, including both general-purpose and medically tuned models. Zero-shot experiments reveal that even if they are very powerful, not all LVLMs can accurately identify imaging modality and anatomy, while all of them perform poorly in accurate risk classification. To address this limitation, LLaVa-NeXT-Vicuna is adapted to the ultrasound domain using low-rank adaptation (LoRA), resulting in substantial improvements in stroke risk stratification. The integration of multimodal tabular data in the form of text further enhances specificity and balanced accuracy, yielding competitive performance compared to prior convolutional neural network (CNN) baselines trained on the same dataset. Our findings highlight both the promise and limitations of LVLMs in ultrasound-based cardiovascular risk prediction, underscoring the importance of multimodal integration, model calibration, and domain adaptation for clinical translation.
颈动脉粥样斑块病的可靠风险评估仍然是临床上的一个主要挑战,因为它需要以一种对临床医生透明且可解释的方式,整合各种临床和成像信息。本研究调查了最先进的大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在颈动脉斑块多模态评估中的潜力,通过整合超声成像(USI)与结构化临床、人口统计学、实验室和蛋白质生物标志物数据。本研究提出了一种模拟现实诊断场景的框架,通过访谈式问题序列进行比较,涉及一系列开源LVLMs,包括通用模型和经过医学调整模型。零样本实验表明,尽管它们非常强大,但并非所有LVLM都能准确识别成像模式和解剖学特征,所有模型在准确的风险分类方面的表现都不佳。为了解决这一局限性,使用低秩适应(LoRA)将LLaVa-NeXT-Vicuna适应于超声领域,极大提高了中风风险分层的效果。以文本形式整合多模态表格数据进一步提高了特异性和平衡精度,与在相同数据集上训练的先前卷积神经网络(CNN)基准测试相比,表现出竞争性能。我们的研究结果突出了LVLMs在基于超声的心血管风险预测中的潜力和局限性,强调多模态整合、模型校准和领域适应对于临床转化的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了最先进的大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在多模态颈动脉斑块评估中的潜力,通过整合超声成像与结构化临床、人口学、实验室和蛋白质生物标志物数据,模拟真实诊断场景。研究发现,虽然LVLMs功能强大,但并不是所有模型都能准确识别成像模态和解剖结构,且在风险分类方面的表现较差。通过适应LoRA的LLaVa-NeXT-Vicuna模型在超声领域的应用,对中风风险分层有了显著改善。多模态表格数据的文本形式整合进一步提高了特异性和平衡精度,与在同一数据集上训练的卷积神经网络(CNN)基准测试相比具有竞争力。研究结果强调了LVLMs在超声心动图风险预测中的前景和局限性,突出了多模态整合、模型校准和领域适应对于临床转化的重要性。
Key Takeaways
风险评估在颈动脉粥样化疾病中是一个重大挑战,需要整合多种临床和成像信息,需要具有透明度且易于临床医生理解。
先进的大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)用于多模态颈动脉斑块评估的研究得到调查。这些模型结合了超声成像与多种临床数据。
LVLMs在某些情况下表现出局限性,特别是在准确识别成像模态和解剖结构方面,以及风险分类方面。
通过LoRA适应的LLaVa-NeXT-Vicuna模型在超声领域应用改善了中风风险分层的效果。
多模态数据的整合进一步提高了风险评估的特异性和准确性。与之前在同一数据集上训练的CNN基准测试相比,该整合显示出竞争力。
研究结果揭示了LVLMs在超声心动图风险预测中的潜力和局限性。这表明未来的研究需要进一步关注模型的校准和适应性,以更好地适应临床实践。强调多模态信息融合在该领域的重要性和应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

Med-K2N: Flexible K-to-N Modality Translation for Medical Image Synthesis
Authors:Feng Yuan, Yifan Gao, Yuehua Ye, Haoyue Li, Xin Gao
Cross-modal medical image synthesis research focuses on reconstructing missing imaging modalities from available ones to support clinical diagnosis. Driven by clinical necessities for flexible modality reconstruction, we explore K to N medical generation, where three critical challenges emerge: How can we model the heterogeneous contributions of different modalities to various target tasks? How can we ensure fusion quality control to prevent degradation from noisy information? How can we maintain modality identity consistency in multi-output generation? Driven by these clinical necessities, and drawing inspiration from SAM2’s sequential frame paradigm and clinicians’ progressive workflow of incrementally adding and selectively integrating multi-modal information, we treat multi-modal medical data as sequential frames with quality-driven selection mechanisms. Our key idea is to “learn” adaptive weights for each modality-task pair and “memorize” beneficial fusion patterns through progressive enhancement. To achieve this, we design three collaborative modules: PreWeightNet for global contribution assessment, ThresholdNet for adaptive filtering, and EffiWeightNet for effective weight computation. Meanwhile, to maintain modality identity consistency, we propose the Causal Modality Identity Module (CMIM) that establishes causal constraints between generated images and target modality descriptions using vision-language modeling. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our proposed Med-K2N outperforms state-of-the-art methods by significant margins on multiple benchmarks. Source code is available.
跨模态医学图像合成研究主要集中在利用现有成像模式重建缺失的成像模式,以支持临床诊断。受到临床对灵活模式重建的需求驱动,我们探索了从K到N的医学图像生成方法,其中出现了三个关键挑战:我们如何建模不同模态对各项任务的异质贡献?我们如何确保融合质量控制以防止噪声信息的退化?如何在多输出生成中保持模态身份一致性?受到这些临床需求的驱动,并从SAM2的顺序框架范式和临床医生逐步添加和选择性整合多模态信息的流程中汲取灵感,我们将多模态医学数据视为具有质量驱动选择机制的顺序帧。我们的核心思想是为每对模态任务“学习”自适应权重,并通过逐步增强“记忆”有益的融合模式。为此,我们设计了三个协作模块:用于全局贡献评估的PreWeightNet,用于自适应过滤的ThresholdNet,以及用于有效权重计算EffiWeightNet。同时,为了保持模态身份的一致性,我们提出了因果模态身份模块(CMIM),它使用视觉语言建模在生成的图像和目标模态描述之间建立因果约束。大量的实验结果表明,我们提出的Med-K2N在多基准测试上均超过了最先进的方法。源代码已公开。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICLR2026 under review
Summary:
跨模态医学图像合成研究旨在从可用的成像模态重建缺失的成像模态,以支持临床诊断。针对临床灵活的模态重建需求,我们探索了从K到N的医学图像生成方法,其中面临三个关键挑战。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了基于质量驱动的序列框架选择机制的多模态医学数据处理方法,并设计了三个协作模块和因果模态身份模块(CMIM)。实验结果表明,我们提出的Med-K2N在多基准测试中显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 跨模态医学图像合成旨在从已有的成像模态重建缺失的模态,以支持临床诊断。
- 在K到N医学图像生成中面临三个关键挑战:建模不同模态对任务的异质贡献、确保融合质量控制、以及在多输出生成中保持模态身份一致性。
- 借鉴SAM2的序列框架范式和临床医生逐步添加和选择性整合多模态信息的流程,将多模态医学数据视为具有质量驱动选择机制的序列帧。
- 通过设计PreWeightNet、ThresholdNet和EffiWeightNet三个协作模块,解决跨模态融合中的挑战。
- 提出因果模态身份模块(CMIM),通过建立生成图像与目标模态描述之间的因果约束来保持模态身份一致性。
- 广泛实验结果表明,Med-K2N在多个基准测试中显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Demonstration of Fourier-domain Quantum Optical Coherence Tomography for a fast tomographic quantum imaging
Authors:Sylwia M. Kolenderska, Crislane Vieira de Brito, Piotr Kolenderski
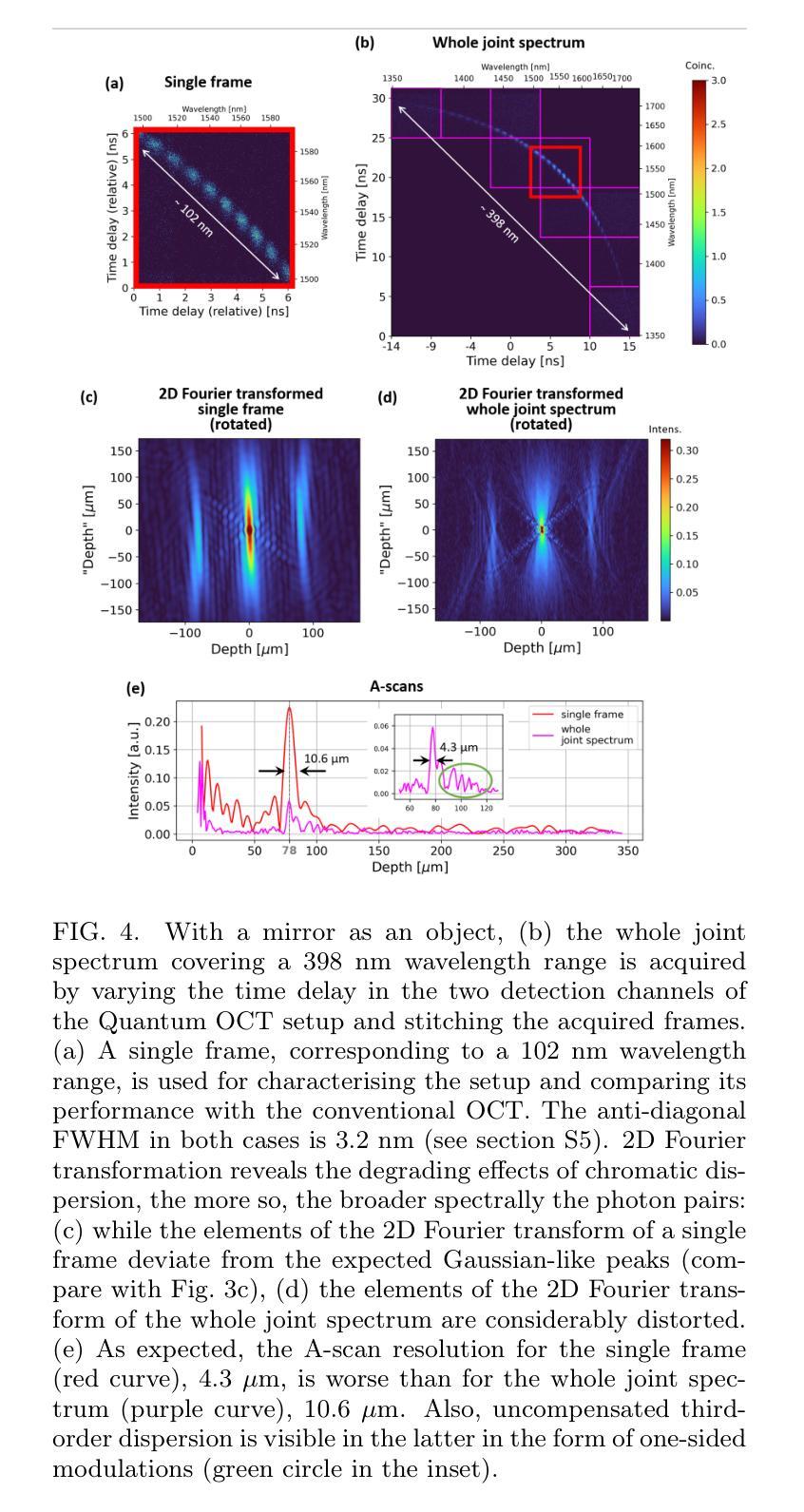
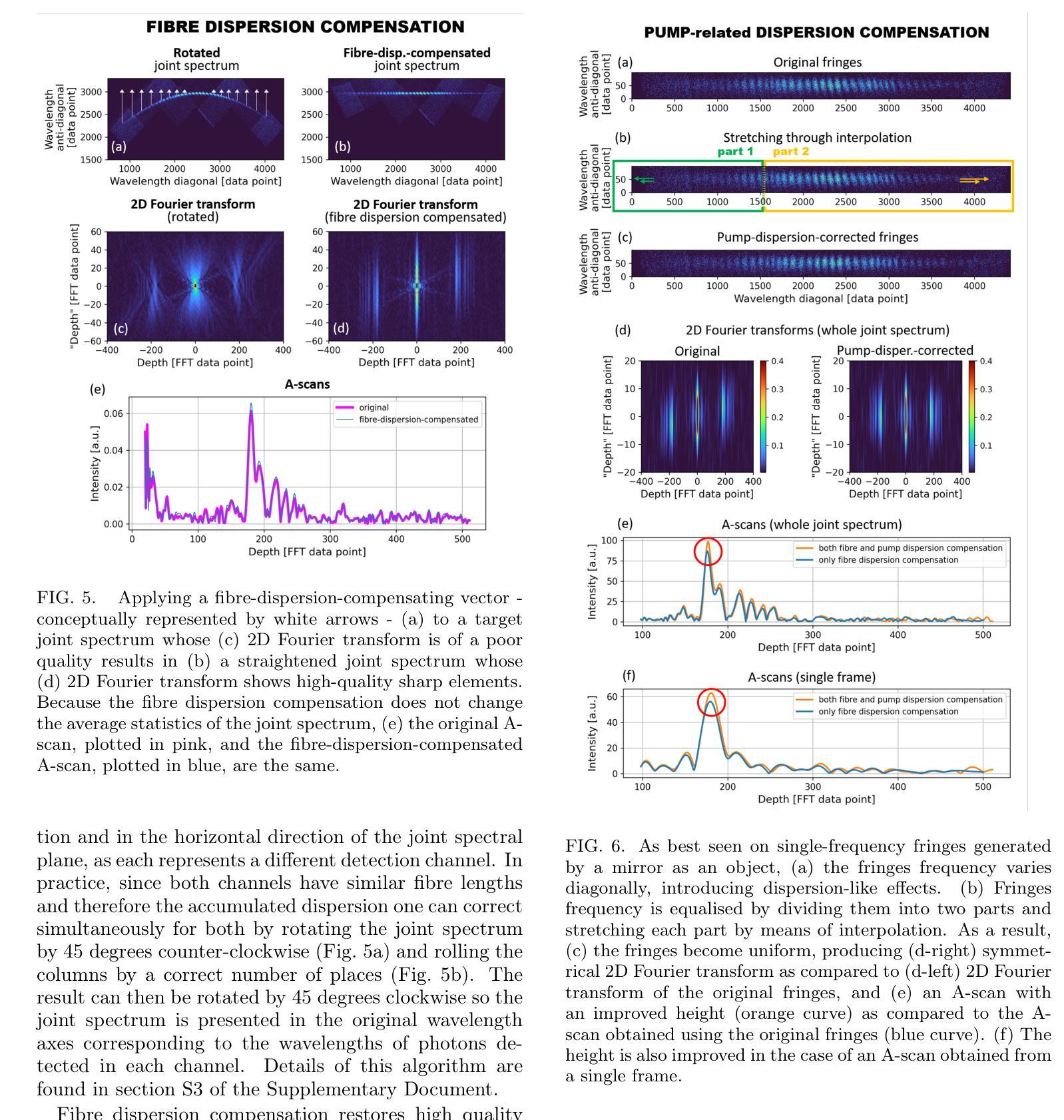
Using spectrally correlated photon pairs instead of classical laser light and coincidence detection instead of light intensity detection, Quantum Optical Coherence Tomography (Q-OCT) outperforms classical OCT in several experimental terms. It provides twice better axial resolution with the same spectral bandwidth and it is immune to even-order chromatic dispersion, including Group Velocity Dispersion responsible for the bulk of axial resolution degradation in the OCT images. Q-OCT has been performed in the time domain configuration, where one line of the two-dimensional image is acquired by axially translating the mirror in the interferometer’s reference arm and measuring the coincidence rate of photons arriving at two single-photon-sensitive detectors. Although successful at producing resolution-doubled and dispersion-cancelled images, it is still relatively slow and cannot compete with its classical counterpart. Here, we experimentally demonstrate Q-OCT in a much faster Fourier-domain configuration, theoretically proposed in 2020, where the reference mirror is fixed and the joint spectrum is acquired by inserting long fibre spools in front of the detectors. We propose two joint spectrum pre-processing algorithms, aimed at compensating resolution-degrading effects within the setup. While the first one targets fibre spool dispersion, an effect specific to this configuration, the other one removes the effects leading to the weakening of even-order dispersion cancellation, the latter impossible to be mitigated in the time-domain alternative. Being additionally contrasted with both the time-domain approach and the conventional OCT in terms of axial resolution, imaging range and multilayer-object imaging, Fourier-domain Q-OCT is shown to be a significant step forward towards a practical and competitive solution in the OCT arena.
利用光谱相关光子对代替经典激光光,并利用符合检测代替光强度检测,量子光学相干层析成像技术(Q-OCT)在几项实验中表现优于传统OCT。它在相同的光谱带宽下提供了两倍的轴向分辨率,并且对偶数色散具有免疫性,包括由群速度色散导致的OCT图像的大部分轴向分辨率退化。Q-OCT已经在时域配置中进行,通过轴向移动干涉仪参考臂中的镜子并测量到达两个单光子敏感探测器的光子符合率来获取二维图像的一行。尽管已成功产生分辨率加倍和色散取消的图像,但它仍然相对较慢,无法与其经典版本竞争。在这里,我们在实验上展示了在更快的傅立叶域配置中的Q-OCT,该配置在理论上于2020年提出,其中参考镜是固定的,通过探测器前插入长的光纤卷筒来获取联合光谱。我们提出了两种联合光谱预处理算法,旨在补偿设置内的分辨率降低效应。第一个针对光纤卷筒色散这一特定配置的影响,而另一个则消除了导致偶数色散取消失效的因素,后者在时域替代方案中无法缓解。通过与时域方法和传统OCT在轴向分辨率、成像范围和多层对象成像方面进行对比,傅立叶域Q-OCT被证明是朝着实用和竞争性的OCT解决方案迈出的重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 28 pages, 19 figures, 1 table
Summary
量子光学相干层析术(Q-OCT)采用光谱相关光子对替代经典激光光,并使用符合检测替代光强度检测,表现出优于传统OCT的性能。它在实验条件下提供了两倍的轴向分辨率,相同的谱带宽,且不受偶数色散影响,包括导致OCT图像大部分轴向分辨率退化的群速度色散。尽管成功实现了分辨率加倍和色散消除的图像,但Q-OCT仍然相对较慢,无法与传统技术竞争。本文在实验上展示了更快的傅立叶域配置的Q-OCT理论方案,在该方案中参考镜是固定的,通过探测器前插入长光纤线轴获得联合光谱。本文提出了两种联合光谱预处理算法,旨在补偿系统内的分辨率退化效应。第一种旨在针对此特定配置的光纤线圈色散问题;另一种消除了导致偶数色散取消无效的因素,后者在时域替代中无法缓解。与使用时域方法和传统OCT的轴向分辨率、成像范围和多层对象成像进行对比后,傅立叶域Q-OCT被认为是朝着实用和竞争性的OCT解决方案的重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- 量子光学相干层析术(Q-OCT)利用光谱相关光子对和符合检测优于传统光学相干层析术(OCT)。
- Q-OCT提供两倍的轴向分辨率和相同的谱带宽。
- Q-OCT不受偶数色散影响,包括群速度色散导致的OCT图像轴向分辨率退化。
- Q-OCT在傅立叶域配置中展示更快实现,其中参考镜固定,通过特定方式获取联合光谱。
- 提出两种联合光谱预处理算法以补偿系统内的分辨率退化效应和特定配置下的光纤线圈色散问题。
- 与时域OCT相比,傅立叶域Q-OCT在轴向分辨率、成像范围和多层对象成像方面更具优势。
点此查看论文截图