⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-07 更新
LEAML: Label-Efficient Adaptation to Out-of-Distribution Visual Tasks for Multimodal Large Language Models
Authors:Ci-Siang Lin, Min-Hung Chen, Yu-Yang Sheng, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have achieved strong performance on general visual benchmarks but struggle with out-of-distribution (OOD) tasks in specialized domains such as medical imaging, where labeled data is limited and expensive. We introduce LEAML, a label-efficient adaptation framework that leverages both scarce labeled VQA samples and abundant unlabeled images. Our approach generates domain-relevant pseudo question-answer pairs for unlabeled data using a QA generator regularized by caption distillation. Importantly, we selectively update only those neurons most relevant to question-answering, enabling the QA Generator to efficiently acquire domain-specific knowledge during distillation. Experiments on gastrointestinal endoscopy and sports VQA demonstrate that LEAML consistently outperforms standard fine-tuning under minimal supervision, highlighting the effectiveness of our proposed LEAML framework.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在通用视觉基准测试中取得了出色的表现,但在特定领域的非常规任务(如医学成像)中却表现挣扎,因为医学成像等领域的标注数据既有限又昂贵。我们引入了LEAML,这是一个标签高效适应框架,它充分利用了稀缺的标注VQA样本和大量的未标注图像。我们的方法使用通过标题蒸馏进行正则化的QA生成器,为未标注数据生成与领域相关的伪问答对。重要的是,我们只选择性地更新与问答最相关的神经元,使QA生成器在蒸馏过程中能够有效地获取特定领域的知识。在胃镜和体育问答方面的实验表明,在最小监督下,LEAML始终优于标准微调方法,突显了我们提出的LEAML框架的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在通用视觉基准测试中,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)表现优异,但在专业领域如医疗成像等面对分布外的任务时面临挑战。针对此问题,我们提出了LEAML框架,该框架利用稀缺的标签化问答样本和大量的未标签图像。我们的方法通过利用标题蒸馏正则化的问答生成器为未标记数据生成领域相关的伪问答对。我们仅选择性更新与问答最相关的神经元,这允许问答生成器在蒸馏过程中有效地获取特定领域的知识。在胃肠道内窥镜和体育问答中的实验表明,在监督不足的情况下,LEAML持续优于标准微调,凸显了LEAML框架的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- MLLMs在通用视觉基准测试中表现良好,但在特定领域的OOD任务中面临挑战。
- LEAML框架旨在解决专业领域中的监督不足问题。
- LEAML结合了标签化的问答样本和大量的未标签图像。
- 利用标题蒸馏正则化的问答生成器为未标记数据生成伪问答对。
- LEAML通过选择性更新与问答最相关的神经元,提高了效率。
- 实验表明LEAML在特定领域的任务中表现优于标准微调。
点此查看论文截图
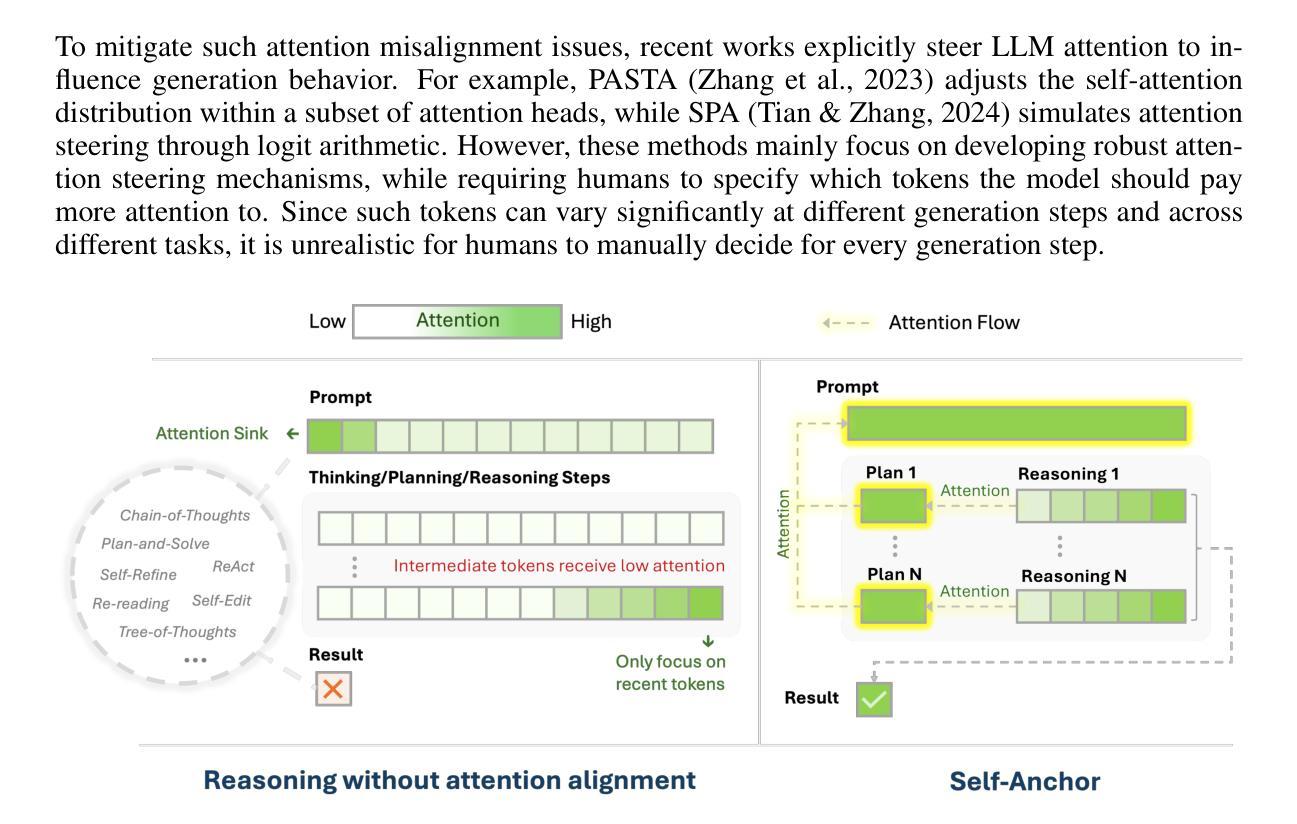
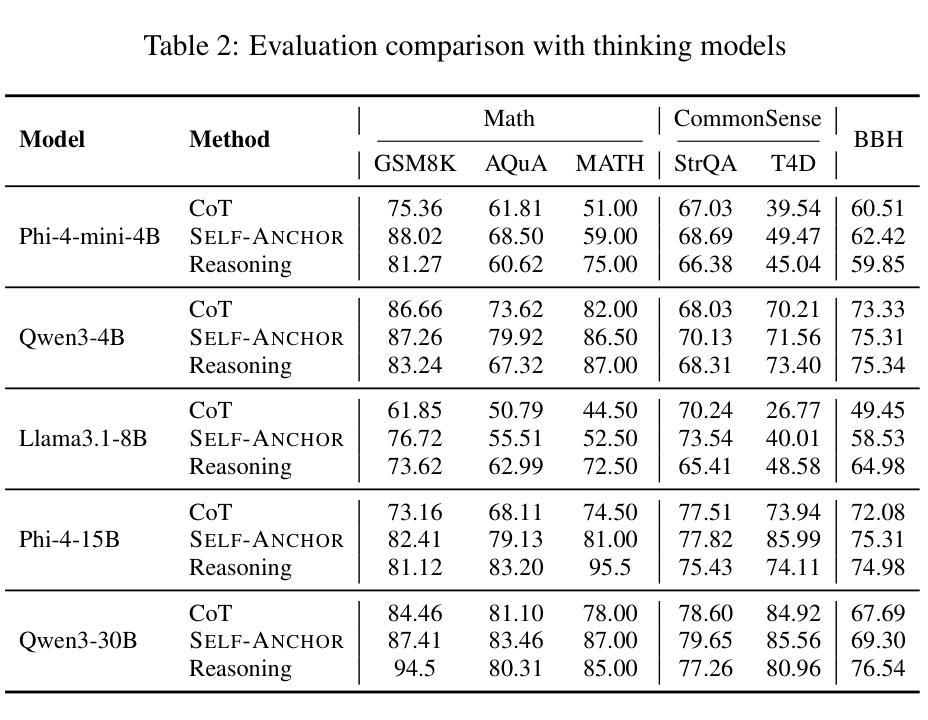
Self-Anchor: Large Language Model Reasoning via Step-by-step Attention Alignment
Authors:Hongxiang Zhang, Yuan Tian, Tianyi Zhang
To solve complex reasoning tasks for Large Language Models (LLMs), prompting-based methods offer a lightweight alternative to fine-tuning and reinforcement learning. However, as reasoning chains extend, critical intermediate steps and the original prompt will be buried in the context, receiving insufficient attention and leading to errors. In this paper, we propose Self-Anchor, a novel pipeline that leverages the inherent structure of reasoning to steer LLM attention. Self-Anchor decomposes reasoning trajectories into structured plans and automatically aligns the model’s attention to the most relevant inference steps, allowing the model to maintain focus throughout generation. Our experiment shows that Self-Anchor outperforms SOTA prompting methods across six benchmarks. Notably, Self-Anchor significantly reduces the performance gap between ``non-reasoning’’ models and specialized reasoning models, with the potential to enable most LLMs to tackle complex reasoning tasks without retraining.
为了解决大型语言模型(LLM)的复杂推理任务,基于提示的方法为微调强化学习提供了一种轻量级的替代方案。然而,随着推理链的延伸,关键的中间步骤和原始提示会被上下文所淹没,得不到足够的关注,从而导致错误。在本文中,我们提出了Self-Anchor,这是一种利用推理内在结构来引导LLM注意的新型管道。Self-Anchor将推理轨迹分解为结构化计划,并自动将模型注意力与最相关的推理步骤对齐,使模型在整个生成过程中保持关注。我们的实验表明,Self-Anchor在六个基准测试上优于SOTA提示方法。值得注意的是,Self-Anchor显著减少了“非推理”模型和专用推理模型之间的性能差距,具有使大多数LLM无需重新训练即可处理复杂推理任务的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于LLM的大型语言模型的推理任务中,随着推理链条的延伸,关键中间步骤和原始提示容易被忽视导致错误。本文提出一种名为Self-Anchor的新型管道,利用推理的内在结构来引导模型注意力。Self-Anchor将推理轨迹分解为结构化计划,并自动将模型注意力与最相关的推理步骤对齐,使模型在生成过程中保持关注重点。实验表明,Self-Anchor在六个基准测试中优于最新提示方法。特别的是,Self-Anchor显著减少了“非推理”模型和专用推理模型之间的性能差距,使大多数LLM能够处理复杂的推理任务而无需重新训练。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在处理复杂推理任务时面临挑战,随着推理链条的延长,关键步骤和原始提示容易在语境中被忽略。
- Self-Anchor是一种新型管道,旨在解决这一问题,通过利用推理的内在结构来引导LLM的注意力。
- Self-Anchor将推理轨迹分解为结构化计划,使模型能够更清晰地识别并关注关键推理步骤。
- Self-Anchor能够自动对齐模型注意力与最相关的推理步骤,提升模型的推理能力。
- 实验表明,Self-Anchor在多个基准测试中表现优异,优于当前的最新提示方法。
- Self-Anchor显著缩小了“非推理”模型和专用推理模型之间的性能差距。
点此查看论文截图
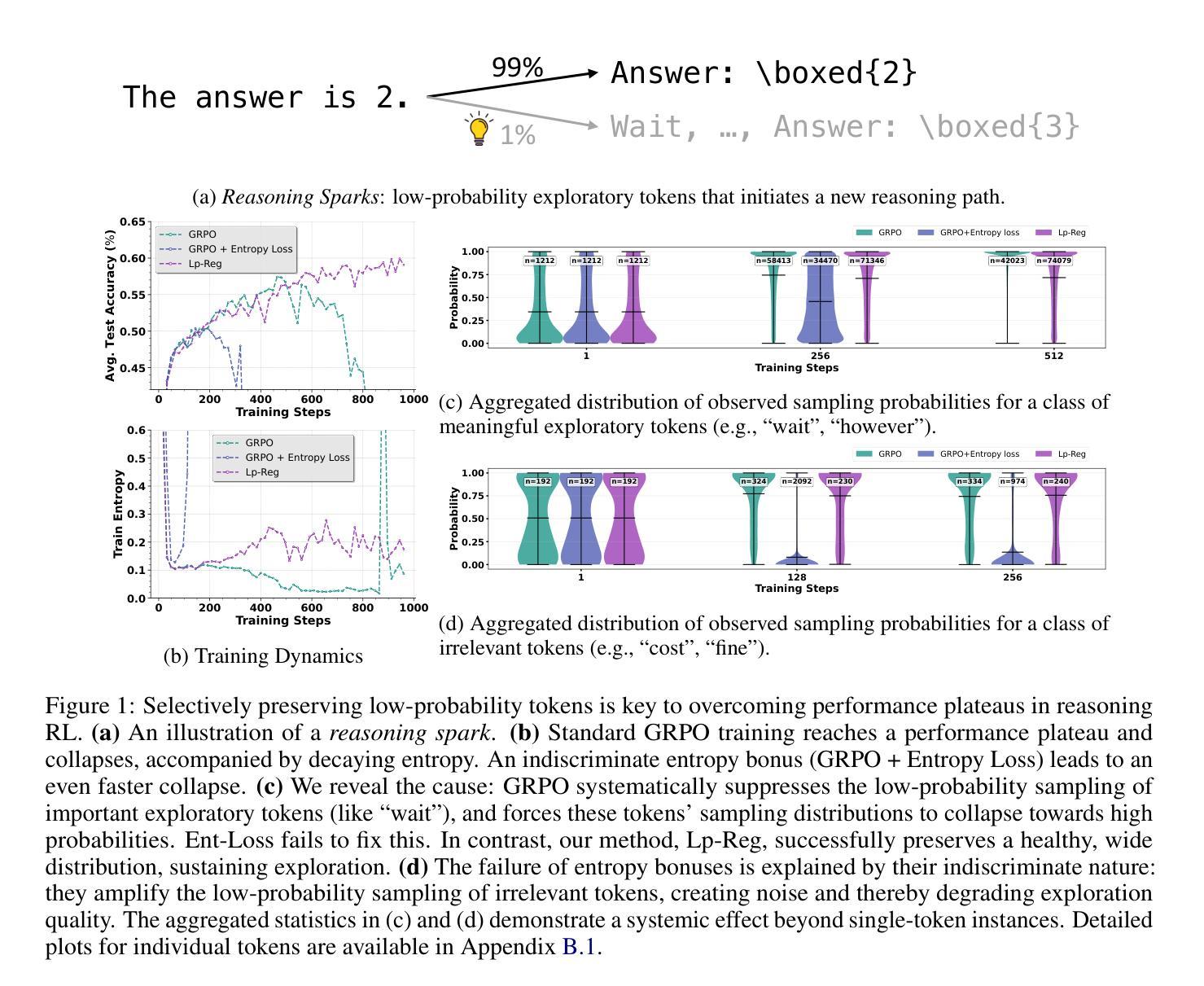
Low-probability Tokens Sustain Exploration in Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Reward
Authors:Guanhua Huang, Tingqiang Xu, Mingze Wang, Qi Yi, Xue Gong, Siheng Li, Ruibin Xiong, Kejiao Li, Yuhao Jiang, Bo Zhou
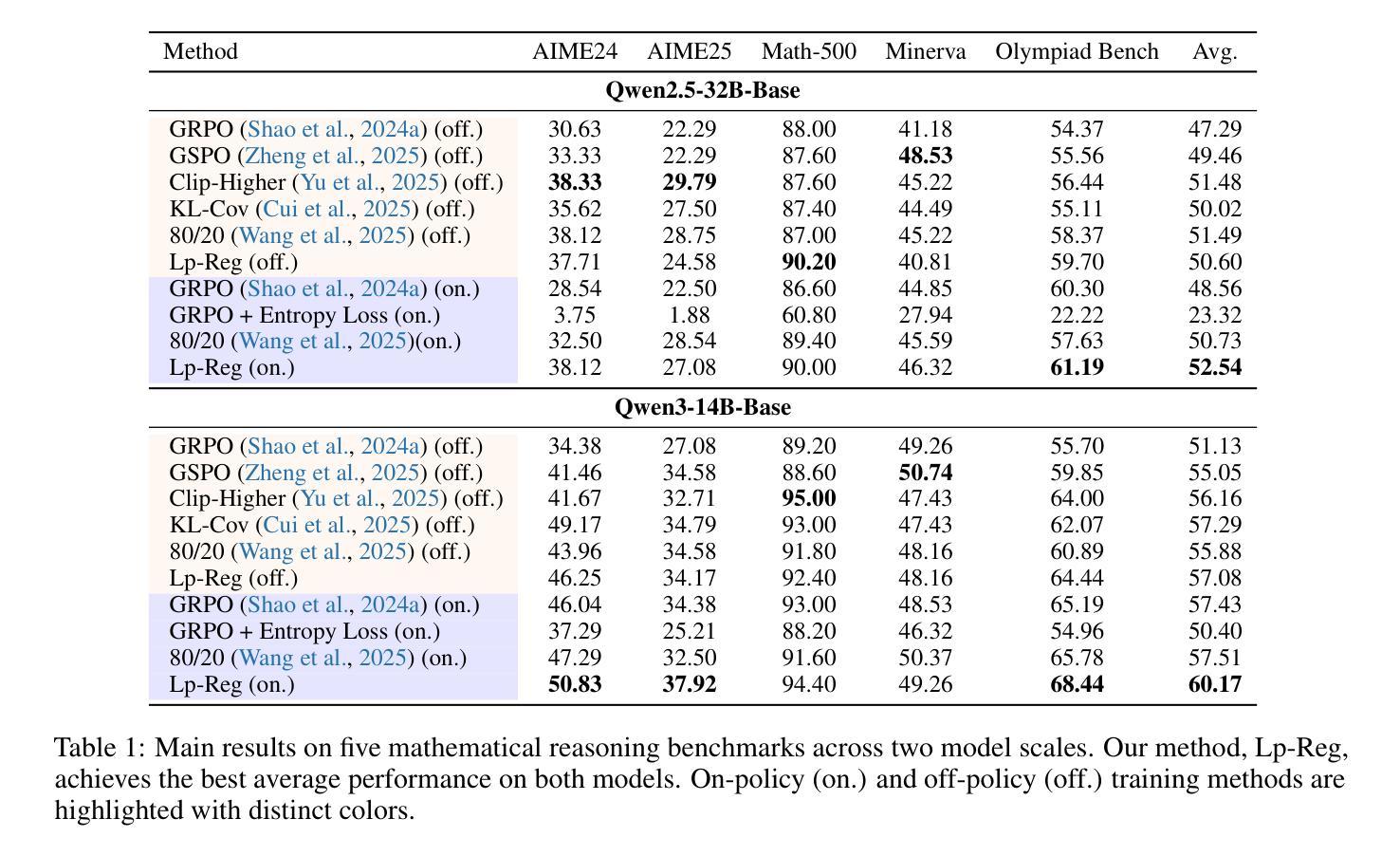
Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has propelled Large Language Models in complex reasoning, yet its scalability is often hindered by a training bottleneck where performance plateaus as policy entropy collapses, signaling a loss of exploration. Previous methods typically address this by maintaining high policy entropy, yet the precise mechanisms that govern meaningful exploration have remained underexplored. Our analysis suggests that an unselective focus on entropy risks amplifying irrelevant tokens and destabilizing training. This paper investigates the exploration dynamics within RLVR and identifies a key issue: the gradual elimination of valuable low-probability exploratory tokens, which we term \textbf{\textit{reasoning sparks}}. We find that while abundant in pre-trained models, these sparks are systematically extinguished during RLVR due to over-penalization, leading to a degeneracy in exploration. To address this, we introduce Low-probability Regularization (Lp-Reg). Its core mechanism regularizes the policy towards a heuristic proxy distribution. This proxy is constructed by filtering out presumed noise tokens and re-normalizing the distribution over the remaining candidates. The result is a less-noisy proxy where the probability of \textit{reasoning sparks} is amplified, which then serves as a soft regularization target to shield these valuable tokens from elimination via KL divergence. Experiments show that Lp-Reg enables stable on-policy training for around 1,000 steps, a regime where baseline entropy-control methods collapse. This sustained exploration leads to state-of-the-art performance, achieving a $60.17%$ average accuracy on five math benchmarks, an improvement of $2.66%$ over prior methods. Code is available at https://github.com/CarlanLark/Lp-Reg.
强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)已推动大型语言模型在复杂推理方面的应用,但其可扩展性常常受到训练瓶颈的阻碍,当策略熵崩溃时,性能会达到平台期,这表明探索的丧失。之前的方法通常通过保持高策略熵来解决这个问题,但控制有意义探索的精确机制仍未得到充分探索。我们的分析表明,对熵的无选择性关注可能放大无关标记并破坏训练稳定性。本文研究了RLVR中的探索动态,并发现了一个关键问题:有价值的低概率探索标记逐渐被淘汰,我们称之为“推理火花”。我们发现,虽然在预训练模型中这些火花非常丰富,但在RLVR期间由于过度惩罚而系统地被消灭,导致探索退化。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了低概率正则化(Lp-Reg)。其核心机制是对策略进行正则化以符合启发式代理分布。该代理通过过滤掉假定为噪声的标记并重新归一化剩余候选者的分布来构建。结果是噪声较少的代理,其中推理火花的概率得到放大,然后作为软正则化目标,通过KL散度保护这些有价值的标记不被淘汰。实验表明,Lp-Reg能够在大约1000步内实现稳定的在线策略训练,这是基线熵控制方法崩溃的领域。这种持续的探索导致了最先进的性能,在五个数学基准测试上达到了60.17%的平均准确率,比先前的方法提高了2.66%。代码可在https://github.com/CarlanLark/Lp-Reg处获取。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
强化学习与可验证奖励(RLVR)在推动大型语言模型进行复杂推理方面取得了进展,但其可扩展性经常受到训练瓶颈的阻碍,表现为性能平台化,标志着探索的丧失。之前的方法通常通过保持高政策熵来解决这一问题,但精确控制有意义探索的机制仍然知之甚少。本文分析了RLVR中的探索动态,并发现了一个关键问题:宝贵的低概率探索性令牌(“推理火花”)的逐渐消除。尽管这些火花在预训练模型中非常丰富,但在RLVR中却被系统消除,原因是过度惩罚导致探索退化。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了低概率正则化(Lp-Reg)。其核心机制是对策略进行正则化,使其朝向启发式代理分布。该代理通过过滤掉假定为噪声令牌并重新归一化剩余候选者的分布来构建。结果是一个噪声较少的代理,其中推理火花的可能性被放大,然后作为软正则化目标,通过KL散度保护这些有价值的令牌免受消除。实验表明,Lp-Reg能够在大约1000步内实现稳定的在策略训练,这是基线熵控制方法崩溃的时期。这种持续的探索导致了最先进的性能,在五个数学基准测试上平均准确度达到60.17%,比先前的方法提高了2.66%。代码可在https://github.com/CarlanLark/Lp-Reg找到。
关键见解
- RLVR在复杂推理中表现优异,但遇到训练瓶颈,表现为性能平台化。
- 现有方法主要关注保持政策熵,但缺乏对有意义探索的精确控制。
- 本文发现低概率探索性令牌(推理火花)的逐渐消除是关键问题。
- 推理火花在预训练模型中丰富,但在RLVR训练过程中被过度惩罚而消除。
- 引入Low-probability Regularization(Lp-Reg)来解决这一问题,通过构建启发式代理分布来保护推理火花。
- Lp-Reg能够实现稳定的在策略训练,并在多个基准测试中达到最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

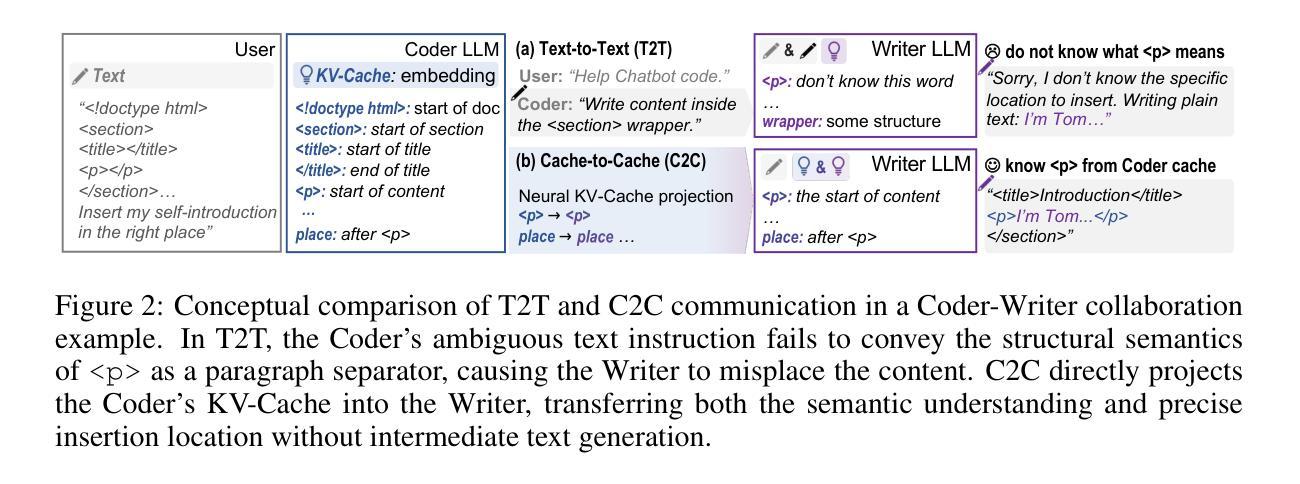
Cache-to-Cache: Direct Semantic Communication Between Large Language Models
Authors:Tianyu Fu, Zihan Min, Hanling Zhang, Jichao Yan, Guohao Dai, Wanli Ouyang, Yu Wang
Multi-LLM systems harness the complementary strengths of diverse Large Language Models, achieving performance and efficiency gains unattainable by a single model. In existing designs, LLMs communicate through text, forcing internal representations to be transformed into output token sequences. This process both loses rich semantic information and incurs token-by-token generation latency. Motivated by these limitations, we ask: Can LLMs communicate beyond text? Oracle experiments show that enriching the KV-Cache semantics can improve response quality without increasing cache size, supporting KV-Cache as an effective medium for inter-model communication. Thus, we propose Cache-to-Cache (C2C), a new paradigm for direct semantic communication between LLMs. C2C uses a neural network to project and fuse the source model’s KV-cache with that of the target model to enable direct semantic transfer. A learnable gating mechanism selects the target layers that benefit from cache communication. Compared with text communication, C2C utilizes the deep, specialized semantics from both models, while avoiding explicit intermediate text generation. Experiments show that C2C achieves 8.5-10.5% higher average accuracy than individual models. It further outperforms the text communication paradigm by approximately 3.0-5.0%, while delivering an average 2.0x speedup in latency. Our code is available at https://github.com/thu-nics/C2C.
多LLM系统利用不同大型语言模型的互补优势,实现了单一模型无法达到的性能和效率提升。在现有设计中,LLM通过文本进行交流,强制将内部表示转换为输出令牌序列。这一过程既丢失了丰富的语义信息,又产生了逐个令牌的生成延迟。针对这些局限性,我们提出一个问题:LLM能否以文本以外的方式进行交流?Oracle实验表明,丰富KV-Cache语义可以提高响应质量,而不增加缓存大小,支持KV-Cache作为跨模型通信的有效媒介。因此,我们提出了Cache-to-Cache(C2C),这是一种LLM之间直接语义交流的新范式。C2C使用神经网络将源模型的KV缓存投影并与目标模型的缓存融合,以实现直接的语义转换。一种可学习的门控机制选择受益于缓存通信的目标层。与文本交流相比,C2C利用了两个模型的深层专业语义,避免了显式的中间文本生成。实验表明,C2C比单个模型平均提高了8.5-10.5%的准确率。它进一步优于文本交流范式,大约提高了3.0-5.0%的性能,同时实现了平均2.0倍的延迟速度提升。我们的代码可在https://github.com/thu-nics/C2C找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多LLM系统通过利用不同大型语言模型的互补优势,实现了性能和效率的提升。现有设计中,LLM通过文本进行交流,导致语义信息丢失并产生逐词生成延迟。为解决这些问题,研究提出Cache-to-Cache(C2C)通信范式,实现LLM之间的直接语义交流。C2C利用神经网络将源模型的KV缓存投影并与目标模型融合,实现语义的直接传递。实验表明,C2C相比文本通信,利用了两者的深度语义,避免了中间文本的显式生成,提高了平均准确率和效率。
Key Takeaways
- 多LLM系统可以整合不同LLM的互补优势,提升性能和效率。
- 现有LLM通过文本交流存在语义信息丢失和延迟问题。
- Cache-to-Cache(C2C)通信范式可实现LLM间的直接语义交流。
- C2C利用神经网络投影和融合模型KV缓存,实现语义直接传递。
- C2C相比文本通信,能提高平均准确率并避免中间文本的显式生成。
- C2C通信范式在效率和性能上优于单个模型和文本通信。
点此查看论文截图
Neural Correlates of Language Models Are Specific to Human Language
Authors:Iñigo Parra
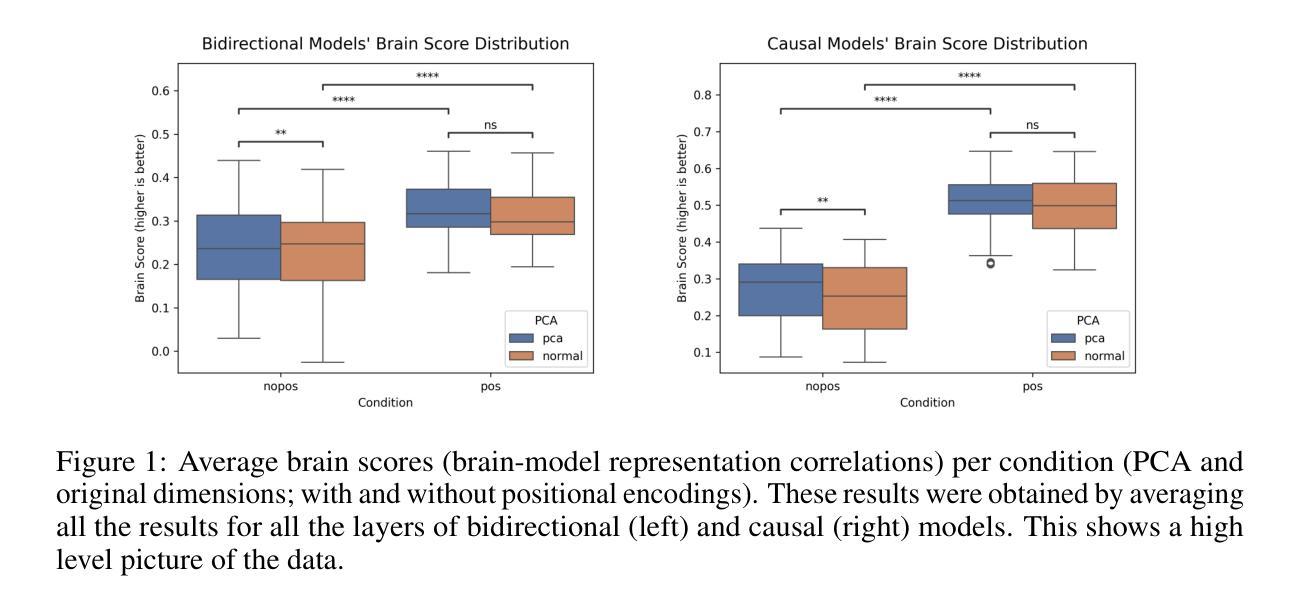
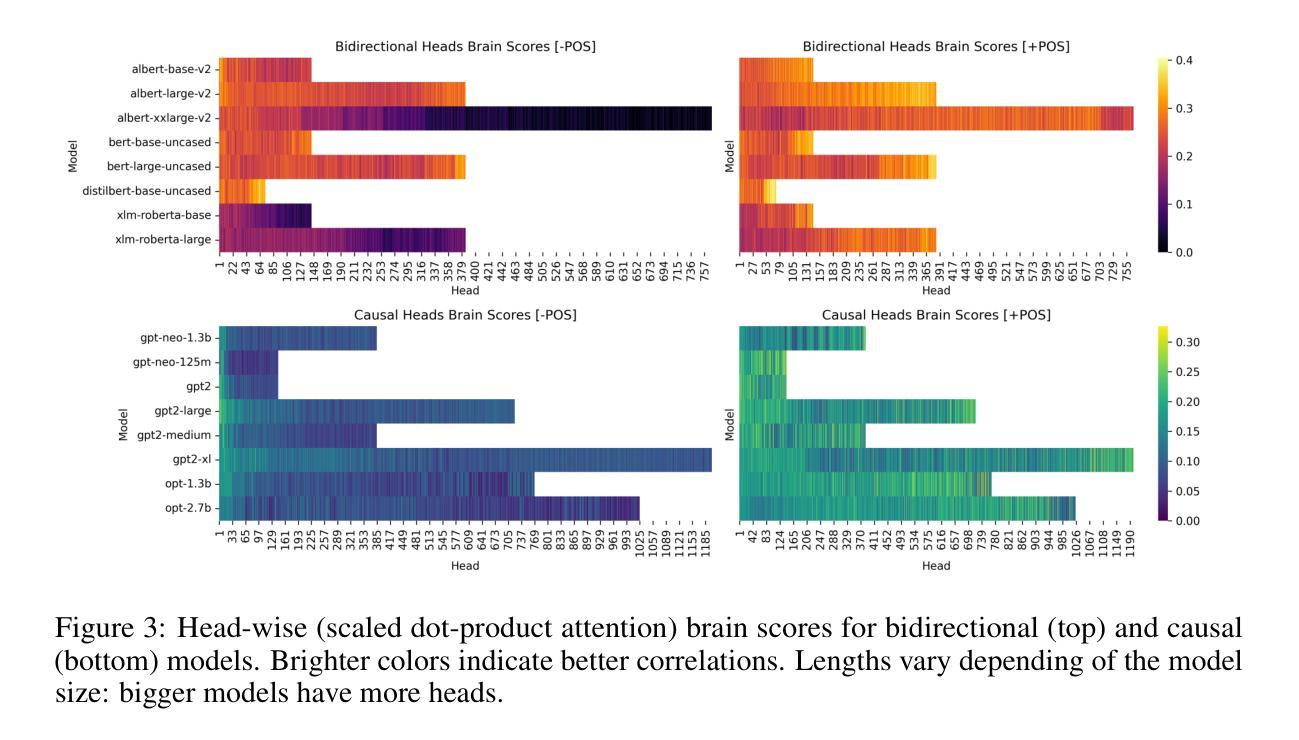
Previous work has shown correlations between the hidden states of large language models and fMRI brain responses, on language tasks. These correlations have been taken as evidence of the representational similarity of these models and brain states. This study tests whether these previous results are robust to several possible concerns. Specifically this study shows: (i) that the previous results are still found after dimensionality reduction, and thus are not attributable to the curse of dimensionality; (ii) that previous results are confirmed when using new measures of similarity; (iii) that correlations between brain representations and those from models are specific to models trained on human language; and (iv) that the results are dependent on the presence of positional encoding in the models. These results confirm and strengthen the results of previous research and contribute to the debate on the biological plausibility and interpretability of state-of-the-art large language models.
先前的工作已经显示出大型语言模型的隐藏状态与语言任务中的功能性磁共振成像(fMRI)大脑响应之间存在关联。这些关联被视为这些模型与大脑状态在代表性方面的相似性证据。本研究旨在测试这些先前结果是否能够对多种可能的担忧保持稳健。具体来说,本研究表明:(i)在降维之后仍然可以发现之前的结果,因此这并非归因于维数诅咒;(ii)在使用新的相似性度量方法时确认了之前的结果;(iii)大脑表示与模型之间的关联特定于经过人类语言训练的模型;(iv)结果依赖于模型中是否存在位置编码。这些结果证实了先前研究的结果并使其得到加强,为关于最新大型语言模型的生物合理性和可解释性的争论做出了贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To be presented at NeurIPS 2025 Workshops
Summary:大型语言模型的隐藏状态与语言任务中的fMRI脑反应之间存在关联,被视为这些模型与脑状态的表征相似性的证据。本研究测试了这些先前结果是否稳健可靠。具体而言,本研究发现:i)降维后仍然出现之前的结果,因此不是由于维数诅咒所致;ii)使用新的相似性度量标准后确认了之前的结果;iii)脑表征与模型之间的关联特定于经过人类语言训练的模型;iv)结果依赖于模型中是否存在位置编码。这些结果证实了先前研究的结果,为关于最新大型语言模型的生物合理性和可解释性的争论做出了贡献。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型语言模型的隐藏状态与fMRI脑反应之间的关联被视为模型与脑状态表征相似性的证据。
- 研究结果稳健,不因降维而消失,排除维数诅咒的影响。
- 新的相似性度量标准验证了先前的研究结果。
- 脑与模型之间的关联特定于经过人类语言训练的模型。
- 结果依赖于模型中是否存在位置编码。
- 研究结果证实了先前的研究,为大型语言模型的生物合理性提供了支持。
点此查看论文截图
EditLens: Quantifying the Extent of AI Editing in Text
Authors:Katherine Thai, Bradley Emi, Elyas Masrour, Mohit Iyyer
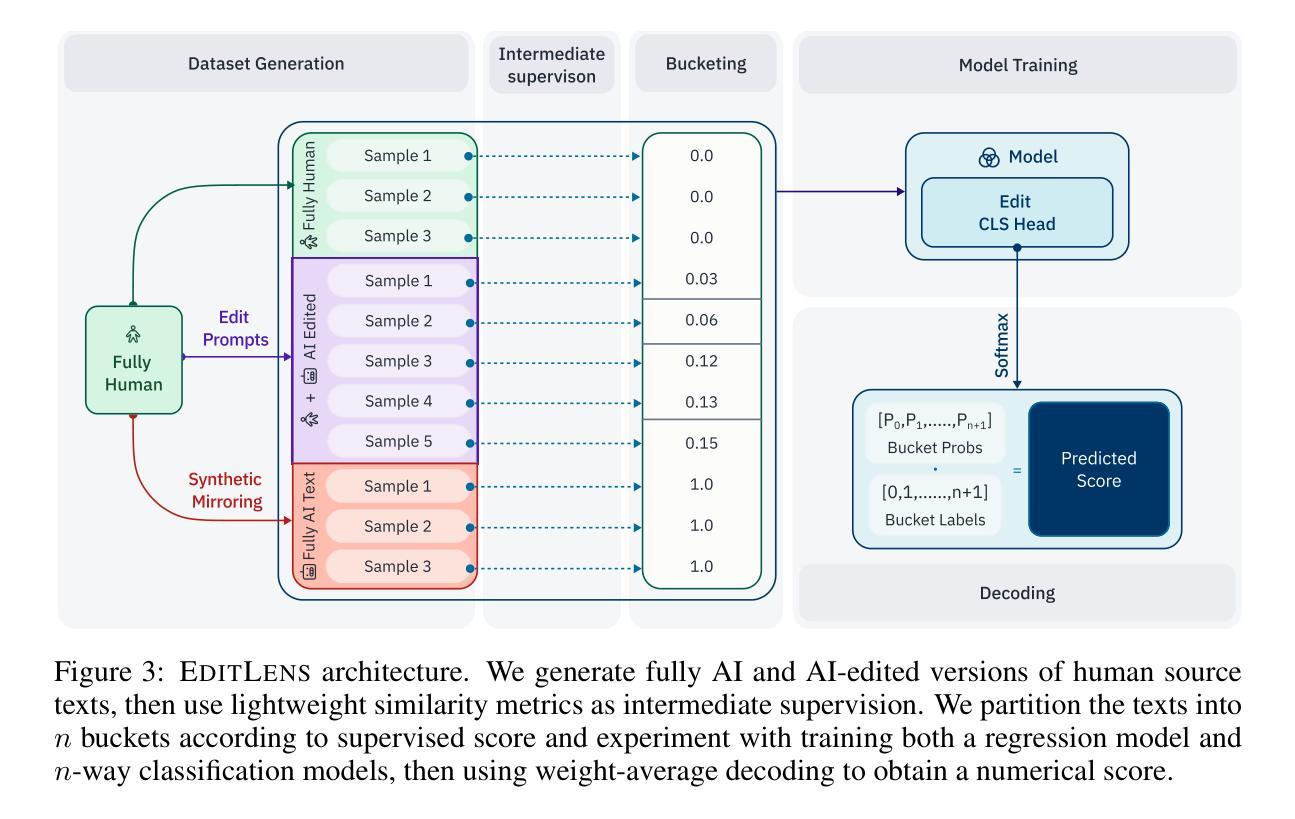
A significant proportion of queries to large language models ask them to edit user-provided text, rather than generate new text from scratch. While previous work focuses on detecting fully AI-generated text, we demonstrate that AI-edited text is distinguishable from human-written and AI-generated text. First, we propose using lightweight similarity metrics to quantify the magnitude of AI editing present in a text given the original human-written text and validate these metrics with human annotators. Using these similarity metrics as intermediate supervision, we then train EditLens, a regression model that predicts the amount of AI editing present within a text. Our model achieves state-of-the-art performance on both binary (F1=94.7%) and ternary (F1=90.4%) classification tasks in distinguishing human, AI, and mixed writing. Not only do we show that AI-edited text can be detected, but also that the degree of change made by AI to human writing can be detected, which has implications for authorship attribution, education, and policy. Finally, as a case study, we use our model to analyze the effects of AI-edits applied by Grammarly, a popular writing assistance tool. To encourage further research, we commit to publicly releasing our models and dataset.
很大一部分对大型语言模型的查询要求它们编辑用户提供的文本,而不是从头开始生成新文本。虽然之前的工作主要集中在检测完全由人工智能生成的文本,但我们证明人工智能编辑的文本与人类书写和人工智能生成的文本是可以区分的。首先,我们提出使用轻量级相似度度量标准来衡量给定原始人类书写文本中AI编辑的程度,并使用人类注释者对这些度量标准进行验证。使用这些相似度度量作为中间监督,我们然后训练了EditLens,一个回归模型,可以预测文本中AI编辑的程度。我们的模型在二元(F1=94.7%)和三元(F1=90.4%)分类任务中实现了区分人类、人工智能和混合写作方面的最新技术性能。我们不仅证明了可以检测到AI编辑的文本,而且证明了可以检测到AI对人类写作所做的改变程度,这对作者归属、教育和政策都有影响。最后,作为一个案例研究,我们使用我们的模型分析了流行写作助手Grammarly应用的AI编辑的影响。为了鼓励进一步研究,我们承诺公开发布我们的模型和数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型处理用户查询时,有很大一部分是编辑用户提供的文本,而非从头生成新文本。我们展示了AI编辑的文本与人工撰写和AI生成的文本之间的区别。我们提出使用轻量级相似度指标来衡量给定原始人类文本中AI编辑的程度,并通过人类注释者进行验证。基于这些相似度指标作为中间监督,我们训练了EditLens模型,该模型能够预测文本中的AI编辑程度。模型在区分人类、AI和混合写作的二元和三元分类任务上均达到最新技术水平。我们不仅证明了可以检测到AI编辑的文本,而且可以检测到AI对人类写作所做的改变程度,这对作者归属、教育和政策都有影响。最后,我们以Grammarly这一流行的写作辅助工具为例,使用我们的模型分析了AI编辑的效果。我们致力于公开我们的模型和数据集,以鼓励进一步研究。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在处理查询时,更多是对用户提供的文本进行编辑,而非生成新文本。
- AI编辑的文本与人工撰写和AI生成的文本之间存在显著区别。
- 提出了使用轻量级相似度指标来衡量原始人类文本中AI编辑的程度。
- EditLens模型可以预测文本中的AI编辑程度,并在分类任务上表现优异。
- AI编辑的文本及其对人类写作的改变程度可以被检测,对多个领域有影响。
- 以Grammarly为例,展示了AI编辑的实际应用及其效果分析。
点此查看论文截图

Improving Cooperation in Collaborative Embodied AI
Authors:Hima Jacob Leven Suprabha, Laxmi Nag Laxminarayan Nagesh, Ajith Nair, Alvin Reuben Amal Selvaster, Ayan Khan, Raghuram Damarla, Sanju Hannah Samuel, Sreenithi Saravana Perumal, Titouan Puech, Venkataramireddy Marella, Vishal Sonar, Alessandro Suglia, Oliver Lemon
The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into multiagent systems has opened new possibilities for collaborative reasoning and cooperation with AI agents. This paper explores different prompting methods and evaluates their effectiveness in enhancing agent collaborative behaviour and decision-making. We enhance CoELA, a framework designed for building Collaborative Embodied Agents that leverage LLMs for multi-agent communication, reasoning, and task coordination in shared virtual spaces. Through systematic experimentation, we examine different LLMs and prompt engineering strategies to identify optimised combinations that maximise collaboration performance. Furthermore, we extend our research by integrating speech capabilities, enabling seamless collaborative voice-based interactions. Our findings highlight the effectiveness of prompt optimisation in enhancing collaborative agent performance; for example, our best combination improved the efficiency of the system running with Gemma3 by 22% compared to the original CoELA system. In addition, the speech integration provides a more engaging user interface for iterative system development and demonstrations.
将大型语言模型(LLM)集成到多智能体系统中为协作推理和与人工智能代理人的合作开启了新的可能性。本文探讨了不同的提示方法,并评估了它们在提高智能体协作行为和决策制定方面的有效性。我们增强了CoELA(一个为利用LLM进行多智能体通信、推理和任务协调而设计的协作实体代理框架),该框架适用于共享虚拟空间。通过系统实验,我们研究了不同的LLM和提示工程策略,以找出能最大化协作性能的优化组合。此外,我们通过集成语音功能,实现了无缝的基于语音的协作交互。我们的研究结果突出了提示优化在提高协作智能体性能方面的有效性;例如,我们最好的组合与Gemma3相比,将系统运行效率提高了22%。此外,语音集成还为迭代系统开发和演示提供了更具吸引力的用户界面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF In proceedings of UKCI 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)多智能体系统的集成开启了协作推理和智能体协作的新可能性。本文探讨了不同的提示方法,并评估了它们在提高智能体协作行为和决策制定方面的有效性。我们增强了CoELA框架,该框架旨在利用LLM构建协作实体智能体,用于共享虚拟空间中的多智能体通信、推理和任务协调。通过系统实验,我们研究了不同的LLM和提示工程策略,以找出优化组合,最大化协作性能。此外,我们通过集成语音功能,实现无缝的基于语音的协作交互。研究结果表明提示优化在提高协作智能体性能方面的有效性;例如,我们的最佳组合将使用Gemma3的系统运行效率提高了22%,与原始CoELA系统相比。此外,语音集成为用户提供了一个更具吸引力的界面,用于迭代系统开发和演示。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs和多智能体系统的集成提高了协作推理和AI智能体协作的可能性。
- 研究探讨了不同提示方法在提高智能体协作行为和决策制定中的有效性。
- CoELA框架被增强,利用LLM进行多智能体通信、推理和任务协调。
- 系统实验研究了不同的LLM和提示工程策略,找到了优化组合以最大化协作性能。
- 语音功能的集成实现了无缝的基于语音的协作交互,增强了用户体验。
- 提示优化在提高协作智能体性能方面效果显著。
点此查看论文截图
MM-Nav: Multi-View VLA Model for Robust Visual Navigation via Multi-Expert Learning
Authors:Tianyu Xu, Jiawei Chen, Jiazhao Zhang, Wenyao Zhang, Zekun Qi, Minghan Li, Zhizheng Zhang, He Wang
Visual navigation policy is widely regarded as a promising direction, as it mimics humans by using egocentric visual observations for navigation. However, optical information of visual observations is difficult to be explicitly modeled like LiDAR point clouds or depth maps, which subsequently requires intelligent models and large-scale data. To this end, we propose to leverage the intelligence of the Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model to learn diverse navigation capabilities from synthetic expert data in a teacher-student manner. Specifically, we implement the VLA model, MM-Nav, as a multi-view VLA (with 360 observations) based on pretrained large language models and visual foundation models. For large-scale navigation data, we collect expert data from three reinforcement learning (RL) experts trained with privileged depth information in three challenging tailor-made environments for different navigation capabilities: reaching, squeezing, and avoiding. We iteratively train our VLA model using data collected online from RL experts, where the training ratio is dynamically balanced based on performance on individual capabilities. Through extensive experiments in synthetic environments, we demonstrate that our model achieves strong generalization capability. Moreover, we find that our student VLA model outperforms the RL teachers, demonstrating the synergistic effect of integrating multiple capabilities. Extensive real-world experiments further confirm the effectiveness of our method.
视觉导航策略被广泛认为是一个具有前景的方向,因为它通过使用以自我为中心的视觉观察来模仿人类的导航方式。然而,视觉观察的光学信息难以像激光雷达点云或深度地图那样进行显式建模,这需要智能模型和大规模数据。为此,我们提出利用视觉-语言-动作(VLA)模型的智能,以师徒方式从合成专家数据中学习各种导航能力。具体来说,我们实现了VLA模型MM-Nav,它是一种基于预训练的大型语言模型和视觉基础模型的多视角VLA(具有360度观察)。对于大规模导航数据,我们从三位强化学习(RL)专家收集专家数据,这些专家使用特权深度信息在三个针对不同导航能力量身定制的挑战环境中接受训练:到达、挤压和避免。我们迭代地使用来自RL专家的在线收集数据来训练我们的VLA模型,其中训练比例是根据个人能力的表现进行动态平衡的。通过合成环境的广泛实验,我们证明我们的模型具有很强的泛化能力。此外,我们发现我们的学生VLA模型的表现优于RL老师,这证明了整合多种能力的协同作用。大量现实世界实验进一步证实了我们的方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://pku-epic.github.io/MM-Nav-Web/
Summary
视觉导航策略被广泛认为是一个有前途的方向,因为它通过使用以自我为中心的观察来进行导航,从而模仿人类。然而,视觉观察的光学信息难以像激光雷达点云或深度图那样进行显式建模,这需要智能模型和大规模数据。为此,我们提出利用视觉语言行动(VLA)模型的智能,以师徒方式从合成专家数据中学习各种导航能力。我们实现了基于预训练的大型语言模型和视觉基础模型的MM-Nav多视图VLA模型(具有360度观察)。为了获取大规模导航数据,我们从三个强化学习专家收集的专家数据中收集数据,这些专家使用特权深度信息在三个针对不同导航能力的量身定制的环境中接受训练:到达、挤压和避免。我们迭代地训练我们的VLA模型,使用从强化学习专家在线收集的数据,其中训练比率是根据对个别能力的表现进行动态平衡的。在合成环境中的大量实验表明,我们的模型具有很强的泛化能力。此外,我们发现我们的学生VLA模型的表现优于强化学习老师,证明了整合多种能力的协同效应。在现实世界中的大量实验进一步证实了我们的方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉导航策略模仿人类使用视觉观察进行导航,被认为是前景广阔的方向。
- 光学信息的建模是视觉导航中的一大挑战,需要智能模型和大规模数据。
- 提出利用VLA模型的智能,从合成专家数据中学习多种导航能力。
- 实现名为MM-Nav的多视图VLA模型,具备360度观察能力。
- 通过收集来自强化学习专家的数据来训练模型,这些专家在具有挑战性的环境中接受训练,针对不同导航能力如到达、挤压和避免。
- 模型展现出强大的泛化能力,并且学生VLA模型表现优于强化学习老师,证明了整合多种能力的协同效应。
点此查看论文截图

Semantic Similarity in Radiology Reports via LLMs and NER
Authors:Beth Pearson, Ahmed Adnan, Zahraa Abdallah
Radiology report evaluation is a crucial part of radiologists’ training and plays a key role in ensuring diagnostic accuracy. As part of the standard reporting workflow, a junior radiologist typically prepares a preliminary report, which is then reviewed and edited by a senior radiologist to produce the final report. Identifying semantic differences between preliminary and final reports is essential for junior doctors, both as a training tool and to help uncover gaps in clinical knowledge. While AI in radiology is a rapidly growing field, the application of large language models (LLMs) remains challenging due to the need for specialised domain knowledge. In this paper, we explore the ability of LLMs to provide explainable and accurate comparisons of reports in the radiology domain. We begin by comparing the performance of several LLMs in comparing radiology reports. We then assess a more traditional approach based on Named-Entity-Recognition (NER). However, both approaches exhibit limitations in delivering accurate feedback on semantic similarity. To address this, we propose Llama-EntScore, a semantic similarity scoring method using a combination of Llama 3.1 and NER with tunable weights to emphasise or de-emphasise specific types of differences. Our approach generates a quantitative similarity score for tracking progress and also gives an interpretation of the score that aims to offer valuable guidance in reviewing and refining their reporting. We find our method achieves 67% exact-match accuracy and 93% accuracy within +/- 1 when compared to radiologist-provided ground truth scores - outperforming both LLMs and NER used independently. Code is available at: \href{https://github.com/otmive/llama_reports}{github.com/otmive/llama\_reports}
放射学报告评估是放射科医生培训的重要组成部分,对于确保诊断的准确性起着关键作用。作为标准报告工作流程的一部分,初级放射科医生通常会编写初步报告,然后由高级放射科医生进行审查和编辑以产生最终报告。识别初步报告和最终报告之间的语义差异对初级医生至关重要,既作为培训工具,也有助于发现临床知识方面的不足。尽管人工智能在放射学领域是一个快速发展的领域,但由于需要专业领域的知识,大型语言模型(LLM)的应用仍然具有挑战性。在本文中,我们探讨了LLM在放射学报告中提供可解释和准确比较的能力。我们首先比较了多个LLM在比较放射学报告方面的性能。然后我们评估了一种基于命名实体识别(NER)的更传统的方法。然而,这两种方法在提供语义相似性方面的准确反馈方面都表现出局限性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了Llama-EntScore,一种使用Llama 3.1和NER组合的语义相似性评分方法,具有可调权重,可以强调或淡化特定类型的差异。我们的方法生成定量相似性分数以跟踪进度,并对分数进行解释,旨在为审查和改进报告提供有价值的指导。我们发现,与放射科医生提供的真实分数相比,我们的方法达到了67%的精确匹配准确率和93%的准确率(在+/- 1范围内)——超越了独立使用的LLM和NER。代码可在github.com/otmive/llama_reports获得。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文探讨了大型语言模型(LLMs)在放射学报告比较中的应用。研究通过结合Llama 3.1模型和命名实体识别(NER)技术,提出了一种新的语义相似性评分方法Llama-EntScore。该方法用于评估初步报告和最终报告之间的语义差异,旨在帮助放射科医生培训和知识提升。实验表明,该方法相较于单一的LLMs和NER模型表现出更高的准确性。
Key Takeaways:
- 放射学报告评估是放射科医生培训的重要组成部分,对于确保诊断准确性至关重要。
- 初步报告通常由初级放射科医生编制,然后由高级放射科医生审查并编辑成最终报告。
- 语义差异识别对于初级医生既是训练工具,也有助于发现临床知识的差距。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在放射学领域的应用具有挑战性,需要专业的领域知识。
- 本文探讨了LLMs在放射学报告比较中的应用,并提出了Llama-EntScore方法。
- Llama-EntScore方法结合了Llama 3.1模型和NER技术,旨在评估初步报告和最终报告之间的语义相似性。
点此查看论文截图
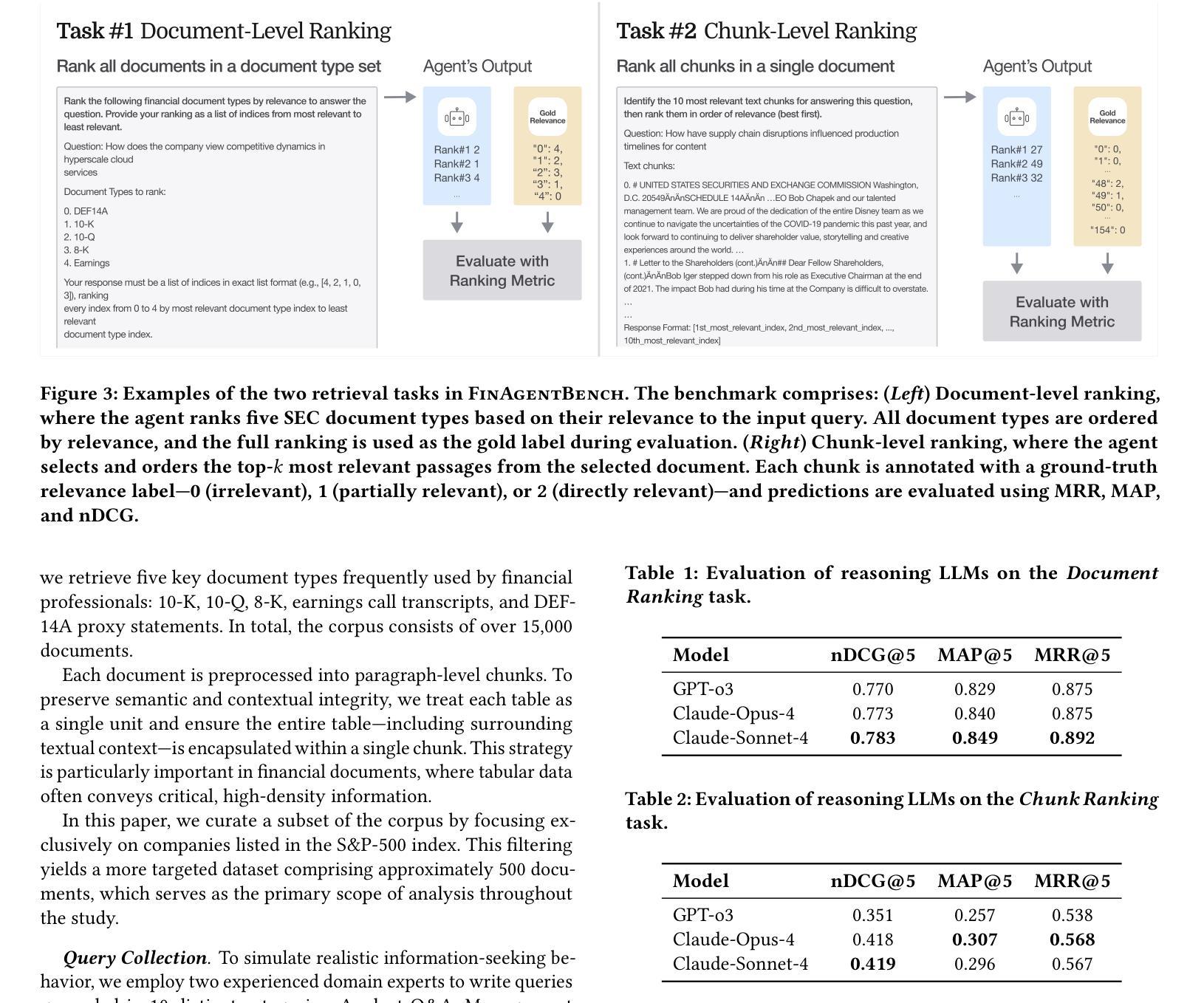
FinAgentBench: A Benchmark Dataset for Agentic Retrieval in Financial Question Answering
Authors:Chanyeol Choi, Jihoon Kwon, Alejandro Lopez-Lira, Chaewoon Kim, Minjae Kim, Juneha Hwang, Jaeseon Ha, Hojun Choi, Suyeol Yun, Yongjin Kim, Yongjae Lee
Accurate information retrieval (IR) is critical in the financial domain, where investors must identify relevant information from large collections of documents. Traditional IR methods – whether sparse or dense – often fall short in retrieval accuracy, as it requires not only capturing semantic similarity but also performing fine-grained reasoning over document structure and domain-specific knowledge. Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have opened up new opportunities for retrieval with multi-step reasoning, where the model ranks passages through iterative reasoning about which information is most relevant to a given query. However, there exists no benchmark to evaluate such capabilities in the financial domain. To address this gap, we introduce FinAgentBench, the first large-scale benchmark for evaluating retrieval with multi-step reasoning in finance – a setting we term agentic retrieval. The benchmark consists of 26K expert-annotated examples on S&P-500 listed firms and assesses whether LLM agents can (1) identify the most relevant document type among candidates, and (2) pinpoint the key passage within the selected document. Our evaluation framework explicitly separates these two reasoning steps to address context limitations. This design enables to provide a quantitative basis for understanding retrieval-centric LLM behavior in finance. We evaluate a suite of state-of-the-art models and further demonstrated how targeted fine-tuning can significantly improve agentic retrieval performance. Our benchmark provides a foundation for studying retrieval-centric LLM behavior in complex, domain-specific tasks for finance.
准确的情报检索(IR)在金融领域至关重要,投资者需要从大量文档中找出相关信息。传统的IR方法,无论是稀疏的还是密集的,往往在检索准确性方面存在不足,因为它不仅需要捕捉语义相似性,还需要对文档结构和特定领域的知识进行精细的推理。大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展为具有多步骤推理的检索提供了新的机会,该模型通过迭代推理来排列段落,确定哪些信息对给定查询最为相关。然而,金融领域缺乏评估这种能力的基准测试。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了FinAgentBench,这是第一个用于评估金融领域多步骤推理检索的大型基准测试——我们称之为代理检索。该基准测试包含关于标准普尔500上市公司的2.6万个专家注释示例,并评估LLM代理是否能(1)在候选者中识别出最相关的文档类型,以及(2)在选定文档中指出关键段落。我们的评估框架明确地将这两个推理步骤分开,以解决上下文局限性。这种设计能够提供定量依据,以了解金融领域中以检索为中心的LLM行为。我们评估了一系列最先进的模型,并进一步展示了有针对性的微调如何显着提高代理检索性能。我们的基准测试为研究金融领域的复杂特定任务中以检索为中心的LLM行为提供了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages
Summary
在金融领域中,准确的信息检索(IR)至关重要。传统IR方法往往无法准确检索信息,因为除了捕捉语义相似性外,还需要对文档结构和特定领域的知识进行精细推理。最近的大型语言模型(LLM)的进步为具有多步骤推理的检索提供了新的机会。然而,金融领域缺乏评估这种能力的基准测试。为解决此空白,我们引入了FinAgentBench,这是第一个用于评估金融领域中具有多步骤推理的检索的大型基准测试。该基准测试包含针对标普500上市公司的2.6万份专家注释样本,并评估LLM代理是否能确定候选文档中最相关的文档类型以及在选定文档中定位关键段落。我们的评估框架明确地将这两个推理步骤分开,以解决上下文局限性问题。这种设计为理解金融领域中以检索为中心的LLM行为提供了定量依据。我们评估了一系列最新模型,并展示了有针对性的微调如何显着提高代理检索性能。我们的基准测试为研究金融领域的复杂特定任务中针对检索为中心的LLM行为奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 金融领域的信息检索至关重要,传统方法存在局限性。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的进步为金融信息检索中的多步骤推理提供了新机会。
- 缺乏评估金融领域中多步骤推理检索能力的基准测试。
- 引入FinAgentBench作为首个针对金融领域的多步骤推理检索的基准测试。
- 该基准测试包含针对标普500上市公司的专家注释样本,评估LLM代理识别最相关文档类型和定位关键段落的能力。
- 评估框架明确区分识别文档类型与定位关键段落两个步骤。
点此查看论文截图
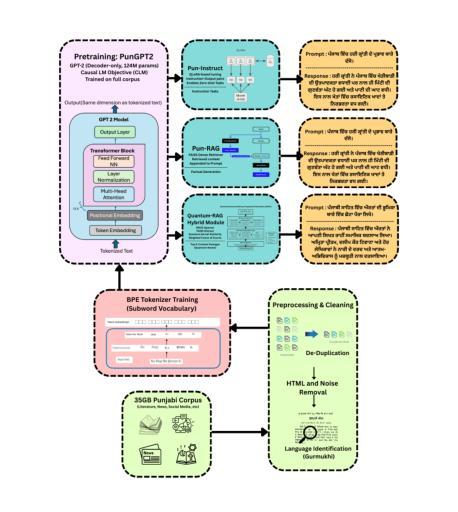
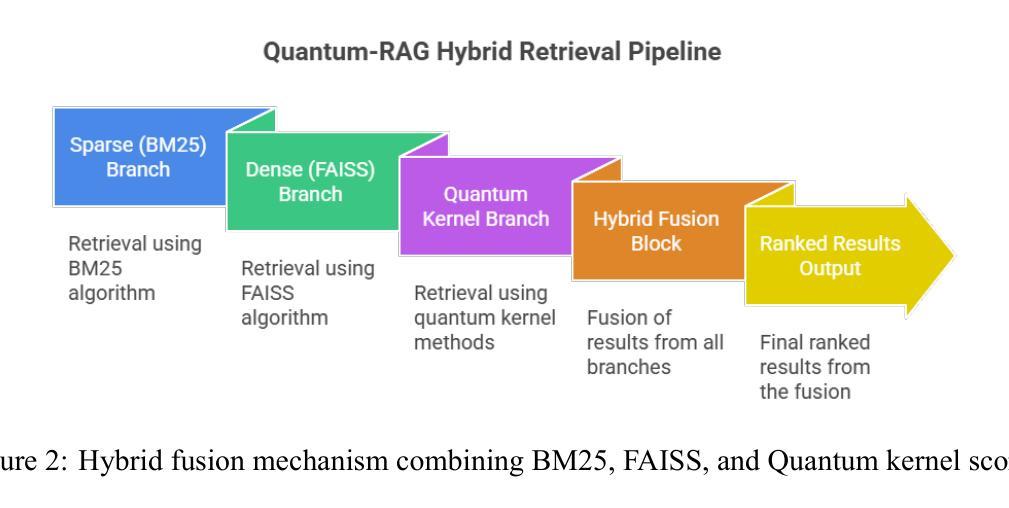
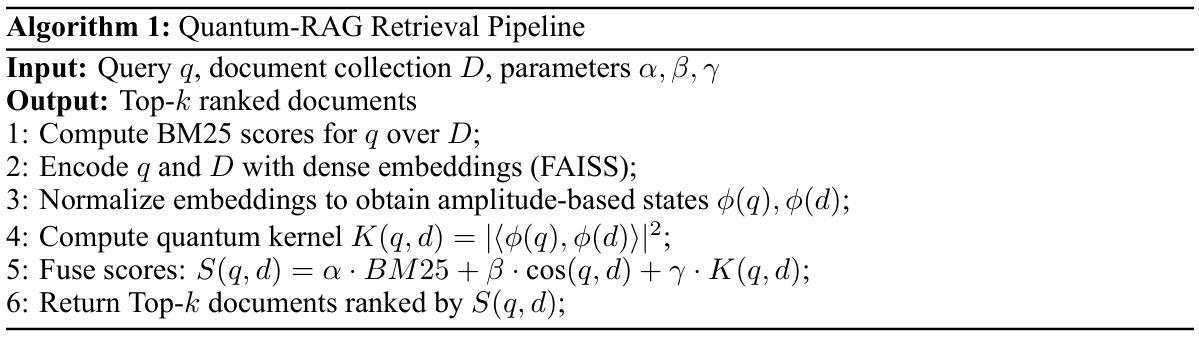
Quantum-RAG and PunGPT2: Advancing Low-Resource Language Generation and Retrieval for the Punjabi Language
Authors:Jaskaranjeet Singh, Rakesh Thakur
Despite rapid advances in large language models (LLMs), low-resource languages remain excluded from NLP, limiting digital access for millions. We present PunGPT2, the first fully open-source Punjabi generative model suite, trained on a 35GB corpus covering literature, religious texts, news, social discourse, etc. PunGPT2 captures Punjabi’s syntactic and morphological richness through a tokenizer optimized for Gurmukhi and Shahmukhi scripts. We introduce Pun-RAG, a retrieval-augmented framework integrating PunGPT2 with a FAISS retriever over a curated Punjabi knowledge base, and Pun-Instruct, an instruction-tuned variant using QLoRA for robust zero-shot summarization, translation, and question answering. Our key innovation, Quantum-RAG, fuses sparse, dense, and quantum kernel embeddings for efficient, context-aware retrieval with low memory overhead, marking the first practical quantum-inspired retrieval in a low-resource LLM. Our models outperform multilingual baselines (mBERT, mT5, MuRIL, BLOOM) on FLORES-200, IndicGenBench, and a new PunjabiEval suite. Quantum-RAG yields +7.4 Recall@10 over FAISS and +3.5 BLEU over mT5 on PunjabiEval. We publicly release all training scripts, hyperparameters, evaluation pipelines, the 35GB Punjabi corpus, the PunjabiEval benchmark, and all model weights, establishing new state-of-the-art results for Punjabi language generation and retrieval.
尽管大型语言模型(LLM)迅速进步,但低资源语言仍然被排除在NLP之外,限制了数百万人的数字访问。我们推出了PunGPT2,这是第一个完全开源的旁遮普语生成模型套件,它基于一个包含文献、宗教文本、新闻、社会话语等内容的35GB语料库进行训练。PunGPT2通过针对古尔姆基和沙姆基脚本优化的分词器捕捉旁遮普语的句法和形态丰富性。我们引入了Pun-RAG,这是一个结合了PunGPT2与针对精选旁遮普知识库的FAISS检索器的检索增强框架,以及Pun-Instruct,这是一个使用QLoRA进行稳健的零射击摘要、翻译和问答的指令调整变体。我们的关键创新是Quantum-RAG,它融合了稀疏、密集和量子核嵌入,用于实现具有低内存开销的高效、上下文感知检索,这是低资源LLM中首个实用的量子启发式检索。我们的模型在FLORES-200、IndicGenBench和新的PunjabiEval套件上的表现超过了多语言基线(mBERT、mT5、MuRIL、BLOOM)。Quantum-RAG在PunjabiEval上的Recall@10比FAISS高出7.4,BLEU比mT5高出3.5。我们公开发布所有的训练脚本、超参数、评估管道、35GB的旁遮普语料库、PunjabiEval基准测试以及所有的模型权重,为旁遮普语的语言生成和检索树立了新的最新成果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
虽然大型语言模型(LLM)发展迅速,但低资源语言在NLP中仍被边缘化,限制了数百万人的数字访问。为此,我们推出了PunGPT2,这是第一个完全开源的旁遮普语生成模型套件,经过35GB语料库的训练,涵盖了文献、宗教文本、新闻、社会话语等。我们还介绍了Pun-RAG和Quantum-RAG,前者是一个与PunGPT2集成的检索增强框架,后者融合了稀疏、密集和量子核嵌入,实现了高效、语境感知的检索和内存低消耗。我们的模型在FLORES-200、IndicGenBench和新的PunjabiEval套件上的表现超过了多语言基线,建立了旁遮普语语言和检索的新里程碑。
Key Takeaways:
- 低资源语言在NLP中仍然面临挑战,限制了数字访问。
- PunGPT2是首个完全开源的旁遮普语生成模型套件,经过35GB语料库训练。
- Pun-RAG是一个与PunGPT2集成的检索增强框架,提供了语境感知的检索功能。
- Quantum-RAG融合了稀疏、密集和量子核嵌入,实现了高效检索和内存低消耗。
- 旁遮普语模型在多个基准测试上的表现超过了多语言基线。
- Quantum-RAG在PunjabiEval上的召回率和BLEU得分均有所提高。
点此查看论文截图
Tuning LLM-based Code Optimization via Meta-Prompting: An Industrial Perspective
Authors:Jingzhi Gong, Rafail Giavrimis, Paul Brookes, Vardan Voskanyan, Fan Wu, Mari Ashiga, Matthew Truscott, Mike Basios, Leslie Kanthan, Jie Xu, Zheng Wang
There is a growing interest in leveraging multiple large language models (LLMs) for automated code optimization. However, industrial platforms deploying multiple LLMs face a critical challenge: prompts optimized for one LLM often fail with others, requiring expensive model-specific prompt engineering. This cross-model prompt engineering bottleneck severely limits the practical deployment of multi-LLM systems in production environments. We introduce Meta-Prompted Code Optimization (MPCO), a framework that automatically generates high-quality, task-specific prompts across diverse LLMs while maintaining industrial efficiency requirements. MPCO leverages metaprompting to dynamically synthesize context-aware optimization prompts by integrating project metadata, task requirements, and LLM-specific contexts. It is an essential part of the ARTEMIS code optimization platform for automated validation and scaling. Our comprehensive evaluation on five real-world codebases with 366 hours of runtime benchmarking demonstrates MPCO’s effectiveness: it achieves overall performance improvements up to 19.06% with the best statistical rank across all systems compared to baseline methods. Analysis shows that 96% of the top-performing optimizations stem from meaningful edits. Through systematic ablation studies and meta-prompter sensitivity analysis, we identify that comprehensive context integration is essential for effective meta-prompting and that major LLMs can serve effectively as meta-prompters, providing actionable insights for industrial practitioners.
对于利用多个大型语言模型(LLM)进行自动化代码优化的兴趣正在增长。然而,部署多个LLM的工业平台面临一个关键问题:针对一个LLM优化的提示往往在其他LLM上失败,这需要进行昂贵的模型特定提示工程。这种跨模型提示工程瓶颈严重限制了多LLM系统在生产环境中的实际部署。我们引入了Meta提示代码优化(MPCO)框架,该框架能够在保持工业效率要求的同时,在多种LLM中自动生成高质量的任务特定提示。MPCO利用元提示技术,通过整合项目元数据、任务要求和LLM特定上下文,动态合成上下文感知优化提示。它是ARTEMIS代码优化平台的自动化验证和扩展的重要组成部分。我们在五个真实世界的代码库上进行了全面的评估,通过366小时的运行时基准测试证明了MPCO的有效性:与基准方法相比,它在总体上实现了高达19.06%的性能提升,在所有系统中表现最佳。分析表明,96%的最佳性能优化源于有意义的编辑。通过系统的剔除研究和元提示敏感性分析,我们发现全面的上下文整合对于有效的元提示至关重要,并且主要的LLM可以有效地作为元提示器,为工业从业者提供可操作的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ASE’25 Industry Showcase
Summary
该文本介绍了如何利用多个大型语言模型(LLM)进行自动化代码优化的问题。针对部署多个LLM的工业平台面临的关键挑战,即针对一个LLM优化的提示在其它LLM上经常失效,需要昂贵的模型特定提示工程。为此,引入了Meta-Prompted代码优化(MPCO)框架,该框架能够自动生成高质量的任务特定提示,适用于不同的LLM,同时满足工业效率要求。MPCO利用元提示技术,通过整合项目元数据、任务要求和LLM特定上下文,动态合成上下文感知的优化提示。它是ARTEMIS代码优化平台的重要组成部分,用于自动化验证和扩展。在五个真实世界代码库上的综合评估显示,MPCO总体上提高了高达19.06%的性能,并且在所有系统中表现最佳。分析表明,96%的最佳优化来自于有意义的编辑。通过系统的剖析研究和元提示敏感性分析,发现全面的上下文整合对于有效的元提示至关重要,主要LLM可以有效地作为元提示器,为工业从业者提供可操作的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 多个大型语言模型(LLM)在自动化代码优化中的应用日益受到关注。
- 部署多个LLM的工业平台面临的一个关键挑战是模型间的提示工程瓶颈。
- Meta-Prompted代码优化(MPCO)框架能够自动生成跨不同LLM的高质量任务特定提示。
- MPCO结合项目元数据、任务要求和LLM特定上下文来动态合成优化提示。
- MPCO是ARTEMIS代码优化平台的重要组成部分,能够提高自动化验证和扩展的效率。
- 在真实世界代码库上的评估显示,MPCO相比基准方法提高了显著的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Highly Efficient and Effective LLMs with Multi-Boolean Architectures
Authors:Ba-Hien Tran, Van Minh Nguyen
Weight binarization has emerged as a promising strategy to reduce the complexity of large language models (LLMs). Existing approaches fall into post-training binarization, which is simple but causes severe performance loss, and training-aware methods, which depend on full-precision latent weights, adding complexity and limiting efficiency. We propose a novel framework that represents LLMs with multi-kernel Boolean parameters and, for the first time, enables direct finetuning LMMs in the Boolean domain, eliminating the need for latent weights. This enhances representational capacity and dramatically reduces complexity during both finetuning and inference. Extensive experiments across diverse LLMs show our method outperforms recent ultra low-bit quantization and binarization techniques.
权重二值化作为一种策略,已在大规模语言模型(LLM)的复杂度降低方面展现出巨大潜力。现有方法分为训练后二值化,这种方法虽然简单但会导致性能严重损失,以及依赖于全精度潜在权重的训练感知方法,这增加了复杂性和限制了效率。我们提出了一种新的框架,该框架使用多核布尔参数表示LLM,并首次实现了布尔域内LLM的直接微调,无需使用潜在权重。这提高了表示能力,并在微调期间和推理期间大大降低了复杂度。在多种LLM上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法优于最新的超低比特量化和二值化技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint. Under Review
Summary
本文提出一种基于多核布尔参数表示的大型语言模型(LLM)新型框架,可直接在布尔域进行LLM微调,无需使用潜在权重,提高了表示能力,并大幅降低了微调与推理时的复杂度。此框架突破现有训练后二元化与训练感知方法的局限,实验证明其性能优于最近的超低精度量化与二元化技术。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的复杂性可通过权重二值化策略降低。
- 现有方法包括训练后的二值化,虽然简单但性能损失严重;以及依赖全精度潜在权重的训练感知方法,增加了复杂性和限制了效率。
- 提出的框架首次实现了在布尔域内直接微调LLM,消除了对潜在权重的需要。
- 该框架提高了表示能力,并大幅降低了微调与推理时的复杂度。
- 提出的框架优于现有的超低精度量化与二元化技术。
- 框架采用多核布尔参数表示,增强了模型的灵活性和效率。
点此查看论文截图
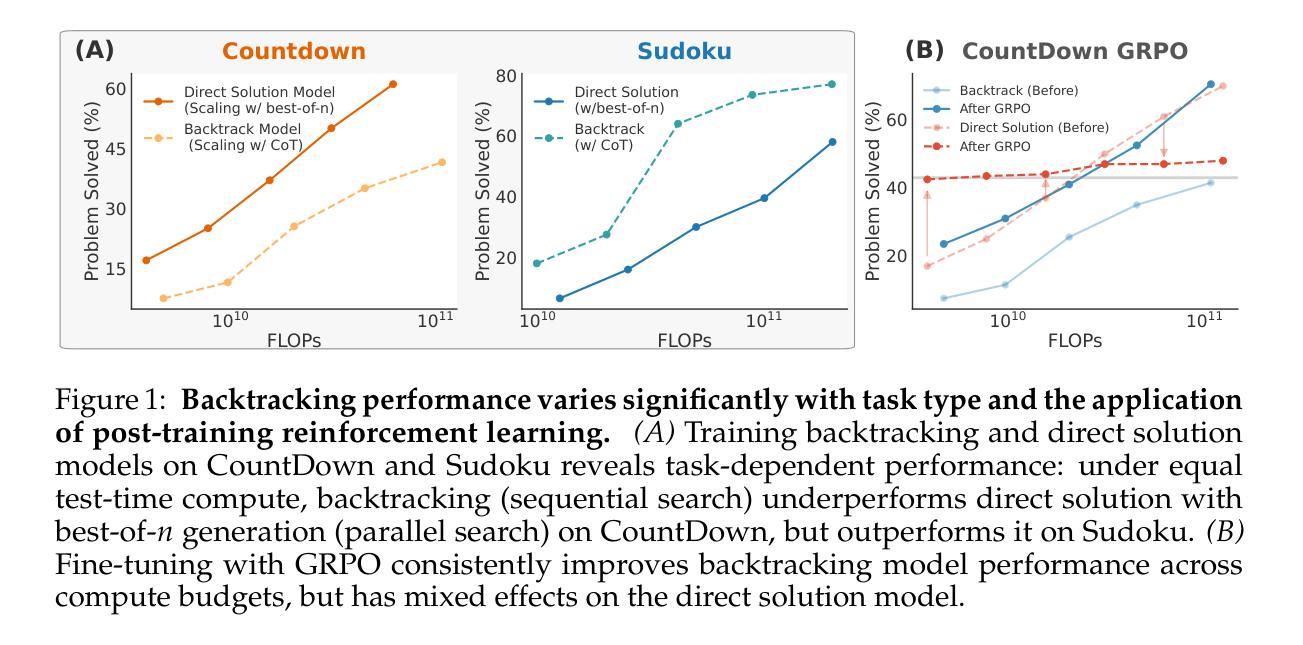
To Backtrack or Not to Backtrack: When Sequential Search Limits Model Reasoning
Authors:Tian Qin, David Alvarez-Melis, Samy Jelassi, Eran Malach
Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have significantly improved their reasoning abilities, particularly through techniques involving search and backtracking. Backtracking naturally scales test-time compute by enabling sequential, linearized exploration via long chain-of-thought (CoT) generation. However, this is not the only strategy for scaling test time-compute: parallel sampling with best-of-N selection provides an alternative that generates diverse solutions simultaneously. Despite the growing adoption of sequential search, its advantages over parallel sampling-especially under a fixed compute budget-remain poorly understood. In this paper, we systematically compare these two approaches on two challenging reasoning tasks: CountDown and Sudoku. Surprisingly, we find that sequential search underperforms parallel sampling on CountDown but outperforms it on Sudoku, suggesting that backtracking is not universally beneficial. We identify two factors that can cause backtracking to degrade performance: (1) training on fixed search traces can lock models intro suboptimal strategies, and (2) explicit CoT supervision can discourage implicit (non verbalized) reasoning. Extending our analysis to reinforcement learning (RL), we show that models with backtracking capabilities benefit significantly from RL fine-tuning, while models without backtracking see limited, mixed gains. Together, these findings challenge the assumption that backtracking universally enhances LLM reasoning, instead revealing a complex interaction between task structure, training data, model scale, and learning paradigm.
近期大型语言模型(LLM)的进步显著提高了其推理能力,特别是通过涉及搜索和回溯的技术。回溯通过启用序列化、线性化的探索(通过长链条思维生成),自然地扩展了测试时间的计算。然而,这并不是扩展测试时间计算的唯一策略:并行采样与最佳N选择相结合,可以同时生成多种解决方案。尽管序贯搜索的采用日益增加,但其相对于并行采样的优势,特别是在固定计算预算下,仍鲜为人知。在本文中,我们在两个具有挑战性的推理任务CountDown和数独上系统地比较了这两种方法。令人惊讶的是,我们发现序贯搜索在CountDown上的表现不如并行采样,但在数独上的表现优于并行采样,这表明回溯并非普遍有益。我们确定了可能导致回溯降低性能的两大因素:(1)在固定搜索轨迹上进行训练会使模型陷入次优策略;(2)明确的思维链监督可能会抑制隐含(未言语化)的推理。我们将分析扩展到强化学习(RL),发现具有回溯能力的模型从RL微调中受益匪浅,而没有回溯能力的模型则收效甚微。总体而言,这些发现挑战了回溯普遍提高LLM推理能力的假设,反而揭示了任务结构、训练数据、模型规模和学习范式之间的复杂交互。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF COLM 2025 Camera Ready
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的近期进展显著提高了其推理能力,主要通过搜索和回溯技术实现。本文通过对比顺序搜索和并行采样两种方法,发现其在不同推理任务上的表现存在差异。顺序搜索在解决数独问题时表现较好,但在倒计时任务上表现不佳。研究发现,训练固定搜索轨迹和显式思维监督可能导致回溯性能下降。强化学习(RL)微调对具有回溯能力的模型有很大益处,而对无回溯模型则效果有限。这些发现挑战了回溯普遍提升LLM推理能力的假设,揭示了任务结构、训练数据、模型规模和学习范式之间的复杂交互。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的推理能力通过搜索和回溯技术得到显著提高。
- 顺序搜索和并行采样在推理任务上的表现存在差异,并无普遍优势。
- 训练固定搜索轨迹和显式思维监督可能导致回溯性能下降。
- 强化学习(RL)微调对具有回溯能力的模型有很大益处。
- 任务结构、训练数据、模型规模和学习范式之间交互影响LLM的推理能力。
- 顺序搜索在解决数独问题时表现较好,但在倒计时任务上表现不佳。
点此查看论文截图
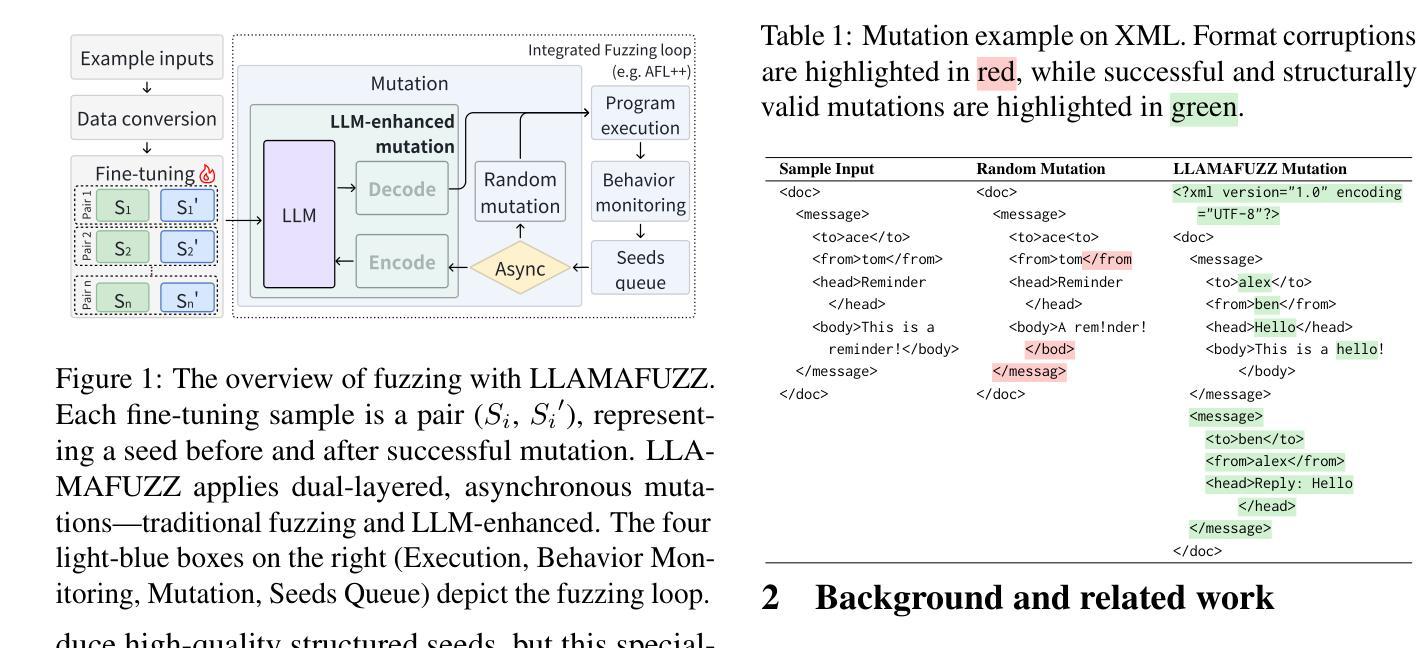
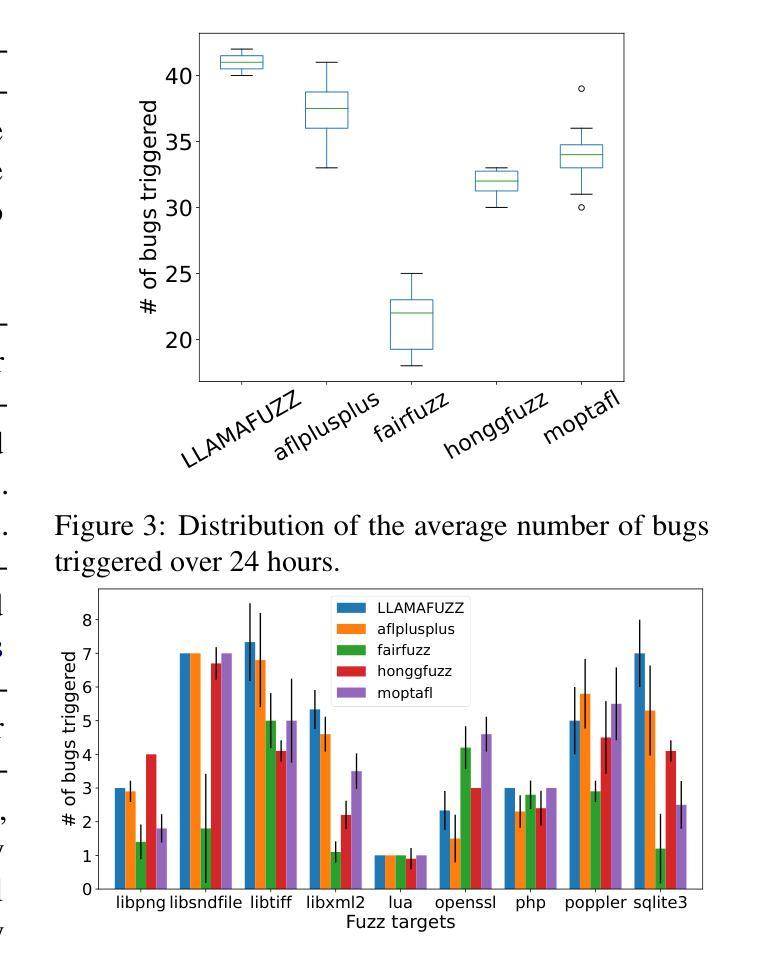
LLAMAFUZZ: Large Language Model Enhanced Greybox Fuzzing
Authors:Hongxiang Zhang, Yuyang Rong, Yifeng He, Hao Chen
Greybox fuzzing has achieved success in revealing bugs and vulnerabilities in programs. However, randomized mutation strategies have limited the fuzzer’s performance on structured data. Specialized fuzzers can handle complex structured data, but require additional efforts in grammar and suffer from low throughput. In this paper, we explore the potential of utilizing the Large Language Model to enhance greybox fuzzing for structured data. We utilize the pre-trained knowledge of LLM about data conversion and format to generate new valid inputs. We further fine-tuned it with paired mutation seeds to learn structured format and mutation strategies effectively. Our LLM-based fuzzer, LLAMAFUZZ, integrates the power of LLM to understand and mutate structured data to fuzzing. We conduct experiments on the standard bug-based benchmark Magma and a wide variety of real-world programs. LLAMAFUZZ outperforms our top competitor by 41 bugs on average. We also identified 47 unique bugs across all trials. Moreover, LLAMAFUZZ demonstrated consistent performance on both bug trigger and bug reached. Compared to AFL++, LLAMAFUZZ achieved 27.19% more branches in real-world program sets on average. We also demonstrate a case study to explain how LLMs enhance the fuzzing process in terms of code coverage.
灰盒模糊测试在揭示程序和漏洞中的错误方面取得了成功。然而,随机突变策略在结构化数据上限制了模糊测试的性能。专业模糊测试器可以处理复杂结构化数据,但需要额外的语法努力,并且吞吐量较低。在本文中,我们探讨了利用大型语言模型提升结构化数据的灰盒模糊测试潜力。我们利用LLM关于数据转换和格式的预训练知识来生成新的有效输入。我们进一步使用配对突变种子对其进行微调,以有效学习结构化格式和突变策略。我们基于LLM的模糊测试器LLAMAFUZZ结合了LLM理解和突变结构化数据的能力来进行模糊测试。我们在基于错误的基准测试Magma和各种实际程序上进行了实验。LLAMAFUZZ平均比我们的顶级竞争对手多发现了41个错误。我们还识别出了所有试验中的47个独特错误。此外,LLAMAFUZZ在触发错误和达到错误方面都表现出了一致的性能。与AFL++相比,LLAMAFUZZ在真实程序集上的平均分支覆盖率提高了27.19%。我们还通过一个案例研究来解释LLM如何提升模糊测试过程中的代码覆盖率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探索了利用大型语言模型(LLM)增强灰盒模糊测试在结构化数据上的潜力。通过利用LLM的预训练知识进行数据转换和格式生成新的有效输入,并通过配对突变种子进行微调,学习结构化格式和突变策略。基于LLM的模糊测试器LLAMAFUZZ结合了LLM理解和突变结构化数据的能力,对标准基准Magma和各种真实程序进行了实验。结果显示,LLAMAFUZZ平均比顶级竞争对手多发现41个bug,在所有试验中发现了47个独特bug。此外,LLAMAFUZZ在bug触发和bug检测方面都表现出了一致的性能。相较于AFL++,LLAMAFUZZ在真实程序集上的平均分支覆盖率提高了27.19%。同时,通过案例研究展示了LLM如何增强模糊测试过程中的代码覆盖率。
Key Takeaways
- LLM被用于增强灰盒模糊测试在结构化数据上的性能。
- LLAMAFUZZ利用LLM的预训练知识生成新的有效输入并学习结构化数据和突变策略。
- 在标准基准Magma和真实程序上的实验显示,LLAMAFUZZ比顶级竞争对手更优秀。
- LLAMAFUZZ发现了更多的独特bug,并且在bug触发和检测方面表现稳定。
- 与AFL++相比,LLAMAFUZZ在真实程序集上的平均分支覆盖率有所提高。
- LLAMAFUZZ通过结合LLM的能力,提高了模糊测试过程中的代码覆盖率。
点此查看论文截图
Understanding How CodeLLMs (Mis)Predict Types with Activation Steering
Authors:Francesca Lucchetti, Arjun Guha
Large Language Models (LLMs) are widely used by software engineers for programming tasks. However, research shows that LLMs often lack a deep understanding of program semantics. Even minor changes to syntax, such as renaming variables, can significantly degrade performance across various tasks. In this work, we examine the task of type prediction: given a partially typed program, can a model predict a missing type annotations such that the resulting program is more typed? We construct a dataset of adversarial examples where models initially predict the correct types, but begin to fail after semantically irrelevant edits. This is problematic, as models should ideally generalize across different syntactic forms of semantically equivalent code. This lack of robustness suggests that models may have a shallow understanding of code semantics. Despite this, we provide evidence that LLMs do, in fact, learn robust mechanisms for type prediction-though these mechanisms often fail to activate in adversarial scenarios. By using activation steering, a method that manipulates a model’s internal activations to guide it toward using latent knowledge, we restore accurate predictions on adversarial inputs. We show that steering successfully activates a type prediction mechanism that is shared by both Python and TypeScript, and is more effective than prompting with in-context examples. Across five different models, our comprehensive evaluation demonstrates that LLMs can learn generalizable representations of code semantics that transfer across programming languages.
大型语言模型(LLM)被软件工程师广泛应用于编程任务。然而,研究表明,LLM通常缺乏对程序语义的深入理解。即使是对语法的微小更改,如变量重命名,也可能在各种任务中显著降低性能。在这项工作中,我们研究了类型预测任务:给定一个部分类型的程序,模型能否预测缺失的类型注释,以使程序更具类型化?我们构建了一个对抗性示例数据集,模型最初预测的类型是正确的,但在语义无关编辑后开始失败。这是一个问题,因为模型理想情况下应该能够概括语义等效代码的不同语法形式。这种稳健性的缺乏表明,模型可能对代码语义的理解很浅薄。尽管如此,我们提供了证据表明LLM实际上学习了用于类型预测的稳定机制——尽管这些机制在对抗场景中往往无法激活。通过使用激活转向(一种通过操纵模型的内部激活来引导其使用潜在知识的方法),我们恢复了对抗性输入上的准确预测。我们证明了转向成功地激活了Python和TypeScript共有的类型预测机制,并且比使用上下文示例进行提示更为有效。我们在五个不同模型上的全面评估表明,LLM可以学习可概括的代码语义表示,这些表示可以跨编程语言进行迁移。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 40 pages, 67 figures. To be published at BlackBoxNLP 2025
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在编程任务中被广泛应用,但对程序语义的理解往往不够深入。研究指出,即使语法上的微小变化,如变量重命名,也可能对模型在各种任务上的性能产生重大影响。本研究旨在解决类型预测问题:给定部分类型的程序,模型能否预测缺失的类型注释以使程序更加完整?研究发现,尽管模型最初能正确预测类型,但在语义无关编辑后容易出错。虽然模型缺乏稳健性表明它们对代码语义的理解可能很浅薄,但证据表明LLM实际上学习了用于类型预测的稳健机制。通过使用激活控制法激活模型内部的潜在知识导向机制,我们能够成功恢复对敌对输入的准确预测。研究表明,控制法激活的类型预测机制在Python和TypeScript中都有共享,且比上下文示例提示更为有效。全面评估显示LLM能够学习跨编程语言的代码语义的一般表示。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs广泛应用于编程任务,但对程序语义的理解有限。
- 微小语法变化可能导致LLMs在类型预测等任务上的性能显著下降。
- 模型在语义无关编辑后容易在类型预测任务上出错,表明其缺乏稳健性。
- LLMs实际上学习了用于类型预测的稳健机制,但这些机制在特定情境下可能无法激活。
- 通过激活控制法,可以成功恢复LLM对敌对输入的准确类型预测。
- 控制法激活的类型预测机制在Python和TypeScript中具有共享性。
点此查看论文截图
