⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-07 更新
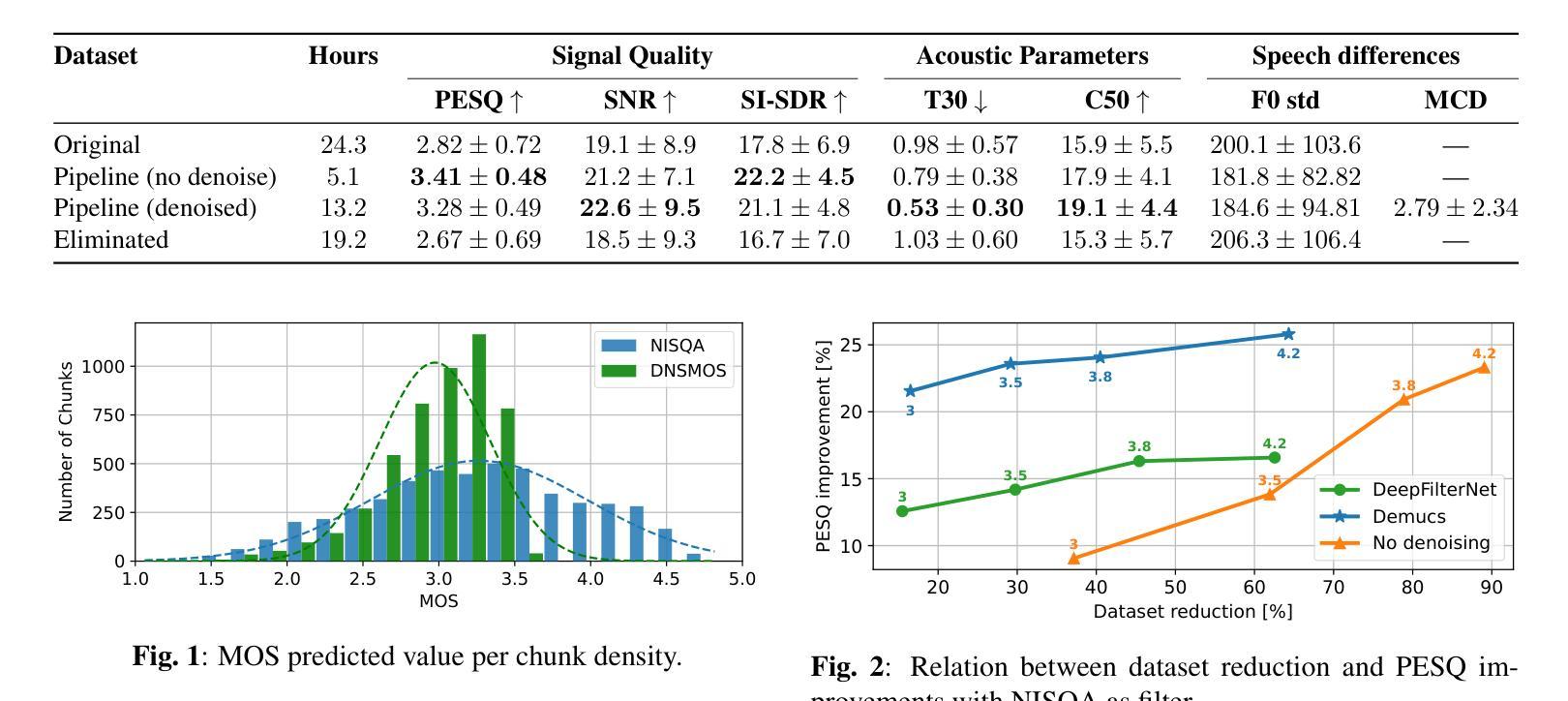
Evaluation of preprocessing pipelines in the creation of in-the-wild TTS datasets
Authors:Matías Di Bernardo, Emmanuel Misley, Ignacio Correa, Mateo García Iacovelli, Simón Mellino, Gala Lucía Gonzalez Barrios
This work introduces a reproducible, metric-driven methodology to evaluate preprocessing pipelines for in-the-wild TTS corpora generation. We apply a custom low-cost pipeline to the first in-the-wild Argentine Spanish collection and compare 24 pipeline configurations combining different denoising and quality filtering variants. Evaluation relies on complementary objective measures (PESQ, SI-SDR, SNR), acoustic descriptors (T30, C50), and speech-preservation metrics (F0-STD, MCD). Results expose trade-offs between dataset size, signal quality, and voice preservation; where denoising variants with permissive filtering provide the best overall compromise for our testbed. The proposed methodology allows selecting pipeline configurations without training TTS models for each subset, accelerating and reducing the cost of preprocessing development for low-resource settings.
本文介绍了一种可复制的、以度量驱动的方法,用于评估用于野外TTS语料库生成的预处理管道。我们将自定义的低成本管道应用于第一个野外阿根廷西班牙收集集,并比较了结合不同降噪和质量过滤方案的24种管道配置。评估依赖于补充的客观度量(PESQ、SI-SDR、SNR)、声学描述符(T30、C50)和语音保存度量(F0-STD、MCD)。结果揭示了数据集大小、信号质量和语音保留之间的权衡;其中允许过滤的降噪变体为测试台提供了最佳的总体平衡。所提出的方法允许在选择管道配置时无需针对每个子集训练TTS模型,从而加快并降低低资源设置下预处理开发的成本。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 4 figures, Submitted to ICASSP 2026
Summary
本文介绍了一种可复现的、以度量标准驱动的方法,用于评估用于野生TTS语料库生成的预处理管道。通过对首个野生阿根廷西班牙语集合应用自定义的低成本管道,并比较了结合不同降噪和质量过滤变体的24种管道配置。评估依赖于多种客观度量标准(如PESQ、SI-SDR和SNR)、声学描述符(如T30和C50)以及语音保留度量(如F0-STD和MCD)。结果揭示了数据集大小、信号质量和语音保留之间的权衡;其中采用宽松过滤的降噪变体为测试平台提供了最佳总体折衷方案。所提出的方法允许在选择管道配置时无需针对每个子集训练TTS模型,从而加快并降低低资源环境下的预处理开发成本。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种评估预处理管道的新方法,该方法针对野生TTS语料库生成。
- 对阿根廷西班牙语集合进行了自定义低成本管道处理。
- 对比了多种管道配置,涉及不同的降噪和质量过滤变体。
- 评估基于客观度量标准、声学描述符和语音保留度量。
- 研究发现数据集大小、信号质量和语音保留之间存在权衡。
- 宽松过滤的降噪变体在测试平台上表现出最佳总体折衷。
点此查看论文截图
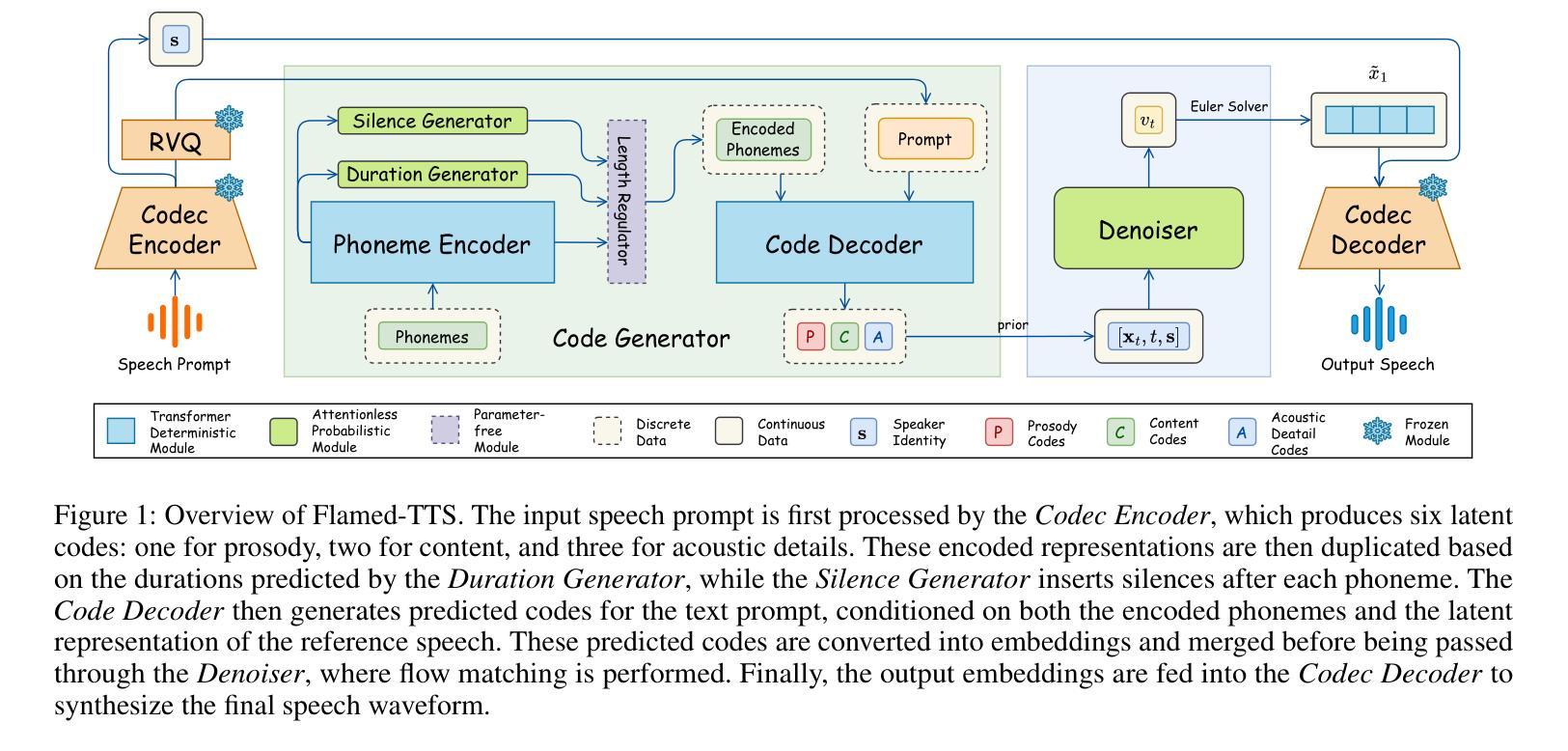
Flamed-TTS: Flow Matching Attention-Free Models for Efficient Generating and Dynamic Pacing Zero-shot Text-to-Speech
Authors:Hieu-Nghia Huynh-Nguyen, Huynh Nguyen Dang, Ngoc-Son Nguyen, Van Nguyen
Zero-shot Text-to-Speech (TTS) has recently advanced significantly, enabling models to synthesize speech from text using short, limited-context prompts. These prompts serve as voice exemplars, allowing the model to mimic speaker identity, prosody, and other traits without extensive speaker-specific data. Although recent approaches incorporating language models, diffusion, and flow matching have proven their effectiveness in zero-shot TTS, they still encounter challenges such as unreliable synthesis caused by token repetition or unexpected content transfer, along with slow inference and substantial computational overhead. Moreover, temporal diversity-crucial for enhancing the naturalness of synthesized speech-remains largely underexplored. To address these challenges, we propose Flamed-TTS, a novel zero-shot TTS framework that emphasizes low computational cost, low latency, and high speech fidelity alongside rich temporal diversity. To achieve this, we reformulate the flow matching training paradigm and incorporate both discrete and continuous representations corresponding to different attributes of speech. Experimental results demonstrate that Flamed-TTS surpasses state-of-the-art models in terms of intelligibility, naturalness, speaker similarity, acoustic characteristics preservation, and dynamic pace. Notably, Flamed-TTS achieves the best WER of 4% compared to the leading zero-shot TTS baselines, while maintaining low latency in inference and high fidelity in generated speech. Code and audio samples are available at our demo page https://flamed-tts.github.io.
零样本文本转语音(TTS)最近取得了显著进展,使得模型能够使用简短、有限上下文提示来从文本合成语音。这些提示充当语音范例,使模型能够在没有大量特定说话人数据的情况下模仿说话人的身份、语调和其他特征。虽然最近采用语言模型、扩散和流程匹配的方法在零样本TTS中证明了其有效性,但它们仍然面临挑战,例如由令牌重复或意外内容传输引起的合成不可靠,以及推理速度慢和计算开销大。此外,对于增强合成语音的自然性至关重要的时间多样性仍很大程度上未被探索。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了Flamed-TTS,这是一种新的零样本TTS框架,侧重于低计算成本、低延迟、高语音保真度和丰富的时间多样性。为了实现这一点,我们重新制定了流程匹配训练范式,并融入了与语音不同属性相对应的离散和连续表示。实验结果表明,Flamed-TTS在可理解性、自然性、说话人相似性、声学特性保持和动态节奏方面超越了最新模型。值得注意的是,Flamed-TTS的词错误率(WER)达到了领先的零样本TTS基准测试的4%,同时在推理过程中保持了低延迟和生成的语音的高保真度。代码和音频样本可在我们的演示页面https://flamed-tts.github.io上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
零短文本到语音(TTS)技术近期取得了显著进展,能够通过简短、有限语境的提示来合成语音。近期采用语言模型、扩散和流程匹配等技术的方法虽然有效,但仍面临合成不可靠、内容转移意外、推理速度慢和计算开销大等挑战。重视计算成本低、延迟低、语音保真度高以及时间多样性丰富的Flamed-TTS框架被提出以解决这些问题。实验结果显示,Flamed-TTS在清晰度、自然度、说话人相似度、声学特性保持力和动态速度等方面超过了现有模型。该框架实现了最低的词错误率(WER)为4%,同时保持了推理阶段的低延迟和生成的语音高保真度。
Key Takeaways
- 零短文本到语音(TTS)技术已显著进步,可通过简短提示合成语音。
- 当前方法虽有效,但仍面临合成不可靠、推理速度慢和计算开销大的挑战。
- Flamed-TTS框架旨在解决这些问题,强调低计算成本、低延迟和高语音保真度。
- Flamed-TTS结合离散和连续表示,对应语音的不同属性。
- 实验结果显示Flamed-TTS在多个方面超越现有模型,包括清晰度、自然度等。
- Flamed-TTS实现了最低的词错误率(WER)为4%。
点此查看论文截图
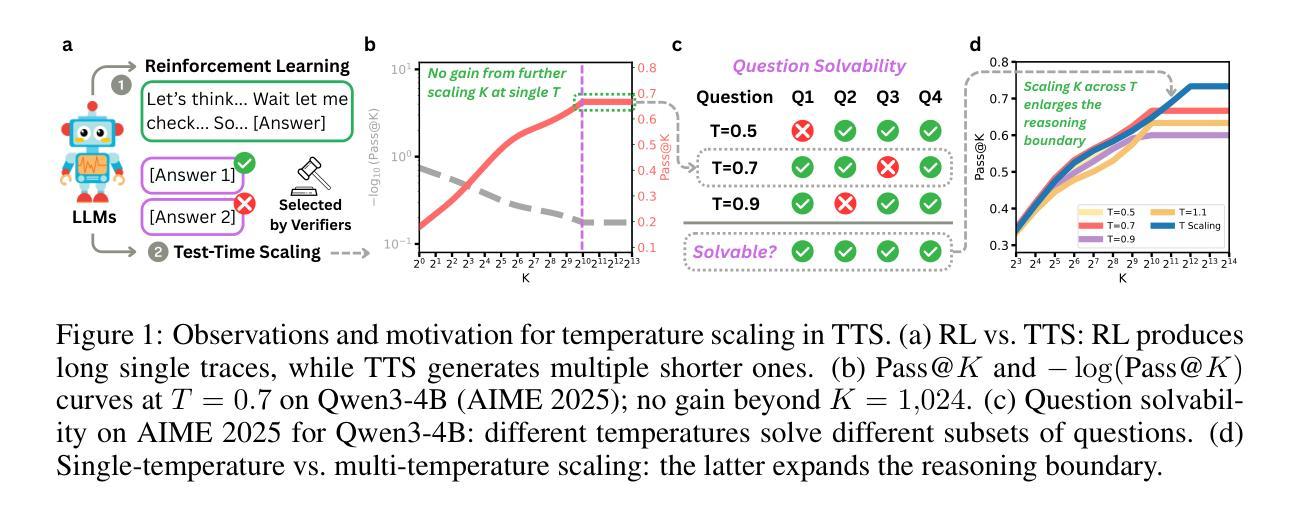
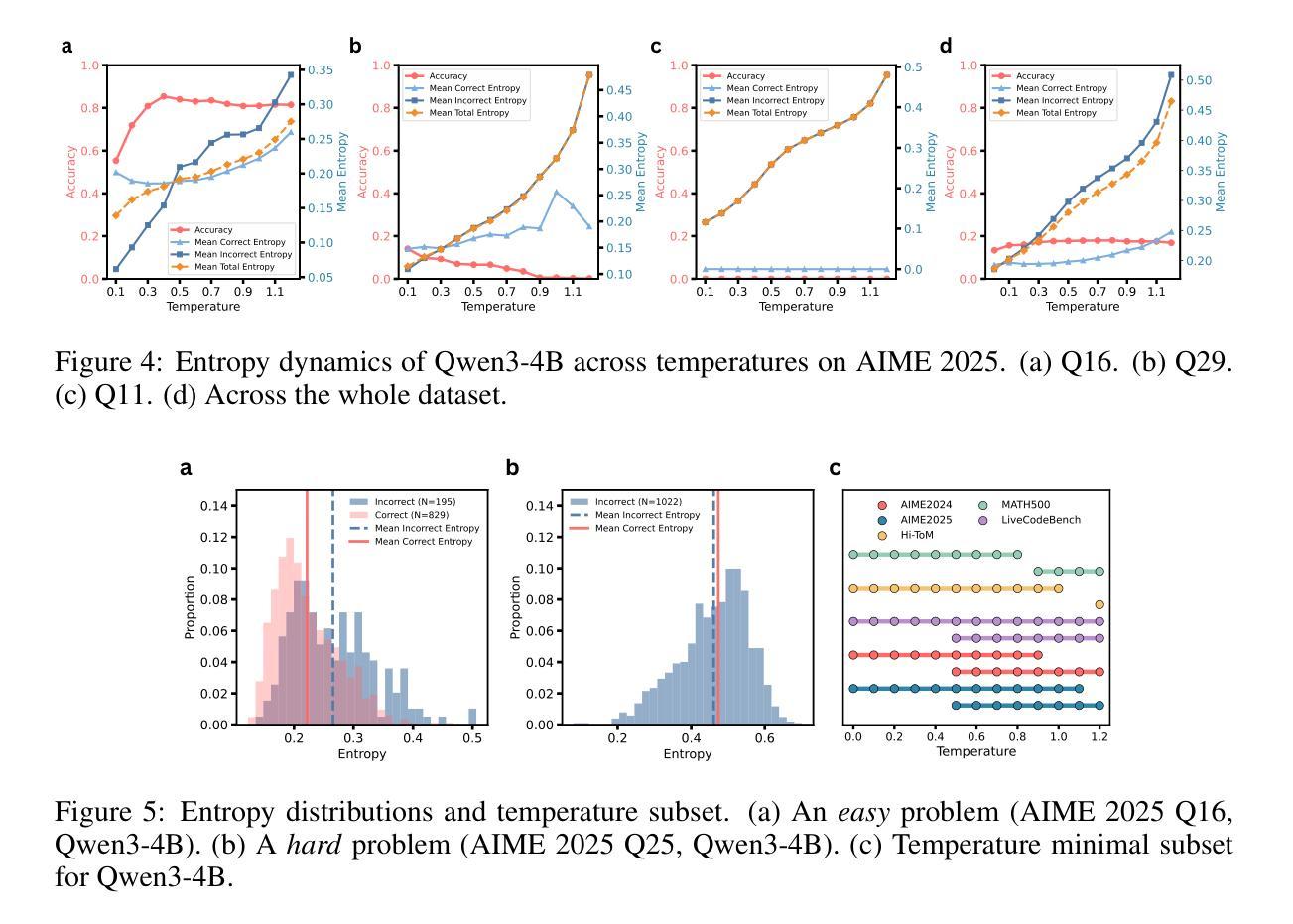
On the Role of Temperature Sampling in Test-Time Scaling
Authors:Yuheng Wu, Azalia Mirhoseini, Thierry Tambe
Large language models (LLMs) can improve reasoning at inference time through test-time scaling (TTS), where multiple reasoning traces are generated and the best one is selected. Prior work shows that increasing the number of samples K steadily improves accuracy. In this paper, we demonstrate that this trend does not hold indefinitely: at large K, further scaling yields no gains, and certain hard questions remain unsolved regardless of the number of traces. Interestingly, we find that different sampling temperatures solve different subsets of problems, implying that single-temperature scaling explores only part of a model’s potential. We therefore propose scaling along the temperature dimension, which enlarges the reasoning boundary of LLMs. Averaged over Qwen3 (0.6B, 1.7B, 4B, 8B) and five representative reasoning benchmarks (AIME 2024/2025, MATH500, LiveCodeBench, Hi-ToM), temperature scaling yields an additional 7.3 points over single-temperature TTS. Temperature scaling also enables base models to reach performance comparable to reinforcement learning (RL)-trained counterparts, without additional post-training. We further provide a comprehensive analysis of this phenomenon and design a multi-temperature voting method that reduces the overhead of temperature scaling. Overall, our findings suggest that TTS is more powerful than previously thought, and that temperature scaling offers a simple and effective way to unlock the latent potential of base models.
大型语言模型(LLM)可以通过测试时间缩放(TTS)在推理时间提高推理能力,其中会生成多个推理轨迹并选择最佳的一个。先前的研究表明,增加样本数量K稳步提高准确性。在本文中,我们证明这一趋势并非无限持续:在较大的K值下,进一步的缩放不会产生任何收益,并且无论轨迹数量如何,某些难题仍然无法解决。有趣的是,我们发现不同的采样温度可以解决不同的问题子集,这意味着单一温度的缩放只能探索模型的一部分潜力。因此,我们提出沿温度维度进行缩放,这扩大了大型语言模型的推理边界。在Qwen3(0.6B、1.7B、4B、8B)和五个代表性推理基准测试(AIME 2024/2025、MATH500、LiveCodeBench、Hi-ToM)上进行平均,温度缩放比单一温度TTS额外提高了7.3点。温度缩放还使基础模型的性能达到与强化学习(RL)训练的对等水平,而无需进行额外的后训练。我们还对此现象进行了综合分析,并设计了一种多温度投票方法,降低了温度缩放的开销。总体而言,我们的研究结果表明,TTS比先前认为的更强大,温度缩放提供了一种简单有效的方法来解锁基础模型的潜在能力。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大规模语言模型(LLM)可以通过测试时缩放(TTS)在推理时间提高推理能力,其中会生成多个推理轨迹并选择最佳的一个。本文发现,随着样本数量K的增加,准确率稳步提高的趋势并非无限持续:在较大的K值下,进一步的缩放不会带来收益,某些难题仍然无法解决,无论生成多少个轨迹。有趣的是,我们发现不同的采样温度可以解决不同的问题子集,意味着单一温度的缩放只能探索模型的一部分潜力。因此,我们提出沿温度维度进行缩放,以扩大LLM的推理边界。在Qwen3和五个代表性推理基准测试上平均,温度缩放较单温度TTS产生了额外的7.3点收益。温度缩放还使基础模型的性能达到与强化学习(RL)训练相当的水平,无需额外的后训练。我们还对此现象进行了综合分析,并设计了一种多温度投票方法,降低了温度缩放的开销。总体而言,我们的研究结果表明TTS比以往认为的更强大,温度缩放是一种简单有效的方法,可以解锁基础模型的潜在能力。
关键见解
- 测试时缩放(TTS)能够提升大规模语言模型(LLM)的推理能力,通过生成多个推理轨迹并选择最佳轨迹来实现。
- 单纯增加样本数量K并不能无限提高准确率,在达到一定点后进一步缩放无收益。
- 不同的采样温度可以解决不同类型的问题,单一温度的缩放只能利用模型的部分潜力。
- 提出沿温度维度进行缩放,以扩大LLM的推理边界。
- 温度缩放在多个基准测试上较单温度TTS有显著性能提升。
- 温度缩放使基础模型的性能与经过强化学习(RL)训练后的模型相当,且无需额外的后训练过程。
点此查看论文截图
KAME: Tandem Architecture for Enhancing Knowledge in Real-Time Speech-to-Speech Conversational AI
Authors:So Kuroki, Yotaro Kubo, Takuya Akiba, Yujin Tang
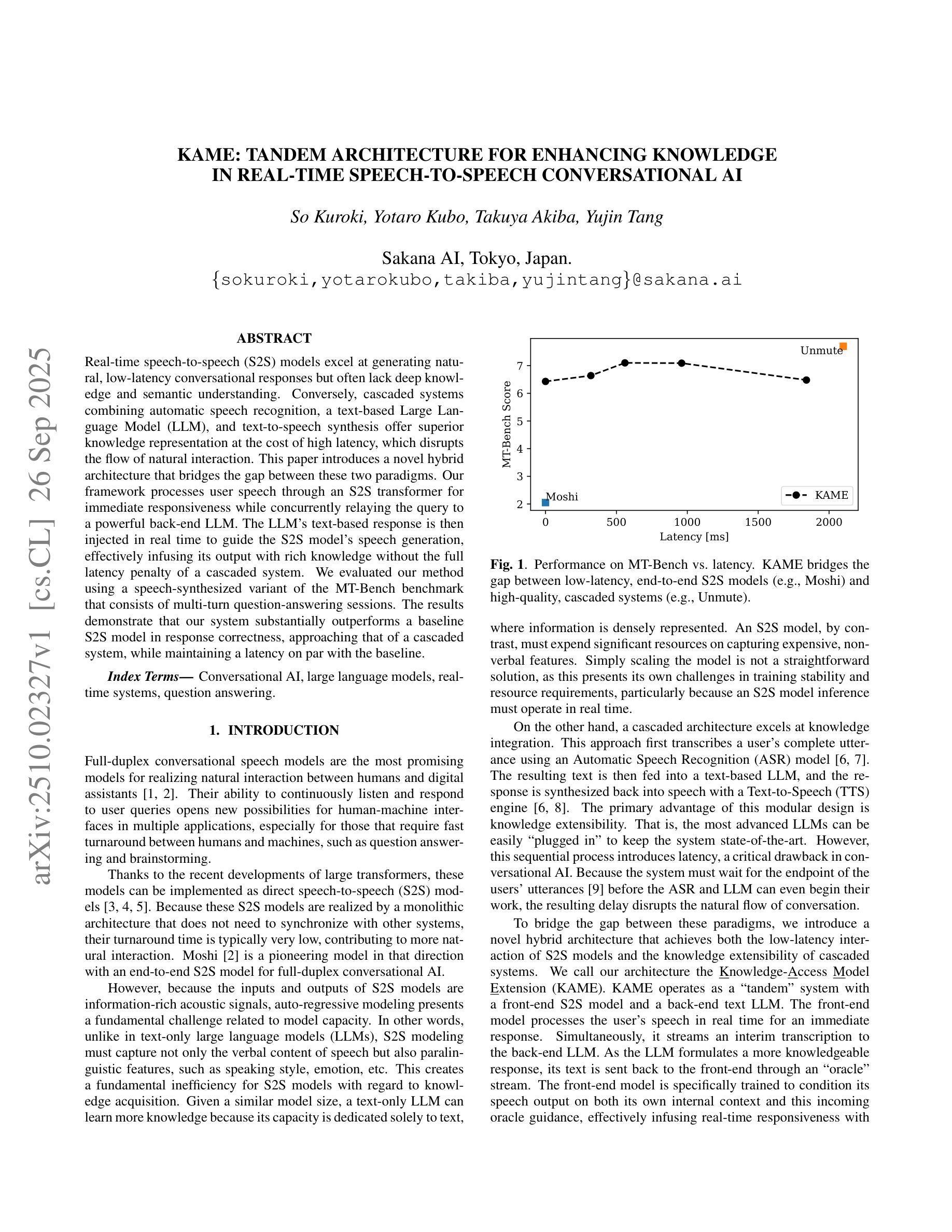
Real-time speech-to-speech (S2S) models excel at generating natural, low-latency conversational responses but often lack deep knowledge and semantic understanding. Conversely, cascaded systems combining automatic speech recognition, a text-based Large Language Model (LLM), and text-to-speech synthesis offer superior knowledge representation at the cost of high latency, which disrupts the flow of natural interaction. This paper introduces a novel hybrid architecture that bridges the gap between these two paradigms. Our framework processes user speech through an S2S transformer for immediate responsiveness while concurrently relaying the query to a powerful back-end LLM. The LLM’s text-based response is then injected in real time to guide the S2S model’s speech generation, effectively infusing its output with rich knowledge without the full latency penalty of a cascaded system. We evaluated our method using a speech-synthesized variant of the MT-Bench benchmark that consists of multi-turn question-answering sessions. The results demonstrate that our system substantially outperforms a baseline S2S model in response correctness, approaching that of a cascaded system, while maintaining a latency on par with the baseline.
实时语音到语音(S2S)模型擅长生成自然、低延迟的对话响应,但往往缺乏深度知识和语义理解。相反,级联系统将自动语音识别、基于文本的大型语言模型(LLM)和文本到语音合成相结合,以较高的延迟为代价提供了卓越的知识表示,从而破坏了自然交互的流程。本文介绍了一种弥这两种范式之间鸿沟的新型混合架构。我们的框架通过S2S变压器处理用户语音,以实现即时响应,同时并行将查询发送到功能强大的后端LLM。LLM的基于文本的响应然后实时注入,以指导S2S模型的语音生成,有效地将丰富的知识融入其输出中,而不会受到级联系统全延迟的惩罚。我们使用由多轮问答会话组成的MT-Bench基准语音合成变种来评估我们的方法。结果表明,我们的系统在响应正确性方面大大优于基线S 2S模型,接近级联系统的性能,同时保持与基线相当的延迟。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
实时语音到语音(S2S)模型擅长生成自然、低延迟的对话响应,但往往缺乏深度知识和语义理解。相反,级联系统结合了自动语音识别、基于文本的大型语言模型(LLM)和文本到语音的合成,提供了卓越的知识表示,但代价是较高的延迟,破坏了自然交互的流畅性。本文介绍了一种新型的混合架构,旨在弥合这两种范式之间的差距。该框架通过S2S变压器处理用户语音,以实现即时响应,同时并行将查询传送到后端强大的LLM。LLM的基于文本的响应被实时注入,以引导S2S模型的语音生成,有效地将其输出与丰富的知识融合在一起,而无需承受级联系统的全延迟惩罚。我们使用由多回合问答会话组成的MT-Bench基准语音合成变种对方法进行评估。结果表明,我们的系统在响应正确性方面大幅优于基线S2S模型,接近级联系统的表现,同时保持与基线相当的延迟。
关键见解
- 实时语音到语音(S2S)模型虽然响应迅速,但缺乏深度知识和语义理解。
- 级联系统结合自动语音识别、大型语言模型和文本到语音的合成,提供卓越的知识表示,但延迟较高。
- 新混合架构结合S2S模型的即时响应和级联系统的知识表示。
- 该混合架构通过后端大型语言模型(LLM)实时指导S2S模型的语音生成。
- 新方法在提高响应正确性的同时,维持低延迟,接近级联系统的性能。
- 评估使用多回合问答会话的基准语音合成变种,证明了方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图
SpeechCT-CLIP: Distilling Text-Image Knowledge to Speech for Voice-Native Multimodal CT Analysis
Authors:Lukas Buess, Jan Geier, David Bani-Harouni, Chantal Pellegrini, Matthias Keicher, Paula Andrea Perez-Toro, Nassir Navab, Andreas Maier, Tomas Arias-Vergara
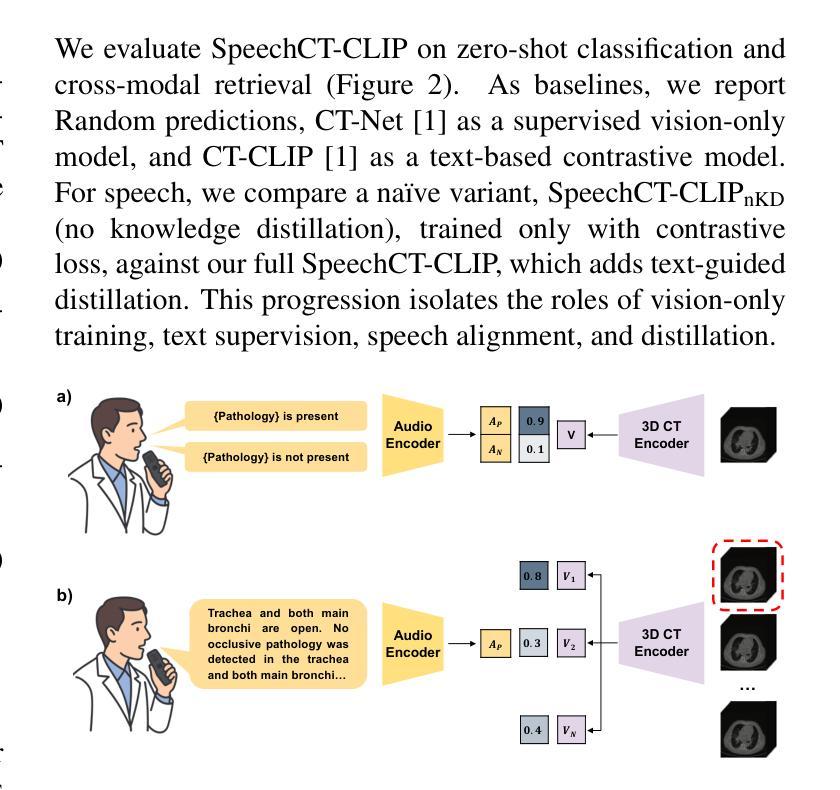
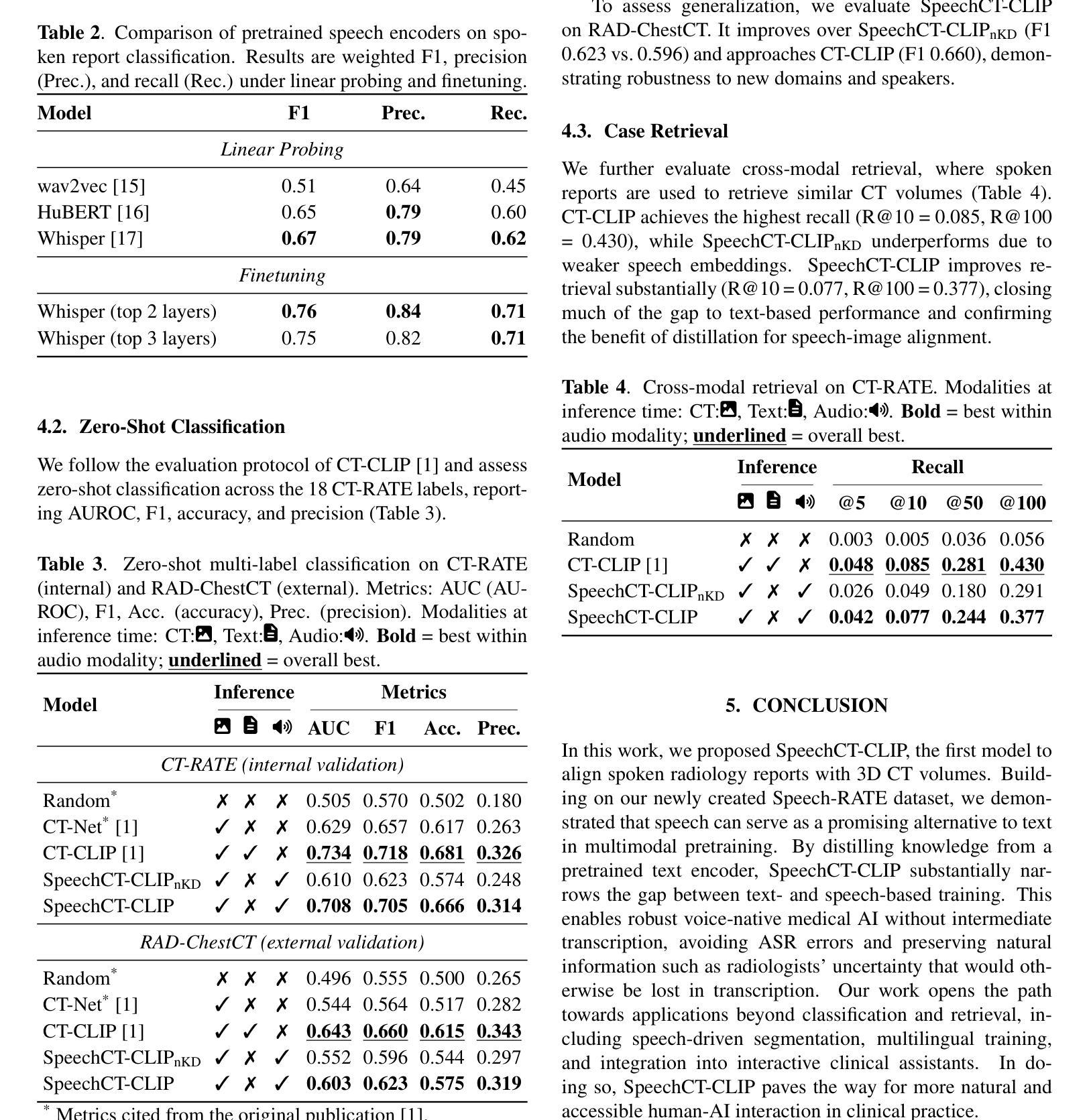
Spoken communication plays a central role in clinical workflows. In radiology, for example, most reports are created through dictation. Yet, nearly all medical AI systems rely exclusively on written text. In this work, we address this gap by exploring the feasibility of learning visual-language representations directly from spoken radiology reports. Specifically, we synthesize a large-scale dataset (Speech-RATE) of spoken radiology reports and train SpeechCT-CLIP, a contrastive model that aligns speech and 3D CT volumes in a shared representation space. While naive speech-based models underperform compared to text-trained counterparts, we show that knowledge distillation from a pretrained text-image CLIP model effectively transfers semantic alignment capabilities from text to speech, substantially narrowing this gap. Experiments demonstrate improved zero-shot classification F1 from 0.623 to 0.705, recovering 88% of the performance difference, and strong retrieval results without requiring text at inference. These findings highlight speech as a practical alternative to text in multimodal pretraining and open the door to voice-driven diagnostic support tools in clinical practice.
口头沟通在临床工作中起着核心作用。以放射科为例,大多数报告都是通过口授生成的。然而,几乎所有的医疗人工智能系统都依赖于书面文本。在这项工作中,我们通过探索直接从口头放射学报告中学习视觉语言表示的可能性来解决这一差距。具体来说,我们合成了一个大规模的放射学报告语音数据集(Speech-RATE),并训练了SpeechCT-CLIP对比模型,该模型在共享表示空间中对齐语音和3D CT体积。与基于文本的模型相比,简单的语音模型表现较差,但我们证明了从预训练的文本图像CLIP模型进行知识蒸馏可以有效地将语义对齐能力从文本转移到语音,从而大大缩小了这一差距。实验表明,零样本分类的F1分数从0.623提高到0.705,恢复了88%的性能差异,并且在不需要文本的情况下检索结果强大。这些发现凸显了语音在多模态预训练中作为文本的实用替代品的地位,并为临床实践中的语音驱动诊断支持工具打开了大门。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to ICASSP 2026; under review
Summary
本文解决了医疗领域中口头报告与医疗AI系统之间的鸿沟问题。研究团队构建了一个大规模的口头报告数据集Speech-RATE,并开发了一个对比模型SpeechCT-CLIP,该模型将语音和3D CT体积在共享表示空间中对齐。尽管基于语音的模型在初始状态下表现不如文本训练的模型,但通过从预训练的文本图像CLIP模型进行知识蒸馏,成功将语义对齐能力从文本转移到语音,显著缩小了差距。实验表明,零样本分类的F1分数从0.623提高到0.705,恢复了88%的性能差异,并且无需文本推理即可实现强大的检索结果。这一发现强调了语音在跨模态预训练中的实用性,并为临床实践中使用语音驱动的辅助诊断工具打开了大门。
Key Takeaways
- 口头沟通在临床工作中占据重要地位,但现有医疗AI系统主要依赖书面文本。
- 研究人员创建了一个大规模的口头报告数据集Speech-RATE。
- 开发了一个对比模型SpeechCT-CLIP,能够将语音和3D CT体积在共享表示空间中对齐。
- 基于语音的模型初始表现不如文本训练的模型,但通过知识蒸馏技术从预训练的文本图像CLIP模型转移语义对齐能力,提高了语音模型的表现。
- 实验结果显示,零样本分类的F1分数显著提高,并实现了强大的检索结果,无需文本推理。
- 缩小了语音和文本在医疗AI应用中的性能差距。
点此查看论文截图

AlignDiT: Multimodal Aligned Diffusion Transformer for Synchronized Speech Generation
Authors:Jeongsoo Choi, Ji-Hoon Kim, Kim Sung-Bin, Tae-Hyun Oh, Joon Son Chung
In this paper, we address the task of multimodal-to-speech generation, which aims to synthesize high-quality speech from multiple input modalities: text, video, and reference audio. This task has gained increasing attention due to its wide range of applications, such as film production, dubbing, and virtual avatars. Despite recent progress, existing methods still suffer from limitations in speech intelligibility, audio-video synchronization, speech naturalness, and voice similarity to the reference speaker. To address these challenges, we propose AlignDiT, a multimodal Aligned Diffusion Transformer that generates accurate, synchronized, and natural-sounding speech from aligned multimodal inputs. Built upon the in-context learning capability of the DiT architecture, AlignDiT explores three effective strategies to align multimodal representations. Furthermore, we introduce a novel multimodal classifier-free guidance mechanism that allows the model to adaptively balance information from each modality during speech synthesis. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AlignDiT significantly outperforms existing methods across multiple benchmarks in terms of quality, synchronization, and speaker similarity. Moreover, AlignDiT exhibits strong generalization capability across various multimodal tasks, such as video-to-speech synthesis and visual forced alignment, consistently achieving state-of-the-art performance. The demo page is available at https://mm.kaist.ac.kr/projects/AlignDiT.
本文我们解决了多模态到语音生成的任务,该任务旨在从多种输入模式(文本、视频和参考音频)中合成高质量语音。由于该任务在影视制作、配音和虚拟角色等领域的广泛应用,它已受到越来越多的关注。尽管最近有进展,但现有方法仍面临语音清晰度、音视频同步、语音自然度和与参考说话人的声音相似性等方面的局限性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了AlignDiT,这是一种多模态对齐扩散Transformer,它可以从对齐的多模态输入中生成准确、同步和自然的声音。AlignDiT基于DiT架构的上下文学习能力,探索了三种有效的策略来进行多模态表示对齐。此外,我们引入了一种新的无分类器引导机制,使模型在语音合成过程中能够自适应地平衡各模态的信息。大量实验表明,AlignDiT在多个基准测试上的质量、同步和说话人相似性方面显著优于现有方法。而且,AlignDiT在各种多模态任务中表现出强大的泛化能力,如视频到语音的合成和视觉强制对齐,一直保持着最先进的表现。演示页面可访问:https://mm.kaist.ac.kr/projects/AlignDiT。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM Multimedia 2025
Summary
本文研究了多模态到语音生成任务,旨在从文本、视频和参考音频等多种输入模态合成高质量语音。针对现有方法的挑战,提出了AlignDiT模型,采用多模态对齐扩散Transformer生成准确、同步且自然的语音。该模型通过三种有效策略实现多模态表示对齐,并引入新型的多模态无分类器引导机制,使模型在语音合成时能够自适应地平衡各模态的信息。实验表明,AlignDiT在多个基准测试中显著优于现有方法,具有强大的跨各种多模态任务的一般化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文关注多模态到语音生成任务,旨在从多种输入模态(文本、视频和参考音频)生成高质量语音。
- 现有方法面临语音清晰度、音视频同步、语音自然度和与参考语音的相似性等方面的挑战。
- 提出的AlignDiT模型基于扩散Transformer,实现了多模态表示的对齐。
- AlignDiT采用三种有效策略进行多模态对齐,包括扩散过程和上下文学习。
- 引入的多模态无分类器引导机制使模型在语音合成时能自适应平衡各模态的信息。
- 实验结果显示AlignDiT在多个基准测试中表现优异,显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图
