⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-09 更新
Multimodal Feature Prototype Learning for Interpretable and Discriminative Cancer Survival Prediction
Authors:Shuo Jiang, Zhuwen Chen, Liaoman Xu, Yanming Zhu, Changmiao Wang, Jiong Zhang, Feiwei Qin, Yifei Chen, Zhu Zhu
Survival analysis plays a vital role in making clinical decisions. However, the models currently in use are often difficult to interpret, which reduces their usefulness in clinical settings. Prototype learning presents a potential solution, yet traditional methods focus on local similarities and static matching, neglecting the broader tumor context and lacking strong semantic alignment with genomic data. To overcome these issues, we introduce an innovative prototype-based multimodal framework, FeatProto, aimed at enhancing cancer survival prediction by addressing significant limitations in current prototype learning methodologies within pathology. Our framework establishes a unified feature prototype space that integrates both global and local features of whole slide images (WSI) with genomic profiles. This integration facilitates traceable and interpretable decision-making processes. Our approach includes three main innovations: (1) A robust phenotype representation that merges critical patches with global context, harmonized with genomic data to minimize local bias. (2) An Exponential Prototype Update Strategy (EMA ProtoUp) that sustains stable cross-modal associations and employs a wandering mechanism to adapt prototypes flexibly to tumor heterogeneity. (3) A hierarchical prototype matching scheme designed to capture global centrality, local typicality, and cohort-level trends, thereby refining prototype inference. Comprehensive evaluations on four publicly available cancer datasets indicate that our method surpasses current leading unimodal and multimodal survival prediction techniques in both accuracy and interoperability, providing a new perspective on prototype learning for critical medical applications. Our source code is available at https://github.com/JSLiam94/FeatProto.
生存分析在临床决策中起着至关重要的作用。然而,当前使用的模型往往难以解释,从而降低了它们在临床环境中的实用性。虽然原型学习提供了一种潜在的解决方案,但传统的方法侧重于局部相似性和静态匹配,忽略了更广泛的肿瘤上下文,以及与基因组数据的强烈语义对齐。为了克服这些问题,我们引入了一种创新的基于原型的多模式框架——FeatProto,旨在通过解决病理学领域当前原型学习方法中的重大局限性,增强癌症生存预测。我们的框架建立了一个统一的特征原型空间,该空间整合了全幻灯片图像(WSI)的局部和全局特征以及基因组图谱。这种整合促进了可追溯和可解释性的决策过程。我们的方法包括三个主要创新点:(1)一种强大的表型表示,将关键补丁与全局上下文合并,与基因组数据协调,以最小化局部偏见。(2)一种指数原型更新策略(EMA ProtoUp),它维持稳定的跨模态关联,并采用漫游机制使原型能够灵活地适应肿瘤异质性。(3)一种分层原型匹配方案,旨在捕捉全局中心性、局部典型性和群体水平趋势,从而细化原型推理。在四个公开的癌症数据集上的综合评估表明,我们的方法在准确性和可操作性方面超越了当前领先的单模式和多模式生存预测技术,为原型学习在关键医疗应用方面提供了新的视角。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/JSLiam94/FeatProto获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于原型的多模态框架FeatProto,用于提高癌症生存预测的准确性。它通过整合全局和局部特征,建立统一特征原型空间,将全视野图像(WSI)的基因组数据与肿瘤整体背景相结合,以实现可追踪和可解释性的决策过程。本文提出的方法包括强大的表型表示、指数原型更新策略(EMA ProtoUp)和层次原型匹配方案,可在四个公开癌症数据集上实现更高的准确性和可操作性。
Key Takeaways
- 当前生存分析模型在临床医学中的解释性较差,影响了其在临床决策中的应用。
- 传统原型学习方法关注局部相似性和静态匹配,忽略了肿瘤整体背景和基因组数据的语义对齐。
- FeatProto框架通过整合全局和局部特征,建立统一特征原型空间,提高了癌症生存预测的准确性。
- 该框架采用强大的表型表示,结合基因组数据,减少局部偏见。
- 采用指数原型更新策略(EMA ProtoUp)维持跨模态关联的稳定性,并通过漫游机制灵活适应肿瘤异质性。
- 层次原型匹配方案能够捕捉全局中心性、局部典型性和群体水平趋势,从而优化原型推理。
点此查看论文截图
A public cardiac CT dataset featuring the left atrial appendage
Authors:Bjoern Hansen, Jonas Pedersen, Klaus F. Kofoed, Oscar Camara, Rasmus R. Paulsen, Kristine Soerensen
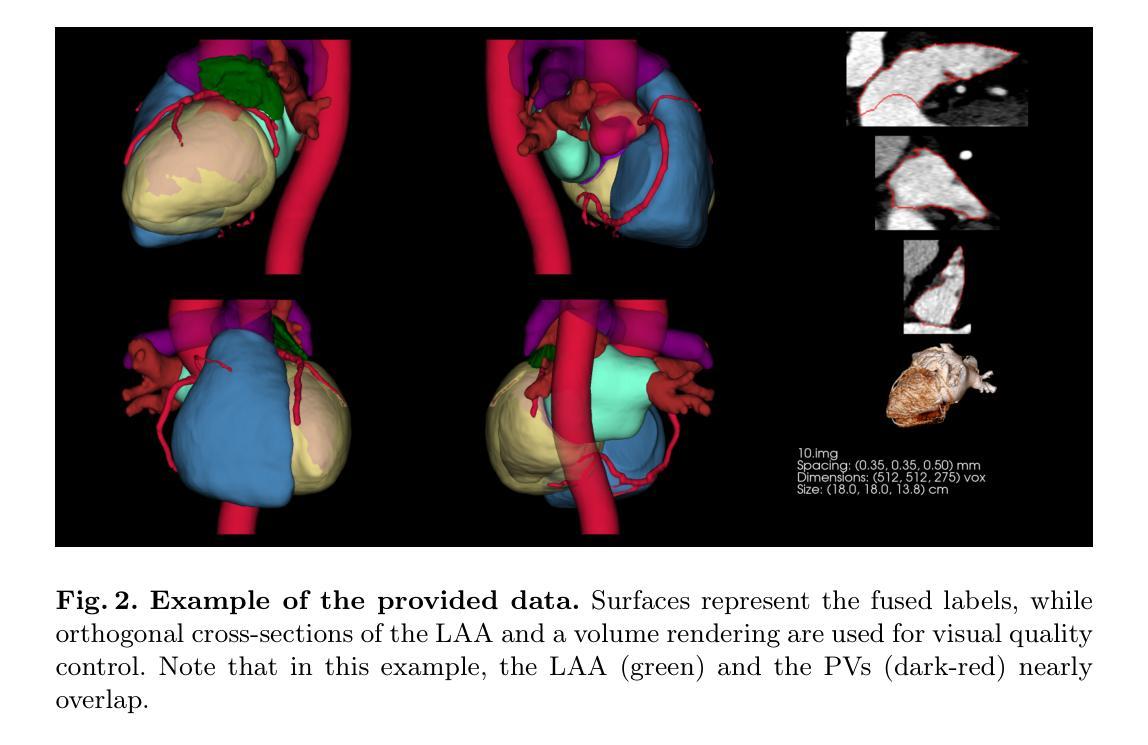
Despite the success of advanced segmentation frameworks such as TotalSegmentator (TS), accurate segmentations of the left atrial appendage (LAA), coronary arteries (CAs), and pulmonary veins (PVs) remain a significant challenge in medical imaging. In this work, we present the first open-source, anatomically coherent dataset of curated, high-resolution segmentations for these structures, supplemented with whole-heart labels produced by TS on the publicly available ImageCAS dataset consisting of 1000 cardiac computed tomography angiography (CCTA) scans. One purpose of the data set is to foster novel approaches to the analysis of LAA morphology. LAA segmentations on ImageCAS were generated using a state-of-the-art segmentation framework developed specifically for high resolution LAA segmentation. We trained the network on a large private dataset with manual annotations provided by medical readers guided by a trained cardiologist and transferred the model to ImageCAS data. CA labels were improved from the original ImageCAS annotations, while PV segmentations were refined from TS outputs. In addition, we provide a list of scans from ImageCAS that contains common data flaws such as step artefacts, LAAs extending beyond the scanner’s field of view, and other types of data defects.
尽管TotalSegmentator(TS)等先进分割框架取得了成功,但左心耳(LAA)、冠状动脉(CA)和肺静脉(PV)的精确分割在医学成像中仍是一项重大挑战。在这项工作中,我们提供了第一个开源的、解剖结构连贯的数据集,包含这些结构的精选高分辨率分割,以及由TS在公开可用的ImageCAS数据集上生成的整个心脏标签。该数据集的一个目的是促进LAA形态分析的新方法。ImageCAS上的LAA分割是使用专为高分辨率LAA分割开发的最先进分割框架生成的。我们在一个大型私有数据集上训练了网络,该数据集的标注由受训的心脏病医生指导的医学阅读者提供,并将模型转移到ImageCAS数据上。CA标签是对原始ImageCAS注释的改进,而PV分割是对TS输出的细化。此外,我们还列出了ImageCAS中的一些扫描结果,其中包含常见的数据缺陷,如阶梯效应、LAA超出扫描仪的视野以及其他类型的数据缺陷。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures, published at STACOM2025
Summary
本摘要以公开可用的ImageCAS数据集为基础,介绍了一个针对左心房附肢(LAA)、冠状动脉(CA)和肺静脉(PV)的高分辨率、解剖连贯性的数据集。数据集包含使用先进的分割框架(如TotalSegmentator)生成的标签,旨在促进对这些结构分析的新方法的研究,特别是在LAA形态分析方面。同时,也提供了包含常见数据缺陷的扫描列表。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了针对左心房附肢(LAA)、冠状动脉(CA)和肺静脉(PV)的高分辨率解剖连贯性数据集。
- 数据集是公开可用的,并且是首个开源的此类数据集。
- 数据集包含使用先进的分割框架(如TotalSegmentator)生成的标签。
- 数据集旨在促进对这些结构分析的新方法的研究,特别是在LAA形态分析方面。
- LAA分割是在ImageCAS数据集上生成的,使用了专门为高分辨率LAA分割开发的先进分割框架。
- 冠状动脉(CA)的标签在原始ImageCAS注释的基础上进行了改进,而肺静脉(PV)的分割则基于TS输出进行了细化。
点此查看论文截图
Efficient Universal Models for Medical Image Segmentation via Weakly Supervised In-Context Learning
Authors:Jiesi Hu, Yanwu Yang, Zhiyu Ye, Jinyan Zhou, Jianfeng Cao, Hanyang Peng, Ting Ma
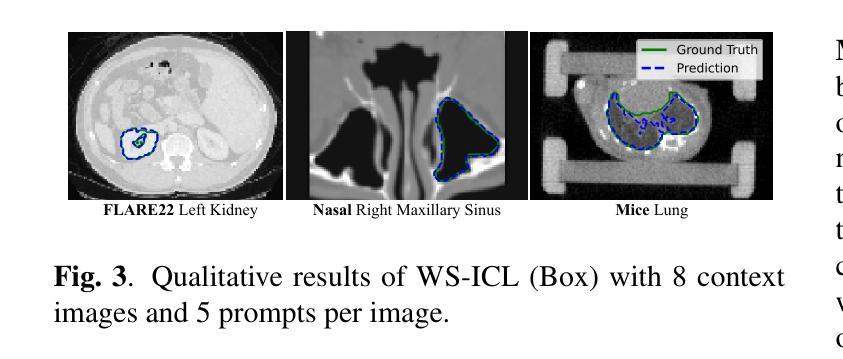
Universal models for medical image segmentation, such as interactive and in-context learning (ICL) models, offer strong generalization but require extensive annotations. Interactive models need repeated user prompts for each image, while ICL relies on dense, pixel-level labels. To address this, we propose Weakly Supervised In-Context Learning (WS-ICL), a new ICL paradigm that leverages weak prompts (e.g., bounding boxes or points) instead of dense labels for context. This approach significantly reduces annotation effort by eliminating the need for fine-grained masks and repeated user prompting for all images. We evaluated the proposed WS-ICL model on three held-out benchmarks. Experimental results demonstrate that WS-ICL achieves performance comparable to regular ICL models at a significantly lower annotation cost. In addition, WS-ICL is highly competitive even under the interactive paradigm. These findings establish WS-ICL as a promising step toward more efficient and unified universal models for medical image segmentation. Our code and model are publicly available at https://github.com/jiesihu/Weak-ICL.
医学图像分割的通用模型,如交互式和上下文学习(ICL)模型,虽然具有良好的泛化能力,但需要大量的标注。交互式模型需要对每张图像进行多次用户提示,而ICL则依赖于密集的像素级标签。为解决这一问题,我们提出了弱监督上下文学习(WS-ICL),这是一种新的ICL范式,它利用弱提示(如边界框或点)而不是密集的标签来进行上下文。这种方法通过消除对精细遮罩和所有图像重复用户提示的需求,显著减少了标注工作量。我们在三个独立的标准上评估了所提出的WS-ICL模型。实验结果表明,WS-ICL在标注成本显著降低的情况下,实现了与常规ICL模型相当的性能。此外,即使在交互式模式下,WS-ICL也具有很强的竞争力。这些发现表明,WS-ICL是朝着更高效和统一的医学图像分割通用模型迈出的有希望的一步。我们的代码和模型已在https://github.com/jiesihu/Weak-ICL公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割的通用模型,如交互式和上下文学习(ICL)模型,虽然具有良好的泛化能力,但需要大量的标注。交互式模型需要针对每张图像进行多次用户提示,而ICL则依赖于密集的像素级标签。为解决这一问题,我们提出了弱监督上下文学习(WS-ICL)这一新的ICL方法,它利用弱提示(如边界框或点)代替密集的标签来提供上下文信息。这种方法通过消除对精细掩膜和所有图像重复用户提示的需求,大大降低了标注工作量。我们在三个独立的标准基准测试上对WS-ICL模型进行了评估。实验结果表明,WS-ICL在性能上可与常规的ICL模型相媲美,同时大大降低了标注成本。此外,即使在交互式模式下,WS-ICL也表现出高度的竞争力。这些发现表明WS-ICL是朝着更高效和统一的医学图像分割通用模型的重要一步。
Key Takeaways
- ICL模型在医学图像分割中具有良好泛化能力,但需大量标注。
- WS-ICL是一种新的ICL方法,利用弱提示提供上下文信息,降低标注工作量。
- WS-ICL不需要精细掩膜和所有图像的重复用户提示。
- WS-ICL在性能上可与常规ICL模型相媲美,同时降低标注成本。
- WS-ICL在交互式模式下也表现出竞争力。
- WS-ICL是朝着更高效和统一的医学图像分割模型的重要一步。
点此查看论文截图
acia-workflows: Automated Single-cell Imaging Analysis for Scalable and Deep Learning-based Live-cell Imaging Analysis Workflows
Authors:Johannes Seiffarth, Keitaro Kasahara, Michelle Bund, Benita Lückel, Richard D. Paul, Mathias Pesch, Lennart Witting, Michael Bott, Dietrich Kohlheyer, Katharina Nöh
Live-cell imaging (LCI) technology enables the detailed spatio-temporal characterization of living cells at the single-cell level, which is critical for advancing research in the life sciences, from biomedical applications to bioprocessing. High-throughput setups with tens to hundreds of parallel cell cultivations offer the potential for robust and reproducible insights. However, these insights are obscured by the large amount of LCI data recorded per experiment. Recent advances in state-of-the-art deep learning methods for cell segmentation and tracking now enable the automated analysis of such large data volumes, offering unprecedented opportunities to systematically study single-cell dynamics. The next key challenge lies in integrating these powerful tools into accessible, flexible, and user-friendly workflows that support routine application in biological research. In this work, we present acia-workflows, a platform that combines three key components: (1) the Automated live-Cell Imaging Analysis (acia) Python library, which supports the modular design of image analysis pipelines offering eight deep learning segmentation and tracking approaches; (2) workflows that assemble the image analysis pipeline, its software dependencies, documentation, and visualizations into a single Jupyter Notebook, leading to accessible, reproducible and scalable analysis workflows; and (3) a collection of application workflows showcasing the analysis and customization capabilities in real-world applications. Specifically, we present three workflows to investigate various types of microfluidic LCI experiments ranging from growth rate comparisons to precise, minute-resolution quantitative analyses of individual dynamic cells responses to changing oxygen conditions. Our collection of more than ten application workflows is open source and publicly available at https://github.com/JuBiotech/acia-workflows.
活细胞成像(LCI)技术能够在单细胞水平上对活细胞进行详细的时空特征表征,这对于推动生命科学领域的研究,从生物医学应用到生物加工都至关重要。具有数十到数百个并行细胞培养的高通量设置提供了稳健且可重复的洞察力。然而,这些洞察被每次实验记录的大量LCI数据所掩盖。最近先进的深度学习方法在细胞分割和跟踪方面的最新进展现在能够实现这些大数据量的自动分析,为系统地研究单细胞动态提供了前所未有的机会。下一个关键挑战在于将这些强大工具集成到可访问、灵活和用户友好的工作流程中,以支持生物学研究中的常规应用。在这项工作中,我们提出了acia-workflows平台,该平台结合了三个关键组件:(1)Automated live-Cell Imaging Analysis(acia)Python库,支持图像分析管道模块化设计,提供八种深度学习分割和跟踪方法;(2)将图像分析管道、其软件依赖项、文档和可视化组装成单个Jupyter Notebook的工作流程,从而实现可访问、可重复和可扩展的分析工作流程;(3)一系列应用程序工作流程,展示实际应用程序中的分析和定制功能。具体来说,我们推出了三个工作流程来研究各种微流体LCI实验,从生长率比较到对变化氧气条件下单个动态细胞的精确分钟分辨率定量分析。我们提供的十多个应用程序工作流程是开源的,可在 https://github.com/JuBiotech/acia-workflows 公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
活体细胞成像技术可实现单细胞水平的时空特征详细表征,对生命科学领域的研究至关重要。通过数十到数百个并行细胞培养的高通量设置,可获得稳健且可重复的见解。然而,这些见解被大量成像数据所掩盖。最近先进的深度学习细胞分割和跟踪方法为自动分析大量数据提供了可能,为研究单细胞动态提供了前所未有的机会。下一个关键挑战在于将这些强大工具集成到可访问、灵活和用户友好的工作流中,以支持生物学研究的常规应用。本研究提出了acia-workflows平台,该平台结合了三个关键组件:支持图像分析管道模块化设计的Automated live-Cell Imaging Analysis(acia)Python库、装配图像分析管道、其软件依赖项、文档和可视化的工作流,以及展示实际应用中分析和定制功能的应用程序工作流集合。
Key Takeaways
- 活体细胞成像技术对于生命科学领域的研究至关重要,可实现单细胞水平的详细时空表征。
- 高通量设置为获取稳健和可重复的见解提供了机会,但大量数据掩盖了这些见解。
- 先进的深度学习方法实现了对大量数据的自动分析,为研究单细胞动态提供了前所未有的机会。
- 当前挑战在于将强大工具集成到易于访问、灵活和用户友好的工作流中。
- acia-workflows平台结合了图像分析管道的关键组件,支持模块化的设计。
- 该平台提供了包括生长速率比较和动态细胞对变化氧气条件的响应在内的多种微流体成像实验的分析工作流。
点此查看论文截图
Deformable Image Registration for Self-supervised Cardiac Phase Detection in Multi-View Multi-Disease Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Images
Authors:Sven Koehler, Sarah Kaye Mueller, Jonathan Kiekenap, Gerald Greil, Tarique Hussain, Samir Sarikouch, Florian André, Norbert Frey, Sandy Engelhardt
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) is the gold standard for assessing cardiac function, but individual cardiac cycles complicate automatic temporal comparison or sub-phase analysis. Accurate cardiac keyframe detection can eliminate this problem. However, automatic methods solely derive end-systole (ES) and end-diastole (ED) frames from left ventricular volume curves, which do not provide a deeper insight into myocardial motion. We propose a self-supervised deep learning method detecting five keyframes in short-axis (SAX) and four-chamber long-axis (4CH) cine CMR. Initially, dense deformable registration fields are derived from the images and used to compute a 1D motion descriptor, which provides valuable insights into global cardiac contraction and relaxation patterns. From these characteristic curves, keyframes are determined using a simple set of rules. The method was independently evaluated for both views using three public, multicentre, multidisease datasets. M&Ms-2 (n=360) dataset was used for training and evaluation, and M&Ms (n=345) and ACDC (n=100) datasets for repeatability control. Furthermore, generalisability to patients with rare congenital heart defects was tested using the German Competence Network (GCN) dataset. Our self-supervised approach achieved improved detection accuracy by 30% - 51% for SAX and 11% - 47% for 4CH in ED and ES, as measured by cyclic frame difference (cFD), compared with the volume-based approach. We can detect ED and ES, as well as three additional keyframes throughout the cardiac cycle with a mean cFD below 1.31 frames for SAX and 1.73 for LAX. Our approach enables temporally aligned inter- and intra-patient analysis of cardiac dynamics, irrespective of cycle or phase lengths. GitHub repository: https://github.com/Cardio-AI/cmr-multi-view-phase-detection.git
心血管磁共振成像(CMR)是评估心脏功能的金标准,但个体心脏周期使得自动时间比较或亚阶段分析复杂化。准确的心脏关键帧检测可以消除这个问题。然而,自动方法仅从左心室体积曲线中得出收缩末期(ES)和舒张末期(ED)帧,无法深入了解心肌运动。我们提出了一种基于自监督深度学习的检测短轴(SAX)五个关键帧和四腔长轴(4CH)电影CMR四个关键帧的方法。首先,从图像中得出密集的可变形注册字段,用于计算一维运动描述符,该描述符提供了对全局心脏收缩和舒张模式的宝贵见解。从这些特征曲线中,使用简单的规则集确定关键帧。该方法使用三种公共多中心多疾病数据集对两种视图进行了独立评估。M&Ms-2(n=360)数据集用于训练和评估,M&Ms(n=345)和ACDC(n=100)数据集用于重复性控制。此外,使用德国专长网络(GCN)数据集测试了对患有罕见先天性心脏缺陷的患者的通用性。我们的自监督方法通过循环帧差异(cFD)测量,在SAX方面提高了30%~51%的检测精度,在4CH的ED和ES方面提高了11%~47%的精度。我们可以检测ED和ES以及心脏周期中的另外三个关键帧,SAX的平均cFD低于1.31帧,LAX低于1.73帧。我们的方法能够在不考虑周期或相位长度的情况下,进行时间和空间上对齐的患者的心脏动态分析。GitHub仓库地址:https://github.com/Cardio-AI/cmr-multi-view-phase-detection.git。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Main 30 pages, 6 figures
Summary
心脏磁共振成像(CMR)是评估心脏功能的金标准,但自动时间比较或亚相位分析因个体心脏周期的差异而复杂化。我们提出了一种基于深度学习的自监督方法,可以检测短轴和长轴心脏磁共振成像中的关键帧,并提供对心脏收缩和舒张模式的深入了解。该方法在多个公共数据集上进行了独立评估,实现了较高的检测精度。GitHub地址:https://github.com/Cardio-AI/cmr-multi-view-phase-detection.git。此研究推动了更精确的CM全局评估和心脏病患者的个体差异评估研究发展。此方法为实现精确的跨学科心血管诊断奠定了基础。 此技术有望成为医疗领域的里程碑。同时通过对多种数据集的应用和测试证明了其在临床实践中的可行性和适用性。这项研究将促进更准确的全球心脏评估和个体差异评估,并有望推动心血管疾病诊疗的精准化。该方法的开源实现也为进一步研究和应用提供了便利。我们相信这项研究将为未来的医疗领域带来重要的突破和进步。该方法提高了检测准确性,为跨领域心血管研究提供了重要工具,可能有助于提高疾病诊断和治疗的效率和准确性。关于开源存储库的详细信息将在文末给出,我们可以基于此开源代码做更多深入的探索和试验以解决实际问题并扩大其在不同领域的实际应用范围,相信这将对医疗行业产生积极影响。简而言之,本方法改进了现有心脏磁共振成像的评估方法,使更精确的评估和跨患者比较成为可能。对于心脏疾病的诊断和治疗具有重大意义。通过精确的关键帧检测,我们能够更好地理解心脏的动态行为,从而为医生提供更准确的诊断依据。我们的方法还为未来的研究提供了新的可能性。 在我们的模型中还可以提取疾病识别特征的全面训练流程报告研究已在GitHub平台上公开发布展示及相关参数的实时调优将会改进以解释性研究功能以及潜在的未来应用为基准来构建新的算法模型来推动医学图像分析领域的发展并促进跨学科合作以开发更加智能高效的医疗诊断工具以解决当前医学面临的挑战包括疾病的早期发现预测以及精准治疗等本方法将在未来临床诊断和治疗中发挥重要作用提升患者的生活质量以及疾病的治愈率针对先天性心脏病等疾病也将实现精准诊断和个体化治疗提供更有效的诊断方法和改善治疗结局的手段可以大大提高医疗保健的质量推动全球医疗健康事业的发展和进步让人类健康事业得以更进一步推动精细化医疗的普及和发展提升全球医疗水平为医学领域带来革命性的变革为医学图像分析领域的发展注入新的活力。Key Takeaways:
点此查看论文截图

Modulated INR with Prior Embeddings for Ultrasound Imaging Reconstruction
Authors:Rémi Delaunay, Christoph Hennersperger, Stefan Wörz
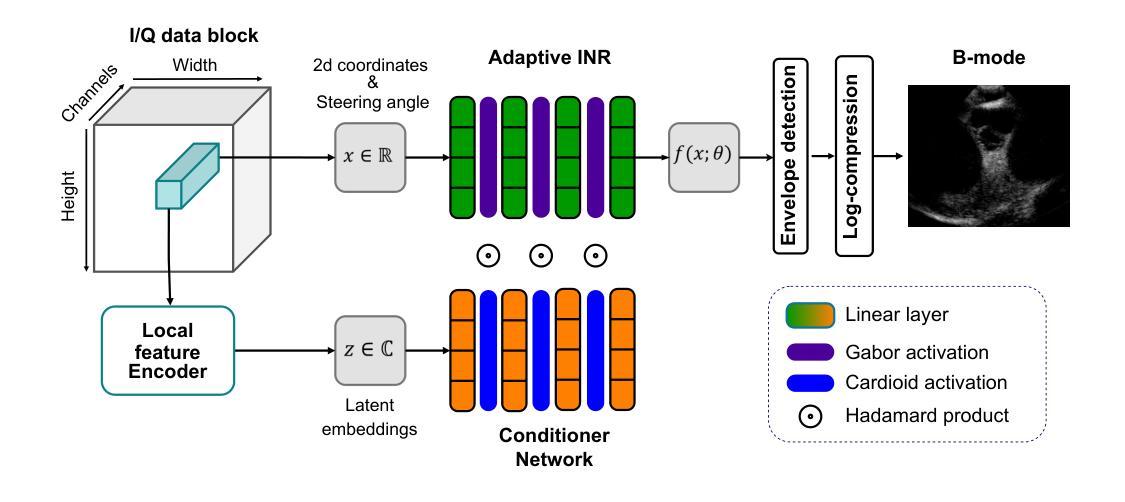
Ultrafast ultrasound imaging enables visualization of rapid physiological dynamics by acquiring data at exceptionally high frame rates. However, this speed often comes at the cost of spatial resolution and image quality due to unfocused wave transmissions and associated artifacts. In this work, we propose a novel modulated Implicit Neural Representation (INR) framework that leverages a coordinate-based neural network conditioned on latent embeddings extracted from time-delayed I/Q channel data for high-quality ultrasound image reconstruction. Our method integrates complex Gabor wavelet activation and a conditioner network to capture the oscillatory and phase-sensitive nature of I/Q ultrasound signals. We evaluate the framework on an in vivo intracardiac echocardiography (ICE) dataset and demonstrate that it outperforms the compared state-of-the-art methods. We believe these findings not only highlight the advantages of INR-based modeling for ultrasound image reconstruction, but also point to broader opportunities for applying INR frameworks across other medical imaging modalities.
超高速超声成像能够通过以极高帧率获取数据,实现快速生理动态的可视化。然而,由于波的不聚焦传输和相关伪影,这种速度往往会牺牲空间分辨率和图像质量。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新型调制隐式神经网络(INR)框架,它利用基于坐标的神经网络对从时延I/Q通道数据中提取的潜在嵌入进行条件处理,以实现高质量的超声图像重建。我们的方法结合了复杂的Gabor小波激活和条件网络,以捕捉I/Q超声信号的振荡和相位敏感特性。我们在体内心内超声心动图(ICE)数据集上评估了该框架,并证明其优于现有最先进的对比方法。我们相信,这些发现不仅突出了基于INR建模在超声图像重建方面的优势,还指出了将INR框架应用于其他医学成像模式的更广阔机会。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to International Workshop on Advances in Simplifying Medical Ultrasound (ASMUS 2025)
Summary
高速超声成像可实现快速生理动态的可视化,但其高帧率带来的空间分辨率和图像质量损失问题亟待解决。本研究提出一种新型调制隐式神经网络(INR)框架,利用基于坐标的神经网络处理延迟的I/Q通道数据以进行高质量超声图像重建。该研究集成了复杂Gabor小波激活器和条件网络,以捕捉I/Q超声信号的振荡和相位敏感性。在活体心脏内超声(ICE)数据集上的评估显示,该方法优于现有技术。这些发现不仅突出了INR模型在超声图像重建中的优势,也暗示了INR框架在其他医学成像模态中的应用潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究使用隐式神经网络(INR)框架进行高质量超声图像重建。
- INR框架结合了坐标神经网络和延迟的I/Q通道数据。
- 研究利用了复杂Gabor小波激活器和条件网络来捕捉超声信号的振荡和相位敏感性。
- 在活体心脏内超声(ICE)数据集上的评估表明,该方法性能优于现有技术。
- 此研究展示了INR模型在超声图像重建中的优势。
- 调制隐式神经网络(INR)框架可应用于其他医学成像模态。
点此查看论文截图
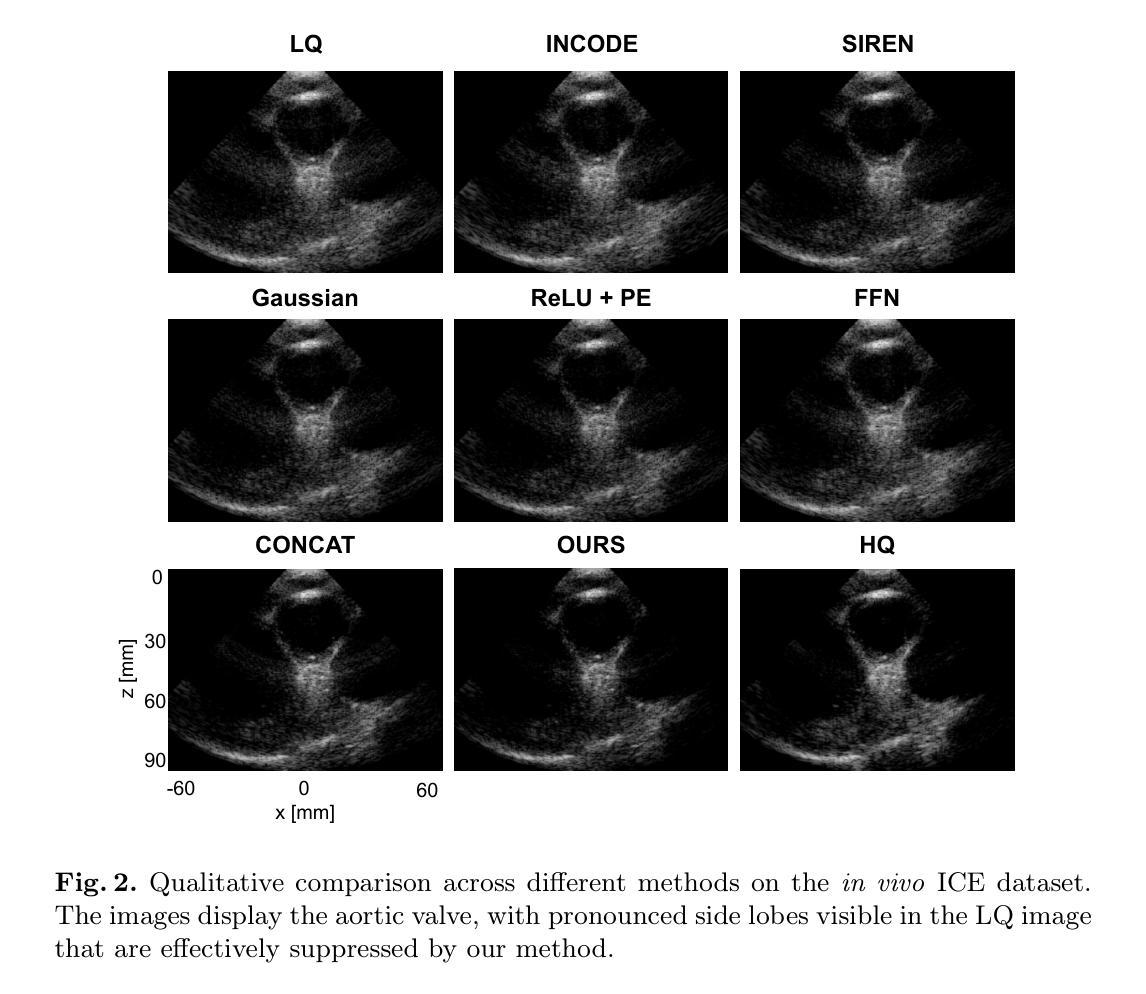
A Hierarchical Geometry-guided Transformer for Histological Subtyping of Primary Liver Cancer
Authors:Anwen Lu, Mingxin Liu, Yiping Jiao, Hongyi Gong, Geyang Xu, Jun Chen, Jun Xu
Primary liver malignancies are widely recognized as the most heterogeneous and prognostically diverse cancers of the digestive system. Among these, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (ICC) emerge as the two principal histological subtypes, demonstrating significantly greater complexity in tissue morphology and cellular architecture than other common tumors. The intricate representation of features in Whole Slide Images (WSIs) encompasses abundant crucial information for liver cancer histological subtyping, regarding hierarchical pyramid structure, tumor microenvironment (TME), and geometric representation. However, recent approaches have not adequately exploited these indispensable effective descriptors, resulting in a limited understanding of histological representation and suboptimal subtyping performance. To mitigate these limitations, ARGUS is proposed to advance histological subtyping in liver cancer by capturing the macro-meso-micro hierarchical information within the TME. Specifically, we first construct a micro-geometry feature to represent fine-grained cell-level pattern via a geometric structure across nuclei, thereby providing a more refined and precise perspective for delineating pathological images. Then, a Hierarchical Field-of-Views (FoVs) Alignment module is designed to model macro- and meso-level hierarchical interactions inherent in WSIs. Finally, the augmented micro-geometry and FoVs features are fused into a joint representation via present Geometry Prior Guided Fusion strategy for modeling holistic phenotype interactions. Extensive experiments on public and private cohorts demonstrate that our ARGUS achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in histological subtyping of liver cancer, which provide an effective diagnostic tool for primary liver malignancies in clinical practice.
原发性肝脏恶性肿瘤被公认为是消化系统内最具有异质性和预后多样性的癌症。其中,肝细胞癌(HCC)和肝内胆管癌(ICC)是两种主要的组织亚型,它们在组织形态和细胞结构方面比其他常见肿瘤表现出更大的复杂性。全幻灯片图像(WSI)中特征的复杂表示包含了关于肝脏癌症组织亚型的层次金字塔结构、肿瘤微环境(TME)和几何表示的大量关键信息。然而,最近的方法并没有充分利用这些不可或缺的有效描述符,导致对组织表征的理解有限,以及亚型分类性能不佳。为了缓解这些限制,ARGUS被提出来通过捕捉肿瘤微环境中宏观到微观的层次信息,推进肝脏癌症的组织亚型分类。具体来说,我们首先构建一个微观几何特征来表示细胞核之间精细的细胞级模式,从而为病理图像分割提供一个更精细和精确的角度。然后,设计了一个分层视野(FoVs)对齐模块,以模拟全幻灯片图像中固有的宏观和中间层次的交互作用。最后,增强型微观几何和视野特征通过当前的几何先验引导融合策略,被融合成一个联合表示,以模拟整体表型交互。在公共和私人队列的大量实验表明,我们的ARGUS在肝脏癌症的组织亚型分类上达到了最先进的性能,为临床实践中的原发性肝脏恶性肿瘤提供了一种有效的诊断工具。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 2 figures, accepted by IEEE BIBM 2025
Summary
本文介绍了肝癌中最具异质性和预后多样性的两种主要组织亚型——肝细胞癌和肝内胆管癌。文章指出全幻灯片图像中包含丰富的关键信息,对于肝癌组织亚型分类具有重要意义。然而,现有方法未能充分利用这些有效的描述符号,导致组织表征理解有限和分型性能不佳。因此,本文提出了ARGUS方法,通过捕捉肿瘤微环境中宏观、中观和微观的层次信息,改进肝癌组织分型。实验证明,该方法在肝癌组织分型上达到了最新技术水平,为临床实践中的原发性肝癌诊断提供了有效的工具。
Key Takeaways
- 肝癌具有高度的异质性和预后多样性,其中肝细胞癌和肝内胆管癌是主要亚型。
- 全幻灯片图像包含丰富的信息,对于肝癌组织亚型分类至关重要。
- 现有方法未能充分利用描述符号,导致组织表征理解和分型性能有限。
- ARGUS方法通过捕捉肿瘤微环境中的宏观、中观和微观层次信息,改进肝癌组织分型。
- ARGUS方法包括构建微观几何特征、设计视野对齐模块以及融合特征的策略。
- 实验证明,ARGUS方法在肝癌组织分型上达到了最新技术水平。
点此查看论文截图
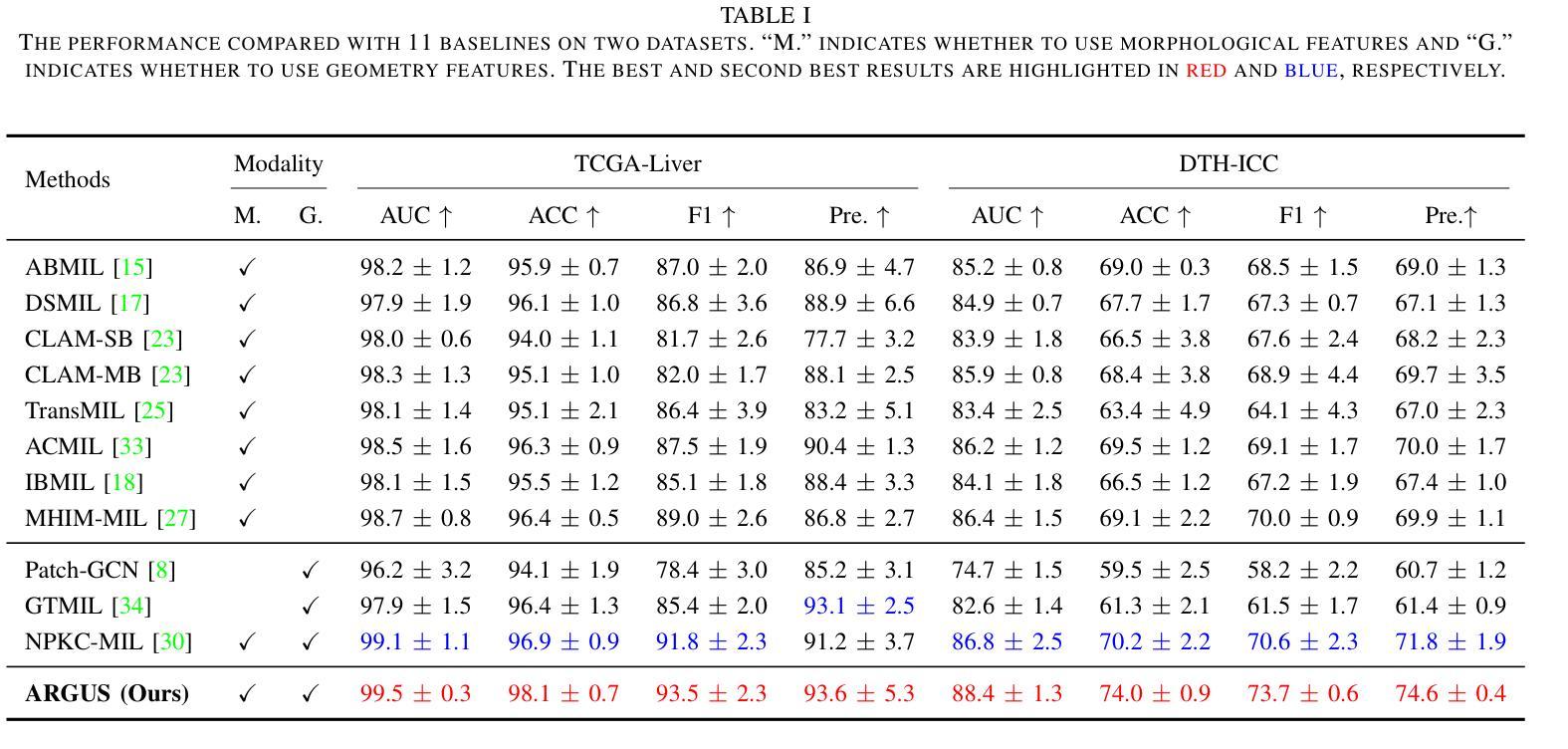
TFM Dataset: A Novel Multi-task Dataset and Integrated Pipeline for Automated Tear Film Break-Up Segmentation
Authors:Guangrong Wan, Jun liu, Tang tang, Lianghao Shi, Wenjun Luo, TingTing Xu
Tear film break-up (TFBU) analysis is critical for diagnosing dry eye syndrome, but automated TFBU segmentation remains challenging due to the lack of annotated datasets and integrated solutions. This paper introduces the Tear Film Multi-task (TFM) Dataset, the first comprehensive dataset for multi-task tear film analysis, comprising 15 high-resolution videos (totaling 6,247 frames) annotated with three vision tasks: frame-level classification (‘clear’, ‘closed’, ‘broken’, ‘blur’), Placido Ring detection, and pixel-wise TFBU area segmentation. Leveraging this dataset, we first propose TF-Net, a novel and efficient baseline segmentation model. TF-Net incorporates a MobileOne-mini backbone with re-parameterization techniques and an enhanced feature pyramid network to achieve a favorable balance between accuracy and computational efficiency for real-time clinical applications. We further establish benchmark performance on the TFM segmentation subset by comparing TF-Net against several state-of-the-art medical image segmentation models. Furthermore, we design TF-Collab, a novel integrated real-time pipeline that synergistically leverages models trained on all three tasks of the TFM dataset. By sequentially orchestrating frame classification for BUT determination, pupil region localization for input standardization, and TFBU segmentation, TF-Collab fully automates the analysis. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed TF-Net and TF-Collab, providing a foundation for future research in ocular surface diagnostics. Our code and the TFM datasets are available at https://github.com/glory-wan/TF-Net
泪膜破裂分析(TFBU)对于干眼综合征的诊断至关重要,但由于缺乏标注数据集和集成解决方案,自动化TFBU分割仍然是一个挑战。本文介绍了泪膜多任务(TFM)数据集,这是用于多任务泪膜分析的首个综合数据集,包含15个高清视频(总计6247帧),标注了三个视觉任务:帧级别分类(清晰、闭合、破裂、模糊)、Placido环检测和像素级TFBU区域分割。利用该数据集,我们首次提出了TF-Net,这是一种新颖且高效的分割基线模型。TF-Net采用MobileOne-mini骨干网与重新参数化技术,并增强特征金字塔网络,以实现准确性和计算效率的平衡,适用于实时临床应用。此外,我们通过将TF-Net与几种最先进的医学图像分割模型进行比较,在TFM分割子集上建立了基准性能。此外,我们设计了TF-Collab,这是一个新颖的一体化实时管道,协同利用在TFM数据集所有三个任务上训练的模型。通过按顺序协调帧分类以测定BUT、瞳孔区域定位以实现输入标准化和TFBU分割,TF-Collab实现了全自动分析。实验结果表明TF-Net和TF-Collab的有效性,为眼表诊断的未来研究提供了基础。我们的代码和TFM数据集可通过https://github.com/glory-wan/TF-Net获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对干眼综合征诊断中的泪膜破裂分析的重要性,以及现有自动化TFBU分割面临的挑战。为解决这些问题,本文引入了Tear Film Multi-task(TFM)数据集,这是首个用于多任务泪膜分析的综合数据集。利用该数据集,提出了TF-Net,一种高效且准确的分割模型,用于实时临床应用。此外,还建立了TF-Collab,一个全新的实时集成流程,通过协同利用在TFM数据集上训练的三个任务模型,实现全自动化分析。
Key Takeaways
- Tear Film Break-up (TFBU) 分析对干眼综合征诊断至关重要。
- 自动化TFBU分割面临缺乏标注数据集和综合解决方案的挑战。
- 引入Tear Film Multi-task (TFM) 数据集,包含高分辨率视频和多种视觉任务标注。
- 提出TF-Net模型,结合MobileOne-mini backbone和重参数化技术,实现准确和高效的分割。
- TF-Net在TFM分割子集上建立了基准性能。
- 设计TF-Collab,一个全新的实时集成流程,通过协同三个任务模型实现全自动化分析。
点此查看论文截图

nnSAM2: nnUNet-Enhanced One-Prompt SAM2 for Few-shot Multi-Modality Segmentation and Composition Analysis of Lumbar Paraspinal Muscles
Authors:Zhongyi Zhang, Julie A. Hides, Enrico De Martino, Abdul Joseph Fofanah, Gervase Tuxworth
Purpose: To develop and validate No-New SAM2 (nnsam2) for few-shot segmentation of lumbar paraspinal muscles using only a single annotated slice per dataset, and to assess its statistical comparability with expert measurements across multi-sequence MRI and multi-protocol CT. Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 1,219 scans (19,439 slices) from 762 participants across six datasets. Six slices (one per dataset) served as labeled examples, while the remaining 19,433 slices were used for testing. In this minimal-supervision setting, nnsam2 used single-slice SAM2 prompts to generate pseudo-labels, which were pooled across datasets and refined through three sequential, independent nnU-Net models. Segmentation performance was evaluated using the Dice similarity coefficient (DSC), and automated measurements-including muscle volume, fat ratio, and CT attenuation-were assessed with two one-sided tests (TOST) and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC). Results: nnsam2 outperformed vanilla SAM2, its medical variants, TotalSegmentator, and the leading few-shot method, achieving DSCs of 0.94-0.96 on MR images and 0.92-0.93 on CT. Automated and expert measurements were statistically equivalent for muscle volume (MRI/CT), CT attenuation, and Dixon fat ratio (TOST, P < 0.05), with consistently high ICCs (0.86-1.00). Conclusion: We developed nnsam2, a state-of-the-art few-shot framework for multi-modality LPM segmentation, producing muscle volume (MRI/CT), attenuation (CT), and fat ratio (Dixon MRI) measurements that were statistically comparable to expert references. Validated across multimodal, multicenter, and multinational cohorts, and released with open code and data, nnsam2 demonstrated high annotation efficiency, robust generalizability, and reproducibility.
目的:开发并验证No-New SAM2(nnsam2)方法,用于仅使用每个数据集的一个已标注切片对腰椎旁肌肉进行小样本分割,并评估其在多序列MRI和多协议CT下与专家测量的统计可比性。方法:我们回顾性分析了来自六个数据集的762名参与者的1,219次扫描(共19,439张切片)。其中六张切片(每张数据集一张)作为标注示例,其余19,433张切片用于测试。在这种最小监督设置下,nnsam2使用单切片SAM2提示生成伪标签,这些伪标签在数据集之间进行汇总,并通过三个独立且顺序的nnU-Net模型进行改进。使用Dice相似系数(DSC)评估分割性能,并使用两个单侧检验(TOST)和组内相关系数(ICC)评估自动化测量,包括肌肉体积、脂肪比和CT衰减。结果:nnsam2的表现优于普通SAM2、其医学变体、TotalSegmentator以及主流的少样本方法,在MR图像上达到DSC 0.94-0.96,在CT上达到DSC 0.92-0.93。自动化和专家测量的肌肉体积(MRI/CT)、CT衰减和Dixon脂肪比(TOST,P < 0.05)在统计上是等效的,且ICC始终很高(0.86-1.00)。结论:我们开发了先进的少样本多模态LPM分割框架nnsam2,能够生成与专家参考统计相当的肌肉体积(MRI/CT)、衰减(CT)和脂肪比(Dixon MRI)测量值。经过多模态、多中心和跨国队列的验证,并以开放代码和数据发布,nnsam2表现出高标注效率、稳健的通用性和可重复性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于单一标注切片开发并验证了No-New SAM2(nnsam2)用于腰椎旁肌肉组织的少样本分割技术,该技术能够在多序列MRI和多协议CT上实现与专家测量结果的统计可比性。通过对来自不同数据集的大量扫描数据进行回顾性分析和模型训练,验证了nnsam2的有效性和可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- nnsam2被开发用于腰椎旁肌肉组织的少样本分割,仅需要一个标注切片即可进行训练。
- 该方法在多序列MRI和多协议CT上实现了与专家测量结果的统计可比性。
- 通过分析大量扫描数据验证了nnsam2的有效性和可靠性。
- nnsam2使用单一切片SAM2提示生成伪标签,并通过三个独立的nnU-Net模型进行精细化处理。
- 分割性能通过Dice相似系数进行评估,实现了高分割精度。
- 自动测量结果与专家测量结果相比具有统计学等效性,包括肌肉体积、脂肪比和CT衰减等。
点此查看论文截图

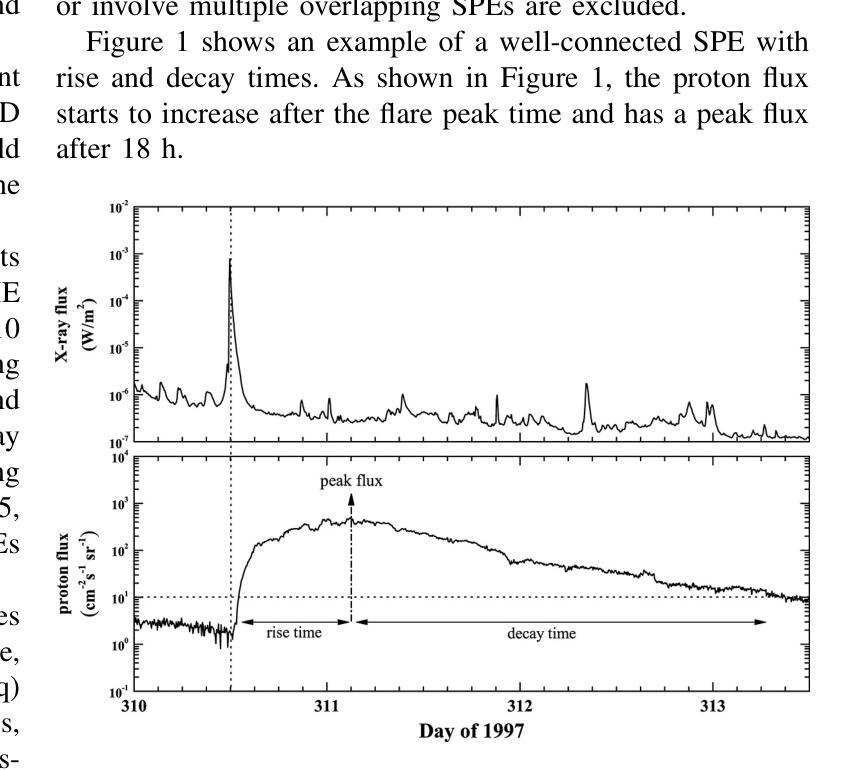
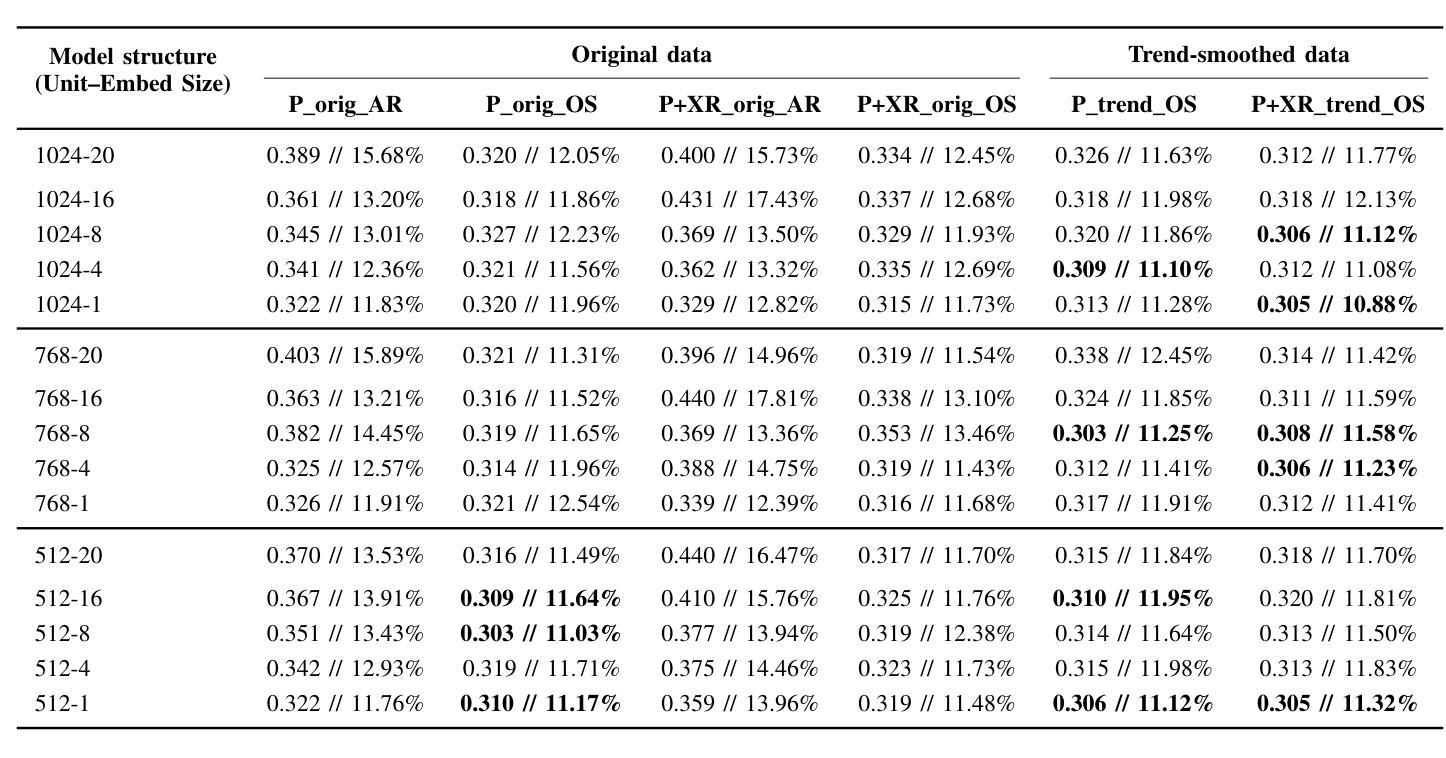
Comparing LSTM-Based Sequence-to-Sequence Forecasting Strategies for 24-Hour Solar Proton Flux Profiles Using GOES Data
Authors:Kangwoo Yi, Bo Shen, Qin Li, Haimin Wang, Yong-Jae Moon, Jaewon Lee, Hwanhee Lee
Solar Proton Events (SPEs) cause significant radiation hazards to satellites, astronauts, and technological systems. Accurate forecasting of their proton flux time profiles is crucial for early warnings and mitigation. This paper explores deep learning sequence-to-sequence (seq2seq) models based on Long Short-Term Memory networks to predict 24-hour proton flux profiles following SPE onsets. We used a dataset of 40 well-connected SPEs (1997-2017) observed by NOAA GOES, each associated with a >=M-class western-hemisphere solar flare and undisturbed proton flux profiles. Using 4-fold stratified cross-validation, we evaluate seq2seq model configurations (varying hidden units and embedding dimensions) under multiple forecasting scenarios: (i) proton-only input vs. combined proton+X-ray input, (ii) original flux data vs. trend-smoothed data, and (iii) autoregressive vs. one-shot forecasting. Our major results are as follows: First, one-shot forecasting consistently yields lower error than autoregressive prediction, avoiding the error accumulation seen in iterative approaches. Second, on the original data, proton-only models outperform proton+X-ray models. However, with trend-smoothed data, this gap narrows or reverses in proton+X-ray models. Third, trend-smoothing significantly enhances the performance of proton+X-ray models by mitigating fluctuations in the X-ray channel. Fourth, while models trained on trendsmoothed data perform best on average, the best-performing model was trained on original data, suggesting that architectural choices can sometimes outweigh the benefits of data preprocessing.
太阳质子事件(SPEs)对卫星、宇航员和技术系统造成重大辐射危害。准确地预测其质子流量时间分布对于提前预警和缓解至关重要。本文探讨了基于长短时记忆网络的深度学习序列到序列(seq2seq)模型,用于预测SPE发生后24小时的质子流量分布。我们使用了NOAA GOES观测到的40个联系紧密的SPEs数据集(1997-2017年),每个事件都与西部半球太阳耀斑的M级或以上级别以及未受干扰的质子流量分布相关。采用4折分层交叉验证,我们评估了不同配置的seq2seq模型(变化隐藏单元和嵌入维度)在多种预测场景下的表现:(i)仅质子输入与组合质子+X射线输入,(ii)原始流量数据与趋势平滑数据,以及(iii)自回归与一次性预测。我们的主要结果如下:首先,一次性预测产生的误差始终低于自回归预测,避免了迭代方法中出现的误差累积。其次,在原始数据上,仅质子模型的表现优于质子+X射线模型。然而,在趋势平滑的数据上,这一差距缩小或甚至逆转了。第三,趋势平滑会显著改善质子+X射线模型的表现,通过减轻X射线通道的波动来实现。第四,虽然在趋势平滑数据上训练的模型平均表现最佳,但表现最好的模型是在原始数据上训练的,这表明架构的选择有时可能会超过数据预处理的优点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages; accepted as a workshop paper at ICDM 2025
Summary
本文利用深度学习序列到序列模型(seq2seq)结合长期短期记忆网络(LSTM),对太阳质子事件(SPEs)发生后的24小时质子流量进行预测。文章通过多项实验验证了不同的模型配置,发现趋势平滑处理能够提高模型性能,特别是在包含质子及X射线输入的模型中表现明显。最佳模型基于原始数据训练得到,说明模型架构的选择有时能够抵消数据预处理的潜在优势。本文研究成果对提前预警和缓解SPE引发的辐射危害具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- 深宎学习序列到序列模型(seq2seq)结合LSTM网络用于预测SPE发生后的24小时质子流量。
- 实验验证了不同的模型配置,包括隐藏单元和嵌入维度的变化。
- 发现趋势平滑处理能够提高模型性能,特别是在包含质子及X射线输入的模型中。
- 最佳模型基于原始数据训练得到,强调模型架构选择的重要性。
点此查看论文截图
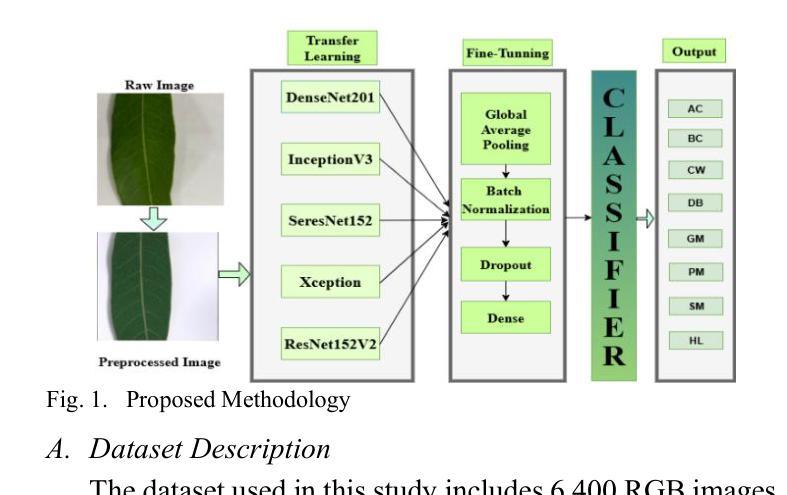
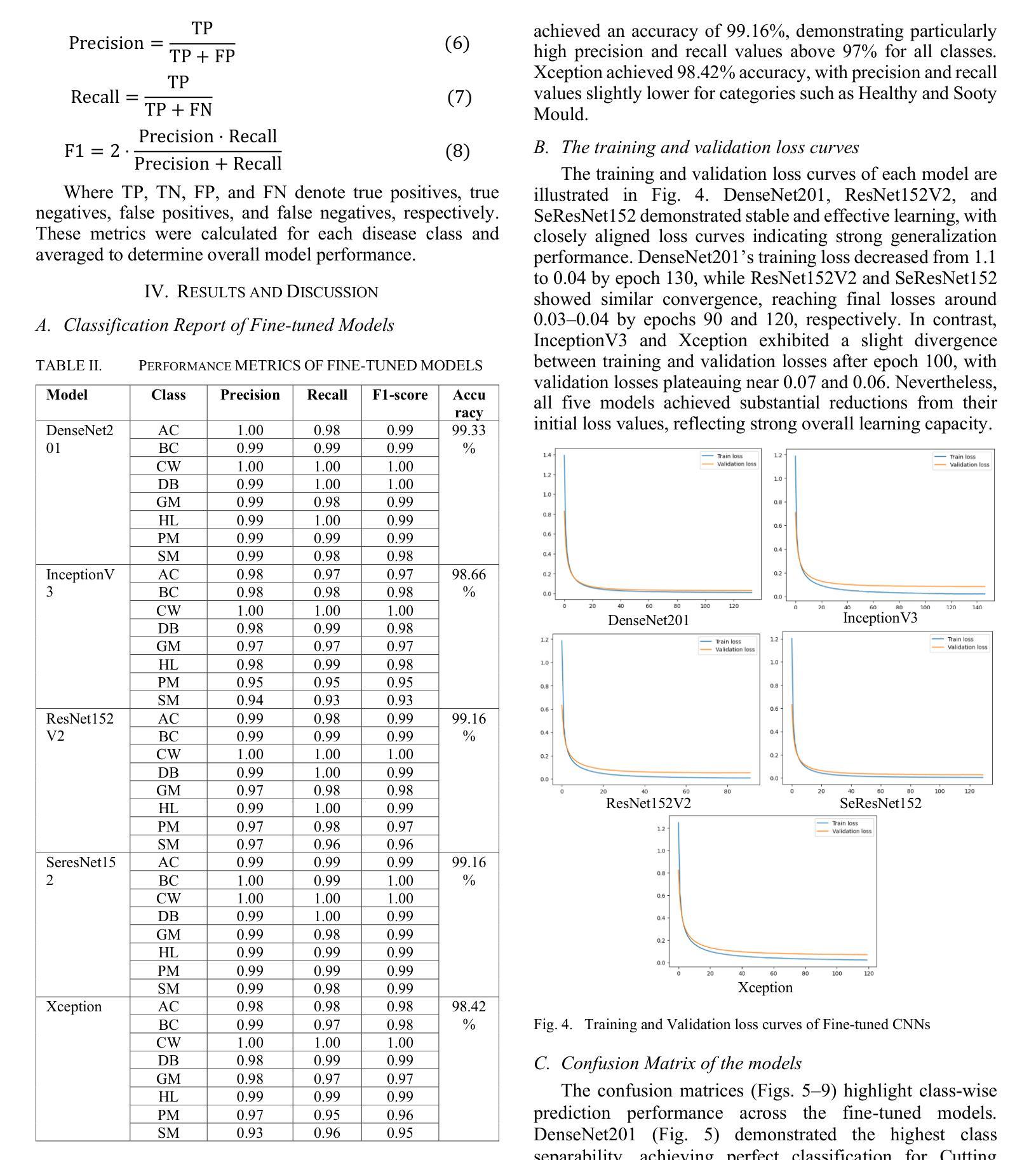
Fine-Tuned CNN-Based Approach for Multi-Class Mango Leaf Disease Detection
Authors:Jalal Ahmmed, Faruk Ahmed, Rashedul Hasan Shohan, Md. Mahabub Rana, Mahdi Hasan
Mango is an important fruit crop in South Asia, but its cultivation is frequently hampered by leaf diseases that greatly impact yield and quality. This research examines the performance of five pre-trained convolutional neural networks, DenseNet201, InceptionV3, ResNet152V2, SeResNet152, and Xception, for multi-class identification of mango leaf diseases across eight classes using a transfer learning strategy with fine-tuning. The models were assessed through standard evaluation metrics, such as accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and confusion matrices. Among the architectures tested, DenseNet201 delivered the best results, achieving 99.33% accuracy with consistently strong metrics for individual classes, particularly excelling in identifying Cutting Weevil and Bacterial Canker. Moreover, ResNet152V2 and SeResNet152 provided strong outcomes, whereas InceptionV3 and Xception exhibited lower performance in visually similar categories like Sooty Mould and Powdery Mildew. The training and validation plots demonstrated stable convergence for the highest-performing models. The capability of fine-tuned transfer learning models, for precise and dependable multi-class mango leaf disease detection in intelligent agricultural applications.
芒果是南亚重要的果树作物,但其栽培经常受到叶片疾病的困扰,对产量和质量产生很大影响。本研究采用迁移学习策略,通过微调,对五种预训练的卷积神经网络(DenseNet201、InceptionV3、ResNet152V2、SeResNet152和Xception)进行了多类芒果叶病识别性能的研究。这些模型通过准确率、精确度、召回率、F1分数和混淆矩阵等标准评价指标进行了评估。在测试的架构中,DenseNet201取得了最佳结果,其准确率达到99.33%,并且各类别的指标表现一直强劲,特别是在识别切割锯木虫和细菌性溃疡方面表现出色。此外,ResNet152V2和SeResNet152也取得了良好的效果,而InceptionV3和Xception在视觉上相似的类别(如煤烟病和粉状白粉病)中表现较差。训练图和验证图显示了高性能模型的稳定收敛性。微调迁移学习模型在智能农业应用中精确可靠的多类芒果叶病检测能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Double column 6 pages, 10 figures, ieee conference style
Summary
本研究利用迁移学习策略微调五种预训练卷积神经网络,包括DenseNet201、InceptionV3、ResNet152V2、SeResNet152和Xception,对南亚热带地区芒果叶病害进行多类识别。研究中通过准确率、精确度、召回率、F1分数和混淆矩阵等标准评价指标对模型进行评估。结果表明,DenseNet201表现最佳,准确率高达99.33%,对切割钻心症和细菌性溃疡病识别尤为出色。其他模型如ResNet152V2和SeResNet152表现良好,而InceptionV3和Xception在视觉上相似的类别如霉斑病和白粉病中的表现较差。高性能模型的训练和验证图显示稳定收敛。这些微调后的迁移学习模型可用于智能农业应用中的精准可靠芒果叶多病害检测。
Key Takeaways
- 研究利用五种预训练卷积神经网络对芒果叶病害进行多类识别。
- DenseNet201在芒果叶病害识别中表现最佳,准确率高。
- ResNet152V2和SeResNet152在芒果叶病害识别中表现良好。
- InceptionV3和Xception在视觉上相似的类别识别中表现较差。
- 迁移学习策略能有效应用于芒果叶病害的精准检测。
- 研究通过标准评价指标全面评估了各模型的表现。
点此查看论文截图

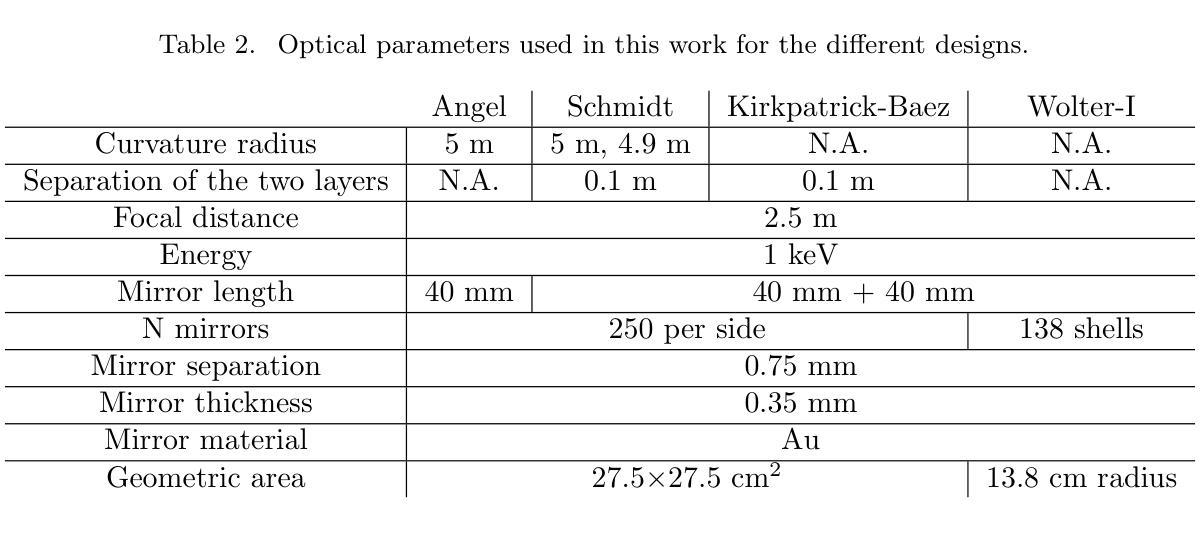
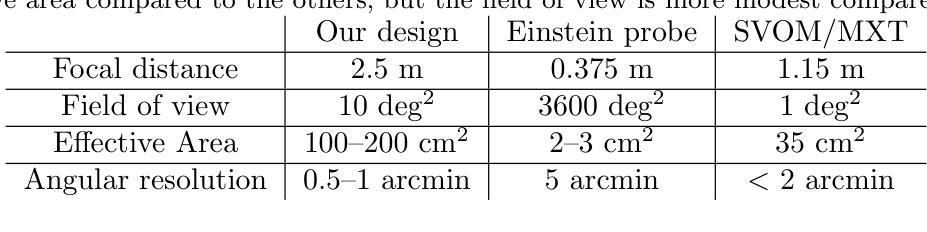
Study of Lobster and Kirkpatrick-Baez Designs for a Small Mission dedicated to Gravitational Wave Transient Localization
Authors:John Rankin, Sergio Campana, Giovanni Pareschi, Daniele Spiga, Stefano Basso, Marta Maria Civitani, Paolo Conconi, Vincenzo Cotroneo
The localization of X-ray counterparts to gravitational wave events requires a telescope with accurate localization capability in a field of view comparable to the region constrained by the gravitational wave detectors. In the context of a small, dedicated, mission, we investigate which optical design could satisfy this capability. We compare the possible optical designs that have been proposed for X-rays: the Lobster Eye design (both in the Angel and Schmidt variant) - inspired by the eyes of crustaceans - consisting of many small capillaries where grazing incidence reflection occurs, the Kirkpatrick-Baez design, where double reflection occurs on two orthogonal parabolic mirrors, and the standard Wolter-I design. We find that the first two designs, compared to the latter, can achieve a significantly larger field of view, and have a good localization capability if the focal length is longer than existing Lobster Eye designs. The Kirkpatrick-Baez design presents the best angular resolution, but the best overall field of view is obtained with a Lobster system: we present a small optical module able to achieve an effective area $>$100 cm$^2$ at 1 keV in a field of view of 10 deg$^2$.
对引力波事件的X射线对应物的定位要求有一种望远镜,其定位精度要相当高,且在其视场范围需要与由引力波探测器所约束的区域相当。在一个小型的专门任务中,我们调查了哪种光学设计可以满足这一能力。我们对已提出的用于X射线的可能光学设计进行了比较:龙虾眼设计(包括天使和施密特变体)——这是受甲壳动物眼睛的启发,由许多发生掠射反射的小毛细血管组成,柯克帕特里克-贝兹设计,其中两次反射发生在两个正交的抛物面镜上,以及标准的沃尔特I型设计。我们发现,与后者相比,前两种设计可以实现更大的视场,如果焦距长于现有的龙虾眼设计,则具有良好的定位能力。柯克帕特里克-贝兹设计具有最佳的角分辨率,但最佳总体视场是由龙虾系统获得的:我们提出了一种小型光学模块,能够在10平方度的视场范围内实现大于100平方厘米的有效面积在只有只有几度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
对于X射线对应引力波事件定位的需求,需要望远镜具有准确的定位能力,其视场需与引力波探测器所限定的区域相当。在小型专用任务的背景下,我们调查了哪些光学设计可以满足这种能力。比较了为X射线提出的光学设计方案,包括龙虾眼设计(天使和施密特变体),其由许多小毛细血管组成,发生倾斜入射反射;基尔克帕特里克-贝兹设计,其中两次反射发生在两个正交抛物镜上;以及标准的沃尔特-I设计。我们发现前两种设计与后者相比,可以实现更大的视场,如果焦距长于现有龙虾眼设计,则具有良好的定位能力。基尔克帕特里克-贝兹设计具有最佳角分辨率,但整体最佳视场是由龙虾系统获得的:我们提出一种小型光学模块,能在10 deg$^2$的视场上实现大于100 cm$^2$的有效面积,在1 keV时表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 对于定位X射线对应引力波事件,需要望远镜具备在较大视场上进行准确定位的能力。
- 龙虾眼设计和基尔克帕特里克-贝兹设计相较于标准沃尔特-I设计,能够实现更大的视场。
- 龙虾眼设计的优势在于其独特的结构能够实现良好的定位能力,尤其在焦距较长的情况下。
- 基尔克帕特里克-贝兹设计在角分辨率上具有最佳表现。
- 最佳的整体视场是通过龙虾系统实现的。
- 提出了一种新型小型光学模块,能在较大的视场上实现较大的有效面积,尤其在1 keV时表现优异。
点此查看论文截图
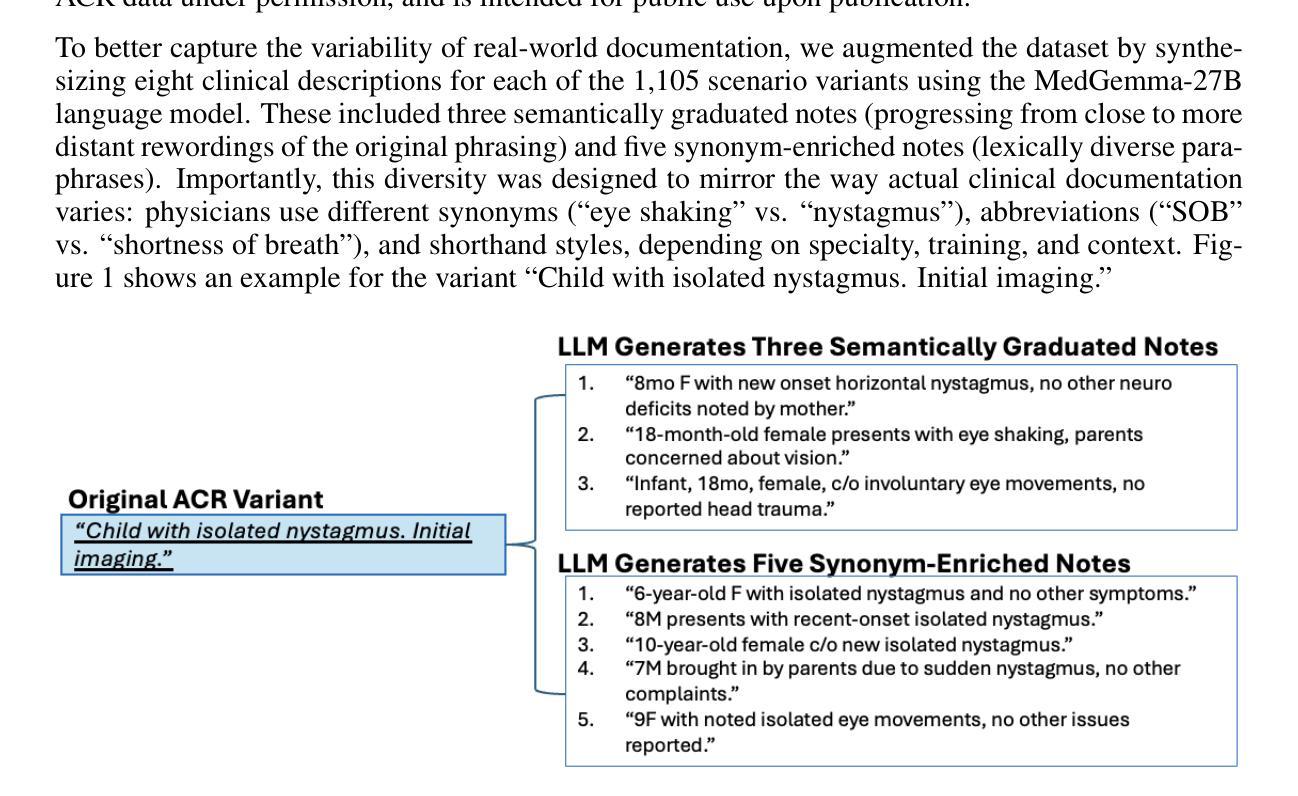
Bridging Clinical Narratives and ACR Appropriateness Guidelines: A Multi-Agent RAG System for Medical Imaging Decisions
Authors:Satrio Pambudi, Filippo Menolascina
The selection of appropriate medical imaging procedures is a critical and complex clinical decision, guided by extensive evidence-based standards such as the ACR Appropriateness Criteria (ACR-AC). However, the underutilization of these guidelines, stemming from the difficulty of mapping unstructured patient narratives to structured criteria, contributes to suboptimal patient outcomes and increased healthcare costs. To bridge this gap, we introduce a multi-agent cognitive architecture that automates the translation of free-text clinical scenarios into specific, guideline-adherent imaging recommendations. Our system leverages a novel, domain-adapted dense retrieval model, ColBERT, fine-tuned on a synthetically generated dataset of 8,840 clinical scenario-recommendation pairs to achieve highly accurate information retrieval from the ACR-AC knowledge base. This retriever identifies candidate guidelines with a 93.9% top-10 recall, which are then processed by a sequence of LLM-based agents for selection and evidence-based synthesis. We evaluate our architecture using GPT-4.1 and MedGemma agents, demonstrating a state-of-the-art exact match accuracy of 81%, meaning that in 81% of test cases the predicted procedure set was identical to the guideline’s reference set, and an F1-score of 0.879. This represents a 67-percentage-point absolute improvement in accuracy over a strong standalone GPT-4.1 baseline, underscoring the contribution that our architecture makes to a frontier model. These results were obtained on a challenging test set with substantial lexical divergence from the source guidelines. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/demo-iclr-B567/
选择适当的医学成像程序是一项重要而复杂的临床决策,由诸如ACR适宜性标准(ACR-AC)等基于大量证据的标准指导。然而,由于将非结构化患者叙述映射到结构化标准上的难度,这些指南的利用不足导致了患者结果不理想和医疗保健成本增加。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了一种多智能体认知架构,该架构可以自动将自由文本临床情景转化为特定的、符合指南的成像建议。我们的系统利用了一种新型的、适应领域的密集检索模型ColBERT,它在8840个临床情景建议对上合成的数据集上进行微调,以从ACR-AC知识库中实现高度准确的信息检索。该检索器以93.9%的前十召回率识别候选指南,然后经由一系列基于LLM的智能体进行选择和基于证据的综合处理。我们使用GPT 4.1和MedGemma智能体评估我们的架构,表现出了最先进的精确匹配准确率81%,这意味着在81%的测试案例中,预测的程序集与指南的参考集相同,以及F1分数为0.879。相较于强大的独立GPT 4.1基线,我们的架构在准确性上实现了高达67个百分点的绝对提升,突显了我们的架构对前沿模型的贡献。这些结果是在一个具有与来源指南显著词汇差异的具有挑战性的测试集上获得的。我们的代码可在 https://anonymous.4open.science/r/demo-iclr-B567/ 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种多智能体认知架构,该架构能够将自由文本的临床场景自动转化为符合指南的成像建议。通过使用域适应密集检索模型ColBERT,结合合成数据集进行微调,系统实现了从ACR-AC知识库中高度准确的信息检索。该架构使用GPT-4.1和MedGemma智能体进行评估,在挑战测试集上取得了显著的成绩改进。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像程序的选择是一个受证据标准(如ACR适宜性标准)指导的重要且复杂的临床决策。
- 未充分利用这些指南源于将非结构化患者叙事映射到结构化标准的困难,可能导致患者结果不佳和医疗保健成本增加。
- 提出了一种多智能体认知架构,能够自动将自由文本临床场景转化为具体的、符合指南的成像建议。
- 使用域适应密集检索模型ColBERT,在合成数据集上微调,实现高度准确的信息从ACR-AC知识库中检索。
- 检索模型能够在前十个候选指南中达到93.9%的召回率。
- 使用GPT-4.1和MedGemma智能体评估架构,获得业界最佳精确匹配准确率81%,F1分数为0.879。
点此查看论文截图
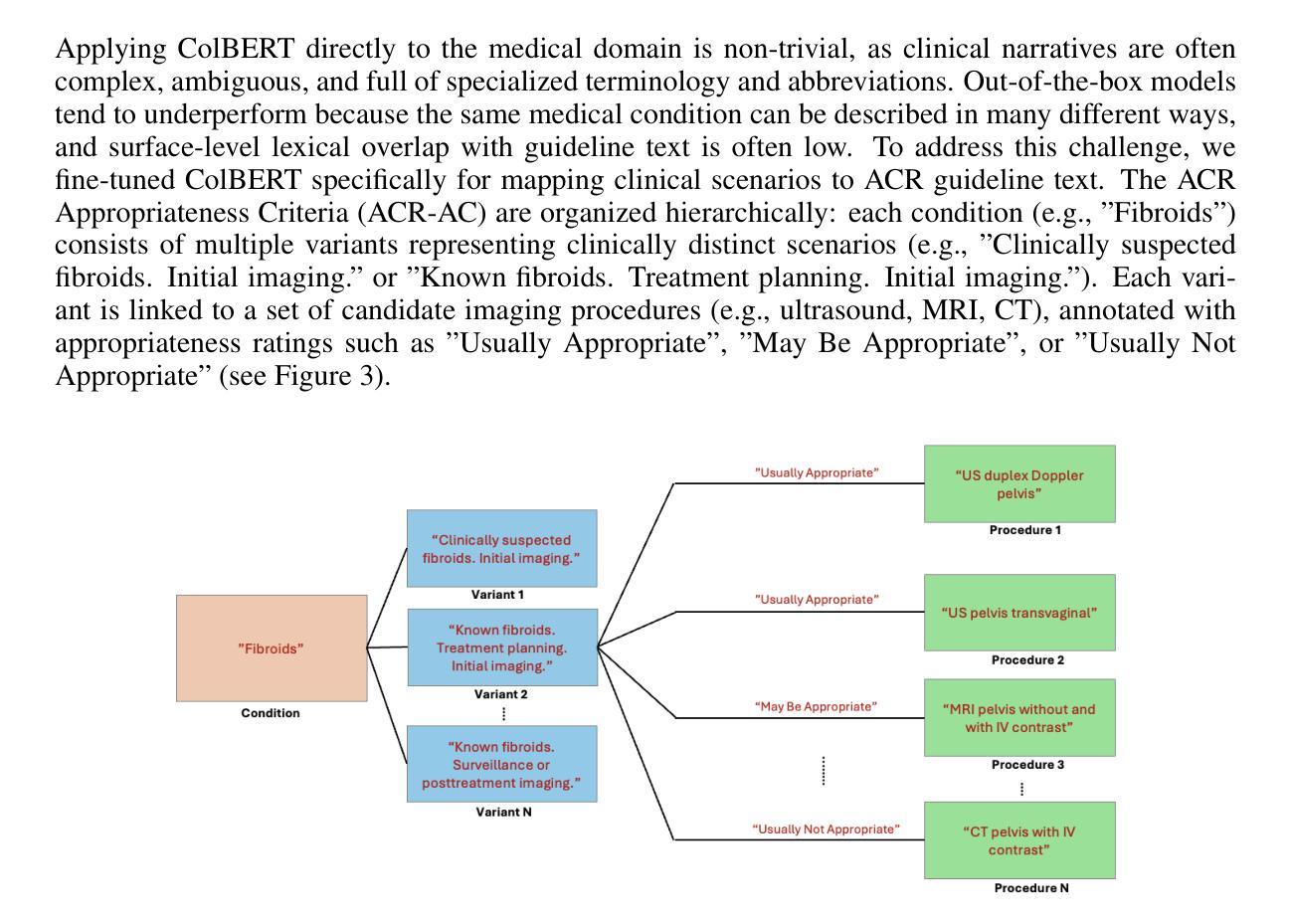
Bidirectional Mammogram View Translation with Column-Aware and Implicit 3D Conditional Diffusion
Authors:Xin Li, Kaixiang Yang, Qiang Li, Zhiwei Wang
Dual-view mammography, including craniocaudal (CC) and mediolateral oblique (MLO) projections, offers complementary anatomical views crucial for breast cancer diagnosis. However, in real-world clinical workflows, one view may be missing, corrupted, or degraded due to acquisition errors or compression artifacts, limiting the effectiveness of downstream analysis. View-to-view translation can help recover missing views and improve lesion alignment. Unlike natural images, this task in mammography is highly challenging due to large non-rigid deformations and severe tissue overlap in X-ray projections, which obscure pixel-level correspondences. In this paper, we propose Column-Aware and Implicit 3D Diffusion (CA3D-Diff), a novel bidirectional mammogram view translation framework based on conditional diffusion model. To address cross-view structural misalignment, we first design a column-aware cross-attention mechanism that leverages the geometric property that anatomically corresponding regions tend to lie in similar column positions across views. A Gaussian-decayed bias is applied to emphasize local column-wise correlations while suppressing distant mismatches. Furthermore, we introduce an implicit 3D structure reconstruction module that back-projects noisy 2D latents into a coarse 3D feature volume based on breast-view projection geometry. The reconstructed 3D structure is refined and injected into the denoising UNet to guide cross-view generation with enhanced anatomical awareness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CA3D-Diff achieves superior performance in bidirectional tasks, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in visual fidelity and structural consistency. Furthermore, the synthesized views effectively improve single-view malignancy classification in screening settings, demonstrating the practical value of our method in real-world diagnostics.
双视角乳腺造影术包括颅尾(CC)和内外斜(MLO)投影,提供了相互补充的解剖学视角,对乳腺癌诊断至关重要。然而,在现实的临床工作流程中,由于采集错误或压缩伪影等原因,某一视角可能会缺失、损坏或退化,限制了后续分析的有效性。视角到视角的翻译可以帮助恢复缺失的视角并提高病变对齐。然而,与天然图像相比,这一任务在乳腺造影中非常具有挑战性,因为存在大的非刚性变形和严重的组织重叠在X射线投影中,这掩盖了像素级的对应关系。在本文中,我们提出了基于条件扩散模型的列感知和隐式三维扩散(CA3D-Diff)双向乳腺造影视图翻译框架。为了解决跨视图的结构不匹配问题,我们首先设计了一种列感知交叉注意机制,该机制利用几何属性,即解剖对应区域倾向于位于不同视图中的相似列位置。应用高斯衰减偏差以强调局部列相关性,同时抑制远距离不匹配。此外,我们引入了一个隐式三维结构重建模块,该模块将噪声二维潜在变量反投影到基于乳腺视图投影几何的粗糙三维特征体积中。重建的三维结构经过细化并注入去噪UNet中,以指导具有增强解剖学意识的跨视图生成。大量实验表明,CA3D-Diff在双向任务上表现出卓越的性能,在视觉保真度和结构一致性方面优于最新技术方法。此外,合成的视图有效地提高了单视角恶性肿瘤分类在筛查环境中的性能,证明了我们的方法在真实世界诊断中的实用价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF BIBM2025 accept, 8 pages, 4 figures
摘要
双视角乳腺摄影(包括颅尾投影和内外斜位投影)为乳腺癌诊断提供了互补的解剖视图。然而,在实际的临床工作流程中,某一视角可能缺失、损坏或退化,这会影响后续分析的有效性。视图到视图的转换可以帮助恢复缺失的视图并提高病变对齐的准确性。本文提出一种基于条件扩散模型的双向乳腺摄影视图转换框架——列感知与隐式三维扩散(CA3D-Diff)。为解决跨视图结构错位问题,我们设计了一种列感知交叉注意力机制,利用几何属性中解剖对应区域倾向于位于相似列位置的特点。此外,我们引入了一种隐式三维结构重建模块,根据乳房视图投影几何将噪声二维潜在变量投影到粗糙的三维特征体积中。重建的三维结构经过优化后注入去噪UNet中,以指导具有增强解剖意识的跨视图生成。实验表明,CA3D-Diff在双向任务上实现卓越性能,在视觉保真度和结构一致性方面超越现有方法。此外,合成的视图有效提高单视图恶性肿瘤分类的筛查效果,证明了我们方法在真实世界诊断中的实用价值。
关键见解
- 双视角乳腺摄影对于乳腺癌诊断至关重要,但实际应用中可能存在视角缺失、损坏或退化的问题。
- 视图到视图的转换有助于恢复缺失的视图并提高病变对齐的准确性。
- 论文提出了一种新型的双向乳腺摄影视图转换框架——CA3D-Diff,基于条件扩散模型。
- CA3D-Diff采用列感知交叉注意力机制解决跨视图结构错位问题,利用解剖对应区域的几何属性。
- 隐式三维结构重建模块用于将噪声二维潜在变量投影到三维特征体积中,增强解剖意识。
- 实验显示CA3D-Diff在视觉保真度和结构一致性方面超越现有方法,合成的视图在单视图恶性肿瘤分类中具有实用价值。
点此查看论文截图

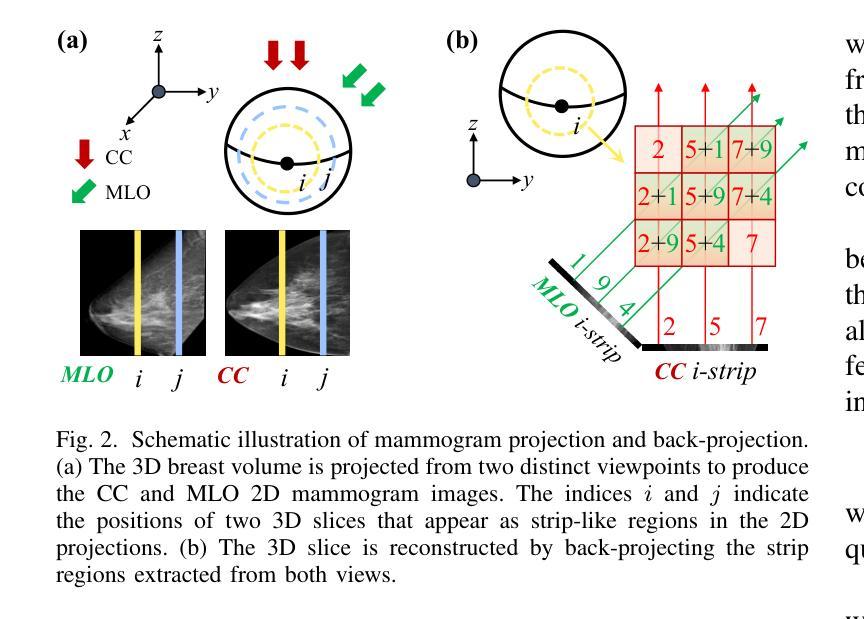
Do Superpixel Segmentation Methods Influence Deforestation Image Classification?
Authors:Hugo Resende, Fabio A. Faria, Eduardo B. Neto, Isabela Borlido, Victor Sundermann, Silvio Jamil F. Guimarães, Álvaro L. Fazenda
Image segmentation is a crucial step in various visual applications, including environmental monitoring through remote sensing. In the context of the ForestEyes project, which combines citizen science and machine learning to detect deforestation in tropical forests, image segments are used for labeling by volunteers and subsequent model training. Traditionally, the Simple Linear Iterative Clustering (SLIC) algorithm is adopted as the segmentation method. However, recent studies have indicated that other superpixel-based methods outperform SLIC in remote sensing image segmentation, and might suggest that they are more suitable for the task of detecting deforested areas. In this sense, this study investigated the impact of the four best segmentation methods, together with SLIC, on the training of classifiers for the target application. Initially, the results showed little variation in performance among segmentation methods, even when selecting the top five classifiers using the PyCaret AutoML library. However, by applying a classifier fusion approach (ensemble of classifiers), noticeable improvements in balanced accuracy were observed, highlighting the importance of both the choice of segmentation method and the combination of machine learning-based models for deforestation detection tasks.
图像分割是各种视觉应用中的关键步骤,包括通过遥感进行环境监测。在ForestEyes项目的背景下,该项目结合公民科学和机器学习来检测热带森林的砍伐活动,图像段落被志愿者用于标注和随后的模型训练。传统上,采用Simple Linear Iterative Clustering(SLIC)算法作为分割方法。然而,最近的研究表明,其他基于超像素的方法在遥感图像分割中优于SLIC,并且可能更适合检测砍伐区的任务。因此,本研究调查了四种最佳分割方法以及SLIC对目标应用分类器训练的影响。初步结果表明,分割方法之间的性能变化不大,即使在使用PyCaret AutoML库选择前五个分类器时也是如此。然而,通过应用分类器融合方法(分类器组合),观察到平衡精度的明显提高,这突出了选择分割方法和结合机器学习模型进行砍伐检测任务的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 3 figures, paper accepted to present at CIARP 2025
Summary
在ForestEyes项目中,图像分割是检测热带森林砍伐工作的重要步骤之一。传统上采用Simple Linear Iterative Clustering (SLIC)算法进行图像分割,但本研究探讨了四种最佳分割方法和SLIC对目标应用分类器训练的影响。结果显示,采用分类器融合方法(分类器集合)能够提高平衡精度,这表明分割方法的选择以及机器学习模型的组合对砍伐检测任务至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 图像分割在包括环境遥感监测在内的各种视觉应用中至关重要。
- ForestEyes项目结合公民科学和机器学习检测热带森林砍伐情况。
- 传统上采用SLIC算法进行图像分割。
- 有研究表明其他超像素分割方法在遥感图像分割上优于SLIC。
- 不同分割方法对分类器训练影响较小,但采用分类器融合方法能显著提高平衡精度。
- 分割方法的选择对砍伐检测任务至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

The best performance in the CARE 2025 – Liver Task (LiSeg-Contrast): Contrast-Aware Semi-Supervised Segmentation with Domain Generalization and Test-Time Adaptation
Authors:Jincan Lou, Jingkun Chen, Haoquan Li, Hang Li, Wenjian Huang, Weihua Chen, Fan Wang, Jianguo Zhang
Accurate liver segmentation from contrast-enhanced MRI is essential for diagnosis, treatment planning, and disease monitoring. However, it remains challenging due to limited annotated data, heterogeneous enhancement protocols, and significant domain shifts across scanners and institutions. Traditional image-to-image translation frameworks have made great progress in domain generalization, but their application is not straightforward. For example, Pix2Pix requires image registration, and cycle-GAN cannot be integrated seamlessly into segmentation pipelines. Meanwhile, these methods are originally used to deal with cross-modality scenarios, and often introduce structural distortions and suffer from unstable training, which may pose drawbacks in our single-modality scenario. To address these challenges, we propose CoSSeg-TTA, a compact segmentation framework for the GED4 (Gd-EOB-DTPA enhanced hepatobiliary phase MRI) modality built upon nnU-Netv2 and enhanced with a semi-supervised mean teacher scheme to exploit large amounts of unlabeled volumes. A domain adaptation module, incorporating a randomized histogram-based style appearance transfer function and a trainable contrast-aware network, enriches domain diversity and mitigates cross-center variability. Furthermore, a continual test-time adaptation strategy is employed to improve robustness during inference. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework consistently outperforms the nnU-Netv2 baseline, achieving superior Dice score and Hausdorff Distance while exhibiting strong generalization to unseen domains under low-annotation conditions.
从对比增强MRI进行准确的肝脏分割对于诊断、治疗规划和疾病监测至关重要。然而,由于标注数据有限、增强协议异质化以及扫描仪和机构间的领域漂移,这仍然是一个挑战。传统的图像到图像翻译框架在领域通用化方面取得了很大进展,但其应用并不直接。例如,Pix2Pix需要进行图像注册,而循环GAN无法无缝集成到分割管道中。同时,这些方法最初是用于处理跨模态场景的,经常会引入结构失真并面临训练不稳定的问题,这可能会在我们的单模态场景中造成缺陷。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了CoSSeg-TTA,这是一个紧凑的分割框架,用于GED4(Gd-EOB-DTPA增强肝胆期MRI)模态,基于nnU-Netv2构建,并使用半监督均值教师方案来利用大量未标记的体积数据。一个领域适应模块,结合基于随机直方图的风格外观转移函数和可训练的对比感知网络,丰富了领域多样性并减轻了跨中心变异性。此外,采用连续测试时间适应策略,以提高推理过程中的稳健性。大量实验表明,我们的框架始终优于nnU-Netv2基线,在达到较高的Dice分数和Hausdorff距离的同时,在低注释条件下对未见领域表现出强大的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文提出一种针对GED4模态的紧凑分割框架CoSSeg-TTA,该框架基于nnU-Netv2,并采用半监督均值教师方案,利用大量未标记体积数据。通过领域适应模块和持续测试时适应策略,该框架提高了领域多样性和跨中心变异的应对能力,且在低标注条件下表现出良好的泛化性能,相较于nnU-Netv2基准框架有更优秀的Dice分数和Hausdorff距离。
Key Takeaways
- 肝脏分割在对比增强MRI中非常重要,但存在标注数据有限、增强协议异质性和跨扫描仪和机构领域漂移等挑战。
- 传统图像到图像翻译框架在领域通用化方面取得进展,但在单模态场景中应用存在困难,如Pix2Pix需要图像配准,cycle-GAN无法无缝集成到分割管道中。
- 提出的CoSSeg-TTA框架针对GED4模态,基于nnU-Netv2并增强半监督均值教师方案,利用大量未标记体积数据。
- 领域适应模块通过随机直方图样式的风格转换功能和可训练的对比感知网络,丰富了领域多样性和减轻了跨中心变异。
- 采用持续测试时适应策略,提高推理时的稳健性。
- 实验表明,CoSSeg-TTA框架比nnU-Netv2基线更优秀,具有更高的Dice分数和更小的Hausdorff距离。
点此查看论文截图

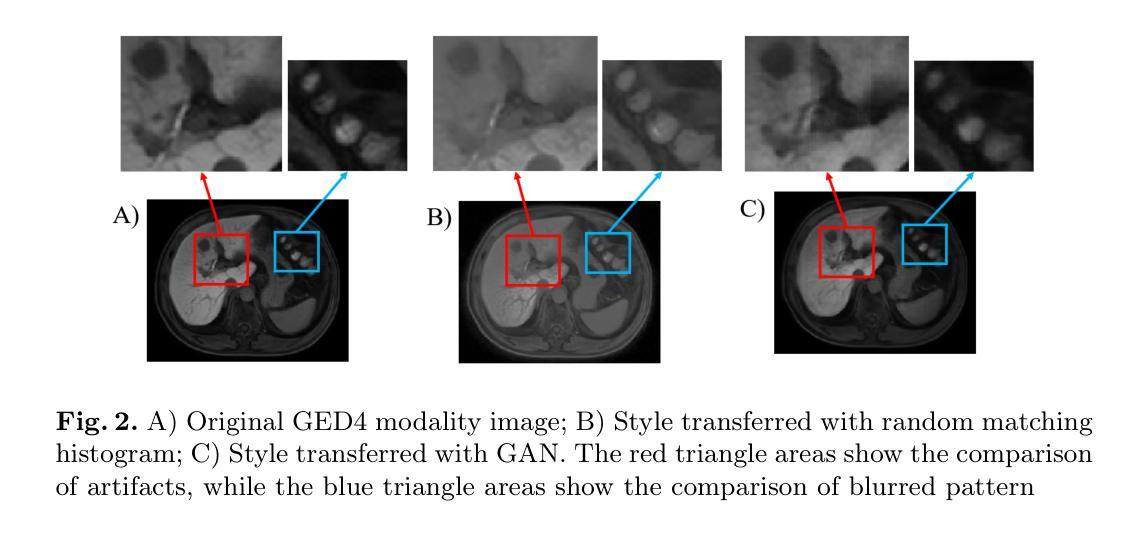
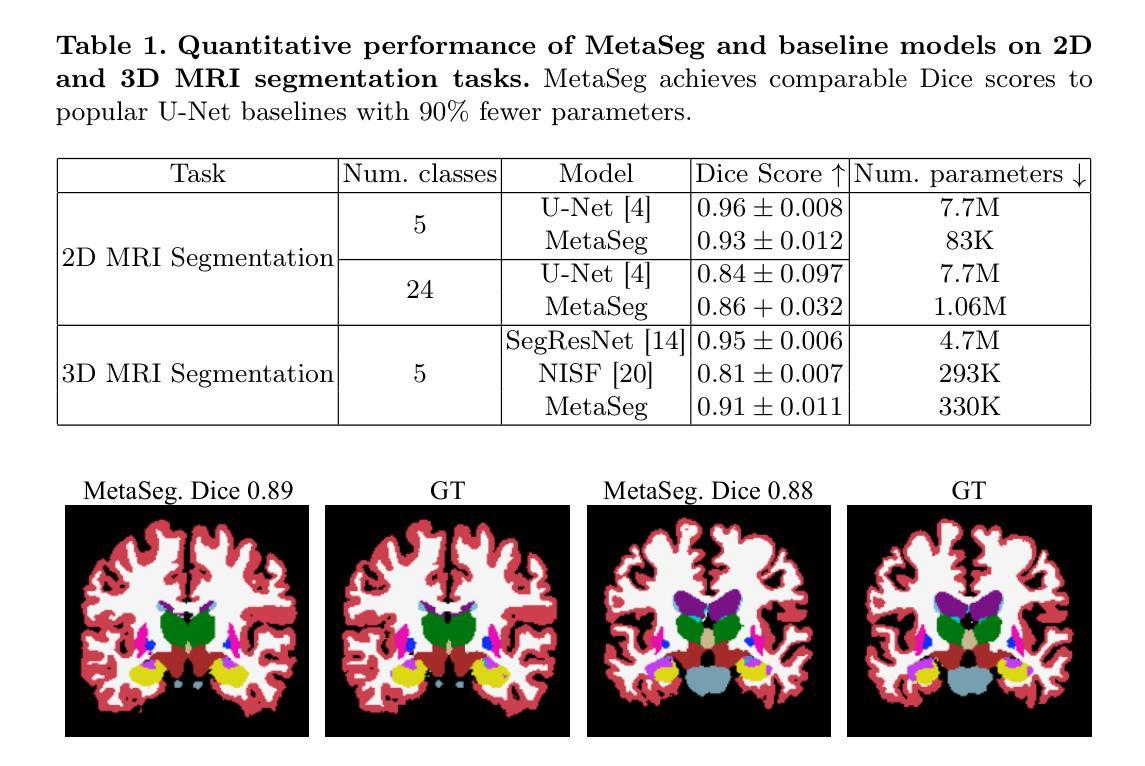
Fit Pixels, Get Labels: Meta-learned Implicit Networks for Image Segmentation
Authors:Kushal Vyas, Ashok Veeraraghavan, Guha Balakrishnan
Implicit neural representations (INRs) have achieved remarkable successes in learning expressive yet compact signal representations. However, they are not naturally amenable to predictive tasks such as segmentation, where they must learn semantic structures over a distribution of signals. In this study, we introduce MetaSeg, a meta-learning framework to train INRs for medical image segmentation. MetaSeg uses an underlying INR that simultaneously predicts per pixel intensity values and class labels. It then uses a meta-learning procedure to find optimal initial parameters for this INR over a training dataset of images and segmentation maps, such that the INR can simply be fine-tuned to fit pixels of an unseen test image, and automatically decode its class labels. We evaluated MetaSeg on 2D and 3D brain MRI segmentation tasks and report Dice scores comparable to commonly used U-Net models, but with $90%$ fewer parameters. MetaSeg offers a fresh, scalable alternative to traditional resource-heavy architectures such as U-Nets and vision transformers for medical image segmentation. Our project is available at https://kushalvyas.github.io/metaseg.html .
隐式神经表示(INR)在学习表达性强且紧凑的信号表示方面取得了显著的成就。然而,它们并不适合用于预测任务,如分割任务,必须在多种信号分布上学习语义结构。在这项研究中,我们介绍了MetaSeg,这是一种用于医学图像分割的元学习框架。MetaSeg使用一个基础INR,同时预测像素强度值和类别标签。然后它使用一个元学习程序来找到图像和分割图训练数据集上INR的最佳初始参数,以便简单地对看不见的测试图像进行微调,并自动解码其类别标签。我们在二维和三维脑部MRI分割任务上评估了MetaSeg,报告的Dice得分与常用的U-Net模型相当,但参数减少了90%。MetaSeg为传统的资源密集型架构(如U-Net和视觉转换器)提供了一种新的、可扩展的替代方案,用于医学图像分割。我们的项目可在https://kushalvyas.github.io/metaseg.html上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF MICCAI 2025 (oral). Final peer-reviewed copy accessible at publisher DOI https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-032-04947-6_19 . Project page, https://kushalvyas.github.io/metaseg.html
Summary
本摘要介绍了一种用于医学图像分割的元学习框架MetaSeg,结合了隐式神经表示(INR)和元学习技术。MetaSeg可训练INR预测像素强度和类别标签,并利用元学习找到最佳初始参数,使得模型能在未见过的测试图像上进行微调并自动解码类别标签。在2D和3D脑MRI分割任务上,MetaSeg表现与U-Net模型相当,但参数减少了90%。它为医学图像分割提供了传统资源密集型架构的可行替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- MetaSeg结合了隐式神经表示(INR)和元学习,旨在解决医学图像分割任务。
- INR可以同时预测像素强度和类别标签。
- 元学习用于找到最佳初始参数,使模型能在未见过的测试图像上快速适应。
- MetaSeg在2D和3D脑MRI分割任务上表现出色,与U-Net模型相比,Dice得分相当。
- MetaSeg的参数数量减少了90%,相比传统架构更为高效。
- MetaSeg提供了一个可行且可扩展的替代方案,用于替代资源密集型的医学图像分割架构,如U-Nets和视觉转换器。
点此查看论文截图
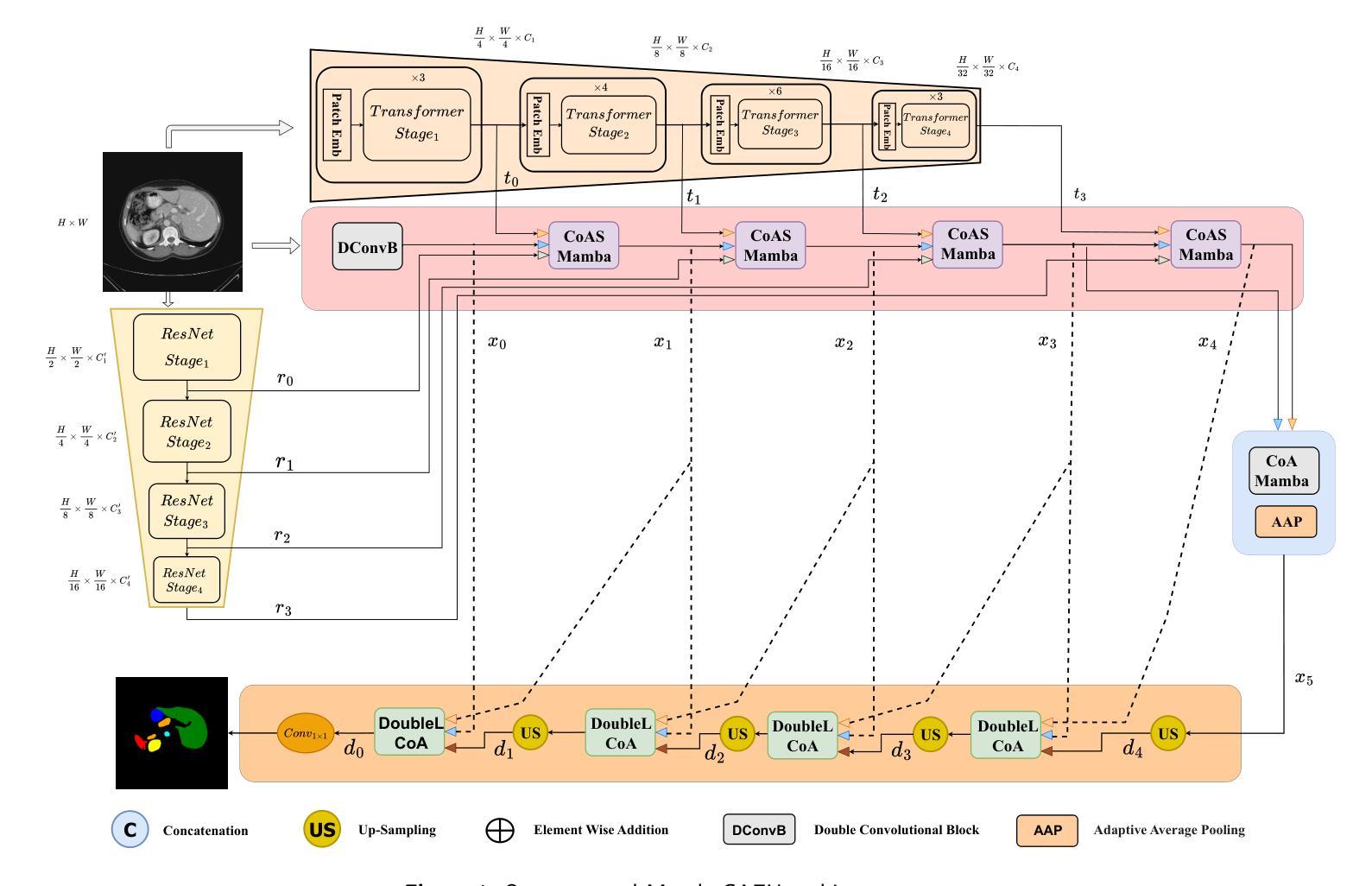
MambaCAFU: Hybrid Multi-Scale and Multi-Attention Model with Mamba-Based Fusion for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:T-Mai Bui, Fares Bougourzi, Fadi Dornaika, Vinh Truong Hoang
In recent years, deep learning has shown near-expert performance in segmenting complex medical tissues and tumors. However, existing models are often task-specific, with performance varying across modalities and anatomical regions. Balancing model complexity and performance remains challenging, particularly in clinical settings where both accuracy and efficiency are critical. To address these issues, we propose a hybrid segmentation architecture featuring a three-branch encoder that integrates CNNs, Transformers, and a Mamba-based Attention Fusion (MAF) mechanism to capture local, global, and long-range dependencies. A multi-scale attention-based CNN decoder reconstructs fine-grained segmentation maps while preserving contextual consistency. Additionally, a co-attention gate enhances feature selection by emphasizing relevant spatial and semantic information across scales during both encoding and decoding, improving feature interaction and cross-scale communication. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods in accuracy and generalization, while maintaining comparable computational complexity. By effectively balancing efficiency and effectiveness, our architecture offers a practical and scalable solution for diverse medical imaging tasks. Source code and trained models will be publicly released upon acceptance to support reproducibility and further research.
近年来,深度学习在分割复杂医学组织和肿瘤方面表现出了接近专家的性能。然而,现有模型往往是针对特定任务的,在不同模态和解剖区域的性能表现不一。在临床医学环境中,平衡模型的复杂性和性能仍然是一个挑战,因为准确性和效率都至关重要。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种混合分割架构,它采用三分支编码器,集成了卷积神经网络(CNN)、Transformer和基于Mamba的注意力融合(MAF)机制,以捕捉局部、全局和长距离依赖关系。基于多尺度注意力机制的CNN解码器能够重建精细的分割图,同时保持上下文一致性。此外,协同注意力门通过在编码和解码过程中强调跨尺度的相关空间和语义信息,增强了特征选择,提高了特征交互和跨尺度通信。在多个基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在准确性和泛化能力上超过了最先进的方法,同时保持了相当的计算复杂度。通过有效地平衡效率和效果,我们的架构为各种医学成像任务提供了实用且可扩展的解决方案。论文被接受后,我们将公开源代码和训练好的模型,以支持可重复性和进一步研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习在医学图像分割中表现接近专家水平,但仍存在模型任务特定、跨模态和解剖区域性能差异等问题。提出一种混合分割架构,包含三分支编码器,结合CNN、Transformer和Mamba基于注意力的融合机制,捕获局部、全局和长距离依赖关系。多尺度注意力CNN解码器重建精细分割图并保持上下文一致性。实验证明该方法在准确性与泛化性能上超越现有先进技术,同时保持相当的计算复杂度。有效平衡效率与效果,为医学成像任务提供实用且可扩展的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在医学图像分割中表现优异,但仍存在模型任务特定和跨模态性能差异问题。
- 提出一种混合分割架构,包含三分支编码器,结合CNN、Transformer和Mamba基于注意力的融合机制。
- 该架构能够捕获局部、全局和长距离依赖关系,提高分割精度。
- 多尺度注意力CNN解码器可重建精细分割图并保持上下文一致性。
- 通过实验证明,该方法在准确性与泛化性能上超越现有技术。
- 该方法在计算复杂度上表现良好,具有实际应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

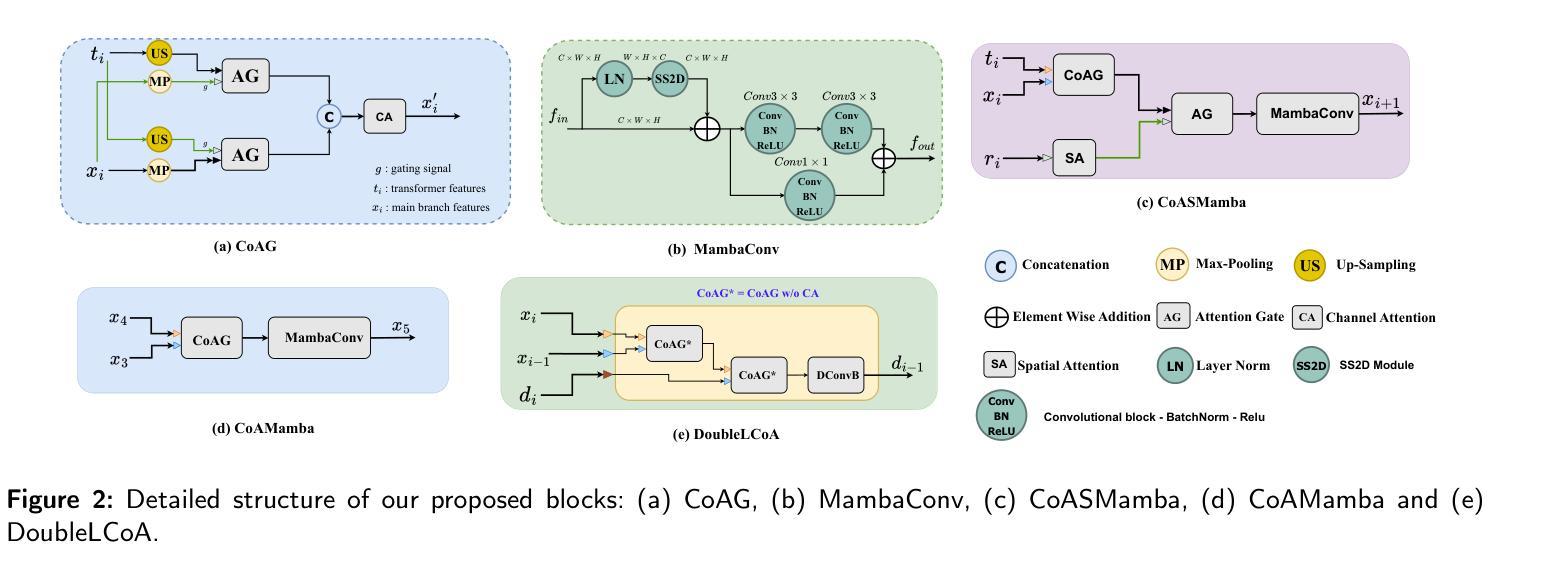
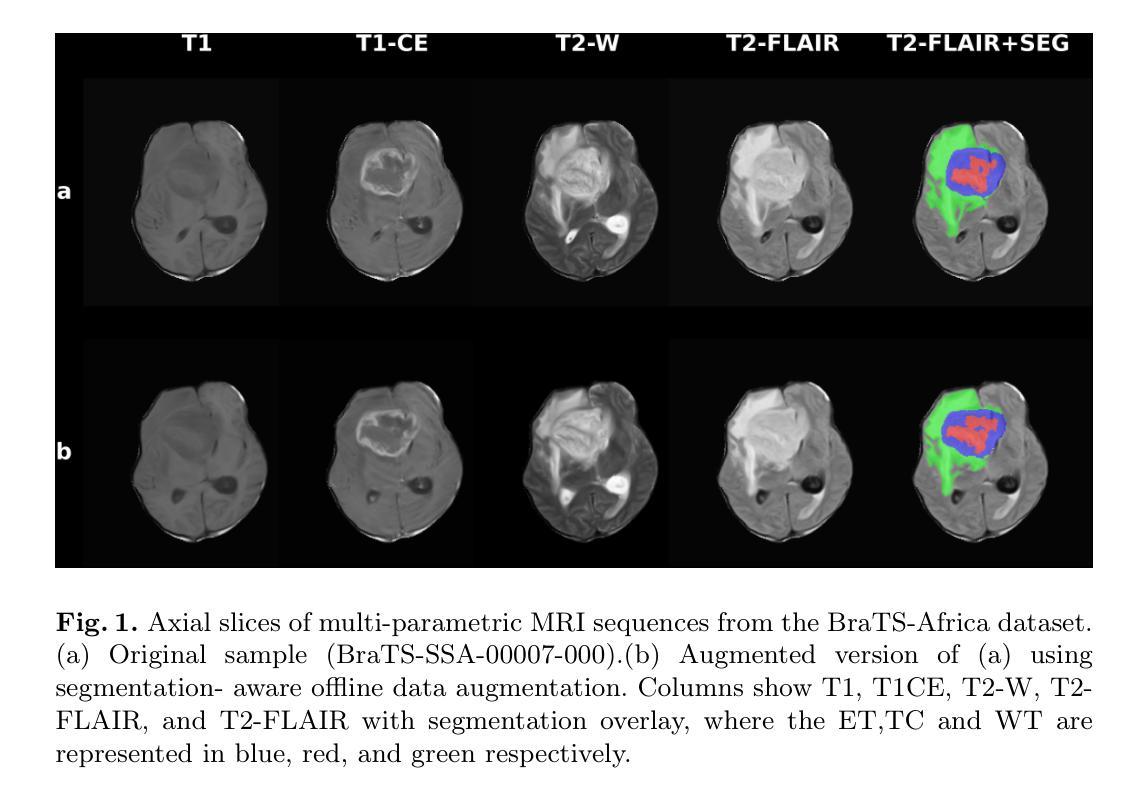
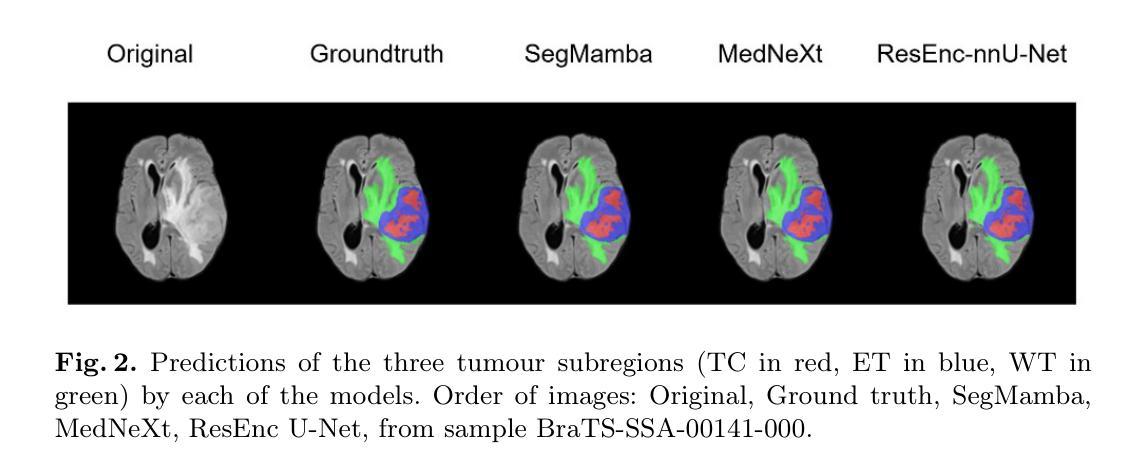
How We Won BraTS-SSA 2025: Brain Tumor Segmentation in the Sub-Saharan African Population Using Segmentation-Aware Data Augmentation and Model Ensembling
Authors:Claudia Takyi Ankomah, Livingstone Eli Ayivor, Ireneaus Nyame, Leslie Wambo, Patrick Yeboah Bonsu, Aondona Moses Iorumbur, Raymond Confidence, Toufiq Musah
Brain tumors, particularly gliomas, pose significant chall-enges due to their complex growth patterns, infiltrative nature, and the variability in brain structure across individuals, which makes accurate diagnosis and monitoring difficult. Deep learning models have been developed to accurately delineate these tumors. However, most of these models were trained on relatively homogenous high-resource datasets, limiting their robustness when deployed in underserved regions. In this study, we performed segmentation-aware offline data augmentation on the BraTS-Africa dataset to increase the data sample size and diversity to enhance generalization. We further constructed an ensemble of three distinct architectures, MedNeXt, SegMamba, and Residual-Encoder U-Net, to leverage their complementary strengths. Our best-performing model, MedNeXt, was trained on 1000 epochs and achieved the highest average lesion-wise dice and normalized surface distance scores of 0.86 and 0.81 respectively. However, the ensemble model trained for 500 epochs produced the most balanced segmentation performance across the tumour subregions. This work demonstrates that a combination of advanced augmentation and model ensembling can improve segmentation accuracy and robustness on diverse and underrepresented datasets. Code available at: https://github.com/SPARK-Academy-2025/SPARK-2025/tree/main/SPARK2025_BraTs_MODELS/SPARK_NeuroAshanti
脑肿瘤,特别是胶质瘤,由于其复杂的生长模式、浸润性和个体间脑结构的变化,给准确诊断和治疗带来了巨大挑战。深度学习模型已被开发出来精准地勾画这些肿瘤。然而,大多数模型是在相对均匀且资源充足的数据集上进行训练的,这在部署到服务不足的地区时限制了其稳健性。在这项研究中,我们对BraTS-Africa数据集进行了分割感知的离线数据增强,以增加数据样本量和多样性,从而提高模型的泛化能力。我们进一步构建了三种不同架构的集合:MedNeXt、SegMamba和Residual-Encoder U-Net,以利用它们的互补优势。我们表现最佳的模型MedNeXt训练了1000个周期,并获得了最高的平均病变级dice评分和归一化表面距离评分,分别为0.86和0.81。然而,训练了500个周期的集成模型在肿瘤亚区产生了最平衡的分割性能。这项工作表明,先进的增强技术和模型集成相结合可以提高多样化和代表性不足的数据集的分割精度和稳健性。相关代码可访问:https://github.com/SPARK-Academy-2025/SPARK-2025/tree/main/SPARK2025_BraTs_MODELS/SPARK_NeuroAshanti
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Brain Tumor Segmentation Challenge, Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) Conference, 11 Pages, 2 Figures, 2 Tables
Summary
本研究针对非洲数据集BraTS-Africa进行线下数据增强,以增加样本数量和多样性,提高模型的泛化能力。通过构建三个不同架构的模型融合,实现肿瘤分割的准确性与鲁棒性提升。其中,MedNeXt模型表现最佳,平均病灶级别的Dice系数和归一化表面距离得分分别为0.86和0.81。同时,训练500轮次的融合模型在肿瘤各子区域分割性能上表现最均衡。本研究证明了高级数据增强和模型融合的组合可有效提升分割准确性和鲁棒性,特别是在多样性和代表性不足的数据集上。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究针对脑肿瘤,特别是胶质瘤的复杂生长模式和个体差异带来的诊断困难,采用深度学习模型进行肿瘤分割。
- 研究中对非洲数据集BraTS-Africa进行线下数据增强,以增加样本数量和多样性,提高模型的泛化能力。
- 构建了三个不同的模型架构并融合,以提高肿瘤分割的准确性和鲁棒性。
- MedNeXt模型表现最佳,但融合模型在训练500轮次时在肿瘤各子区域分割性能上表现更均衡。
- 融合模型在多样性和代表性不足的数据集上表现出较高的分割准确性和鲁棒性。
- 该研究证明了高级数据增强和模型融合的重要性,特别是在处理复杂和多样化的数据集时。
点此查看论文截图
DuPLUS: Dual-Prompt Vision-Language Framework for Universal Medical Image Segmentation and Prognosis
Authors:Numan Saeed, Tausifa Jan Saleem, Fadillah Maani, Muhammad Ridzuan, Hu Wang, Mohammad Yaqub
Deep learning for medical imaging is hampered by task-specific models that lack generalizability and prognostic capabilities, while existing ‘universal’ approaches suffer from simplistic conditioning and poor medical semantic understanding. To address these limitations, we introduce DuPLUS, a deep learning framework for efficient multi-modal medical image analysis. DuPLUS introduces a novel vision-language framework that leverages hierarchical semantic prompts for fine-grained control over the analysis task, a capability absent in prior universal models. To enable extensibility to other medical tasks, it includes a hierarchical, text-controlled architecture driven by a unique dual-prompt mechanism. For segmentation, DuPLUS is able to generalize across three imaging modalities, ten different anatomically various medical datasets, encompassing more than 30 organs and tumor types. It outperforms the state-of-the-art task specific and universal models on 8 out of 10 datasets. We demonstrate extensibility of its text-controlled architecture by seamless integration of electronic health record (EHR) data for prognosis prediction, and on a head and neck cancer dataset, DuPLUS achieved a Concordance Index (CI) of 0.69. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning enables rapid adaptation to new tasks and modalities from varying centers, establishing DuPLUS as a versatile and clinically relevant solution for medical image analysis. The code for this work is made available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DuPLUS-6C52
医疗影像深度学习受限于缺乏通用性和预后能力的特定任务模型,而现有的“通用”方法则存在条件过于简单和医疗语义理解不足的问题。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了DuPLUS,这是一个用于高效多模式医疗影像分析的深度学习框架。DuPLUS引入了一种新颖的视觉语言框架,该框架利用分层语义提示对分析任务进行精细控制,这是先前通用模型所不具备的功能。为了实现扩展到其他医疗任务,它包括一种分层的文本控制架构,该架构由独特的双重提示机制驱动。对于分割任务,DuPLUS能够在三种成像模式、十个不同的解剖结构医疗数据集中进行推广,涵盖了超过30个器官和肿瘤类型。它在8个数据集中的表现优于最先进的特定任务和通用模型。我们通过无缝集成电子健康记录(EHR)数据来进行预后预测,展示了其文本控制架构的扩展性。在头颈癌数据集中,DuPLUS的Concordance Index(CI)达到了0.69。参数高效的微调使得能够适应新任务和模式中心的各种变化,确立了DuPLUS在医疗影像分析领域的通用性和临床相关性解决方案。这项工作的代码可在以下网址找到:https://anonymous.4open.science/r/DuPLUS-6C52
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对医学图像分析深度学习模型的局限性,提出了一种新的深度学习框架DuPLUS。该框架引入了一种新颖的视语言框架,利用层次语义提示对分析任务进行精细控制,并在多种医学数据集上实现了跨模态、跨解剖结构的推广。同时,通过结合电子健康记录数据,实现了预后预测等功能,展现了其通用性和临床实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像深度学习的局限性:现有模型缺乏通用性和预后能力,而通用模型则存在简单的条件设置和医学语义理解不足的问题。
- DuPLUS框架的引入:为解决这些问题,提出了DuPLUS深度学习框架,用于高效的多模态医学图像分析。
- 视语言框架和层次语义提示:DuPLUS引入了一种新颖的视语言框架,利用层次语义提示进行精细的任务控制,这是先前通用模型所缺乏的功能。
- 模型的推广和性能:DuPLUS能够在三种成像模态、十个不同的解剖结构数据集上推广,涵盖超过30个器官和肿瘤类型,并在8个数据集上优于最新的任务特定和通用模型。
- 电子健康记录数据的整合:通过无缝集成电子健康记录数据,DuPLUS实现了预后预测等功能,展示了其文本控制架构的扩展性。
- 在头颈癌数据集上的表现:在头颈癌数据集上,DuPLUS达到了0.69的协和指数,显示了其临床实用性。