⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-09 更新
ArchitectHead: Continuous Level of Detail Control for 3D Gaussian Head Avatars
Authors:Peizhi Yan, Rabab Ward, Qiang Tang, Shan Du
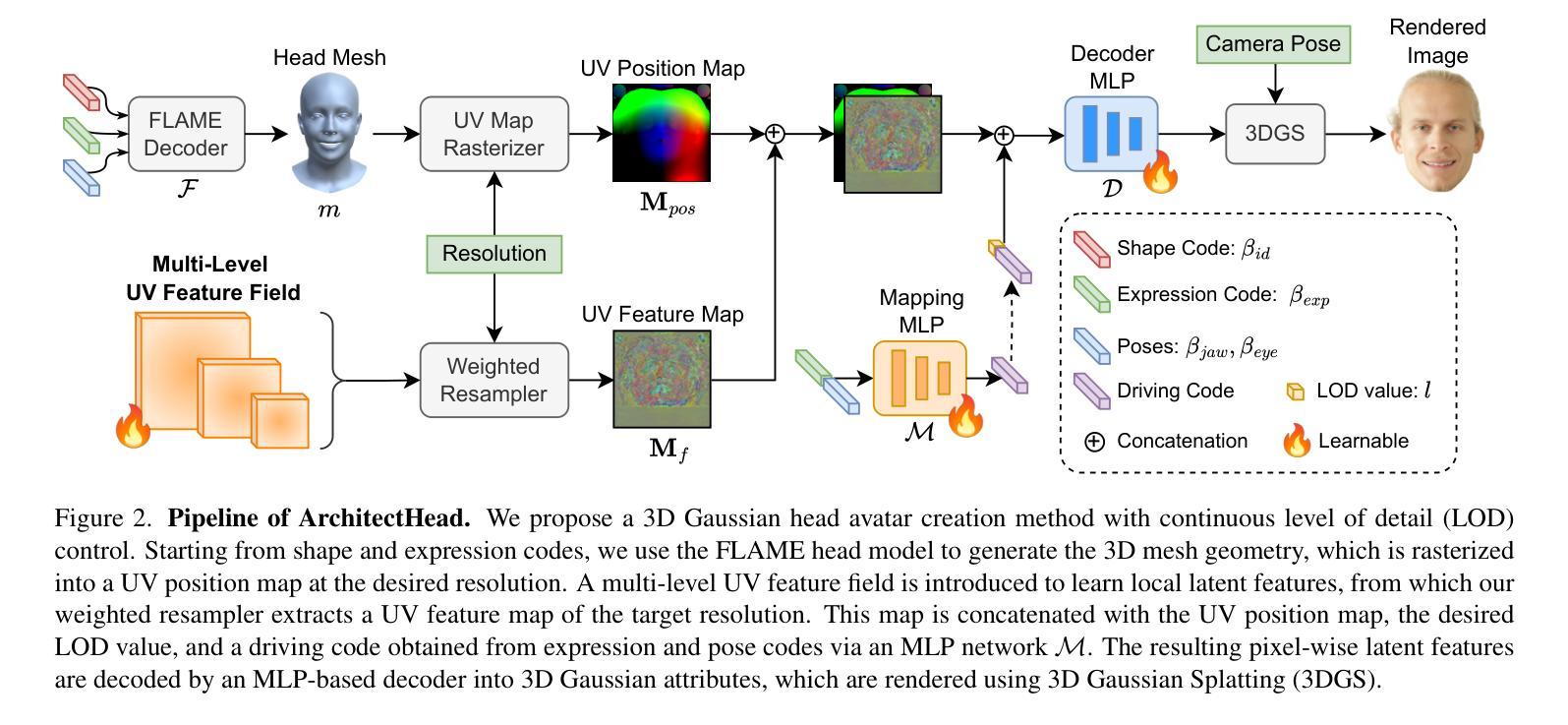
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has enabled photorealistic and real-time rendering of 3D head avatars. Existing 3DGS-based avatars typically rely on tens of thousands of 3D Gaussian points (Gaussians), with the number of Gaussians fixed after training. However, many practical applications require adjustable levels of detail (LOD) to balance rendering efficiency and visual quality. In this work, we propose “ArchitectHead”, the first framework for creating 3D Gaussian head avatars that support continuous control over LOD. Our key idea is to parameterize the Gaussians in a 2D UV feature space and propose a UV feature field composed of multi-level learnable feature maps to encode their latent features. A lightweight neural network-based decoder then transforms these latent features into 3D Gaussian attributes for rendering. ArchitectHead controls the number of Gaussians by dynamically resampling feature maps from the UV feature field at the desired resolutions. This method enables efficient and continuous control of LOD without retraining. Experimental results show that ArchitectHead achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) quality in self and cross-identity reenactment tasks at the highest LOD, while maintaining near SOTA performance at lower LODs. At the lowest LOD, our method uses only 6.2% of the Gaussians while the quality degrades moderately (L1 Loss +7.9%, PSNR –0.97%, SSIM –0.6%, LPIPS Loss +24.1%), and the rendering speed nearly doubles.
基于三维高斯理论(3DGS)的研究,已成功实现了三维头像的光照现实即时渲染技术。现有的基于3DGS的头像通常需要数万三维高斯点来完成渲染效果,且一旦训练完成,高斯点的数量就无法更改。然而在实际应用中,为了满足渲染效率和视觉质量的平衡,往往需要对细节层次(LOD)进行灵活调整。在此研究中,我们提出了“ArchitectHead”这一全新的框架,用以创建支持连续LOD控制的三维高斯头像。我们的核心理念在于在二维UV特征空间内对高斯参数进行设定,并提出由多层可学习特征图构成的UV特征场以编码其潜在特征。然后,一个轻量级的神经网络解码器将这些潜在特征转化为用于渲染的三维高斯属性。ArchitectHead通过动态从UV特征场重新采样特征图并调整至所需分辨率来控制高斯点的数量。这种方法能够在无需重新训练的情况下,实现对LOD的高效连续控制。实验结果表明,在最高LOD下,ArchitectHead在自我和跨身份重建任务中达到了领先水平(SOTA),同时在较低LOD下也保持了接近SOTA的性能表现。在最低LOD状态下,我们的方法仅使用6.2%的高斯点便能维持适中的质量下降(L1损失增加7.9%,PSNR下降0.97%,SSIM下降0.6%,LPIPS损失增加24.1%),同时渲染速度几乎翻倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于3D高斯Splatting(3DGS)的头像渲染技术。现有技术通常使用固定数量的高斯点,无法实现细节层次的调整(LOD)。本文提出的”ArchitectHead”框架首次实现了在3D高斯头像渲染中对LOD的连续控制。通过参数化二维UV特征空间的高斯,并使用多层可学习特征图编码潜在特征,结合轻量级神经网络解码器,实现了从潜在特征到3D高斯属性的转换。ArchitectHead通过动态重采样UV特征场的特征图来实现对高斯点数目的控制,从而在不同细节层次之间实现高效且连续的调整,无需重新训练。实验结果表明,ArchitectHead在最高细节层次上实现了先进的自我和跨身份重塑任务性能,同时在较低细节层次上保持了接近最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术已用于创建具有真实感的实时渲染的3D头像。
- 现有技术使用固定数量的高斯点,难以实现细节层次的调整(LOD)。
- ArchitectHead框架首次实现了基于3DGS的头像渲染中的LOD连续控制。
- ArchitectHead通过参数化二维UV特征空间的高斯并使用多层可学习特征图进行编码。
- 使用轻量级神经网络解码器将潜在特征转换为3D高斯属性以实现渲染。
- 通过动态重采样UV特征场的特征图来控制Gaussians的数量,实现不同LOD之间的调整,无需重新训练。
点此查看论文截图

Progressive Gaussian Transformer with Anisotropy-aware Sampling for Open Vocabulary Occupancy Prediction
Authors:Chi Yan, Dan Xu
The 3D occupancy prediction task has witnessed remarkable progress in recent years, playing a crucial role in vision-based autonomous driving systems. While traditional methods are limited to fixed semantic categories, recent approaches have moved towards predicting text-aligned features to enable open-vocabulary text queries in real-world scenes. However, there exists a trade-off in text-aligned scene modeling: sparse Gaussian representation struggles to capture small objects in the scene, while dense representation incurs significant computational overhead. To address these limitations, we present PG-Occ, an innovative Progressive Gaussian Transformer Framework that enables open-vocabulary 3D occupancy prediction. Our framework employs progressive online densification, a feed-forward strategy that gradually enhances the 3D Gaussian representation to capture fine-grained scene details. By iteratively enhancing the representation, the framework achieves increasingly precise and detailed scene understanding. Another key contribution is the introduction of an anisotropy-aware sampling strategy with spatio-temporal fusion, which adaptively assigns receptive fields to Gaussians at different scales and stages, enabling more effective feature aggregation and richer scene information capture. Through extensive evaluations, we demonstrate that PG-Occ achieves state-of-the-art performance with a relative 14.3% mIoU improvement over the previous best performing method. Code and pretrained models will be released upon publication on our project page: https://yanchi-3dv.github.io/PG-Occ
近年来,三维占用预测任务取得了显著进展,在基于视觉的自动驾驶系统中发挥了至关重要的作用。虽然传统方法局限于固定的语义类别,但最近的方法已经转向预测文本对齐的特征,以便在真实世界场景中实现开放式词汇文本查询。然而,文本对齐场景建模存在权衡:稀疏的高斯表示很难捕捉场景中的小物体,而密集表示则会产生巨大的计算开销。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了PG-Occ,一种创新的渐进式高斯变换框架,可实现开放式词汇三维占用预测。我们的框架采用渐进式在线致密化策略,这是一种前馈策略,逐步增强三维高斯表示以捕捉场景的精细细节。通过迭代增强表示,该框架实现了越来越精确和详细的场景理解。另一个关键贡献是引入了具有时空融合的各向异性感知采样策略,该策略自适应地为不同尺度和阶段的高斯分配感受野,从而实现更有效的特征聚合和更丰富的场景信息捕获。通过广泛评估,我们证明PG-Occ达到了最先进的性能,相对于之前性能最佳的方法,相对提高了14.3%的mIoU。代码和预训练模型将在我们的项目页面发布时公布:https://yanchi-3dv.github.io/PG-Occ。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://yanchi-3dv.github.io/PG-Occ
Summary
近年来,三维占用预测任务在基于视觉的自动驾驶系统中取得了显著进展。传统方法受限于固定语义类别,而新方法趋向于预测文本对齐特征,以实现现实世界场景中的开放词汇文本查询。但文本对齐场景建模存在权衡:稀疏高斯表示难以捕捉场景中的小物体,而密集表示则带来显著的计算开销。为解决这些限制,我们提出了PG-Occ,一种创新的渐进式高斯变换框架,可实现开放词汇表的三维占用预测。
Key Takeaways
- 3D occupancy prediction task has seen remarkable progress in recent years, crucial for autonomous driving systems.
- 传统方法受限于固定语义类别,而新方法预测文本对齐特征以实现开放词汇查询。
- 文本对齐场景建模存在稀疏与密集表示之间的权衡。
- PG-Occ采用渐进式在线密化策略,逐步增强三维高斯表示以捕捉精细场景细节。
- 框架引入了一种具有时空融合功能的各向异性感知采样策略,能自适应地为不同尺度和阶段的高斯分配感受野。
- 通过评估,PG-Occ相较于之前最佳方法实现了相对14.3%的mIoU改进。
点此查看论文截图
Optimized Minimal 4D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Minseo Lee, Byeonghyeon Lee, Lucas Yunkyu Lee, Eunsoo Lee, Sangmin Kim, Seunghyeon Song, Joo Chan Lee, Jong Hwan Ko, Jaesik Park, Eunbyung Park
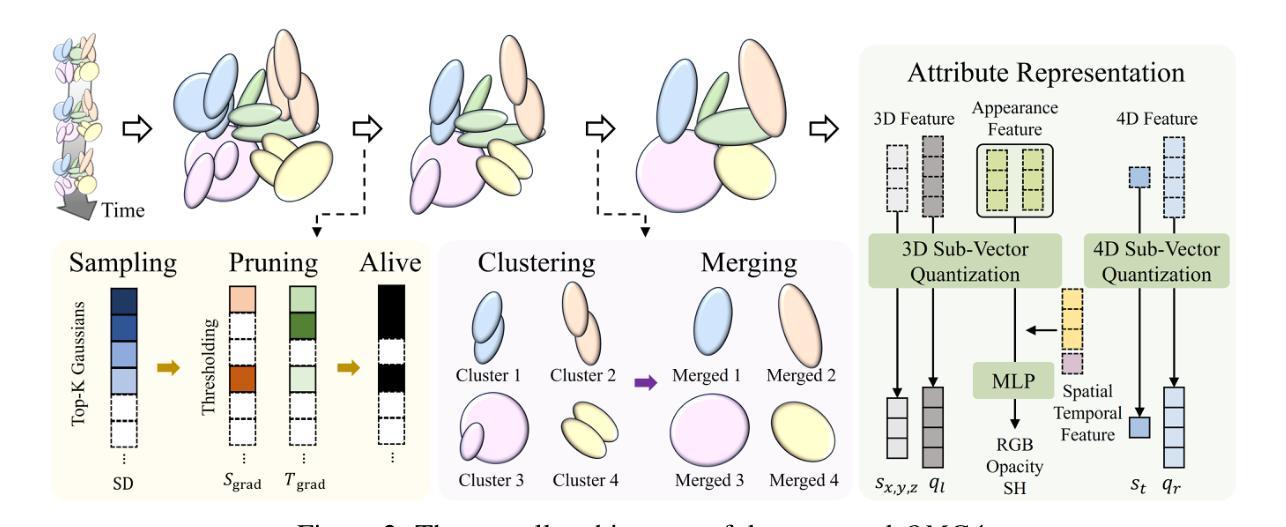
4D Gaussian Splatting has emerged as a new paradigm for dynamic scene representation, enabling real-time rendering of scenes with complex motions. However, it faces a major challenge of storage overhead, as millions of Gaussians are required for high-fidelity reconstruction. While several studies have attempted to alleviate this memory burden, they still face limitations in compression ratio or visual quality. In this work, we present OMG4 (Optimized Minimal 4D Gaussian Splatting), a framework that constructs a compact set of salient Gaussians capable of faithfully representing 4D Gaussian models. Our method progressively prunes Gaussians in three stages: (1) Gaussian Sampling to identify primitives critical to reconstruction fidelity, (2) Gaussian Pruning to remove redundancies, and (3) Gaussian Merging to fuse primitives with similar characteristics. In addition, we integrate implicit appearance compression and generalize Sub-Vector Quantization (SVQ) to 4D representations, further reducing storage while preserving quality. Extensive experiments on standard benchmark datasets demonstrate that OMG4 significantly outperforms recent state-of-the-art methods, reducing model sizes by over 60% while maintaining reconstruction quality. These results position OMG4 as a significant step forward in compact 4D scene representation, opening new possibilities for a wide range of applications. Our source code is available at https://minshirley.github.io/OMG4/.
4D高斯贴图技术已经成为动态场景表示的新范式,能够实现复杂运动的实时渲染。然而,它面临存储开销的主要挑战,因为高保真重建需要数百万个高斯。尽管已有若干研究试图减轻这种内存负担,但它们仍在压缩率和视觉质量方面存在局限性。在这项工作中,我们提出了OMG4(优化最小4D高斯贴图),这是一种构建紧凑显著高斯集合的框架,能够忠实地代表4D高斯模型。我们的方法分三个阶段逐步删除高斯:(1)高斯采样,以识别对重建保真度至关重要的基本元素;(2)高斯修剪,以消除冗余;(3)高斯合并,以融合具有相似特征的基本元素。此外,我们整合了隐式外观压缩并将子向量量化(SVQ)推广到4D表示,进一步减少了存储量同时保持了质量。在标准基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,OMG4显著优于最新的先进技术,在保持重建质量的同时将模型大小减少了60%以上。这些成果标志着OMG4在紧凑4D场景表示方面取得了重大进展,为广泛的应用程序打开了新的可能性。我们的源代码可在https://minshirley.github.io/OMG4/获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 8 figures
Summary
优化后的最小四维高斯采样技术OMG4成功解决了存储冗余问题,在保持重建质量的同时显著减少了模型大小。该技术通过关键高斯采样、去除冗余和高斯融合等三个阶段逐步优化四维高斯模型,集成了隐式外观压缩技术并扩展了四维表示的子向量量化技术。实验结果证明了OMG4的显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- OMG4是一种针对四维高斯模型的有效框架,通过构建紧凑的关键高斯集来忠实表示四维场景。
- OMG4采用三个阶段的优化方法:关键高斯采样、去除冗余和高斯融合。
- 集成隐式外观压缩技术以进一步减少存储需求。
- 扩展了子向量量化技术至四维表示,以在保持质量的同时降低存储需求。
- 实验结果表明,OMG4显著优于最新的先进技术,在减少模型大小的同时保持重建质量。
- OMG4技术对于紧凑四维场景表示具有重大意义,为广泛的应用提供了新的可能性。
点此查看论文截图
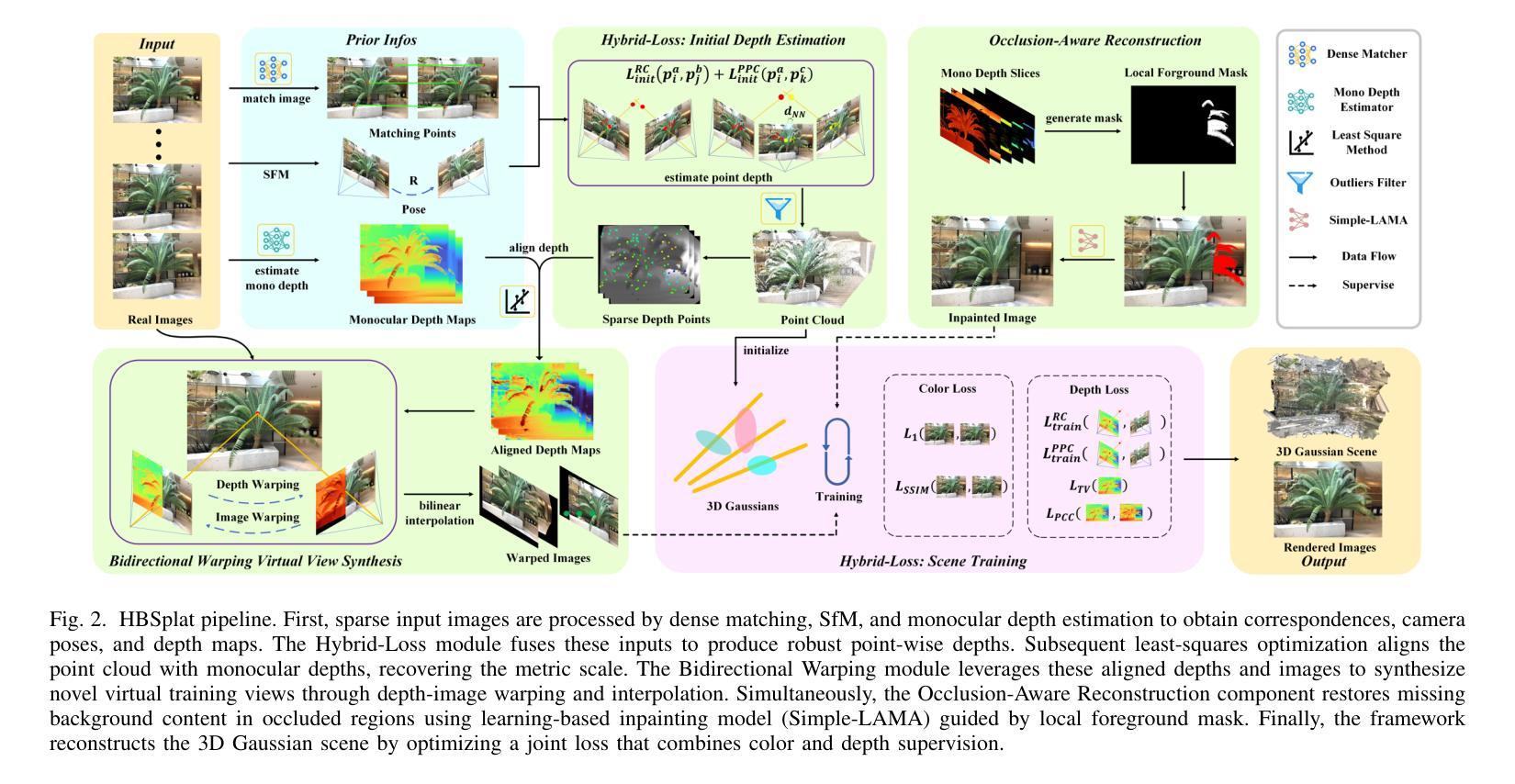
HBSplat: Robust Sparse-View Gaussian Reconstruction with Hybrid-Loss Guided Depth and Bidirectional Warping
Authors:Yu Ma, Guoliang Wei, Yue Cheng
Novel View Synthesis (NVS) from sparse views presents a formidable challenge in 3D reconstruction, where limited multi-view constraints lead to severe overfitting, geometric distortion, and fragmented scenes. While 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) delivers real-time, high-fidelity rendering, its performance drastically deteriorates under sparse inputs, plagued by floating artifacts and structural failures. To address these challenges, we introduce HBSplat, a unified framework that elevates 3DGS by seamlessly integrating robust structural cues, virtual view constraints, and occluded region completion. Our core contributions are threefold: a Hybrid-Loss Depth Estimation module that ensures multi-view consistency by leveraging dense matching priors and integrating reprojection, point propagation, and smoothness constraints; a Bidirectional Warping Virtual View Synthesis method that enforces substantially stronger constraints by creating high-fidelity virtual views through bidirectional depth-image warping and multi-view fusion; and an Occlusion-Aware Reconstruction component that recovers occluded areas using a depth-difference mask and a learning-based inpainting model. Extensive evaluations on LLFF, Blender, and DTU benchmarks validate that HBSplat sets a new state-of-the-art, achieving up to 21.13 dB PSNR and 0.189 LPIPS, while maintaining real-time inference. Code is available at: https://github.com/eternalland/HBSplat.
在3D重建中,从稀疏视角进行Novel View Synthesis(NVS)是一项巨大的挑战。有限的多视角约束会导致严重的过度拟合、几何失真和场景碎片化。虽然3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)可以实现实时、高保真渲染,但在稀疏输入的情况下,其性能会急剧下降,受到浮动伪影和结构失败的困扰。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了HBSplat这一统一框架,它通过无缝集成稳健的结构线索、虚拟视图约束和遮挡区域完成来提升3DGS。我们的核心贡献有三点:一是Hybrid-Loss深度估计模块,它通过利用密集匹配先验知识并整合再投影、点传播和平滑约束来确保多视角一致性;二是双向扭曲虚拟视图合成方法,它通过双向深度图像扭曲和多视角融合来创建高保真虚拟视图,从而实施更严格的约束;三是遮挡感知重建组件,它使用深度差异掩膜和基于学习的修复模型来恢复遮挡区域。在LLFF、Blender和DTU基准测试上的广泛评估证明,HBSplat达到了最新技术水准,实现了高达21.13 dB的PSNR和0.189的LPIPS指标,同时保持实时推理。相关代码可访问:https://github.com/eternalland/HBSplat。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 21 figures
Summary
本文介绍了针对稀疏视角下的Novel View Synthesis(NVS)的挑战,通过引入HBSplat框架来提升3DGS性能的方法。该方法结合了结构线索、虚拟视图约束和遮挡区域完成技术,通过Hybrid-Loss深度估计模块、双向扭曲虚拟视图合成方法和遮挡感知重建组件等技术手段,实现了高保真度的虚拟视图合成和遮挡区域的恢复。在LLFF、Blender和DTU等多个数据集上的实验结果表明,HBSplat达到了实时性能的新水平。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了稀疏视角下的Novel View Synthesis(NVS)的挑战性问题,如过拟合、几何失真和场景碎片化等。
- 指出3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)在稀疏输入下的性能问题,包括浮动伪影和结构失败等问题。
- 提出了一种新的统一框架HBSplat,通过集成结构线索、虚拟视图约束和遮挡区域完成技术,解决上述问题。
- Hybrid-Loss深度估计模块实现了多视图一致性,利用密集匹配先验,并整合重投影、点传播和平滑约束等技术。
- Bidirectional Warping Virtual View Synthesis方法创建高质量虚拟视图,通过双向深度图像扭曲和多视图融合施加更强的约束。
- Occlusion-Aware Reconstruction组件使用深度差异掩膜和学习型修复模型恢复遮挡区域。
点此查看论文截图

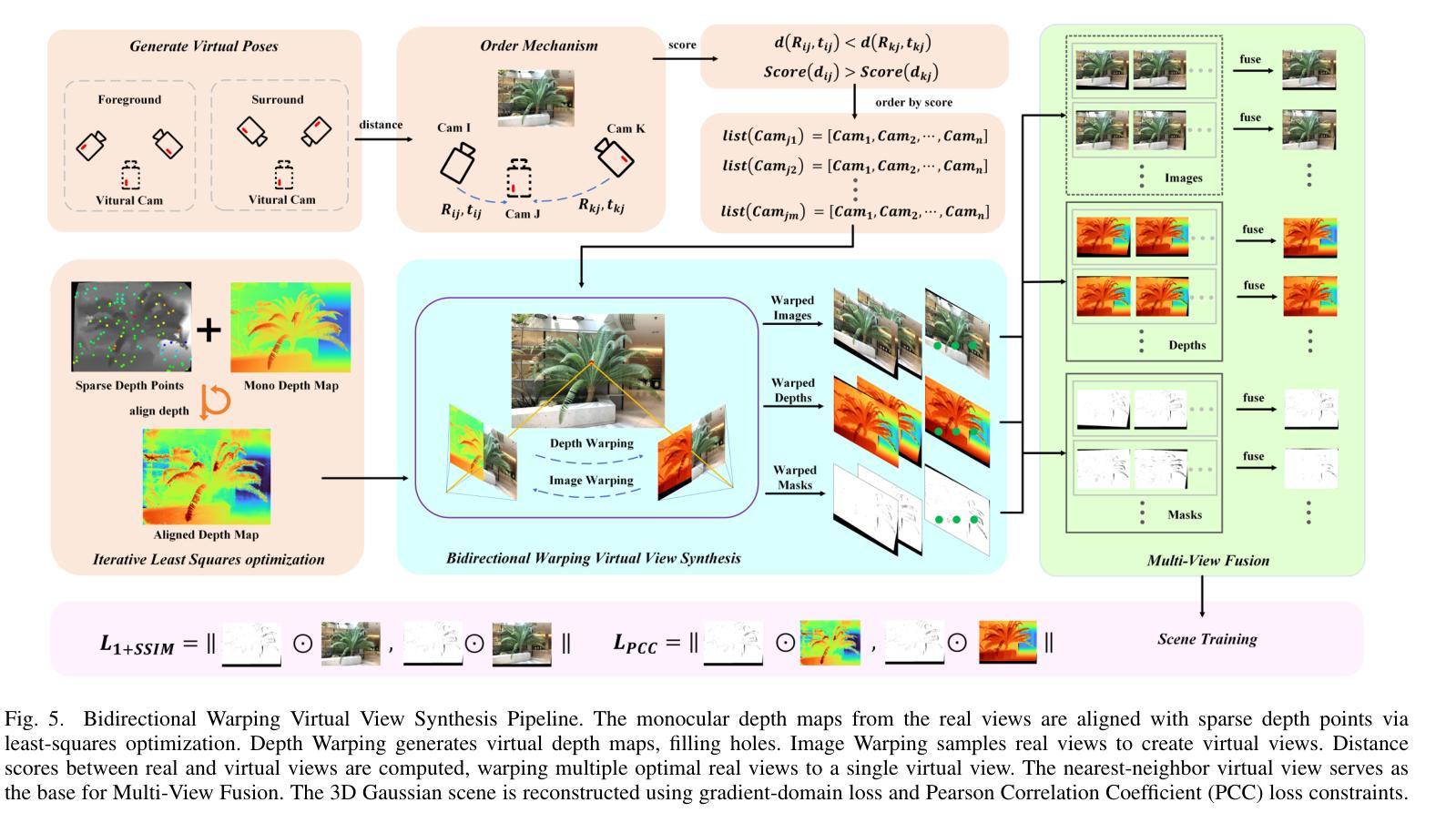
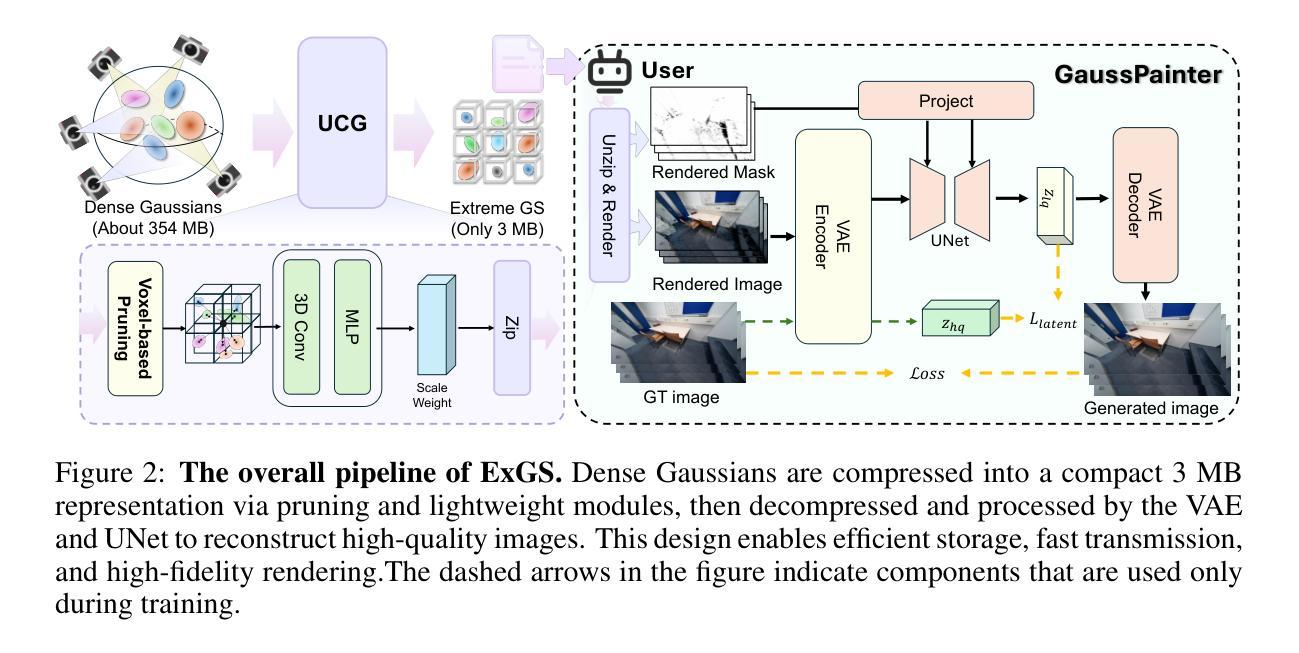
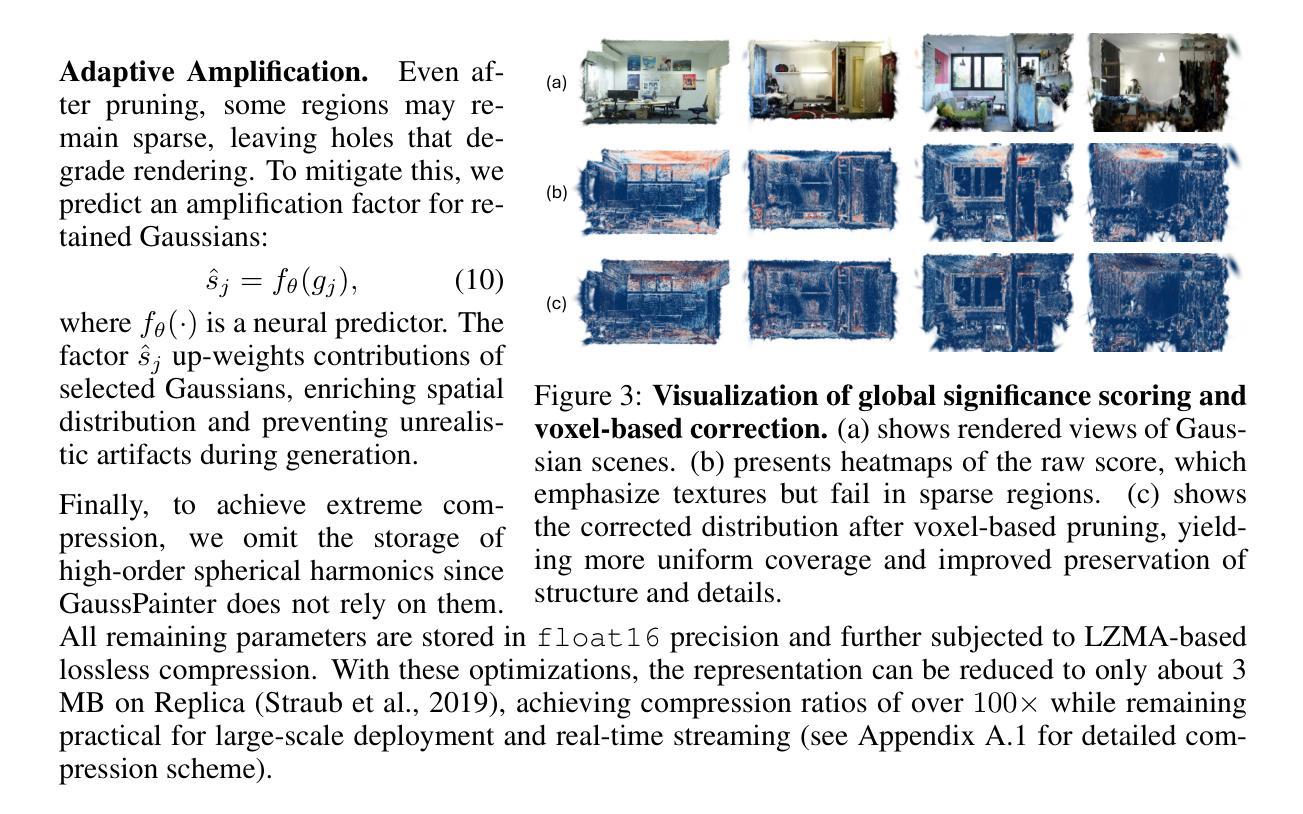
ExGS: Extreme 3D Gaussian Compression with Diffusion Priors
Authors:Jiaqi Chen, Xinhao Ji, Yuanyuan Gao, Hao Li, Yuning Gong, Yifei Liu, Dan Xu, Zhihang Zhong, Dingwen Zhang, Xiao Sun
Neural scene representations, such as 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), have enabled high-quality neural rendering; however, their large storage and transmission costs hinder deployment in resource-constrained environments. Existing compression methods either rely on costly optimization, which is slow and scene-specific, or adopt training-free pruning and quantization, which degrade rendering quality under high compression ratios. In contrast, recent data-driven approaches provide a promising direction to overcome this trade-off, enabling efficient compression while preserving high rendering quality. We introduce ExGS, a novel feed-forward framework that unifies Universal Gaussian Compression (UGC) with GaussPainter for Extreme 3DGS compression. UGC performs re-optimization-free pruning to aggressively reduce Gaussian primitives while retaining only essential information, whereas GaussPainter leverages powerful diffusion priors with mask-guided refinement to restore high-quality renderings from heavily pruned Gaussian scenes. Unlike conventional inpainting, GaussPainter not only fills in missing regions but also enhances visible pixels, yielding substantial improvements in degraded renderings. To ensure practicality, it adopts a lightweight VAE and a one-step diffusion design, enabling real-time restoration. Our framework can even achieve over 100X compression (reducing a typical 354.77 MB model to about 3.31 MB) while preserving fidelity and significantly improving image quality under challenging conditions. These results highlight the central role of diffusion priors in bridging the gap between extreme compression and high-quality neural rendering. Our code repository will be released at: https://github.com/chenttt2001/ExGS
神经场景表示,如3D高斯插值(3DGS),已经实现了高质量神经渲染;然而,其较大的存储和传输成本阻碍了其在资源受限环境中的部署。现有的压缩方法要么依赖于昂贵且耗时的优化,要么是特定场景的,或者采用无训练裁剪和量化,这在高压缩比下会降低渲染质量。相比之下,最近的数据驱动方法为解决这一权衡提供了有前景的方向,能够在保持高质量渲染的同时实现有效的压缩。我们介绍了ExGS,这是一种新型前馈框架,它将通用高斯压缩(UGC)与GaussPainter相结合,用于极端3DGS压缩。UGC通过无优化再处理的裁剪方法大幅度减少高斯原始数据,同时仅保留必要信息;而GaussPainter则利用强大的扩散先验和掩膜导向细化,从高度裁剪的高斯场景中恢复高质量渲染。不同于传统的补全技术,GaussPainter不仅填补缺失区域,还增强可见像素,在渲染质量下降的情况下实现显著改进。为确保实用性,它采用了轻量级的VAE和一步扩散设计,实现实时恢复。我们的框架甚至可以在保持保真度的同时实现超过100倍的压缩(将一个典型的354.77 MB模型缩减至约3.31 MB),并在具有挑战性的条件下显著提高图像质量。这些结果突显了扩散先验在极端压缩与高质量神经渲染之间的桥梁作用。我们的代码仓库将在:https://github.com/chenttt2001/ExGS发布。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
神经场景表示(如3D高斯拼贴技术)实现了高质量神经渲染,但其存储和传输成本较高,限制了其在资源受限环境中的部署。现有压缩方法要么依赖于耗时且场景特定的优化,要么采用无训练裁剪和量化,这在高压缩比下会降低渲染质量。相反,最近的数据驱动方法为平衡压缩效率和渲染质量提供了希望。本研究介绍了一种新型前馈框架ExGS,它将通用高斯压缩(UGC)与GaussPainter相结合,用于实现极端3DGS压缩。UGC通过无优化裁剪大幅减少高斯原始数据,同时保留必要信息;而GaussPainter则利用强大的扩散先验和遮罩引导细化,从高度裁剪的高斯场景中恢复高质量渲染。与常规补全不同,GaussPainter不仅填补缺失区域,还增强可见像素,显著改善退化渲染质量。为确保实用性,它采用轻量级VAE和一步扩散设计,实现实时恢复。本框架甚至能在保持保真度的同时实现超过100倍的压缩(将典型的354.77MB模型缩减至约3.31MB),并在挑战条件下显著提高图像质量。这些结果突显扩散先验在弥合极端压缩与高质量神经渲染之间的差距中的关键作用。我们的代码仓库将在https://github.com/chenttt2001/ExGS发布。
关键发现
- 神经场景表示(如3DGS)实现了高质量神经渲染,但存在存储和传输成本高的挑战。
- 现有压缩方法面临优化成本高昂或渲染质量下降的权衡问题。
- 数据驱动方法能在保持高质量渲染的同时实现高效压缩。
- 新型前馈框架ExGS结合了通用高斯压缩(UGC)和GaussPainter技术,实现极端3DGS压缩。
- UGC通过无优化裁剪保留必要信息,而GaussPainter利用扩散先验进行高质量渲染恢复。
- GaussPainter不仅填补缺失区域,还增强可见像素,改善退化渲染质量。
点此查看论文截图

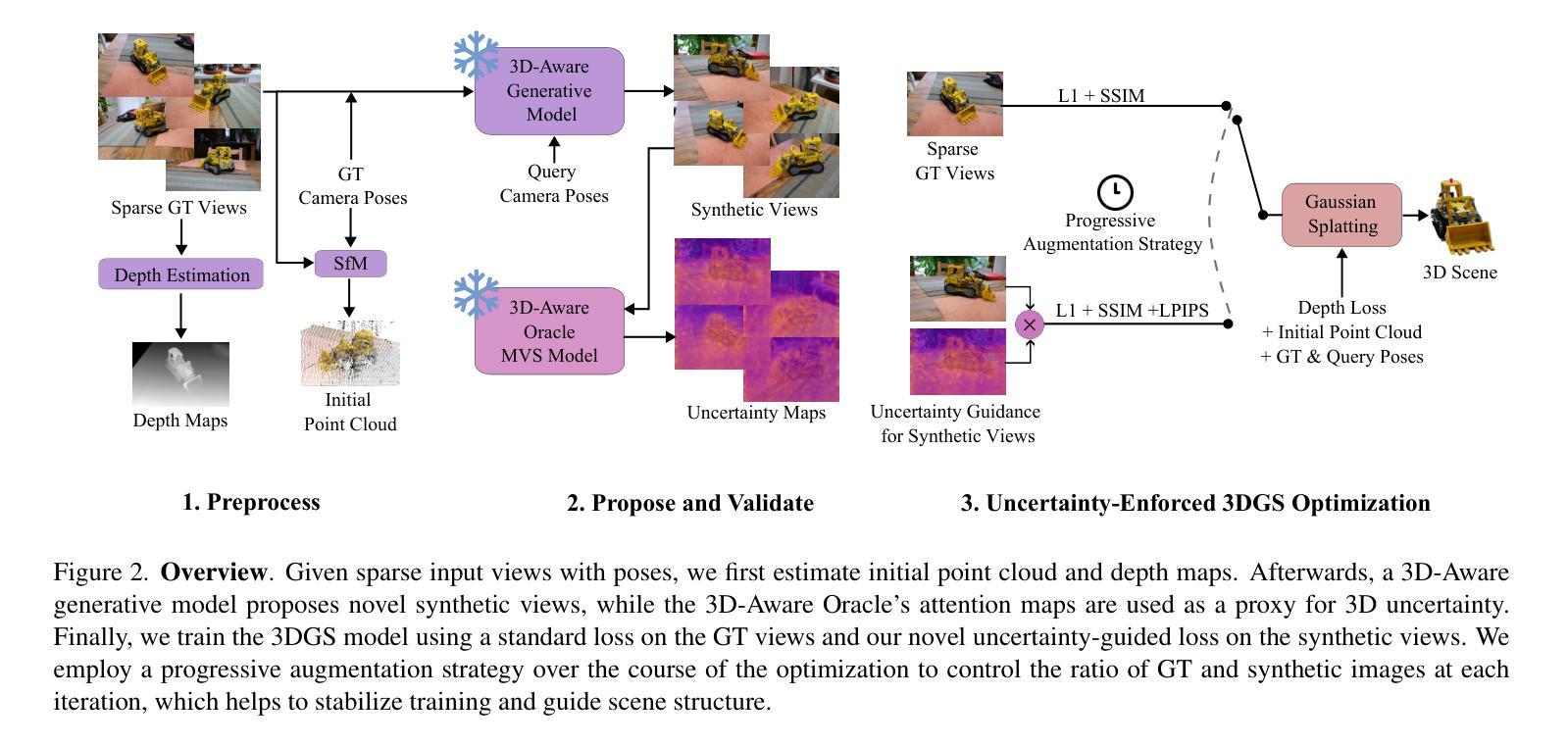
OracleGS: Grounding Generative Priors for Sparse-View Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Atakan Topaloglu, Kunyi Li, Michael Niemeyer, Nassir Navab, A. Murat Tekalp, Federico Tombari
Sparse-view novel view synthesis is fundamentally ill-posed due to severe geometric ambiguity. Current methods are caught in a trade-off: regressive models are geometrically faithful but incomplete, whereas generative models can complete scenes but often introduce structural inconsistencies. We propose OracleGS, a novel framework that reconciles generative completeness with regressive fidelity for sparse view Gaussian Splatting. Instead of using generative models to patch incomplete reconstructions, our “propose-and-validate” framework first leverages a pre-trained 3D-aware diffusion model to synthesize novel views to propose a complete scene. We then repurpose a multi-view stereo (MVS) model as a 3D-aware oracle to validate the 3D uncertainties of generated views, using its attention maps to reveal regions where the generated views are well-supported by multi-view evidence versus where they fall into regions of high uncertainty due to occlusion, lack of texture, or direct inconsistency. This uncertainty signal directly guides the optimization of a 3D Gaussian Splatting model via an uncertainty-weighted loss. Our approach conditions the powerful generative prior on multi-view geometric evidence, filtering hallucinatory artifacts while preserving plausible completions in under-constrained regions, outperforming state-of-the-art methods on datasets including Mip-NeRF 360 and NeRF Synthetic.
稀疏视角下的新型视图合成因严重的几何模糊性而本质上是不适定的。当前的方法陷入了权衡之中:回归模型在几何上忠实但不完整,而生成模型可以完成场景但经常引入结构不一致性。我们提出了OracleGS,这是一个新的框架,旨在调和生成模型的完整性与回归模型的忠实性,用于稀疏视角的高斯拼贴。我们并不使用生成模型来修复不完整的重建,而是采用“提出并验证”的框架。首先,我们利用预训练的3D感知扩散模型合成新型视图来提出一个完整的场景。然后,我们将多视角立体(MVS)模型重新用作一个3D感知的“专家”,以验证生成视图的3D不确定性,并使用其注意力图来揭示生成视图在多视角证据支持良好的区域,以及因遮挡、缺乏纹理或直接不一致而陷入高度不确定性的区域。这种不确定性信号直接指导了通过不确定性加权损失对3D高斯拼贴模型的优化。我们的方法以多视角几何证据为条件,对生成模型进行强大的先验约束,过滤掉幻觉伪影,同时在约束不足的区域内保留合理的完成度,在包括Mip-NeRF 360和NeRF Synthetic在内的数据集上的表现优于当前的主流方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page available at: https://atakan-topaloglu.github.io/oraclegs/
Summary
本文提出了OracleGS框架,融合了生成模型的完整性与回归模型的忠实性,用于稀疏视角的高斯Splatting。该框架采用预训练的3D感知扩散模型合成新视角以提出完整场景,并利用多视角立体(MVS)模型作为3D感知的oracle验证生成的视角的3D不确定性。这种不确定性信号直接指导了通过不确定性加权损失优化的3D高斯Splatting模型。该框架以多视角几何证据为条件,在生成模型中融入合理的先验知识,有效过滤了虚构的伪像,同时保留了可能完成未约束区域的场景,超越了包括Mip-NeRF 360和NeRF合成数据集在内的现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- OracleGS解决了稀疏视角下的视图合成问题,结合了生成模型的完整性和回归模型的忠实性。
- 提出了一种“propose-and-validate”框架,利用预训练的3D感知扩散模型提出完整场景,并使用多视角立体模型验证其不确定性。
- 利用注意力图揭示生成视图与多视角证据之间的对应关系,以及因遮挡、缺乏纹理或直接不一致导致的高不确定性区域。
- 不确定性信号指导了通过不确定性加权损失优化的3D高斯Splatting模型。
- 该方法以多视角几何证据为条件,将强大的生成先验融入其中,过滤了虚构的伪像。
- 该方法在包括Mip-NeRF 360和NeRF合成数据集在内的数据集上超越了现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

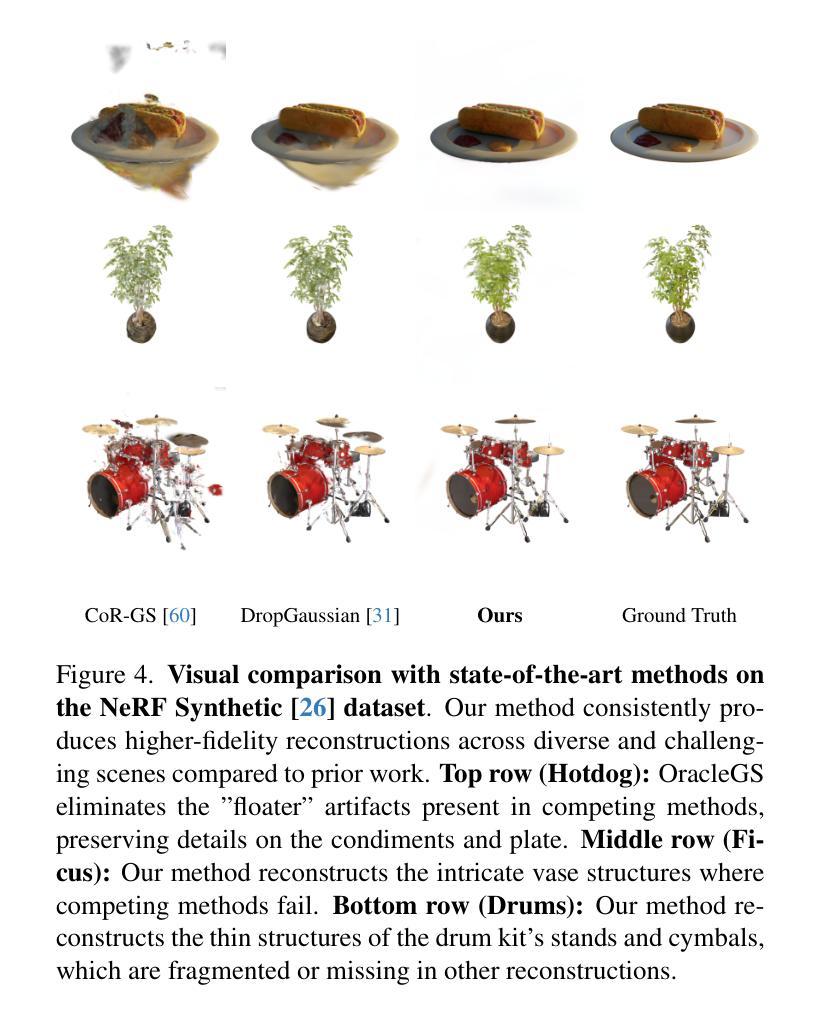
Robust Neural Rendering in the Wild with Asymmetric Dual 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Chengqi Li, Zhihao Shi, Yangdi Lu, Wenbo He, Xiangyu Xu
3D reconstruction from in-the-wild images remains a challenging task due to inconsistent lighting conditions and transient distractors. Existing methods typically rely on heuristic strategies to handle the low-quality training data, which often struggle to produce stable and consistent reconstructions, frequently resulting in visual artifacts.In this work, we propose \modelname{}, a novel framework that leverages the stochastic nature of these artifacts: they tend to vary across different training runs due to minor randomness. Specifically, our method trains two 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) models in parallel, enforcing a consistency constraint that encourages convergence on reliable scene geometry while suppressing inconsistent artifacts. To prevent the two models from collapsing into similar failure modes due to confirmation bias, we introduce a divergent masking strategy that applies two complementary masks: a multi-cue adaptive mask and a self-supervised soft mask, which leads to an asymmetric training process of the two models, reducing shared error modes. In addition, to improve the efficiency of model training, we introduce a lightweight variant called Dynamic EMA Proxy, which replaces one of the two models with a dynamically updated Exponential Moving Average (EMA) proxy, and employs an alternating masking strategy to preserve divergence. Extensive experiments on challenging real-world datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms existing approaches while achieving high efficiency. See the project website at https://steveli88.github.io/AsymGS.
从野生图像中进行3D重建仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为存在光照条件不一致和短暂干扰物等问题。现有方法通常依赖于启发式策略来处理低质量训练数据,这往往难以产生稳定和一致的重建结果,经常导致视觉伪影。在这项工作中,我们提出了名为“模型名称”的新框架,该框架利用这些伪影的随机性:它们倾向于在不同的训练运行中有所不同,这是由于存在轻微随机性。具体来说,我们的方法并行训练两个3D高斯展布(3DGS)模型,实施一致性约束,以鼓励可靠的场景几何收敛,同时抑制不一致的伪影。为了防止两个模型因确认偏见而陷入相似的失败模式,我们引入了一种发散掩蔽策略,该策略应用两种互补掩蔽:多线索自适应掩蔽和自我监督软掩蔽,这导致两个模型的不对称训练过程,减少共享错误模式。此外,为了提高模型训练的效率,我们引入了一个轻量级变体,称为动态EMA代理,它用动态更新的指数移动平均(EMA)代理替换其中一个模型,并采用交替掩蔽策略来保持发散。在具有挑战性的真实世界数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法始终优于现有方法,同时实现了高效率。请参阅项目网站:https://steveli88.github.io/AsymGS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2025 Spotlight; Project page: https://steveli88.github.io/AsymGS/
Summary
本文提出了一种新的框架模型名来解决野外图像3D重建中的挑战性问题,该框架通过利用伪随机艺术的特点进行并行训练两个3DGS模型并引入一致性约束来提高重建的稳定性和一致性。此外,为了优化模型训练效率,引入了动态EMA代理的轻量级变体,并在交替掩蔽策略的帮助下保持差异性。实验证明,该方法在真实世界数据集上的表现优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 模型利用伪随机艺术的特点进行训练,以提高重建的稳定性和一致性。
- 通过并行训练两个模型并引入一致性约束来增强模型性能。
- 通过引入两种互补的掩蔽策略来防止模型陷入相同的错误模式。
- 动态EMA代理和交替掩蔽策略用于提高模型训练效率。
- 在真实世界数据集上的实验证明,该方法在性能上优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

Motion Blender Gaussian Splatting for Dynamic Scene Reconstruction
Authors:Xinyu Zhang, Haonan Chang, Yuhan Liu, Abdeslam Boularias
Gaussian splatting has emerged as a powerful tool for high-fidelity reconstruction of dynamic scenes. However, existing methods primarily rely on implicit motion representations, such as encoding motions into neural networks or per-Gaussian parameters, which makes it difficult to further manipulate the reconstructed motions. This lack of explicit controllability limits existing methods to replaying recorded motions only, which hinders a wider application in robotics. To address this, we propose Motion Blender Gaussian Splatting (MBGS), a novel framework that uses motion graphs as an explicit and sparse motion representation. The motion of a graph’s links is propagated to individual Gaussians via dual quaternion skinning, with learnable weight painting functions that determine the influence of each link. The motion graphs and 3D Gaussians are jointly optimized from input videos via differentiable rendering. Experiments show that MBGS achieves state-of-the-art performance on the highly challenging iPhone dataset while being competitive on HyperNeRF. We demonstrate the application potential of our method in animating novel object poses, synthesizing real robot demonstrations, and predicting robot actions through visual planning. The source code, models, video demonstrations can be found at http://mlzxy.github.io/motion-blender-gs.
高斯描图法已经成为重建动态场景的一种强大工具。然而,现有的方法主要依赖于隐式运动表示,例如将运动编码到神经网络或每个高斯参数中,这使得进一步操纵重建的运动变得困难。这种缺乏明确的可控性限制了现有方法仅能回放记录的运动,阻碍了其在机器人领域的更广泛应用。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了运动混合器高斯描图法(MBGS),这是一种使用运动图作为明确且稀疏的运动表示的新型框架。图连接的运动通过双重四元数蒙皮传播到各个高斯分布上,通过可学习的权重绘制函数来确定每个连接的影响。运动图和3D高斯分布通过可微分渲染从输入视频中进行联合优化。实验表明,MBGS在极具挑战性的iPhone数据集上达到了最先进的性能,同时在HyperNeRF上表现良好。我们展示了该方法在动画新物体姿态、合成真实机器人演示以及通过视觉规划预测机器人动作方面的应用潜力。源代码、模型和视频演示可在http://mlzxy.github.io/motion-blender-gs找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF CoRL 2025
Summary
高斯涂斑技术已成为重建动态场景的高保真工具。然而,现有方法主要依赖隐式运动表示,如将运动编码到神经网络或每个高斯参数中,这使得进一步操纵重建运动变得困难。这种缺乏明确可控性的限制使现有方法仅限于回放记录的运动,阻碍了其在机器人领域的更广泛应用。为解决此问题,我们提出使用运动图作为显式且稀疏的运动表示的全新框架——Motion Blender Gaussian Splatting(MBGS)。图链接的运动通过双重四元数蒙皮传播到各个高斯分布,可通过学习权重绘制函数来确定每个链接的影响。运动图和3D高斯分布通过可微分渲染从输入视频联合优化。实验表明,MBGS在极具挑战性的iPhone数据集上达到了最先进的性能,同时在HyperNeRF上具有很强的竞争力。我们展示了该方法在动画新物体姿态、合成真实机器人演示以及通过视觉规划预测机器人动作方面的应用潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯涂斑技术已用于高保真重建动态场景。
- 现有方法主要依赖隐式运动表示,限制了运动的进一步操纵和广泛应用。
- 提出了一种新型框架MBGS,使用运动图作为显式且稀疏的运动表示。
- 通过双重四元数蒙皮将运动图的链接运动传播到各个高斯分布。
- 运动图和3D高斯分布通过可微分渲染联合优化。
- MBGS在iPhone数据集上表现先进,同时在HyperNeRF上具有很强的竞争力。
- MBGS在动画新物体姿态、合成机器人演示以及预测机器人动作方面有潜在应用。
点此查看论文截图

GSRF: Complex-Valued 3D Gaussian Splatting for Efficient Radio-Frequency Data Synthesis
Authors:Kang Yang, Gaofeng Dong, Sijie Ji, Wan Du, Mani Srivastava
Synthesizing radio-frequency (RF) data given the transmitter and receiver positions, e.g., received signal strength indicator (RSSI), is critical for wireless networking and sensing applications, such as indoor localization. However, it remains challenging due to complex propagation interactions, including reflection, diffraction, and scattering. State-of-the-art neural radiance field (NeRF)-based methods achieve high-fidelity RF data synthesis but are limited by long training times and high inference latency. We introduce GSRF, a framework that extends 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) from the optical domain to the RF domain, enabling efficient RF data synthesis. GSRF realizes this adaptation through three key innovations: First, it introduces complex-valued 3D Gaussians with a hybrid Fourier-Legendre basis to model directional and phase-dependent radiance. Second, it employs orthographic splatting for efficient ray-Gaussian intersection identification. Third, it incorporates a complex-valued ray tracing algorithm, executed on RF-customized CUDA kernels and grounded in wavefront propagation principles, to synthesize RF data in real time. Evaluated across various RF technologies, GSRF preserves high-fidelity RF data synthesis while achieving significant improvements in training efficiency, shorter training time, and reduced inference latency.
根据发射器和接收器位置(例如接收信号强度指示器RSSI)合成无线电频率(RF)数据对于无线联网和感应应用(如室内定位)至关重要。然而,由于复杂的传播交互(包括反射、衍射和散射),这仍然是一个挑战。最先进的基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的方法能够实现高保真RF数据合成,但由于训练时间长和推理延迟高而受到限制。我们引入了GSRF,一个将三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)从光学领域扩展到射频领域的框架,以实现高效的射频数据合成。GSRF通过三个关键创新实现了这一适应:首先,它引入了具有混合傅里叶-勒让德基数的复数三维高斯值,以模拟方向和相位相关的辐射率。其次,它采用正交拼贴技术进行高效的射线-高斯交集识别。第三,它结合了实时执行的复数射线追踪算法,该算法基于射频定制CUDA内核和波前传播原理,以合成射频数据。经过对各种射频技术的评估,GSRF保持了高保真射频数据合成,同时在训练效率、缩短训练时间和降低推理延迟方面取得了显著改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了基于高斯合成器扩展射频数据的框架GSRF。它将光学领域的三维高斯分块扩展到射频领域,实现了高效的射频数据合成。通过引入复数三维高斯混合傅里叶-勒让德基模型、正交分块高效射线-高斯交点识别和基于波前传播原理的复杂射线追踪算法,GSRF在高保真射频数据合成的同时,提高了训练效率,缩短了训练时间和推理延迟。
Key Takeaways
- GSRF框架扩展了三维高斯合成(3DGS)从光学领域到射频领域,实现高效射频数据合成。
- GSRF引入复数三维高斯混合傅里叶-勒让德基模型,以模拟方向性和相位依赖的辐射强度。
- 通过正交分块技术,GSRF能高效识别射线和高斯交点的交互。
- GSRF采用基于波前传播原理的复杂射线追踪算法,合成射频数据。
- GSRF在高保真射频数据合成的同时,提高了训练效率,缩短了训练时间和推理延迟。
点此查看论文截图

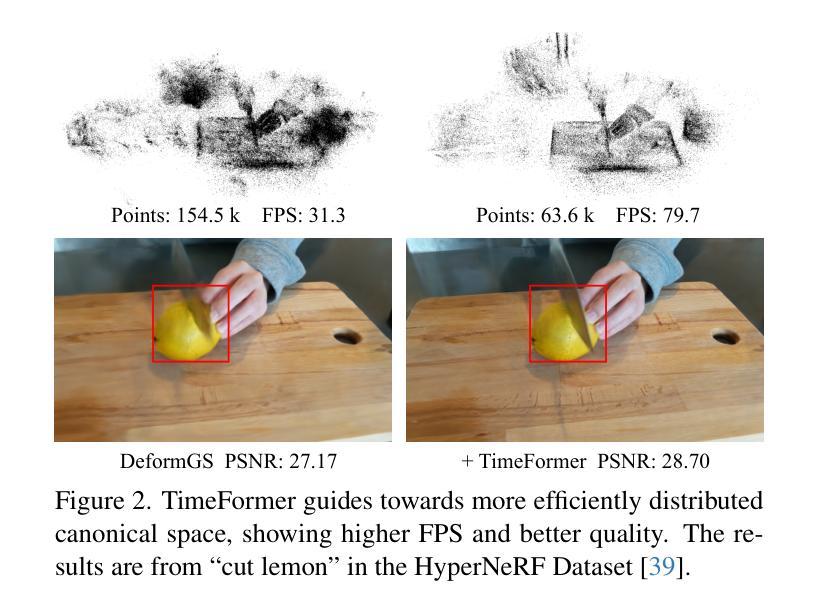
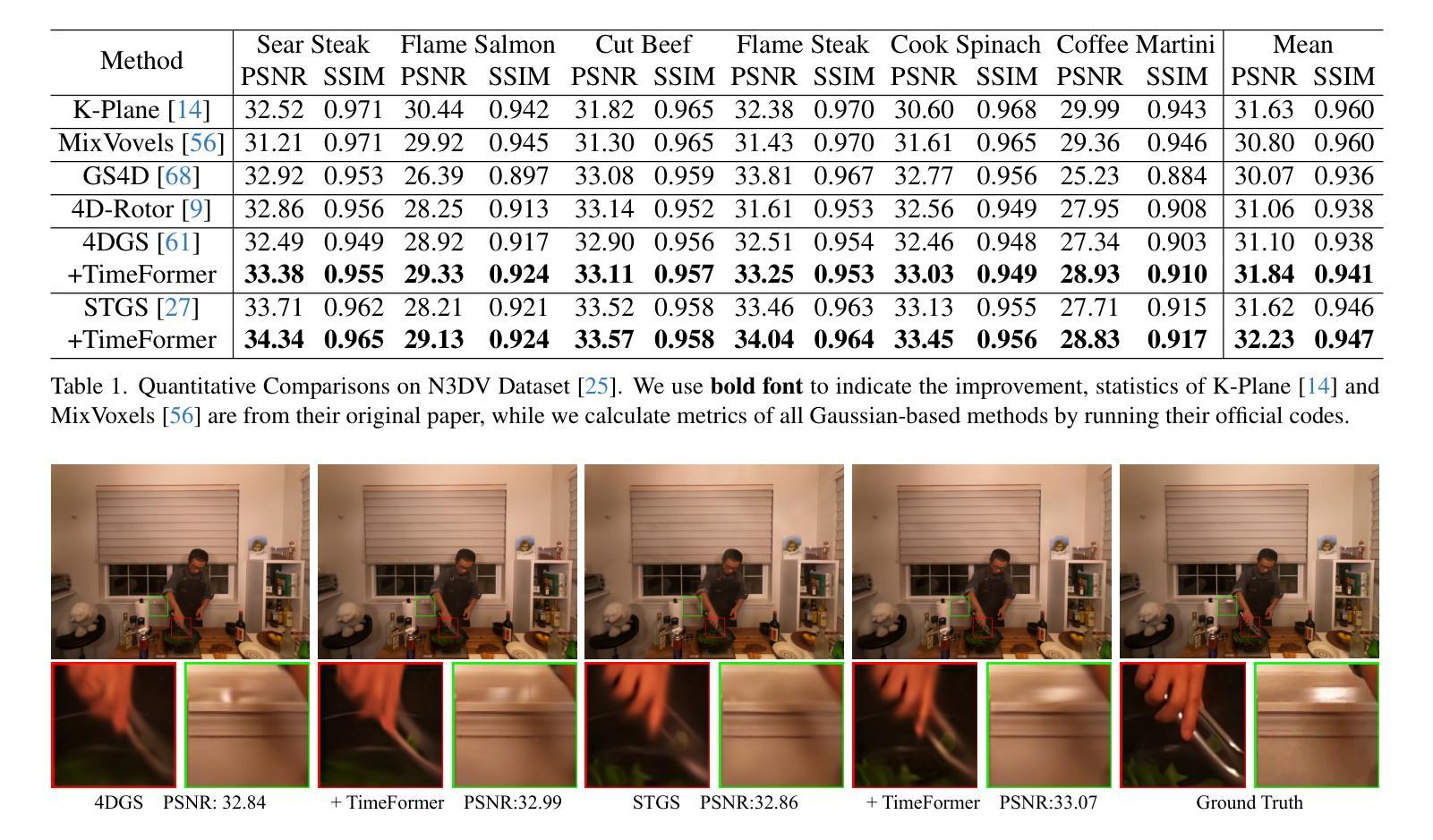
TimeFormer: Capturing Temporal Relationships of Deformable 3D Gaussians for Robust Reconstruction
Authors:DaDong Jiang, Zhihui Ke, Xiaobo Zhou, Zhi Hou, Xianghui Yang, Wenbo Hu, Tie Qiu, Chunchao Guo
Dynamic scene reconstruction is a long-term challenge in 3D vision. Recent methods extend 3D Gaussian Splatting to dynamic scenes via additional deformation fields and apply explicit constraints like motion flow to guide the deformation. However, they learn motion changes from individual timestamps independently, making it challenging to reconstruct complex scenes, particularly when dealing with violent movement, extreme-shaped geometries, or reflective surfaces. To address the above issue, we design a plug-and-play module called TimeFormer to enable existing deformable 3D Gaussians reconstruction methods with the ability to implicitly model motion patterns from a learning perspective. Specifically, TimeFormer includes a Cross-Temporal Transformer Encoder, which adaptively learns the temporal relationships of deformable 3D Gaussians. Furthermore, we propose a two-stream optimization strategy that transfers the motion knowledge learned from TimeFormer to the base stream during the training phase. This allows us to remove TimeFormer during inference, thereby preserving the original rendering speed. Extensive experiments in the multi-view and monocular dynamic scenes validate qualitative and quantitative improvement brought by TimeFormer. Project Page: https://patrickddj.github.io/TimeFormer/
动态场景重建是计算机三维视觉领域的一个长期挑战。最近的方法通过将三维高斯拼贴技术扩展到动态场景,并利用运动流等显式约束来引导变形,来解决这个问题。然而,这些方法独立地从各个时间戳学习运动变化,使得重建复杂场景变得具有挑战性,尤其是在处理剧烈的运动、极端形状的几何结构或反射表面时更是如此。为了解决上述问题,我们设计了一个即插即用的模块,名为TimeFormer,使现有的可变形三维高斯重建方法能够从学习角度隐式地模拟运动模式。具体来说,TimeFormer包括一个跨时间Transformer编码器,该编码器可以自适应地学习可变形三维高斯的时间关系。此外,我们还提出了一种双流优化策略,将TimeFormer在训练阶段学到的运动知识转移到基础流中。这允许我们在推理阶段移除TimeFormer,从而保持原始渲染速度。在多角度和单眼动态场景的大量实验验证了TimeFormer带来的定性和定量改进。项目页面:https://patrickddj.github.io/TimeFormer/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICCV 2025
Summary
动态场景重建是3D视觉领域的一个长期挑战。针对现有方法在复杂动态场景重建中的不足,如无法处理剧烈运动、极端形状几何或反射表面等,本文设计了一个名为TimeFormer的即插即用模块。该模块能增强现有可变形3D高斯重建方法的能力,使其能够隐式地从学习角度对运动模式进行建模。TimeFormer包括一个跨时间Transformer编码器,可自适应地学习可变形3D高斯值的临时关系。此外,还提出了一个两流优化策略,将在训练阶段从TimeFormer中学到的运动知识转移到基础流中。在推理阶段,可移除TimeFormer,从而保持原始渲染速度。通过多视角和单目动态场景的广泛实验验证了TimeFormer带来的定性和定量改进。
Key Takeaways
- 动态场景重建是3D视觉领域的长期挑战。
- 现有方法通过添加变形场和应用运动流等显式约束来扩展3D高斯贴片以适应动态场景。
- 现有方法独立学习各个时间戳的运动变化,对于复杂场景、剧烈运动、极端形状几何或反射表面的处理存在挑战。
- TimeFormer被设计为一个即插即用的模块,旨在增强现有可变形3D高斯重建方法的能力,使其能够隐式建模运动模式。
- TimeFormer包括一个跨时间Transformer编码器,可以自适应地学习可变形3D高斯值的临时关系。
- 提出了一个两流优化策略,将运动知识从TimeFormer转移到基础流中,并在训练阶段应用。
- 在推理阶段,可以移除TimeFormer以保持原始渲染速度,经过多视角和单目动态场景的广泛实验验证,TimeFormer能够提高定性和定量的表现。
点此查看论文截图

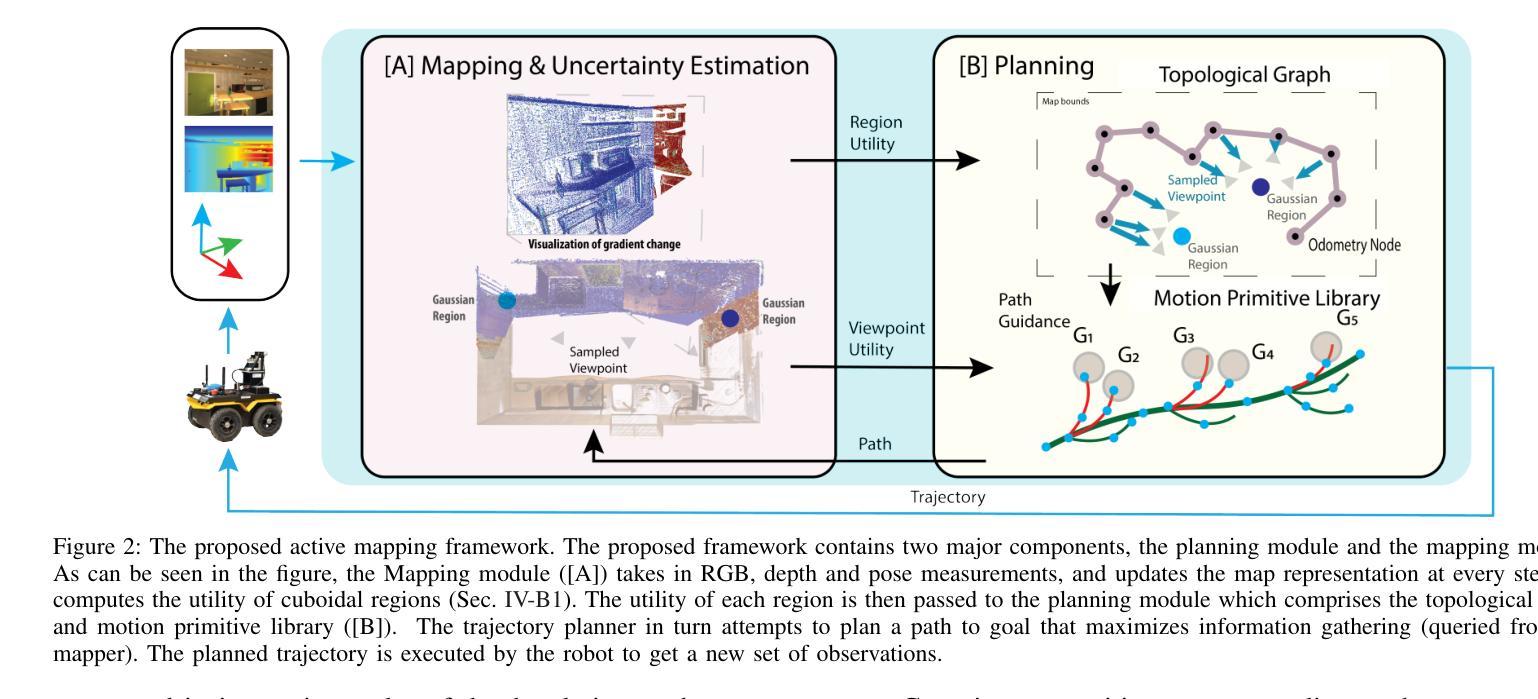
RT-GuIDE: Real-Time Gaussian Splatting for Information-Driven Exploration
Authors:Yuezhan Tao, Dexter Ong, Varun Murali, Igor Spasojevic, Pratik Chaudhari, Vijay Kumar
We propose a framework for active mapping and exploration that leverages Gaussian splatting for constructing dense maps. Further, we develop a GPU-accelerated motion planning algorithm that can exploit the Gaussian map for real-time navigation. The Gaussian map constructed onboard the robot is optimized for both photometric and geometric quality while enabling real-time situational awareness for autonomy. We show through viewpoint selection experiments that our method yields comparable Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR) and similar reconstruction error to state-of-the-art approaches, while being orders of magnitude faster to compute. In closed-loop physics-based simulation and real-world experiments, our algorithm achieves better map quality (at least 0.8dB higher PSNR and more than 16% higher geometric reconstruction accuracy) than maps constructed by a state-of-the-art method, enabling semantic segmentation using off-the-shelf open-set models. Experiment videos and more details can be found on our project page: https://tyuezhan.github.io/RT GuIDE/
我们提出一个利用高斯喷溅技术进行密集地图构建的主动映射和探索框架。此外,我们开发了一个GPU加速的运动规划算法,该算法可以利用高斯地图进行实时导航。在机器人内部构建的高斯地图针对光度和几何质量进行了优化,同时提高了自主性的实时情境意识。我们通过视点选择实验表明,我们的方法在峰值信噪比(PSNR)上产生了与最新技术相当的结果,重建误差相似,但计算速度却快得多。在闭环物理仿真和真实世界实验中,我们的算法在地图质量方面表现更好(至少高出0.8dB的PSNR和超过16%的几何重建精度),超越了当前最先进的地图构建方法,并使用现成的开放集模型实现了语义分割。实验视频和更多细节可以在我们的项目页面找到:https://tyuezhan.github.io/RT指引/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种利用高斯映射进行主动地图构建和探索的框架,并开发了一种GPU加速的运动规划算法,用于实时导航。该高斯地图在机器人上构建,优化光度和几何质量,提高实时态势感知能力。实验显示,该方法在峰值信噪比(PSNR)和重建误差方面与最新方法相当,但计算速度更快。在闭环物理仿真和真实实验中,该算法构建的地图质量优于现有方法,提高了至少0.8dB的PSNR和超过16%的几何重建精度,并实现了语义分割。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于高斯映射的主动地图构建和探索框架。
- 开发了一种GPU加速的运动规划算法,用于实时导航。
- 高斯地图在机器人上构建,同时优化光度和几何质量。
- 高斯地图能提高实时态势感知能力。
- 实验显示,该方法在计算速度和地图质量方面优于现有方法。
- 该算法构建的地图质量提高至少0.8dB的PSNR和超过16%的几何重建精度。
点此查看论文截图