⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-09 更新
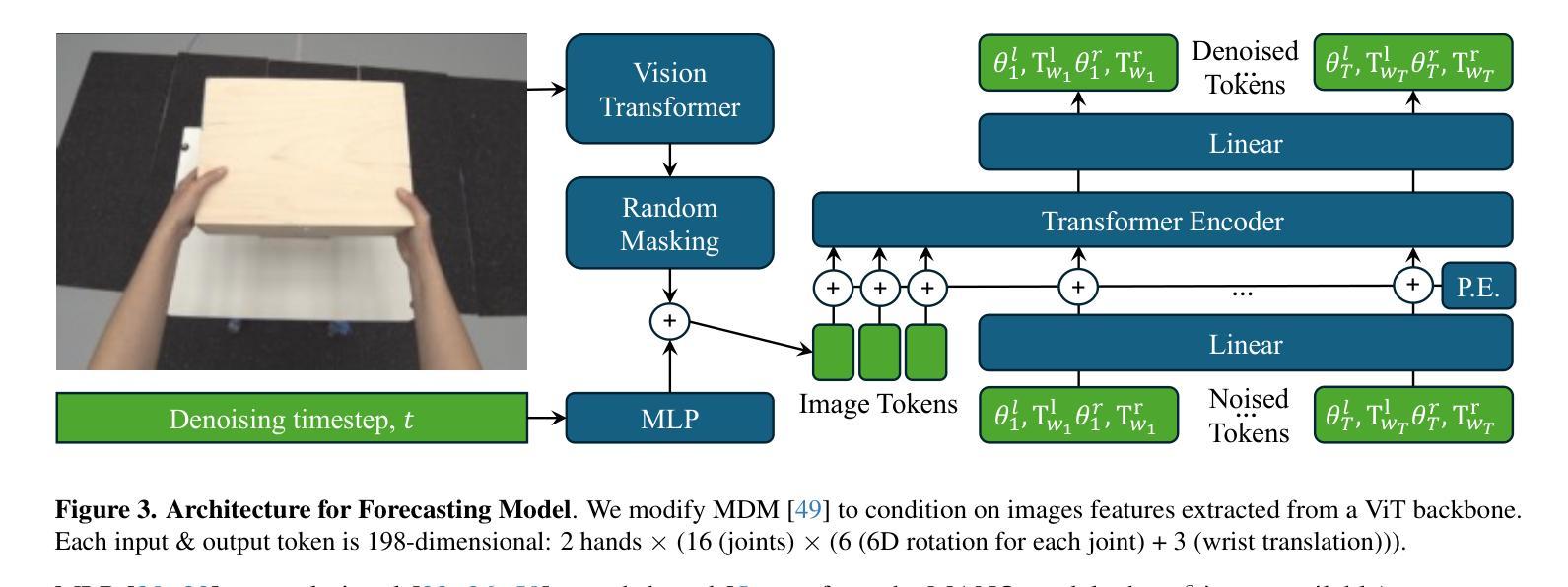
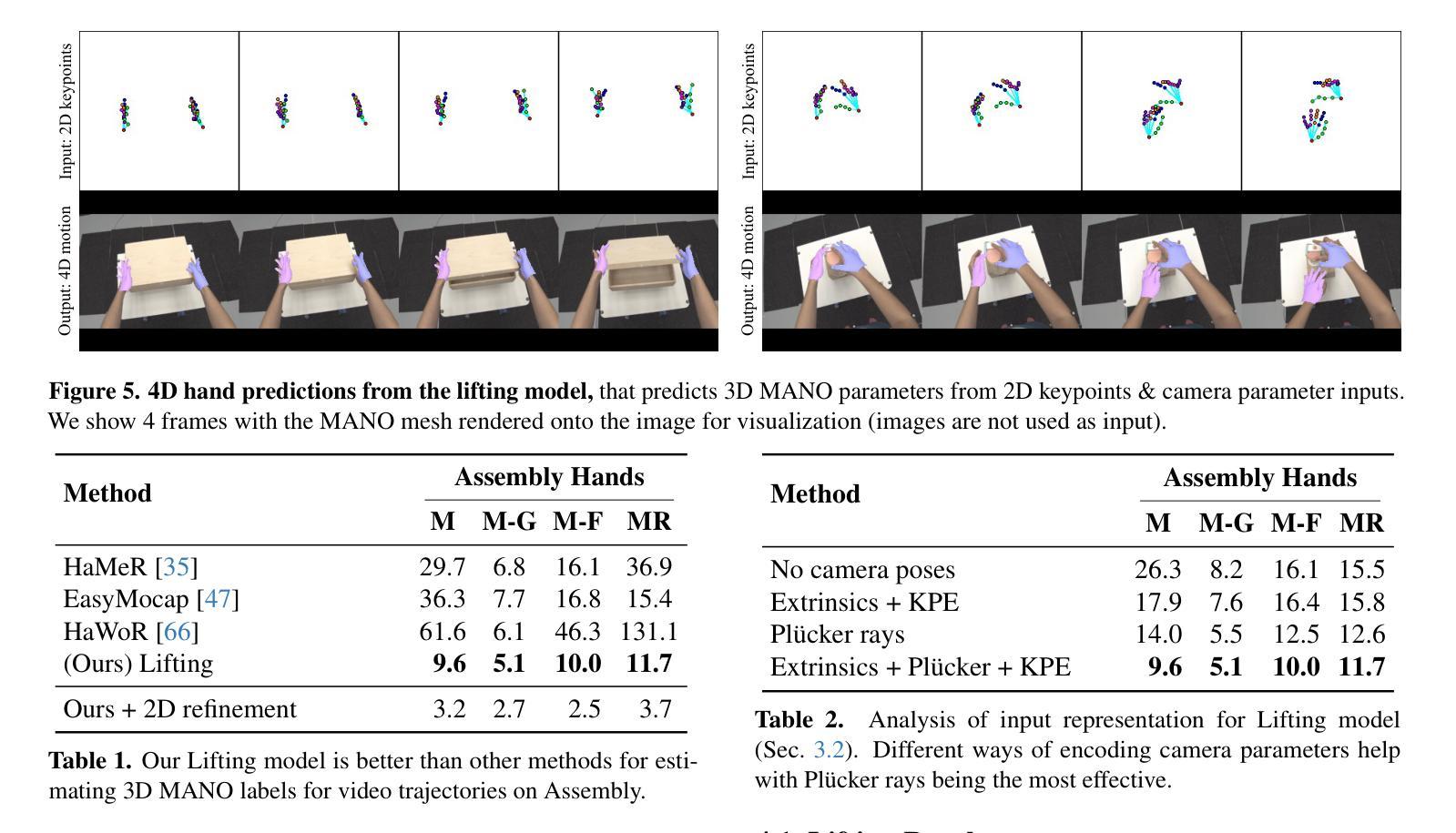
Bimanual 3D Hand Motion and Articulation Forecasting in Everyday Images
Authors:Aditya Prakash, David Forsyth, Saurabh Gupta
We tackle the problem of forecasting bimanual 3D hand motion & articulation from a single image in everyday settings. To address the lack of 3D hand annotations in diverse settings, we design an annotation pipeline consisting of a diffusion model to lift 2D hand keypoint sequences to 4D hand motion. For the forecasting model, we adopt a diffusion loss to account for the multimodality in hand motion distribution. Extensive experiments across 6 datasets show the benefits of training on diverse data with imputed labels (14% improvement) and effectiveness of our lifting (42% better) & forecasting (16.4% gain) models, over the best baselines, especially in zero-shot generalization to everyday images.
我们解决了在日常环境中从单幅图像预测双手3D动作和关节活动的问题。为了解决多样环境中缺乏3D手部标注的问题,我们设计了一个标注流程,包括使用扩散模型将2D手部关键点序列提升到4D手部动作。对于预测模型,我们采用了扩散损失来模拟手部运动分布中的多模态性。在六个数据集上的广泛实验表明,在具有插值标签的多样数据上进行训练的好处(提高了14%),以及我们的提升模型(提高了42%)和预测模型(提高了16.4%)相较于最佳基线模型的优越性,特别是在零样本推广到日常图像中的表现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://ap229997.github.io/projects/forehand4d
Summary:针对日常环境下的单图像双手动作预测和姿态估计问题,本研究采用扩散模型设计了一种标注管道,实现由二维手部关键点序列到四维手部运动的提升。通过采用扩散损失以应对手部运动分布的多模态问题。实验证明在多个数据集上的训练数据增强(采用填补标签方法提高模型泛化能力)的优势以及相比基准模型的提升,尤其在零样本图像上取得了显著的预测结果改进。通过训练和使用此技术,有望实现手部动作的准确预测。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究解决了从单图像预测双手在环境中的三维动作和姿态的问题。
- 设计了一种基于扩散模型的标注管道,用于将二维手部关键点序列提升到四维手部运动。
- 采用扩散损失来应对手部运动分布的多模态问题,以改善预测准确性。
- 在六个数据集上进行了广泛的实验,证明了通过填补标签的训练数据增强能够提高模型性能。
- 与现有最佳基线相比,该研究的手部提升和预测模型性能有所提升,特别是在零样本图像上取得了显著改进。
点此查看论文截图
Diffusion-Based Image Editing for Breaking Robust Watermarks
Authors:Yunyi Ni, Finn Carter, Ze Niu, Emily Davis, Bo Zhang
Robust invisible watermarking aims to embed hidden information into images such that the watermark can survive various image manipulations. However, the rise of powerful diffusion-based image generation and editing techniques poses a new threat to these watermarking schemes. In this paper, we present a theoretical study and method demonstrating that diffusion models can effectively break robust image watermarks that were designed to resist conventional perturbations. We show that a diffusion-driven ``image regeneration’’ process can erase embedded watermarks while preserving perceptual image content. We further introduce a novel guided diffusion attack that explicitly targets the watermark signal during generation, significantly degrading watermark detectability. Theoretically, we prove that as an image undergoes sufficient diffusion-based transformation, the mutual information between the watermarked image and the embedded watermark payload vanishes, resulting in decoding failure. Experimentally, we evaluate our approach on multiple state-of-the-art watermarking schemes (including the deep learning-based methods StegaStamp, TrustMark, and VINE) and demonstrate near-zero watermark recovery rates after attack, while maintaining high visual fidelity of the regenerated images. Our findings highlight a fundamental vulnerability in current robust watermarking techniques against generative model-based attacks, underscoring the need for new watermarking strategies in the era of generative AI.
鲁棒性隐形水印技术旨在将隐藏信息嵌入图像中,使水印能够抵御各种图像操作而保持不变。然而,基于扩散的图像生成和编辑技术的兴起,给这些水印方案带来了新的威胁。在本文中,我们进行了理论研究并展示了一种方法,证明扩散模型可以有效地破坏为抵抗传统扰动而设计的稳健图像水印。我们表明,扩散驱动的“图像再生”过程可以消除嵌入的水印,同时保留感知图像内容。我们进一步引入了一种新的引导扩散攻击,明确针对生成过程中的水印信号,显著降低了水印的可检测性。从理论上讲,我们证明了当图像经历足够的基于扩散的变换时,水印图像与嵌入的水印负载之间的互信息消失,导致解码失败。实验上,我们评估了我们的方法对于多种最先进的水印方案(包括基于深度学习的StegaStamp、TrustMark和VINE方法)的影响,并展示了在攻击后近乎为零的水印恢复率,同时保持再生图像的高视觉保真度。我们的研究凸显了当前稳健水印技术在面对生成模型攻击时的基本脆弱性,强调了生成人工智能时代需要新的水印策略。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
本文研究了扩散模型对鲁棒性图像水印的影响。实验表明,扩散模型可以有效破坏设计用于抵抗常规干扰的鲁棒图像水印。通过扩散驱动的“图像再生”过程,可以在保留感知图像内容的同时消除嵌入的水印。此外,还介绍了一种针对水印信号的新型引导扩散攻击,该攻击在生成过程中明确瞄准水印信号,大大降低了水印的可检测性。理论上证明,当图像经历足够的基于扩散的变换时,水印图像与嵌入的水印负载之间的互信息消失,导致解码失败。实验上,我们对多种先进的水印方案进行了评估,并展示了在受到攻击后近零的水印恢复率,同时保持再生图像的高视觉保真度。本文强调了当前鲁棒水印技术在面对生成模型攻击时的基本脆弱性,强调了生成人工智能时代需要新的水印策略。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型能够破坏设计用于抵抗常规干扰的鲁棒图像水印。
- 通过扩散驱动的“图像再生”过程可以消除嵌入的水印而不影响图像的感知内容。
- 引导扩散攻击能够针对水印信号进行攻击,显著降低水印的可检测性。
- 当图像经历足够的基于扩散的变换时,水印与图像内容之间的互信息会消失,导致解码失败。
- 实验证明,多种先进的水印方案在受到攻击后难以实现水印恢复。
- 现有的鲁棒水印技术在面对生成模型攻击时存在基本脆弱性。
点此查看论文截图
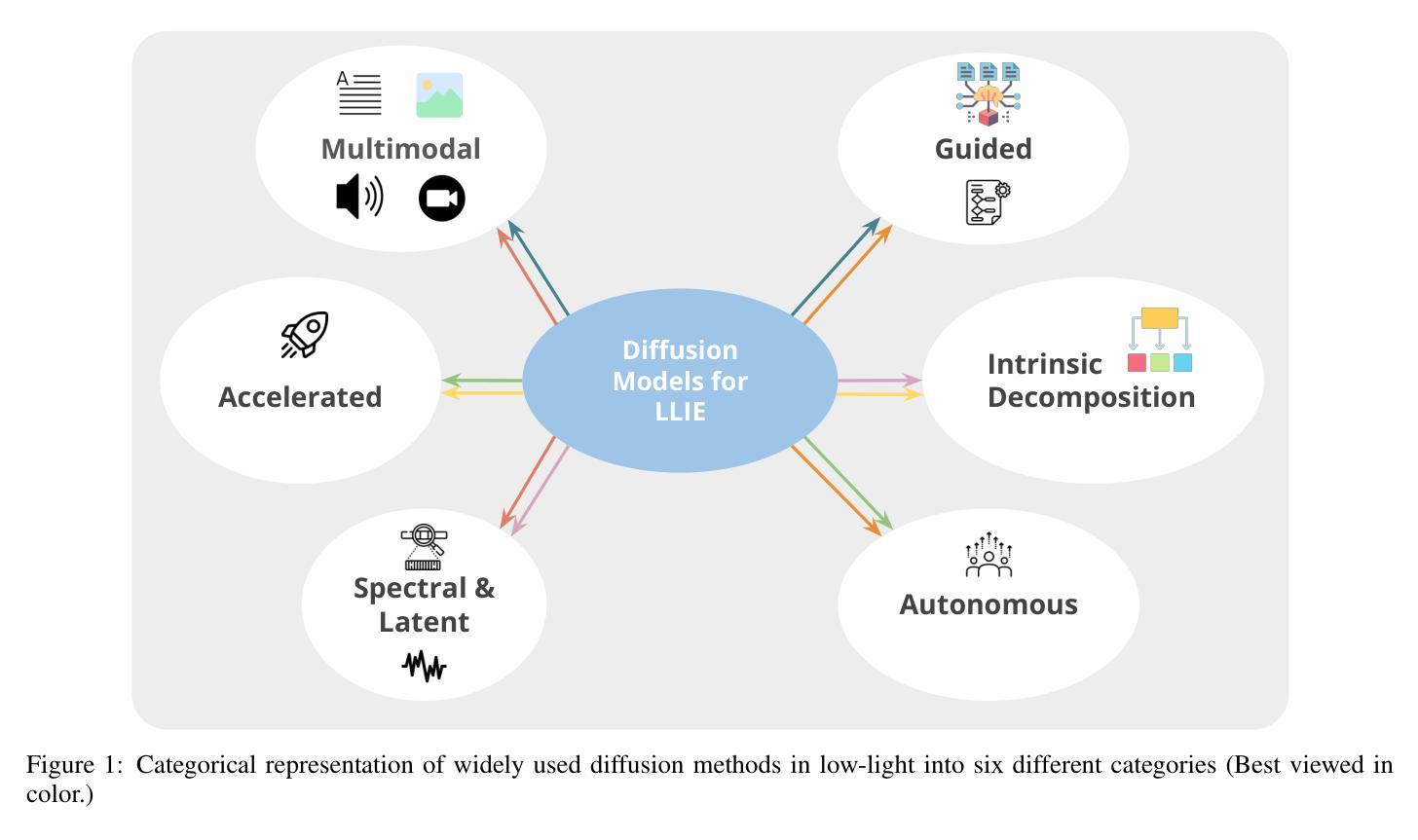
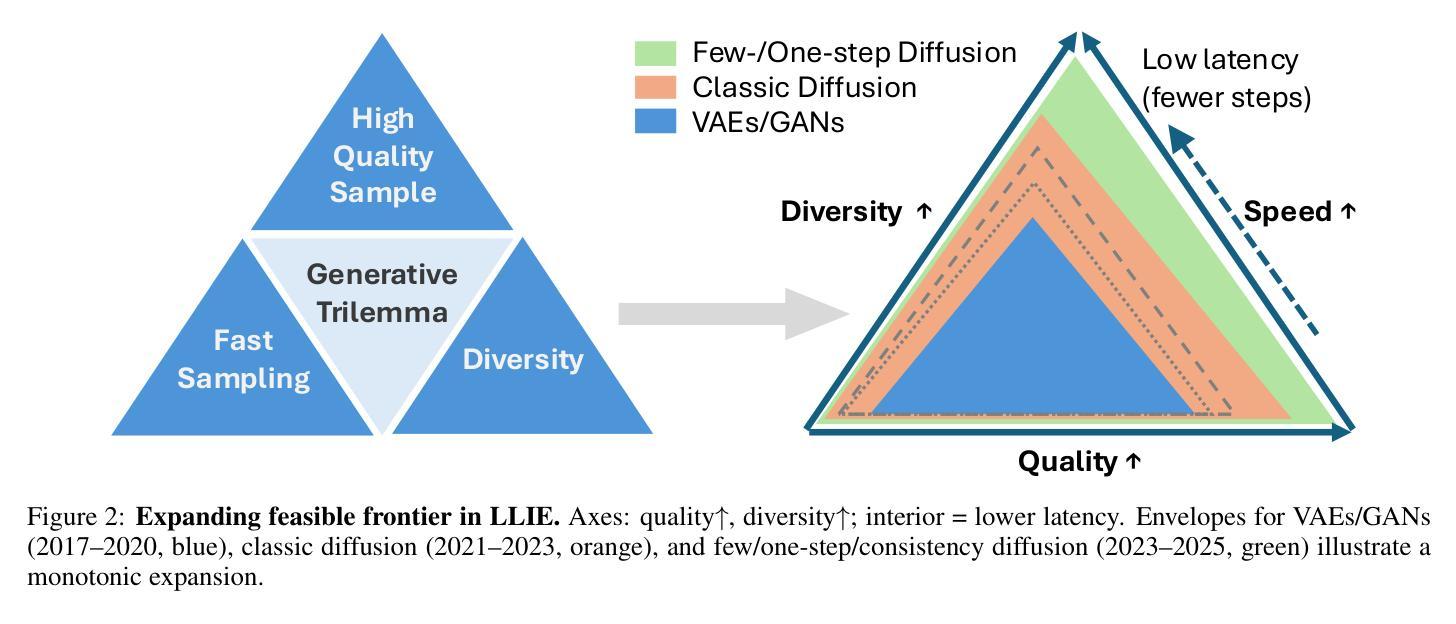
Diffusion Models for Low-Light Image Enhancement: A Multi-Perspective Taxonomy and Performance Analysis
Authors:Eashan Adhikarla, Yixin Liu, Brian D. Davison
Low-light image enhancement (LLIE) is vital for safety-critical applications such as surveillance, autonomous navigation, and medical imaging, where visibility degradation can impair downstream task performance. Recently, diffusion models have emerged as a promising generative paradigm for LLIE due to their capacity to model complex image distributions via iterative denoising. This survey provides an up-to-date critical analysis of diffusion models for LLIE, distinctively featuring an in-depth comparative performance evaluation against Generative Adversarial Network and Transformer-based state-of-the-art methods, a thorough examination of practical deployment challenges, and a forward-looking perspective on the role of emerging paradigms like foundation models. We propose a multi-perspective taxonomy encompassing six categories: Intrinsic Decomposition, Spectral & Latent, Accelerated, Guided, Multimodal, and Autonomous; that map enhancement methods across physical priors, conditioning schemes, and computational efficiency. Our taxonomy is grounded in a hybrid view of both the model mechanism and the conditioning signals. We evaluate qualitative failure modes, benchmark inconsistencies, and trade-offs between interpretability, generalization, and inference efficiency. We also discuss real-world deployment constraints (e.g., memory, energy use) and ethical considerations. This survey aims to guide the next generation of diffusion-based LLIE research by highlighting trends and surfacing open research questions, including novel conditioning, real-time adaptation, and the potential of foundation models.
低光图像增强(LLIE)对于监控、自主导航和医学影像等安全关键应用至关重要,在这些应用中,能见度下降会损害下游任务的性能。最近,由于能够通过迭代去噪对复杂图像分布进行建模,扩散模型已成为LLIE的一种有前景的生成范式。这篇综述提供了关于扩散模型在LLIE中的最新批判性分析,其特色包括与生成对抗网络和基于Transformer的最先进方法的深入性能比较评估、实际部署挑战的彻底检查以及新兴范式(如基础模型)作用的前瞻性视角。我们提出了一个多维度的分类体系,包括六大类别:内在分解、光谱与潜在、加速、指导、多模态和自主,这些方法涵盖了物理先验、条件方案和计算效率方面的增强方法。我们的分类体系既考虑了模型机制也考虑了条件信号的混合视图。我们评估了定性失败模式、基准不一致性以及在解释性、泛化和推理效率之间的权衡。我们还讨论了现实世界的部署约束(例如内存、能源使用)和伦理考量。本综述旨在通过突出趋势和提出开放的研究问题来指导下一代基于扩散的LLIE研究,包括新颖的条件、实时适应和潜在的基础模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在低光照图像增强(LLIE)领域表现出巨大的潜力,已成为当前的研究热点。本文提供了对扩散模型在LLIE领域的最新批判性分析,与生成对抗网络和基于Transformer的先进方法进行了深入的性能比较,探讨了实际部署挑战,并展望了基础模型等新兴范式的作用。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在LLIE领域具有巨大潜力,已成为研究热点。
- 扩散模型与其他先进方法(如生成对抗网络和基于Transformer的方法)进行了性能比较。
- 深入探讨了扩散模型在实际部署中的挑战。
- 提出了一个包含六类的多视角分类法,以映射增强方法、物理先验、条件方案和计算效率之间的关系。
- 评估了定性失败模式、基准不一致性,以及解释性、通用性和推理效率之间的权衡。
- 讨论了现实世界的部署约束,如内存、能源使用等。
点此查看论文截图
AgeBooth: Controllable Facial Aging and Rejuvenation via Diffusion Models
Authors:Shihao Zhu, Bohan Cao, Ziheng Ouyang, Zhen Li, Peng-Tao Jiang, Qibin Hou
Recent diffusion model research focuses on generating identity-consistent images from a reference photo, but they struggle to accurately control age while preserving identity, and fine-tuning such models often requires costly paired images across ages. In this paper, we propose AgeBooth, a novel age-specific finetuning approach that can effectively enhance the age control capability of adapterbased identity personalization models without the need for expensive age-varied datasets. To reduce dependence on a large amount of age-labeled data, we exploit the linear nature of aging by introducing age-conditioned prompt blending and an age-specific LoRA fusion strategy that leverages SVDMix, a matrix fusion technique. These techniques enable high-quality generation of intermediate-age portraits. Our AgeBooth produces realistic and identity-consistent face images across different ages from a single reference image. Experiments show that AgeBooth achieves superior age control and visual quality compared to previous state-of-the-art editing-based methods.
近期扩散模型的研究重点是从参考照片生成身份一致的图像,但它们在保持身份的同时,很难准确控制年龄,并且微调此类模型通常需要跨年龄的配对图像,成本较高。在本文中,我们提出了AgeBooth,这是一种新型的年龄特定微调方法,可以有效提高基于适配器的个性化模型的年龄控制能力,而无需昂贵的年龄变化数据集。为了减少对大量年龄标注数据的依赖,我们通过引入年龄条件提示混合和基于SVDMix矩阵融合技术的年龄特定LoRA融合策略,利用衰老的线性特性。这些技术能够生成高质量的中间年龄肖像。我们的AgeBooth能够从单一参考图像生成不同年龄段真实且身份一致的面部图像。实验表明,与基于编辑的现有先进方法相比,AgeBooth在年龄控制和视觉质量方面达到了更优越的效果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为AgeBooth的新型年龄特定微调方法,该方法可有效提高基于适配器的身份个性化模型的年龄控制能力,而无需昂贵的年龄变化数据集。通过引入年龄条件提示混合和基于SVDMix矩阵融合技术的年龄特定LoRA融合策略,减少了大量年龄标签数据的依赖。AgeBooth能够从单一参考图像生成不同年龄段真实且身份一致的人脸图像,并在实验上实现了比基于编辑的方法更优秀的年龄控制和视觉品质。
Key Takeaways
- AgeBooth是一种新型年龄特定微调方法,可提高扩散模型在生成身份一致图像时的年龄控制能力。
- AgeBooth可在无需昂贵的年龄变化数据集的情况下实现高效性能。
- 通过引入年龄条件提示混合策略,减少了大量标签数据的依赖。
- 利用SVDMix矩阵融合技术的年龄特定LoRA融合策略是提高模型性能的关键。
- AgeBooth能够从单一参考图像生成不同年龄段真实且身份一致的人脸图像。
- AgeBooth在年龄控制和视觉品质方面优于现有的基于编辑的方法。
点此查看论文截图
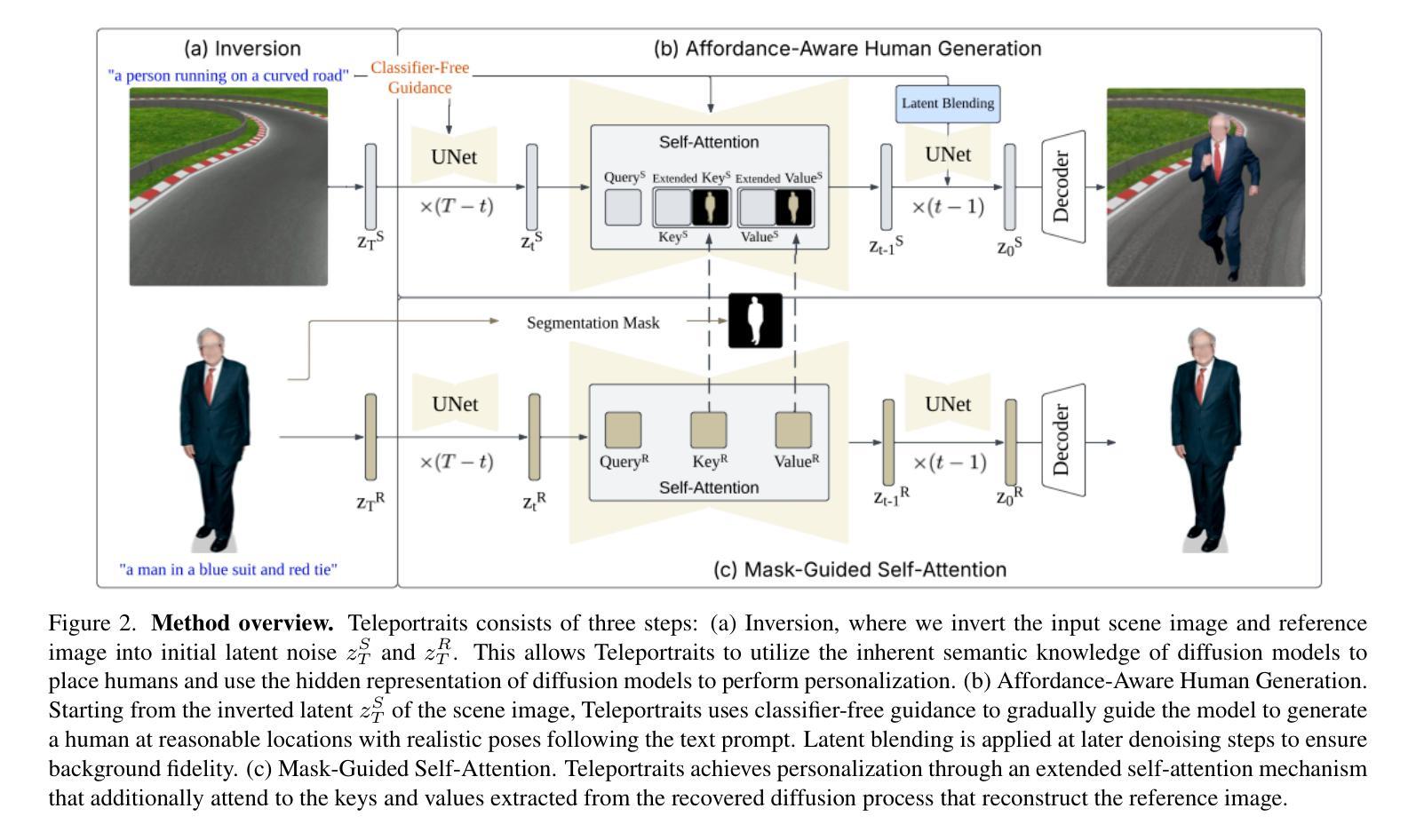
Teleportraits: Training-Free People Insertion into Any Scene
Authors:Jialu Gao, K J Joseph, Fernando De La Torre
The task of realistically inserting a human from a reference image into a background scene is highly challenging, requiring the model to (1) determine the correct location and poses of the person and (2) perform high-quality personalization conditioned on the background. Previous approaches often treat them as separate problems, overlooking their interconnections, and typically rely on training to achieve high performance. In this work, we introduce a unified training-free pipeline that leverages pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models. We show that diffusion models inherently possess the knowledge to place people in complex scenes without requiring task-specific training. By combining inversion techniques with classifier-free guidance, our method achieves affordance-aware global editing, seamlessly inserting people into scenes. Furthermore, our proposed mask-guided self-attention mechanism ensures high-quality personalization, preserving the subject’s identity, clothing, and body features from just a single reference image. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to perform realistic human insertions into scenes in a training-free manner and achieve state-of-the-art results in diverse composite scene images with excellent identity preservation in backgrounds and subjects.
将来自参考图像的人类现实地插入背景场景中的任务极具挑战性,需要模型(1)确定人的正确位置和姿势,(2)根据背景进行高质量个性化操作。以前的方法通常将它们视为单独的问题,忽略了它们之间的相互作用,通常依赖于训练来实现高性能。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种利用预训练文本到图像扩散模型的统一无训练管道。我们证明扩散模型本身具备在复杂场景中放置人的知识,而无需特定任务训练。通过结合反演技术与无分类器引导,我们的方法实现了感知能力的全局编辑,无缝地将人插入场景中。此外,我们提出的掩膜引导自注意力机制确保了高质量个性化,仅从单张参考图像中保留主体的身份、服装和身体特征。据我们所知,我们是首次以无训练的方式在场景中执行逼真的人类插入,并在具有多种复合场景图像的背景和主体中实现了卓越的身份保留,达到了业界领先水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
参考图像中的人物真实插入背景场景是一个具有挑战性的任务,需要模型确定人的正确位置和姿态,以及根据背景进行高质量个性化调整。以前的方法常常将其视为两个问题分开处理,忽略了它们之间的联系,并通常依赖于训练来实现高性能。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个无需训练的统一流程,利用预训练的文本到图像的扩散模型。我们展示了扩散模型本身就具备在复杂场景中放置人物的知识,无需特定任务训练。通过结合反演技术与无分类器引导,我们的方法实现了负担感知全局编辑,无缝地将人物插入场景中。此外,我们提出的掩膜引导自注意力机制确保了高质量的个人化调整,仅从一张参考图像中保留主体的身份、服装和身体特征。据我们所知,我们是第一个以无需训练的方式在场景中实现逼真的人物插入,并在复合场景图像中取得了出色的身份保留结果。
Key Takeaways
- 插入人物到背景场景是一个具有挑战的任务,需要模型确定人的正确位置和姿态,并要求高质量个性化调整。
- 以前的处理方法常常将这个问题分为两部分处理,忽略了它们之间的内在联系。
- 本研究利用预训练的文本到图像的扩散模型,提出了一个无需训练的统一流程来处理这个任务。
- 扩散模型本身具备在复杂场景中放置人物的知识。
- 结合反演技术和无分类器引导的方法实现了负担感知全局编辑。
- 提出的掩膜引导自注意力机制确保了高质量的个人化调整,保留了主体的身份、服装和身体特征。
点此查看论文截图

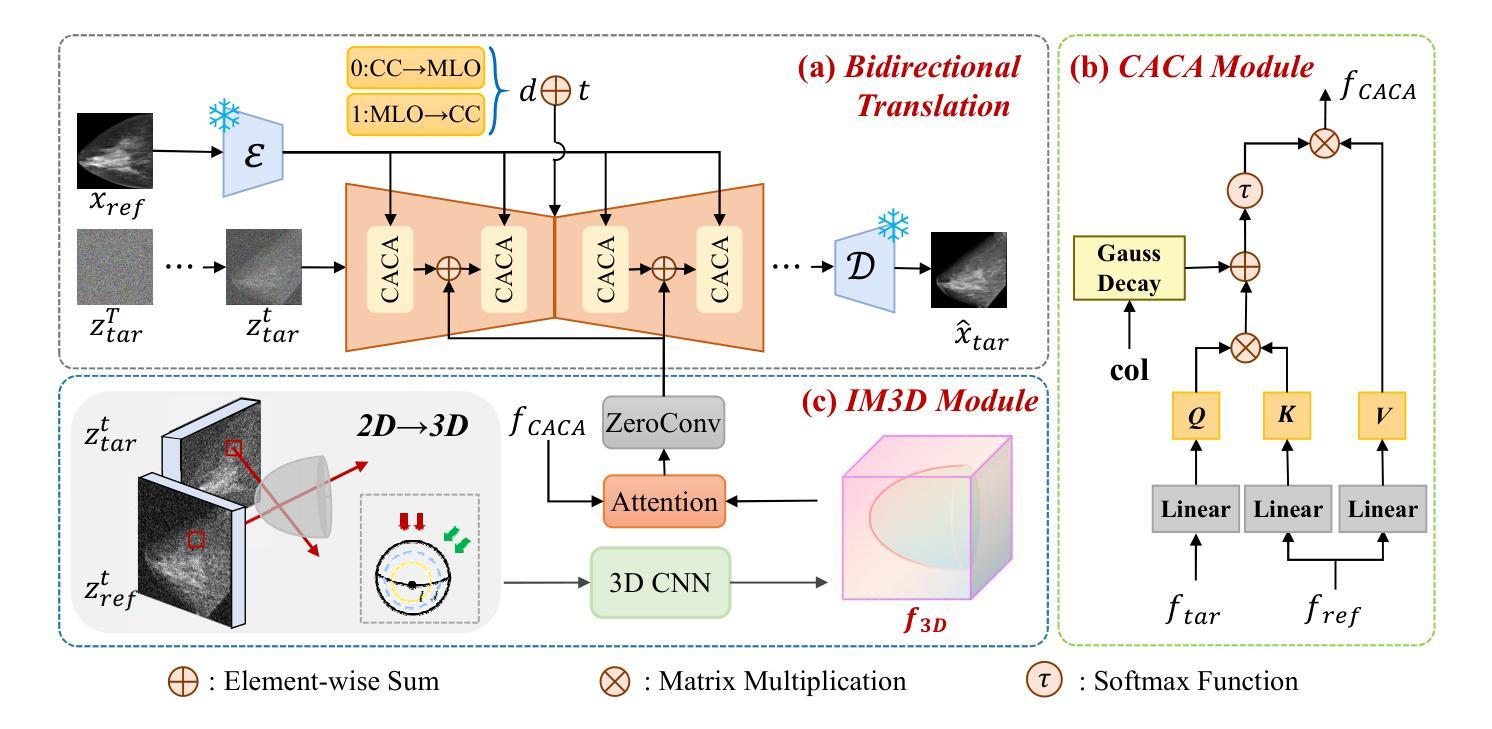
Bidirectional Mammogram View Translation with Column-Aware and Implicit 3D Conditional Diffusion
Authors:Xin Li, Kaixiang Yang, Qiang Li, Zhiwei Wang
Dual-view mammography, including craniocaudal (CC) and mediolateral oblique (MLO) projections, offers complementary anatomical views crucial for breast cancer diagnosis. However, in real-world clinical workflows, one view may be missing, corrupted, or degraded due to acquisition errors or compression artifacts, limiting the effectiveness of downstream analysis. View-to-view translation can help recover missing views and improve lesion alignment. Unlike natural images, this task in mammography is highly challenging due to large non-rigid deformations and severe tissue overlap in X-ray projections, which obscure pixel-level correspondences. In this paper, we propose Column-Aware and Implicit 3D Diffusion (CA3D-Diff), a novel bidirectional mammogram view translation framework based on conditional diffusion model. To address cross-view structural misalignment, we first design a column-aware cross-attention mechanism that leverages the geometric property that anatomically corresponding regions tend to lie in similar column positions across views. A Gaussian-decayed bias is applied to emphasize local column-wise correlations while suppressing distant mismatches. Furthermore, we introduce an implicit 3D structure reconstruction module that back-projects noisy 2D latents into a coarse 3D feature volume based on breast-view projection geometry. The reconstructed 3D structure is refined and injected into the denoising UNet to guide cross-view generation with enhanced anatomical awareness. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CA3D-Diff achieves superior performance in bidirectional tasks, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in visual fidelity and structural consistency. Furthermore, the synthesized views effectively improve single-view malignancy classification in screening settings, demonstrating the practical value of our method in real-world diagnostics.
双视角乳腺摄影(包括颅尾向(CC)和内外斜位(MLO)投影)为乳腺癌诊断提供了重要的互补解剖视角。然而,在现实的临床工作中,某一视角可能会丢失、损坏或退化,可能是由于采集错误或压缩造成的伪影等原因所致,这会限制下游分析的有效性。视角间的翻译(View-to-view translation)有助于恢复丢失的视角并改善病灶的对齐。然而,与自然图像不同,这一任务在乳腺摄影中具有极大的挑战性,原因在于X射线投影中存在较大的非刚性变形和严重的组织重叠,导致像素级对应关系被遮蔽。在本文中,我们提出了基于条件扩散模型的列感知和隐式三维扩散(CA3D-Diff)新型双向乳腺摄影视角翻译框架。为了解决跨视角的结构不对齐问题,我们首先设计了一种列感知交叉注意力机制,该机制利用几何属性,即解剖上对应的区域倾向于位于不同视角的相似列位置。应用高斯衰减偏差来强调局部列相关性,同时抑制远距离不匹配。此外,我们引入了一个隐式三维结构重建模块,该模块将噪声的二维潜在特征反向投影到基于乳腺视图投影几何的粗糙三维特征体积中。重建的三维结构经过优化后注入去噪UNet中,以指导跨视角生成增强了解剖结构意识。大量实验表明,CA3D-Diff在双向任务中表现出卓越的性能,在视觉保真度和结构一致性方面超过了最先进的方法。此外,合成的视图有效地提高了单视角恶性分类在筛查设置中的性能,证明了我们的方法在真实世界诊断中的实用价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF BIBM2025 accept, 8 pages, 4 figures
Summary
论文提出一种基于条件扩散模型的双向乳腺钼靶摄影视图转换框架,名为Column-Aware and Implicit 3D Diffusion(CA3D-Diff)。该框架通过列感知交叉注意力机制和隐式三维结构重建模块,解决了跨视图结构不匹配的问题,实现了双向的乳腺钼靶摄影视图转换。CA3D-Diff在双向任务上表现优越,合成的视图有效提高了单视图恶性分类的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 双视角乳腺钼靶摄影(包括颅尾位和内外斜位投影)对乳腺癌诊断至关重要。
- 实际临床工作中,某一视角的缺失、损坏或退化会影响后续分析的有效性。
- 视图到视图的转换可以恢复缺失的视图并改进病变对准。
- 论文提出了CA3D-Diff框架,基于条件扩散模型进行双向乳腺钼靶摄影视图转换。
- CA3D-Diff采用列感知交叉注意力机制,利用解剖上对应区域在跨视图中的列位置相似性。
- 隐式三维结构重建模块将噪声的二维潜在特征投影到基于乳腺视图几何的粗糙三维特征体积中。
点此查看论文截图
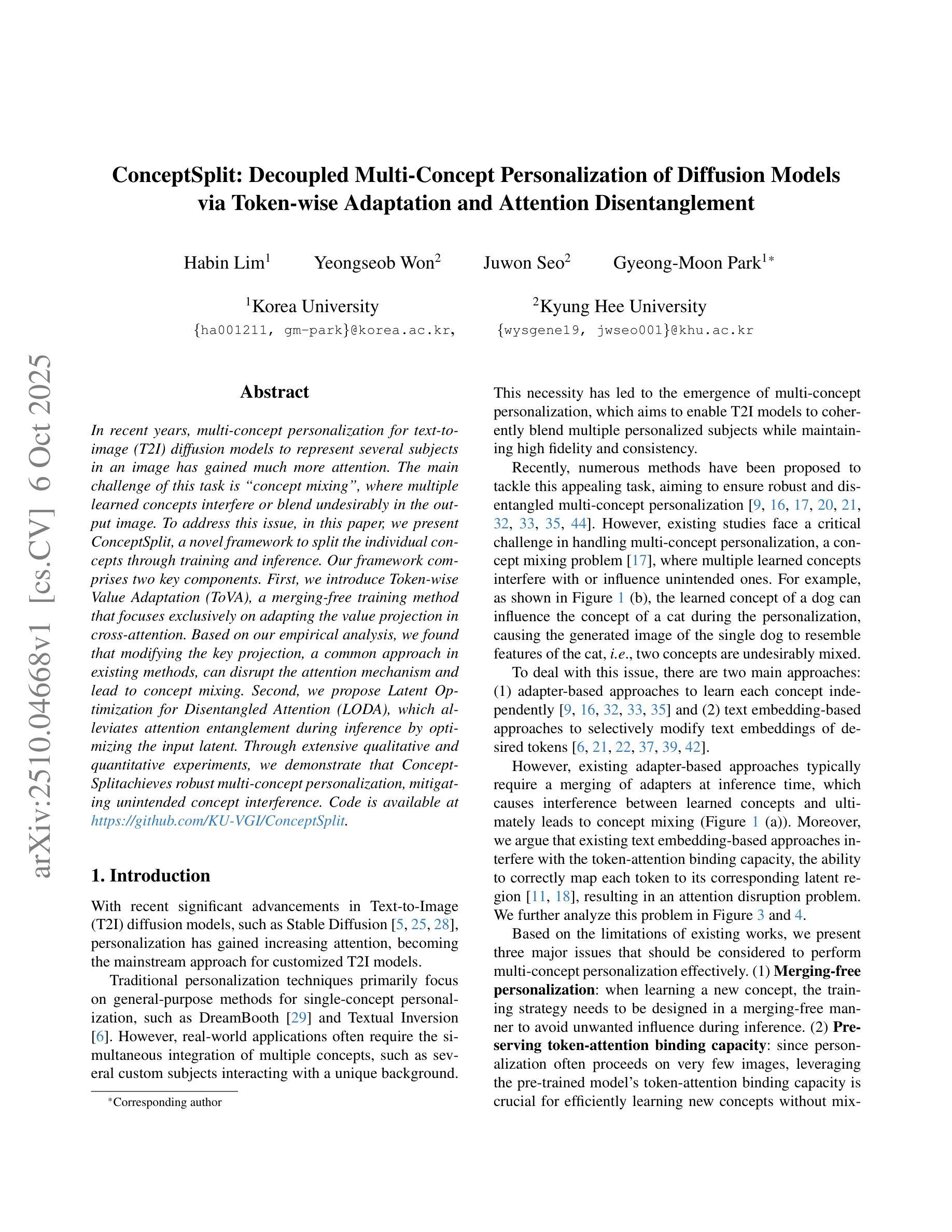
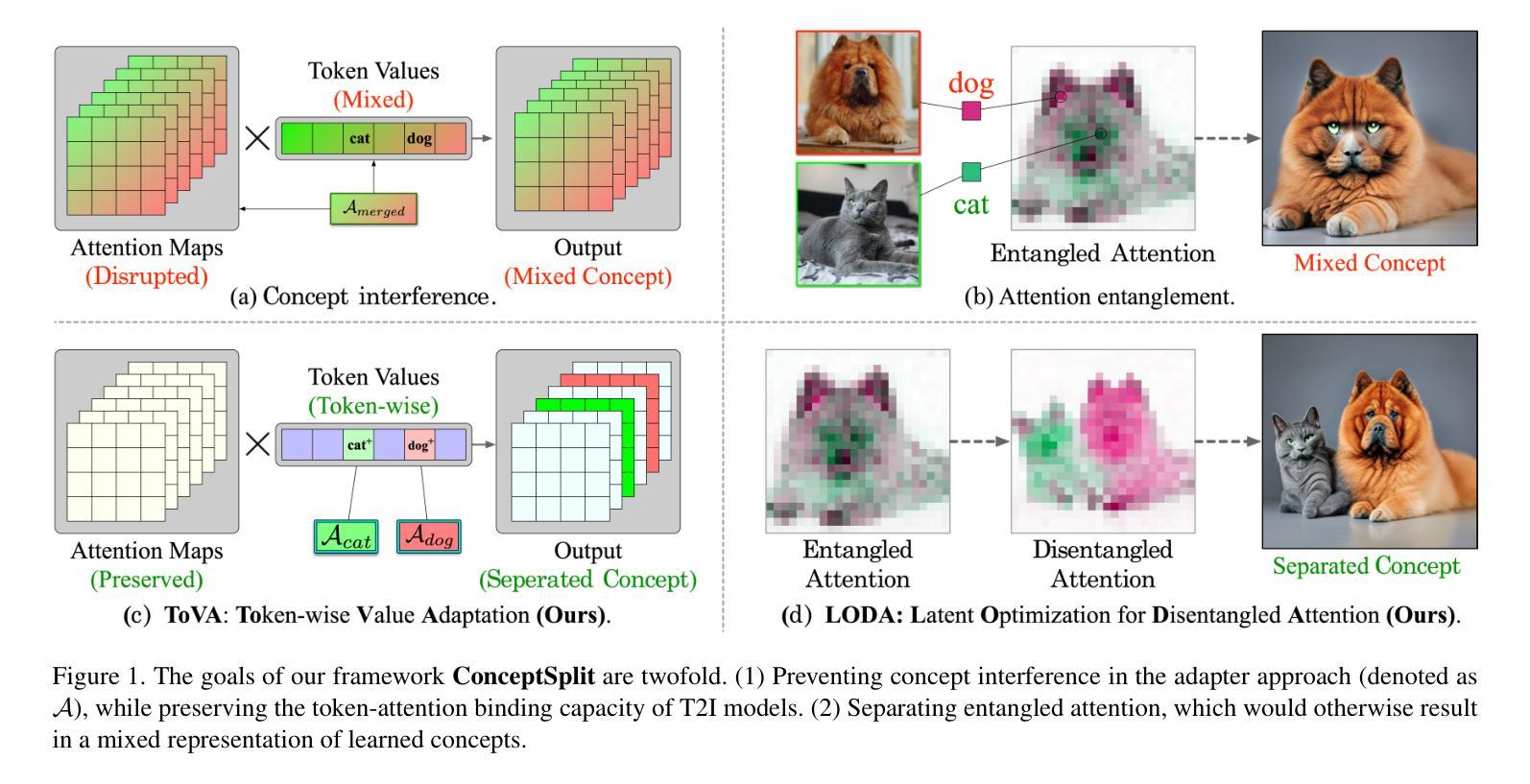
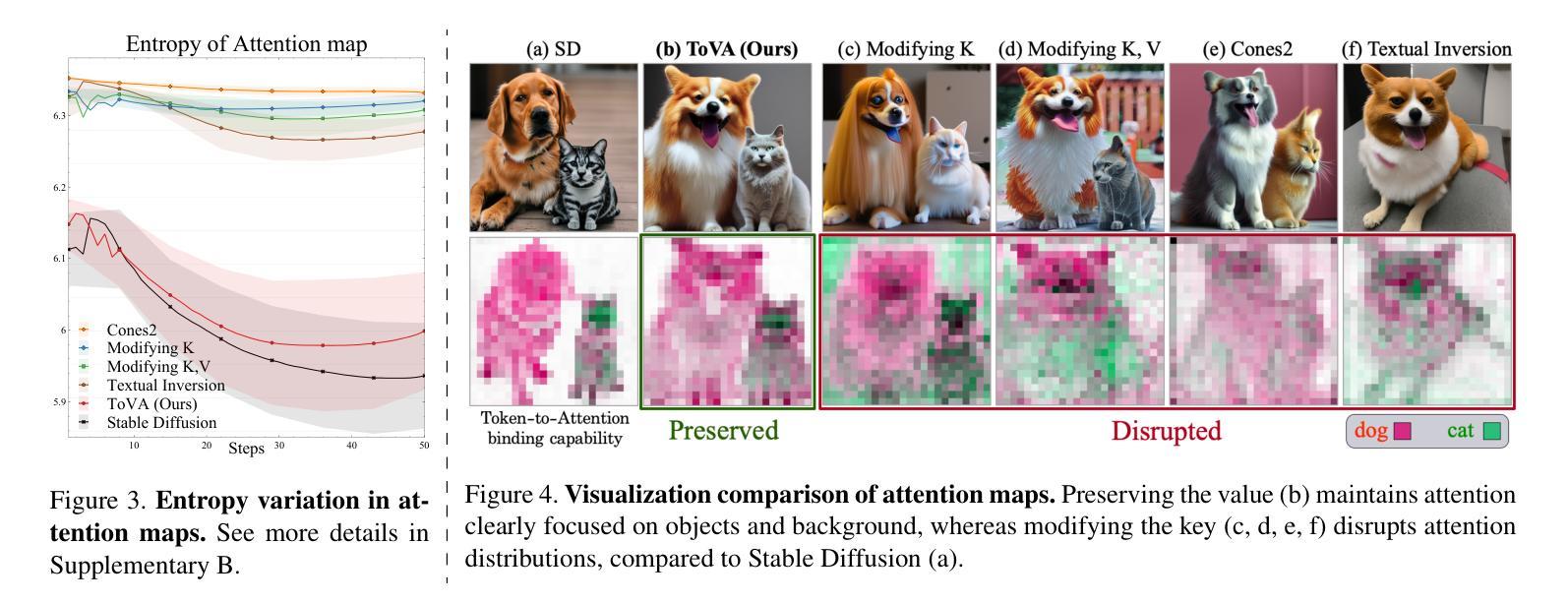
ConceptSplit: Decoupled Multi-Concept Personalization of Diffusion Models via Token-wise Adaptation and Attention Disentanglement
Authors:Habin Lim, Yeongseob Won, Juwon Seo, Gyeong-Moon Park
In recent years, multi-concept personalization for text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models to represent several subjects in an image has gained much more attention. The main challenge of this task is “concept mixing”, where multiple learned concepts interfere or blend undesirably in the output image. To address this issue, in this paper, we present ConceptSplit, a novel framework to split the individual concepts through training and inference. Our framework comprises two key components. First, we introduce Token-wise Value Adaptation (ToVA), a merging-free training method that focuses exclusively on adapting the value projection in cross-attention. Based on our empirical analysis, we found that modifying the key projection, a common approach in existing methods, can disrupt the attention mechanism and lead to concept mixing. Second, we propose Latent Optimization for Disentangled Attention (LODA), which alleviates attention entanglement during inference by optimizing the input latent. Through extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments, we demonstrate that ConceptSplit achieves robust multi-concept personalization, mitigating unintended concept interference. Code is available at https://github.com/KU-VGI/ConceptSplit
近年来,文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的多概念个性化(即在一个图像中表示多个主题)引起了广泛关注。这项任务的主要挑战是“概念混合”,即多个学习到的概念在输出图像中产生了干扰或产生了不希望看到的混合。为了解决这个问题,本文提出了一种新的框架ConceptSplit,通过训练和推理来拆分个人概念。我们的框架包含两个关键组件。首先,我们引入了Token级别的价值适应(ToVA),这是一种无合并的训练方法,专注于适应跨注意力的值投影。基于我们的经验分析,我们发现修改关键投影(现有方法中的常见做法)可能会破坏注意力机制并导致概念混合。其次,我们提出了用于解纠缠注意力的潜在优化(LODA),通过在推理过程中优化输入潜在量,减轻注意力纠缠。通过广泛的质量和数量实验,我们证明了ConceptSplit实现了稳健的多概念个性化,减轻了意外的概念干扰。代码可在https://github.com/KU-VGI/ConceptSplit找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 13 figures, to be published in ICCV 2025
Summary
文本主要介绍了针对文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的多概念个性化表示的挑战及解决方案。提出一种名为ConceptSplit的新框架,包含Token-wise Value Adaptation(ToVA)和Latent Optimization for Disentangled Attention(LODA)两个关键组件,以在训练和推理过程中分离个人概念,实现稳健的多概念个性化,缓解无意中的概念干扰。
Key Takeaways
- 多概念个性化在文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型中受到关注,主要挑战在于概念混合。
- ConceptSplit框架被提出以解决概念混合问题,包含Token-wise Value Adaptation(ToVA)和Latent Optimization for Disentangled Attention(LODA)两个关键组件。
- ToVA是一种无合并的训练方法,专注于跨注意力中的值投影适应。
- 现有方法中的关键投影修改可能会破坏注意力机制并导致概念混合。
- LODA通过优化输入潜在变量来缓解推理过程中的注意力纠缠。
- 通过定性和定量实验,证明ConceptSplit能够实现稳健的多概念个性化,并减轻无意中的概念干扰。
点此查看论文截图
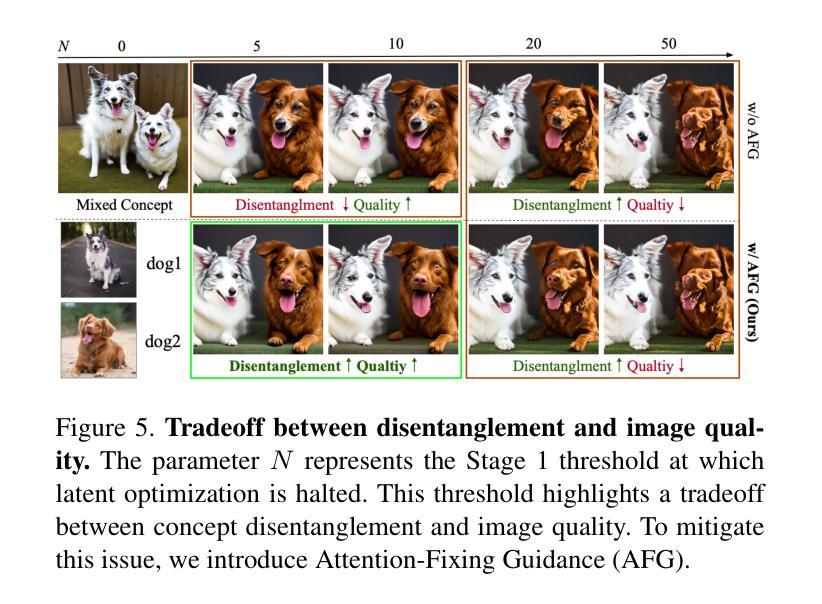

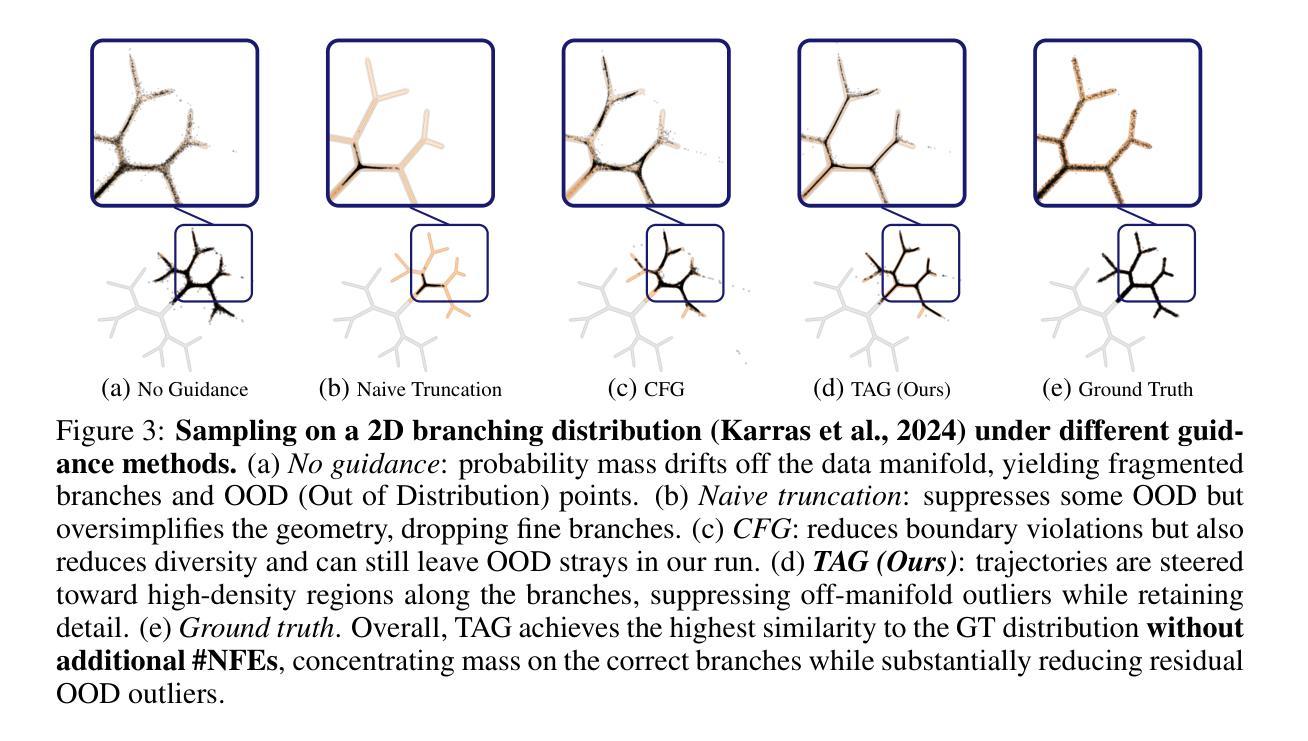
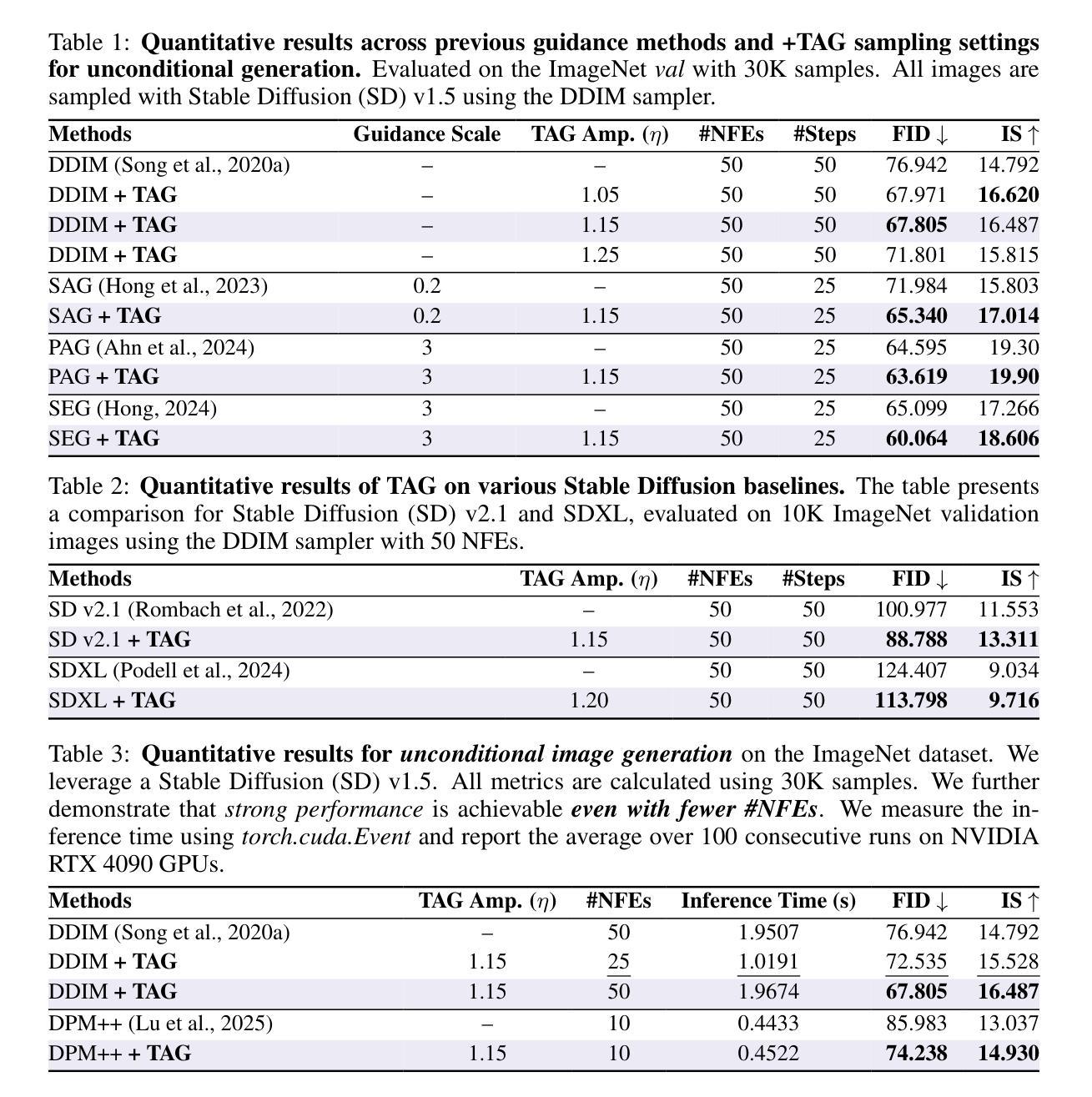
TAG:Tangential Amplifying Guidance for Hallucination-Resistant Diffusion Sampling
Authors:Hyunmin Cho, Donghoon Ahn, Susung Hong, Jee Eun Kim, Seungryong Kim, Kyong Hwan Jin
Recent diffusion models achieve the state-of-the-art performance in image generation, but often suffer from semantic inconsistencies or hallucinations. While various inference-time guidance methods can enhance generation, they often operate indirectly by relying on external signals or architectural modifications, which introduces additional computational overhead. In this paper, we propose Tangential Amplifying Guidance (TAG), a more efficient and direct guidance method that operates solely on trajectory signals without modifying the underlying diffusion model. TAG leverages an intermediate sample as a projection basis and amplifies the tangential components of the estimated scores with respect to this basis to correct the sampling trajectory. We formalize this guidance process by leveraging a first-order Taylor expansion, which demonstrates that amplifying the tangential component steers the state toward higher-probability regions, thereby reducing inconsistencies and enhancing sample quality. TAG is a plug-and-play, architecture-agnostic module that improves diffusion sampling fidelity with minimal computational addition, offering a new perspective on diffusion guidance.
最近的扩散模型在图像生成方面达到了最先进的性能,但经常遭受语义不一致或幻觉的困扰。虽然各种推理时间引导方法可以增强生成,但它们通常间接地依赖于外部信号或架构修改,这增加了额外的计算开销。在本文中,我们提出了“切线放大引导”(TAG),这是一种更高效和直接的引导方法,它仅作用于轨迹信号,无需修改基础扩散模型。TAG利用中间样本作为投影基础,放大估计分数相对于此基础的切线分量,以校正采样轨迹。我们通过利用一阶泰勒展开来正式化这一引导过程,这证明放大切线分量可以使状态转向高概率区域,从而减少不一致性,提高样本质量。TAG是一个即插即用的、与架构无关的模块,以最小的计算增加提高了扩散采样的保真度,为扩散引导提供了新的视角。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 9 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文提出了Tangential Amplifying Guidance(TAG)方法,通过操作采样轨迹来直接提高扩散模型的性能,而无需依赖外部信号或修改模型架构。该方法利用中间样本作为投影基础,放大估计分数的切线分量来校正采样轨迹。通过使用一阶泰勒展开式,证明放大切线分量可以使状态转向高概率区域,从而减少不一致性并提高样本质量。TAG是一个即插即用的、与架构无关的模块,能够在增加最少计算量的情况下提高扩散采样的保真度,为扩散指导提供了新的视角。
Key Takeaways
- TAG方法通过操作采样轨迹直接提高扩散模型的性能。
- TAG利用中间样本作为投影基础,放大估计分数的切线分量来校正采样轨迹。
- 一阶泰勒展开式被用于形式化这一过程,证明放大切线分量有助于提高采样质量。
- TAG方法无需依赖外部信号或修改模型架构。
- TAG是一个与架构无关的模块,可以很容易地集成到现有的扩散模型中。
- TAG在提高扩散采样保真度的同时,只增加了极少的计算量。
点此查看论文截图

Asynchronous Denoising Diffusion Models for Aligning Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Zijing Hu, Yunze Tong, Fengda Zhang, Junkun Yuan, Jun Xiao, Kun Kuang
Diffusion models have achieved impressive results in generating high-quality images. Yet, they often struggle to faithfully align the generated images with the input prompts. This limitation arises from synchronous denoising, where all pixels simultaneously evolve from random noise to clear images. As a result, during generation, the prompt-related regions can only reference the unrelated regions at the same noise level, failing to obtain clear context and ultimately impairing text-to-image alignment. To address this issue, we propose asynchronous diffusion models – a novel framework that allocates distinct timesteps to different pixels and reformulates the pixel-wise denoising process. By dynamically modulating the timestep schedules of individual pixels, prompt-related regions are denoised more gradually than unrelated regions, thereby allowing them to leverage clearer inter-pixel context. Consequently, these prompt-related regions achieve better alignment in the final images. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our asynchronous diffusion models can significantly improve text-to-image alignment across diverse prompts. The code repository for this work is available at https://github.com/hu-zijing/AsynDM.
扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面取得了令人印象深刻的结果。然而,它们通常难以忠实地将生成的图像与输入提示对齐。这一限制源于同步去噪,其中所有像素同时从随机噪声演化成清晰图像。因此,在生成过程中,提示相关区域只能引用同一噪声水平的无关区域,无法获得清晰的上下文,最终损害文本到图像的对齐。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了异步扩散模型——一种新型框架,为不同的像素分配不同的时间步长,并重新制定像素级的去噪过程。通过动态调制个别像素的时间步长调度,提示相关区域的去噪速度比无关区域更缓慢,从而允许它们利用更清晰的像素间上下文。因此,这些提示相关区域在最终图像中实现了更好的对齐。大量实验表明,我们的异步扩散模型可以在各种提示中显著提高文本到图像的对齐效果。该工作的代码仓库可在 https://github.com/hu-zijing/AsynDM 获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 11 figures, 5 tables
Summary
扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面表现出色,但在将生成图像与输入提示对齐方面存在困难。本文提出了一种新的异步扩散模型框架,为不同像素分配不同的时间步长并重新制定像素级的去噪过程。通过动态调制个别像素的时间步长表,与提示相关的区域去噪比无关区域更缓慢,从而可以利用更清晰的像素间上下文。因此,这些与提示相关的区域在最终图像中实现了更好的对齐。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面表现出色,但在文本到图像对齐方面存在挑战。
- 同步去噪是导致该挑战的主要原因,其中所有像素同时从随机噪声演变为清晰图像。
- 异步扩散模型框架被提出以解决这一问题,该框架为不同像素分配不同的时间步长。
- 与提示相关的区域在去噪过程中比无关区域更缓慢,从而利用更清晰的像素间上下文。
- 这种策略允许与提示相关的区域在最终图像中实现更好的对齐。
- 异步扩散模型在多种提示下显著改善了文本到图像的对齐。
- 相关代码仓库已公开发布。
点此查看论文截图

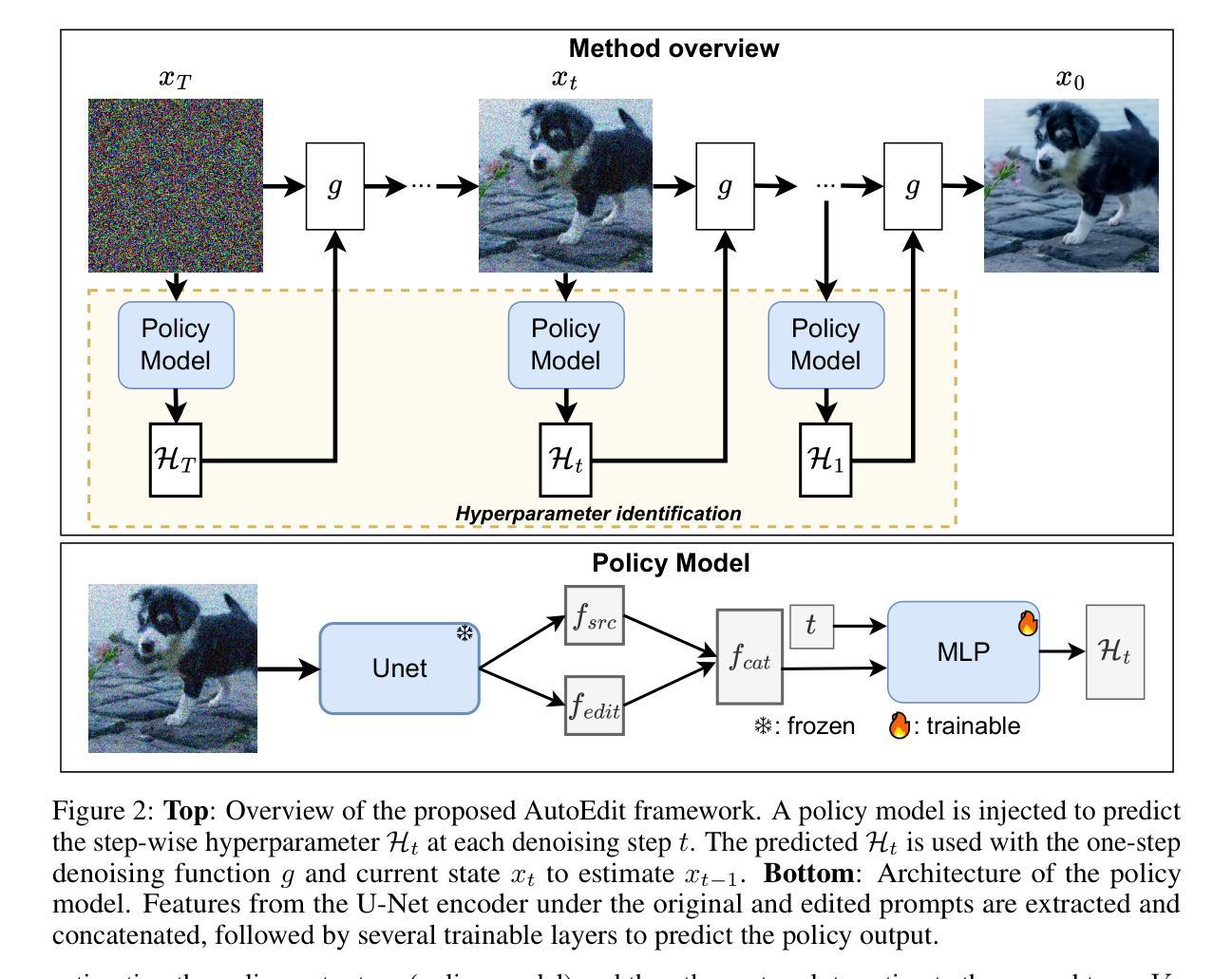
AutoEdit: Automatic Hyperparameter Tuning for Image Editing
Authors:Chau Pham, Quan Dao, Mahesh Bhosale, Yunjie Tian, Dimitris Metaxas, David Doermann
Recent advances in diffusion models have revolutionized text-guided image editing, yet existing editing methods face critical challenges in hyperparameter identification. To get the reasonable editing performance, these methods often require the user to brute-force tune multiple interdependent hyperparameters, such as inversion timesteps and attention modification. This process incurs high computational costs due to the huge hyperparameter search space. We consider searching optimal editing’s hyperparameters as a sequential decision-making task within the diffusion denoising process. Specifically, we propose a reinforcement learning framework, which establishes a Markov Decision Process that dynamically adjusts hyperparameters across denoising steps, integrating editing objectives into a reward function. The method achieves time efficiency through proximal policy optimization while maintaining optimal hyperparameter configurations. Experiments demonstrate significant reduction in search time and computational overhead compared to existing brute-force approaches, advancing the practical deployment of a diffusion-based image editing framework in the real world. Codes can be found at https://github.com/chaupham1709/AutoEdit.git.
最近扩散模型方面的进展彻底改变了文本引导的图像编辑,但现有的编辑方法在超参数识别方面面临重大挑战。为了获得合理的编辑性能,这些方法通常要求用户暴力调整多个相互依赖的超参数,如反转时间步长和注意力修改。由于超参数搜索空间巨大,这一过程产生了高昂的计算成本。我们将寻找最佳编辑超参数视为扩散去噪过程中的一个顺序决策任务。具体来说,我们提出了一种强化学习框架,该框架建立了一个马尔可夫决策过程,该过程在去噪步骤中动态调整超参数,并将编辑目标整合到奖励函数中。该方法通过近端策略优化实现了时间效率,同时保持了最佳超参数配置。实验表明,与现有的暴力方法相比,该方法在搜索时间和计算开销方面大大减少了,这推动了基于扩散的图像编辑框架在现实世界中的实际应用。代码可在https://github.com/chaupham1709/AutoEdit.git找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Provided code link
Summary
文本提出一种新的基于强化学习框架的扩散模型编辑超参数自动优化方法。该方法通过建立马尔可夫决策过程来动态调整编辑过程中的超参数,并将编辑目标整合到奖励函数中,提高了计算效率和超参数配置的优化水平。实验结果表明,与现有的暴力搜索方法相比,该方法在搜索时间和计算开销方面显著减少,推动了扩散模型图像编辑框架在实际应用中的部署。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本引导的图像编辑中的最新进展。
- 现有编辑方法面临超参数识别方面的挑战。
- 现有方法需要用户通过暴力方式调整多个相互依赖的超参数,如反演时间步长和注意力修改等。
- 提出一种基于强化学习的框架来解决最优编辑超参数的搜索问题。
- 建立马尔可夫决策过程,在降噪步骤中动态调整超参数。
- 将编辑目标整合到奖励函数中,以提高时间效率和保持超参数配置的优化。
点此查看论文截图
Robust Concept Erasure in Diffusion Models: A Theoretical Perspective on Security and Robustness
Authors:Zixuan Fu, Yan Ren, Finn Carter, Chenyue Wen, Le Ku, Daheng Yu, Emily Davis, Bo Zhang
Diffusion models have achieved unprecedented success in image generation but pose increasing risks in terms of privacy, fairness, and security. A growing demand exists to \emph{erase} sensitive or harmful concepts (e.g., NSFW content, private individuals, artistic styles) from these models while preserving their overall generative capabilities. We introduce \textbf{SCORE} (Secure and Concept-Oriented Robust Erasure), a novel framework for robust concept removal in diffusion models. SCORE formulates concept erasure as an \emph{adversarial independence} problem, theoretically guaranteeing that the model’s outputs become statistically independent of the erased concept. Unlike prior heuristic methods, SCORE minimizes the mutual information between a target concept and generated outputs, yielding provable erasure guarantees. We provide formal proofs establishing convergence properties and derive upper bounds on residual concept leakage. Empirically, we evaluate SCORE on Stable Diffusion and FLUX across four challenging benchmarks: object erasure, NSFW removal, celebrity face suppression, and artistic style unlearning. SCORE consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods including EraseAnything, ANT, MACE, ESD, and UCE, achieving up to \textbf{12.5%} higher erasure efficacy while maintaining comparable or superior image quality. By integrating adversarial optimization, trajectory consistency, and saliency-driven fine-tuning, SCORE sets a new standard for secure and robust concept erasure in diffusion models.
扩散模型在图像生成方面取得了前所未有的成功,但同时在隐私、公平和安全方面带来了日益增加的风险。因此,存在一种日益增长的需求,需要从这些模型中删除敏感或有害的概念(例如,NSFW内容、个人隐私问题、艺术风格等),同时保持其整体的生成能力。我们引入了SCORE(安全和面向概念稳健擦除),这是一个用于扩散模型中稳健概念删除的新型框架。SCORE将概念擦除表述为对抗独立性问题,从理论上保证了模型的输出与擦除的概念在统计上独立。与之前的启发式方法不同,SCORE最小化目标概念与生成输出之间的互信息,从而提供可证明的擦除保证。我们提供了正式证明来建立收敛属性并推导出剩余概念泄漏的上限。在实证方面,我们对Stable Diffusion和FLUX在四项具有挑战性的基准测试上评估了SCORE:对象擦除、NSFW删除、名人面部抑制和艺术风格去除。SCORE在各项性能指标上均表现最佳,超越了包括EraseAnything、ANT、MACE、ESD和UCE等最新技术方法,实现了高达**12.5%**的更高的擦除效率,同时保持或提高了图像质量。通过集成对抗优化、轨迹一致性和显著性驱动微调,SCORE为扩散模型中的安全稳健概念擦除设定了新的标准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF updated version
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型在图像生成领域取得的巨大成功,同时也指出了其在隐私、公平性和安全性方面日益增长的风险。为了解决这些问题,提出了一种名为SCORE的新型框架,用于在扩散模型中实现稳健的概念去除。SCORE将概念删除表述为对抗性独立问题,理论上保证了模型输出与删除概念之间的统计独立性。在多个基准测试中,SCORE表现出卓越的性能,实现了高达12.5%的删除效率提升,同时保持或提高了图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成领域的成功带来了隐私、公平性和安全性方面的风险。
- 提出了名为SCORE的新型框架,用于稳健地删除扩散模型中的特定概念。
- SCORE将概念删除表述为对抗性独立问题,确保模型输出与删除概念之间的统计独立性。
- SCORE通过整合对抗性优化、轨迹一致性和显著性驱动微调,实现了高效的概念删除。
- 在多个基准测试中,SCORE显著优于其他方法,包括EraseAnything、ANT、MACE、ESD和UCE。
- SCORE在删除效率上提高了高达12.5%,同时保持了图像质量。
点此查看论文截图
Divergence Minimization Preference Optimization for Diffusion Model Alignment
Authors:Binxu Li, Minkai Xu, Jiaqi Han, Meihua Dang, Stefano Ermon
Diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in generating realistic and versatile images from text prompts. Inspired by the recent advancements of language models, there is an increasing interest in further improving the models by aligning with human preferences. However, we investigate alignment from a divergence minimization perspective and reveal that existing preference optimization methods are typically trapped in suboptimal mean-seeking optimization. In this paper, we introduce Divergence Minimization Preference Optimization (DMPO), a novel and principled method for aligning diffusion models by minimizing reverse KL divergence, which asymptotically enjoys the same optimization direction as original RL. We provide rigorous analysis to justify the effectiveness of DMPO and conduct comprehensive experiments to validate its empirical strength across both human evaluations and automatic metrics. Our extensive results show that diffusion models fine-tuned with DMPO can consistently outperform or match existing techniques, specifically consistently outperforming all baseline models across different base models and test sets, achieving the best PickScore in every case, demonstrating the method’s superiority in aligning generative behavior with desired outputs. Overall, DMPO unlocks a robust and elegant pathway for preference alignment, bridging principled theory with practical performance in diffusion models.
扩散模型在根据文本提示生成现实且多样化的图像方面取得了显著的成功。受语言模型最新进展的启发,人们越来越感兴趣通过符合人类偏好来进一步改进模型。然而,我们从分歧最小化角度研究对齐问题,并揭示现有的偏好优化方法通常陷入次优的平均值寻求优化。在本文中,我们介绍了分歧最小化偏好优化(DMPO),这是一种通过最小化反向KL分歧来对齐扩散模型的新型有原则的方法,它在渐近情况下与原始强化学习具有相同的优化方向。我们提供了严格的分析来证明DMPO的有效性,并通过实验全面验证了其在人类评估和自动指标方面的实证实力。我们的广泛结果表明,使用DMPO微调过的扩散模型可以持续超越或匹配现有技术,特别是在不同的基准模型和测试集上持续超越所有基准模型,并且在每个案例中均获得最佳的PickScore,证明了该方法在将生成行为与期望输出对齐方面的优越性。总的来说,DMPO为偏好对齐解锁了稳健而优雅的途径,在原则理论与扩散模型的实践性能之间架起了一座桥梁。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型通过文本提示生成真实且多样化的图像,取得了显著的成功。随着语言模型的最新发展,人们越来越有兴趣通过与人类偏好对齐来改进这些模型。本文从分歧最小化角度研究对齐问题,并揭示现有偏好优化方法通常陷入次优均值寻求优化。本文介绍了一种新型的、基于分歧最小化偏好优化(DMPO)的扩散模型对齐方法,通过最小化反向KL分歧,该方法在优化方向上与原强化学习相同。本文进行了严格的分析来证明DMPO的有效性,并通过综合实验验证了其在人类评价和自动指标上的优越性。通过DMPO微调扩散模型能在不同基准模型和测试集上始终超越或匹配现有技术,且在每个案例中均获得最佳PickScore,证明了该方法在将生成行为与期望输出对齐方面的优越性。总体而言,DMPO为偏好对齐提供了稳健而优雅的途径,将原则理论与实际性能相结合。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型能够通过文本提示生成逼真的图像。
- 通过与语言模型的结合,人们正努力改进扩散模型以更好地与人类偏好对齐。
- 现有偏好优化方法存在次优均值寻求优化的问题。
- 提出了新型的基于分歧最小化偏好优化(DMPO)的方法来对扩散模型进行优化。
- DMPO通过最小化反向KL分歧来优化模型,其优化方向与原始强化学习相同。
- DMPO的有效性得到了严格的分析和实验验证,其在多个基准模型和测试集上的表现优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

Do We Need All the Synthetic Data? Targeted Synthetic Image Augmentation via Diffusion Models
Authors:Dang Nguyen, Jiping Li, Jinghao Zheng, Baharan Mirzasoleiman
Synthetically augmenting training datasets with diffusion models has been an effective strategy for improving generalization of image classifiers. However, existing techniques struggle to ensure the diversity of generation and increase the size of the data by up to 10-30x to improve the in-distribution performance. In this work, we show that synthetically augmenting part of the data that is not learned early in training with faithful images-containing same features but different noise-outperforms augmenting the entire dataset. By analyzing a two-layer CNN, we prove that this strategy improves generalization by promoting homogeneity in feature learning speed without amplifying noise. Our extensive experiments show that by augmenting only 30%-40% of the data, our method boosts generalization by up to 2.8% in a variety of scenarios, including training ResNet, ViT, ConvNeXt, and Swin Transformer on CIFAR-10/100, and TinyImageNet, with various optimizers including SGD and SAM. Notably, our method applied with SGD outperforms the SOTA optimizer, SAM, on CIFAR-100 and TinyImageNet.
利用扩散模型对训练数据集进行合成增强,是提高图像分类器泛化能力的有效策略。然而,现有技术在确保生成多样性和通过扩大数据规模(最多达10-30倍)以提高分布内性能方面遇到了困难。在这项工作中,我们展示了一种合成增强策略,该策略专门针对训练过程中早期未学会的部分数据进行增强,通过加入包含相同特征但噪声不同的忠实图像,其效果优于增强整个数据集。通过分析两层卷积神经网络,我们证明了该策略通过促进特征学习速度的均一性,提高了泛化能力,同时不会放大噪声。我们的大量实验表明,通过仅增强30%-40%的数据,我们的方法在多种场景下提高了泛化性能高达2.8%。这些场景包括在CIFAR-10/100和TinyImageNet上训练ResNet、ViT、ConvNeXt和Swin Transformer模型,以及使用SGD和SAM等多种优化器。值得注意的是,我们的方法与SGD相结合,在CIFAR-100和TinyImageNet上的性能优于当前最佳优化器SAM。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
利用扩散模型合成扩充训练数据集是提高图像分类器泛化能力的有效策略。然而,现有技术在确保生成多样性和通过扩大数据集规模(高达10-30倍)以提高内部性能分布方面面临挑战。本研究显示,仅对训练早期未学会的部分数据进行合成扩充,同时引入包含相同特征但不同噪声的忠实图像,其效果优于扩充整个数据集。通过分析两层卷积神经网络,我们证明该策略通过促进特征学习速度的同质性,提高了泛化能力,同时不会放大噪声。大量实验表明,仅扩充30%-40%的数据,我们的方法在多种场景下将泛化能力提高了2.8%。这些场景包括在CIFAR-10/100、TinyImageNet上使用ResNet、ViT、ConvNeXt和Swin Transformer进行训练,以及使用SGD和SAM等多种优化器。值得注意的是,我们的方法与SGD一起应用在CIFAR-100和TinyImageNet上的表现优于SOTA优化器SAM。
关键见解
- 扩散模型合成扩充训练数据集有助于提高图像分类器的泛化能力。
- 现有技术面临的挑战在于确保生成的多样性和扩大数据集规模以提高内部性能分布。
- 仅对训练早期未学会的部分数据进行合成扩充,引入忠实图像,其效果更佳。
- 该策略通过促进特征学习速度的同质性和降低噪声,提高模型的泛化能力。
- 仅扩充30%-40%的数据,就能在多种场景下显著提高模型的泛化能力。
- 在多种图像分类任务(如CIFAR-10/100、TinyImageNet)和多种优化器(如SGD和SAM)下验证了该方法的有效性。
- 与其他优化器相比,该方法与SGD结合使用时在特定任务上的表现更佳。
点此查看论文截图

HOG-Diff: Higher-Order Guided Diffusion for Graph Generation
Authors:Yiming Huang, Tolga Birdal
Graph generation is a critical yet challenging task as empirical analyses require a deep understanding of complex, non-Euclidean structures. Diffusion models have recently made significant achievements in graph generation, but these models are typically adapted from image generation frameworks and overlook inherent higher-order topology, leaving them ill-suited for capturing the topological properties of graphs. In this work, we propose Higher-order Guided Diffusion (HOG-Diff), a principled framework that progressively generates plausible graphs with inherent topological structures. HOG-Diff follows a coarse-to-fine generation curriculum guided by higher-order topology and implemented via diffusion bridges. We further prove that our model exhibits a stronger theoretical guarantee than classical diffusion frameworks. Extensive experiments on both molecular and generic graph generation tasks demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms or remains competitive with state-of-the-art baselines. Our code is available at https://github.com/Yiminghh/HOG-Diff.
图的生成是一项至关重要且具有挑战性的任务,因为它需要对复杂的非欧几里得结构进行深入理解。虽然扩散模型在图的生成方面最近取得了重大进展,但这些模型通常是从图像生成框架中改编而来,忽略了固有的高阶拓扑结构,导致它们不适合捕捉图的拓扑属性。在这项工作中,我们提出了高阶引导扩散(HOG-Diff),这是一个基于原理的框架,能够逐步生成具有固有拓扑结构的合理图。HOG-Diff遵循由高阶拓扑引导的由粗到细的生成课程,并通过扩散桥实现。我们还证明,我们的模型相比传统的扩散框架具有更强的理论保证。在分子和通用图生成任务上的大量实验表明,我们的方法始终优于或保持与最新基线方法的竞争力。我们的代码可在https://github.com/Yiminghh/HOG-Diff获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了高阶引导扩散(HOG-Diff)框架,用于逐步生成具有内在拓扑结构的图。该框架通过高阶拓扑引导粗到细的生成课程,并通过扩散桥实现。实验证明,该方法在分子和通用图生成任务上均表现出优异的性能,且较传统扩散框架有更强的理论保证。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图形生成中具有显著成果,但现有模型忽略高阶拓扑结构,难以捕捉图形的拓扑属性。
- 提出高阶引导扩散(HOG-Diff)框架,旨在逐步生成具有内在拓扑结构的图形。
- HOG-Diff采用粗到细的生成课程,通过高阶拓扑引导,并通过扩散桥实现。
- HOG-Diff具有比传统扩散框架更强的理论保证。
- 在分子和通用图生成任务上,HOG-Diff性能卓越,较现有方法表现出竞争力。
- 该研究的代码已公开可访问。
点此查看论文截图
SEE-DPO: Self Entropy Enhanced Direct Preference Optimization
Authors:Shivanshu Shekhar, Shreyas Singh, Tong Zhang
Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) has been successfully used to align large language models (LLMs) according to human preferences, and more recently it has also been applied to improving the quality of text-to-image diffusion models. However, DPO-based methods such as SPO, Diffusion-DPO, and D3PO are highly susceptible to overfitting and reward hacking, especially when the generative model is optimized to fit out-of-distribution during prolonged training. To overcome these challenges and stabilize the training of diffusion models, we introduce a self-entropy regularization mechanism in reinforcement learning from human feedback. This enhancement improves DPO training by encouraging broader exploration and greater robustness. Our regularization technique effectively mitigates reward hacking, leading to improved stability and enhanced image quality across the latent space. Extensive experiments demonstrate that integrating human feedback with self-entropy regularization can significantly boost image diversity and specificity, achieving state-of-the-art results on key image generation metrics.
直接偏好优化(DPO)已成功用于根据人类偏好对齐大型语言模型(LLM),最近也应用于提高文本到图像扩散模型的质量。然而,基于DPO的方法,如SPO、Diffusion-DPO和D3PO,非常容易过度拟合和奖励黑客行为,特别是当生成模型在长时间的训练过程中被优化以适应非分布数据时。为了克服这些挑战并稳定扩散模型的训练,我们引入了基于人类反馈的强化学习中的自我熵正则化机制。这种增强通过鼓励更广泛的探索和更大的稳健性,改进了DPO训练。我们的正则化技术有效地减轻了奖励黑客行为,提高了潜伏空间中的稳定性和图像质量。大量实验表明,将人类反馈与自我熵正则化相结合,可以显著提高图像的多样性和特异性,并在关键图像生成指标上达到最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在文本到图像扩散模型中应用直接偏好优化(DPO)方法时面临的挑战,如过度拟合和奖励滥用。为解决这些问题并稳定扩散模型的训练,引入了一种基于强化学习的自我熵正则化机制。这种机制能够改善DPO训练,提高模型的稳健性和图像质量。实验表明,结合人类反馈的自我熵正则化可以显著提高图像的多样性和特异性,达到图像生成的关键指标的最先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- 直接偏好优化(DPO)已成功应用于文本到图像扩散模型的优化。
- DPO方法面临过度拟合和奖励滥用的问题。
- 自我熵正则化机制被引入以解决DPO方法的挑战并稳定扩散模型的训练。
- 自我熵正则化机制鼓励模型进行更广泛的探索,提高稳健性。
- 结合人类反馈的自我熵正则化能显著提高图像的多样性和特异性。
- 该方法达到图像生成的关键指标的最先进水平。
点此查看论文截图


Fast constrained sampling in pre-trained diffusion models
Authors:Alexandros Graikos, Nebojsa Jojic, Dimitris Samaras
Large denoising diffusion models, such as Stable Diffusion, have been trained on billions of image-caption pairs to perform text-conditioned image generation. As a byproduct of this training, these models have acquired general knowledge about image statistics, which can be useful for other inference tasks. However, when confronted with sampling an image under new constraints, e.g. generating the missing parts of an image, using large pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models is inefficient and often unreliable. Previous approaches either utilized backpropagation through the denoiser network, making them significantly slower and more memory-demanding than simple text-to-image generation, or only enforced the constraint locally, failing to capture critical long-range correlations in the sampled image. In this work, we propose an algorithm that enables fast, high-quality generation under arbitrary constraints. We show that in denoising diffusion models, we can employ an approximation to Newton’s optimization method that allows us to speed up inference and avoid the expensive backpropagation operations. Our approach produces results that rival or surpass the state-of-the-art training-free inference methods while requiring a fraction of the time. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our algorithm under both linear (inpainting, super-resolution) and non-linear (style-guided generation) constraints. An implementation is provided at https://github.com/cvlab-stonybrook/fast-constrained-sampling.
大型去噪扩散模型(如Stable Diffusion)已经接受了数十亿张图像标题对的训练,用于执行文本条件图像生成。作为这种训练的副产品,这些模型已经获得了关于图像统计的通用知识,这对于其他推理任务可能是有用的。然而,当面临在新的约束下采样图像时,例如生成图像缺失的部分,使用大型预训练文本到图像扩散模型效率低下且往往不可靠。以前的方法要么通过去噪器网络进行反向传播,这使得它们比简单的文本到图像生成慢得多且更占内存,要么只局部强制执行约束,无法捕获采样图像中关键的长程关联。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种算法,能够在任意约束下实现快速、高质量生成。我们表明,在去噪扩散模型中,我们可以采用牛顿优化方法的近似值,这允许我们加快推理速度并避免昂贵的反向传播操作。我们的方法产生的结果可与最先进的无训练推理方法相匹敌或超越,同时所需时间大大减少。我们在线性(填充、超分辨率)和非线性(风格引导生成)约束下展示了算法的有效性。相关实现可访问 https://github.com/cvlab-stonybrook/fast-constrained-sampling 了解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型去噪扩散模型,如Stable Diffusion,已训练于数十亿图像-标题对上,执行文本条件图像生成。模型在训练过程中获得了关于图像统计的通用知识,可用于其他推理任务。然而,当面临在新的约束下采样图像时,如生成图像的缺失部分,使用大型预训练文本到图像扩散模型效率低下且常不可靠。以前的方法要么通过去噪器网络进行反向传播,使其比简单文本到图像生成更慢、更占内存,要么仅局部强制执行约束,无法捕获采样图像中关键的长程关联。本研究提出了一种算法,可在任意约束下实现快速、高质量生成。我们展示了在扩散模型中采用牛顿优化方法的近似,可以加快推理速度并避免昂贵的反向传播操作。我们的算法在与最新无训练推理方法比较时效果显著,所需时间更少。我们在线性(如补全、超分辨率)和非线性(如风格引导生成)约束下验证了算法的有效性。具体实现请参见https://github.com/cvlab-stonybrook/fast-constrained-sampling。
Key Takeaways
- 大型去噪扩散模型如Stable Diffusion已训练于数十亿图像-标题对,具备文本条件图像生成能力,并获得了图像统计的通用知识。
- 面对新的约束(如生成图像的缺失部分),直接使用大型预训练扩散模型效率低下且不稳定。
- 现有方法存在的问题:通过去噪器网络进行反向传播导致速度慢、内存需求大;仅局部约束无法捕获长程关联。
- 本研究提出了一种新的算法,能在任意约束下实现快速、高质量生成,采用牛顿优化方法的近似以加快推理速度并避免反向传播操作。
- 该算法在多种线性与非线性约束下均表现出显著效果,包括补全、超分辨率和风格引导生成等任务。
- 该算法相较于现有方法更高效,所需时间更少。
点此查看论文截图



Cross-Domain Graph Data Scaling: A Showcase with Diffusion Models
Authors:Wenzhuo Tang, Haitao Mao, Danial Dervovic, Ivan Brugere, Saumitra Mishra, Yuying Xie, Jiliang Tang
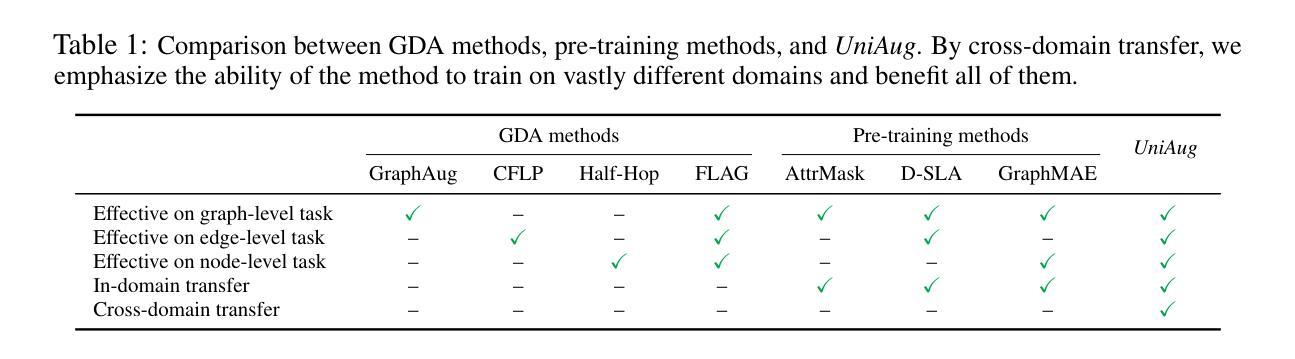
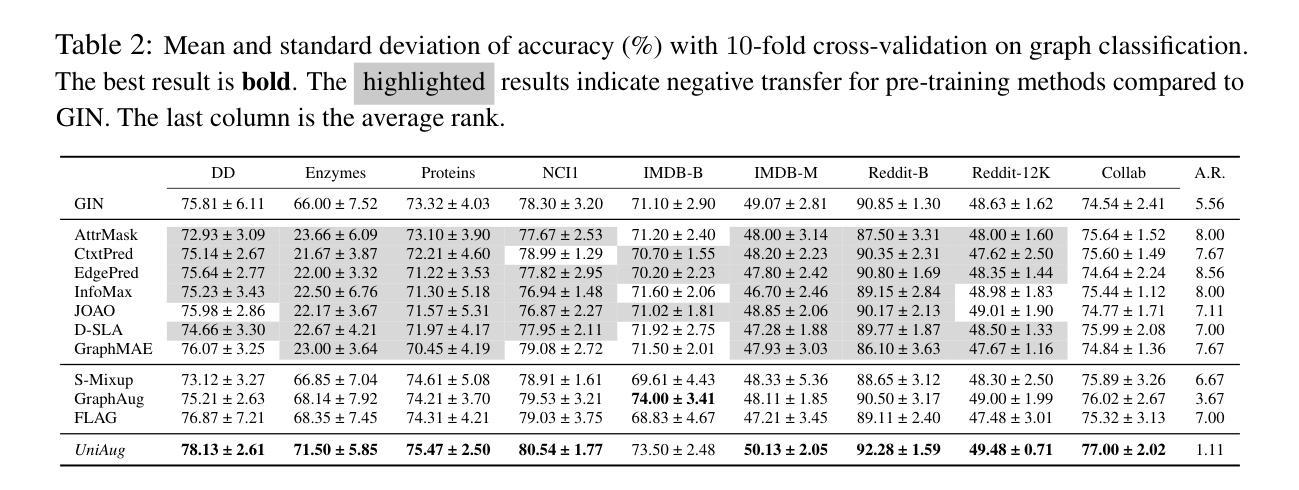
Models for natural language and images benefit from data scaling behavior: the more data fed into the model, the better they perform. This ‘better with more’ phenomenon enables the effectiveness of large-scale pre-training on vast amounts of data. However, current graph pre-training methods struggle to scale up data due to heterogeneity across graphs. To achieve effective data scaling, we aim to develop a general model that is able to capture diverse data patterns of graphs and can be utilized to adaptively help the downstream tasks. To this end, we propose UniAug, a universal graph structure augmentor built on a diffusion model. We first pre-train a discrete diffusion model on thousands of graphs across domains to learn the graph structural patterns. In the downstream phase, we provide adaptive enhancement by conducting graph structure augmentation with the help of the pre-trained diffusion model via guided generation. By leveraging the pre-trained diffusion model for structure augmentation, we consistently achieve performance improvements across various downstream tasks in a plug-and-play manner. To the best of our knowledge, this study represents the first demonstration of a data-scaling graph structure augmentor on graphs across domains.
模型的自然语言和图像受益于数据缩放行为:输入模型的数据越多,其性能就越好。“越多越好”的现象证明了大规模预训练在大量数据上的有效性。然而,由于图之间的异质性,当前的图预训练方法难以扩大数据规模。为了实现有效的数据缩放,我们的目标是开发一个能够捕获图的多样数据模式并可用于自适应帮助下游任务的通用模型。为此,我们提出了基于扩散模型的通用图结构增强器UniAug。我们首先在跨域的数千个图上对离散扩散模型进行预训练,以学习图结构模式。在下游阶段,我们通过借助预训练的扩散模型进行引导生成来进行图结构增强,提供自适应增强。通过利用预训练的扩散模型进行结构增强,我们在各种下游任务中通过即插即用方式始终实现了性能改进。据我们所知,这项研究代表了跨域图上数据缩放图结构增强器的首次展示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS’25
Summary
模型的自然语言与图像受益于数据规模化的行为:输入模型的数据越多,其表现性能越好。这种现象使得大规模预训练在大量数据上非常有效。然而,由于图的异质性,当前图预训练方法在扩大数据规模时面临困难。为了实现有效的数据规模化,我们旨在开发一个能够捕捉图的多样数据模式并能自适应地帮助下游任务的通用模型。为此,我们提出了基于扩散模型的通用图结构增强器UniAug。我们首先在不同的域上对成千上万的图进行离散扩散模型的预训练,以学习图结构模式。在下游阶段,我们通过预训练的扩散模型进行图结构增强,通过引导生成实现自适应增强。利用预训练的扩散模型进行结构增强,我们在各种下游任务中实现了性能的提升,是一种即插即用的方式。据我们所知,本研究是首次在跨域图上进行数据规模化的图结构增强器的展示。
Key Takeaways
- 数据规模化对于提升模型性能至关重要,特别是在自然语言处理和图像处理领域。
- 当前图预训练方法面临异质性问题,限制了数据规模的扩大。
- UniAug是一个基于扩散模型的通用图结构增强器,旨在解决这一问题。
- UniAug通过预训练学习图结构模式,并在下游任务中进行自适应增强。
- UniAug通过引导生成实现图结构增强,提升模型在各种下游任务中的性能。
- UniAug是首个跨域图数据规模化的图结构增强器的展示。
点此查看论文截图