⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2025-10-09 更新
Microscopic study of nuclei synthesis in pycnonuclear reaction $^{12}$C + $^{12}$C in neutron stars
Authors:S. P. Maydanyuk, Ju-Jun Xie, V. S. Vasilevsky, K. A. Shaulskyi
Purpose To investigate synthesis of nuclei in pycnonuclear reactions in dense medium of neutron stars on the basis of understanding, how the compound nucleus is formed during collision of two nuclei. To implement microscopic formulation of nuclear interactions and fusion in pycnonuclear reactions in dense medium. Methods (1) Nuclei synthesis in pycnonuclear reaction in dense medium of neutron star is investigated in the folding approximation of the cluster model. (2) Formation of compound nucleus in dense medium is studied with the method of Multiple Internal Reflections. Results (1) Wave functions of resonance states of $^{24}$Mg are determined by interaction of two $^{12}$C nuclei. (2) Clear maxima of probability of formation of compound nucleus in dense stellar medium are established at first time. (3) Difference between quasibound energies for potential of Woods-Saxon type and folding potentials with the shell-model approximation for wave functions is essential. (4) Formation of the compound nucleus is much more probable in the quasibound states than in states of zero-point vibrations. (5) Only the first quasibound energies for $^{12}$C + $^{12}$Care smaller than the barrier maximums. At these energies compound nuclear system has barrier which prevents its decay going through tunneling phenomenon. This is the new excited nucleus $^{24}$Mg synthesised in the neutron star. \item[Conclusions] Cluster approach with folding potential provides significant modification of picture of formation of compound nucleus, previously obtained concerning the potential of Woods-Saxon type. The highest precision is provided by the folding potential, created by semi-realistic nucleon-nucleon potential and shell-model description of the internal structure of interacting $p$-shell nuclei.
目的:在理解两个核碰撞过程中复合核形成的基础上,探讨中子星致密介质中热核反应的核合成。实现在致密介质中热核反应的核相互作用和融合的微观表述。方法:(1)在团簇模型的折叠近似中研究中子星致密介质中热核反应的核合成。(2)采用多重内部反射法研究致密介质中复合核的形成。结果:(1)$^{24}$Mg的共振态波函数是由两个$^{12}$C核的相互作用所决定的。(2)首次明确建立了在致密恒星介质中形成复合核的概率最大值。(3)Woods-Saxon型势与折叠势之间的准束缚能以及波函数的壳模型近似之间存在显著差异。(4)在准束缚态下形成复合核的可能性远大于在零点振动态下。(5)只有$^{12}$C和$^{12}$C的第一准束缚能小于势垒最大值。在这些能量下,复合核系统具有通过隧道效应防止其衰变的势垒。这是在中子星中合成的新激发态核$^{24}$Mg。结论:采用折叠势的团簇方法显著改变了先前关于Woods-Saxon型势所得到的复合核形成图像。最高精度是由半现实核子-核子势和p壳核内部结构壳模型描述所创建的折叠势提供的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 17 captured figures
Summary
在一项关于中子星内致密介质中的热核合成反应的研究中,科学家们采用微观公式探讨了热核相互作用与核聚变的细节过程。通过对双层模型折叠近似法的研究,确定了合成原子核的可能波函数。同时,利用多重内部反射法研究了致密介质中复合核的形成过程。研究结果显示,在共振状态下,两个碳核的相互作用决定了镁原子核的共振状态波函数;在致密恒星介质中首次建立了复合核形成的概率峰值;并且得出在某些情况下合成原子核会形成类似于全新结构的第钠个比较可靠的标志是用于实现自身由小型自引力基本粒流提供的致密核子系统;合成过程的主要特点在于形成复合核的可能性与准束缚态相比在零点振动状态下较小。此外,研究还指出,只有部分能量低于最大值的准束缚态下的碳核合成系统具有阻止其通过隧道效应衰变的屏障,从而合成出新的激发态原子核镁。最后得出结论,采用核簇的折叠势法为描绘复合核形成的过程带来了重大改变,该理论更精确的是基于半现实的核子势及内部结构的壳模型描述。该研究深化了我们对中子星内致密介质中热核合成反应的理解。同时,也为未来的相关研究提供了理论支持。同时提供了基于该研究的新的视角和理论工具。研究还指出了一些可能的未来研究方向。比如探究如何根据这个模型进行更好的数值模拟以研究更深层次的热核合成反应等方向都是未来值得关注的重点方向。综上所述,本研究对于推动核物理领域的发展具有重要意义。通过这项研究我们进一步理解了原子核的合成过程以及在中子星环境下可能发生的反应机制,同时也对原子核物理学的发展起到了推动作用。
Key Takeaways:
一、中子星内致密介质中的热核合成反应研究采用微观公式探讨了热核相互作用与核聚变的细节过程。
二、通过双层模型折叠近似法确定了合成原子核的可能波函数;利用多重内部反射法研究了复合核在致密介质中的形成过程。
三、研究确定了合成原子核的概率峰值点。揭示了碳碳碰撞生成镁原子的可能机制以及特定的反应条件;并且确认了新合成原子核具有特定特性(如零点振动状态下的较小可能性)。
四、只有部分能量下的碳核合成系统具有阻止其通过隧道效应衰变的屏障,从而成功合成出新的激发态原子核镁。
五、采用折叠势法的核簇模型为复合核的形成过程提供了重大改变的描述;此方法由半现实的核子势及内部结构的壳模型提供更高的精度描绘。
六、该研究深化了我们对中子星内致密介质中热核合成反应的理解,为未来相关研究提供了理论支持;此外还可能带来新的应用前景。
点此查看论文截图
ReactDiff: Fundamental Multiple Appropriate Facial Reaction Diffusion Model
Authors:Luo Cheng, Song Siyang, Yan Siyuan, Yu Zhen, Ge Zongyuan
The automatic generation of diverse and human-like facial reactions in dyadic dialogue remains a critical challenge for human-computer interaction systems. Existing methods fail to model the stochasticity and dynamics inherent in real human reactions. To address this, we propose ReactDiff, a novel temporal diffusion framework for generating diverse facial reactions that are appropriate for responding to any given dialogue context. Our key insight is that plausible human reactions demonstrate smoothness, and coherence over time, and conform to constraints imposed by human facial anatomy. To achieve this, ReactDiff incorporates two vital priors (spatio-temporal facial kinematics) into the diffusion process: i) temporal facial behavioral kinematics and ii) facial action unit dependencies. These two constraints guide the model toward realistic human reaction manifolds, avoiding visually unrealistic jitters, unstable transitions, unnatural expressions, and other artifacts. Extensive experiments on the REACT2024 dataset demonstrate that our approach not only achieves state-of-the-art reaction quality but also excels in diversity and reaction appropriateness.
在双人对话中自动生成多样且人性化的面部反应仍然是人机交互系统的一个关键挑战。现有方法无法模拟真实人类反应中固有的随机性和动态性。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了ReactDiff,这是一种新型的时空扩散框架,用于生成多样化的面部反应,可以针对任何给定的对话上下文做出适当的反应。我们的关键见解是,合理的人类反应表现出时间上的平滑性和连贯性,并符合人类面部解剖结构的约束。为了实现这一点,ReactDiff将两个重要的先验知识(时空面部运动学)融入扩散过程:i) 面部行为的时空运动学;ii) 面部动作单元的依赖关系。这两个约束引导模型朝向真实的人类反应流形,避免了视觉上不真实的抖动、不稳定的过渡、不自然的表情和其他伪影。在REACT2024数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法不仅达到了最先进的反应质量,而且在多样性和反应适宜性方面也表现出色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM Multimedia
Summary
自动化生成二元对话中多样且人性化的面部反应仍是人机交互系统的一大挑战。现有方法无法模拟真实人类反应中的随机性和动力学特性。为解决此问题,我们提出ReactDiff,一种新型的时间扩散框架,用于生成与给定对话上下文相适应的多样面部反应。我们的关键见解是,合理的人类反应表现出时间上的平滑和连贯性,并符合人类面部解剖学的约束。为实现这一点,ReactDiff将两个关键先验(时空面部运动学和面部动作单元依赖)融入扩散过程中。这两方面的约束使模型面向现实的人类反应流形,避免视觉上的抖动、不稳定的过渡、不自然的表情和其他伪像。在REACT2024数据集上的大量实验证明,我们的方法不仅实现了最先进的反应质量,而且在多样性和反应适宜性方面也表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 自动生成多样化的面部反应是人际交往系统的关键挑战。
- 目前的方法无法模拟真实人类反应的随机性和动力学特性。
- ReactDiff框架通过结合时空面部运动学和面部动作单元依赖来生成逼真的面部反应。
- ReactDiff实现了时间上的平滑和连贯性的反应。
- 该方法遵循人类面部解剖学的约束,避免产生不自然的表情和其他伪像。
- 在REACT2024数据集上的实验表明,该方法达到了最先进的反应质量。
点此查看论文截图
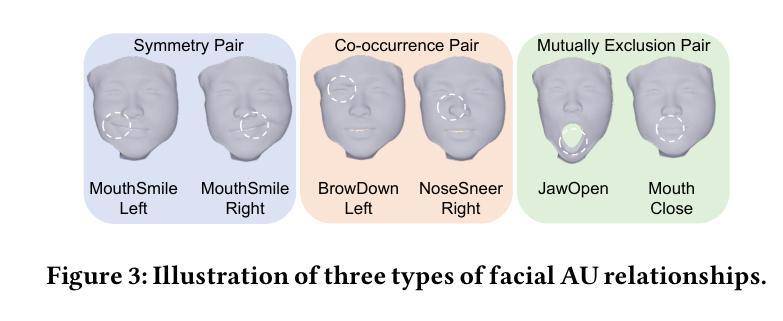
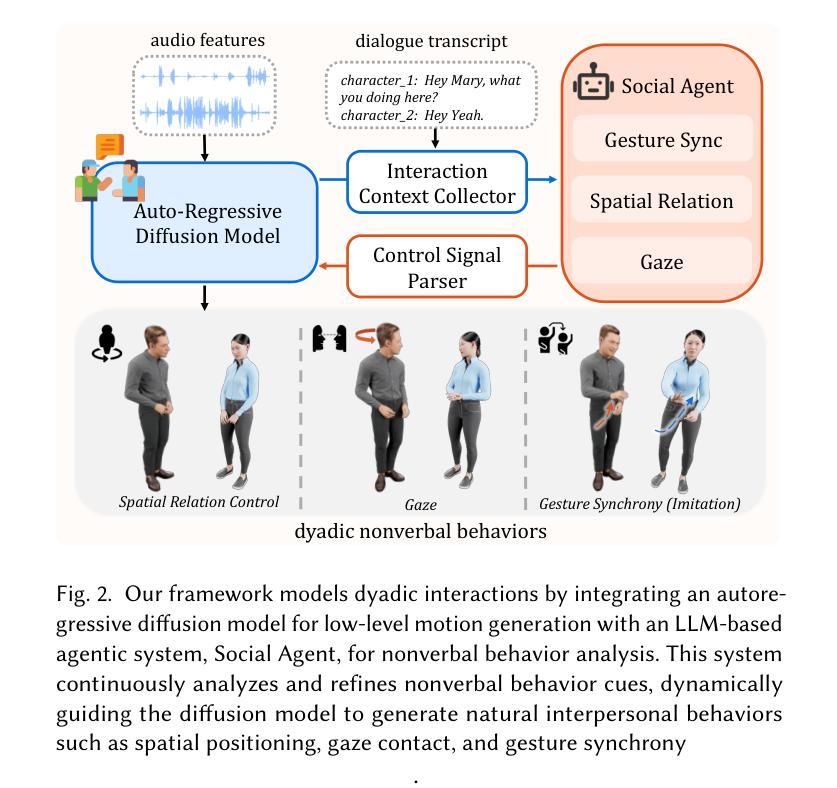
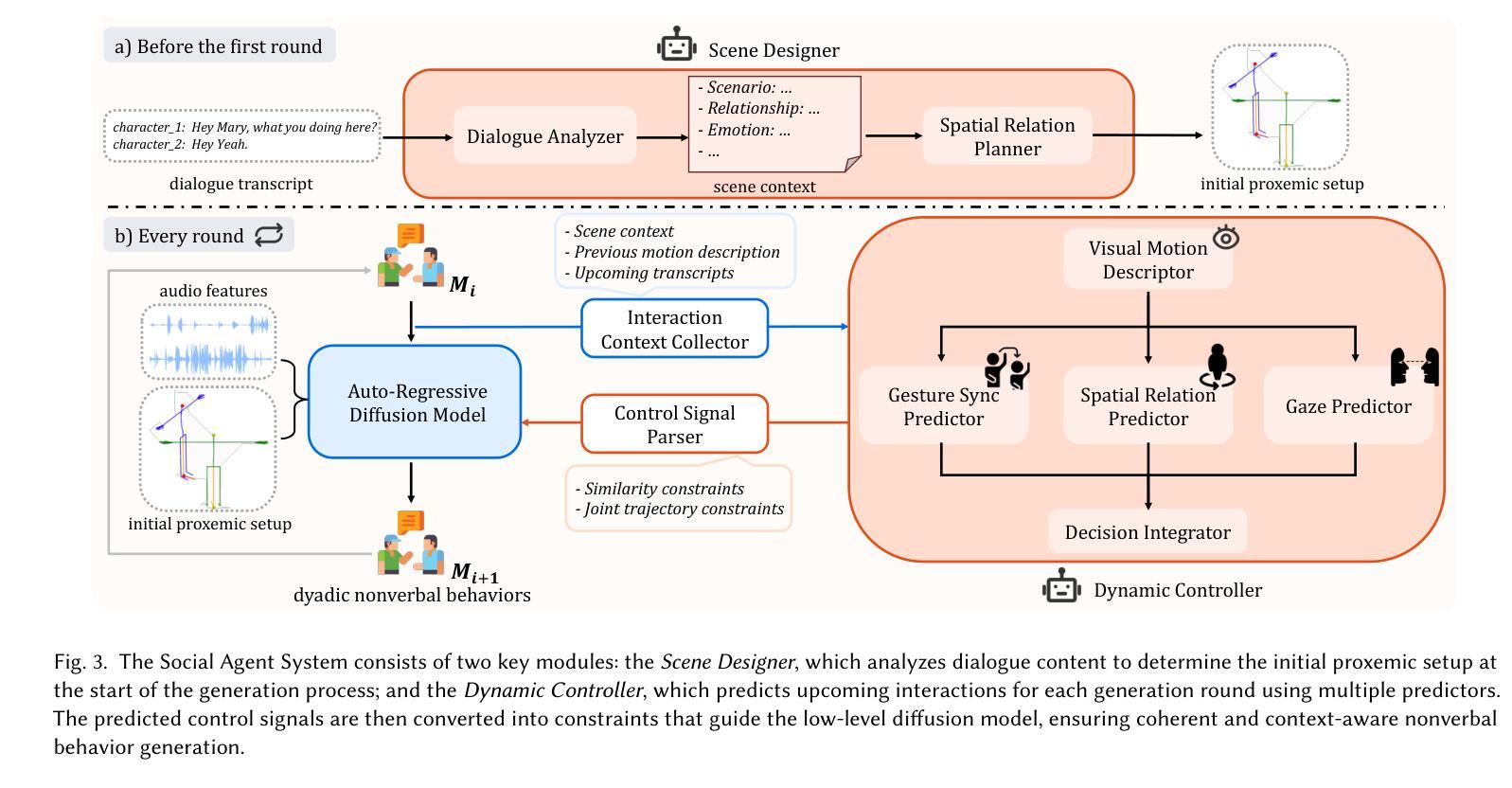
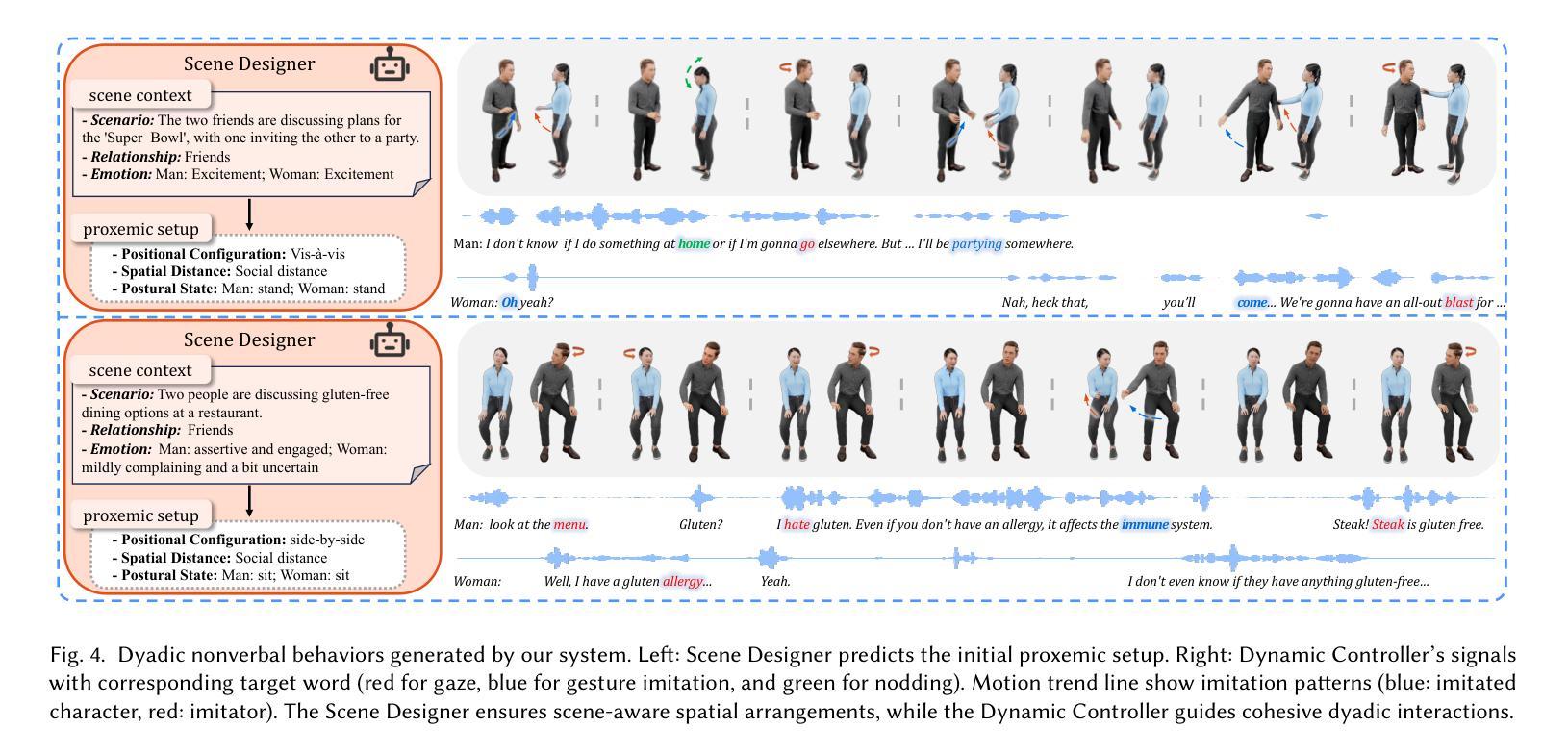
Social Agent: Mastering Dyadic Nonverbal Behavior Generation via Conversational LLM Agents
Authors:Zeyi Zhang, Yanju Zhou, Heyuan Yao, Tenglong Ao, Xiaohang Zhan, Libin Liu
We present Social Agent, a novel framework for synthesizing realistic and contextually appropriate co-speech nonverbal behaviors in dyadic conversations. In this framework, we develop an agentic system driven by a Large Language Model (LLM) to direct the conversation flow and determine appropriate interactive behaviors for both participants. Additionally, we propose a novel dual-person gesture generation model based on an auto-regressive diffusion model, which synthesizes coordinated motions from speech signals. The output of the agentic system is translated into high-level guidance for the gesture generator, resulting in realistic movement at both the behavioral and motion levels. Furthermore, the agentic system periodically examines the movements of interlocutors and infers their intentions, forming a continuous feedback loop that enables dynamic and responsive interactions between the two participants. User studies and quantitative evaluations show that our model significantly improves the quality of dyadic interactions, producing natural, synchronized nonverbal behaviors.
我们提出了Social Agent,这是一个新的框架,用于合成二元对话中现实且上下文恰当的伴随语音的非言语行为。在这个框架中,我们开发了一个由大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的主体系统,以引导对话流程并为双方确定适当的交互行为。此外,我们提出了一种基于自回归扩散模型的新型双人姿态生成模型,该模型能从语音信号中合成协调动作。主体系统的输出被转化为手势生成器的高级指导,从而在行为和运动层面产生逼真的动作。此外,主体系统会定期检查对话者的动作并推断其意图,形成一个连续的反馈循环,使两个参与者之间能够进行动态和响应式的交互。用户研究和定量评估表明,我们的模型显著提高了二元交互的质量,产生了自然、同步的非言语行为。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SIGGRAPH ASIA 2025 (Conference Track); Project page: https://pku-mocca.github.io/Social-Agent-Page/
Summary
社交代理框架,用于合成现实且语境恰当的对话中的非言语行为。提出一个由大型语言模型驱动的代理系统,用于指导对话流程并确定双方适当的交互行为。此外,提出了基于自回归扩散模型的双人姿态生成模型,从语音信号中合成协调动作。代理系统的输出被转化为对姿态生成器的高级指导,实现了行为和动作级别的逼真动作。此外,代理系统会不时检查对话者的动作并推断其意图,形成一个持续的反馈循环,使两个参与者之间的交互更加动态和响应性。用户研究和定量评估表明,该模型显著提高了双人交互的质量,产生了自然、同步的非言语行为。
Key Takeaways
- 社交代理框架用于合成对话中的非言语行为,确保真实性和语境适宜性。
- 利用大型语言模型驱动的代理系统指导对话流程并决定交互行为。
- 姿态生成模型基于自回归扩散模型,能从语音信号中合成协调动作。
- 代理系统输出转化为对姿态生成器的高级指导,实现行为和动作级别的逼真表现。
- 代理系统具备检查对话者动作并推断意图的能力,形成动态反馈循环。
- 用户研究和定量评估证实该模型能提高双人交互质量。
点此查看论文截图
When AI Gets Persuaded, Humans Follow: Inducing the Conformity Effect in Persuasive Dialogue
Authors:Rikuo Sasaki, Michimasa Inaba
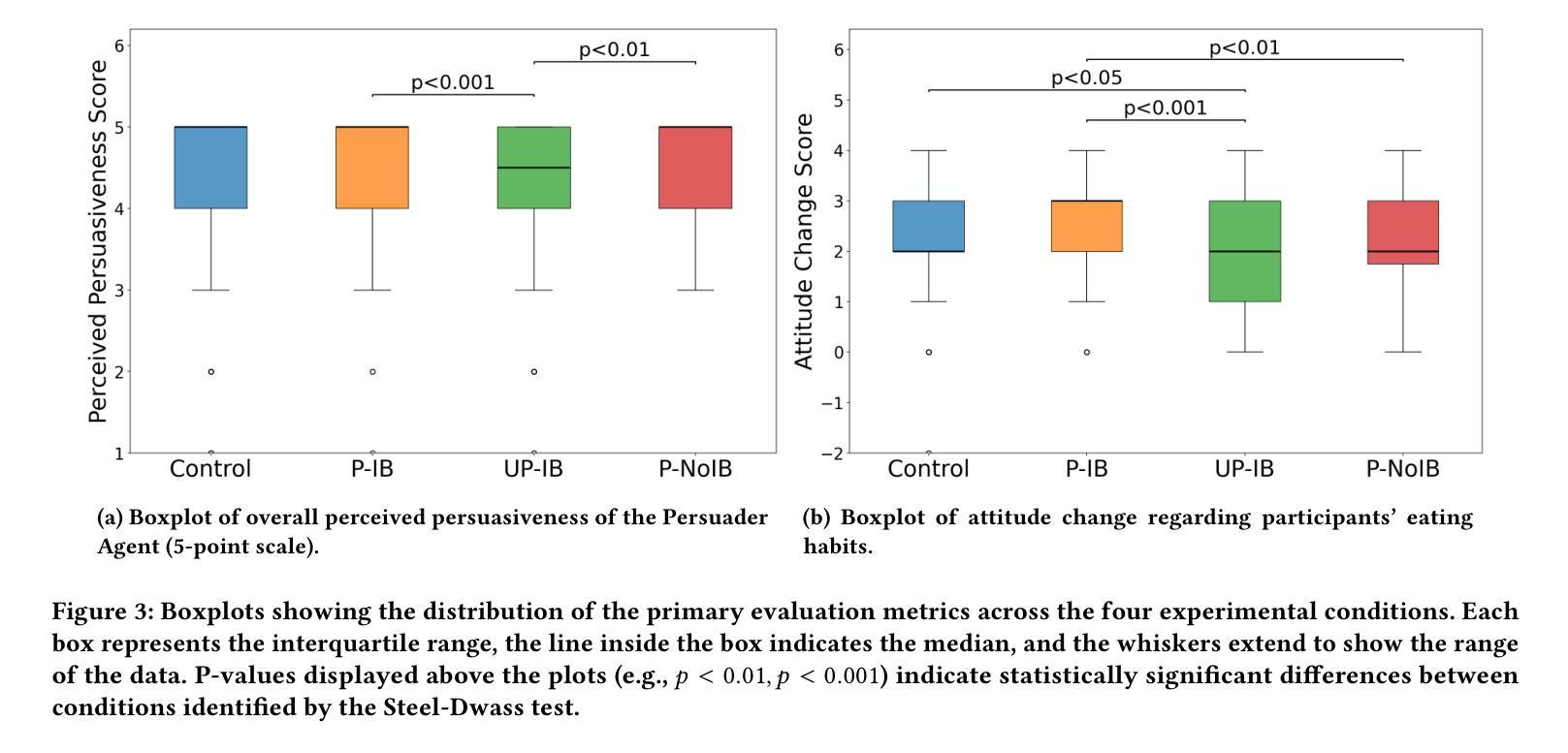
Recent advancements in AI have highlighted its application in captology, the field of using computers as persuasive technologies. We hypothesized that the “conformity effect,” where individuals align with others’ actions, also occurs with AI agents. This study verifies this hypothesis by introducing a “Persuadee Agent” that is persuaded alongside a human participant in a three-party persuasive dialogue with a Persuader Agent. We conducted a text-based dialogue experiment with human participants. We compared four conditions manipulating the Persuadee Agent’s behavior (persuasion acceptance vs. non-acceptance) and the presence of an icebreaker session. Results showed that when the Persuadee Agent accepted persuasion, both perceived persuasiveness and actual attitude change significantly improved. Attitude change was greatest when an icebreaker was also used, whereas an unpersuaded AI agent suppressed attitude change. Additionally, it was confirmed that the persuasion acceptance of participants increased at the moment the Persuadee Agent was persuaded. These results suggest that appropriately designing a Persuadee Agent can improve persuasion through the conformity effect.
近年来,人工智能的进步突显了其在计算机作为说服技术领域的广泛应用,即“捕诉学”(captology)。我们假设,“一致性效应”,即个人与他人行为一致的现象,也存在于人工智能代理中。本研究通过引入一个“被说服者代理”(Persuadee Agent),该代理在人类参与者与另一个说服者代理(Persuader Agent)的三方对话中被说服,从而验证了这一假设。我们进行了基于文本对话的实验,实验参与者为人类。我们比较了四种条件下的操作结果,分别是被说服者代理的行为(接受劝说与非接受劝说)以及破冰对话环节的存在与否。结果显示,当被说服者代理接受劝说时,感知到的说服力和实际态度变化均显著改善。当同时使用破冰会话时,态度变化最为明显;而未受到说服的人工智能代理则抑制了态度的变化。此外,证实了参与者在被说服者代理接受劝说之际其说服接受度有所提升。这些结果表明,适当设计被说服者代理可以通过一致性效应提高说服效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 19 figures. International Conference on Human-Agent Interaction (HAI 2025), November 10-13, 2025, Yokohama, Japan
总结
AI在说服学领域的应用发展已经得到了突显,即利用计算机作为说服技术。本研究假设“服从效应”——人们会模仿他人的行为,也在AI代理中发挥作用。通过引入一个“Persuadee Agent”,与人类参与者一同参与一个三方说服对话,验证了这一假设。实验结果显示,当Persuadee Agent接受说服时,感知到的说服力和实际态度变化都有显著提高。使用破冰环节可以产生最大的态度变化,而未接受说服的AI代理则抑制了态度变化。此外,确认了在Persuadee Agent被说服的那一刻,参与者的接受说服程度有所增加。这表明恰当设计的Persuadee Agent能够通过服从效应提高说服效果。
关键见解
- AI在说服学中的应用日益凸显,利用计算机作为说服技术已成为研究热点。
- 本研究验证了“服从效应”在AI代理中的存在。
- 当AI代理接受说服时,感知到的说服力和实际态度变化均显著提高。
- 破冰环节的使用可以产生最大的态度变化。
- 未接受说服的AI代理会抑制态度变化。
- 在特定的时刻,如AI代理被说服的那一刻,参与者的接受说服程度会增加。
点此查看论文截图
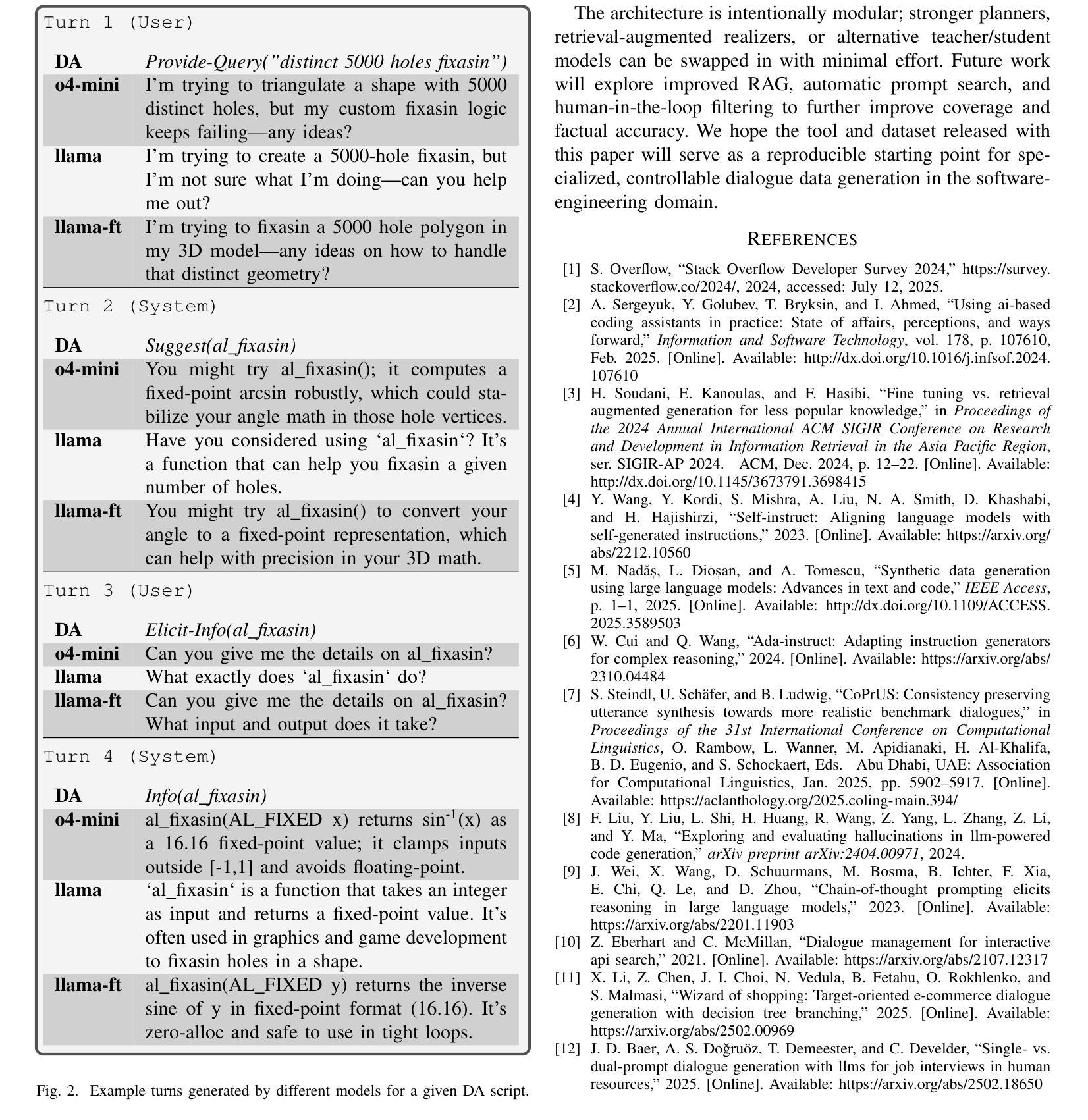
APIDA-Chat: Structured Synthesis of API Search Dialogues to Bootstrap Conversational Agents
Authors:Zachary Eberhart, Collin McMillan
Large-language-model assistants are suitable for explaining popular APIs, yet they falter on niche or proprietary libraries because the multi-turn dialogue data needed for fine-tuning are scarce. We present APIDA-Chat, an open-source pipeline that converts symbolic dialogue-act “scripts” into realistic, domain-grounded API Search conversations using a lightweight model for inexpensive training data generation. Phase I pairs a legacy dialogue planner with a high-capability teacher LLM (o4-mini) to synthesize a “gold set” of realized dialogues; then, a smaller Llama 3.2 3B student model is fine-tuned on this corpus. Phase II drops the teacher and reuses the same planner with the fine-tuned model, allowing rapid, low-cost synthesis of new dialogues without exposing source code to external services. The fine-tuned student improves BLEU from 0.38 to 0.50 and BERTScore from 0.88 to 0.91 versus the base model while running entirely on a single consumer GPU. All components are modular and publicly released to serve as a conservative baseline for future work. APIDA-Chat is open-sourced at https://github.com/Zeberhart/apida-chat and a video demo is available at https://youtu.be/YqmZBHyGbPs .
大语言模型助手适合解释流行的API,但在专业或专有库中却举步维艰,因为微调所需的多轮对话数据非常稀缺。我们推出了APIDA-Chat,这是一个开源管道,它将符号式对话行为“脚本”转化为现实、基于领域的API搜索对话,使用轻量级模型进行低成本训练数据生成。第一阶段将传统的对话规划器与高性能教师大型语言模型(o4-mini)配对,合成一组已实现的对话“金集”;然后,在语料库上对较小规模的Llama 3.2 3B学生模型进行微调。第二阶段放弃教师模型,重复使用同一规划器与已微调过的模型,在不向外部服务暴露源代码的情况下,快速低成本地合成新的对话。经过微调的学生的BLEU得分从0.38提高到0.50,BERTScore从0.88提高到0.91,相较于基础模型有所提升,同时全部运行在单个消费级GPU上。所有组件模块化且已公开发布,作为未来工作的保守基线。APIDA-Chat已开源,可在https://github.com/Zeberhart/apida-chat获取,视频演示可在https://youtu.be/YqmZBHyGbPs观看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 2 figures. To be published in Proceedings of the 40th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Automated Software Engineering
Summary
大型语言模型助手在解释流行API方面表现出色,但在小众或专有库方面表现不佳,因为缺乏微调所需的多轮对话数据。我们推出了APIDA-Chat,一个开源管道,能将符号对话行为“剧本”转化为现实、基于领域的API搜索对话,使用轻型模型进行低成本训练数据生成。第一阶段将传统的对话规划器与高性能教师LLM(o4-mini)配对,合成“黄金集”对话;然后,在语料库上微调较小的Llama 3.2 3B学生模型。第二阶段放弃教师,仅使用规划器和微调过的模型,可在不向外部服务暴露源代码的情况下快速、低成本地合成新对话。经过微调的学生模型相较于基础模型,BLEU得分从0.38提升至0.50,BERTScore从0.88提升至0.91,并且可在单个消费者GPU上完全运行。所有组件模块化并公开发布,作为未来工作的保守基线。APIDA-Chat已在GitHub上开源,视频演示可在YouTube上观看。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型助手在解释流行API方面表现出色,但在处理小众或专有库时受限。
- APIDA-Chat是一个将符号对话转化为现实对话的开源管道,特别适用于API搜索领域。
- APIDA-Chat采用两个阶段:第一阶段合成黄金集对话,第二阶段快速合成新对话,无需暴露源代码。
- 微调后的学生模型性能有所提升,BLEU和BERTScore得分均有提高。
- APIDA-Chat所有组件模块化,可在消费者GPU上运行。
- APIDA-Chat已公开发布并作为保守基线供未来研究使用。
点此查看论文截图

Uncertainty quantification of reacting fluids interacting with porous media using a hybrid physics-based and data-driven approach
Authors:Diba Behnoudfar, Kyle E. Niemeyer
Accurately simulating coupled physical processes under uncertainty is essential for reliable modeling and design in performance-critical applications such as combustion systems. Ablative heat shield design, as a specific example of this class, involves modeling multi-physics interactions between reacting flows and a porous material. Repeatedly evaluating these models to quantify parametric uncertainties would be prohibitively computationally expensive. In this work, we combine physics-based modeling using a single-domain approach with data-driven reduced-order modeling to quantify uncertainty via the operator inference method. The detailed physics-based simulations reproduce the measured surface temperature of an object exposed to high-enthalpy flow in a plasma wind tunnel experiment within 5%. We further use the model to demonstrate the effect of complex flow situations on the dynamic interactions between the porous heat shield material and the surrounding gas. The parametric reduced-order model, built on physics-based simulation data, successfully captures variations in quantities of interest resulting from changes in the permeability and heat transfer coefficient of the porous material in two separate studies: solid fuel combustion and emission of buoyant reacting plumes in quiescent air and ablation in a wind tunnel.
在燃烧系统等性能关键应用中,准确模拟不确定性下的耦合物理过程对于可靠建模和设计至关重要。作为此类设计的一个具体例子,烧蚀热防护设计涉及模拟反应流动与多孔材料之间的多物理相互作用。反复评估这些模型以量化参数不确定性在计算上将是极其昂贵的。在这项工作中,我们结合基于物理的建模方法(采用单域方法)和基于数据驱动的降阶建模来通过操作推断法量化不确定性。基于物理的详细模拟在等离子体风洞实验中重现了暴露于高熵流动下的物体表面温度,误差在5%以内。我们进一步使用该模型来演示复杂流动情况对多孔热防护材料与周围气体之间动态相互作用的影响。参数化的降阶模型基于物理仿真数据,成功捕获了两次独立研究中关注的数量变化,这些变化是由多孔材料的渗透性和传热系数的变化引起的:固体燃料燃烧和静止空气中上升反应羽流的排放以及风洞中的烧蚀。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本指出,准确模拟不确定环境下的耦合物理过程对于性能关键应用中的可靠建模和设计至关重要。以热防护罩设计为例,需要模拟反应流与多孔材料之间的多物理相互作用。然而,反复评估这些模型以量化参数不确定性在计算上是非常昂贵的。因此,该研究结合了基于物理的建模和数据驱动的降阶建模,通过操作符推断方法量化不确定性。基于物理的模拟能够再现等离子风洞实验中物体的高熵流表面温度,并进一步研究复杂流动对多孔热防护材料与周围气体之间动态相互作用的影响。参数化降阶模型成功捕捉到了感兴趣量的变化,这些变化来源于两次研究中多孔材料渗透性和传热系数的变化:固体燃料燃烧和静止空气中浮力反应气团的排放以及风洞中的烧蚀。
Key Takeaways
- 模拟不确定环境下的耦合物理过程对于性能关键应用中的可靠建模和设计至关重要。
- 以热防护罩设计为例,需要模拟反应流与多孔材料之间的多物理相互作用。
- 反复评估模型以量化参数不确定性计算成本高。
- 结合基于物理的建模和数据驱动的降阶建模能够量化不确定性。
- 基于物理的模拟能够再现物体在等离子风洞实验中的高熵流表面温度。
- 参数化降阶模型能够捕捉由多孔材料参数变化引起的感兴趣量的变化。
点此查看论文截图

MEDAL: A Framework for Benchmarking LLMs as Multilingual Open-Domain Dialogue Evaluators
Authors:John Mendonça, Alon Lavie, Isabel Trancoso
Evaluating the quality of open-domain chatbots has become increasingly reliant on LLMs acting as automatic judges. However, existing meta-evaluation benchmarks are static, outdated, and lacking in multilingual coverage, limiting their ability to fully capture subtle weaknesses in evaluation. We introduce MEDAL, an automated multi-agent framework for curating more representative and diverse open-domain dialogue evaluation benchmarks. Our approach leverages several state-of-the-art LLMs to generate user-chatbot multilingual dialogues, conditioned on varied seed contexts. Then, a strong LLM (GPT-4.1) is used for a multidimensional analysis of the performance of the chatbots, uncovering noticeable cross-lingual performance differences. Guided by this large-scale evaluation, we curate a new meta-evaluation multilingual benchmark and human-annotate samples with nuanced quality judgments. This benchmark is then used to assess the ability of several reasoning and non-reasoning LLMs to act as evaluators of open-domain dialogues. Using MEDAL, we uncover that state-of-the-art judges fail to reliably detect nuanced issues such as lack of empathy, commonsense, or relevance.
评估开放领域聊天机器人的质量越来越依赖于作为自动评委的大型语言模型(LLMs)。然而,现有的元评估基准测试是静态的、过时的,并且缺乏多语言覆盖,限制了它们全面捕捉评估中细微弱点的能力。我们引入了 MEDAL,这是一个自动化的多智能体框架,用于创建更具代表性和多样性的开放领域对话评估基准测试。我们的方法利用若干最先进的LLMs来生成基于各种种子上下文的用户聊天机器人多语言对话。然后,一个强大的LLM(GPT-4.1)用于对聊天机器人的性能进行多维分析,揭示出明显的跨语言性能差异。在大型评估的指导下,我们创建了一个新的元评估多语言基准测试,并对样本进行了微妙的质量判断进行人工标注。然后,使用这个基准测试来评估多个推理和非推理LLMs作为开放领域对话评估者的能力。使用 MEDAL,我们发现最先进的评委无法可靠地检测到诸如缺乏同理心、常识或相关性等细微问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF October ARR
Summary
本文介绍了评估开放领域聊天机器人质量的新方法MEDAL。该方法利用多语言大型语言模型(LLM)生成用户与聊天机器人的对话,并进行多维度的分析评估聊天机器人的性能。研究发现,现有的评估基准测试存在局限性,而新的多语言基准测试能够发现显著的语言间性能差异。此外,文章还指出,即使是最新、最先进的大型语言模型评价器也存在局限性,无法可靠地检测如缺乏同理心、常识或相关性等细微问题。
Key Takeaways
- 现有开放领域聊天机器人评估基准测试存在局限性,需要新的评估方法。
- MEDAL是一个自动化多代理框架,用于建立更具代表性和多样性的开放领域对话评估基准。
- MEDAL利用多种先进的大型语言模型生成用户与聊天机器人的对话。
- 多维度分析表明,不同语言间聊天机器人性能存在显著差异。
- 新建立的多语言基准测试用于评估聊天机器人的质量。
- 最新、最先进的大型语言模型评价器在评估聊天机器人时存在局限性。