Diffusion Models
⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 Google的大语言模型Gemini-Pro的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-05-02 更新
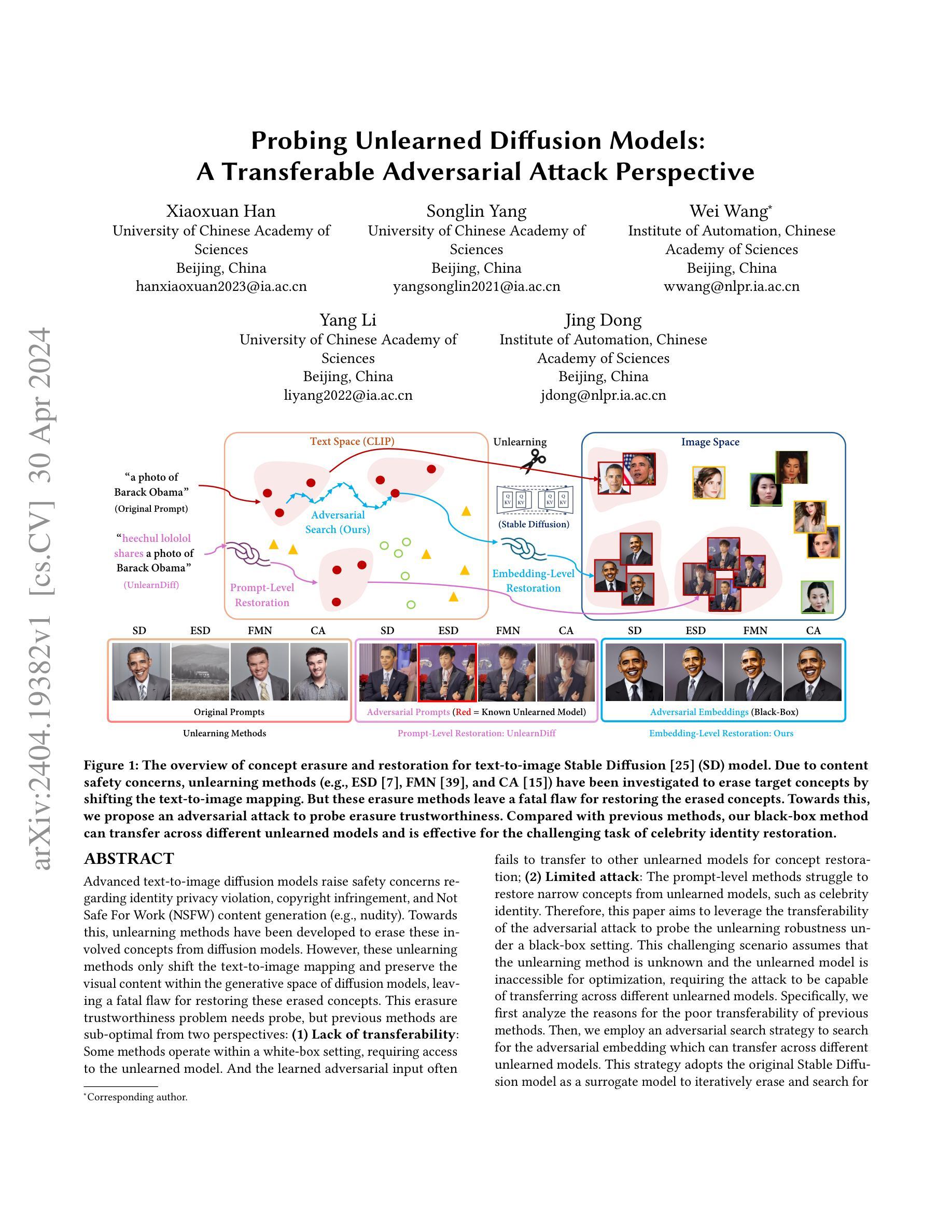
Probing Unlearned Diffusion Models: A Transferable Adversarial Attack Perspective
Authors:Xiaoxuan Han, Songlin Yang, Wei Wang, Yang Li, Jing Dong
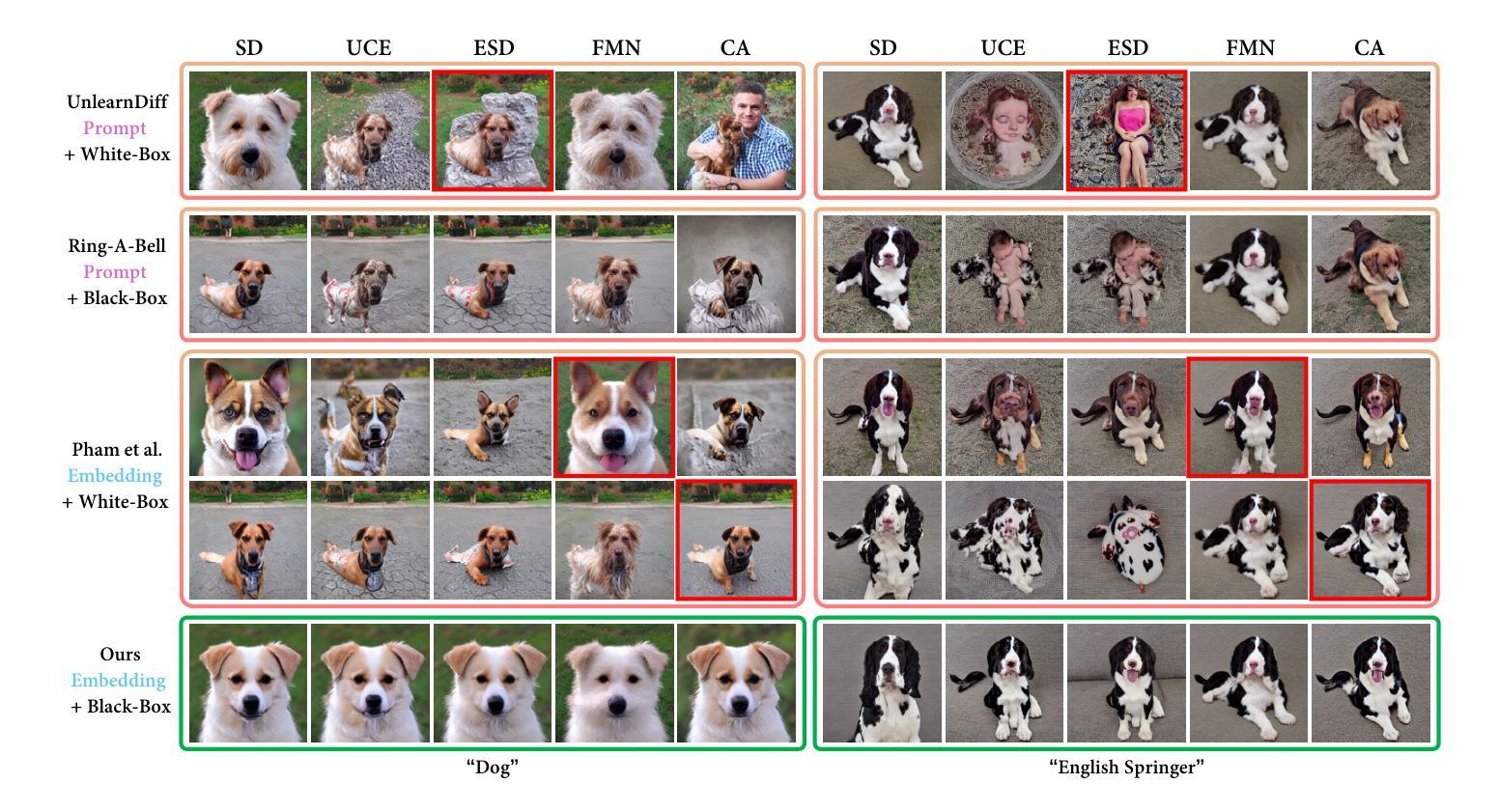
Advanced text-to-image diffusion models raise safety concerns regarding identity privacy violation, copyright infringement, and Not Safe For Work content generation. Towards this, unlearning methods have been developed to erase these involved concepts from diffusion models. However, these unlearning methods only shift the text-to-image mapping and preserve the visual content within the generative space of diffusion models, leaving a fatal flaw for restoring these erased concepts. This erasure trustworthiness problem needs probe, but previous methods are sub-optimal from two perspectives: (1) Lack of transferability: Some methods operate within a white-box setting, requiring access to the unlearned model. And the learned adversarial input often fails to transfer to other unlearned models for concept restoration; (2) Limited attack: The prompt-level methods struggle to restore narrow concepts from unlearned models, such as celebrity identity. Therefore, this paper aims to leverage the transferability of the adversarial attack to probe the unlearning robustness under a black-box setting. This challenging scenario assumes that the unlearning method is unknown and the unlearned model is inaccessible for optimization, requiring the attack to be capable of transferring across different unlearned models. Specifically, we employ an adversarial search strategy to search for the adversarial embedding which can transfer across different unlearned models. This strategy adopts the original Stable Diffusion model as a surrogate model to iteratively erase and search for embeddings, enabling it to find the embedding that can restore the target concept for different unlearning methods. Extensive experiments demonstrate the transferability of the searched adversarial embedding across several state-of-the-art unlearning methods and its effectiveness for different levels of concepts.
Summary
扩散模型的反学习研究存在安全隐患,本文提出了一种迁移性的对抗攻击方法来探测反学习鲁棒性,在黑盒设置下有效恢复被擦除的概念。
Key Takeaways
- 反学习方法会将文本到图像的映射关系进行重新分布,但保留了扩散模型生成空间中的视觉内容。
- 目前探测反学习鲁棒性的方法缺乏可迁移性和攻击力。
- 本文提出了一个对抗性搜索策略,可以在黑盒设置下跨不同的反学习模型迁移对抗嵌入。
- 采用原始 Stable Diffusion 模型作为代理模型来迭代擦除和搜索嵌入。
- 实验表明,搜索的对抗嵌入可以跨多个最先进的反学习方法迁移,并且对不同层次的概念都能有效恢复。
- 本文提出的方法弥补了当前探测反学习鲁棒性方法的不足,为评估和提高反学习的有效性提供了新的思路。
- 该方法可以用于评估反学习的鲁棒性,并为提高反学习的有效性提供指导。
论文标题:探测未学习扩散模型:可转移对抗攻击视角
作者:
- Xiaoxuan Han
- Songlin Yang
- Wei Wang
- Yang Li
- Jing Dong
第一作者单位:中国科学院大学
关键词:
- Diffusion Model
- Machine Unlearning
- Adversarial Attack
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.19382 Github 链接:https://github.com/hxxdtd/PUND
摘要:
(1) 研究背景: 文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面取得了显著进展,但也带来了身份隐私、版权和不安全内容等安全问题。为了缓解这些问题,提出了概念擦除方法来消除涉及的概念。
(2) 过往方法与问题: 现有的概念擦除方法通过改变文本到图像的映射来实现“擦除”任务,但未能擦除扩散模型生成空间内的视觉内容,为恢复这些擦除的概念留下了致命缺陷。此外,这些方法缺乏可转移性,并且在恢复狭窄概念(例如名人身份)方面存在局限性。
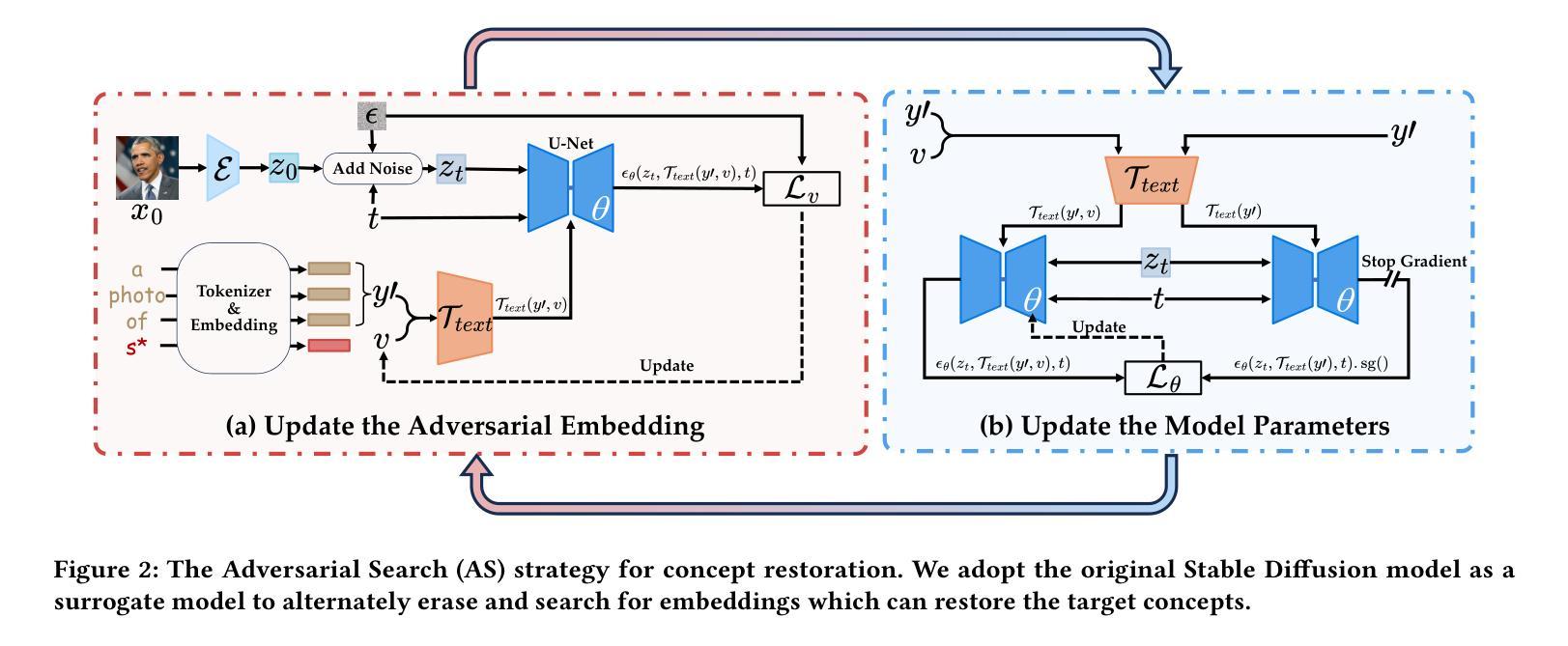
(3) 本文方法: 本文提出了一种可转移的对抗攻击来探测未学习扩散模型的鲁棒性。该攻击采用对抗搜索策略,在原始 Stable Diffusion 模型上迭代擦除和搜索嵌入,以找到可以在不同的未学习模型之间转移的对抗嵌入。
(4) 实验结果: 实验表明,所搜索的对抗嵌入在各种最先进的未学习方法中具有可转移性,并且在从宽泛到狭窄的不同概念级别上都表现出有效性。这些结果支持了本文提出的方法能够探测未学习扩散模型的鲁棒性,并为恢复擦除的概念提供了新的思路。
方法:
(1):提出一种可转移的对抗攻击方法,探测未学习扩散模型的鲁棒性;
(2):采用对抗搜索策略,在原始 Stable Diffusion 模型上迭代擦除和搜索嵌入,找到可以在不同未学习模型之间转移的对抗嵌入;
(3):使用对抗嵌入作为攻击源,在不同的未学习扩散模型上进行攻击,评估模型的鲁棒性;
(4):通过实验验证所搜索的对抗嵌入在各种最先进的未学习方法中具有可转移性,并且在从宽泛到狭窄的不同概念级别上都表现出有效性。
结论:
(1):本文提出了一种可转移的对抗攻击方法,探测未学习扩散模型的鲁棒性,为恢复擦除的概念提供了新的思路。 (2):Innovation point: 提出了一种可转移的对抗攻击方法,该方法在不同未学习模型之间具有可转移性,并且在从宽泛到狭窄的不同概念级别上都表现出有效性。Performance: 实验结果表明,所搜索的对抗嵌入在各种最先进的未学习方法中具有可转移性,并且在从宽泛到狭窄的不同概念级别上都表现出有效性。Workload: 该方法需要使用对抗搜索策略,在原始 Stable Diffusion 模型上迭代擦除和搜索嵌入,这可能需要大量的计算资源。
点此查看论文截图



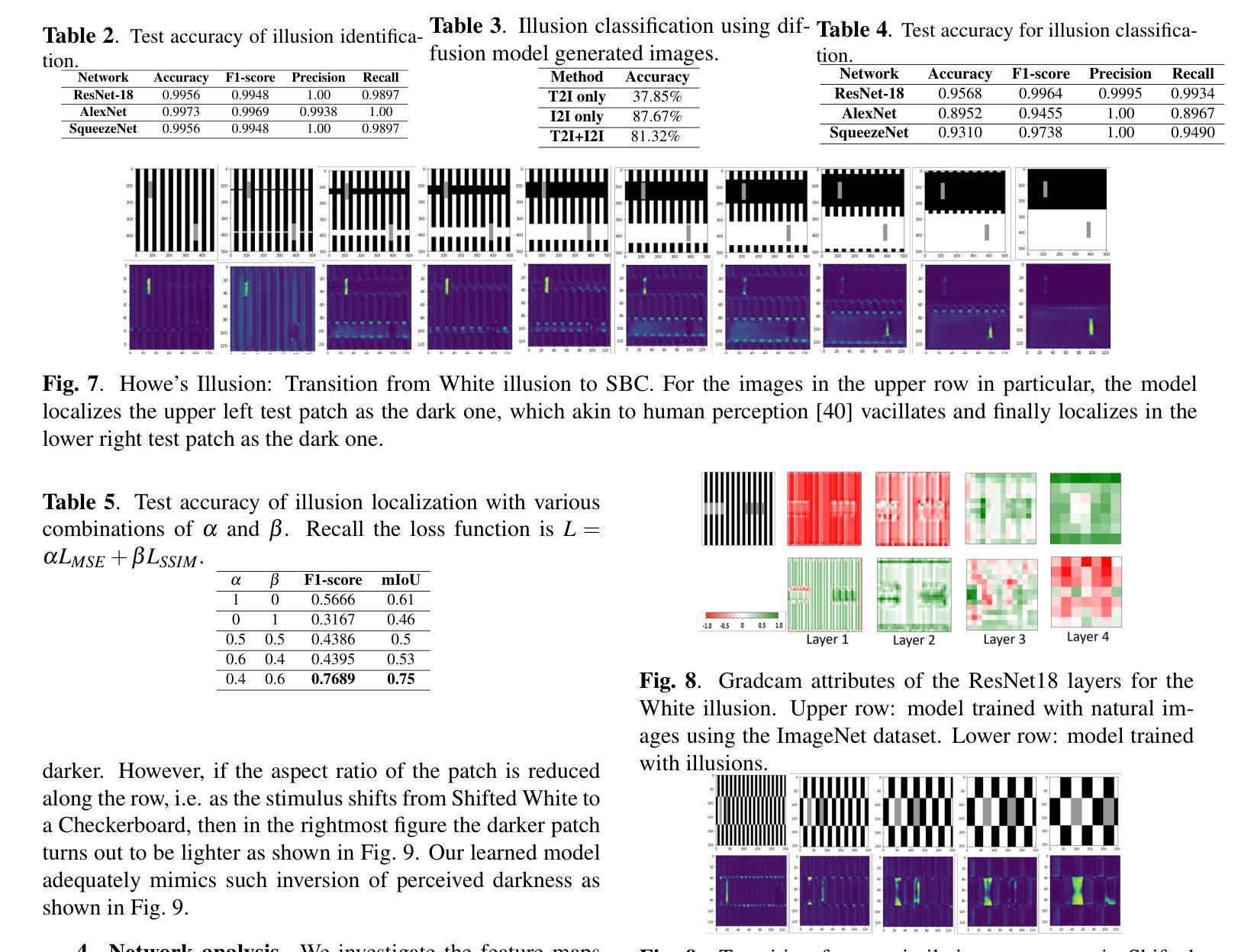
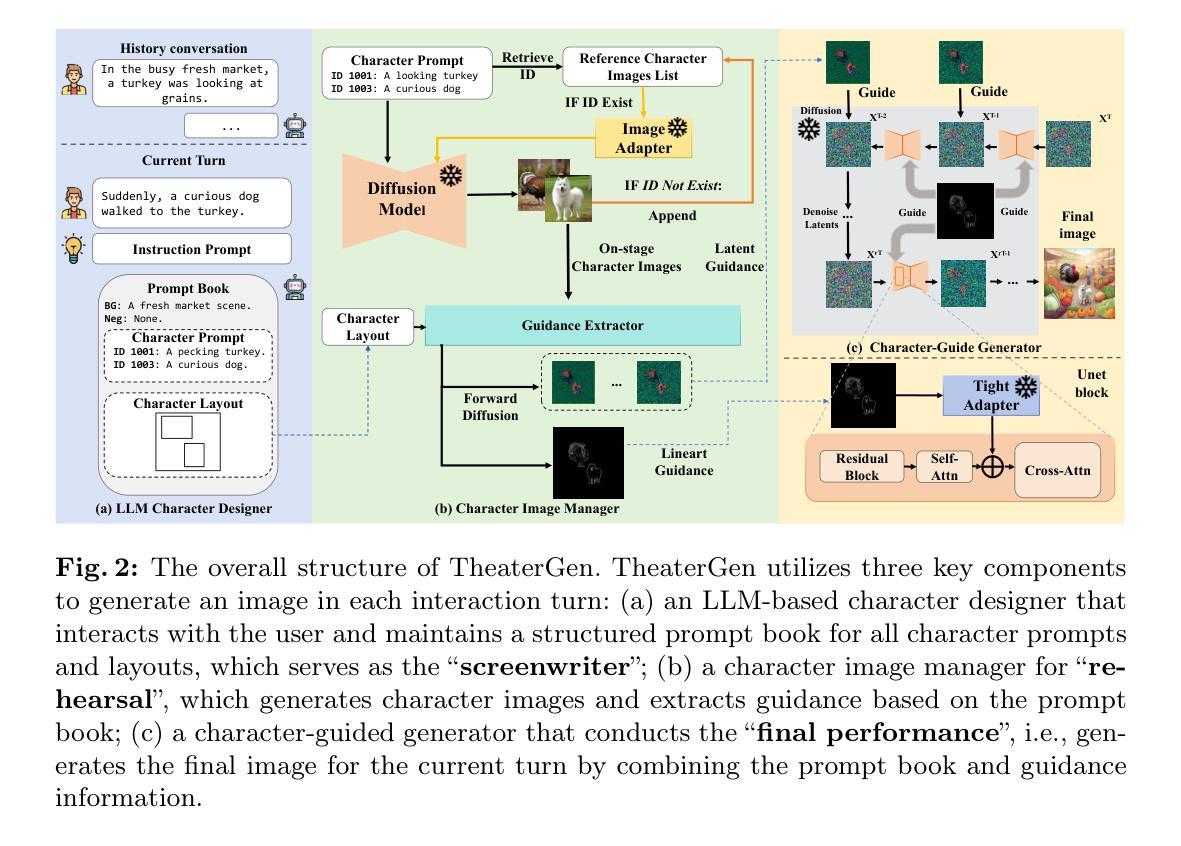
TheaterGen: Character Management with LLM for Consistent Multi-turn Image Generation
Authors:Junhao Cheng, Baiqiao Yin, Kaixin Cai, Minbin Huang, Hanhui Li, Yuxin He, Xi Lu, Yue Li, Yifei Li, Yuhao Cheng, Yiqiang Yan, Xiaodan Liang
Recent advances in diffusion models can generate high-quality and stunning images from text. However, multi-turn image generation, which is of high demand in real-world scenarios, still faces challenges in maintaining semantic consistency between images and texts, as well as contextual consistency of the same subject across multiple interactive turns. To address this issue, we introduce TheaterGen, a training-free framework that integrates large language models (LLMs) and text-to-image (T2I) models to provide the capability of multi-turn image generation. Within this framework, LLMs, acting as a “Screenwriter”, engage in multi-turn interaction, generating and managing a standardized prompt book that encompasses prompts and layout designs for each character in the target image. Based on these, Theatergen generate a list of character images and extract guidance information, akin to the “Rehearsal”. Subsequently, through incorporating the prompt book and guidance information into the reverse denoising process of T2I diffusion models, Theatergen generate the final image, as conducting the “Final Performance”. With the effective management of prompt books and character images, TheaterGen significantly improves semantic and contextual consistency in synthesized images. Furthermore, we introduce a dedicated benchmark, CMIGBench (Consistent Multi-turn Image Generation Benchmark) with 8000 multi-turn instructions. Different from previous multi-turn benchmarks, CMIGBench does not define characters in advance. Both the tasks of story generation and multi-turn editing are included on CMIGBench for comprehensive evaluation. Extensive experimental results show that TheaterGen outperforms state-of-the-art methods significantly. It raises the performance bar of the cutting-edge Mini DALLE 3 model by 21% in average character-character similarity and 19% in average text-image similarity.
Summary
对话生成模型 TheaterGen 无需额外训练,即可实现文本到图像的多轮生成,提升图像语义和上下文一致性。
Key Takeaways
- TheaterGen 创新性地将大语言模型融入文本到图像模型,实现多轮图像生成。
- 大语言模型作为“编剧”,生成标准化提示手册,管理角色提示和设计。
- TheaterGen 基于手册生成角色图像,提取指导信息。
- 反向去噪过程将手册和指导信息融入扩散模型,生成图像。
- CMIGBench 是首个不预先定义角色的多轮图像生成基准测试。
- TheaterGen 显著优于其他方法,在 Mini DALLE 3 模型上提升平均角色相似度 21%,平均文本图像相似度 19%。
- TheaterGen 可用于故事生成和多轮编辑任务。
- TheaterGen 为文本到图像生成领域带来了突破。
Title: TheaterGen:基于 LLM 的多轮图像生成中的角色管理
Authors: Junhao Cheng, Baiqiao Yin, Kaixin Cai, Minbin Huang, Hanhui Li, Yuxin He, Xi Lu, Yue Li, Yifei Li, Yuhao Cheng, Yiqiang Yan, Xiaodan Liang
Affiliation: 中山大学深圳校区
Keywords: Diffusion models · Consistency · Multi-turn image generation
Urls: https://howe140.github.io/theatergen.io/ , Github: https://github.com/donahowe/Theatergen
Summary:
(1): 当前的扩散模型在文本生成图像方面取得了显著进展。然而,在实际场景中需求较高的多轮图像生成仍然面临着图像和文本之间的语义一致性以及同一主题在多个交互轮次中的上下文一致性等挑战。 (2): 现有的方法主要集中在文本提示的改进和扩散模型的训练上,但对于多轮图像生成中的角色管理和一致性问题关注较少。 (3): 本文提出 TheaterGen,这是一个无训练框架,它集成了大语言模型 (LLM) 和文本到图像 (T2I) 模型,以提供多轮图像生成的能力。在这个框架中,LLM 充当“编剧”,参与多轮交互,生成和管理一个标准化的提示手册,其中包含目标图像中每个角色的提示和布局设计。基于角色提示和布局,生成角色图像列表并从中提取指导信息,类似于“排练”。随后,通过将提示手册和指导信息融入 T2I 扩散模型的反向去噪过程中,生成最终图像,即进行“最终表演”。通过有效管理提示手册和角色图像,TheaterGen 显着提高了合成图像中的语义和上下文一致性。此外,我们引入了包含 8000 个多轮指令的专门基准 CMIGBench(一致的多轮图像生成基准)。与以前的多轮基准不同,CMIGBench 不预先定义角色,因此具有很大的多样性。CMIGBench 上包含故事生成和多轮编辑任务,以进行综合评估。 (4): 广泛的实验结果表明,TheaterGen 明显优于最先进的方法。例如,它将尖端的 Mini DALL·E 3 模型在平均字符-字符相似度方面的性能提高了 21%,在平均文本-图像相似度方面的性能提高了 19%。方法:
(1):提出基于大语言模型(LLM)的角色设计师,生成包含角色提示和布局的结构化提示手册;
(2):设计角色图像管理器,生成舞台角色图像及其对应的线条引导和潜在引导;
(3):将提示手册和两种引导输入基于角色的生成器中,合成最终图像。
- 结论:
(1):本文提出了 TheaterGen,一个无训练框架,它集成了大语言模型 (LLM) 和文本到图像 (T2I) 模型,以提供多轮图像生成的能力。通过有效管理提示手册和角色图像,TheaterGen 显着提高了合成图像中的语义和上下文一致性。此外,我们引入了包含 8000 个多轮指令的专门基准 CMIGBench(一致的多轮图像生成基准)。与以前的多轮基准不同,CMIGBench 不预先定义角色,因此具有很大的多样性。CMIGBench 上包含故事生成和多轮编辑任务,以进行综合评估。
(2):创新点:提出基于大语言模型(LLM)的角色设计师,生成包含角色提示和布局的结构化提示手册;设计角色图像管理器,生成舞台角色图像及其对应的线条引导和潜在引导;将提示手册和两种引导输入基于角色的生成器中,合成最终图像。性能:广泛的实验结果表明,TheaterGen 明显优于最先进的方法。例如,它将尖端的 Mini DALL·E 3 模型在平均字符-字符相似度方面的性能提高了 21%,在平均文本-图像相似度方面的性能提高了 19%。工作量:TheaterGen 是一个无训练框架,不需要额外的训练成本。
点此查看论文截图


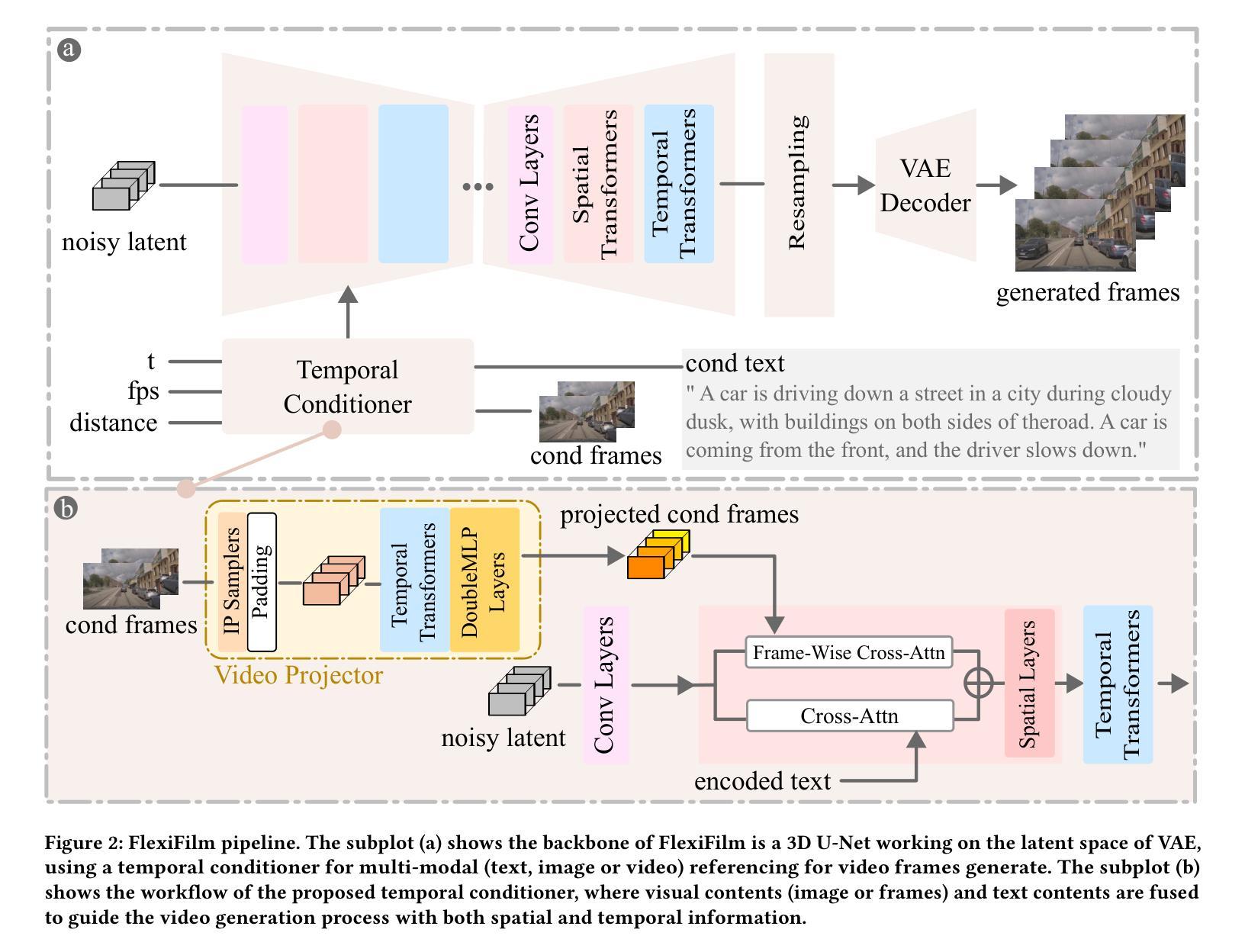
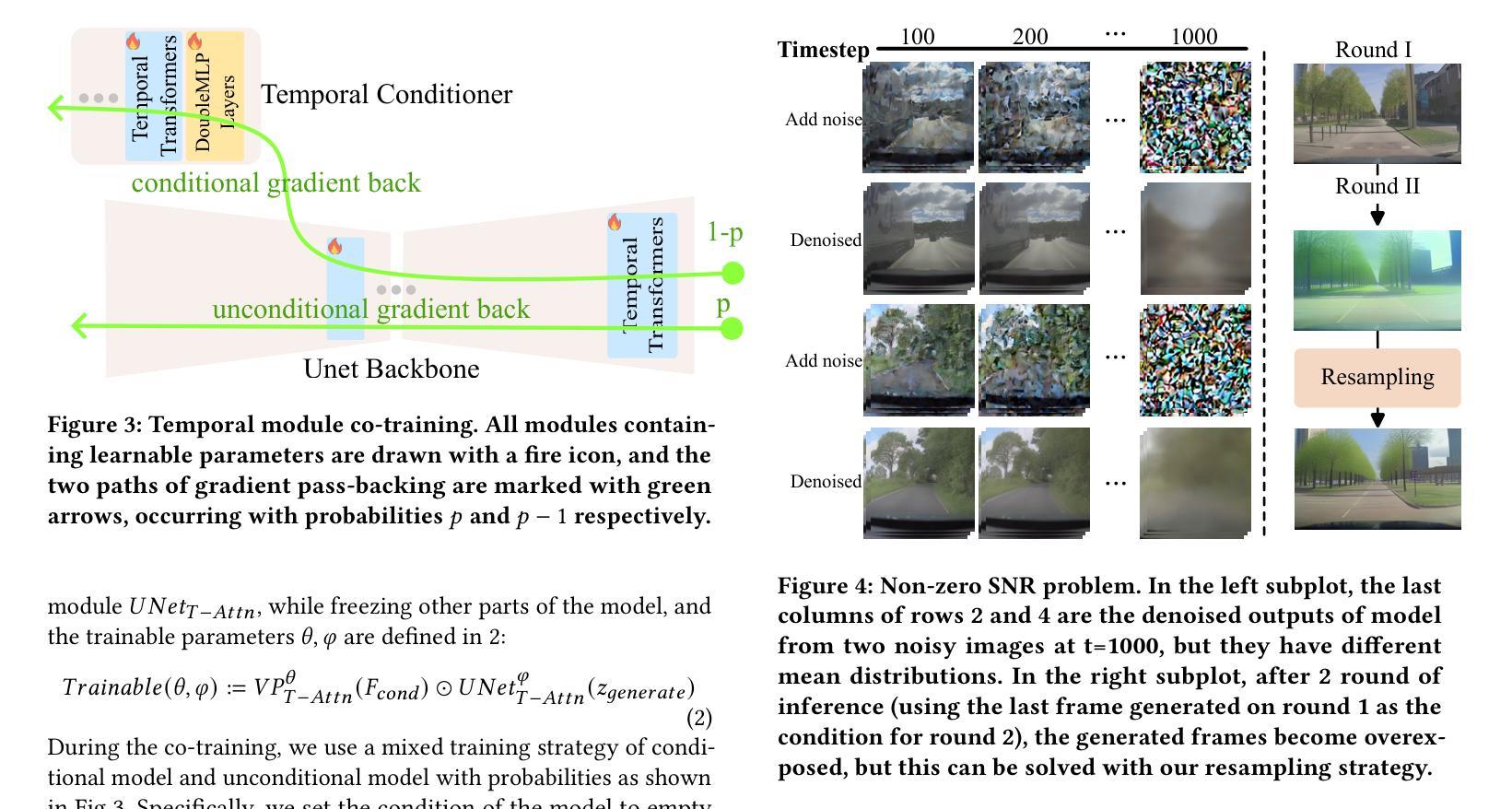
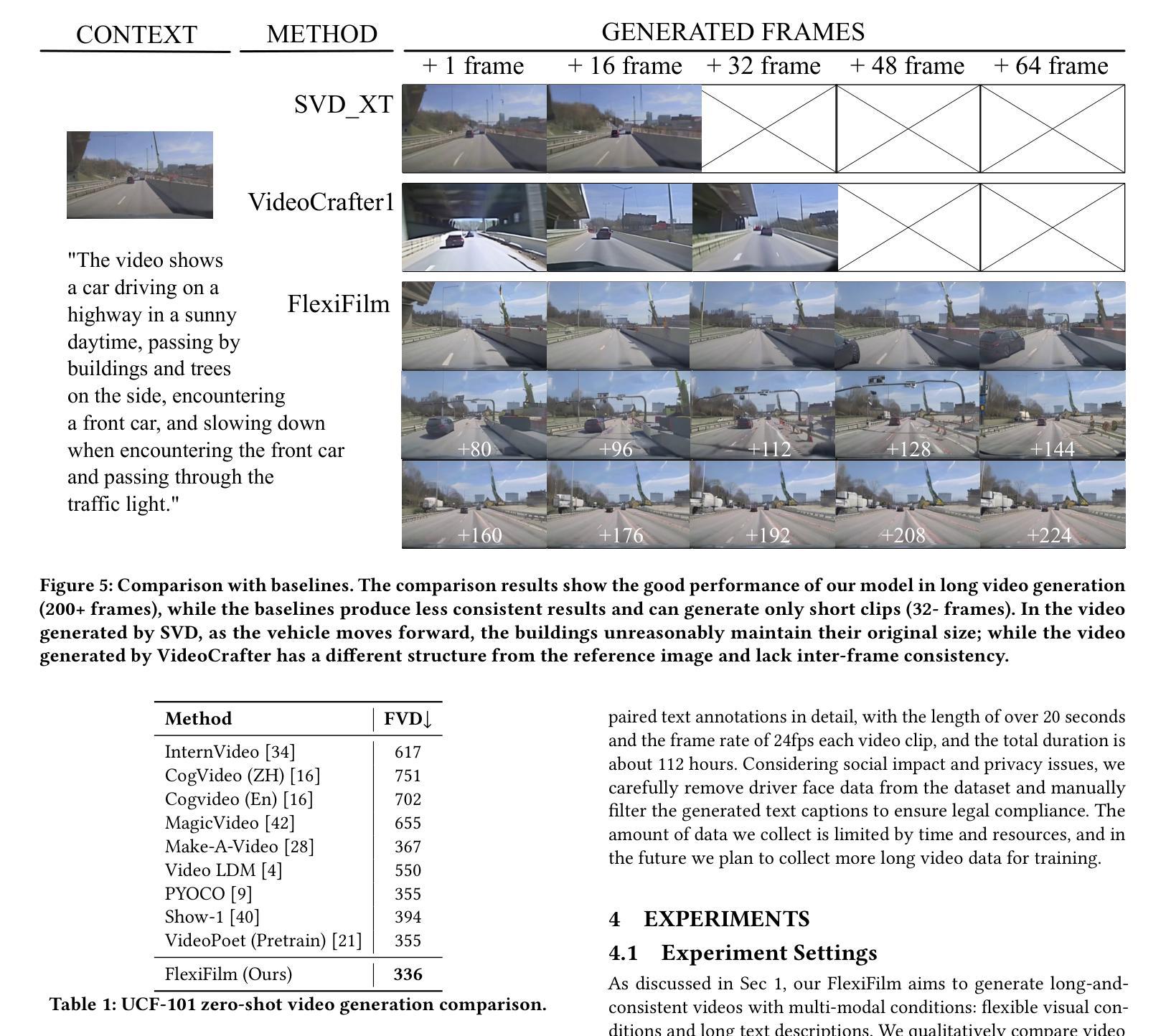
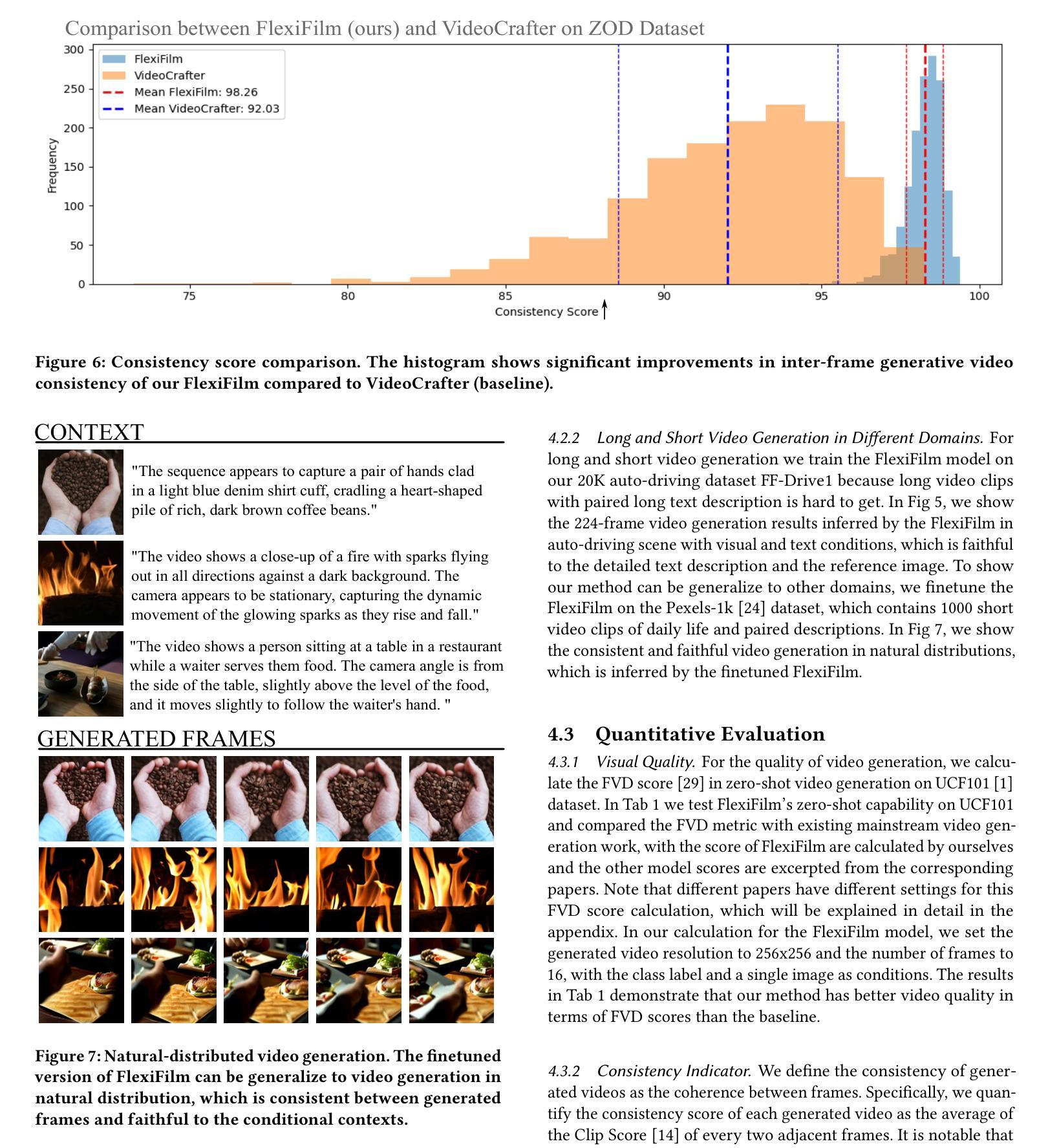
Title: FlexiFilm: 长视频生成中的时空一致性 (FlexiFilm: Temporal Coherence in Long Video Generation)
Authors: Yichen Ouyang, Jianhao Yuan, Hao Zhao, Tiejun Huang, Gaoang Wang, Bo Zhao
Affiliation: 南京大学 (Nanjing University)
Keywords: Long video generation, Diffusion models, Temporal conditioner, Resampling strategy
Urls: Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.09413, Github: None
Summary:
(1): 长视频生成面临时空一致性挑战,现有基于扩散的视频生成模型在长视频生成中表现不佳。
(2): 过去的方法采用简单的条件机制和采样策略,导致时空不一致和过曝问题。
(3): 本文提出 FlexiFilm,一种针对长视频生成量身定制的扩散模型。FlexiFilm 引入时间条件器,建立生成和多模态条件之间更一致的关系,并采用重采样策略解决过曝问题。
(4): 在长视频生成任务上,FlexiFilm 优于竞争对手,生成长度超过 30 秒的长且一致的视频。定量和定性分析都支持其目标。
- 方法:
(1):提出 FlexiFilm,一种针对长视频生成量身定制的扩散模型,引入时间条件器,建立生成和多模态条件之间更一致的关系;
(2):采用重采样策略解决过曝问题,在长视频生成任务上优于竞争对手,生成长度超过 30 秒的长且一致的视频。
- 结论:
(1):本工作针对长视频生成中时空一致性问题,提出 FlexiFilm 模型,有效提升了长视频生成质量; (2):创新点:引入时间条件器和重采样策略,增强时空一致性;性能:在长视频生成任务上优于竞争对手,可生成长度超过 30 秒的长且一致的视频;工作量:模型设计和训练复杂度较高。
点此查看论文截图


Anywhere: A Multi-Agent Framework for Reliable and Diverse Foreground-Conditioned Image Inpainting
Authors:Tianyidan Xie, Rui Ma, Qian Wang, Xiaoqian Ye, Feixuan Liu, Ying Tai, Zhenyu Zhang, Zili Yi
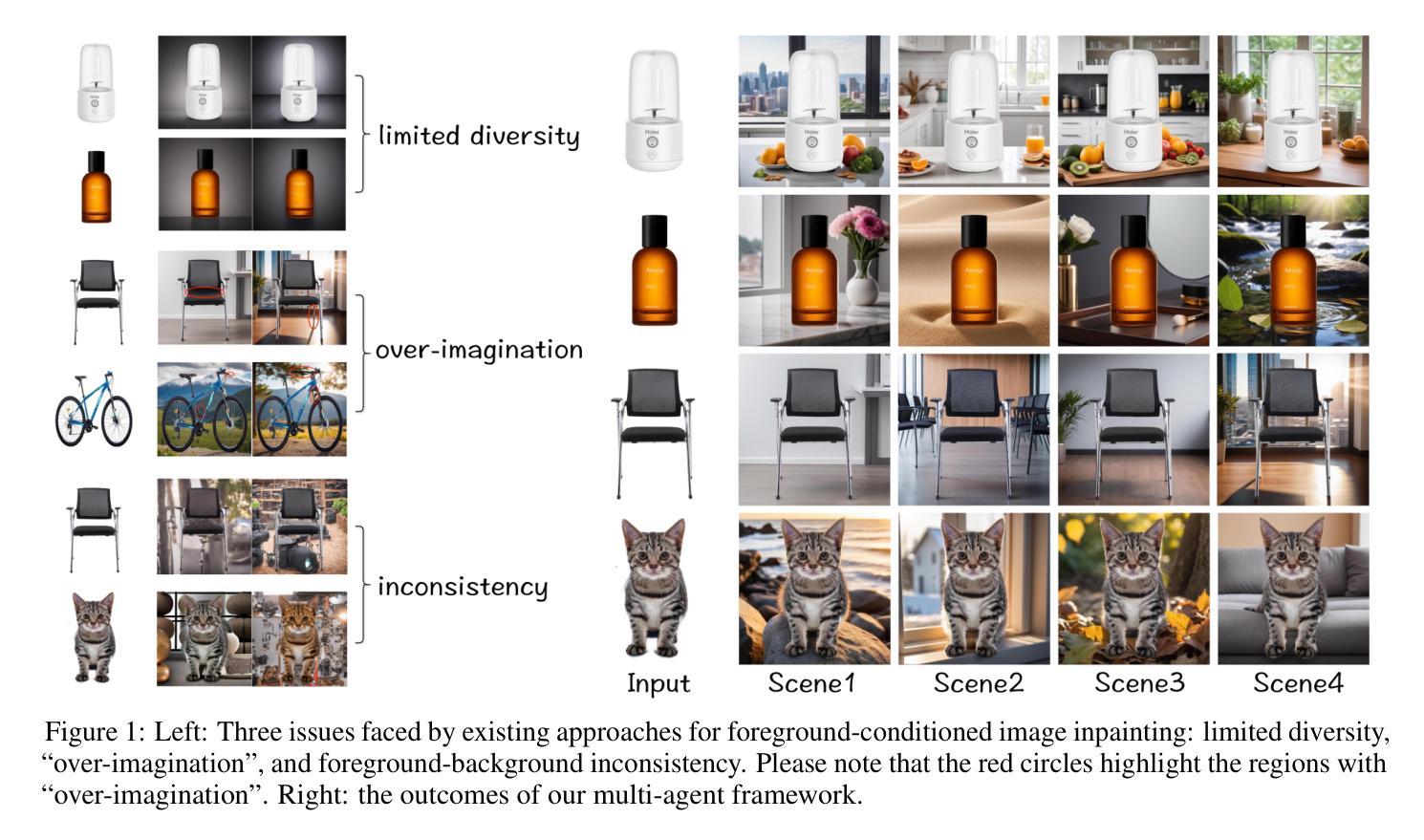
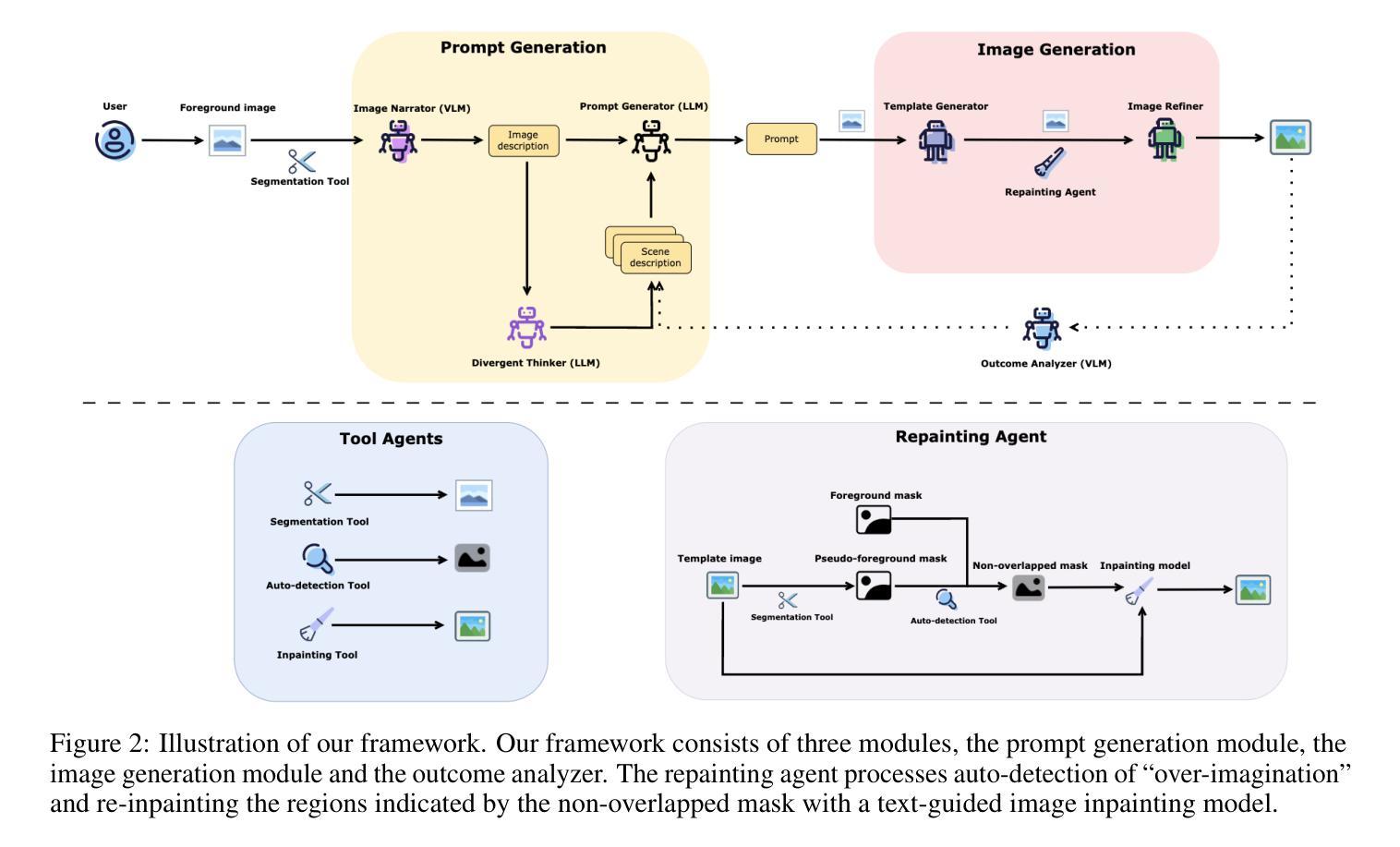
Recent advancements in image inpainting, particularly through diffusion modeling, have yielded promising outcomes. However, when tested in scenarios involving the completion of images based on the foreground objects, current methods that aim to inpaint an image in an end-to-end manner encounter challenges such as “over-imagination”, inconsistency between foreground and background, and limited diversity. In response, we introduce Anywhere, a pioneering multi-agent framework designed to address these issues. Anywhere utilizes a sophisticated pipeline framework comprising various agents such as Visual Language Model (VLM), Large Language Model (LLM), and image generation models. This framework consists of three principal components: the prompt generation module, the image generation module, and the outcome analyzer. The prompt generation module conducts a semantic analysis of the input foreground image, leveraging VLM to predict relevant language descriptions and LLM to recommend optimal language prompts. In the image generation module, we employ a text-guided canny-to-image generation model to create a template image based on the edge map of the foreground image and language prompts, and an image refiner to produce the outcome by blending the input foreground and the template image. The outcome analyzer employs VLM to evaluate image content rationality, aesthetic score, and foreground-background relevance, triggering prompt and image regeneration as needed. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our Anywhere framework excels in foreground-conditioned image inpainting, mitigating “over-imagination”, resolving foreground-background discrepancies, and enhancing diversity. It successfully elevates foreground-conditioned image inpainting to produce more reliable and diverse results.
PDF 16 pages, 9 figures, project page: https://anywheremultiagent.github.io
Summary
通过 Anywhere 多智能体框架,利用 VLM、LLM 和图像生成模型,通过语义分析、文本引导的图像生成和结果分析器,实现前景调控图像修复,解决过度想象、前景背景不一致和多样性差的问题。
Key Takeaways
- 引入 Anywhere,一种用于前景调控图像修复的多智能体框架。
- 利用 VLM 和 LLM 进行语义分析,生成最佳语言提示。
- 使用文本引导的 Canny-to-Image 生成模型创建模板图像。
- 使用图像精炼器融合输入前景和模板图像以生成输出。
- 使用 VLM 进行结果分析,评估图像内容合理性、美学分数和前景背景相关性。
- 触发提示和图像再生,以解决过度想象、前景背景差异和多样性差的问题。
- Anywhere 框架在前景调控图像修复中表现出色,生成更可靠、更多样化的结果。
Title: ANYWHERE:基于前景条件的图像修复的多智能体框架
Authors: Tianyidan Xie, Rui Ma, Qian Wang, Xiaoqian Ye, Feixuan Liu, Ying Tai, Zhenyu Zhang, Zili Yi
Affiliation: 南京大学新软件技术国家重点实验室
Keywords: Image inpainting, Multi-agent framework, Foreground-conditioned, Diversity, Reliability
Urls: https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.18598v1, https://github.com/anywheremultiagent/anywhere
Summary:
(1):图像修复在图像处理中有着重要的应用,近年来基于扩散模型的图像修复方法取得了显著进展。然而,当应用于基于前景对象完成图像的任务时,现有的端到端图像修复方法面临着“过度想象”、“前景与背景不一致”以及多样性受限等挑战。 (2):针对上述问题,本文提出了一个开创性的多智能体框架——Anywhere。Anywhere采用了一个复杂的管道框架,包括视觉语言模型(VLM)、大语言模型(LLM)和图像生成模型等多种智能体。该框架由三个主要组件组成:提示生成模块、图像生成模块和结果分析器。提示生成模块对输入的前景图像进行语义分析,利用VLM预测相关的语言描述,并利用LLM推荐最优的语言提示。在图像生成模块中,我们采用了一个文本引导的Canny-to-Image生成模型,基于前景图像的边缘图和语言提示创建模板图像,并使用图像精修器通过融合输入前景和模板图像生成结果。结果分析器利用VLM评估图像内容合理性、美学分数和前景-背景相关性,并根据需要触发提示和图像再生。 (3):广泛的实验表明,我们的Anywhere框架在基于前景条件的图像修复任务中表现出色,它缓解了“过度想象”,解决了前景与背景的不一致性,并增强了多样性。它成功地将基于前景条件的图像修复提升到了一个新的水平,产生了更加可靠和多样化的结果。 (4):在基于前景条件的图像修复任务上,Anywhere框架取得了比现有方法更好的性能,证明了其方法的有效性。方法:
(1):提出一个多智能体框架——Anywhere,该框架由提示生成模块、图像生成模块和结果分析器组成;
(2):提示生成模块利用视觉语言模型(VLM)和大语言模型(LLM)预测相关的语言描述和推荐最优的语言提示;
(3):图像生成模块采用文本引导的Canny-to-Image生成模型,基于前景图像的边缘图和语言提示创建模板图像,并使用图像精修器生成结果;
(4):结果分析器利用VLM评估图像内容合理性、美学分数和前景-背景相关性,并根据需要触发提示和图像再生。
- 结论:
(1)本工作提出了一个多智能体框架 Anywhere,该框架有效解决了基于前景条件的图像修复任务中存在的“过度想象”、“前景与背景不一致”以及多样性受限等挑战,将基于前景条件的图像修复提升到了一个新的水平;
(2)创新点:Anywhere 采用了多智能体框架,结合了视觉语言模型、大语言模型和图像生成模型,实现了基于前景条件的图像修复任务的端到端完成;
性能:Anywhere 在基于前景条件的图像修复任务上取得了比现有方法更好的性能,证明了其方法的有效性;
工作量:Anywhere 框架的实现相对复杂,需要训练多个智能体模型,工作量较大。
点此查看论文截图


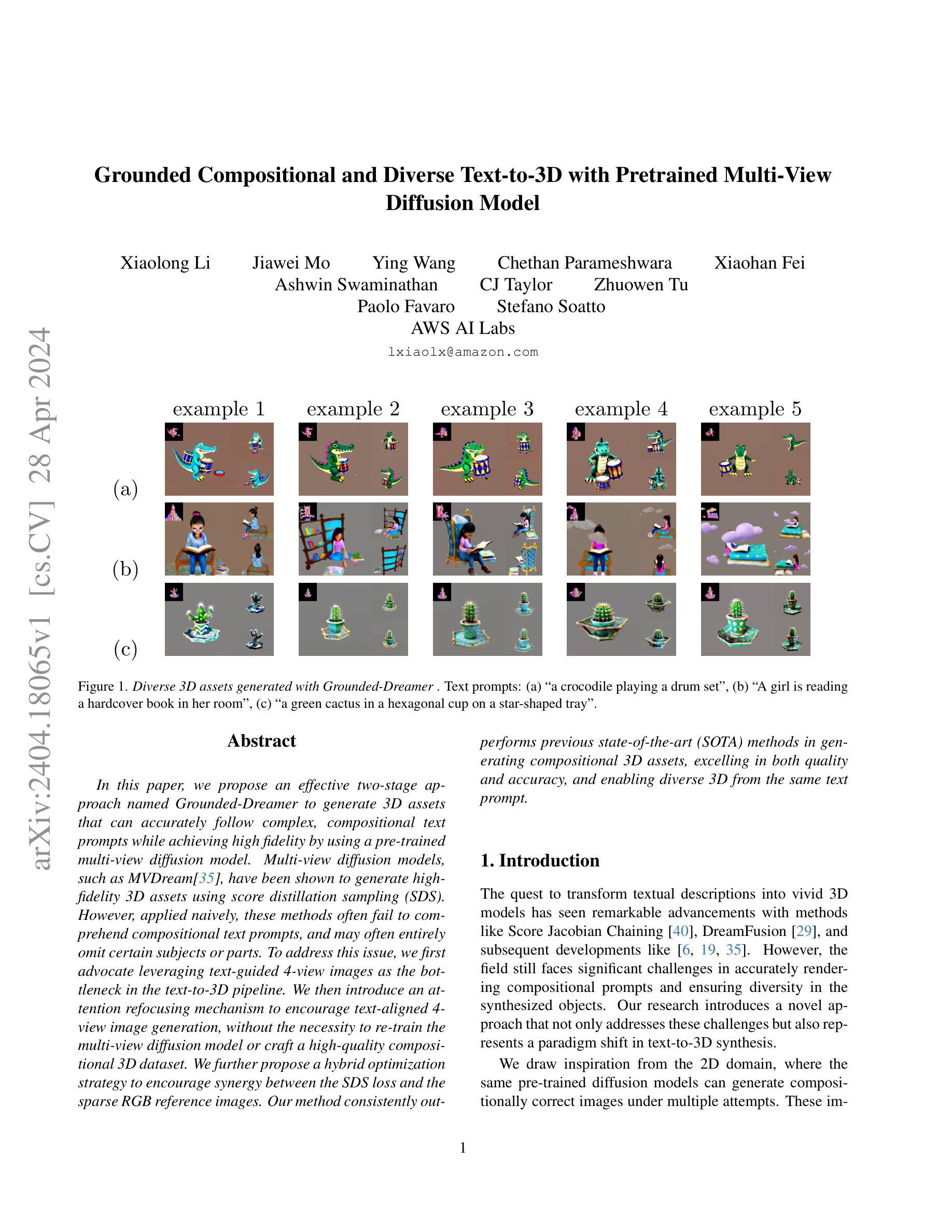
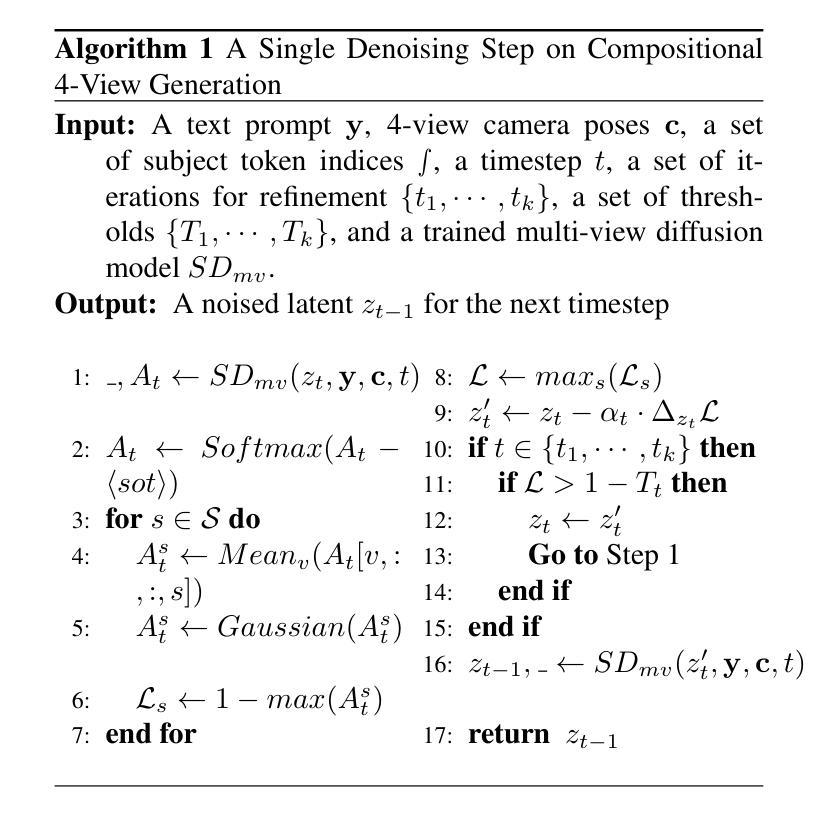
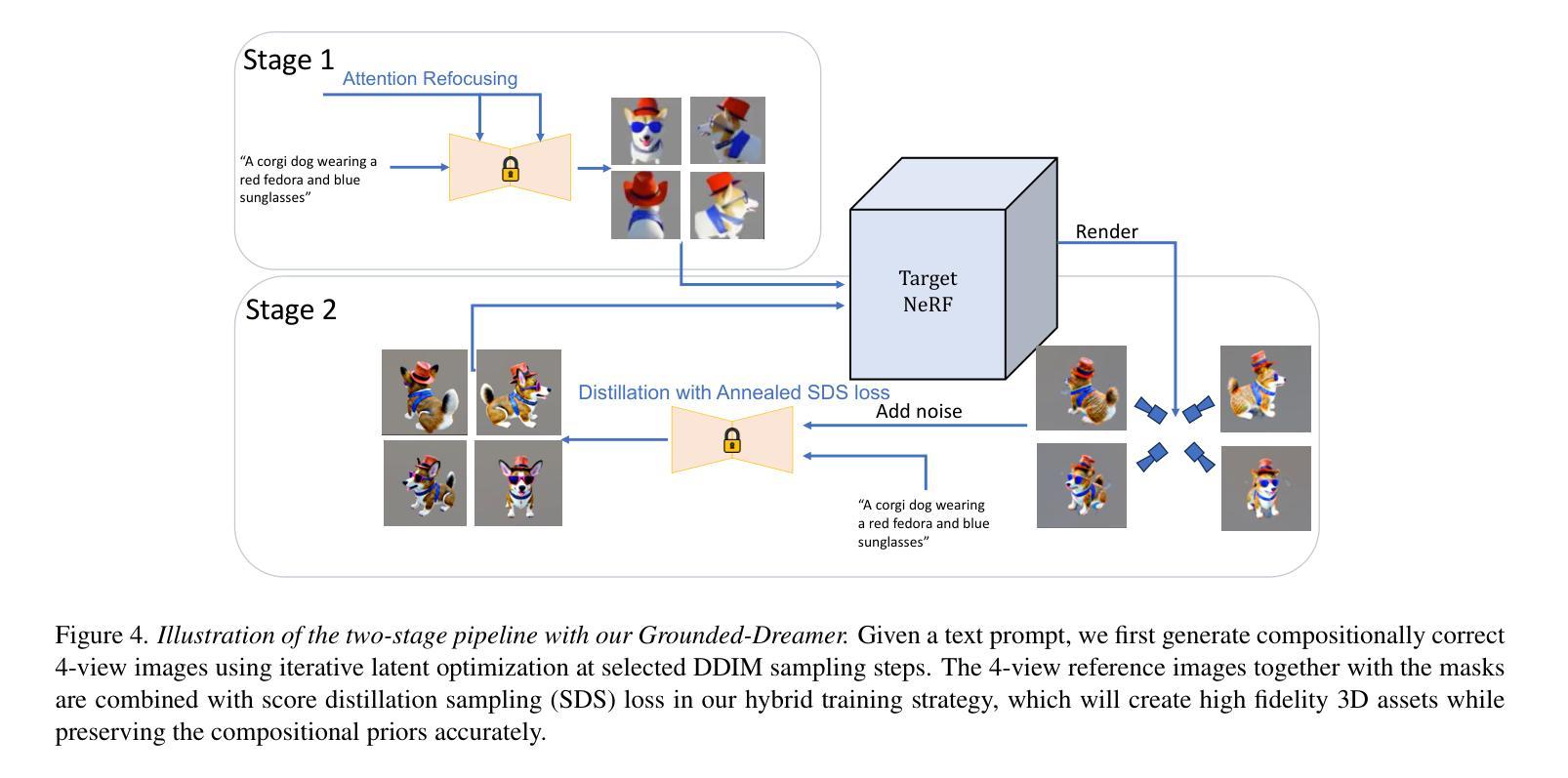
- 论文标题:基于预训练多视图的接地式组合式和多样化文本到 3D
- 作者:Xudong Zhang, Huchuan Lu, Yinda Zhang, Xiaoguang Han, Joshua B. Tenenbaum, Jiajun Wu
- 单位:麻省理工学院(Massachusetts Institute of Technology)
- 关键词:文本到 3D、组合式生成、多视图扩散模型、接地式合成
- 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2302.04742.pdf,Github:无
摘要: (1):研究背景:现有的文本到 3D 方法在生成组合式文本提示时存在困难,经常遗漏某些主体或部分。 (2):过去方法:MVDream 等多视图扩散模型可以生成高保真 3D 资产,但无法理解组合式文本提示。 (3):研究方法:提出了一种两阶段方法 Grounded-Dreamer,利用预训练的多视图扩散模型,通过注意重新聚焦机制和混合优化策略,鼓励文本对齐的 4 视图图像生成,并促进 SDS 损失和稀疏 RGB 参考图像之间的协同作用。 (4):方法性能:方法在生成组合式 3D 资产方面优于现有技术,在质量和准确性方面均表现出色,并能够从相同的文本提示中生成多样化的 3D。
Methods:
(1):利用预训练的多视图扩散模型 MVDream,通过注意重新聚焦机制和混合优化策略,生成文本对齐的 4 视图图像。
(2):采用 SDS 损失和稀疏 RGB 参考图像之间的协同作用,促进 3D 资产的生成。
(3):使用文本提示作为条件,生成多样化的 3D 资产。
- 结论:
(1):本文提出了一种新颖的文本到 3D 合成两阶段框架,有效克服了组合准确性和多样性的挑战。第一阶段利用多视图扩散模型从文本生成空间相干视图,而第二阶段将稀疏视图 NeRF 与文本引导扩散先验协同起来,用于精细的 3D 重建。这种方法不仅提高了复杂文本提示生成 3D 模型的保真度和组合完整性,还为未来无缝 2D 到 3D 过渡和模型多功能性方面的探索铺平了道路。我们的方法展示了文本到 3D 合成方面的重大飞跃,为该不断发展的领域的进一步进步提供了坚实的基础。 (2):创新点:利用预训练多视图扩散模型,通过注意力重新聚焦机制和混合优化策略,鼓励文本对齐的 4 视图图像生成,并促进 SDS 损失和稀疏 RGB 参考图像之间的协同作用,促进 3D 资产的生成;性能:在生成组合式 3D 资产方面优于现有技术,在质量和准确性方面均表现出色,并能够从相同的文本提示中生成多样化的 3D;工作量:利用了预训练的多视图扩散模型,减少了训练时间和计算资源的消耗。
点此查看论文截图


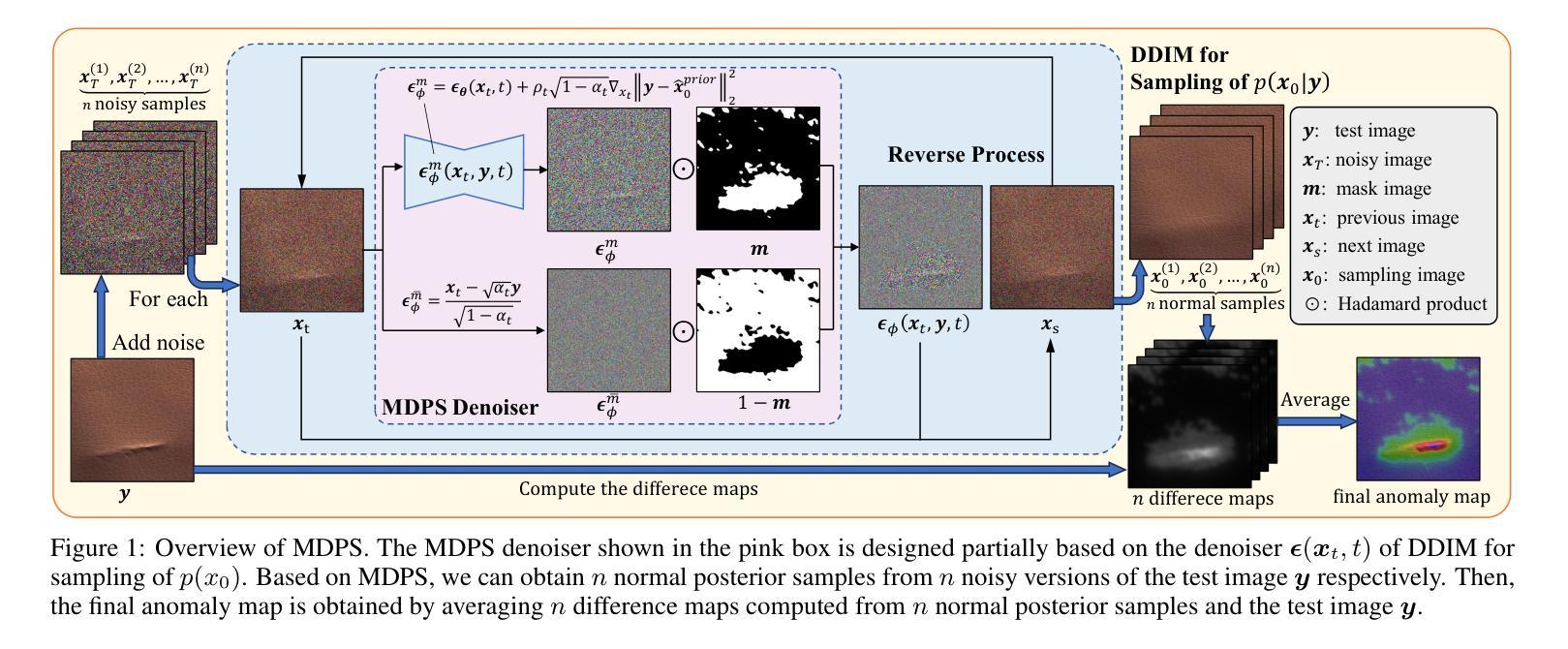
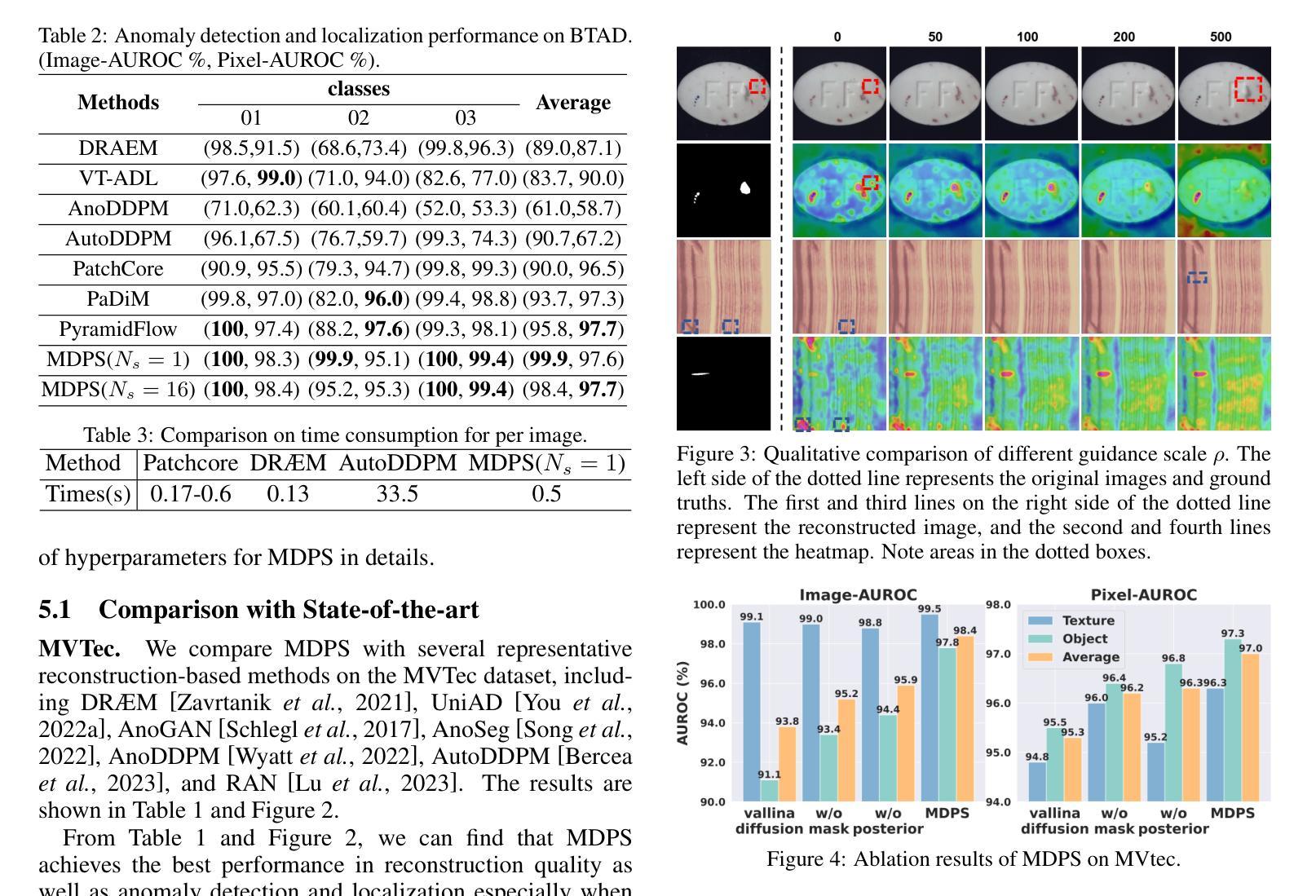
Unsupervised Anomaly Detection via Masked Diffusion Posterior Sampling
Authors:Di Wu, Shicai Fan, Xue Zhou, Li Yu, Yuzhong Deng, Jianxiao Zou, Baihong Lin
Reconstruction-based methods have been commonly used for unsupervised anomaly detection, in which a normal image is reconstructed and compared with the given test image to detect and locate anomalies. Recently, diffusion models have shown promising applications for anomaly detection due to their powerful generative ability. However, these models lack strict mathematical support for normal image reconstruction and unexpectedly suffer from low reconstruction quality. To address these issues, this paper proposes a novel and highly-interpretable method named Masked Diffusion Posterior Sampling (MDPS). In MDPS, the problem of normal image reconstruction is mathematically modeled as multiple diffusion posterior sampling for normal images based on the devised masked noisy observation model and the diffusion-based normal image prior under Bayesian framework. Using a metric designed from pixel-level and perceptual-level perspectives, MDPS can effectively compute the difference map between each normal posterior sample and the given test image. Anomaly scores are obtained by averaging all difference maps for multiple posterior samples. Exhaustive experiments on MVTec and BTAD datasets demonstrate that MDPS can achieve state-of-the-art performance in normal image reconstruction quality as well as anomaly detection and localization.
Summary
利用扩散模型对正态图像采样,并通过差分映射计算异常分数。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在异常检测中展现出了良好的应用前景。
- MDPS 方法将图像重建问题数学建模为基于掩码噪声观测模型和基于贝叶斯框架的扩散图像先验的正态图像后验采样。
- MDPS 可以有效地计算每次正态后验样本和给定测试图像之间的差分映射。
- 异常分数通过对多个后验样本的差分映射进行平均得到。
- MDPS 在图像重建质量和异常检测与定位方面均取得了最先进的效果。
- MDPS 具有较高的可解释性,为异常检测提供了新的思路。
- MDPS 在 MVTec 和 BTAD 数据集上进行了全面实验,证明了其优越性。
Title: 无监督异常检测的掩码扩散后验采样
Authors: Di Wu, Shicai Fan, Xue Zhou, Li Yu, Yuzhong Deng, Jianxiao Zou, Baihong Lin
Affiliation: 电子科技大学自动化工程学院
Keywords: 无监督异常检测, 扩散模型, 后验采样, 掩码噪声观测模型
Urls: https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.17900, Github: https://github.com/KevinBHLin/
Summary:
(1): 异常检测是计算机视觉领域的一项基本任务,在医学诊断、智能制造、自动驾驶等领域有着广泛的应用。由于异常样本的稀有性和多样性,近年来研究主要集中在无监督异常检测上,即模型只从正常样本中学习,但可以检测异常数据。
(2): 现有的无监督异常检测方法主要有重建方法、生成对抗网络方法、扩散模型方法等。其中,重建方法是较早且最常用的神经网络方法之一。然而,传统的重建模型如自动编码器和生成对抗网络存在重建质量较差、训练不稳定等问题。
(3): 本文提出了一种基于贝叶斯框架的无监督异常检测新方法,称为掩码扩散后验采样(MDPS)。该方法将正常图像重建问题数学建模为基于掩码噪声观测模型和扩散模型的正常图像后验采样,并设计了一种从像素级和感知级角度设计的度量,可以有效计算每个正常后验样本与给定测试图像之间的差异图。异常分数通过对多个后验样本的差异图求平均得到。
(4): 在 MVTec 和 BTAD 数据集上进行的详尽实验表明,MDPS 在正常图像重建质量、异常检测和定位方面均取得了最先进的性能。这些性能足以支持作者提出的目标。
Methods:
(1):本文提出了一种基于贝叶斯框架的无监督异常检测新方法,称为掩码扩散后验采样(MDPS)。
(2):MDPS将正常图像重建问题数学建模为基于掩码噪声观测模型和扩散模型的正常图像后验采样。
(3):MDPS设计了一种从像素级和感知级角度设计的度量,可以有效计算每个正常后验样本与给定测试图像之间的差异图。
(4):异常分数通过对多个后验样本的差异图求平均得到。
结论:
(1):本文提出了一种基于贝叶斯框架的无监督异常检测新方法 MDPS,该方法将正常图像重建问题数学建模为基于掩码噪声观测模型和扩散模型的正常图像后验采样,并设计了一种从像素级和感知级角度设计的度量,可以有效计算每个正常后验样本与给定测试图像之间的差异图,异常分数通过对多个后验样本的差异图求平均得到。
(2):创新点:MDPS基于贝叶斯框架,将正常图像重建问题数学建模为基于掩码噪声观测模型和扩散模型的正常图像后验采样,并设计了一种从像素级和感知级角度设计的度量;性能:在 MVTec 和 BTAD 数据集上进行的详尽实验表明,MDPS 在正常图像重建质量、异常检测和定位方面均取得了最先进的性能;工作量:MDPS 由于扩散后验采样而导致较高的计算成本。
点此查看论文截图


Causal Diffusion Autoencoders: Toward Counterfactual Generation via Diffusion Probabilistic Models
Authors:Aneesh Komanduri, Chen Zhao, Feng Chen, Xintao Wu
Diffusion probabilistic models (DPMs) have become the state-of-the-art in high-quality image generation. However, DPMs have an arbitrary noisy latent space with no interpretable or controllable semantics. Although there has been significant research effort to improve image sample quality, there is little work on representation-controlled generation using diffusion models. Specifically, causal modeling and controllable counterfactual generation using DPMs is an underexplored area. In this work, we propose CausalDiffAE, a diffusion-based causal representation learning framework to enable counterfactual generation according to a specified causal model. Our key idea is to use an encoder to extract high-level semantically meaningful causal variables from high-dimensional data and model stochastic variation using reverse diffusion. We propose a causal encoding mechanism that maps high-dimensional data to causally related latent factors and parameterize the causal mechanisms among latent factors using neural networks. To enforce the disentanglement of causal variables, we formulate a variational objective and leverage auxiliary label information in a prior to regularize the latent space. We propose a DDIM-based counterfactual generation procedure subject to do-interventions. Finally, to address the limited label supervision scenario, we also study the application of CausalDiffAE when a part of the training data is unlabeled, which also enables granular control over the strength of interventions in generating counterfactuals during inference. We empirically show that CausalDiffAE learns a disentangled latent space and is capable of generating high-quality counterfactual images.
摘要:
基于扩散的因果表征学习框架 CausalDiffAE,通过指定因果模型实现反事实生成。
关键要点:
- 提出 CausalDiffAE,将编码器与逆扩散相结合,从高维数据中提取因果表征。
- 通过因果编码机制将数据映射到因果相关潜在因子。
- 使用神经网络参数化潜在因子之间的因果机制。
- 提出变分目标和辅助标签信息来解纠缠因果变量。
- 基于 DDIM 提出受干预影响的反事实生成程序。
- 研究了仅部分训练数据有标签的情况,可在推理中细粒度控制反事实的干预强度。
- 实证表明 CausalDiffAE 学习到了解纠缠的潜在空间,能够生成高质量的反事实图像。
- 标题:因果扩散自编码器:基于扩散概率模型的反事实生成
- 作者:Aneesh Komanduri、Chen Zhao、Feng Chen、Xintao Wu
- 第一作者单位:阿肯色大学
- 关键词:扩散概率模型、因果建模、反事实生成、表示学习
- 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.17735, Github代码链接:无
- 摘要: (1) 研究背景:扩散概率模型(DPMs)在高质量图像生成方面已成为最先进的技术。然而,DPMs 具有任意噪声潜在空间,没有可解释或可控制的语义。尽管在提高图像样本质量方面进行了大量的研究,但使用扩散模型进行表示控制生成的工作却很少。具体来说,使用 DPMs 进行因果建模和可控反事实生成是一个尚未探索的领域。 (2) 过去的方法及其问题:目前还没有关于使用 DPMs 进行因果建模和反事实生成的工作。这限制了 DPMs 在需要因果推理和反事实生成的任务中的应用。 (3) 本文提出的研究方法:本文提出了 CausalDiffAE,一个基于扩散的因果表示学习框架,以根据指定的因果模型生成反事实。CausalDiffAE 使用编码器从高维数据中提取高级语义因果变量,并使用反向扩散对随机变化进行建模。它提出了一个因果编码机制,将高维数据映射到因果相关的潜在因子,并使用神经网络参数化潜在因子之间的因果机制。为了强制因果变量的解纠缠,CausalDiffAE 制定了变分目标并利用先验中的辅助标签信息来正则化潜在空间。它提出了一个基于 DDIM 的反事实生成过程,该过程受 do 干预的影响。最后,为了解决标签监督有限的情况,CausalDiffAE 还研究了在训练数据的一部分未标记时的应用,这也使得在推理过程中对生成反事实的干预强度进行精细控制。 (4) 本文方法在什么任务上取得了什么性能:实验表明,CausalDiffAE 学习了一个解纠缠的潜在空间,并且能够生成高质量的反事实图像。该性能支持了本文提出的因果表示学习框架在反事实生成任务中的有效性。
</ol>
Some Error for method(比如是不是没有Methods这个章节)
8. 结论:
(1):本工作的意义是什么? 本工作提出了 CausalDiffAE,这是一个基于扩散的因果表示学习和反事实生成框架。我们提出了一个因果编码机制,将图像映射到因果相关的因子。我们通过神经网络学习因子之间的因果机制。我们制定了一个基于变分的扩散目标来强制潜在空间的解纠缠,以实现潜在空间操作。我们提出了一个基于 DDIM 的反事实生成算法,该算法受 do 干预的影响。对于有限监督的情况,我们提出了我们模型的弱监督扩展,它联合学习了一个无条件模型和一个条件模型。该目标还使得能够对生成的 counterfactuals 进行细粒度控制。我们使用定性和定量指标实证地展示了我们模型的能力。未来的工作包括探索文本到图像扩散模型中的反事实生成。
(2):总结本文在创新点、性能和工作量三个维度上的优缺点: 创新点: * 提出了一种基于扩散的因果表示学习框架 CausalDiffAE。 * 提出了一种因果编码机制,将高维数据映射到因果相关的潜在因子。 * 提出了一种基于变分的扩散目标来强制潜在空间的解纠缠。 * 提出了一种基于 DDIM 的反事实生成算法,该算法受 do 干预的影响。
性能: * 实验表明,CausalDiffAE 学习了一个解纠缠的潜在空间,并且能够生成高质量的反事实图像。
工作量: * 该方法需要大量的数据和计算资源来训练。 * 该方法在训练过程中需要大量的超参数调整。
点此查看论文截图